Composite follicular lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Article information
Abstract
Composite lymphoma is very rare and a combination of Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma and even histiocytic tumors can occur. Because of the unfamiliarity, not only can this cause diagnostic problems, but can also affect treatment plan. We report a case of composite lymphoma in a 40-year-old male. Initial biopsy showed a composite lymphoma of follicular lymphoma grade 1 and classic Hodgkin lymphoma. After chemotherapy, another lymph node was taken because of disease progression, which revealed follicular lymphoma, grade 3a without Hodgkin lymphoma component.
Composite lymphoma was initially recognized by Custer [1] as two or more distinct lymphomas that occur in the same patient. This definition was later refined by Kim et al. [2] as simultaneous occurrence of more than one type of lymphoma in the same organ or tissue site of the same patient. Composite lymphoma is rare and may consist of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) with Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) [3,4], B-cell NHL with T-cell NHL [5–8], T-cell or B-cell NHL with other histologic type(s) of the same lineage [9], or NHL with histiocytic or dendritic cell tumors [10]. Excluding follicular lymphoma (FL) associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, the most common composite lymphoma is FL of low grade associated with classic HL [3,4,11] followed by FL associated with mantle cell lymphoma [9,12]. Histologically, composite lymphomas display a mixed pattern, or less commonly, distinct zonal distribution of each lymphoma component [3,5]. Composite lymphoma may pose a diagnostic challenge, especially when two lymphoma components are mixed in the same lymph node. Herein we report a case of composite HL and FL of mixed histologic pattern.
CASE REPORT
Clinical findings
A 40-year-old man was diagnosed with HL at an outside hospital and was referred for treatment. He showed a neck mass and weight loss. Laboratory tests were within normal limits except for a positive hepatitis B antigen test. A positron emission tomography (PET)–computed tomography (CT) scan revealed multiple right level I, II, and V hypermetabolic lymph nodes of the neck, both axillae, and retropancreatic regions. Abdominal CT scan revealed no organomegaly, but mild irregular hypermetabolism was noted in the spleen and along the marrow space by PET-CT. Under the diagnosis of classic HL, nodular sclerosis, stage IV, the patient was treated with doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD) chemotherapy, and an antiviral agent for hepatitis B was administered. A few months later, abdominal CT scan revealed slightly increased sizes of multiple lymph nodes at the portocaval, aortocaval, left paraaortic, and small bowel mesentery. Lymph node biopsy from a level IV node was diagnosed as FL, grade 3a. Bone marrow biopsy was negative. Six cycles of rituximab with bendamustine were planned.
Pathologic findings
All the lymph node biopsies were reviewed. The biopsy was evaluated with immunohistochemical stains including staining for CD20, CD3, CD30, CD15, PAX5, BCL2, CD10, and Ki-67 (Leica Biosystems, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK). Immunohistochemistry was performed using a Leica BOND-III automated stainer (Leica Biosystems, Melbourne, Australia). Epstein-Barr virus was detected by in situ hybridization (ISH) using a Bond Ready-to-Use ISH Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–encoded RNA probe (Leica Biosystems, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK).
The initial biopsy that was diagnosed as HL at outside clinic was reviewed. Enlarged follicles were found at the peripheral part of the node but the center showed diffuse area. Large neoplastic Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells were easily recognizable in the diffuse area but also found in the peripheral area between the neoplastic follicles. Histiocytes were mixed but eosinophils were not prominent. Reed-Sternberg cells were positive for CD30, CD15, and PAX5, but negative for CD20 and CD3. PAX5 staining was relatively weak in comparison with the neighboring non-neoplastic B cells. Neoplastic follicles were positive for CD20, CD10, and BCL2, but negative for CD30 and CD15. Therefore, we concluded that it was a composite lymphoma of FL grade 1 and classic HL (Figs. 1A–I, 2A–C). EBV was negative in both HL and FL cells. The second biopsy performed in our hospital showed only FL without HL component but this time the grade of FL was 3a because of centroblastic proliferation (Fig. 2D–F).

Composite follicular lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma of initial biopsy. (A) Lymph node shows nodular area representing follicular lymphoma and diffuse area containing Hodgkin lymphoma. (B) Follicular lymphoma, grade 1. (C) Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin lymphoma. (D) CD10-positive cells of follicular lymphoma. (E) BCL2-positive follicular lymphoma. (F) CD21-positve follicular dendritic cell meshwork of follicular lymphoma. (G) CD30 in Reed-Sternberg cells. (H) CD15 in Reed-Sternberg cells. (I) PAX5 weak positive in Reed-Sternberg cells (arrows).
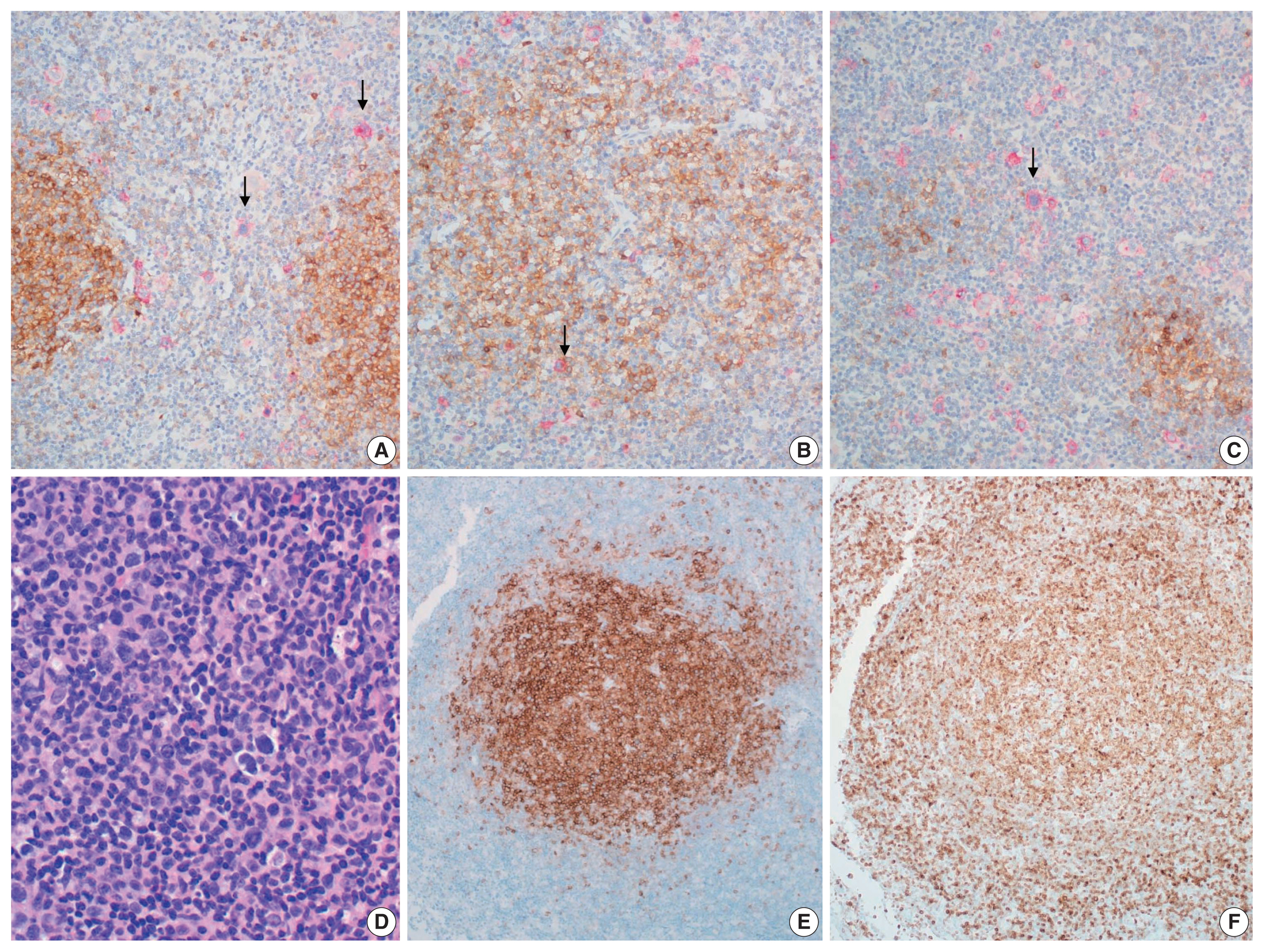
(A–C) Composite follicular lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma of initial biopsy. Double stain for CD10 to show follicular lymphoma (brown) and CD30 to identify Hodgkin lymphoma (red). (A) CD30-positive Reed-Sternberg cells (arrows) are scattered in between follicular lymphoma. (B) A few CD30-positive Reed-Sternberg cells (arrow) within neoplastic follicles of follicular lymphoma. (C) Diffuse permeation of Hodgkin lymphoma to follicular lymphoma area. Reed-Sternberg cells (arrow) are scattered in diffuse area and small nodular remnant of neoplastic follicles. (D–F) Follicular lymphoma of recurrent lesion: (D) follicular lymphoma, grade 3a, (E) CD10, (F) BCL2.
DISCUSSION
Composite FL and HL is extremely rare and only 25 cases have been reported in the literature written in English to date [3,4,11–16]. While composite lymphoma usually is indicated histopathologically by at least two morphologically distinct lymphomatous proliferations, the proof that these proliferations are separate and distinct neoplasms requires immunologic analysis. The true incidence of composite lymphoma may be underestimated because as in this case, separate tumor components can be easily overlooked on initial microscopic examination.
In the initial biopsy of the present case, neoplastic follicles in the periphery of the lymph node were misinterpreted as a component of HL because the cellular atypia of the follicle was not recognized, and HL frequently has a vague follicular pattern.
While distinct clonal origin of separate tumor component of composite lymphoma has been reported in one study [12], it is well known that separate tumor components share a common clonal relationship, including a BCL2 translocation [3,11,13]. Recent next generation sequencing study revealed both components also share the same mutational variants but have pathogenic variants that are specific for each component as well [3]. These findings indicate that two distinct lymphomas sharing a common cytogenetic abnormality derived from the same precursor, overlaid with a subtype-specific mutation occurring in each subclone, can lead to composite HL and FL. In addition, EBV infection observed in HL cells, but not FL cells of the composite lymphoma [3] emphasizes the role of EBV infection in the pathogenesis of HL [17] and suggests that EBV infection also contributes to the formation of composite lymphoma. Composite lymphoma may pose both a diagnostic and managerial challenge [3]. A previous report demonstrated that the HL component in composite lymphoma pursues an indolent clinical course compared with de novo HL. No recurrence of the HL component was reported even without ABVD treatment for HL. In contrast, patients treated with ABVD only or who were untreated, experienced recurrence of FL like the present case [3]. Although the number of cases is too small to provide definitive information for treatment or to establish concrete guidelines for management [18], the above report may give a hint on how best to treat composite FL and HL.
Notes
Ethics Statement
All procedures performed in the current study were approved by the Institutional Review Board (2021GR0492) in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments. Informed consent was waived.
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets generated or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: MJJ, YHK. Review of data: HNK, ESY, DSK, CWC. Writing—original draft: HNK, YHK. Writing—review & editing: MJJ, CWC, YHK.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Funding Statement
No funding to declare.
