Landscape of EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma: a single institute experience with comparison of PANAMutyper testing and targeted next-generation sequencing
Article information
Abstract
Background
Activating mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are predictive biomarkers for response to EGFR–tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Here, we characterized the clinicopathologic features associated with EGFR mutations via peptide nucleic acid clamping-assisted fluorescence melting curve analysis (PANAMutyper) and evaluated the feasibility of targeted deep sequencing for detecting the mutations.
Methods
We examined EGFR mutations in exons 18 through 21 for 2,088 LUADs from July 2017 to April 2020 using PANAMutyper. Of these, we performed targeted deep sequencing in 73 patients and evaluated EGFR-mutation status and TKI clinical response.
Results
EGFR mutation was identified in 55.7% of LUADs by PANAMutyper, with mutation rates higher in females (69.3%) and never smokers (67.1%) and highest in the age range of 50 to 59 years (64.9%). For the 73 patients evaluated using both methods, next-generation sequencing (NGS) identified EGFR mutation–positive results in 14 of 61 patients (23.0%) who were EGFR-negative according to PANAMutyper testing. Of the 10 patients reportedly harboring a sensitizing mutation according to NGS, seven received TKI treatment, with all showing partial response or stable disease. In the 12 PANAMutyper-positive cases, NGS identified two additional mutations in exon 18, whereas a discordant negative result was observed in two cases.
Conclusions
Although PANAMutyper identified high frequencies of EGFR mutations, targeted deep sequencing revealed additional uncommon EGFR mutations. These findings suggested that appropriate use of NGS may benefit LUAD patients with otherwise negative screening test results.
Molecular diagnostics for targetable genetic alterations have become the standard of care in the management of lung cancer patients [1]. In particular, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations have been more frequently found in lung adenocarcinomas (LUADs) in Asian than Western populations [2], with the overall EGFR mutation rate up to ~54% among Korean patients with adenocarcinoma [3–5]. EGFR mutation testing has become the most important step in treatment decision-making for lung cancer patients in Korea because of the high frequency of EGFR mutations and the availability of targeted therapeutic agents.
For EGFR testing, the College of American Pathologists/American Society of Clinical Oncology/International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer guidelines recommends that testing methods must be capable of detecting molecular alterations in specimens with as few as 20% cancer cells. Furthermore, assays capable of detecting abnormality in as few as 5% of tumor cells should be used for the EGFR T790M mutation [6]. In Korea, peptide nucleic acid (PNA) clamping-based reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the Cobas EGFR mutation test (Roche, Indianapolis, IN, USA), pyrosequencing, and next-generation sequencing (NGS) are commonly used for EGFR mutation testing [7].
Recently, Park and Shim [8] reported that NGS testing is highly recommended for the diagnosis of Korean lung cancer patients, given its ability to reveal a considerable number of additional EGFR, anaplastic lymphoma kinase, and proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ROS alterations, as well as other targetable alterations. However, high costs, specialized implements and bioinformatics, complex test processes, and the relatively long turnaround time hinder its implementation as a standard method for detecting genetic alterations [9].
In this study, we screened EGFR mutations using PNA clamping-assisted fluorescence melting curve analysis (PANAMutyper, Panagene, Daejeon, Korea) and performed an in-depth characterization of the clinicopathologic features associated with EGFR mutations in LUAD patients at our institution. Additionally, we evaluated the feasibility of targeted NGS for detection of the mutations in comparison with the PNA method and assessed clinical responses to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in groups defined by these different detection methods.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients and specimens
We reviewed the EGFR mutation results of PANAMutyper tests on LUADs conducted between July 2017 and April 2020 at Seoul National University Bundang Hospital. Of the 2,203 tests, 115 were repetitive tests for the same tumor or its metastatic lesion. To prevent duplicate counts, only one test result from each tumor was selected for the main calculations, and the other results were analyzed separately. Fifteen pairs of tests performed for synchronous or metachronous double primary tumors in the same patient were not considered repetitive and not excluded. As a result, we analyzed the test results of 2,088 distinct tumors from 2,073 patients. Clinical and pathologic information was obtained from electronic medical records and pathology reports.
PANAMutyper assay
PANAMuytper is a PNA-mediated real-time PCR-based assay. Mutant DNA is selectively amplified by using wild-type DNA-specific PNA clamp probes, after which mutant-specific PNA detection probes are used to genotype EGFR mutations by fluorescence melting curve analysis. This assay can detect and discriminate 47 types of EGFR mutation (Supplementary Table S1), including three resulting in G719X substitutions, 29 exon 19 deletions (Exon19del), one T790M substitution, one S768I substitution, 10 exon 20 insertions (Exon20ins), two L858R substitutions, and one L861Q substitution with a high level of sensitivity [10].
Mutation analysis using the PANAMutyper R EGFR kit (Panagene) was performed according to manufacturer instructions. To maximize the proportion of neoplastic cells, target lesions were annotated on the corresponding hematoxylin and eosin-stained slide and selectively dissected for DNA extraction whenever possible. Test results were reported as positive or negative for each of seven categories, and those with more than one mutation were considered compound mutations. For patients with the T790M mutation, history of TKI administration and results of previous molecular tests were reviewed to distinguish between de novo and acquired T790M mutation. When comparing the results of repeated tests, additional detection of the T790M mutation after TKI treatment was considered concordant, and any other type of difference was considered discordant.
NGS analysis
Among the 2,073 patients, targeted sequencing that included the EGFR gene was performed in 73 patients at the request of clinicians. Briefly, genomic DNA was extracted using the Qiagen formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), customized panels were designed (Supplementary Table S2) using SureSelect biotinylated RNA library baits (Aligent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), and target enrichment was performed using the SureSelect XT HS target enrichment kit (Aligent Technologies). Paired-end massively parallel sequencing (2 × 150 bp) was performed with an Illumina Miseq reagent kit (v2.0) on a MiSeqDx sequencer (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Variants with at least 2% of allele frequency and 100 × depth were included for analysis.
Statistical analysis
The proportions of mutation-positive cases were calculated along with the 95% confidence interval according to the Wilson score interval. Frequencies of the mutations in different groups were compared using a χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test. To evaluate the association between clinicopathologic variables and EGFR mutation, binary logistic regression analysis was performed. Responses to EGFR-TKI treatment were evaluated by reviewing electronic medical records and based on Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (v1.1) criteria. Time-to-treatment discontinuation (TTD) was defined as the date of treatment initiation to the date of discontinuation and used to estimate the benefit of TKI treatment. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS ver. 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA), and a p-value < .05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
Prevalence of EGFR mutations according to the PANAMutyper test
Table 1 summarizes the clinicopathologic characteristics and corresponding EGFR mutation rates. EGFR mutation was detected in 55.7% of 2,088 LUADs by the PANAMutyper test, with the positivity rate highest (64.9%) between the ages of 50 and 59 years. Additionally, EGFR mutation was more common in females (69.3% vs. 41.0%, p < .001) and in never smokers (67.1% vs. 40.0%, p < .001). Moreover, we observed similar trends in mutation frequency according to age group, sex, and smoking status upon division into subgroups (Fig. 1). Furthermore, EGFR mutation was observed more frequently in resection samples as compared with biopsies (59.5% vs. 49.6%, p < .001), with biopsies for metastatic lymph nodes yielding lower positivity rates as compared with other procedures. Associations of age group, sex, smoking status, and specimen type with EGFR mutation rate were statistically significant according to both univariable and multivariable analyses (Supplementary Table S3).
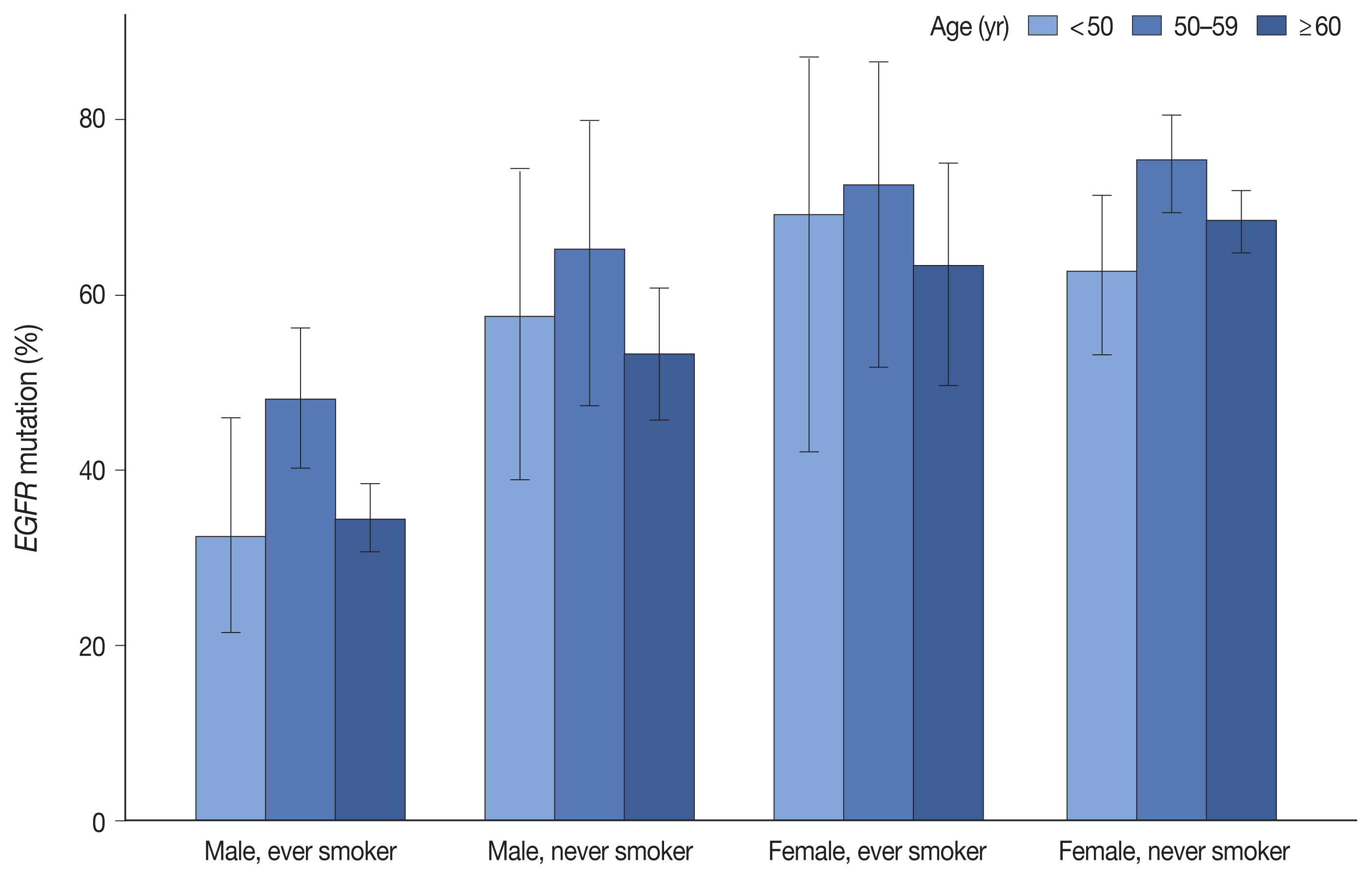
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation frequencies according to age, sex, and smoking status. The preferential occurrence of EGFR mutation in females and never smokers is observed. Notably, the frequency was the highest at the sixth decade of age, regardless of sex and smoking status.
For primary lung-resection specimens, histologic subtypes were assigned according to the predominant pattern or distinct entities and analyzed separately. As a result, invasive non-mucinous adenocarcinomas with predominant lepidic (65.5%), acinar (69.1%), papillary (70.1%), and micropapillary (71.2%) patterns showed relatively similar rates of EGFR-mutation positivity, whereas a lower frequency was observed in solid adenocarcinomas (33.1%). EGFR mutations were identified in 63.4% of minimally invasive adenocarcinomas (MIAs) and similar to other invasive non-mucinous adenocarcinomas. By contrast, EGFR mutations were observed in only 31.3% (5 of 16 cases) of adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS). For invasive mucinous adenocarcinomas (IMAs), EGFR mutation was positive in five of 91 cases (5.5%).
EGFR mutation subtypes
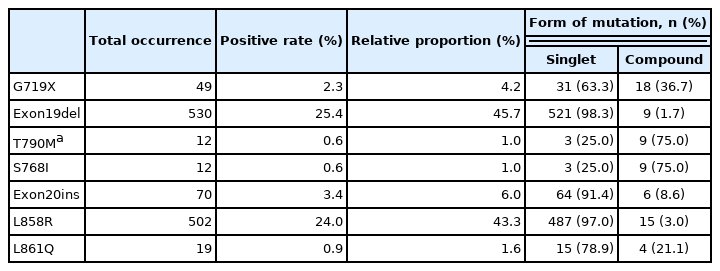
Among the positive tests, Exon19del and L858R substitution accounted for 45.7% and 43.3%, respectively, followed by Exon20ins (6.0%), G719X (4.2%), L861Q (1.6%), and S768I (1.0%) (Table 2). Exon19del, Exon20ins, and L858R mutations were mainly in the form of singlets, whereas compound mutations were relatively frequent for G719X, S768I, T790M, and L861Q. Excluding those with acquired T790M mutation, 35 of the EGFR-mutated cases (3.0%) were detected as compound mutations (Supplementary Table S4).
Compared with clinicopathologic variables, the two most prevalent mutations (Exon19del and L858R) were associated with different features (Fig. 2, Supplementary Table S5), with Exon19del more common in patients under 50 years of age, and L858R mutation less common in patients under 50 years of age, compared to those over 60 years of age. Summation of the two mutation frequencies corresponded to the overall positivity rate reaching the highest in patients aged 50 to 59 years (Supplementary Fig. 1S). Additionally, both mutations were more common in female patients and non-smokers; however, Exon19del mutation was more frequent in female smokers than in female non-smokers. Compared with acinar/papillary patterns, Exon19del mutation was more frequent in micropapillary adenocarcinomas and less frequent in lepidic predominant tumors, whereas the opposite trend was observed for the L858R mutation. These differences were also observed in logistic regression analyses for each mutation (Supplementary Table S6).
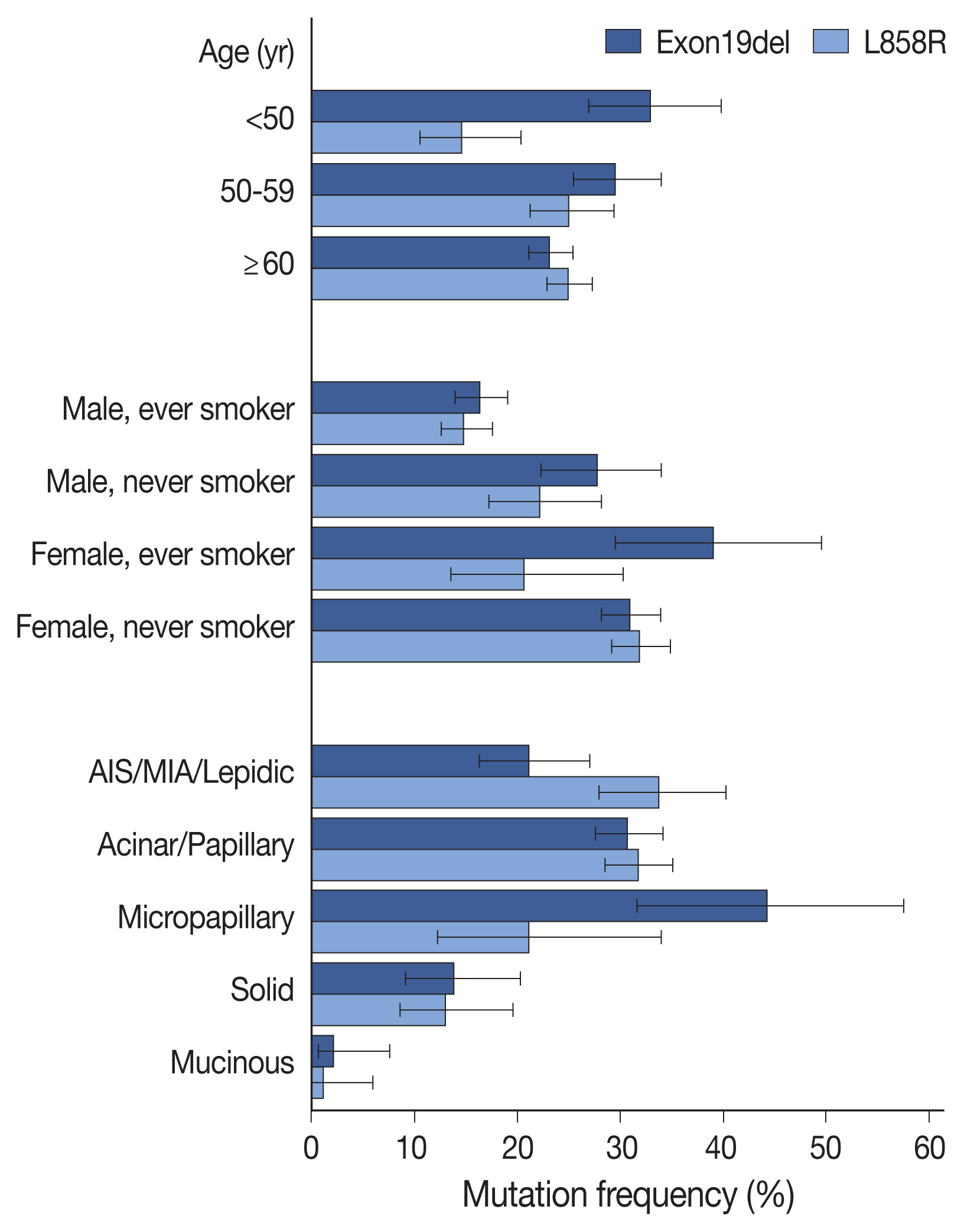
Comparison of mutation frequencies of Exon19del and L858R by clinicopathologic variables. The two most common epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation subtypes showed different patterns. While Exon19del was more frequent in patients younger than 50 years of age, L858R was more common in patients older than 50 years. Also, Exon19del was enriched in micropapillary predominant adenocarcinomas, whereas L858R was more common in lepidic predominant tumors. AIS, adenocarcinoma in situ; MIA, minimally invasive adenocarcinoma.
T790M mutation was detected in 5.0% of cases (105 of 2,088 cases), of which 93 cases constituted acquired mutations and 12 were de novo T790M mutations (corresponding to 0.6% of TKI-naïve patients). In the subgroup of de novo T790M mutations, nine were present as compound mutations, with the most common accompanying mutation being L858R (6 cases), followed by Exon19del and G719X (Supplementary Table S7). Acquisition of T790M mutation following TKI treatment was found in 53.1% of cases (93 of 175 cases). Moreover, the T790M-acquisition rate was 54.2% (32 of 59 cases) in tumors with preceding L858R mutation and 59.6% (56 of 94 cases) in those with the Exon19del mutation. The frequency of compound T790M mutation in Exon19del- and L858R-mutated tumors did not differ significantly between TKI-naïve and TKI-treated patients (p = .156 and p = .516, respectively).
Repetitive tests
For 113 cases, we performed multiple PANAMupyter tests on the same tumor or its metastatic lesion. Of these cases, 106 (93.8%) revealed concordant test results, with discordant results observed in the remaining seven cases (6.2%). For these seven cases, EGFR mutation was detected in only one of the two tests in five cases, and in the other two cases, an additional mutation was detected in the repetitive tests. Although quantitative information could not be obtained for the differentially positive results, the peak height of those melting curves was consistently lower relative to those observed in usual positive cases. Clinicopathologic information for the seven discordant cases is summarized in Supplementary Table S8.
Among 15 pairs of synchronous or metachronous tumors, seven pairs showed identical EGFR-mutation status, with either the same mutation (3 cases) or negative results (4 cases), and eight pairs showed different EGFR-mutation profiles.
Comparison of PANAMutyper and NGS results for 73 patients
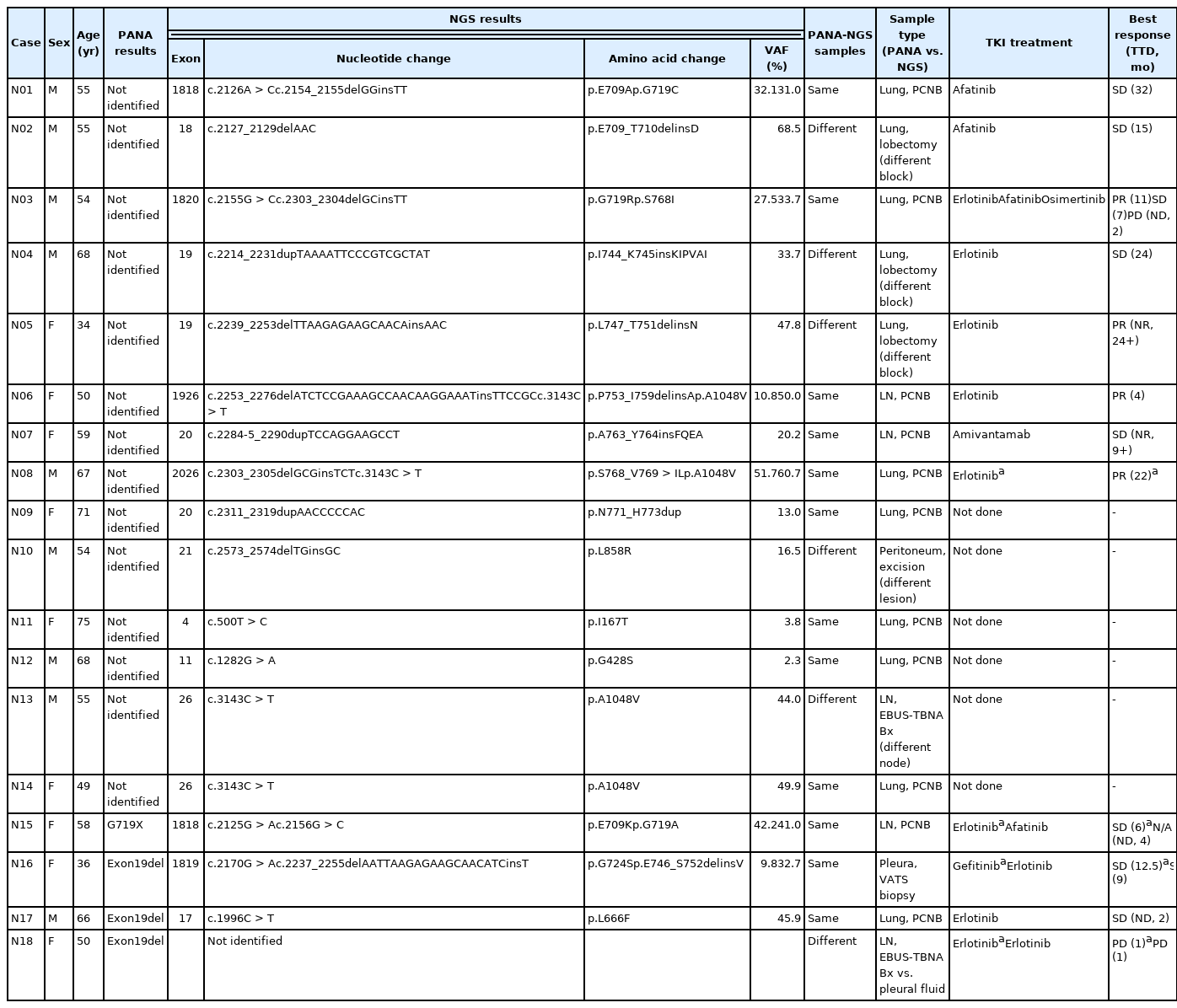
Both PANAMutyper testing and NGS were performed for 73 patients, resulting in 18 cases (24.7%) of discordance in the EGFR-mutation results (Table 3) assessed by both tests. In 61 PANAMutyper-negative cases, NGS revealed an EGFR mutation in 14 cases (23.0%), of which 10 (16.4%) showed mutations in exons 18 through 21 (Fig. 3). Notably, all mutations found in these 10 cases were not included in the list of hotspot mutations by PANAMutyper. Three of these mutations [c.2154_2155GG > TT (G719C), c.2303_2304GC > TT (S768I), and c.2573_ 2574TG > GC (L858R)] eventually caused the same amino acid changes that are targeted by PANAMutyper; however, the specific nucleotide changes were not included in the list of detectable alterations. Additionally, another two mutations [c.2155G > C (G719R) and c.2303_2305delGCGinsTCT (S768_V769 > IL)] produced amino acid changes that were similar to but different from the targeted amino acid changes in the PANAMutyper test. Moreover, two in-frame insertion-deletion mutations of exon 19 and two insertion mutations of exon 20 identified by NGS were not identical to any of the detectable alterations in the PANAMutyper test. Furthermore, two mutations involving E709 resulting from a mutation in exon 18 and one exon 19 insertion mutation (neither of which are targeted by PANAMutyper) were also detected by NGS. Of the 10 patients found to have a sensitizing mutation according to NGS, seven received TKI treatment, with partial response observed in three patients and the other four showing stable disease. The median TTD was 20 months.

Comparison of PANAMutyper and next-generation sequencing (NGS) in PANAMutyper-negative cases (n = 61). NGS revealed targetable mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 18 through 21 in 16.4% of PANAMutyper-negative cases. Most of the detected amino acid changes were not targeted by PANAMutyper, while all the nucleotide changes were not targeted by PANAMutyper. All seven of the ten patients who received EGFR–tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy showed partial response or maintained stable disease. TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
In eight of the 12 cases with positive PANAMutyper results, NGS identified the same EGFR mutation. In one of these, EGFR amplification was also identified along with the previously known Exon19del. In two of the other four cases, additional mutations in exon 18 were identified by NGS (E709X and G724S). By contrast, EGFR mutations detected via PANAMutyper were not identified by NGS in two cases. In one case (N17 [Table 3] and R3 [Supplementary Table S8]), the patient was initially diagnosed with adenocarcinoma with mucinous differentiation, and EGFR mutation was not identified via PANAMutyper. Upon disease progression after chemotherapy, the patient underwent a second biopsy, which revealed the Exon19del mutation identified via PANAMutyper, whereas NGS revealed a KRAS G12D mutation in the absence of Exon19del. Erlotinib was administered for 2 months according to the PANAMutyper result, with the final computed tomography scan showing slight aggravation of the tumor, after which no further information was available as the patient no longer had outpatient visits. In the other case (N18), the PANAMutyper test identified Exon19del, and after 1 month of erlotinib treatment, disease progression with a skin rash was observed. NGS was performed following dissection of tumor cells on the smear slide of a pleural fluid sample based on the lack of previous biopsy material; however, this revealed no EGFR mutation. A subsequent biopsy on a metastatic lesion in the liver resulted in the identification of the same Exon19del mutation by PANAMutyper. Nevertheless, the patient did not benefit from TKI therapy due to disease progression and drug side effects.
There were 10 cases in which PANAMutyper and NGS were ordered concurrently with a follow-up biopsy to evaluate the mutational status of progressive disease after TKI administration. Acquired T790M mutation was detected in two cases, which were also identifiable by concurrent PANAMutyper tests. NGS identified additional EGFR mutations (E709K and G724S) in two cases and one case of EGFR amplification. Notably, in one case, the previously known Exon19del was not identified, although a new substitution mutation (S768_V769 > IL) in EGFR was revealed by NGS. Clinicopathologic and mutational information for these cases are shown in Supplementary Table S9.
DISCUSSION
In this study, the prevalence of EGFR mutations according to PANAMuytper tests in Korean LUAD patients was similar to those of previous reports, and NGS was able to detect rare mutations treatable by EGFR TKIs.
EGFR mutations are enriched in females and non-smokers; however, their association with age remains unclear. Some studies have indicated that EGFR mutations are more prevalent in younger patients [11,12], whereas other studies report opposing results [13,14]. However, one common age-related finding indicates that the Exon19del mutation is more common in younger patients, whereas L858R is more common in older patients [14–18]. Recently, Lee et al. [18] showed that the frequency of EGFR mutation was highest in middle-aged patients based on summing the frequencies of the Exon19del and L858R mutations. Similar results were obtained in the present study, with the frequency of EGFR mutation highest in patients aged 50 to 59 years and corresponding to the middle of the peak ages of patients harboring Exon19del and L858R mutations, regardless of sex and smoking status. In this respect, EGFR-mutated LUADs may be regarded as a group of heterogeneous diseases with different mutation profiles.
According to histologic subtypes, EGFR mutation was far less common in IMAs and solid predominant adenocarcinomas, a result similar to that reported in previous studies [5,18–23]. Interestingly, although MIAs showed a similar EGFR-mutation frequency with other invasive non-mucinous adenocarcinomas, a lower frequency was noted in AIS (63.2% vs. 35.3%). This tendency was also reported in other studies, as well as our previous report [24–26]. Additionally, in the present study, we identified preferential occurrence of the Exon19del mutation as compared with the L858R mutation in micropapillary predominant adenocarcinomas (44.2% vs. 21.2%) and preferential occurrence of L858R to Exon19del in lepidic adenocarcinomas (33.8% vs. 21.2%) (Fig. 2). Though the current predominant pattern-based classification is unlikely to be matched with specific driver mutations, differences in genomic or epigenetic and transcriptional features have been demonstrated along the different histologic patterns [27,28]. These findings might be related to the process of tumorigenesis and may be further elucidated through future studies.
Compared with resection specimens, EGFR mutation was detected less frequently in biopsy materials, especially metastatic lymph nodes. In these cases, the sensitivity of the mutation test might have been affected by the paucity of tumor cells and the diluting effect of surrounding lymphocytes [18]. Thus, caution should be used in the interpretation of test results for cases where the proportion of tumor cells is considerably small. Nevertheless, this explanation may be insufficient, because EGFR mutations can be detected using very small numbers of tumor cells and even in cytology samples [29]. Moreover, the clinical context (e.g., initial workup or a follow-up test after treatment) might be reflected in the method of sample acquisition, thereby affecting the difference between procedures. Because quantitative information could not be obtained from the PANAMutyper test, this study was limited in determining whether the differences in results were a matter of tumor quantity or purity. Similar difficulties were present in determining whether the discordant results of repetitive tests were due to technical problems or the presence of actual heterogeneity. In this regard, other tests, such as droplet digital PCR or NGS enabling estimation of quantitative information, would have an advantage in interpreting ambiguous or unexpected results.
In this study, NGS tests were performed at the request of the clinician mainly to obtain additional information from patients with advanced lung cancer and who had negative results according to PANAMutyper tests or who had progressed while using EGFR-TKIs. Among patients with no EGFR mutation detected according to the PANAMutyper test, NGS results were also negative in most cases; however, there was a significant proportion of cases in which novel rare mutations were found in EGFR exons 18 through 21 (10/61, 16.4%). TKIs were used in seven of these 10 patients, all of whom subsequently demonstrated either partial response or maintained stable disease. Notably, all the newly discovered mutations were those not targeted by the PANAMutyper test; conversely, there were no cases where the PANAMutyper test missed detectable mutations. Therefore, the difference was not due to the detection limit or sensitivity of the tests but rather a consequence of the difference in the mutation-specific targets of the respective assays and sequencing-based methods. Others have also reported the value of NGS in detecting novel EGFR mutations in Korean patients with similar yields (16/175 [8] and 7/81 [30] cases). Given that the number of mutations that can be targeted is limited, NGS clearly has the advantage of avoiding false-negative results.
Additionally, there were 10 cases where the disease progressed during the administration of EGFR-TKIs, and tissue was obtained and submitted again for NGS evaluation with or without another PANAMutyper test. Of these cases, the well-known T790M mutation was found in only two cases, but additional genetic information that could affect the effectiveness of EGFR-TKIs was identified in some of the other cases. In one case, a G724S mutation was identified after disease progression in a patient with the Exon19del mutation. The G724S mutation was identified as being involved in a potential resistance mechanism following osimertinib therapy while retaining sensitivity to second-generation TKIs [31–33]. The case in the present study differed, in that the primary regimen was gefitinib, and that the patient responded to second-line erlotinib treatment. Furthermore, EGFR amplification was identified in a case with Exon19del, where amplification of a wild-type or mutated EGFR allele could potentially act as a resistance mechanism [34,35].
There also exist EGFR-independent resistance mechanisms to EGFR-TKIs, including MET amplification, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 amplification, RAS–mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway activation, phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway activation, and alterations of genes involved in the cell cycle [36]. In the present study, one case showed MET amplification in addition to the EGFR L858R mutation. Additionally, several studies report TP53 mutations as being related to inferior outcomes associated with EGFR-TKIs [37,38]. Although these mutations are being explored, it is evident that co-occurring genomic alterations contribute to the complexity of EGFR-mutated tumors, as well as the resistance mechanism to TKIs, and could be linked to treatment strategies in the future [39–42].
We demonstrated the capability of NGS to identify uncommon activating EGFR mutations, thereby providing benefits to patients through the use of TKIs. Specifically, NGS was able to identify genetic alterations in both EGFR and other genes possibly related to TKI responsiveness. However, considering the facilities and costs required to perform NGS, it does not seem appropriate to replace well-established PCR-based assays as a first-line screening method, especially given the frequency with which EGFR mutations are found in the Korean population. Therefore, as suggested by Park and Shim [8], NGS could be actively used in patients with advanced lung cancer when no targetable alterations are found or unexpected responses to TKIs are observed.
This study has some limitations. This was a retrospective observational study of LUAD patients, suggesting the possibility of selection bias, given that only patients who had undergone molecular testing were reviewed. However, because most patients diagnosed with LUAD in our institution eventually undergo EGFR testing, the current patient cohort is likely to represent the general population.
In conclusion, this study presented the overall frequency and subtype distribution of EGFR mutations in Korean LUAD patients and identified a small group of patients within the cohort that harbored uncommon EGFR mutations, where additional targeted deep sequencing was critical to establishing the treatment plan. According to the clinical presentation, NGS testing could provide information that helped to determine the appropriate targeted treatment.
Supplementary Information
The Data Supplement is available with this article at https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.06.11.
Notes
Ethics Statement
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (Seongnam, Korea) (approval No. B-2107-697-101), and the need for informed consent was waived.
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets generated or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: JL, YBH, JHC. Data curation: JL, SKL. Formal analysis: JL, YBH, JHC. Project administration: YBH, JHC. Supervision: HJK, HK, JHC. Writing—original draft: JL, YBH, JHC. Writing—review & editing: JL, YBH, HJK, HK, JHC. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Conflicts of Interest
J.H.C., a contributing editor of the Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine, was not involved in the editorial evaluation or decision to publish this article. All remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korean Government (MSIT) [grant number 2022 R1A5A6000840]; and partly by the Korean Society of Pathologists [grant number KSPG 2019-02].