Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration in Taiwan: The History and Current Practice
Article information
Abstract
In Taiwan, thyroid cancer is the most common endocrine gland malignancy and the incidence of thyroid cancer has increased four-fold in the past two decades. Fine-needle aspiration is an accurate and cost-effective method of evaluating thyroid nodules and has been the gold-standard diagnostic tool for thyroid tumors in Taiwan since the 1980s. This article reviews the history, current practice, reporting systems, training, and quality assurance for thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology in Taiwan.
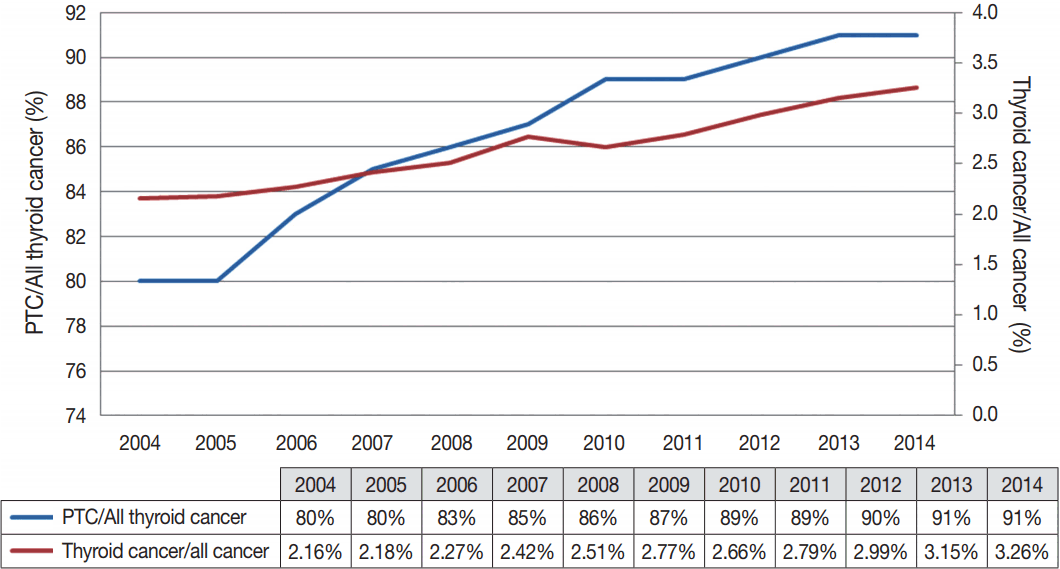
Thyroid cancer is the most common endocrine gland malignancy, accounting for 3.26% of all cancers in Taiwan [1]. The incidence of thyroid cancer is 14.34 per 100,000 persons per year. It has a female predominance at 21.6 per 100,000 women per year (representing the fifth most common malignancy in women) versus 7.06 per 100,000 men per year (the 15th most common malignancy in men). The incidence has increased four-fold in the past two decades (from 3.3 per 100,000 persons per year in 1995). Unlike in South Korea [2], there is no thyroid cancer screening program in Taiwan. However, the general population is increasingly aware of cancer-related issues and health checkups are growing in popularity. Detection of small thyroid nodules via ultrasonography largely accounts for the increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in Taiwan. Papillary thyroid carcinoma, which comprises 91% of all newly diagnosed thyroid cancers, has contributed to the majority of this increase (Fig. 1). Nevertheless, the mortality rate of thyroid cancer remains relatively low (0.86 per 100,000 women per year and 0.47 per 100,000 men per year) and has increased little since 1995 (0.73 per 100,000 women per year and 0.28 per 100,000 men per year).
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is an accurate and cost-effective method of evaluating thyroid nodules. It has been the goldstandard diagnostic tool for thyroid tumors in Taiwan since the 1980s. This article reviews the history, current practice, reporting systems, training, and quality assurance for thyroid FNA cytology in Taiwan.
THE HISTORY OF THYROID FINE-NEEDLE ASPIRATION IN TAIWAN
Before the 1980s, the application of diagnostic cytology in Taiwan was limited to exfoliative cytology, such as sputum, body fluid, and Pap test. The utilization of interventional cytology began with thyroid FNA. Prof. Tien-Chun Chang, an endocrinologist at National Taiwan University Hospital, is considered to be the pioneer of thyroid FNA in Taiwan. In 1979, he performed the first thyroid FNA on a patient with follicular thyroid carcinoma. After this initial attempt, which demonstrated promising diagnostic value, he began an on-site aspiration and cytologic diagnosis service at bedsides and in his thyroid clinic. Instead of using standard May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining, which usually takes less than 10 minutes, he applied Liu staining on cytologic smears, which produced similar staining quality for rapid diagnosis [3]. The Liu stain is a modified Romanowsky stain invented by Prof. Chen-Hui Liu in 1953 for hematologic smears. The entire staining procedure is simple and takes only 2 minutes [3]. Therefore, it is suitable for on-site diagnostic services and has been widely used in Taiwan and China.
In 1981, Prof. Chang published the first article on thyroid FNA in a Taiwanese medical journal and attracted attention among clinicians [4]. Later on, he published a series of articles on the cytologic presentation of non-neoplastic thyroid diseases, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis [5], acute suppurative thyroiditis [6], and granulomatous thyroiditis [7], as well as thyroid carcinomas, such as papillary carcinoma [8] and anaplastic carcinoma [9] in the same journal. With these experiences from local practice, he started to publish articles in international journals in 1989 [10-22]. An anecdote about him is that he performs thyroid FNA while holding the needle like a Chinese brush pen [10]. He published this unique FNA method in Acta Cytologica [10]. Prof. Chang was also the pioneer of ultrasound-guided thyroid FNA [23], cytomorphometry analysis of thyroid tumors [11,14], and immunoperoxidsase staining of thyroglobulin and parathyroid hormone on cytologic smears [12,15]. In 1995, he published the first color atlas of thyroid and parathyroid cytology using Liu staining, which was written in Chinese. This book has been the textbook of choice for thyroid FNA in Taiwan for many years and a second edition was published in 2015 (Fig. 2) [24].
CURRENT THYROID FINE-NEEDLE ASPIRATION PRACTICE IN TAIWAN
Clinicians, especially endocrinologists, used to be both the performer and the interpreter of thyroid FNA. However, after the establishment of Taiwan’s National Health Insurance in 1995, specialized medicine has become the mainstay of healthcare. Physicians from different specialties started taking over the multidisciplinary tasks. Currently, radiologists are the main performers of FNA and pathologists are the main cytologic diagnosticians in Taiwan. Ultrasonography is used in the majority of thyroid FNA cases to guide the procedure.
When clinicians were the main performer of thyroid FNA and interpreter of corresponding cytology, air-dried direct smears and Liu staining were the method of choice for slide preparation. Papanicolaou stain has been commonly applied since pathologists took on thyroid cytology diagnosis, due to its superiority in demonstrating nuclear features that are important in papillary carcinoma diagnosis. Currently, conventional smears for both Papanicolaou staining (on alcohol-fixed slides) and Liu staining (on air-dried smears) are the most common preparations for thyroid FNA cytology in Taiwan. Liquid-based preparation was first introduced and applied in thyroid FNA in 2014, and is becoming more popular due to its high cell yield and standardized quality. In some institutions, immunocytochemical staining and molecular testing are also utilized on thyroid cytologic specimens to further facilitate diagnosis. Thyroid core-needle biopsy is a rare practice in Taiwan.
REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE AND REPORTING SYSTEM FOR THYROID CYTOLOGY IN TAIWAN
Given the history of thyroid FNA in Taiwan, most studies on the diagnostic accuracy and rate of malignancy were published by endocrinologists before the introduction of the Bethesda System. The major issue in previous studies is that investigators used different diagnostic categories, making it difficult to compare the findings of different studies. For example, Prof. Jen-Der Lin from Chang Gung Memorial Hospital used a four-tier system (benign, follicular neoplasm, malignant, and unsatisfactory) to emphasize the follicular pattern and this approach resulted in 16.6% of resected papillary carcinomas being diagnosed as follicular neoplasm [25,26]. In contrast, other groups used different four-tier systems without further specifying the follicular pattern [27,28]. Among all hospitals in Taiwan, only three branches of the Veterans General Hospital, in which American System of thyroid FNA practice was adopted initially, use the Bethesda System or a diagnostic system compatible with the Bethesda System [29].
In Taiwan, the diagnostic criteria for inadequate specimen vary between different individuals. The “more than six groups and each group more than 10 follicular cells” rule proposed by the Bethesda System is usually applied [30]. Most pathologists from Taiwan still consider the specimen negative instead of non-diagnostic in the following situations: a specimen with less than six groups but more than 50 follicular cells in total, or a degenerative hemorrhagic cyst with scant benign follicular cells.
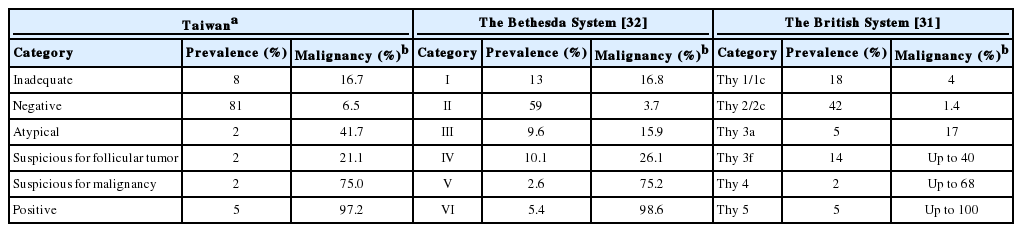
Comparing the diagnostic system used at our hospital with the corresponding categories in the Bethesda System and the British System [31], the frequency of atypical diagnosis is lower in Taiwan (Table 1). However, the rate of malignancy in these categories is compatible to data collected in Western countries. A study from Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung showed a similar trend [29]. We consider microcarcinomas larger than 0.5 cm found on resection specimens, which are usually detectable on ultrasonography, as malignant on follow-up. This could explain the higher rate of malignancy in our negative categories.
CYTOLOGY TRAINING AND QUALITY ASSURANCE IN TAIWAN
Cytology training for medical graduates is integrated into the Anatomic Pathology Residency Training Program. In addition to at least 3 months of cytology practice training, pathology residents are required to take a 2-week intensive course. This course covers various topics in cytology from Pap smear to thyroid FNA. A microscopic exam is held on the last day of the course. Residents need to pass the exam to be qualified. On the anatomic pathology board exam, in addition to surgical pathology, there is a separate cytopathology section. Residents need to get passing scores in both parts in order to pass the anatomic pathology board exam. For board-certified pathologists, annual cytology education activities are required.
The training program for cytotechnologists consists of one year of on-site training at a qualified training institution and a final exam. The training institution must routinely provide both surgical pathology and cytology services and process more than 8,000 Pap smears annually. The cytology lab director must be a qualified cytopathologist (certified by either the International Academy of Cytology or the Taiwan Society of Clinical Cytology) and there must be at least two senior cytotechnologists on site with more than 3 years of work experience. Currently, there are 12 qualified institutions for cytotechnologist training in Taiwan. After training and exams, each qualified cytotechnologist is allowed to screen up to 10,000 cytology cases (Pap smears and non-gynecologic specimens) per year. Currently, there are about 550 practicing cytotechnologists in Taiwan. There have been no systematic surveys of the number of cytotechnologists working with thyroid specimens in Taiwan. Most work at hospitals where thyroid FNA is performed. Cytotechnologists usually perform specimen preparation and screening under the supervision of pathologists. Since 2017, the Taiwan Society of Clinical Cytology has started an inter-laboratory diagnosis comparison program for non-gynecologic cytology, including thyroid FNA. So far, a total of 81 labs have participated. The results are still under analysis and will be given to individual lab.
FUTURE CHALLENGES
Thyroid FNA cytology is being performed more frequently and has become the most common FNA specimen in Taiwan. Therefore, it is important to apply a uniform diagnostic system for consistent communication and management. Newly developed thyroid cytology technologies, such as liquid-based preparation, immunocytochemistry and molecular testing, may facilitate more accurate diagnosis.
Notes
Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.