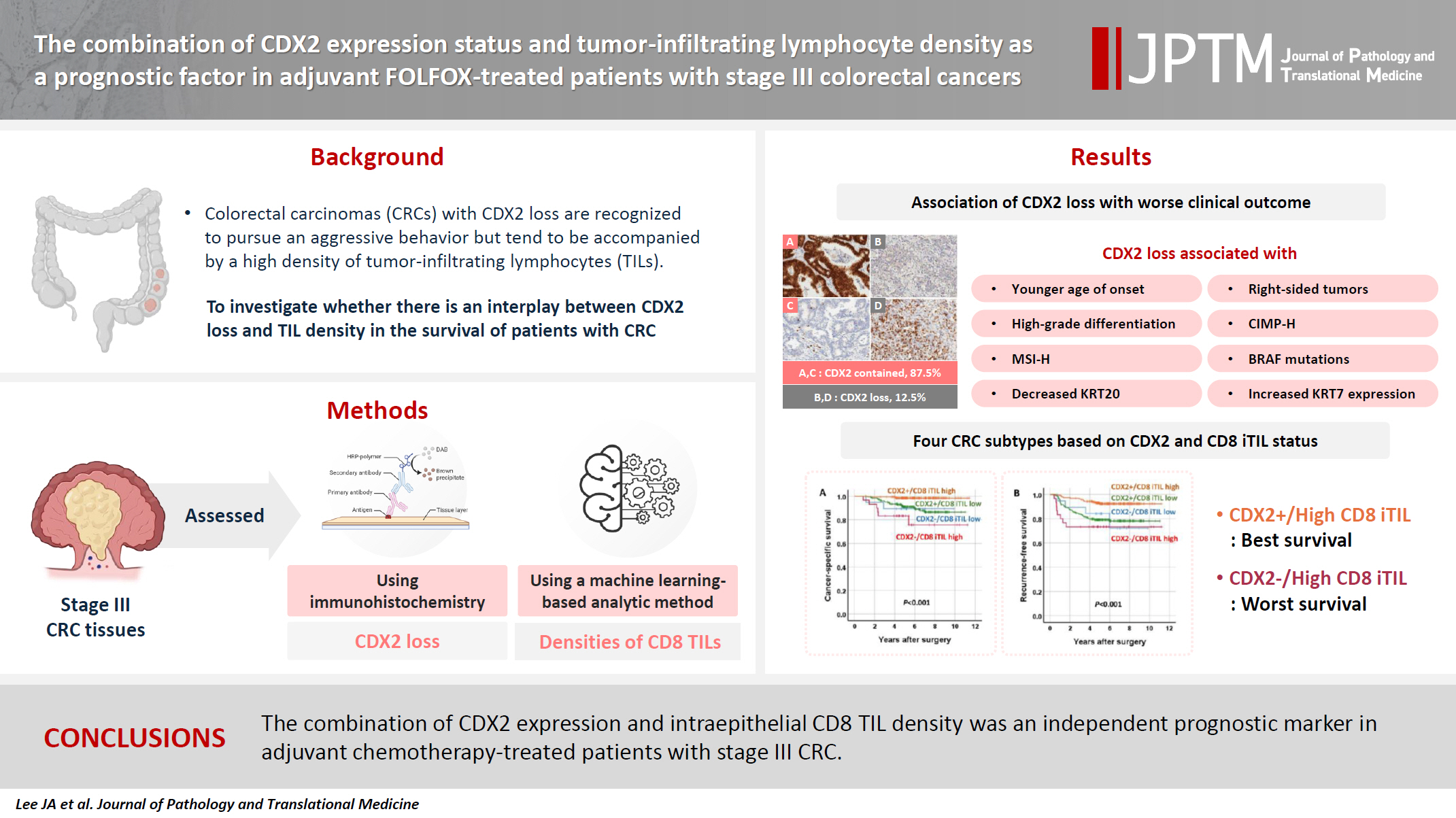
The combination of CDX2 expression status and tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte density as a prognostic factor in adjuvant FOLFOX-treated patients with stage III colorectal cancers
Article information
Abstract
Background
Colorectal carcinomas (CRCs) with caudal-type homeobox 2 (CDX2) loss are recognized to pursue an aggressive behavior but tend to be accompanied by a high density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). However, little is known about whether there is an interplay between CDX2 loss and TIL density in the survival of patients with CRC.
Methods
Stage III CRC tissues were assessed for CDX2 loss using immunohistochemistry and analyzed for their densities of CD8 TILs in both intraepithelial (iTILs) and stromal areas using a machine learning-based analytic method.
Results
CDX2 loss was significantly associated with a higher density of CD8 TILs in both intraepithelial and stromal areas. Both CDX2 loss and a high CD8 iTIL density were found to be prognostic parameters and showed hazard ratios of 2.314 (1.050–5.100) and 0.378 (0.175–0.817), respectively, for cancer-specific survival. A subset of CRCs with retained CDX2 expression and a high density of CD8 iTILs showed the best clinical outcome (hazard ratio of 0.138 [0.023–0.826]), whereas a subset with CDX2 loss and a high density of CD8 iTILs exhibited the worst clinical outcome (15.781 [3.939–63.230]).
Conclusions
Altogether, a high density of CD8 iTILs did not make a difference in the survival of patients with CRC with CDX2 loss. The combination of CDX2 expression and intraepithelial CD8 TIL density was an independent prognostic marker in adjuvant chemotherapy-treated patients with stage III CRC.
INTRODUCTION
Colorectal cancer (CRC) ranks third in cancer prevalence and second in cancer mortality worldwide [1]. The prognostication of patients with CRC is globally based on the tumor, node, metastasis (TNM) staging, which reflects the extent of the cancer. However, there is significant variation in survival among patients who have the same cancer stage [2,3]. Fluoropyrimidine-oxaliplatin combination (FOLFOX) therapy is standard care after surgery for patients with stage III colon cancer. However, it is estimated that a considerable portion of patients with stage III colon cancer do not benefit from adjuvant FOLFOX therapy, and some patients suffer from unnecessary toxicity [4-7]. Thus, it is necessary to develop clinicopathological or molecular biomarkers that help to identify whether patents will benefit from adjuvant combination therapy.
Caudal-type homeobox 2 (CDX2) is a major regulator of intestine-specific genes involved in cell growth and differentiation. CDX2 is a gene that is only active in the small and large intestines and is detected in most CRCs (90%) [8-10]. Patients with CRC which has no CDX2 expression tend to have worse outcomes [8,11]. Although CDX2 loss has been shown to be a marker of poor prognosis in stage II colon cancer [12], CDX2 loss has been demonstrated to be a marker of chemotherapy sensitivity in stage II colon cancer patients, implying that adjuvant chemotherapy might be a treatment option for patients with stage II CDX2-deficient colon cancer [13]. However, another previous study has suggested that CDX2 loss may be a possible negative marker of chemotherapy response in CRC patients with metastases [14].
Regarding the cause of CDX2 loss in CRC, promoter CpG island hypermethylation has been suggested [11]. CDX2 loss is more frequent in CRCs with CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP) than in CRCs without CIMP [8,15] and in CRCs with microsatellite instability (MSI) than in CRCs without MSI [8,11,12,16]. CIMP and MSI have been shown to be associated with enhanced tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) density [17,18]. There is not much information about the TIL status in CRCs that lack CDX2 expression [8], but CRCs that lack CDX2 expression are likely to have higher TIL density than CRCs with retained CDX2 expression because of the relationship between CDX2 loss and MSI or CIMP. In terms of prognosis, it remains unclear whether patients with CDX2-deficient CRC show different clinical outcomes depending on TIL density status.
In the present study, we aimed to identify (1) whether CDX2 loss is associated with poor clinical outcome in adjuvant FOLFOX-treated patients with stage III CRC, (2) whether CDX2 loss is associated with an increased density of TILs, and (3) whether there is an interplay between CDX2 expression and TIL status in patient survival. To resolve the above issues, we performed CDX2 immunohistochemistry (IHC) of cancer tissue samples from stage III CRC patients treated with adjuvant FOLFOX and quantified CD3-positive TILs and CD8-positive TILs in both intraepithelial and stromal areas using a machine learning-based analytic method and then correlated CDX2 expression status with clinicopathological and molecular features. To investigate whether an interplay exists between CDX2 loss and TIL density in the survival of patients with CRC, we examined the combined CDX2 expression and TIL density statuses to understand their impact on survival characteristics.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Samples
Archival tissue blocks of the surgical specimens from 505 patients with stage III CRC who received adjuvant FOLFOX after curative surgery (R0) at Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) between April 2005 and December 2012 were available for construction of a tissue microarray (TMA). Whole-slide immunostaining of CD3 and CD8 was possible in 446 of the 505 patients. Patients were chosen for the present study based on the following criteria: they were over 18 years old, they had adenocarcinoma type of cancer, they had stage III CRC, they had their tumor removed completely with no cancer cells at the edges, and they finished at least six cycles of 5-fluorouracil plus oxaliplatin or four cycles of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin as adjuvant therapy. The present study did not include patients who met any of these criteria: having chemotherapy or radiotherapy before surgery, a genetic condition that causes many polyps in the colon and rectum, an idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease, or a previous diagnosis of any other cancer within 5 years. We reviewed electronic medical records and collected demographic and clinicopathological data, such as age, sex, tumor location, histological differentiation, lymphatic emboli or venous invasion, perineural invasion, and American Joint Committee on Cancer/International Union against Cancer (AJCC/UICC) cancer stage (7th edition).
Immunohistochemistry
One pathologist (S.Y.Y.) selected the paraffin tissue block most representative of the tumor, and whole-slide sections were subjected to IHC with antibodies against CD3 (clone F7.2.38, Dako, Carpenteria, CA, USA) and CD8 (clone SP57, Ventana Medical Systems, Tucson, AZ, USA) [19]. The TMA blocks received cores that were 2 mm across and taken from two separate regions of the tumor. TMA sections of 4-μm thickness were stained with primary antibodies against KRT7 (cytokeratin 7 [CK7], clone OV-TL 12/30, Dako), KRT20 (CK20, clone Ks20.8, Dako), and CDX2 (clone EPR2764Y ready-to-use, Cell Marque, Rocklin, CA, USA). An Aperio AT2 slide scanner (Leica Biosystems, Wetzlar, Germany) was used to scan all the stained slides. To interpret the IHC results, the proportion of tumor cells that expressed KRT7 and KRT20 in their cytoplasm was measured. The threshold was based on scores of 10% and 50% for high KRT7 expression and low KRT20 expression, respectively, following a prior study [8]. To interpret CDX2 IHC results, we used the H score to measure the intensity and extent of nuclear staining. the H score was calculated with this formula: 3 × percentage of strongly stained nuclei + 2 × percentage of moderately stained nuclei + 1 × percentage of weakly stained nuclei. The cutoff value was set at an H score of 20, and an H score of <20 was called loss of expression [20]. The analytic pipeline used the virtual slide files of CD3 and CD8 IHC as input, and its detailed protocol can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.yqvfvw6 [21]. After a user marked the tumor area on a given image, the algorithm divided the area into tiles of 1 mm × 1 mm and calculated the median density (number of cells/mm2) of TILs inside the epithelium (iTILs) and TILs in the stroma (sTILs).
DNA extraction, microsatellite instability analysis, and mutation analysis of KRAS and BRAF
Using a microscope, the parts of the tumor with typical histology and the most tumor cells were marked on glass slides, and the corresponding areas from the unstained tissue slides after deparaffinization were scraped from the glass slides. The tissues that were scraped off were transferred into microtubes with tissue lysis buffer and proteinase K and then left to incubate at 55°C for 24 hours. After centrifugation, the supernatant was transferred to a new tube and kept in a deep freezer. The fluorescent multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method with five microsatellite markers suggested by National Cancer Institute (BAT25, BAT26, D2S123, D5S346, and D17S250) was used to determine the MSI status of each tumor. Tumors were categorized as MSI-H (MSI-high, with ≥2 unstable markers out of 5) or MSS (microsatellite-stable, with 1 or no unstable marker) (n = 503). Real-time PCR-based allelic discrimination was used to examine BRAF mutations at codon 600 (V600E) (n = 492). Codons 12 and 13 of KRAS exon 2 were sequenced to determine their mutation statuses (n = 486).
Bisulfite modification and methylation analysis
Using an EZ DNA methylation kit (Zymo Research, Orange, CA, USA), genomic DNA underwent bisulfite conversion, and then the MethyLight assay was used to assess the methylation level of these CIMP-specific markers (CACNA1G, CDKN2A (p16), CRABP1, IGF2, MLH1, NEUROG1, RUNX3, and SOCS1) (n = 500). The primer sequences and PCR conditions have been previously reported [22,23]. We performed the MethyLight assay three times and used the median value to show the methylation level of each marker. To determine the methylation status of a specific marker, the percentage of methylated reference (PMR) was calculated, and a marker with a median PMR >4 was deemed to be methylated. Each tumor was assessed for CIMP status and grouped into CIMP-H (CIMP-high, ≥ 5 out of 8 methylated markers), CIMP-L (CIMP-low, 1–4 methylated markers), or CIMP-0 (no methylation) as previously reported [17].
Statistical analysis
The normality test was conducted to determine whether TIL density was normally distributed using the Shapiro-Wilks test. The null hypothesis that the TIL density is normally distributed was rejected because the p-value was below .05 for all four types of TILs, including intraepithelial CD3 TILs (CD3 iTILs), stromal CD3 TILs (CD3 sTILs), CD8 iTILs, and CD8 sTILs. Thus, comparison of the TIL density between subsets of CRCs with CDX2 loss and with CDX2 retention was performed using the nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test. Student’s t test was used to compare the age distribution of two groups. For 2 × 2 contingency tables with a sample size of more than 5, a two-sided chi-square test was performed, while a Kruskal-Wallis test was applied for contingency tables with more than 2 × 2 dimensions. We measured the time from surgery to death by CRC as cancer-specific survival (CSS) time and the time from surgery to confirmed recurrence as recurrence-free survival (RFS) time. We censored the data from patients who did not die from CRC or relapse by the last follow-up visit for the CSS and RFS analyses, respectively. We used the Kaplan-Meier log-rank test to compare survival across groups. We estimated the hazard ratio with the Cox proportional hazard model and adjusted for baseline characteristics with a backward stepwise model that included the following covariates that were significant in univariate survival analysis: differentiation (high grade vs. low grade), venous invasion (present vs. absent), lymphatic emboli (present vs. absent), T category (T4 vs. T1–3), N category (N2 vs. N1), CK7 (expressed vs. not expressed), KRAS (mutant vs. wild type), CD3 sTIL, and CD8 sTIL.
RESULTS
The follow-up period for the 505 patients was a mean of 68.2 months (range, 4.1 to 134.8 months). Table 1 shows the demographic data. There were 303 males and 202 females. The tumor subsite was distributed as follows: 150 in the right colon, 289 in the left colon, and 66 in the rectum. CIMP-H and MSIH CRCs were present in 5.4% and 5.6% of stage III CRCs, respectively. KRAS and BRAF mutations occurred in 28.8% and 3.5% of patients, respectively.
Relationships between decreased expression of CDX2 and clinicopathological features
Decreased expression of CDX2 (CDX2 loss) was found in 12.5% of stage III CRCs (Fig. 1). CDX2 loss was associated with a younger age of onset (56.1 vs. 59.8 years, Student’s t test, p = .003). CDX2 loss was more frequent in the right colon than in the left colon and rectum, in CRCs with high-grade histological differentiation than in CRCs with low-grade histological differentiation, in CIMP-H CRCs than in CIMP-L,0 CRCs, in MSI-H CRCs than in MSS CRCs, in CRCs with BRAF mutations than in CRCs without BRAF mutation, in CRCs with decreased expression of KRT20 than in CRCs without decreased expression of KRT20, and in CRCs with KRT7 expression than in CRCs without KRT7 expression (Table 1). CRCs with CDX2 loss showed a higher density of CD8 iTILs and sTILs than CRCs without CDX2 loss (Fig. 2). The significance of the difference was higher in the density of CD8 iTILs than in that of CD8 sTILs. However, the densities of CD3 iTILs and sTILs tended to be higher in CRCs with CDX2 loss than in CRCs with retained CDX2 expression, but the difference did not reach statistical significance (Fig. 2).

Representative cases of colorectal carcinomas (CRCs) with retained caudal-type homeobox 2 (CDX2) expression and a low CD8 intraepithelial tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (iTIL) density (A, C) and with CDX2 loss and a high CD8 iTIL density (B, D).
Association of CDX2 loss with worse clinical outcome
In univariate survival analysis, CDX2 loss was found to be significantly associated with shortened CSS but not RFS (Fig. 3A, B). In addition, several clinicopathological parameters, including tumor differentiation, T category, N category, lymphatic emboli, venous invasion, KRAS mutation, KRT7 expression, CD3 sTILs, CD8 iTILs (Fig. 3C, D), and CD8 sTILs, were found to be significant prognostic factors in the univariate analysis of CSS (Table 2).
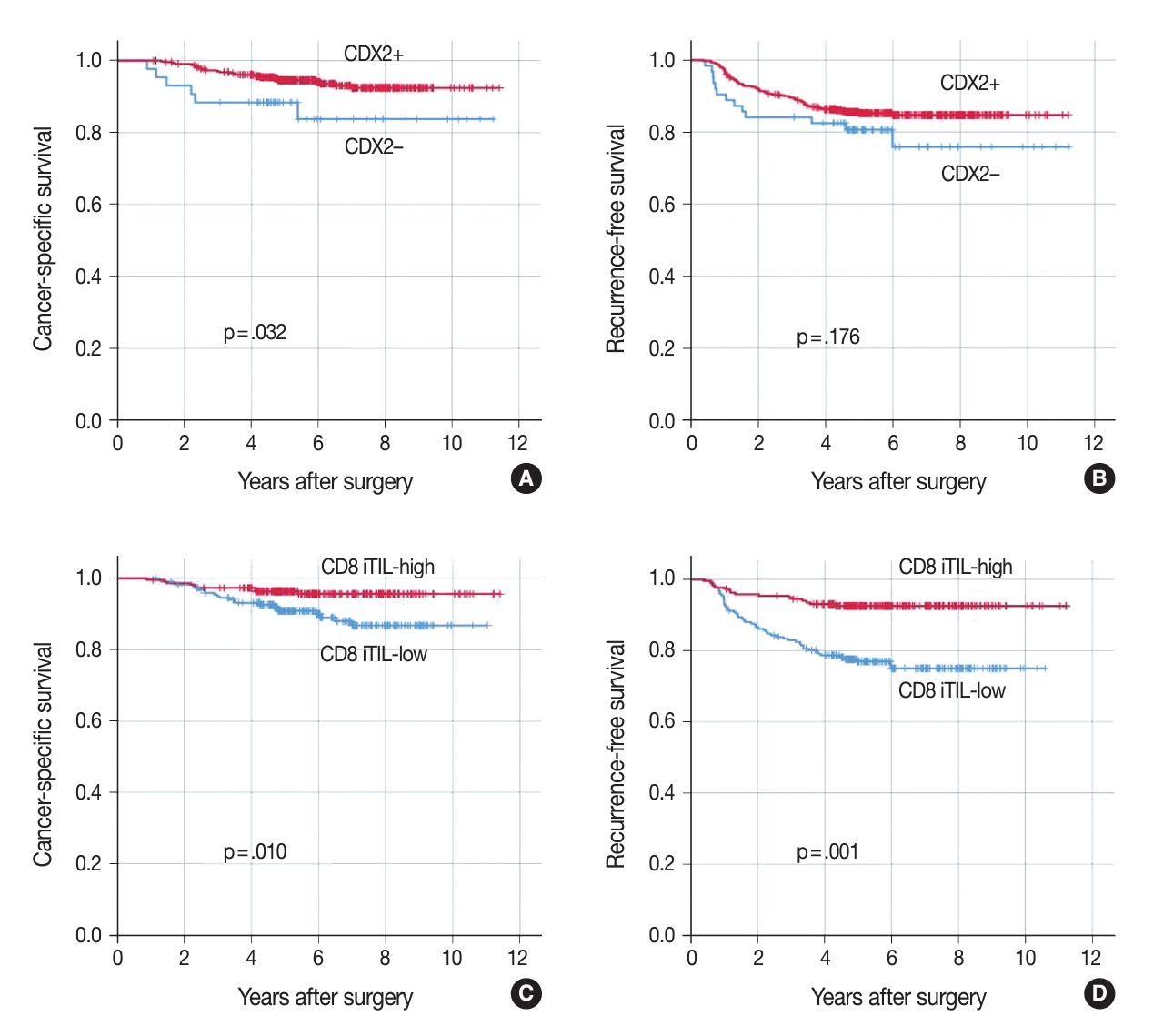
Kaplan-Meier curves of cancer-specific survival (A, C) and recurrence-free survival (B, D) in adjuvant FOLFOX-treated patients with stage III colorectal carcinoma (CRC) according to caudal-type homeobox 2 (CDX2) expression status (A, B) and CD8 intraepithelial tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (iTIL) density status (C, D). CDX2+ (retained expression, n = 442) and CDX2- (loss of expression, n = 63); CD8 iTIL-high (n = 223) and CD8 iTIL-low CRC (n = 223).
Combination of CDX2 expression and CD8 iTIL density status as a prognostic parameter
The combination of CDX2 expression and CD8 iTIL density status generates four subsets of CRCs. In the analysis of CSS using the Kaplan-Meier log-rank test, a subset with retained CDX2 expression and a high density of CD8 iTILs showed the best clinical outcome, whereas subsets with CDX2 loss exhibited worse clinical outcomes, regardless of CD8 iTIL status, than a subset with retained CDX2 expression and a high density of CD8 iTILs (Fig. 4). Statistically, there was no significant survival difference between a subset with CDX2 loss and a high density of CD8 iTILs and a subset with CDX2 loss and a low density of CD8 iTILs (p = .384 and p = .501, CSS and RFS, respectively). In the multivariate analysis, the combination of CDX2 expression and CD8 iTILs was found to be an independent prognostic parameter (Table 3).

Kaplan-Meier survival curves of cancer-specific survival (A) and recurrence-free survival (B). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis with the log-rank test was performed in adjuvant FOLFOX-treated patients with stage III colorectal carcinoma according to the combination of caudal-type homeobox 2 (CDX2) expression and CD8 intraepithelial tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (iTIL) density. CDX2+ (CDX2 retained)/CD8 iTIL-high (n = 188); CDX2+/CD8 iTIL-low (n = 209); CDX2– (CDX2 loss)/CD8 iTIL-high (n = 30); CDX2–/CD8 iTIL-low (n = 19).
DISCUSSION
In the present study, we analyzed a cohort of adjuvant FOLFOX-treated patients with stage III CRC regarding whether CDX2 loss was associated with a shortened survival, whether CDX2 expression status was associated with the intraepithelial or stromal TIL density, and whether there was an interplay between CDX2 expression and TIL density in patient survival. The findings demonstrated that CDX2 loss was a prognostic factor heralding poor prognosis in patients with stage III CRC treated with adjuvant FOLFOX, CDX2 loss was accompanied by increased infiltration of CD8 iTILs and sTILs, and a combined status of CDX2 expression and CD8 iTIL density was an independent prognostic parameter in FOLFOX-treated patients with stage III CRC.
In the present study, CRCs with CDX2 loss showed higher densities of CD8 iTILs and sTILs than CRCs with retained CDX2 expression. However, in terms of prognosis, CDX2 loss might collide with an increased density of CD8 iTILs because CDX2 loss and an increased density of CD8 iTILs were associated with worse and better survival, respectively (Table 2, Fig. 3). Of the four subsets generated by the combination of CDX2 expression and CD8 iTIL density statuses, a subset of CRCs with retained CDX2 expression and high CD8 iTIL density showed the best clinical outcome, which is in accordance with Derangere et al.’s study [24] in which stage III colon cancers harboring high CDX2 expression and a high CD3 TIL were associated with a good prognosis. However, in the present study, the worst clinical outcome was observed in a subset of CRCs with CDX2 loss and high CD8 iTIL density, in contrast to Derangere et al.’s study [24], which showed the worst prognosis in stage III colon cancers with low CDX2 expression and a low CD3 TIL density. The reason for such a discrepancy might be related to the different cutoff values set for CDX2 expression and TIL density for dichotomization. In Derangere et al.’s study [24], three-fourths of colon cancers were classified into tumors with low CDX2 expression, and two-thirds of colon cancers were classified into tumors with a low CD3 TIL density, whereas in our study, one-eighth of CRCs were classified into tumors with CDX2 loss, and one-half of CRCs were classified into tumors with a low CD8 iTIL density.
Because a high CD8 iTIL density is associated with good prognosis, it was expected that tumors with CDX2 loss and a low CD8 iTIL density would be associated with the worst survival. Interestingly, the density of CD8 iTILs did not significantly impact the survival of patients with tumors exhibiting CDX2 loss. The underlying reason for this lack of effect remains challenging to explain. It can be speculated that CD8 iTILs might be not effective in fighting against cancers with CDX2 loss. However, little information is available to support this assumption, and thus, spatial transcriptomics at the single-cell level might provide clues to the explanation. Our result that the number of CD8 iTILs did not affect the survival of patients with tumors that had CDX2 loss seems to contradict the common belief of a better survival of patients with a high CD8 TIL number [25]. But in human cancer, renal cell carcinoma is the tissue type where many CD8 TILs are strongly related to bad clinicopathologic data and worse patient survival [26-28]. Furthermore, in pancreatic cancer, the role of CD8+ T cells is not directly associated with clinicopathological parameters [28]. Thus, loss of CDX2 expression in CRC may indeed indicate a reduction in intestinal differentiation, in which the prognostic role of CD8 TILs might differ from that in CRCs with retained CDX2 expression.
In our study, CDX2 loss was associated with increased infiltration of intraepithelial and stromal CD8-positive lymphocytes. However, the association between CDX2 loss and increased TIL density might be spurious because CDX2 loss was also associated with CIMP-H and MSI-H, which are known to be accompanied by increased TILs. Thus, to elucidate whether CDX2 loss is associated with increased TILs regardless of CIMP and MSI status, we analyzed the relationship between CDX2 loss and increased TIL density in CRCs which are negative for CIMP-H and MSI-H, namely, CIMP-L,0 and MSS CRCs (n = 396). An increased density of CD8 iTILs was found in CIMP-L,0 and MSS CRCs with CDX2 loss (n = 34) compared with CIMP-L,0 and MSS CRCs with retained CDX2 expression (n = 362) (Supplementary Fig. S1). Such a finding indicates that the increased density of CD8 iTILs might be related to CDX2 loss itself.
In summary, we found that in patients with stage III CRC, CDX2 loss was associated with increased infiltration of CD8 iTILs or sTILs, and the density of CD8 iTILs did not significantly impact the survival of patients with CRC exhibiting CDX2 loss. The combination of CDX2 expression and intraepithelial CD8 TIL density was found to be an independent prognostic marker in adjuvant chemotherapy-treated patients with stage III CRC.
Supplementary Information
The Data Supplement is available with this article at https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.26.
Notes
Ethics Statement
The Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital approved this study (1811-061-983) and waived the requirement to obtain informed consent. This study followed the Declaration of Helsinki guidelines.
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets generated or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: JMB, GHK. Formal analysis: JMB, GHK. Funding acquisition: GHK. Investigation: JAL, HEP, HYJ, LJ, SYY, JMB. Methodology: SYY, JMB. Project administration: NYC, JMB. Resources: JMB, JHK, GHK. Supervision: JMB, GHK. Visualization: JAL, GHK. Writing—original draft: JAL, GHK. Writing—review & editing: JAL, GHK. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Conflicts of Interest
J.H.K., a contributing editor of the Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine, was not involved in the editorial evaluation or decision to publish this article. All remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Funding Statement
This study was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korea Government (MSIT) (No. 2021R1A2C1003542, RS-2023-00218623, and RS-2024-00450408).