Multifocal Adenocarcinomas Arising within a Gastric Inverted Hyperplastic Polyp
Article information
Abstract
We present herein the occurrence of multifocal adenocarcinomas with a minute signet ring cell carcinoma that arose within a gastric inverted hyperplastic polyp (IHP) in a 40-year-old woman. Endoscopic ultrasonography demonstrated a heterogeneous hypoechoic mass in the third layer of the gastric wall. The endoscopic submucosal dissection specimen measuring 3.5×3.2×1.8 cm was a well-circumscribed protruding lesion that had a slit-shaped cavity. Histologically, the lesion consisted mainly of endophytic proliferation of hyperplastic columnar cells resembling normal foveolar epithelium. In addition, six foci of adenocarcinomas and a minute focus of signet ring cell carcinoma were randomly distributed in the superficial and deep regions. The adenocarcinoma was gradually transitioning from dysplasia, while the signet ring cell carcinoma was surrounded by hyperplastic foveolar epithelium. This is the first report of a gastric IHP with multifocal intramucosal adenocarcinomas and a signet ring cell carcinoma, and endoscopic submucosal dissection is used to completely resect it.
Gastric inverted hyperplastic polyp (IHP), a rare type of gastric polyp, is characterized by the downward growth of hyperplastic mucosal components into the submucosal layer. Macroscopically, an IHP resembles a subepithelial tumor macroscopically.1 More than 30 cases of gastric IHP have been reported, but the pathogenesis of this tumor is not understood. Defining the process of malignant transformation within a gastric IHP presents a challenge because the lesion is extremely rare. To our knowledge, the occurrence of a well-differentiated adenocarcinoma within a gastric IHP has been reported only once.2 Here we describe multifocal adenocarcinomas that arose within a gastric IHP. We treated this tumor with endoscopic submucosal dissection technique.
CASE REPORT
A 40-year-old woman presented with a one-month history of preprandial epigastric pain. Her medical history included uterine leiomyoma. Physical examination and laboratory data produced no abnormal findings. Endoscopic examination revealed a subepithelial mass in the gastric body that was covered with normal mucosa and showed round superficial nodular changes at the surface. Bridging of surrounding folds was evident (Fig. 1A). Endoscopic ultrasonography demonstrated a heterogeneous hypoechoic tumor in the third layer of the gastric wall (Fig. 1B). With the expectation of a gastric submucosal tumor, endoscopic submucosal dissection was performed to resect the mass completely.
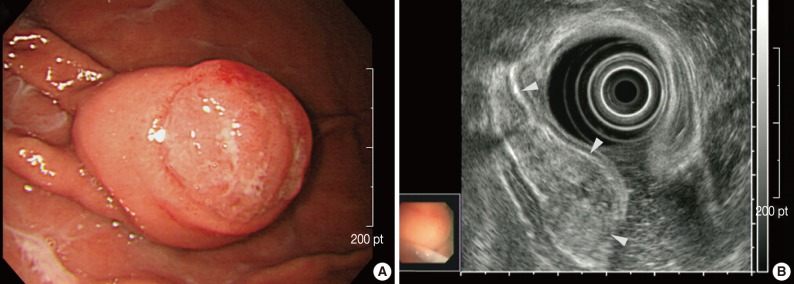
Endoscopic findings. (A) A subepithelial mass in the gastric body shows round superficial nodular change at the surface, with bridging of surrounding folds (right upper corner). (B) Endoscopic ultrasonography shows a heterogeneous hypoechoic tumor in the third layer of the gastric wall (arrowheads).
Grossly, the resected specimen measuring 3.5×3.2×1.8 cm was a well-circumscribed protruding lesion with a slit-shaped cavity in the center (Fig. 2A). Histologically, the lesion consisted mainly of endophytic proliferation of hyperplastic columnar cells that resembled normal foveolar epithelium and were connected with inflamed surface epithelium. Also seen were six foci of adenocarcinomas, which were randomly distributed in the superficial and deep portions of the lesion (Fig. 2B, C). Transitions from hyperplasia to dysplasia (Fig. 2D) and from dysplasia to adenocarcinoma (Fig. 2E) were identified. The cancerous foci displayed distinct morphologic features, including well-formed tubular structures infiltrating the lamina propria (well-differentiated adenocarcinoma) (Fig. 2F), clusters of fused or cribriform glands lined with the tumor cells with obvious piling-up (moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma) (Fig. 2G) and indistinct glandular structures with occasional mucus production due to individual tumor cells (poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma) (Fig. 2H). We also found a minute focus of signet ring cell carcinoma that was surrounded by hyperplastic foveolar epithelium (Fig. 2I). No dysplasia was identified adjacent to the signet ring cell carcinoma. All cancerous foci were confined within the mucosa, and the resection margins were negative for dysplasia or carcinoma.
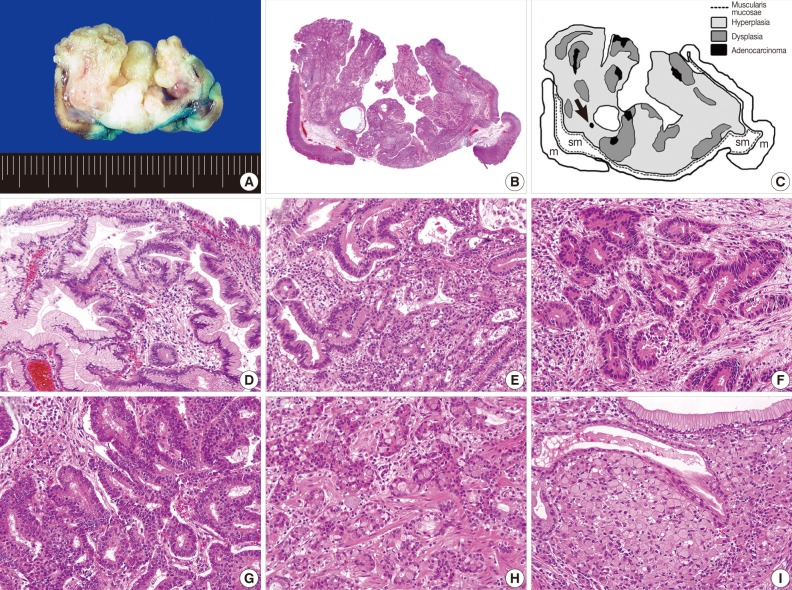
Gross and histologic findings. (A) The mass is a well-circumscribed downward-growing lesion with a slit-shaped cavity in the center. Scanning view (B) and schematic representation (C) of the lesion, which includes regions of hyperplasia and multifocal dysplasia and adenocarcinoma. A black arrow indicates a minute focus of signet ring cell carcinoma. m, mucosa; sm, submucosa. Transitions from hyperplasia (left half) to dysplasia (right half; D) and dysplasia (periphery) to adenocarcinoma (center; E) are apparent. Each cancerous focus displays a distinctive morphology and degree of differentiation, corresponding to well (F), moderately (G) and poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma (H). (I) In contrast with other cancerous foci, the signet ring cell carcinoma is surrounded by hyperplastic epithelium, without a transitional dysplastic component.
Immunohistochemically, almost all cancer cells in the adenocarcinoma (Fig. 3A) and signet ring cell carcinoma (Fig. 3B) and approximately 10% of dysplastic cells (Fig. 3C) were positive for p53 protein (1:2,000, clone DO-7, Novacastra, Newcastle upon Dyne, UK), while hyperplastic epithelium was negative (Fig. 3D). In addition, immunoreactivity to Ki-67 protein (1:250, clone MIB-1, Dakocytomation, Glostrup, Denmark) was detected in approximately 80% of cancer cells and in almost the same percentage of dysplastic cells, while no Ki-67 immunoreactivity was observed in hyperplastic epithelium.
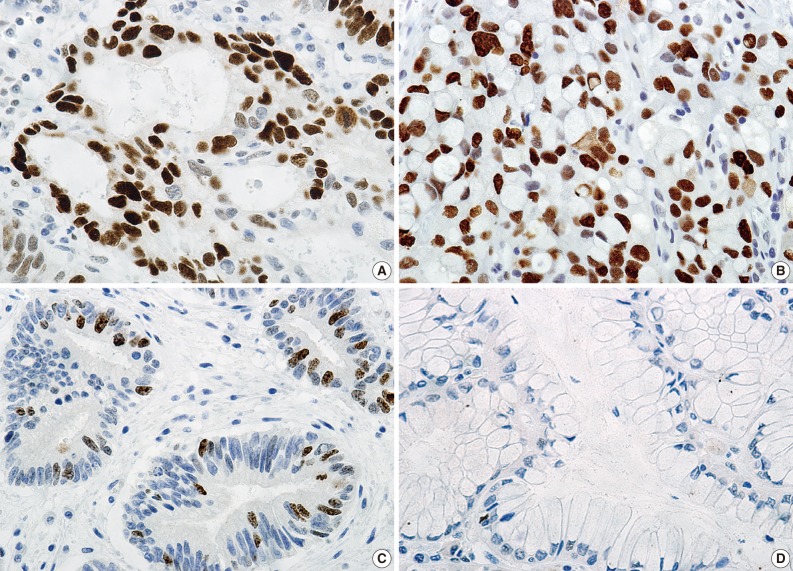
Immunohistochemical findings. Immunoreactivity to p53 protein is detected in almost all cancer cells in the adenocarcinoma (A) and signet ring cell carcinoma (B) and approximately 10% of dysplastic cells (C), but not in the hyperplastic epithelium (D).
The patient was discharged 3 days after endoscopic submucosal dissection without any complication. She has been followed-up as an outpatient with periodic endoscopy, and is healthy at 22 months without any sign of tumor recurrence.
DISCUSSION
Histologically, Gastric IHP consists of marked endophytic proliferation of foveolar-, pyloric- or fundic-type glandular epithelium, leading to a polypoid lesion. The main lesion is located in the submucosa or the inside of muscularis mucosae. In 1993, Kamata et al.1 named the lesion IHP, as it resembles IHP of the colon.3 To date, 35 cases of gastric IHP, including the present case, have been described in the English-language literature. Although the pathogenesis of IHP is not understood, studies suggest that inflammation and subsequent healing may promote the epithelial displacement.4,5 In our patient, the connection between the inflamed overlying mucosa and the hyperplastic component, and the presence of the slit-shaped cavity in the center suggested that repeated mucosal inflammation caused a break in the muscularis mucosae, which permitted the downward herniation and submucosal trapping of mucosal glands.
The occurrence of adenocarcinoma within a gastric IHP was reported for the first time by Kono et al.,2 who observed a single focus of well-differentiated adenocarcinoma emerging from adjacent dysplasia. Six cases of gastric IHP with coexisting adenocarcinoma have been reported.6,7 But in each case, the two lesions developed separately. To our knowledge, therefore, this is the second report of adenocarcinoma that arose within a gastric IHP. The presence of transitions from hyperplasia to dysplasia and from dysplasia to adenocarcinoma may indicate that the cancerous foci might progress through a dysplasia-carcinoma sequence. In the present case, p53 immunoreactivity was absent in hyperplasia, focal in dysplasia, and was diffuse and strong in the adenocarcinoma. These observations, in line with those of Kono et al.,2 suggest that p53 dysregulation may have an important role in the malignant transformation of IHP.
Also worth noting are the poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma and signet ring cell carcinoma we observed in this IHP. Most gastric HPs that undergo malignant transformation are accompanied by well- to moderately differentiated adenocarcinomas.8,9 In fact, an association of poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma or signet ring cell carcinoma with HP is extremely unusual.10-12 To our knowledge, this is the first report of a signet ring cell carcinoma that arose within a gastric IHP. The relationship between dysplasia and signet ring cell carcinoma is unknown, and the progression from dysplasia to carcinoma as generally understood does not adequately explain how signet ring cell carcinoma might develop within an IHP. However, our observation of diffuse, strong p53 immunoreactivity in the signet ring cell carcinoma may help to clarify the pathogenesis.
Several points may be relevant to the treatment of IHP. In view of the generally benign cellular characteristics of IHP, similar to those of HP, overtreatment should be avoided. However, given that dysplasia or even adenocarcinoma may develop within the IHP, the lesion should be resected. As we clearly demonstrated, multifocal adenocarcinomas may be present and randomly distributed in the superficial and deep regions of the gastric IHP. Despite a thorough review of endoscopic photographs, we could not precisely locate the cancerous foci. Furthermore, conventional endoscopic biopsy forceps would not be able to reach the deeply seated adenocarcinoma. In a large lesion, a negative biopsy result cannot reliably exclude the presence of dysplasia or adenocarcinoma, and hence a complete resection with a negative margin and thorough histologic examination should be performed. In the present case, the lesion was successfully resected using endoscopic submucosal dissection technique. For gastric mucosal and submucosal tumors, endoscopic resection is comparable to conventional surgery, but is less invasive and more economical.13 The endoscopic submucosal dissection technique is more reliable than the conventional endoscopic mucosal resection for en bloc resection of a lesion measuring larger than 2 cm.14 We recommend that endoscopic submucosal dissection be used to treat a gastric IHP measuring larger than 2 cm. Undoubtedly, this procedure requires endoscopists with specialized skill and experience, and follow-up with periodic endoscopy to check for recurrence.
We have described the occurrence of multifocal intramucosal adenocarcinomas with a minute signet ring cell carcinoma that arose within a gastric IHP. Our findings reveal that because biopsy cannot exclude the presence of dysplasia or adenocarcinoma, the IHP should be completely resected and analyzed histologically with particular thoroughness.
Notes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.