Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Lessons learned from the first 2 years of experience with thyroid core needle biopsy at an Indonesian national referral hospital
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Maria Francisca Ham, Retno Asti Werdhani, Erwin Danil Julian, Rafi Ilmansyah, Chloe Indira Arfelita Mangunkusumso, Tri Juli Edi Tarigan
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(3):149-160. Published online April 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.02.19
- 3,631 View
- 187 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
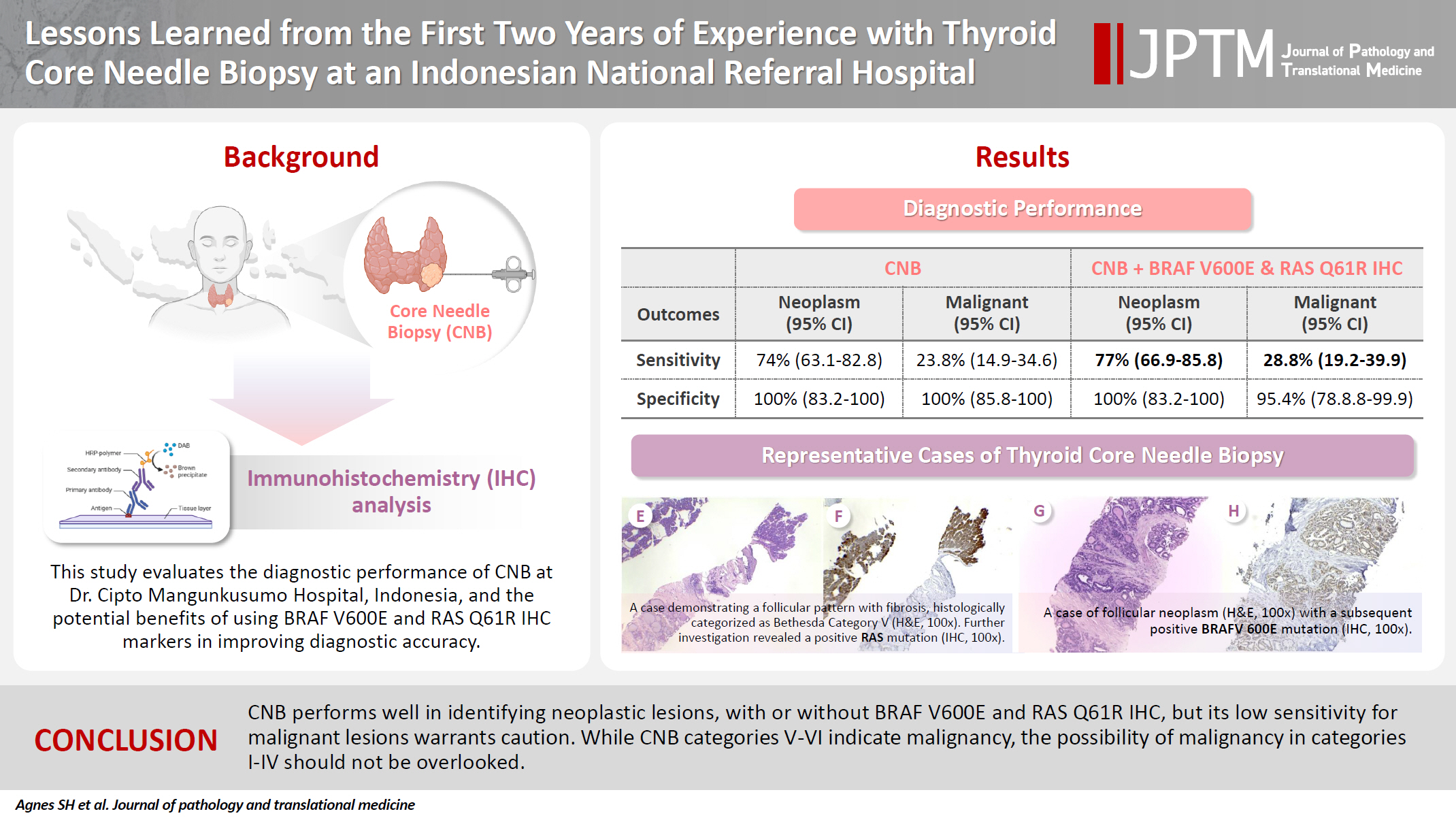
Core needle biopsy (CNB) improves diagnostic accuracy by providing precise tissue sampling for histopathological evaluation, overcoming the limitation of inconclusive fine-needle aspiration results. This study evaluated the diagnostic performance of CNB in assessing thyroid nodules, with additional analysis of the benefits of BRAF V600E and RAS Q61R immunohistochemical (IHC) markers.
Methods
This retrospective study enrolled patients with thyroid nodules who underwent CNB at Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital, Jakarta, from July 2022 to July 2024. CNB diagnoses were classified using the Korean Thyroid Association Criteria. Diagnostic efficacy was evaluated for neoplastic and malignant lesions, both independently and with BRAF V600E and RAS Q61R IHC. The correlation between nodule size and postoperative diagnosis was also analyzed.
Results
A total of 338 thyroid nodule samples was included, and 52.7% were classified as CNB category II. In the 104 samples with postoperative diagnoses, category IV was the most prevalent (39.4%). CNB demonstrated a sensitivity of 74% and a specificity of 100% for neoplastic lesions and 23.8% sensitivity and 100% specificity for malignant lesions. Combining CNB with BRAF V600E and RAS Q1R IHC increased the sensitivity to 77% for neoplastic lesions and 28.8% for malignant lesions. Larger nodules (>3 cm) were significantly associated with neoplastic (p = .005) and malignant lesions (p = .004).
Conclusions
CNB performs well in identifying neoplastic lesions, with or without BRAF V600E and RAS Q61R IHC, but its low sensitivity for malignant lesions warrants caution. While CNB categories V–VI indicate malignancy, the possibility of malignancy in categories I–IV should not be overlooked.

 E-submission
E-submission
 First
First Prev
Prev



