Most downloaded
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Most downloaded
Most-download articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last three month.
Newsletter
- What’s new in hematopathology 2025: myeloid neoplasms in the WHO 5th edition and ICC
- Barina Aqil
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):472-475. Published online October 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.24
- 8,825 View
- 318 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The previous edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of hematolymphoid neoplasms was published in 2008 and later revised in 2017. A new 5th edition of the WHO classification of hematolymphoid neoplasms was released in 2022. Additionally, the Clinical Advisory Committee developed the International Consensus Classification (ICC) of hematolymphoid tumors, which differs from the WHO classification in several key defining features as outlined below.
Original Article
- Characterization of undifferentiated carcinoma of the salivary gland: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analyses in comparison with lymphoepithelial carcinoma
- Sangjoon Choi, Gyuheon Choi, Hee Jin Lee, Joon Seon Song, Yoon Se Lee, Seung-Ho Choi, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):361-370. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.07
- 3,044 View
- 279 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to reclassify a subset of poorly differentiated salivary gland carcinoma that do not conform to any entities of the current World Health Organization (WHO) classification into the category of undifferentiated carcinoma (UDC) because they lack specific histologic differentiation or immunophenotype. Methods: Cases of salivary gland carcinomas from Asan Medical Center (2002–2020) that did not fit any existing WHO classification criteria and were diagnosed as poorly differentiated carcinoma, high-grade carcinoma, or UDC, were retrospectively reviewed. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for p40, neuroendocrine markers, androgen receptor (AR), and gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in situ hybridization (ISH) were performed. Clinical data were collected from the electronic medical records. Results: Six salivary gland carcinomas did not align with any specific entities and lacked distinct differentiation. Two of six cases displayed lymphoepithelial carcinoma (LEC)-like morphology but were negative or showed negligible immunoreactivity for p40 and EBV ISH, distinguishing them from LEC of the salivary gland. Two cases showed strong AR positivity, suggesting a potential overlap with salivary duct carcinoma (SDC) but lacked classic SDC morphologies and GCDFP-15 expression. No cases expressed neuroendocrine markers. Conclusions: This study proposes reclassifying these poorly differentiated or high-grade salivary gland carcinomas as UDC based on their indeterminate differentiation and IHC profiles. This may lead to a clearer diagnostic category and enhance our understanding of these high-grade tumors.
Newsletter
- What’s new in thyroid pathology 2024: updates from the new WHO classification and Bethesda system
- Andrey Bychkov, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):98-101. Published online March 13, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.06
- 26,896 View
- 2,043 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In line with the release of the 5th edition WHO Classification of Tumors of Endocrine Organs (2022) and the 3rd edition of the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (2023), the field of thyroid pathology and cytopathology has witnessed key transformations. This digest brings to the fore the refined terminologies, newly introduced categories, and contentious methodological considerations pivotal to the updated classification.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnosis and management of thyroid nodule
Suganya Sekar, Deepak Thomas Abraham
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2025; 32(5): 167. CrossRef - Impact of thyroid Bethesda category IV (follicular neoplasm) terminology unification on atypia of undetermined significance reporting patterns in thyroid fine-needle aspiration
Shirin Abbasi, Lorena Marcano-Bonilla, Syed Z. Ali
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Challenges, Prognostic Assessment, and Treatment Strategies in High-Grade Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
Chan Kwon Jung, Agnes Stephanie Harahap
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(6): 830. CrossRef - Cytologic and Clinicopathologic Features of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Prominent Hobnail Features on FNAC
Deepali Saxena, Ravi Hari Phulware, Prashant Durgapal, Arvind Kumar, Amit Kumar Tyagi
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2024; 76(5): 4885. CrossRef - FHL1: A novel diagnostic marker for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Yeting Zeng, Dehua Zeng, Xingfeng Qi, Hanxi Wang, Xuzhou Wang, Xiaodong Dai, Lijuan Qu
Pathology International.2024; 74(9): 520. CrossRef - Nouveautés en pathologie thyroïdienne : classification OMS 2022, système Bethesda 2023, biologie moléculaire et testing moléculaire
Mohamed Amine Bani, Sophie Moog, Voichita Suciu, Livia Lamartina, Abir Al Ghuzlan
Bulletin du Cancer.2024; 111(10): 10S5. CrossRef - Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(6): 265. CrossRef - Surgical and Pathological Challenges in Thyroidectomy after Thermal Ablation of Thyroid Nodules
Ting-Chun Kuo, Kuen-Yuan Chen, Hsiang-Wei Hu, Jie-Yang Jhuang, Ming-Tsan Lin, Chin-Hao Chang, Ming-Hsun Wu
Thyroid®.2024; 34(12): 1503. CrossRef
- Diagnosis and management of thyroid nodule
Original Article
- Clinicopathological and molecular mechanisms of CLDN18.2 in gastric cancer aggressiveness: a high-risk population study with multi-omics profiling
- Hengquan Wu, Mei Li, Gang Wang, Peiqing Liao, Peng Zhang, Luxi Yang, Yumin Li, Tao Liu, Wenting He
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):47-57. Published online January 5, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.11
- 1,657 View
- 135 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The tight junction protein claudin18.2 (CLDN18.2) has been implicated in poor prognosis and suboptimal immunotherapy response in gastric cancer (GC). This study investigates the clinicopathological relevance of CLDN18.2 expression and its association with molecular subtypes in GC patients from a high-incidence region, combining transcriptomic and proteomic approaches to explore how CLDN18.2 contributes to progression and metastasis.
Methods
A retrospective cohort of 494 GC patients (2019–2024) underwent immunohistochemical analysis for CLDN18.2, Epstein-Barr virus (Epstein–Barr virus–encoded RNA), p53, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and mismatch repair proteins (MLH1, MSH2, PMS2, and MSH6). CLDN18.2 positivity was defined as moderate to strong (2+/3+) membranous staining in ≥75% of tumor cells. Clinicopathological correlations, biomarker associations, and survival outcomes were evaluated. Transcriptomic and proteomic sequencing was performed to explore molecular mechanisms.
Results
CLDN18.2 positivity was observed in 26.9% (133/494) of gastric adenocarcinomas. CLDN18.2-positive tumors correlated with TNM stage (p = .003) and shorter overall survival (p = .018). No associations were identified with age, sex, HER2 status, microsatellite instability, or Epstein-Barr virus infection. Transcriptomic profiling revealed CLDN18.2-high tumors enriched in pathways involving cell junction disruption, signaling regulation, and immune modulation. Proteomic profiling showed that tumors with high CLDN18.2 were enriched in multiple mechanism-related pathways such as integrated metabolic reprogramming, cytoskeletal recombination, immune microenvironment dysregulation, and pro-survival signaling. These mechanisms may collectively contribute to tumor progression and metastasis.
Conclusions
CLDN18.2 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in GC patients. Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses demonstrate that CLDN18.2 promotes tumor progression and metastasis, underscoring its potential as an independent prognostic factor in regions with a high incidence of GC.
Review Article
- Solitary fibrous tumor: an updated review
- Joon Hyuk Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):20-46. Published online December 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.08
- 1,677 View
- 131 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) is a fibroblastic neoplasm characterized by a branching, thin-walled dilated staghorn-shaped (hemangiopericytoma-like) vasculature and a NAB2::STAT6 gene fusion. SFTs can occur in almost any anatomical location, including superficial and deep soft tissues, visceral organs, and bone. They most commonly occur in extrapleural locations, equally affect both sexes, and are typically present in adults. Although metastasis is rare, SFTs frequently show local recurrence. The diagnosis of SFTs is difficult because of their broad histological and morphological overlap with other neoplasms. An accurate diagnosis is important for guiding disease management and prognosis. Despite advances in molecular diagnostics and therapeutic strategies, the biological complexity and unpredictable clinical behavior of SFTs present significant challenges. This review provides an updated overview of SFT, with a focus on its molecular genetics, histopathological features, and diagnostic considerations.
Original Article
- Spectrum of thyroiditis types: clinical, cytomorphological, and radiological findings
- Anam Singh, Indrajeet Kundu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):421-433. Published online November 6, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.13
- 3,029 View
- 172 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Thyroiditis encompasses a range of inflammatory conditions affecting the thyroid gland. Lymphocytic thyroiditis (LT) is a common form of thyroiditis, with acute suppuration of the thyroid, while tuberculous thyroiditis is relatively rare. Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) remains a safe and cost-effective tool for diagnosing thyroid-related diseases, especially when paired with ultrasound (US) and clinical examination. Methods: This is a cross-sectional study including 21 cases. The cases were reported as thyroiditis on US and FNAC, and the findings were correlated with patient clinical history, symptoms during presentation, and serological profiles. Results: The cases of thyroiditis encompassed the more common forms, LT and subacute granulomatous thyroiditis (SAT), as well as relatively rare forms like tuberculous thyroiditis and thyroid abscess. Cases of follicular neoplasms (FN) arising in the context of LT also are included in this study. The case of tuberculous thyroiditis presented as a bulky thyroid gland that appeared heterogeneous on US with extensive necrosis on FNAC. The cases of thyroid abscess and SAT presented with painful neck swellings, with granulomas in the latter cases. US features of LT showed an array of appearances ranging from pseudonodular to an atrophic thyroid gland. All cases of FN showed a lymphocytic background. Conclusions: Thyroiditis is a commonly encountered condition that needs to be sub-categorized accurately into acute, subacute, and chronic types for appropriate clinical management, as they can sometimes show overlapping features. Though rare, acute suppurative and tuberculous thyroiditis are often encountered and warrant immediate care and treatment.
Newsletter
- What’s new in neuropathology 2024: CNS WHO 5th edition updates
- Heather Smith, Jared T. Ahrendsen
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):346-349. Published online September 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.11
- 22,699 View
- 1,167 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The fifth edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Central Nervous System (CNS) Tumors was released in 2021, just five years following the updated fourth edition. Advanced molecular testing such as next-generation sequencing, RNA fusion analysis, and DNA methylation profiling has led to more precise grading and classification of pre-existing tumor types as well as the recognition of new ones. Herein, we outline the major updates of the 2021 WHO Classification of CNS tumors, with emphasis on the expanded molecular characterization of CNS tumors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bioinformatics insights into ACSL1 and ACSL5: prognostic and immune roles in low-grade glioma
Cheng Zhang, Zhonghua Lv, Hongsheng Liang, Fulan Hu, Haoran Bi
BMC Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Understanding of the Exosomes and Their Associated Biomolecules in the Glioblastoma Biology, Clinical Treatment, and Diagnosis
Aghdas Ramezani, Maryam Rahnama, Fatemeh Mahmoudian, Fatemeh Shirazi, Mahmoud Ganji, Shohreh Bakhshi, Bahman Khalesi, Zahra Sadat Hashemi, Saeed Khalili
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Utility of Intratumoral Susceptibility Signals in Adult Diffuse Gliomas: Tumor Grade Prediction and Correlation with Molecular Markers Within the WHO CNS5 (2021) Classification
José Ignacio Tudela Martínez, Victoria Vázquez Sáez, Guillermo Carbonell, Héctor Rodrigo Lara, Florentina Guzmán-Aroca, Juan de Dios Berna Mestre
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(11): 4004. CrossRef - Glioblastoma in Puerto Rico: A 21-year population-based study
Carlos E Calderon-Valero, Esteban Rivera, Odaly Balasquide, Alejandro E Cedeño-Moran, Aixa De Jesus, Miguel Mayol Del Valle
Neuro-Oncology Advances.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Brain Tumors, AI and Psychiatry: Predicting Tumor-Associated Psychiatric Syndromes with Machine Learning and Biomarkers
Matei Șerban, Corneliu Toader, Răzvan-Adrian Covache-Busuioc
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(17): 8114. CrossRef - Engineered bacteria/bacterial components strategy for glioma
Yan Zhu, Meilin Shen, Qi Chen, Huanghao Yang
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 525: 170539. CrossRef
- Bioinformatics insights into ACSL1 and ACSL5: prognostic and immune roles in low-grade glioma
Original Article
- The significance of papillary architecture in the follow-up biopsies of patients with progestin-treated atypical endometrial hyperplasia
- Wangpan J. Shi, Oluwole Fadare
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):58-68. Published online January 8, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.12
- 1,314 View
- 117 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Follow-up biopsies in patients with progestin-treated atypical endometrial hyperplasia/endometrioid intraepithelial neoplasia (AH/EIN) may show papillary structures, the significance of which is unclear. Methods: The authors reviewed 253 serial specimens of 84 consecutive patients diagnosed with AH/EIN, inclusive of each patient's pre-progestin treatment sample and all post-treatment specimens. We assessed the predictive relationship between papillary architecture in a post-treatment biopsy and two study outcomes: AH/EIN or carcinoma in at least one sample subsequent to the one in which papillae were identified, and/or the last specimen received for that patient. Results: Papillae were identified in only 51.5% of pre-treatment samples but were present in at least one subsequent post-treatment sample for all patients. Post-treatment samples that exhibited papillae and no glandular crowding were associated with AH/EIN in at least one subsequent specimen in 39.7% (29/73) of cases, compared to 24.0% (6/25) in samples with neither papillae nor glandular crowding (p = .227) and 64.0% (16/25) in samples with concurrent gland crowding and papillae (p = .048). Univariate logistic regression analyses showed that the presence of papillae was not associated with study outcomes (odds ratio [OR], 0.99; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.49 to 1.99; p = .985), as compared with gland crowding (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.04 to 2.27; p = .031), or concurrent papillae and gland crowding (OR, 2.36; 95% CI, 1.01 to 5.52; p = .048). Conclusions: In post-treatment samples of progestin-treated AH/EIN, the presence of papillary architecture was not demonstrably associated with study outcomes independent of gland crowding, although the concurrent presence of both features may be significantly predictive.
Case Study
- Drug-induced phospholipidosis of the kidney suspected to be caused by atomoxetine
- Sung-Eun Choi, Kee Hyuck Kim, Minsun Jung, Jeong Hae Kie
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):124-128. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.10
- 1,386 View
- 113 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Drug-induced phospholipidosis (DIP) is characterized by intracellular accumulation of phospholipids with lamellar body formation secondary to drug-altered lipid metabolism, which can trigger inflammation and histopathological changes. Fabry disease and DIP both exhibit zebra bodies on electron microscopy, complicating differential diagnosis. A 17-year-old male with microscopic hematuria and proteinuria had received atomoxetine (40 mg) for 11 months to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Light microscopy showed one glomerulus with perihilar sclerosis and periglomerular fibrosis. Kidney biopsy revealed zebra bodies in podocytes, initially suggesting Fabry disease. However, α-galactosidase A enzyme activity was normal on tandem mass spectrometry. Next-generation sequencing of GLA identified only three benign variants. This represents the first reported case of atomoxetine-induced DIP. When zebra bodies are observed, clinicians should consider DIP caused by cationic amphiphilic drugs alongside Fabry disease. Atomoxetine meets the structural criteria for inducing DIP, and awareness of this potential complication is essential.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Atomoxetine
Reactions Weekly.2026; 2095(1): 19. CrossRef
- Atomoxetine
Review Article
- Breast schwannoma: review of entity and differential diagnosis
- Sandra Ixchel Sanchez, Ashley Cimino-Mathews
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):353-360. Published online November 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.12
- 2,936 View
- 158 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Schwannomas are benign peripheral nerve sheath tumors composed of Schwann cells, which uncommonly involve the breast. Most breast schwannomas are clinically present as a superficial palpable breast mass but may also be detected on screening mammography. Excision is the preferred treatment if symptomatic, and these are not known to recur. Histomorphology is similar to other anatomic sites: bland spindle cells with wavy nuclei, nuclear palisading (Verocay bodies), variably hypercellular (Antoni A) and hypocellular (Antoni B) areas, myxoid stroma, hyalinized vessels and variable cystic degeneration. Classic immunohistochemistry is diffuse and strong labeling for S100 and Sox10. Notable diagnostic pitfalls specific to the breast include myofibroblastoma, particularly the palisaded variant, and fascicular pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia.
Original Article
- Significance of KM55 immunohistochemical staining in the diagnosis and prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Hoe In Jeong, Beom Jin Lim, Minsun Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):69-82. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.17
- 1,682 View
- 109 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) plays a crucial role in IgA nephropathy (IgAN). The monoclonal antibody KM55 has emerged as a simplified method for detecting Gd-IgA1; however, the clinicopathological significance of immunohistochemistry for Gd-IgA1 remains underexplored. This study evaluated the prognostic and clinicopathological significance of KM55 immunohistochemistry in IgAN. Methods: A total of 114 native kidney biopsies showing at least mild mesangial IgA positivity on immunofluorescence were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were categorized as having IgAN or non-IgAN diseases. The KM55 immunohistochemical staining was graded as 0, 1+, 2+, 3, or 4+. Data on Oxford classification, laboratory parameters, and renal outcomes were collected. Results: The IgAN group showed significantly higher KM55 scores than the non-IgAN group (median: 3 vs. 1; p < .001). IgAN cases were further stratified into KM55-high (≥3+, n = 38) and -low groups (≤2+, n = 37). The KM55-high group had significantly higher diastolic blood pressure, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, urine protein/creatinine ratio, and Oxford mesangial hypercellularity scores, along with lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and serum albumin. Cox analysis revealed significantly poorer outcomes in the KM55-high group for chronic kidney disease stage 4 (p = .015), end-stage renal disease (p = .024), and 75% eGFR decline (p = .016). Conclusions: Mesangial Gd-IgA1 deposition graded by KM55 immunohistochemistry may be a useful adjunct for IgAN diagnosis and a potential prognostic biomarker.
Review Article
- Multiple sclerosis: a practical review for pathologists
- Rachel A. Multz, Pouya Jamshidi, Jared T. Ahrendsen
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):203-213. Published online June 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.05.20
- 16,400 View
- 484 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an immune-mediated demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system. It is a chronic disorder resulting in neurologic dysfunction that is disseminated both in time (multiple discrete episodes) and space (involving multiple sites). Histologically, MS is characterized by localized loss of myelin with relative preservation of axons. This review will discuss the epidemiology, clinical, laboratory, radiologic, and pathologic features of multiple sclerosis, as well as briefly touch on the differential diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of the disease, especially as they relate to the pathologic interpretation of tissue specimens.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- White Matter in Crisis: Oligodendrocytes and the Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis
Mario García-Domínguez
Cells.2025; 14(18): 1408. CrossRef - Tumefactive demyelinating lesions: a case report and literature review
Raneem Jaki, Zyad Al-Frejat, Ziad Bitar
BMC Neurology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Liquerologia: Uma ferramenta no diagnóstico de esclerose múltipla e outras doenças neurodegenerativas e desmielinizantes
Laura Maria de Araújo Pereira, Talyta Valeria Siqueira do Monte Guedes, Rafaell Batista Pereira, Davi Abrantes Lucena Messias, Marfran José Cunha Urtiga, Davi Rodrigues Vieira, Samuel da Costa Chaves Trindade Martins, José Guedes da Silva Júnior
Research, Society and Development.2025; 14(12): e72141249815. CrossRef
- White Matter in Crisis: Oligodendrocytes and the Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis
Original Articles
- Frozen section histopathology and preanalytical factors affecting nucleic acid integrity in biobanked fresh-frozen human cancer tissues
- Soungeun Kim, Jaewon Kang, Boyeon Kim, Yoonjin Kwak, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):398-407. Published online September 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.22
- 5,040 View
- 206 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
In this study, we evaluated the effects of storage duration and ischemic time on nucleic acid quality of fresh-frozen tissue (FFT) from colon adenocarcinoma (COAD), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and renal cell carcinoma (RCC) collected at the Cancer Tissue Bank of Seoul National University Hospital. Methods: A total of 102 FFT samples were analyzed to compare DNA integrity number (DIN) and RNA integrity number (RIN) according to storage duration and ischemic time. Additionally, the effects of histopathologic features—such as tumor cell proportion, inflammatory cell infiltration, and stromal fibrosis—on nucleic acid quality were evaluated. Results: DIN and RIN remained stable overall even though the storage duration increased, with no statistically significant differences observed. In particular, there was almost no decrease in RNA quality in HCC and RCC samples, but in COAD samples, RIN tended to decrease slightly as the storage duration increased. No significant difference was confirmed between ischemic time and nucleic acid quality, but in COAD tissue, RNA quality variability tended to increase as the ischemic time increased. Furthermore, RIN increased as the tumor cell proportion increased, whereas inflammatory cell infiltration and extracellular mucin pool were identified as independent negative predictors of RIN. Conclusions: This study confirmed that nucleic acid integrity can be maintained even during long-term storage of FFT and demonstrated that histologic features are closely related to RNA quality. This study would contribute to the establishment of quality assessment and management standards for biobank FFT samples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
Zhiyong Liu, Jianhe Wu, Yuanwei Li, Qiang Lu, Yongjun Yang
BMC Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
- Diagnostic value of cytology in detecting human papillomavirus–independent cervical malignancies: a nation-wide study in Korea
- Hye-Ra Jung, Junyoung Shin, Chong Woo Yoo, Eun Na Kim, Cheol Lee, Kyeongmin Kim, Ho-chang Lee, Yonghee Lee, Ji Hye Kim, Soo Jin Jung, Yumin Chung, Joo Yeon Kim, Hye Eun Park, Tae Hoen Kim, Wonae Lee, Min-Sun Cho, Ran Hong, Yoon Jung Choi, Younghee Choi, Young Sub Lee, Sang-Ryung Lee, Myunghee Kang, Young Jin Seo, Seung-Sook Lee, Yoon-Jung Hwang, Hyun-Jung Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):444-452. Published online November 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.21
- 3,448 View
- 134 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) independent cervical malignancies (HPV-IDCMs) have recently been classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) 5th edition. These malignancies have historically received limited attention due to their rarity and the potential for evasion of HPV-based screening.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 5,854 biopsy-confirmed cervical malignancies from 22 institutions over 3 years (July 2020–June 2023). Histologic classification followed the WHO guidelines. HPV independence was confirmed by dual negativity for p16 and HPV; discordant cases (p16-positive/HPV-negative) underwent additional HPV testing using paraffin-embedded tissue. Cytological results were matched sequentially to histological confirmation.
Results
The prevalence of HPV-IDCM was 4.4% (257/5,854) overall and was 3.6% (208/5,805 cases) among primary cervical malignancy. Patient age of HPV-IDCM was 29 to 89 years (median, 57.79). Its histologic subtypes included primary adenocarcinoma (n = 116), endometrial adenocarcinoma (n = 35), squamous cell carcinoma (n = 72), metastatic carcinoma (n = 14), carcinoma, not otherwise specified (n = 10), neuroendocrine carcinoma (n = 3), and others (n = 7). Among 155 cytology-histological matched cases, the overall and primary Pap test detection rates were 85.2% (132/155) and 83.2% (104/125), respectively. The interval between cytology and histologic confirmation extended up to 38 months.
Conclusions
HPV-IDCMs comprised 3.6% of primary cervical malignancies with a high detection rate via cytology (83.2%). These findings affirm the value of cytological screening, particularly in patients with limited screening history or at risk for HPV-independent lesions, and may guide future screening protocols.
- Attitudes toward artificial intelligence in pathology: a survey-based study of pathologists in northern India
- Manupriya Sharma, Kavita Kumari, Navpreet Navpreet, Sushma Bharti, Rajneesh Kumari
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):382-389. Published online October 2, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.10
- 4,574 View
- 176 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming pathology by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and workflow standardization. Despite its growing presence, AI adoption remains limited, particularly in resource-constrained settings like India. This study assessed the knowledge, awareness, and perceptions of AI among pathologists in Northern India. Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted among 138 practicing pathologists in Northern India between April and June 2024. A structured online questionnaire was used to collect data on demographics, AI awareness, self-reported knowledge, sources of AI education, technological proficiency, and interest in AI-related training programs. Data analysis included descriptive statistics and chi-square tests, with p < .05 considered statistically significant. Results: AI awareness was high (88.4%), with significant sex differences (93.5% in females vs. 78.3% in males, p = .008). However, formal AI training was limited (6.5%), and only 16.7% had used AI as a diagnostic tool. Academic pathologists were more likely to engage with AI literature than their non-academic counterparts (p = .003). Interest in AI workshops was strong (92.8%). Access to whole slide imaging (WSI) correlated with higher AI knowledge (p = .008), as did self-reported technological proficiency (p = .001). Conclusions: Despite high AI awareness among pathologists, significant gaps remain in training, infrastructure, and practical application. Expanding access to digital pathology tools like WSI and improving digital literacy could facilitate AI adoption. Structured educational programs and greater investment in digital infrastructure are crucial for integrating AI into pathology practice.
- Correlations and prognostic impacts of tumor spread through airspaces in surgically resected non–small cell lung cancer: a retrospective study from Jordan
- Ola Abu Al Karsaneh, Amani Al-Rousan, Sofian Al Shboul, Mohammed El-Sadoni, Anas Hayajneh, Moath Alrjoub, Sura Al-Rawabdeh, Tareq Saleh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):92-106. Published online January 9, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.15
- 1,707 View
- 87 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Spread through air spaces (STAS) has been identified as an invasion pattern in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This study evaluated the association between tumor STAS and various clinicopathological parameters of NSCLC, with emphasis on the prognostic role of STAS. Methods: We evaluated 96 cases of NSCLC for STAS. STAS-positive cases were graded according to the distance between the edge of the primary tumor and the furthest STAS, in millimeters, or the number of alveoli separating STAS from the tumor. Results: STAS was observed in 33 patients (34.4%). In 28 cases, STAS was located in airspaces >3 alveoli away from the primary tumor. In 18 cases, STAS was found in airspaces > 2.5 mm away from the edge of the primary tumor. Morphologically, 18 cases of STAS demonstrated a solid nest pattern, eight showed a micropapillary cluster pattern, and seven exhibited a single-cell pattern. In multivariate analysis, only high tumor grade (p = .001) was independently associated with STAS in NSCLC. The presence of STAS (p = .047), lymphovascular invasion (p = .001), positive surgical margin (p = .021), adenocarcinoma histology (p = .020), and postoperative therapy (p = .049) showed a statistically significant lower overall survival (OS). However, multivariate analyses showed that STAS is not an independent predictor of OS in NSCLC. In addition, STAS-positive cases with an extension of >2.5 mm had significantly lower disease-free survival (DFS) (p = .018). Conclusions: The findings demonstrated that STAS is independently associated with a higher tumor grade and appears to have an adverse impact on OS and DFS in the examined subpopulation.
- Clinicopathological implications of miR-3127 in melanoma
- Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Chau M. Bui, Vuong Gia Huy
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):371-381. Published online October 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.08
- 3,995 View
- 148 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Cutaneous melanoma is the most lethal of all skin cancers. Recent studies suggested that miR-3127 is dysregulated in multiple tumor types and has important roles in tumorigenesis and cancer progression, giving it potential as a prognostic biomarker. The aim of this study was to use bioinformatic analysis to assess miR-3127 expression and correlate expression patterns with disease course in patients with cutaneous melanoma. Methods: miRNA, mRNA sequencing, DNA methylation data, and clinical information of cutaneous melanoma cases were downloaded from the Human Cancer Atlas – Skin Cutaneous Melanoma (TCGA-SKCM). miR-3127 expression was classified into miR-3127–low and miR-3127–high clusters using maximally selected rank statistics. Results: Clustering analysis showed that high expression of miR-3127 (≥20.3 reads per million) was associated with worse progression-free (p < .001) and overall (p = .011) survival compared to low miR-3127 expression. More than five thousand differentially expressed genes between the two miR-3127 sample groups encoded cell differentiation markers, cytokines, growth factors, translocated cancer genes, and oncogenes. Pathway analysis revealed that miR-3127–high samples related to activity of proliferation, DNA repair, and ultraviolet response. Conclusions: The expression level of miR-3127 could act as a prognostic indicator for patients with melanoma.
Review Article
- A comprehensive review of ossifying fibromyxoid tumor: insights into its clinical, pathological, and molecular landscape
- Kyriakos Chatzopoulos, Antonia Syrnioti, Mohamed Yakoub, Konstantinos Linos
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):6-19. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.02
- 1,894 View
- 83 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor (OFMT) is a rare mesenchymal neoplasm first described in 1989. It typically arises in the superficial soft tissues of the extremities as a slow-growing, painless mass. Histologically, it is commonly characterized by a multilobular architecture composed of uniform epithelioid cells embedded in a fibromyxoid matrix, often surrounded by a rim of metaplastic bone. While classic cases are readily identifiable, the tumor's histopathological heterogeneity can mimic a range of benign and malignant neoplasms, posing significant diagnostic challenges. Molecularly, most OFMTs harbor PHF1 rearrangements, commonly involving fusion partners such as EP400, MEAF6, or TFE3. This review underscores the importance of an integrated diagnostic approach- incorporating histopathological, immunohistochemical, and molecular data- to accurately classify OFMT and distinguish it from its mimics. Expanding awareness of its morphologic and molecular spectrum is essential for precise diagnosis, optimal patient management, and a deeper understanding of this enigmatic neoplasm.
Review
- Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):265-282. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.11
- 15,407 View
- 621 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the most common thyroid malignancy, characterized by a range of subtypes that differ in their cytologic features, clinical behavior, and prognosis. Accurate cytologic evaluation of PTC using fine-needle aspiration is essential but can be challenging due to the morphologic diversity among subtypes. This review focuses on the distinct cytologic characteristics of various PTC subtypes, including the classic type, follicular variant, tall cell, columnar cell, hobnail, diffuse sclerosing, Warthin-like, solid/trabecular, and oncocytic PTCs. Each subtype demonstrates unique nuclear features, architectural patterns, and background elements essential for diagnosis and differentiation from other thyroid lesions. Recognizing these distinct cytologic patterns is essential for identifying aggressive subtypes like tall cell, hobnail, and columnar cell PTCs, which have a higher risk of recurrence, metastasis, and poorer clinical outcomes. Additionally, rare subtypes such as diffuse sclerosing and Warthin-like PTCs present unique cytologic profiles that must be carefully interpreted to avoid diagnostic errors. The review also highlights the cytologic indicators of lymph node metastasis and high-grade features, such as differentiated high-grade thyroid carcinoma. The integration of molecular testing can further refine subtype diagnosis by identifying specific genetic mutations. A thorough understanding of these subtype-specific cytologic features and molecular profiles is vital for accurate diagnosis, risk stratification, and personalized management of PTC patients. Future improvements in diagnostic techniques and standardization are needed to enhance cytologic evaluation and clinical decision-making in thyroid cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
Adeel M. Ashraf, Faisal Hassan, Adrian A. Dawkins, Julie C. Dueber, Derek B. Allison, Thèrése J. Bocklage
Cytopathology.2026; 37(1): 108. CrossRef - Using a new type of visible light-based emission fluorescence microscope to identify the benign and malignant nature of thyroid tissue during the surgical process: Analysis of diagnostic results
Yu Miao, Liu Xiaowei, Li Muyang, Gao Jian, Chen Lu
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2026; 57: 105324. CrossRef - Clinical Behavior of Aggressive Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Retrospective Case–Control Study
Jovan Ilic, Nikola Slijepcevic, Katarina Tausanovic, Bozidar Odalovic, Goran Zoric, Marija Milinkovic, Branislav Rovcanin, Milan Jovanovic, Matija Buzejic, Duska Vucen, Boban Stepanovic, Sara Ivanis, Milan Parezanovic, Milan Marinkovic, Vladan Zivaljevic
Cancers.2026; 18(2): 345. CrossRef - Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Dina Khoirunnisa, Salinah, Maria Francisca Ham
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 75: 152434. CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shin Je Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyo
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - Structure-based molecular screening and dynamic simulation of phytocompounds targeting VEGFR-2: a novel therapeutic approach for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Shuai Wang, Lingqian Zhang, Wenjun Zhang, Xiong Zeng, Jie Mei, Weidong Xiao, Lijie Yang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shinje Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(3): 307. CrossRef - A Case of Warthin-Like Variant of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Amy Chow, Israa Laklouk
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Propensity score-matched analysis of the ‘2+2’ parathyroid strategy in total thyroidectomy with central neck dissection
Hao Gong, Simei Yao, Tianyuchen Jiang, Yi Yang, Yuhan Jiang, Zhujuan Wu, Anping Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
Original Articles
- PSMA expression in hepatic colorectal cancer metastasis
- Eundong Park, Michel Kmeid, Xin Wang, Haiyan Qiu, Clifton G. Fulmer, Marcello P. Toscano, Nusret Bekir Subasi, Maciej Gracz, Hwajeong Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):107-123. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.20
- 1,254 View
- 74 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is expressed in the neovasculature of various malignancies, such as colorectal cancer (CRC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, PSMA expression in hepatic CRC metastasis has not been studied in detail. Methods: The PSMA expression in primary CRC and corresponding hepatic metastasis was evaluated by immunohistochemistry in a metastatic CRC cohort (n = 56), which was divided into subgroups according to treatment history and timing of metastasis. Demographic and histological characteristics of primary CRC were collected and their relationships with PSMA expression were examined. Additionally, the PSMA expression in resected HCC (n = 76) was compared with that of hepatic CRC metastasis. Results: In primary CRC, PSMA level showed a positive association with tumor size. Lower PSMA expression in hepatic metastasis was associated with higher primary CRC grade, advanced pTNM stage at the time of CRC resection, presence of tumor deposit, and unresectability of metastatic lesion. PSMA expression in primary CRC correlated with that in hepatic metastasis only in concurrent and untreated metastasis subgroup. PSMA expression in primary CRC and hepatic metastasis, regardless of treatment history and timing of metastasis, was not significantly different from that of HCC. Conclusions: Several adverse pathological features of primary CRC were associated with a lower PSMA expression in hepatic metastasis. PSMA expression in hepatic metastasis correlated with that of primary CRC only in concurrent and untreated subgroup. Primary HCC and hepatic CRC metastasis show comparable levels of PSMA expression.
- E-cadherin expression and tumor-stroma ratio as prognostic biomarkers of peritoneal recurrence in advanced gastric cancer: a digital image analysis-based stratification study
- Somang Lee, Binnari Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):408-420. Published online November 6, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.27
- 2,427 View
- 111 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Gastric cancer remains a significant global health burden, with a high peritoneal recurrence rates after curative surgery. E-cadherin and the tumor-stroma ratio (TSR) have been proposed as prognostic indicators, but their combined prognostic utility remains unclear. Methods: This retrospective study included 130 patients with T3/T4a gastric cancer who underwent curative gastrectomy at Ulsan University Hospital between 2014 and 2019. Immunohistochemistry for E-cadherin and Vimentin was performed. Digital image analysis using QuPath’s object classifier quantified E-cadherin expression and TSR. Results: Low E-cadherin expression was associated with diffuse-type histology and advanced T stage. Low TSR was linked to younger age, female sex, and XELOX treatment. In Kaplan-Meier analysis, low TSR showed a non-significant trend toward higher peritoneal recurrence (p = .054), while low E-cadherin expression was significantly associated with increased peritoneal recurrence (p = .002). Combined biomarker analysis also revealed a significant difference in recurrence-free survival (RFS) among the four groups (p = .005); patients with both high TSR and high E-cadherin expression experienced the most favorable RFS. In multivariable analysis, E-cadherin expression remained the only independent predictor of peritoneal recurrence (high vs. low; hazard ratio, 0.348; 95% confidence interval, 0.149 to 0.816; p = .015). Conclusions: E-cadherin and TSR reflect distinct tumor biology such as epithelial integrity and stromal composition, and their combined evaluation improves prognostic stratification. Digital image analysis enhances reproducibility and objectivity, supporting their integration into clinical workflows.
- Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor: clinicopathological analysis of 34 cases from Karachi, Pakistan
- Summaya Zafar, Sehar Sulaiman, Madeeha Nisar, Poonum Khan, Nasir Ud Din
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):390-397. Published online October 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.11
- 2,323 View
- 138 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor (AOT) is a benign slow-growing neoplasm of odontogenic epithelial origin that is relatively uncommon. Only a few studies have described its histological features. Hence, we aimed to describe the clinicopathological features of AOT in a cohort of patients. Methods: AOT cases diagnosed between 2009 and 2024 were searched electronically. Glass slides were retrieved from archives and were reviewed by two pathologists to record the associated morphological features. Other data including patient demographics and tumor site were collected by reviewing histopathology reports. Results: The age of patients ranged from 9 to 44 years (mean, 17.7 years), and most were female (55.9%). The maxilla (44.1%) was the most common tumor site. Histologically, a predominantly solid growth pattern (n = 34) accompanied by ducts with a cuboidal/columnar epithelial lining (n = 31), eosinophilic secretions (n = 31), calcifications (n = 31), lattice work pattern (n = 30), and cystic areas (n = 20) were observed. Less frequent features included calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor (CEOT)–like areas (n = 13), osteodentin (n = 6), association with impacted tooth (n = 3), mucin in tubules (n = 7), fibrocollagenous stroma (n = 6), mucin in ducts (n = 3) and ossifying fibroma-like areas (n = 6). The association of ducts with a cuboidal/columnar epithelial lining, lattice work pattern, calcifications, and eosinophilic secretions with gingival tumors was statistically significant (p ≤ .05). Additionally, tooth tumors were significantly associated with CEOT-like areas (p = .03). Conclusions: Our study confirms the trends in the clinicopathological features of AOT in previous case reports. Our results suggest that AOTs usually exhibit a predominantly solid pattern with duct-like spaces. Only a few cases with CEOT-like and ossifying fibroma-like areas were observed, similar to infrequent cases reported in the past.
- Revisiting human sparganosis: a pathologic review from a single institution
- Jeemin Yim, Young A Kim, Jeong Hwan Park, Hye Eun Park, Hyun Beom Song, Ji Eun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):83-91. Published online January 9, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.14
- 1,395 View
- 71 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Sparganosis is a rare parasitic infection caused by Spirometra species. Although it was relatively common in the past, it is now often overlooked. In this study, we review cases diagnosed through histopathological examination at a single institution in recent years to raise awareness of this neglected parasitic disease. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed cases of human sparganosis identified in the pathology archives of a single institution in South Korea between 2004 and 2025. A comprehensive review was conducted, including demographic data, clinical features, lesion locations, imaging findings, exposure history (such as dietary habits), and histopathologic findings. Results: A total of 15 patients were identified, including 10 females and 5 males, with a mean age of 65.1 years. Lesions were most commonly located in the lower extremities and breast. Imaging findings were largely nonspecific, with ultrasonography being the most frequently used modality. In most cases, clinical suspicion of sparganosis was absent, and excision was performed under the impression of a benign or malignant tumor. Histologically, variably degenerated parasitic structures were identified within granulomatous inflammation. However, preserved features such as calcospherules and tegumental structures facilitated definitive diagnosis. Conclusions: This study underscores the importance of recognizing the characteristic histopathological features of sparganosis, which can allow for accurate diagnosis even in the absence of clinical suspicion. Although rare, sparganosis remains a relevant diagnostic consideration in endemic regions, particularly in East Asia.
Case Study
- Primary thyroid diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: fine needle aspiration and histological correlation
- Woo Sung Moon, Yong Tae Hong, Ae Ri Ahn
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):467-471. Published online November 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.28
- 2,450 View
- 103 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary thyroid lymphoma (PTL) is a rare type of cancer that arises within the thyroid gland, representing about 2%–8% of all thyroid malignancies. Fine-needle aspiration cytology is commonly used as the first-line diagnostic approach for thyroid nodules and can assist in identifying PTL when suggestive features are present. Herein, we report the case of a 59-year-old female patient who presented with a rapidly enlarging anterior neck mass over 20 days. Clinically, the case was challenging to distinguish from anaplastic thyroid carcinoma because of the sudden enlargement of the neck mass. However, pathological examination confirmed the diagnosis of primary thyroid diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Fine-needle aspiration cytology proved valuable in avoiding unnecessary surgical resection and guiding appropriate treatment. Additionally, we provide a brief review of the clinical and cytopathological features of primary thyroid lymphomas.
Original Article
- International Academy of Cytology standardized reporting of breast fine-needle aspiration cytology with cyto-histopathological correlation of breast carcinoma
- Shweta Pai
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):241-248. Published online September 13, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.14
- 8,427 View
- 438 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The International Academy of Cytology (IAC) has developed a standardized approach for reporting the findings of breast fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). Accordingly, there are five chief categories of breast lesions, C1 (insufficient material), C2 (benign), C3 (atypical), C4 (suspicious), and C5 (malignant). The prognostication and management of breast carcinoma can be performed readily on the basis of this classification system. The aim of this study was to classify various breast lesions into one of the above-named categories and to further grade the C5 lesions specifically using the Robinson system. The latter grades were then correlated with modified Scarff-Bloom-Richardson (SBR) grades.
Methods
This retrospective study was undertaken in the pathology department of a hospital located in the urban part of the city of Bangalore. All FNAC procedures performed on breast lumps spanning the year 2020 were included in the study.
Results
A total of 205 breast lesions was classified according to the IAC guidelines into C1 (6 cases, 2.9%), C2 (151 cases, 73.7%), C3 (13 cases, 6.3%), C4 (5 cases, 2.5%), and C5 (30 cases, 14.6%) groups. The C5 cases were further graded using Robinson’s system. The latter showed a significant correlation with the SBR system (concordance=83.3%, Spearman correlation=0.746, Kendall’s tau-b=0.736, kappa=0.661, standard error=0.095, p≤.001).
Conclusions
A standardized approach for FNAC reporting of breast lesions, as advocated for by the IAC, improves the quality and clarity of the reports and assures diagnostic reproducibility on a global scale. Further, the cytological grading of C5 lesions provides reliable cyto-prognostic scores that can help assess a tumor’s aggressiveness and predict its histological grade.
Case Study
- Diagnostic challenge in Burkitt lymphoma of the mandible initially misdiagnosed as osteomyelitis: a case report
- Jiwon Do, Jin-Young Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):460-466. Published online November 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.18
- 2,369 View
- 96 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is a highly aggressive B-cell neoplasm that rarely involves the mandible in elderly without apparent immunodeficiency. We report a case of a 72-year-old male who presented with persistent mandibular pain following extraction of tooth #46. Initial imaging findings were consistent with incipient osteomyelitis, and the patient was treated with antibiotics. Despite treatment, pain persisted, and follow-up imaging revealed swelling and diffusion restriction in the lateral pterygoid muscle without evidence of a distinct mass. Biopsy revealed BL confirmed by immunohistochemistry: CD10+, BCL6+, c-MYC+, Ki-67 >95%, and negative for BCL2, MUM-1, and Epstein-Barr virus. Although c-MYC immunopositivity was demonstrated, fluorescence in situ hybridization for MYC rearrangement could not be performed due to limited tissue, representing a diagnostic limitation. Notably, the patient had no trismus despite deep muscle involvement, but complained of facial paresthesia and showed remote swelling in the scapular area during hospitalization. Systemic staging with imaging, cerebrospinal fluid cytology, and imaging revealed disseminated nodal and extranodal involvement including the central nervous system, corresponding to stage IV disease by Lugano classification. This case highlights the diagnostic challenge of distinguishing lymphoma from osteomyelitis and underscores the importance of considering malignancy in cases of refractory mandibular inflammation with atypical features.
Original Article
- Modified plasma-thrombin method using patient-derived plasma for cell block preparation in endobronchial ultrasound–guided transbronchial fine-needle aspiration
- Xizhe Zhang, Chunli Tang, Yingying Gu, Zeyun Lin, Shiqi Tang, Anzi Tan, Mengshi Li, Zhucheng Chen, Yuying Chen, Shi-yue Li, Juhong Jiang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):434-443. Published online November 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.20
- 2,530 View
- 94 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The plasma-thrombin method, which uses expired blood bank plasma as an ancillary component, has been widely used in cell block (CB) preparation. However, the application of expired blood bank plasma raises concerns about nucleic acid contamination. This study investigated the feasibility of using patient-derived plasma as a substitute for blood bank plasma in the modified plasma-thrombin (MPT) method for CB preparation in endobronchial ultrasound–guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) samples. Methods: A prospective study was conducted to compare the adequacy of CB preparation between a previously used self-clotting (SC) method and the MPT method. The EBUS-TBNA specimens from each targeted lesion were divided into paired samples: one processed using the SC method and the other using the MPT method, substituting the blood bank plasma with patient-derived plasma. Results: A total of 82 paired EBUS-TBNA samples from 59 patients were analyzed. The diagnostic yield of the SC method and the MPT method was 86.6% and 97.6%, respectively. Among patients diagnosed with non–small cell lung cancer, the adequacy rate for molecular testing was 79.2% with the SC method and 91.7% with the MPT method. Conclusions: The MPT method significantly improved the cellular yield of EBUS-TBNA–derived CBs. Using patient-derived fresh plasma rather than expired blood bank plasma avoids a known contamination risk. The additional step modestly prolongs the procedure and introduces minimal risks by vein puncture. This approach is generally considered cost-effective.
Newsletter
- What’s new in medical renal pathology 2025: Updates on podocytopathy and immunofluorescence staining in medical kidney
- Astrid Weins, Ibrahim Batal, Paola Romagnani, Geetika Singh, Rahul Raj, Nicole Andeen, Jonathan Zuckerman, Martina Uzzo, Mariam Priya Alexander, Anjali Satoskar
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):269-272. Published online July 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.19
- 5,907 View
- 351 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Diffuse podocytopathy, including minimal change disease and primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, is a common cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults and children. It is increasingly recognized to be autoimmune-mediated associated with anti-nephrin and other emerging anti-slit diaphragm antibodies, and can recur in the kidney allograft. Immunofluorescence is routinely used in evaluation of kidney biopsies, and updates include those on fibrillar diseases, monoclonal staining, lupus-like staining, and use of antibody KM55 in IgA-dominant glomerulonephritis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Opportunities and challenges in recurrent diffuse podocytopathy post-transplantation: the critical value of the definition
Rachel Nuccitelli, Amadea Toutoungis, Elena Martinelli, Simone Sanna-Cherchi, Astrid Weins, Heather K. Morris, Andrew S. Bomback, Ibrahim Batal
Frontiers in Immunology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Opportunities and challenges in recurrent diffuse podocytopathy post-transplantation: the critical value of the definition
Case Study
- Clinicopathological characteristics of digestive system angioleiomyomas: case report and literature review
- Georgios Kalliopitsas, Christos Topalidis, Constantine Halkias, Theodora Gkeka, Konstantinos Sapalidis, Triantafyllia Koletsa
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):453-459. Published online October 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.04
- 2,410 View
- 104 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Angioleiomyomas are benign soft tissue tumors originating from the vascular wall. Although angioleiomyomas mainly occur in extremities, followed by head, neck, and trunk, they can also be found throughout the digestive system and especially in the oral cavity. Herein, the fourth case of a rectal angioleiomyoma in the English literature is reported and the clinicopathological features of digestive system angioleiomyomas were investigated. In contrast to their soft tissue counterparts, digestive system angioleiomyomas mainly affect males at a slightly younger age. Angioleiomyomas are mainly asymptomatic and only rarely elicit pain. Clinicians consider angioleiomyomas infrequently and instead include more common soft tissue or epithelial tumors in their differential diagnosis. To prevent angiomyolipoma misdiagnosis, pathologists should exercise caution when examining an angioleiomyoma composed of adipose tissue, smooth muscle, and blood vessels. Pathologists, radiologists, and surgeons should be aware that angioleiomyomas can occur in the digestive system.
Review
- Breast fine-needle aspiration cytology in the era of core-needle biopsy: what is its role?
- Ahrong Kim, Hyun Jung Lee, Jee Yeon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):26-38. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.01
- Correction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2025;59(2):147
- 13,571 View
- 455 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) has long been recognized as a minimally invasive, cost-effective, and reliable diagnostic tool for breast lesions. However, with the advent of core-needle biopsy (CNB), the role of FNAC has diminished in some clinical settings. This review aims to re-evaluate the diagnostic value of FNAC in the current era, focusing on its complementary use alongside CNB, the adoption of new approaches such as the International Academy of Cytology Yokohama System, and the implementation of rapid on-site evaluation to reduce inadequate sample rates. Advances in liquid-based cytology, receptor expression testing, molecular diagnostics, and artificial intelligence are discussed, highlighting their potential to enhance the diagnostic accuracy of FNAC. Despite challenges, FNAC remains a valuable diagnostic method, particularly in low-resource settings and specific clinical scenarios, and its role continues to evolve with technology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Breast Lesions on Cytology Using International Academy of Cytology Yokohama Standardized Reporting System
Manish Jaiswal, Anurag Gupta, Tripti Verma, Pradyumn Singh, Rita Yadav, Akash Agarwal, Ashish Singhal, Nuzhat Husain, Shamrendra Narayan, Neha Singh
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(3): 184. CrossRef - Personalizing therapies over the course of hormone receptor‐positive/HER2‐negative metastatic breast cancer
Akshara Singareeka Raghavendra, Senthil Damodaran, Carlos H. Barcenas, Suzanne A. Fuqua, Rachel M. Layman, Debu Tripathy
CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Bulk-lysis protocols as a sensitive method for investigation of circulating CK19 cells in the peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer by flow cytometry
Daniella Serafin Couto Vieira, Laura Otto Walter, Maria Eduarda Cunha da Silva, Lisandra de Oliveira Silva, Heloísa Zorzi Costa, Chandra Chiappin Cardoso, Fernando Carlos de Lander Schmitt, Maria Cláudia Santos-Silva
Analytical Methods.2025; 17(23): 4771. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Breast Lesions on Cytology Using International Academy of Cytology Yokohama Standardized Reporting System
Newsletter
- What’s new in genitourinary pathology 2023: WHO 5th edition updates for urinary tract, prostate, testis, and penis
- Bonnie Choy, Maria Tretiakova, Debra L. Zynger
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):45-48. Published online December 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.12.11
- 11,527 View
- 905 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The 5th edition WHO Classification of Urinary and Male Genital Tumours (2022) introduced many significant changes relevant to urologic daily practice, mainly to renal tumors which was covered in the What’s New newsletter in September 2022. In this newsletter, we summarize the notable changes to bladder, prostate, testis, and penis based on the 5th edition of the WHO.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predicting variant histology in bladder cancer: the role of multiparametric MRI and vesical imaging-reporting and data system (VI-RADS)
Serdar Aslan, Merve Nur Tasdemir, Ertugrul Cakir, Ural Oguz, Birgul Tok
Abdominal Radiology.2025; 50(10): 4700. CrossRef - Pictorial review of multiparametric MRI in bladder urothelial carcinoma with variant histology: pearls and pitfalls
Yuki Arita, Sungmin Woo, Lisa Ruby, Thomas C. Kwee, Keisuke Shigeta, Ryo Ueda, Sunny Nalavenkata, Hiromi Edo, Kosuke Miyai, Jeeban Das, Pamela I. Causa Andrieu, Hebert Alberto Vargas
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 49(8): 2797. CrossRef - Oncological outcomes and prognostic implications of T1 histo-anatomic substaging in the management of high-Grade non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: results from a large single centre series
Marco Finati, Antonio Fanelli, Francesco Cinelli, Nicola Schiavone, Ugo Giovanni Falagario, Anna Ricapito, Nicola d’Altilia, Richard Naspro, Angelo Porreca, Felice Crocetto, Biagio Barone, Ciro Imbimbo, Carlo Bettocchi, Francesca Sanguedolce, Luigi Cormio
World Journal of Urology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Predicting variant histology in bladder cancer: the role of multiparametric MRI and vesical imaging-reporting and data system (VI-RADS)
Reviews
- Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cytology in pregnancy
- Ji-Young Kim, Jeong Yun Shim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):283-290. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.17
- 10,795 View
- 449 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cervical cancer screening during pregnancy presents unique challenges for cytologic interpretation. This review focuses on pregnancy-associated cytomorphological changes and their impact on diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical cancer. Pregnancy-induced alterations include navicular cells, hyperplastic endocervical cells, immature metaplastic cells, and occasional decidual cells or trophoblasts. These changes can mimic abnormalities such as koilocytosis, adenocarcinoma in situ, and high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, potentially leading to misdiagnosis. Careful attention to nuclear features and awareness of pregnancy-related changes are crucial for correct interpretation. The natural history of CIN during pregnancy shows higher regression rates, particularly for CIN 2, with minimal risk of progression. Management of abnormal cytology follows modified risk-based guidelines to avoid invasive procedures, with treatment typically deferred until postpartum. The findings reported in this review emphasize the importance of considering pregnancy status in cytological interpretation, highlight potential problems, and provide guidance on differentiating benign pregnancy-related changes from true abnormalities. Understanding these nuances is essential for accurate diagnosis and proper management of cervical abnormalities in pregnant women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The significance of biological samples from pregnant women in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Xue Mi, Maharjan Rashmi, Zangyu Pan, Di Wu, Jinwei Miao
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Oncologic and pregnancy outcomes of cervical high-grade intraepithelial lesions and delivery mode
Olga P. Matylevich, Ilya A. Tarasau, Sviatlana Y. Shelkovich, Aliaksandr F. Martsinkevich
Academia Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- The significance of biological samples from pregnant women in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
- Post-transplant liver biopsies: a concise and practical approach for beginners
- Mohamad Besher Ourfali, David Hirsch, Marianna Scranton, Tony El Jabbour
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):1-10. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.15
- 4,941 View
- 396 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Exposure to post-transplant liver biopsies varies among pathology residencies and largely depends on the institution's training program, particularly if the hospital has a liver transplant program. The interpretation of biopsies from transplanted livers presents its own set of challenges, even for those with a solid understanding of non-transplant medical liver biopsies. In this review, we aim to provide a succinct, step-by-step approach to help you interpret liver transplant biopsies. This article may be beneficial for residents interested in liver pathology, gastrointestinal and liver pathology fellows in the early stages of training, clinical gastroenterology and hepatology fellows, hepatologists and general pathologists who are curious about this niche.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Histological and Molecular Evaluation of Liver Biopsies: A Practical and Updated Review
Joon Hyuk Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(16): 7729. CrossRef
- Histological and Molecular Evaluation of Liver Biopsies: A Practical and Updated Review
Original Article
- AMACR is a highly sensitive and specific immunohistochemical marker for diagnosing prostate cancer on biopsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Johannes Cansius Prihadi, Stevan Kristian Lionardi, Nicolas Daniel Widjanarko, Steven Alvianto, Fransiskus Xaverius Rinaldi, Archie Fontana Iskandar
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):235-248. Published online July 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.04.16
- 6,897 View
- 223 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) is the preferred biomarker for distinguishing malignant from benign glands in prostate biopsies, showing high sensitivity and specificity for prostate cancer. A meta-analysis of immunohistochemistry (IHC) for AMACR is essential to further assess its diagnostic accuracy across diverse sample sources. Methods: A systematic search of databases including MEDLINE, ScienceDirect, ProQuest, Google Scholar, and the Cochrane Library was performed, focusing on studies of AMACR to diagnose prostate cancer, particularly in biopsy samples analyzed through IHC over the last 20 years. Quality of studies was assessed using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies 2 tool, followed by a meta-analysis of regions and subgroups to calculate summary estimates of diagnostic test accuracy. Results: In the final analysis, 37 studies, with a pooled size of 5,898 samples, were included from the examination of 94 full-text papers. Among them, 27 studies with similar sample sources and testing methodologies underwent meta-analysis, yielding a combined sensitivity estimate of 0.90 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.86 to 0.93) and specificity of 0.91 (95% CI, 0.83 to 0.95), both with significant heterogeneity (p < .01). The region beneath the hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.93 to 0.97), positive likelihood ratio was 9.6 (95% CI, 5.3 to 17.4), negative likelihood ratio was 0.11 (95% CI, 0.08 to 0.15), and diagnostic odds ratio was 88 (95% CI, 42 to 181). Conclusions: Our meta-analysis findings substantiate AMACR as a highly accurate tool for diagnosing prostate cancer, specifically in biopsy samples, via immunohistochemical staining. Further studies involving diverse samples are needed to enhance our understanding of the AMACR diagnostic accuracy in a range of clinical settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pathogenesis-Guided Biomarker Assessment: A Shift in Prostate Cancer Diagnostics
Jessica M. Logan, Victoria Malone, John J. O’Leary, Doug A. Brooks
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(24): 11786. CrossRef
- Pathogenesis-Guided Biomarker Assessment: A Shift in Prostate Cancer Diagnostics
Newsletter
- What’s new in adrenal gland pathology: WHO 5th edition for adrenal cortex
- Carol N. Rizkalla, Maria Tretiakova
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):201-204. Published online June 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.06.07
- 6,766 View
- 563 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The 5th edition of WHO Classification of Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Tumors (2022) introduced many significant changes relevant to endocrine daily practice. In this newsletter, we summarize the notable changes to the adrenal cortex based on the 5th edition of the WHO classification [1].
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ectopic adrenal gland in the liver leading to a misdiagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A case report
Min-Qiu Qin, Yi-Peng Zhao, Ju-Ping Xie
World Journal of Hepatology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Ectopic adrenal gland in the liver leading to a misdiagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A case report
Review
- Interpretation of PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer: summary of a consensus meeting of Korean gastrointestinal pathologists
- Soomin Ahn, Yoonjin Kwak, Gui Young Kwon, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Moonsik Kim, Hyunki Kim, Young Soo Park, Hyeon Jeong Oh, Kyoungyul Lee, Sung Hak Lee, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):103-116. Published online April 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.15
- 22,106 View
- 699 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Nivolumab plus chemotherapy in the first-line setting has demonstrated clinical efficacy in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, and is currently indicated as a standard treatment. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression is an important biomarker for predicting response to anti–programmed death 1/PD-L1 agents in several solid tumors, including gastric cancer. In the CheckMate-649 trial, significant clinical improvements were observed in patients with PD-L1 combined positive score (CPS) ≥ 5, determined using the 28-8 pharmDx assay. Accordingly, an accurate interpretation of PD-L1 CPS, especially at a cutoff of 5, is important. The CPS method evaluates both immune and tumor cells and provides a comprehensive assessment of PD-L1 expression in the tumor microenvironment of gastric cancer. However, CPS evaluation has several limitations, one of which is poor interobserver concordance among pathologists. Despite these limitations, clinical indications relying on PD-L1 CPS are increasing. In response, Korean gastrointestinal pathologists held a consensus meeting for the interpretation of PD-L1 CPS in gastric cancer. Eleven pathologists reviewed 20 PD-L1 slides with a CPS cutoff close to 5, stained with the 28-8 pharmDx assay, and determined the consensus scores. The issues observed in discrepant cases were discussed. In this review, we present cases of gastric cancer with consensus PD-L1 CPS. In addition, we briefly touch upon current practices and clinical issues associated with assays used for the assessment of PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Organ Preservation for Gastroesophageal Junction and Gastric Cancers: Ready for Primetime?
Winta Mehtsun, Lola Van Doosselaere, Ugwuji N. Maduekwe
American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning Analysis Based on Dual-energy CT-Derived Iodine Map for Predicting PD-L1 Expression in Gastric Cancer: A Multicenter Study
Lihong Chen, Yuncong Zhao, Xiaomin Tian, Deye Zeng, Yongxiu Tong, Haiping Xu, Yaru You, Caiming Weng, Sen Lin, Keru Chen, Yilin Chen, Yunjing Xue
Academic Radiology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Adjuvant immunotherapy in patients with resected gastric and oesophagogastric junction cancer following preoperative chemotherapy with high risk for recurrence (ypN+ and/or R1): European Organisation of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) 1707 VESTIG
F. Lordick, M.E. Mauer, G. Stocker, C.A. Cella, I. Ben-Aharon, G. Piessen, L. Wyrwicz, G. Al-Haidari, T. Fleitas-Kanonnikoff, V. Boige, R. Lordick Obermannová, U.M. Martens, C. Gomez-Martin, P. Thuss-Patience, V. Arrazubi, A. Avallone, K.K. Shiu, P. Artru
Annals of Oncology.2025; 36(2): 197. CrossRef - PD-L1 as a Biomarker in Gastric Cancer Immunotherapy
Yunjoo Cho, Soomin Ahn, Kyoung-Mee Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 177. CrossRef - PD-L1 importance in malignancies comprehensive insights into the role of PD-L1 in malignancies: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities
Mojdeh Soltani, Mohammad Abbaszadeh, Hamed Fouladseresht, Mark J. M. Sullman, Nahid Eskandari
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - CLDN18.2 expression in gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: prevalence, heterogeneity, and prognostic implications in Spanish patients
Carolina Martinez-Ciarpaglini, María Ortega, Sandra Pérez-Buira, Aitana Bolea, Beatriz Casado Guerra, Carmen Herencia Bellido, Paula Tornero Piñero, Dolores Naranjo-Hans, Brenda Palomar, Hernán Quiceno, Amanda Sardón Fernández, Ariadna Torner Calvo, Feder
Virchows Archiv.2025; 487(6): 1337. CrossRef - Distinct clinicopathological and survival profiles of CLDN18.2 and PD-L1 expression in advanced gastric cancer and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma
D.R. Castillo, M. Guo, P. Shah, M. Hazeltin, D. Tai, F. Al-Manaseer, S. Mlamba, D. Perez, S. Yeremian, S. Guzman, R. Mannan, C. Crook, C. Lau, N. Tawar, G. Brar, M. Raoof, Y. Woo, S.P. Wu, D. Li
ESMO Gastrointestinal Oncology.2025; 10: 100261. CrossRef - Best Practice PD-L1 Staining and Interpretation in Gastric Cancer Using PD-L1 IHC PharmDx 22C3 and PD-L1 IHC PharmDx 28-8 Assays, with Reference to Common Issues and Solutions
Soomin Ahn, Inwoo Hwang, Yuyeon Kim, Somin Lee, Yunjoo Cho, So Young Kang, Deok Geun Kim, Jeeyun Lee, Kyoung-Mee Kim
Biomedicines.2025; 13(11): 2824. CrossRef - Intraperitoneal immune microenvironment and efficacy of intraperitoneal chemotherapy in patients with gastric cancer and peritoneal metastasis
Tomoya Nakanishi, Motohiro Imano, Masashi Kohda, Hiroaki Kato, Naoko Kounami, Atsushi Yamada, Masuhiro Terada, Yoko Hiraki, Osamu Shiraishi, Atsushi Yasuda, Masayuki Shinkai, Takushi Yasuda
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - PD-L1 thresholds predict efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibition in first-line treatment of advanced gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. A systematic review and meta-analysis of seven phase III randomized trials
V. Formica, C. Morelli, L. Fornaro, S. Riondino, M. Rofei, E. Fontana, E.C. Smyth, M. Roselli, H.-T. Arkenau
ESMO Open.2024; 9(11): 103967. CrossRef
- Organ Preservation for Gastroesophageal Junction and Gastric Cancers: Ready for Primetime?
Review Article
- Recent topics on thyroid cytopathology: reporting systems and ancillary studies
- Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Ayana Suzuki
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):214-224. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.04.18
- 4,071 View
- 293 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - As fine-needle aspiration techniques and diagnostic methodologies for thyroid nodules have continued to evolve and reporting systems have been updated accordingly, we need to be up to date with the latest information to achieve accurate diagnoses. However, the diagnostic approaches and therapeutic strategies for thyroid nodules vary across laboratories and institutions. Several differences exist between Western and Eastern practices regarding thyroid fine-needle aspiration. This review describes the reporting systems for thyroid cytopathology and ancillary studies. Updated reporting systems enhance the accuracy, consistency, and clarity of cytology reporting, leading to improved patient outcomes and management strategies. Although a single global reporting system is optimal, reporting systems tailored to each country is acceptable. In such cases, compatibility must be ensured to facilitate data sharing. Ancillary methods include liquid-based cytology, immunocytochemistry, biochemical measurements, flow cytometry, molecular testing, and artificial intelligence, all of which improve diagnostic accuracy. These methods continue to evolve, and cytopathologists should actively adopt the latest methods and information to achieve more accurate diagnoses. We believe this review will be useful to practitioners of routine thyroid cytology.
Original Article
- Diagnostic yield of fine needle aspiration with simultaneous core needle biopsy for thyroid nodules
- Mohammad Ali Hasannia, Ramin Pourghorban, Hoda Asefi, Amir Aria, Elham Nazar, Hojat Ebrahiminik, Alireza Mohamadian
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(3):180-187. Published online April 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.03.04
- 11,239 View
- 237 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) is a widely utilized technique for assessing thyroid nodules; however, its inherent non-diagnostic rate poses diagnostic challenges. The present study aimed to evaluate and compare the diagnostic efficacy of FNA, core needle biopsy (CNB), and their combined application in the assessment of thyroid nodules.
Methods
A total of 56 nodules from 50 patients was analyzed using both FNA and simultaneous CNB. The ultrasound characteristics were categorized according to the American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data Systems classification system. The study compared the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of FNA, CNB, and the combination of the two techniques.
Results
The concordance between FNA and CNB was notably high, with a kappa coefficient of 0.837. The sensitivity for detecting thyroid malignancy was found to be 25.0% for FNA, 66.7% for CNB, and 83.3% for the combined FNA/CNB approach, with corresponding specificities of 84.6%, 97.4%, and 97.4%. The accuracy of the FNA/CNB combination was the highest at 94.1%.
Conclusions
The findings of this study indicate that both CNB and the FNA/CNB combination offer greater diagnostic accuracy for thyroid malignancy compared to FNA alone, with no significant complications reported. Integrating CNB with FNA findings may enhance management strategies and treatment outcomes for patients with thyroid nodules.
Review Article
- Central nervous system tumors with BCOR internal tandem duplications: a systematic review of clinical, radiological, and pathological features in 69 cases
- Ji Young Lee, Sung Sun Kim, Hee Jo Baek, Tae-Young Jung, Kyung-Sub Moon, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Kyung-Hwa Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):273-280. Published online September 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.23
- 3,630 View
- 179 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Central nervous system tumors with BCL6 corepressor (BCOR) internal tandem duplications (ITDs) constitute a rare, recently characterized pediatric neoplasm with distinct molecular and histopathological features. To date, 69 cases have been documented in the literature, including our institutional case. These neoplasms predominantly occur in young children, with the cerebellum representing the most frequent anatomical location. Radiologically, these tumors present as large, well-circumscribed masses frequently demonstrating necrosis, hemorrhage, and heterogeneous enhancement. Histologically, they are characterized by a monomorphic cellular population featuring ependymoma-like perivascular pseudorosettes, myxoid stroma, and elevated mitotic activity. Immunohistochemically, these tumors exhibit sparse glial fibrillary acidic protein expression while consistently demonstrating positive staining for vimentin and CD56. The defining molecular hallmark is a heterozygous ITD within exon 15 of the BCOR gene, with insertions ranging from 9 to 42 amino acids in length. BCOR immunohistochemistry reveals nuclear positivity in 97.9% of examined cases, although this finding is not pathognomonic for BCOR ITDs. This comprehensive review synthesizes data from all published cases of this novel tumor entity, providing a detailed analysis of clinical presentation, neuroimaging findings, histopathological features with differential diagnostic considerations, therapeutic approaches, and prognostic outcomes.
Case Study
- Composite chronic lymphocytic leukemia and mantle cell lymphoma involving the bone marrow: a case report and literature review
- Roksolana Demianets, Susan O’Brien, Khosrow Mahdavi, Chenchen Niu, Sumayya Aslam, Truc Tran, Ying Zhang, Ashley Gamayo, Xiaohui Zhao, Sherif A. Rezk
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):334-339. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.02
- 2,530 View
- 138 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) is a clinically indolent lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by accumulation of mature B-cell lymphocytes. Given the common CD5 co-expression, mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is one of the most important entities in the differential diagnosis. MCL and CLL/SLL might exhibit overlapping morphologic and immunohistochemical features, making diagnosis particularly difficult in cases of composite lymphomas. Here, we present a unique case of composite lymphoma in an 86-year-old male, along with a literature review on the immunophenotypic variability of both MCL and CLL, which should always be confirmed with additional ancillary cytogenetic and molecular studies.
Review
- Next step of molecular pathology: next-generation sequencing in cytology
- Ricella Souza da Silva, Fernando Schmitt
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):291-298. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.22
- 6,637 View
- 380 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The evolving landscape of precision oncology underscores the pivotal shift from morphological diagnosis to treatment decisions driven by molecular profiling. Recent guidelines from the European Society for Medical Oncology recomend the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) across a broader range of cancers, reflecting its superior efficiency and clinical value. NGS not only updates oncology testing by offering quicker, sample-friendly, and sensitive analysis but also reduces the need for multiple individual tests. Cytology samples, often obtained through less invasive methods, can yield high-quality genetic material suitable for molecular analysis. This article focuses on optimizing the use of cytology samples in NGS, and outlines their potential benefits in identifying actionable molecular alterations for targeted therapies across various solid tumors. It also addresses the need for validation studies and the strategies to incorporate or combine different types of samples into routine clinical practice. Integrating cytological and liquid biopsies into routine clinical practice, alongside conventional tissue biopsies, offers a comprehensive approach to tumor genotyping, early disease detection, and monitoring of therapeutic responses across various solid tumor types. For comprehensive biomarker characterization, all patient specimens, although limited, is always valuable.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The World Health Organization Reporting System for Lymph Node, Spleen, and Thymus Cytopathology: Part 1 – Lymph Node
Immacolata Cozzolino, Mats Ehinger, Maria Calaminici, Andrea Ronchi, Mousa A. Al-Abbadi, Helena Barroca, Beata Bode-Lesniewska, David F. Chhieng, Ruth L. Katz, Oscar Lin, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, Martha Bishop Pitman, Arvind Rajwanshi, Fernando C. Schmitt, Ph
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - The impact of cytological preparation techniques on RNA quality: A comparative study on smear samples
Cisel Aydin Mericoz, Gulsum Caylak, Elif Sevin Sanioglu, Zeynep Seçil Satilmis, Ayse Humeyra Dur Karasayar, Ibrahim Kulac
Cancer Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Reimagining cytopathology in the molecular era: Integration or fragmentation?
Sumanta Das, R. Naveen Kumar, Biswajit Dey, Pranjal Kalita
Cytojournal.2025; 22: 94. CrossRef
- The World Health Organization Reporting System for Lymph Node, Spleen, and Thymus Cytopathology: Part 1 – Lymph Node
Original Articles
- Histopathologic classification and immunohistochemical features of papillary renal neoplasm with potential therapeutic targets
- Jeong Hwan Park, Su-Jin Shin, Hyun-Jung Kim, Sohee Oh, Yong Mee Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):321-330. Published online September 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.31
- 6,886 View
- 431 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Papillary renal cell carcinoma (pRCC) is the second most common histological subtype of renal cell carcinoma and is considered a morphologically and molecularly heterogeneous tumor. Accurate classification and assessment of the immunohistochemical features of possible therapeutic targets are needed for precise patient care. We aimed to evaluate immunohistochemical features and possible therapeutic targets of papillary renal neoplasms
Methods
We collected 140 papillary renal neoplasms from three different hospitals and conducted immunohistochemical studies on tissue microarray slides. We performed succinate dehydrogenase B, fumarate hydratase, and transcription factor E3 immunohistochemical studies for differential diagnosis and re-classified five cases (3.6%) of papillary renal neoplasms. In addition, we conducted c-MET, p16, c-Myc, Ki-67, p53, and stimulator of interferon genes (STING) immunohistochemical studies to evaluate their pathogenesis and value for therapeutic targets.
Results
We found that c-MET expression was more common in pRCC (classic) (p = .021) among papillary renal neoplasms and Ki-67 proliferation index was higher in pRCC (not otherwise specified, NOS) compared to that of pRCC (classic) and papillary neoplasm with reverse polarity (marginal significance, p = .080). Small subsets of cases with p16 block positivity (4.5%) (pRCC [NOS] only) and c-Myc expression (7.1%) (pRCC [classic] only) were found. Also, there were some cases showing STING expression and those cases were associated with increased Ki-67 proliferation index (marginal significance, p = .063).
Conclusions
Our findings suggested that there are subsets of pRCC with c-MET, p16, c-MYC, and STING expression and those cases could be potential candidates for targeted therapy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tissue-Based Biomarkers Important for Prognostication and Management of Genitourinary Tumors, Including Surrogate Markers of Genomic Alterations
Leonie Beauchamp, Shreeya Indulkar, Eric Erak, Mohammad Salimian, Andres Matoso
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2025; 18(1): 175. CrossRef - Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity: a case report and literature review
Diego Gonzalez, Kris Kokoneshi, Sam Kwon, Ryan Thomas Mathews, Ryan Michael Antar, Maher Ali, Abiye Kassa, Michael Whalen
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Tissue-Based Biomarkers Important for Prognostication and Management of Genitourinary Tumors, Including Surrogate Markers of Genomic Alterations
- Pancreatic cancer in liquid-based cytology: cytological features and cell block utility from 254 fine-needle aspiration samples
- Jaeyong Min, Wookjin Oh, Baek-hui Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):249-261. Published online July 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.05.27
- 3,106 View
- 212 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Despite the increasing use of liquid-based cytology (LBC) for pancreatic cancer diagnosis, relatively few studies have directly examined such research. This study analyzed the cytopathological features of pancreatic cancer in LBC and demonstrated the utility of cell blocks in diagnosing pancreatic lesions. Methods: A retrospective review identified LBC from 254 pancreatic fine-needle aspirations (FNAs) (221 patients). FNAs were categorized into five subgroups based on cytopathological, clinical, and histopathological findings. Two pathologists evaluated cytological features in LBC samples, cell blocks, and tissue slides. Comparative analysis assessed differences between groups. Results: Compared to benign lesions, LBC of pancreatic cancer more frequently showed a necrotic background, intermediate to high cellularity, mixed architecture, nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio >0.8, anisonucleosis >4:1, irregular and thick nuclear membranes, multinucleated tumor cells, hyperchromatic nuclei, coarse to clumped chromatin, and a prominent single nucleolus. In cases of conventional pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, the palliative treatment subgroup showed a higher incidence of necrotic background than the resection subgroup. In the cell block analysis, tumor cells not identified in LBC slides were detected in 16 FNAs. Additionally, 13 FNAs contributed to differential diagnosis: ancillary tests aided diagnosis in 12 FNAs, while histopathological evaluation of the cell block slide alone was helpful in one case. Conclusions: The cytological features of pancreatic cancer in LBC are similar to those observed in conventional smears, with a necrotic background suggesting advanced (unresectable) disease. The cell block methodology minimizes tumor cell loss and facilitates differential diagnosis by enabling ancillary testing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytology and small biopsy diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Maria Pimenova, Matthew W. Rosenbaum
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2026; 43(2): 150992. CrossRef
- Cytology and small biopsy diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Categorizing high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma into clinically relevant subgroups using deep learning–based histomic clusters
- Byungsoo Ahn, Eunhyang Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):91-104. Published online February 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.23
- 5,320 View
- 254 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSC) exhibits significant heterogeneity, posing challenges for effective clinical categorization. Understanding the histomorphological diversity within HGSC could lead to improved prognostic stratification and personalized treatment approaches. Methods: We applied the Histomic Atlases of Variation Of Cancers model to whole slide images from The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset for ovarian cancer. Histologically distinct tumor clones were grouped into common histomic clusters. Principal component analysis and K-means clustering classified HGSC samples into three groups: highly differentiated (HD), intermediately differentiated (ID), and lowly differentiated (LD). Results: HD tumors showed diverse patterns, lower densities, and stronger eosin staining. ID tumors had intermediate densities and balanced staining, while LD tumors were dense, patternless, and strongly hematoxylin-stained. RNA sequencing revealed distinct patterns in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and energy metabolism, with upregulation in the HD, downregulation in the LD, and the ID positioned in between. Survival analysis showed significantly lower overall survival for the LD compared to the HD and ID, underscoring the critical role of mitochondrial dynamics and energy metabolism in HGSC progression. Conclusions: Deep learning-based histologic analysis effectively stratifies HGSC into clinically relevant prognostic groups, highlighting the role of mitochondrial dynamics and energy metabolism in disease progression. This method offers a novel approach to HGSC categorization. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Learning Disabilities in the 21st Century: Integrating Neuroscience, Education, and Technology for Better Outcomes
Syed Mohammed Basheeruddin Asdaq, Ahmad H. Alhowail, Syed Imam Rabbani, Naira Nayeem, Syed Mohammed Emaduddin Asdaq, Faiqa Nausheen
SAGE Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Learning Disabilities in the 21st Century: Integrating Neuroscience, Education, and Technology for Better Outcomes
Review
- Diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases: from Averill A. Liebow to artificial intelligence
- Eunhee S. Yi, Paul Wawryko, Jay H. Ryu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):1-11. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.17
- 7,799 View
- 437 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Histopathologic criteria of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP)/idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) were defined over the years and endorsed by leading organizations decades after Dr. Averill A. Liebow first coined the term UIP in the 1960s as a distinct pathologic pattern of fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Novel technology and recent research on interstitial lung diseases with genetic component shed light on molecular pathogenesis of UIP/IPF. Two antifibrotic agents introduced in the mid-2010s opened a new era of therapeutic approaches to UIP/IPF, albeit contentious issues regarding their efficacy, side effects, and costs. Recently, the concept of progressive pulmonary fibrosis was introduced to acknowledge additional types of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases with the clinical and pathologic phenotypes comparable to those of UIP/IPF. Likewise, some authors have proposed a paradigm shift by considering UIP as a stand-alone diagnostic entity to encompass other fibrosing interstitial lung diseases that manifest a relentless progression as in IPF. These trends signal a pendulum moving toward the tendency of lumping diagnoses, which poses a risk of obscuring potentially important information crucial to both clinical and research purposes. Recent advances in whole slide imaging for digital pathology and artificial intelligence technology could offer an unprecedented opportunity to enhance histopathologic evaluation of interstitial lung diseases. However, current clinical practice trends of moving away from surgical lung biopsies in interstitial lung disease patients may become a limiting factor in this endeavor as it would be difficult to build a large histopathologic database with correlative clinical data required for artificial intelligence models.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Identification of early genes in the pathophysiology of fibrotic interstitial lung disease in a new model of pulmonary fibrosis
Nathan Hennion, Corentin Bedart, Léonie Vandomber, Frédéric Gottrand, Sarah Humez, Cécile Chenivesse, Jean-Luc Desseyn, Valérie Gouyer
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiological Insights into UIP Pattern: A Comparison Between IPF and Non-IPF Patients
Stefano Palmucci, Miriam Adorna, Angelica Rapisarda, Alessandro Libra, Sefora Fischetti, Gianluca Sambataro, Letizia Antonella Mauro, Emanuele David, Pietro Valerio Foti, Claudia Mattina, Corrado Spatola, Carlo Vancheri, Antonio Basile
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(12): 4162. CrossRef
- Identification of early genes in the pathophysiology of fibrotic interstitial lung disease in a new model of pulmonary fibrosis
Original Articles
- Diagnostic challenges in the assessment of thyroid neoplasms using nuclear features and vascular and capsular invasion: a multi-center interobserver agreement study
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Mutiah Mutmainnah, Maria Francisca Ham, Dina Khoirunnisa, Abdillah Hasbi Assadyk, Husni Cangara, Aswiyanti Asri, Diah Prabawati Retnani, Fairuz Quzwain, Hasrayati Agustina, Hermawan Istiadi, Indri Windarti, Krisna Murti, Muhammad Takbir, Ni Made Mahastuti, Nila Kurniasari, Nungki Anggorowati, Pamela Abineno, Yulita Pundewi Setyorini, Kennichi Kakudo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):299-309. Published online September 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.25
- Correction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2025;59(3):201
- 5,368 View
- 410 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The diagnosis of thyroid neoplasms necessitates the identification of distinct histological features. Various education/hospital centers located in cities across Indonesia likely result in discordances among pathologists when diagnosing thyroid neoplasms.
Methods
This study examined the concordance among Indonesian pathologists in assessing nuclear features and capsular and vascular invasion of thyroid tumors. Fifteen pathologists from different centers independently assessed the same 14 digital slides of thyroid tumor specimens. All the specimens were thyroid neoplasms with known BRAFV600E and RAS mutational status, from a single center. We evaluated the pre- and post-training agreement using the Fleiss kappa. The significance of the training was evaluated using a paired T-test.
Results
Baseline agreement on nuclear features was slight to fair based on a 3-point scoring system (k = 0.14 to 0.28) and poor to fair based on an eight-point system (k = –0.02 to 0.24). Agreements on vascular (κ = 0.35) and capsular invasion (κ = 0.27) were fair, whereas the estimated molecular type showed substantial agreement (κ = 0.74). Following the training, agreement using the eight-point system significantly improved (p = 0.001).
Conclusions
The level of concordance among Indonesian pathologists in diagnosing thyroid neoplasm was relatively poor. Consensus in pathology assessment requires ongoing collaboration and education to refine diagnostic criteria. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Dina Khoirunnisa, Salinah, Maria Francisca Ham
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 75: 152434. CrossRef
- Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Single umbilical artery and associated birth defects in perinatal autopsies: prenatal diagnosis and management
- Manushree Saxena, Bhagyashri Hungund
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):214-218. Published online July 9, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.03
- 16,075 View
- 432 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The umbilical cord forms the connection between the fetus and the placenta at the feto-maternal interface and normally comprises two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein. In some cases, only a single umbilical artery (SUA) is present. This study was conducted to evaluate associations between SUA and other congenital malformations discovered in perinatal autopsies and to ascertain the existence of preferential associations between SUA and certain anomalies.
Methods
We evaluated records of all fetuses sent for autopsy to the Department of Pathology during the 10-year period from 2013 through 2022 (n = 1,277). The data were obtained from the hospital’s pathology laboratory records. The congenital anomalies were grouped by organ or system for analysis and included cardiovascular, urinary tract, nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, musculoskeletal, and lung anomalies.
Results
A SUA was present in 8.61% of the autopsies. The gestational age of the affected fetuses ranged between 13 to 40 weeks. An SUA presented as an isolated single anomaly in 44 cases (3.4%). Of the 110 SUA cases, 60% had other congenital anomalies. There was a significant association between birth defects and SUAs (p < .001). Strong associations between SUA and urinary tract, lung, and musculoskeletal anomalies were observed.
Conclusions
A SUA is usually seen in association with other congenital malformations rather than as an isolated defect. Therefore, examination for associated anomalies when an SUA is detected either antenatally or postnatally is imperative. The findings of this study should be helpful in counseling expectant mothers and their families in cases of SUA. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Single Umbilical Artery with Symmetrical IUGR and Multiple Fetal Anomalies - An Interesting Case Report
Amulya Choudary Kotapati, Bhargavi Khandru, Vijayasree M.
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2025; : 10. CrossRef - Epidemiological and Histopathological Characteristics of Fetuses with Congenital Disorders: A Study in Greece
Despoina Nteli, Maria Nteli, Konstantinos Konstantinidis, Maria Ouzounidou, Paschalis Theotokis, Maria-Eleni Manthou, Iasonas Dermitzakis, Xeni Miliara, Chrysoula Gouta, Stamatia Angelidou, Dimosthenis Miliaras, Soultana Meditskou
Biology.2025; 14(6): 626. CrossRef
- Single Umbilical Artery with Symmetrical IUGR and Multiple Fetal Anomalies - An Interesting Case Report
Editorial
- Advancing pathology through sixty volumes: reflections and future directions
- Chan Kwon Jung, So Yeon Park, Soon Won Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):1-5. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.08
- 2,135 View
- 20 Download
Original Articles
- The spectrum of microvascular patterns in adult diffuse glioma and their correlation with tumor grade
- Soni , Vaishali Walke, Deepti Joshi, Tanya Sharma, Adesh Shrivastava, Amit Agrawal
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):127-133. Published online May 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.11
- 7,242 View
- 353 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Primary brain tumors constitute the leading cause of cancer-related mortality. Among them, adult diffuse gliomas are the most common type, affecting the cerebral hemispheres and displaying a diffuse infiltrative pattern of growth in the surrounding neuropil that accounts for about 80% of all primary intracranial tumors. The hallmark feature of gliomas is blood vessel proliferation, which plays an important role in tumor growth, tumor biological behavior, and disease outcome. High-grade gliomas exhibit increased vascularity, the worst prognosis, and lower survival rates. Several angiogenic receptors and factors are upregulated in glioblastomas and stimulate angiogenesis signaling pathways by means of activating oncogenes and/or down-regulating tumor-suppressor genes. Existing literature has emphasized that different microvascular patterns (MVPs) are displayed in different subtypes of adult diffuse gliomas.
Methods
We examined the distribution and biological characteristics of different MVPs in 50 patients with adult diffuse gliomas. Haematoxylin and eosin staining results, along with periodic acid–Schiff and CD34 dual-stained sections, were examined to assess the vascular patterns and correlate with different grades of diffuse glioma.
Results
The present observational study on adult diffuse glioma evaluated tumor grade and MVPs. Microvascular sprouting was the most common pattern, while a bizarre pattern (type 2) was associated with the presence of a high-grade glioma. Vascular mimicry was observed in 6% of cases, all of which were grade 4 gliomas.
Conclusions
This study supplements the role of neo-angiogenesis and aberrant vasculature patterns in the grading and progression of adult diffuse gliomas, which can be future targets for planning treatment strategies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unlocking therapeutic potential: Exploring nuclear receptors in brain cancer treatment
Sujitha Jayaprakash, Hiu Yan Lam, Ravichandran Vishwa, Bandari BharathwajChetty, Kenneth C-H Yap, Mohammed S. Alqahtani, Mohamed Abbas, Gautam Sethi, Alan Prem Kumar, Ajaikumar B. Kunnumakkara
Chinese Medical Journal.2025; 138(21): 2722. CrossRef - Uptake patterns of Adult-type Non-Enhanced diffuse gliomas on [11C] methionine positron emission tomography
Shoji Yasuda, Naoya Imai, Hirohito Yano, Yuka Ikegame, Soko Ikuta, Takashi Maruyama, Noriyuki Nakayama, Morio Kumagai, Yoshihiro Muragaki, Jun Shinoda, Tsuyoshi Izumo
Neuroradiology.2025; 67(10): 2611. CrossRef - Loss of Fibronectin Fiber Tension in Glioblastoma is Associated with Microvascular Proliferations and Immune Cell Infiltration
Michele Crestani, Isabel Gerber, Arnaud Mieville, Katrin Frauenknecht, Theoni Maragkou, Tibor Hortobagyi, Viola Vogel
Advanced Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - High ORC6 expression is a prognostic indicator of poor survival in glioma patients
Mengjie Wang, Song Feng, Chen Zhang, Feng Jin
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Consequences of Hypoxic Events, Necrosis, and Microvascular Density, in Astrocytoma IDH-Mutant, CNS WHO Grade 4
Cristian Ionut Orasanu, Madalina Bosoteanu, Sorin Vamesu, Raluca Ioana Voda, Anamaria Sincu, Mariana Deacu
Medical Sciences.2025; 14(1): 6. CrossRef - Association of PD-L1 expression with adverse pathological features in adult diffuse astrocytoma
Rania K. Elsaid, Maha M. Abuhashim, Sylvia A. Ashamallah, Khaled M. Abouelkhair, Marwa M. Zaki
Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.2025; 12(1): 526. CrossRef
- Unlocking therapeutic potential: Exploring nuclear receptors in brain cancer treatment
- Characteristics of RET gene mutations in Vietnamese medullary thyroid carcinoma patients: a single-center analysis
- Van Hung Pham, Quoc Thang Pham, Minh Nguyen, Hoa Nhat Ngo, Thao Thi Thu Luu, Nha Dao Thi Minh, Trâm Đặng, Anh Tu Thai, Hoang Anh Vu, Dat Quoc Ngo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):125-132. Published online March 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.01.18
- 5,164 View
- 187 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The RET gene point mutation is the main molecular alteration involved in medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) tumorigenesis. Previous studies in Vietnam mainly consisted of case reports, with limited data on larger sample sizes. In this study, we investigated RET gene mutations in exons 10, 11, and 16 and analyzed clinicopathological features of a series of Vietnamese MTC patients. Methods: We collected 33 tissue samples from patients with MTC and analyzed RET mutations using the Sanger sequencing method. The relationship between hotspot RET mutations (exons 10, 11, 16) and clinicopathological features were investigated. Results: Among the 33 analyzed cases, 17 tumors (52%) harbored RET mutations in exon 10, 11, or 16. A total of 10 distinct genetic alterations were identified, including eight missense mutations and two short indels. Of these, seven were classified as pathogenic mutations based on previous publications, with p.M918T being the most frequent (4 cases), followed by p.C634R (3 cases) and p.C618R (3 cases). Mutations were significantly associated with specific histological patterns, such as the nested/insular pattern (p=.026), giant cells (p=.007), nuclear pleomorphism (p=.018), stippled chromatin (p=.044), and amyloid deposits (p=.024). No mutations were found in germline analyses, suggesting these were somatic alterations. Conclusions: Our results provided the first comprehensive analysis of RET mutations in Vietnamese MTC patients. The most frequent mutation was p.M918T, followed by p.C634R and p.C618R. Mutations in these three exons were linked to specific histopathological features. Information on mutational profiles of patients with MTC will further aid in the development of targeted therapeutics to ensure effective disease management.

 E-submission
E-submission
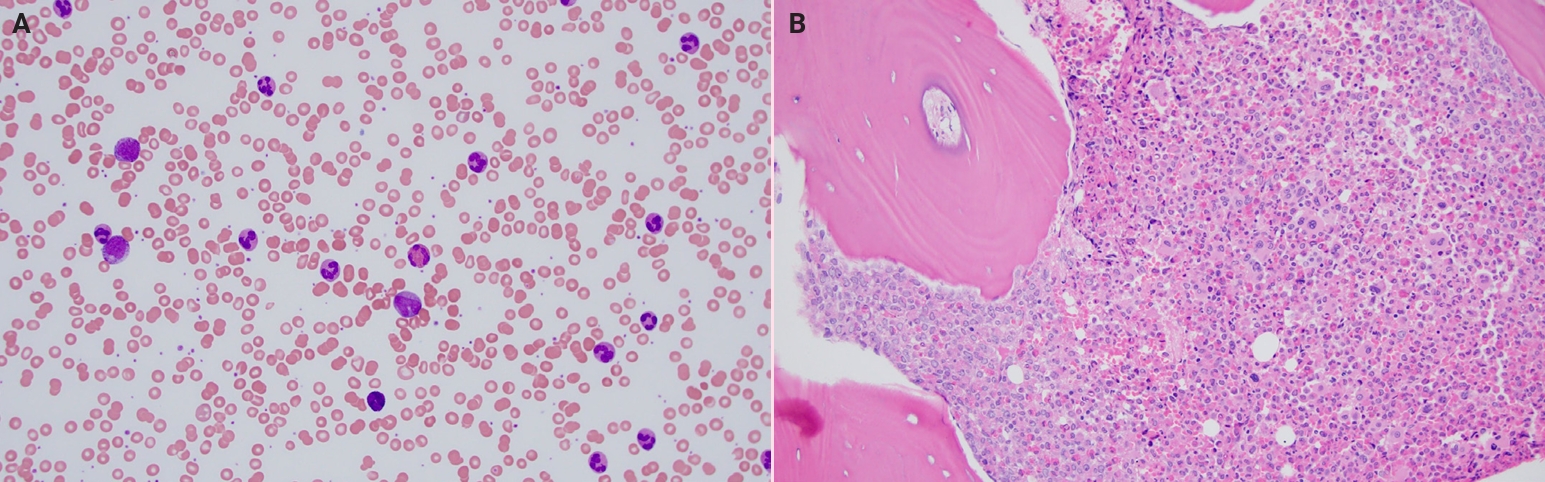
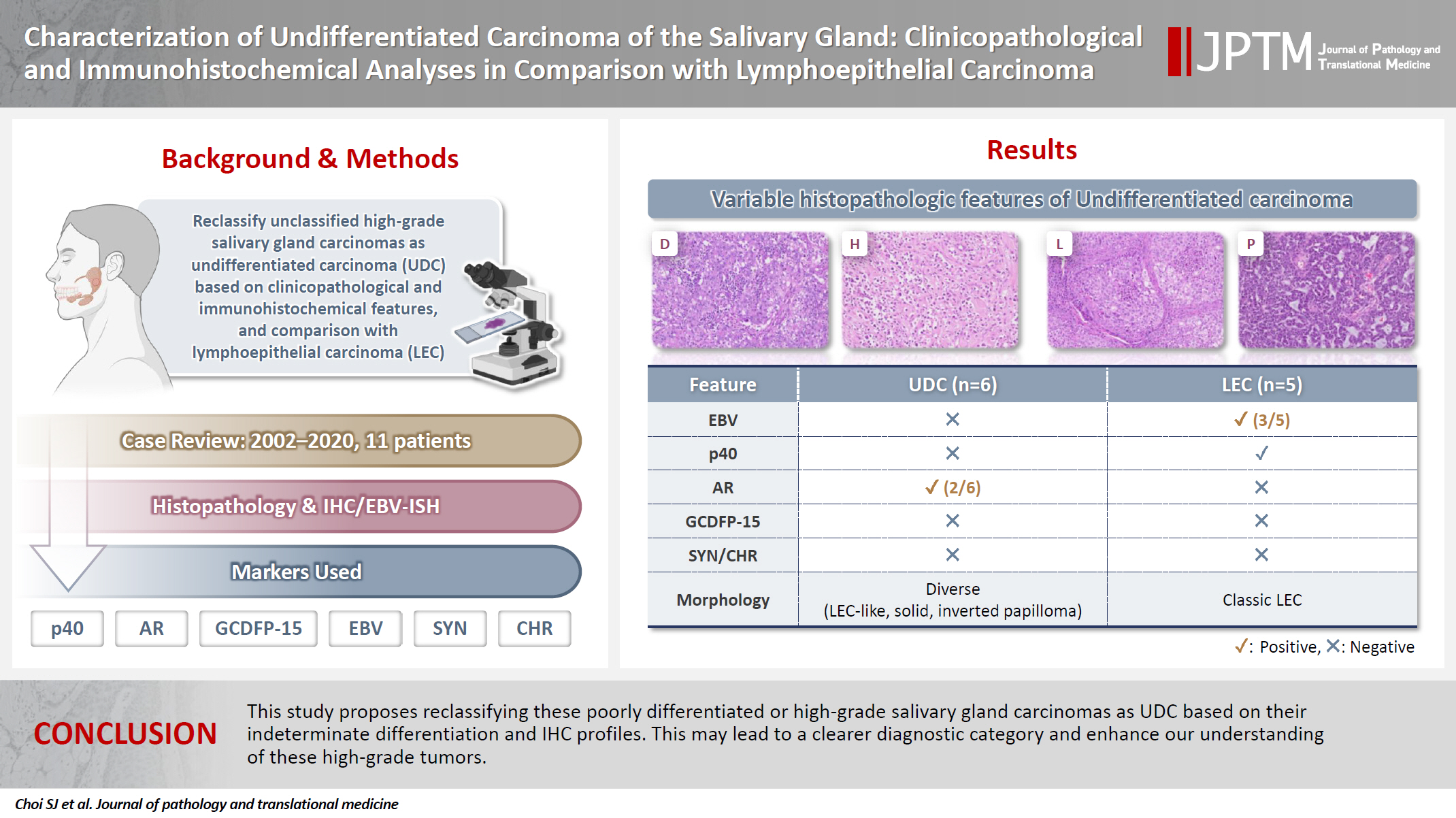




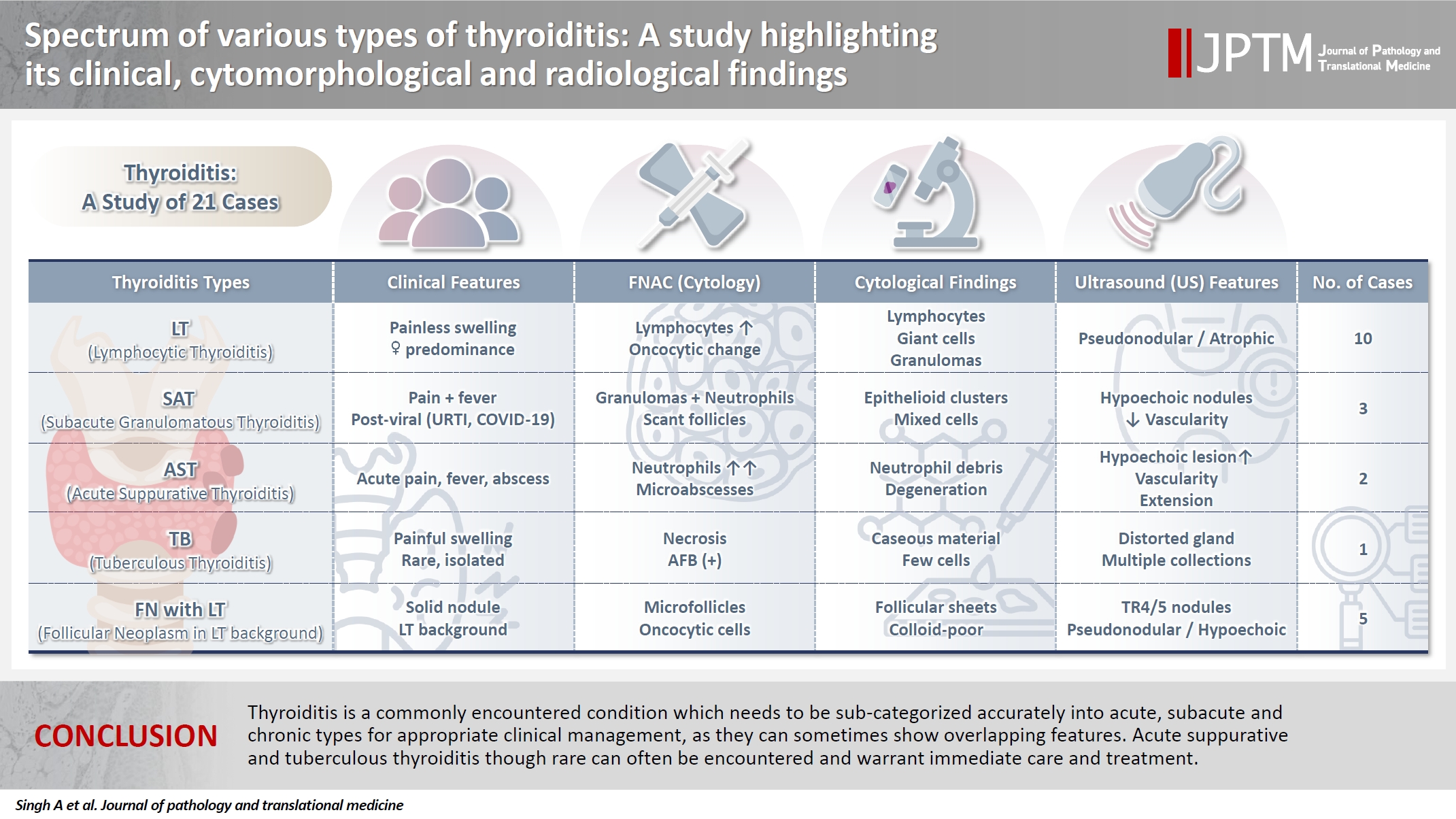



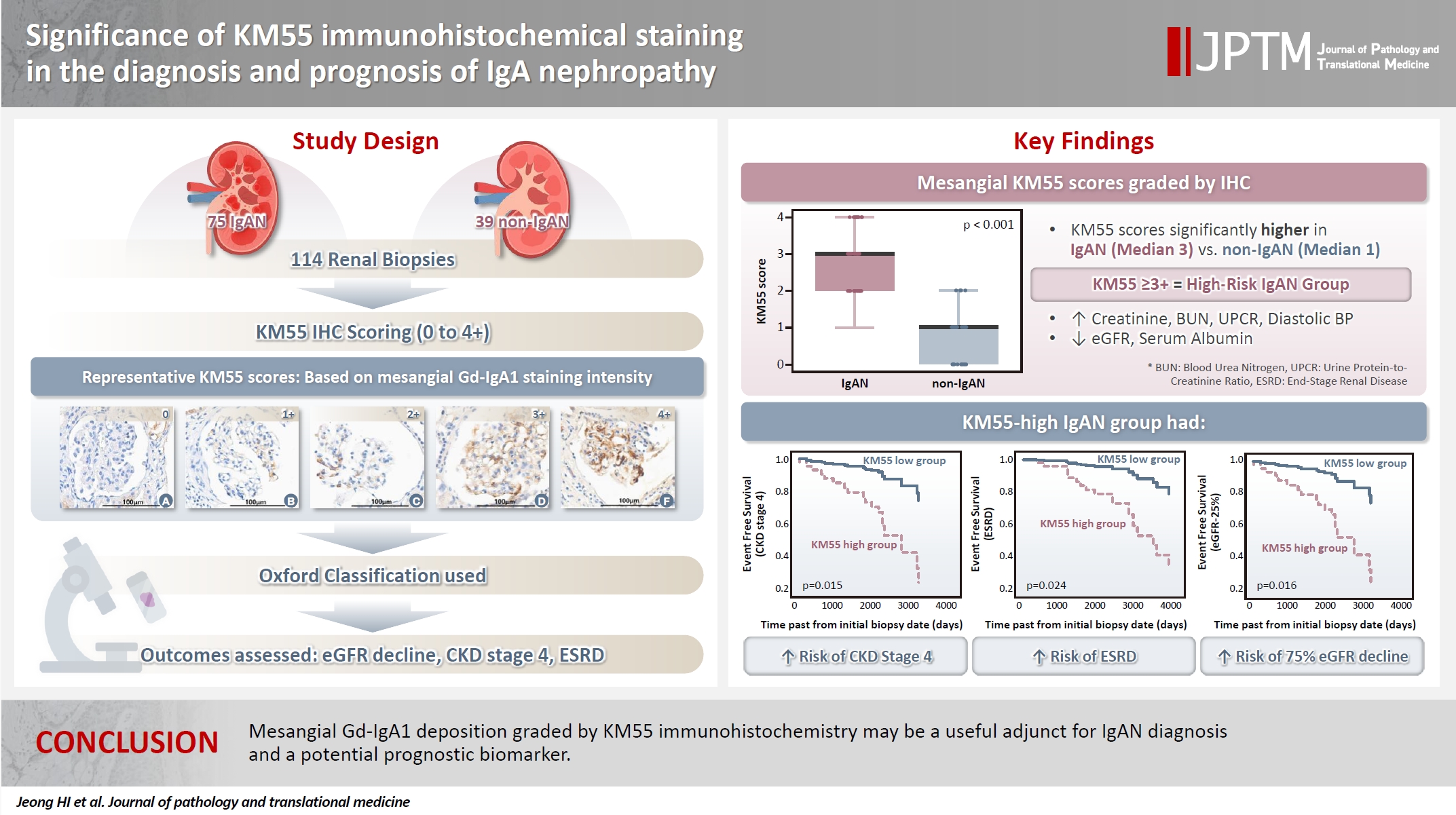
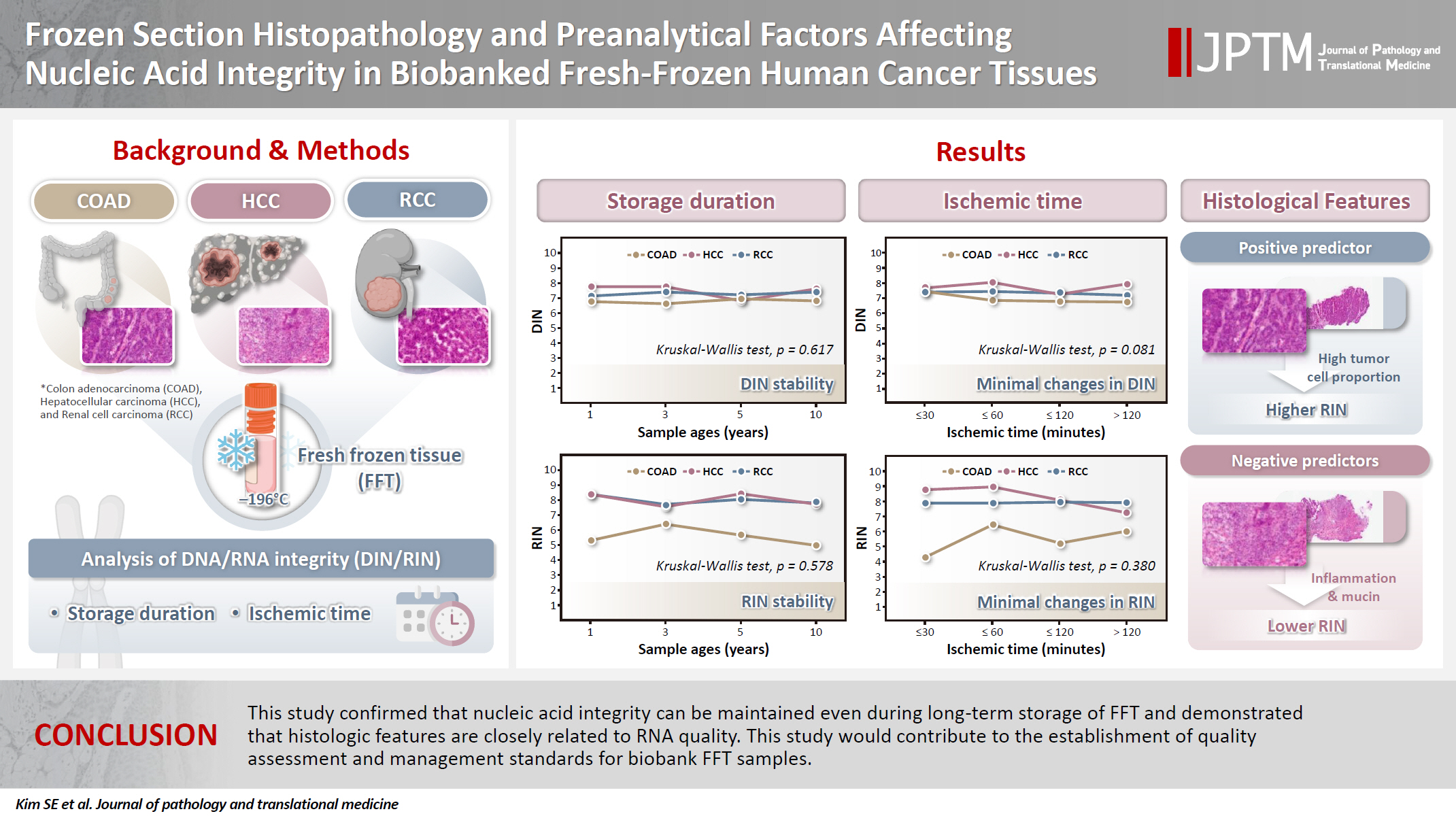


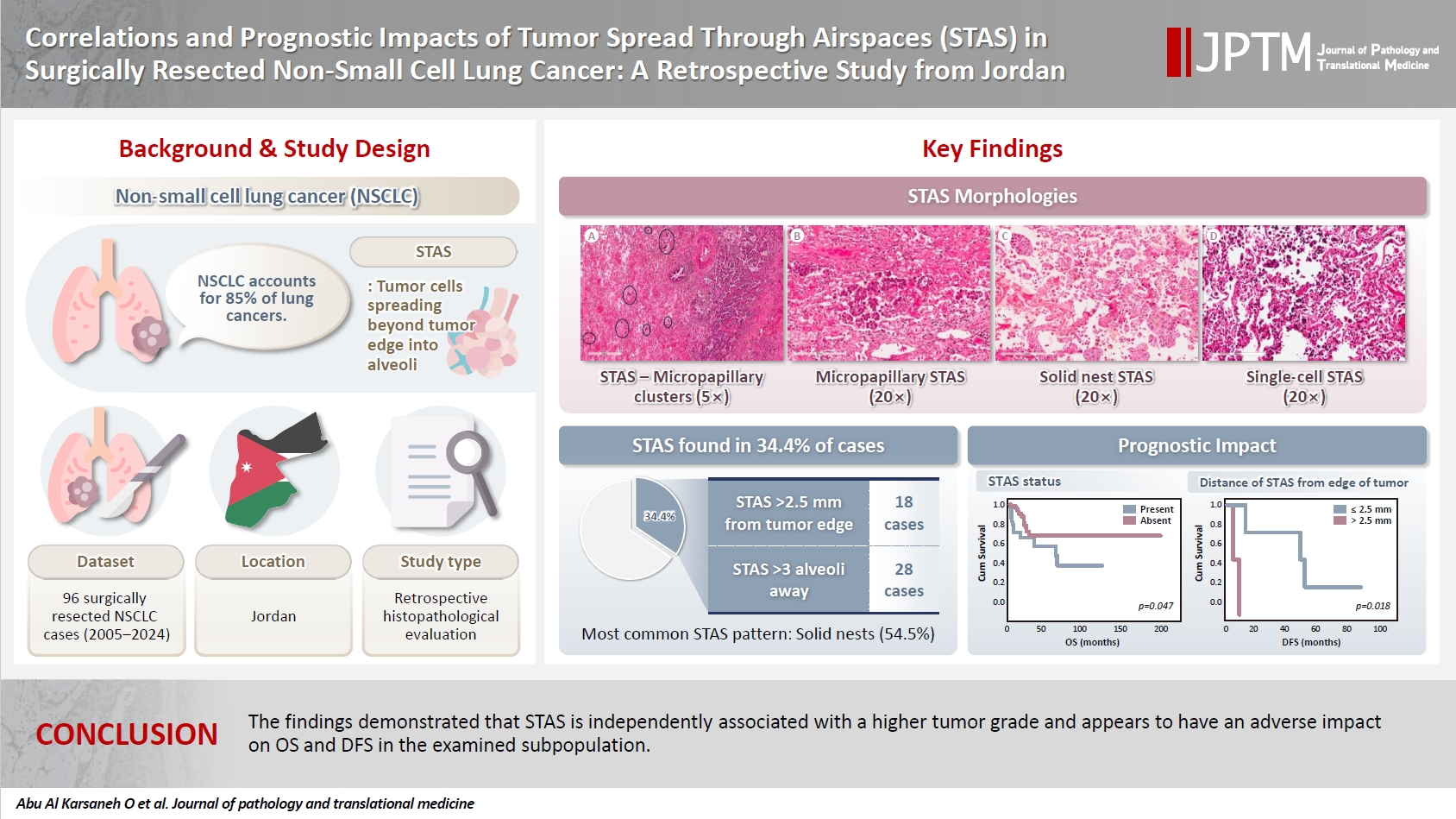
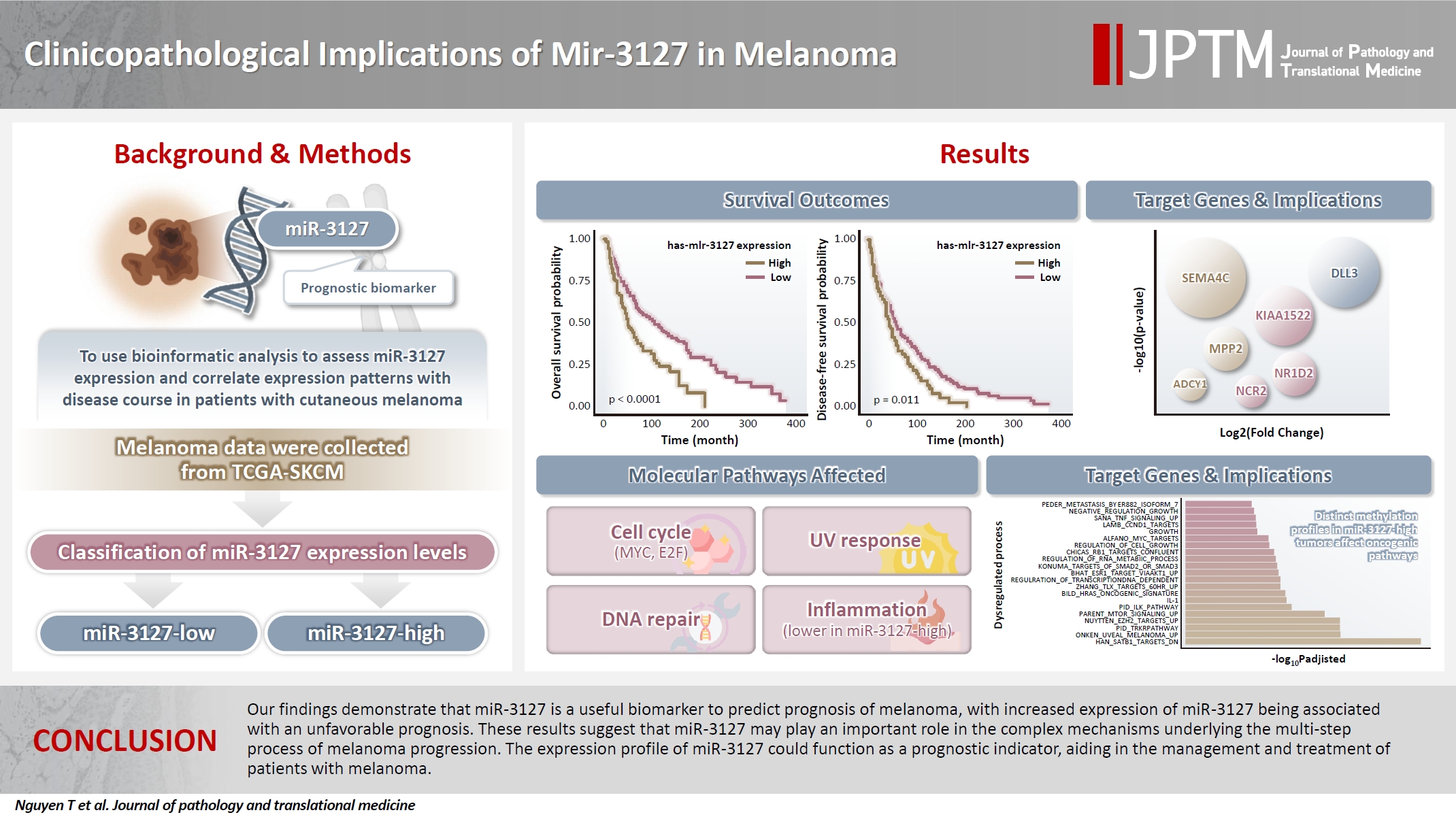

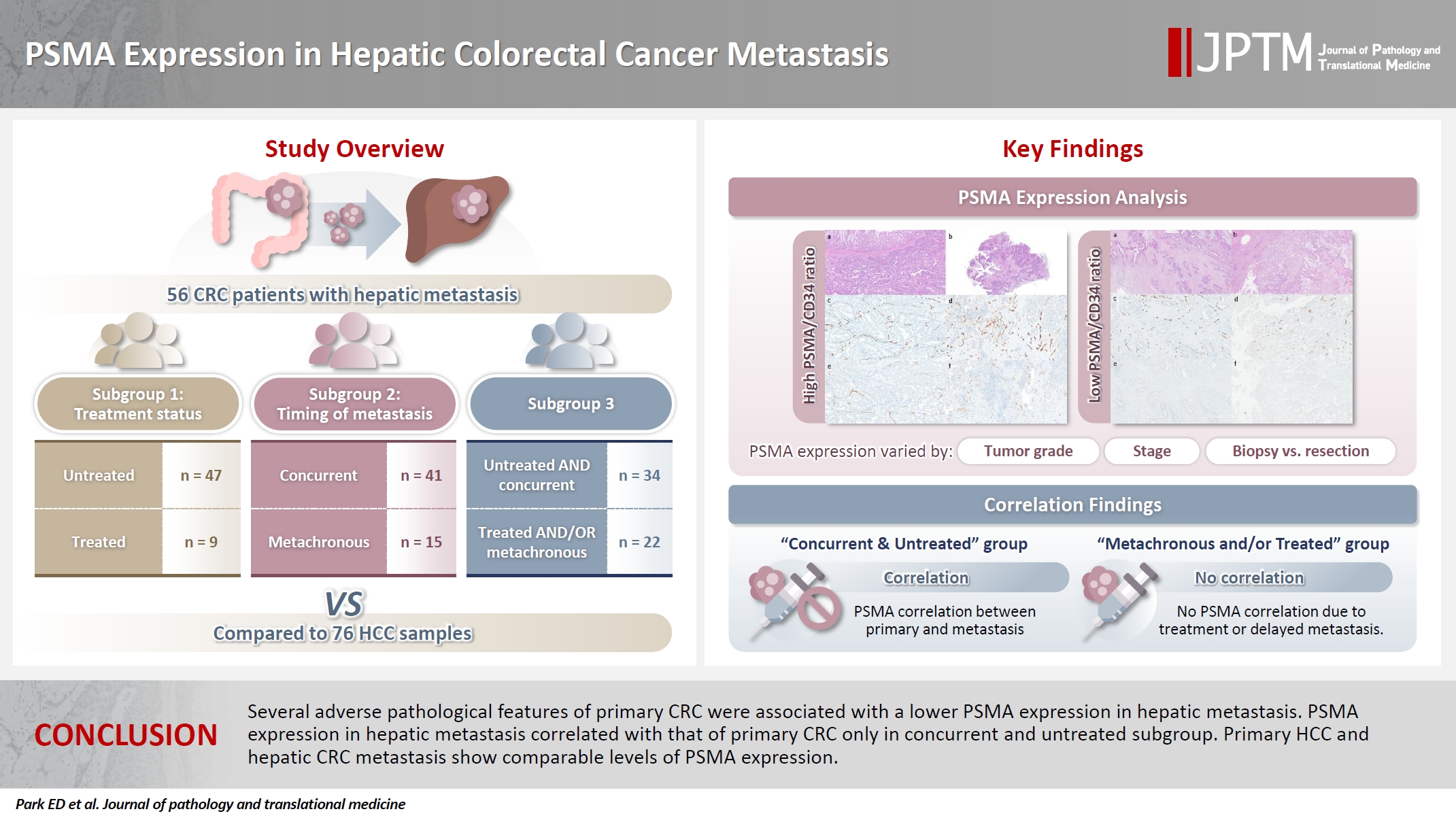

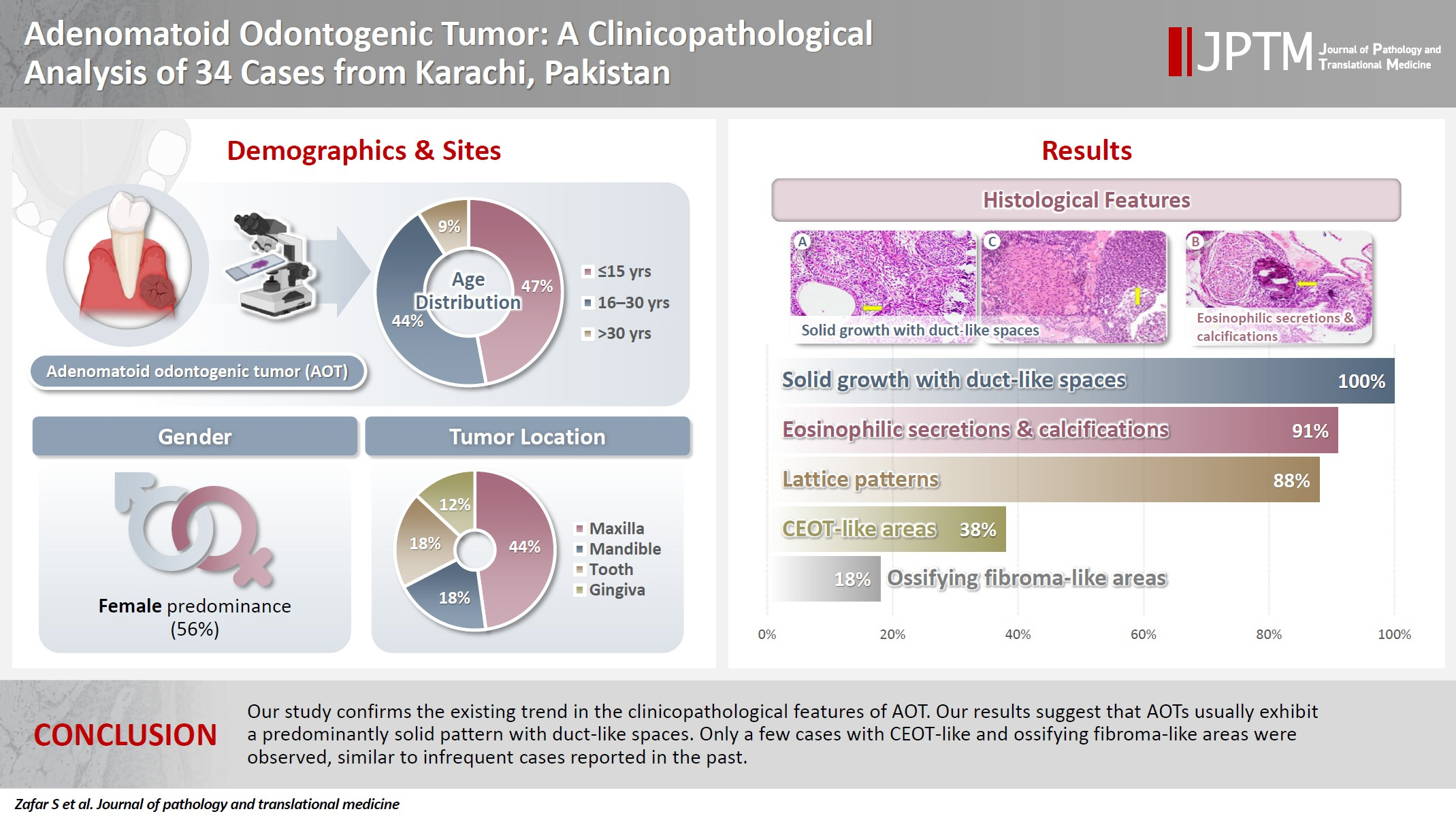

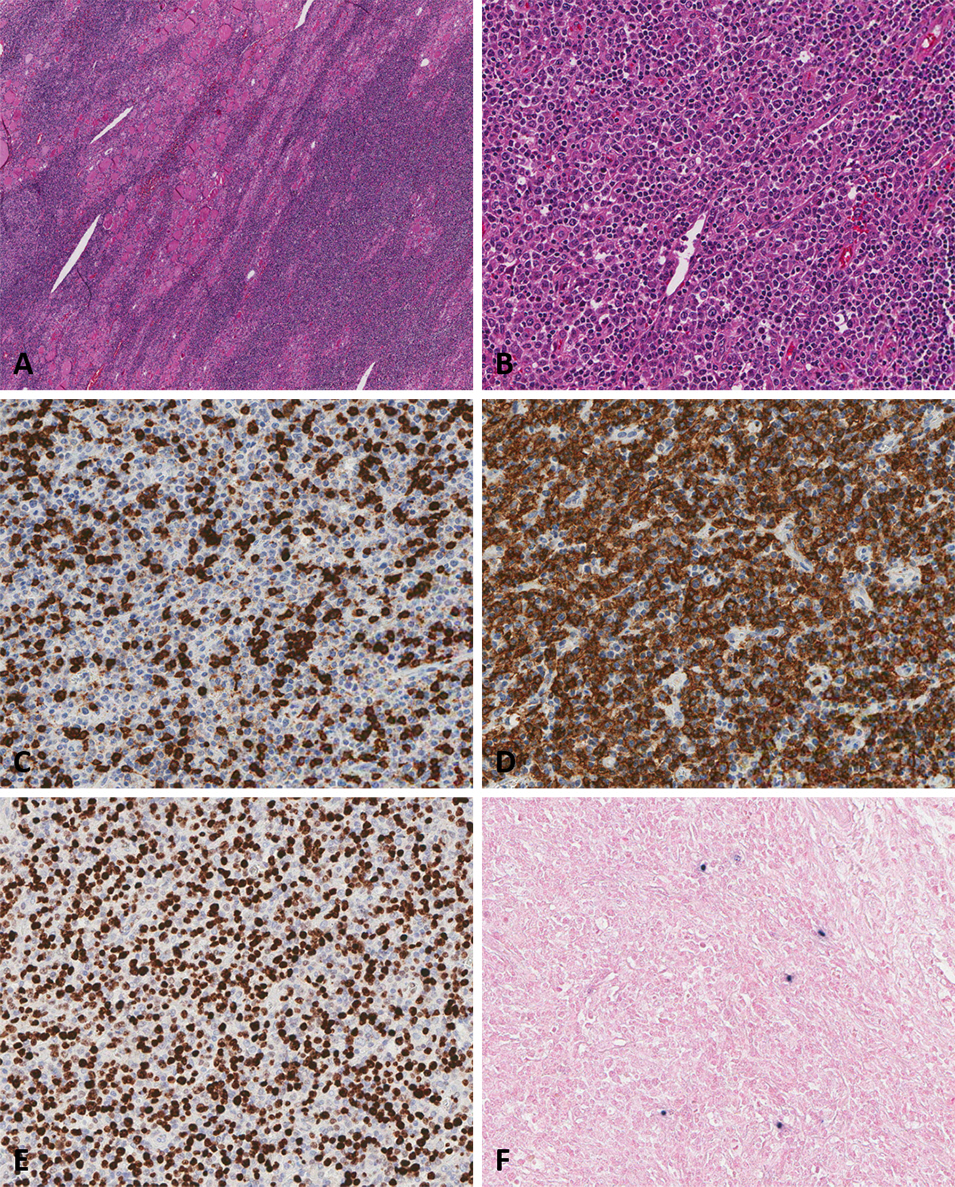




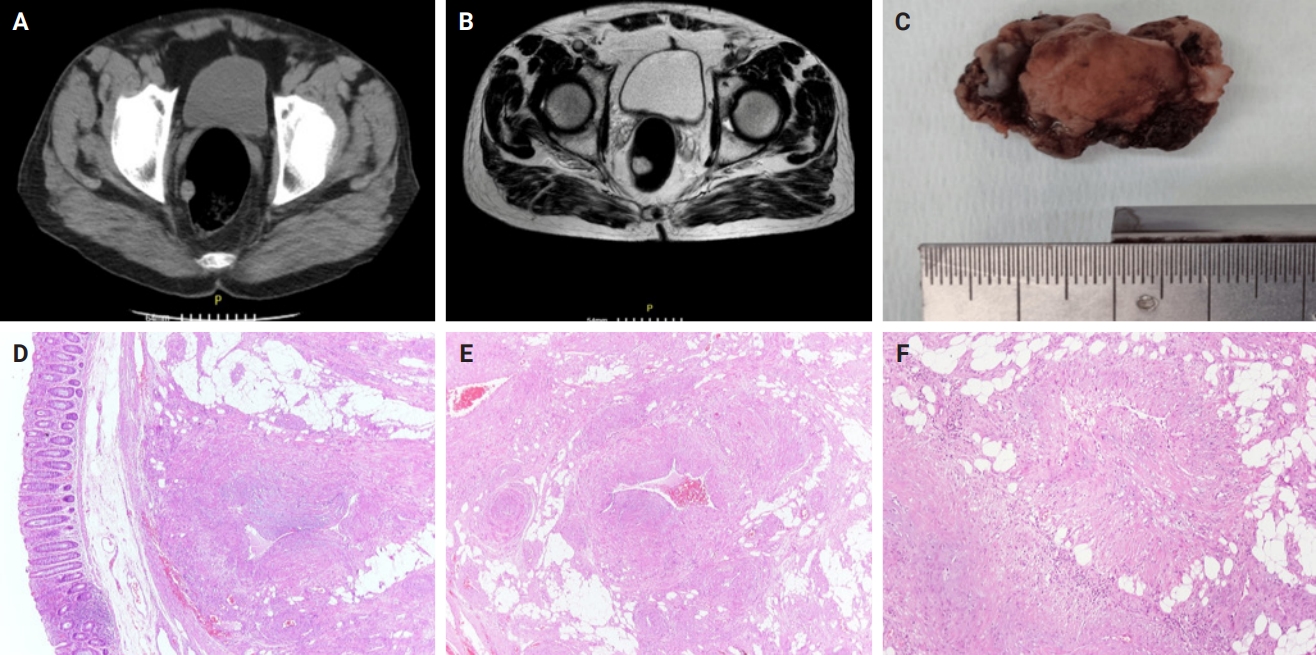






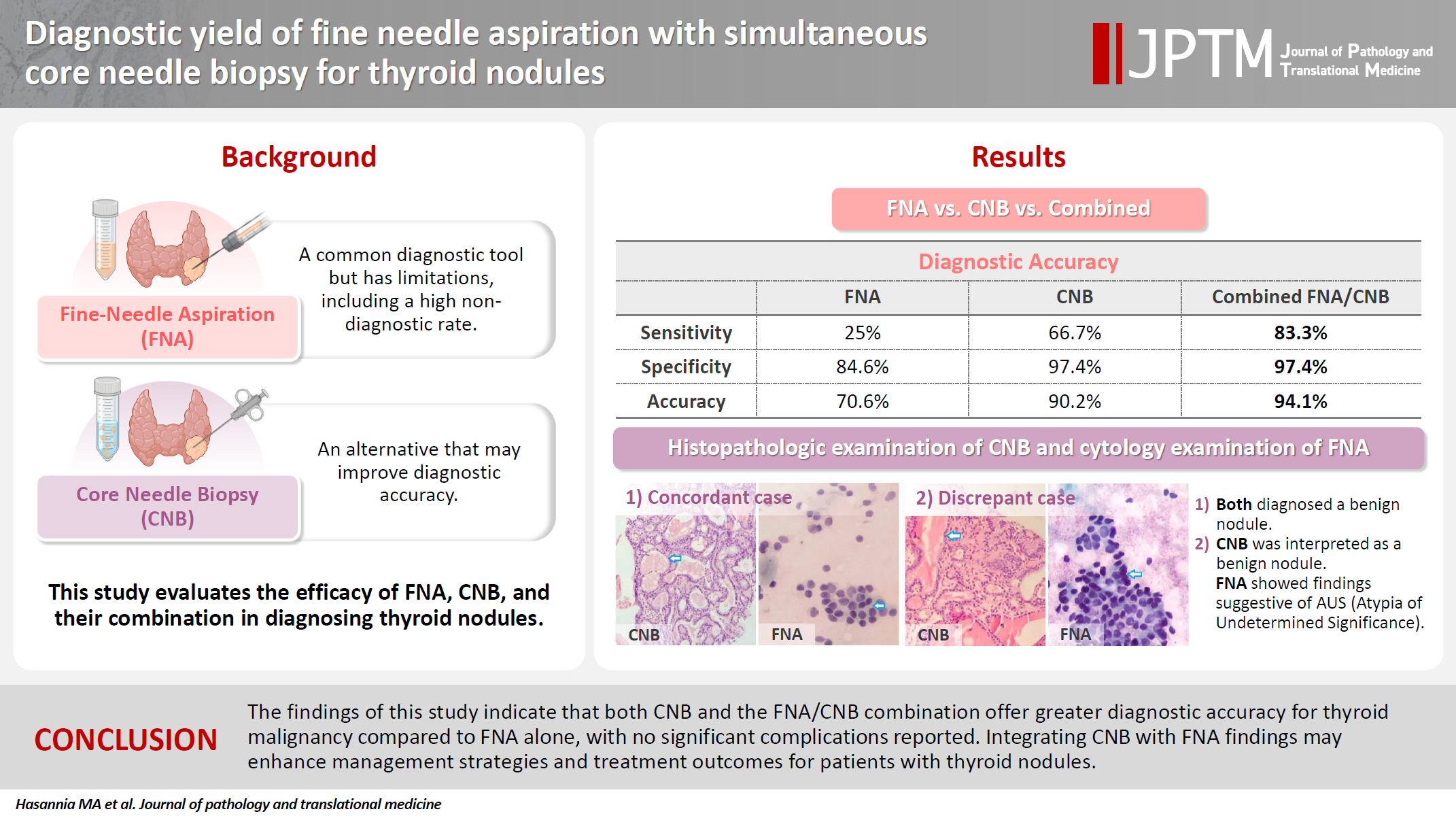

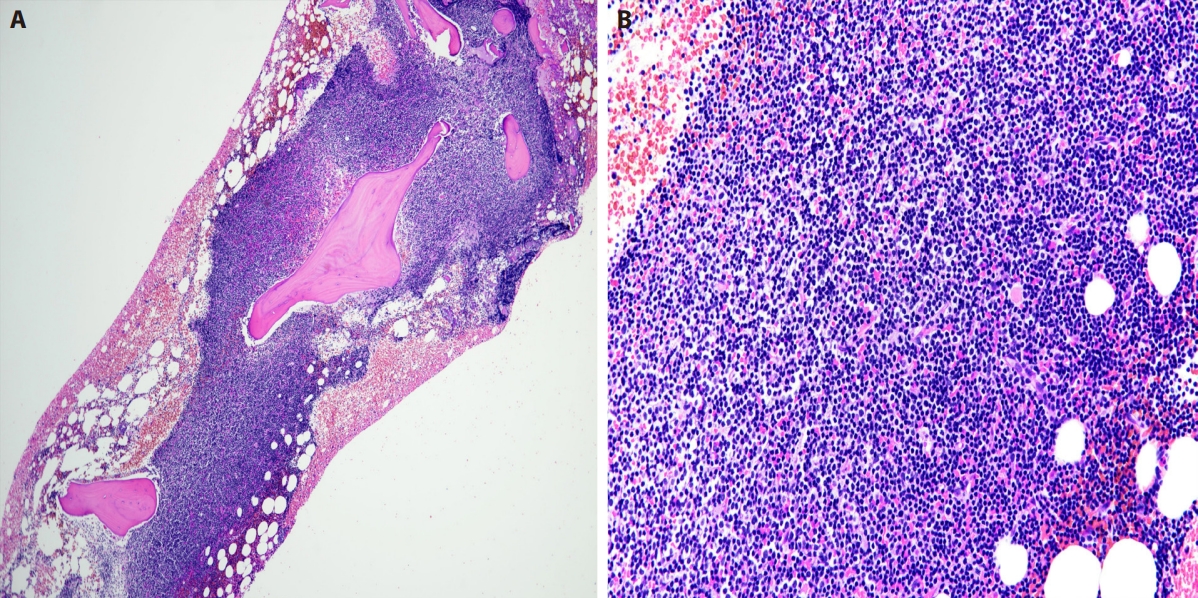








 First
First Prev
Prev



