Most cited
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Most cited
From articles published in Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine during the past two years (2024 ~ ).
Original Article
- TRPS1 expression in non-melanocytic cutaneous neoplasms: an immunohistochemical analysis of 200 cases
- Yi A. Liu, Phyu P. Aung, Yunyi Wang, Jing Ning, Priyadharsini Nagarajan, Jonathan L. Curry, Carlos A. Torres-Cabala, Doina Ivan, Victor G. Prieto, Qingqing Ding, Woo Cheal Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):72-80. Published online February 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.01.23
- 7,407 View
- 394 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Although trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1 (TRPS1) was initially thought to be highly sensitive and specific for carcinomas and mesenchymal tumors of mammary origin, more recent data suggest its expression is not limited to breast neoplasms but also can be seen in other cutaneous neoplasms, such as extramammary Paget disease and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in situ.
Methods
Two-hundred cases of non-melanocytic cutaneous neoplasm, including basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) (n = 41), SCCs (n = 35), Merkel cell carcinomas (MCCs) (n = 25), and adnexal neoplasms (n = 99), were tested for TRPS1 expression using a monoclonal anti- TRPS1 rabbit anti-human antibody.
Results
TRPS1 expression was present in almost all cases of SCC (94%), with a median H-score of 200, while it was either absent or only focally present in most BCCs (90%), with a median H-score of 5. The difference between BCCs and SCCs in H-score was significant (p < .001). All MCCs (100%) lacked TRPS1 expression. TRPS1 expression was frequently seen in most adnexal neoplasms, benign and malignant, in variable intensity and proportion but was consistently absent in apocrine carcinomas. All endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinomas (EMPSGCs) (100%, 6/6) showed diffuse and strong TRPS1 immunoreactivity, with a median H-score of 300, which was significantly different (p < .001) than that of BCCs.
Conclusions
Our study shows that TRPS1 may be an effective discriminatory marker for BCCs and SCCs. It also has a role in distinguishing BCCs from EMPSGCs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastatic Vulvar Paget's Disease Presenting in a Supraclavicular Lymph Node: A Diagnostic Challenge on Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
Thiri Htoo Aung, Neha Seth, Anam Khan, Kasturi Das
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1 (TRPS1) in breast pathology: diagnostic utility and pitfalls
Atif Ali Hashmi, Edi Brogi, Hannah Y. Wen
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Refining NTRK Fusion Detection in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Through Pan-TRK Immunohistochemistry and Histopathologic Features
Hyun Lee, Sue Youn Kim, Ji Min Park, Seung-Hyun Jung, Ozgur Mete, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma: Case report and literature review
Nan Guo, Zhenlin Fan, Yitong Chen, Qian Li, Limin Guo
European Journal of Ophthalmology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Updates on utility of immunohistochemistry in diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer
Hongxia Sun, Aysegul A. Sahin, Qingqing Ding
Human Pathology.2025; 162: 105821. CrossRef - Primary Cutaneous NUT Adnexal Carcinoma With BRD4::NUTM1 Fusion: A 19-Year Follow-Up
Elsayed Ibrahim, Richard K. Yang, Maria A. Gubbiotti, Victor G. Prieto, Woo Cheal Cho
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2025; 47(9): 731. CrossRef - Primary mucinous carcinoma of the skin with co-expression of TRPS1 and GATA3: a case report
Liling Song, Ning Zhu, Lei Jiang, Dong Gao, Guohua Yu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Algorithm for Secondary Extramammary Paget Disease from Institutional Cases and Literature Review
Salin Kiratikanon, Ayaka Fukui, Masahiro Hirata, Jakob M. T. Moran, Masakazu Fujimoto, Mai P. Hoang
Cancers.2025; 17(24): 4014. CrossRef - TRPS1 Expression Is Frequently Seen in a Subset of Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms and Tumors of Uncertain Differentiation: A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall
Moon Joo Kim, Yi A. Liu, Yunyi Wang, Jing Ning, Woo Cheal Cho
Dermatopathology.2024; 11(3): 200. CrossRef - TRPS1 expression in MPNST is correlated with PRC2 inactivation and loss of H3K27me3
Rossana Lazcano, Davis R. Ingram, Gauri Panse, Alexander J. Lazar, Wei-Lien Wang, Jeffrey M. Cloutier
Human Pathology.2024; 151: 105632. CrossRef - Syringocystadenoma Papilliferum-Like Features in Poroma: An Unusual Morphologic Pattern of Poroma or True Synchronous Occurrence of 2 Distinct Neoplasms?
Mouaz Alsawas, Fiorinda F. Muhaj, Phyu P. Aung, Priyadharsini Nagarajan, Woo Cheal Cho
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2024; 46(12): 871. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review of TRPS1 as a Diagnostic Immunohistochemical Marker for Primary Breast Carcinoma: Latest Insights and Diagnostic Pitfalls
Antonia-Carmen Georgescu, Tiberiu-Augustin Georgescu, Simona-Alina Duca-Barbu, Lucian Gheorghe Pop, Daniela Oana Toader, Nicolae Suciu, Dragos Cretoiu
Cancers.2024; 16(21): 3568. CrossRef - Expression of TRPS1 in Metastatic Tumors of the Skin: An Immunohistochemical Study of 72 Cases
Kassiani Boulogeorgou, Christos Topalidis, Triantafyllia Koletsa, Georgia Karayannopoulou, Jean Kanitakis
Dermatopathology.2024; 11(4): 293. CrossRef
- Metastatic Vulvar Paget's Disease Presenting in a Supraclavicular Lymph Node: A Diagnostic Challenge on Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
Reviews
- Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):265-282. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.11
- 15,711 View
- 623 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the most common thyroid malignancy, characterized by a range of subtypes that differ in their cytologic features, clinical behavior, and prognosis. Accurate cytologic evaluation of PTC using fine-needle aspiration is essential but can be challenging due to the morphologic diversity among subtypes. This review focuses on the distinct cytologic characteristics of various PTC subtypes, including the classic type, follicular variant, tall cell, columnar cell, hobnail, diffuse sclerosing, Warthin-like, solid/trabecular, and oncocytic PTCs. Each subtype demonstrates unique nuclear features, architectural patterns, and background elements essential for diagnosis and differentiation from other thyroid lesions. Recognizing these distinct cytologic patterns is essential for identifying aggressive subtypes like tall cell, hobnail, and columnar cell PTCs, which have a higher risk of recurrence, metastasis, and poorer clinical outcomes. Additionally, rare subtypes such as diffuse sclerosing and Warthin-like PTCs present unique cytologic profiles that must be carefully interpreted to avoid diagnostic errors. The review also highlights the cytologic indicators of lymph node metastasis and high-grade features, such as differentiated high-grade thyroid carcinoma. The integration of molecular testing can further refine subtype diagnosis by identifying specific genetic mutations. A thorough understanding of these subtype-specific cytologic features and molecular profiles is vital for accurate diagnosis, risk stratification, and personalized management of PTC patients. Future improvements in diagnostic techniques and standardization are needed to enhance cytologic evaluation and clinical decision-making in thyroid cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
Adeel M. Ashraf, Faisal Hassan, Adrian A. Dawkins, Julie C. Dueber, Derek B. Allison, Thèrése J. Bocklage
Cytopathology.2026; 37(1): 108. CrossRef - Using a new type of visible light-based emission fluorescence microscope to identify the benign and malignant nature of thyroid tissue during the surgical process: Analysis of diagnostic results
Yu Miao, Liu Xiaowei, Li Muyang, Gao Jian, Chen Lu
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2026; 57: 105324. CrossRef - Clinical Behavior of Aggressive Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Retrospective Case–Control Study
Jovan Ilic, Nikola Slijepcevic, Katarina Tausanovic, Bozidar Odalovic, Goran Zoric, Marija Milinkovic, Branislav Rovcanin, Milan Jovanovic, Matija Buzejic, Duska Vucen, Boban Stepanovic, Sara Ivanis, Milan Parezanovic, Milan Marinkovic, Vladan Zivaljevic
Cancers.2026; 18(2): 345. CrossRef - Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Dina Khoirunnisa, Salinah, Maria Francisca Ham
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 75: 152434. CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shin Je Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyo
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - Structure-based molecular screening and dynamic simulation of phytocompounds targeting VEGFR-2: a novel therapeutic approach for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Shuai Wang, Lingqian Zhang, Wenjun Zhang, Xiong Zeng, Jie Mei, Weidong Xiao, Lijie Yang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shinje Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(3): 307. CrossRef - A Case of Warthin-Like Variant of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Amy Chow, Israa Laklouk
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Propensity score-matched analysis of the ‘2+2’ parathyroid strategy in total thyroidectomy with central neck dissection
Hao Gong, Simei Yao, Tianyuchen Jiang, Yi Yang, Yuhan Jiang, Zhujuan Wu, Anping Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytological Findings in Pediatric Thoracic Tumors: A Review of Diagnostic Insights and Pitfalls
Parikshaa Gupta, Pranab Dey
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef
- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
- Interpretation of PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer: summary of a consensus meeting of Korean gastrointestinal pathologists
- Soomin Ahn, Yoonjin Kwak, Gui Young Kwon, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Moonsik Kim, Hyunki Kim, Young Soo Park, Hyeon Jeong Oh, Kyoungyul Lee, Sung Hak Lee, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):103-116. Published online April 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.15
- 22,540 View
- 700 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Nivolumab plus chemotherapy in the first-line setting has demonstrated clinical efficacy in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, and is currently indicated as a standard treatment. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression is an important biomarker for predicting response to anti–programmed death 1/PD-L1 agents in several solid tumors, including gastric cancer. In the CheckMate-649 trial, significant clinical improvements were observed in patients with PD-L1 combined positive score (CPS) ≥ 5, determined using the 28-8 pharmDx assay. Accordingly, an accurate interpretation of PD-L1 CPS, especially at a cutoff of 5, is important. The CPS method evaluates both immune and tumor cells and provides a comprehensive assessment of PD-L1 expression in the tumor microenvironment of gastric cancer. However, CPS evaluation has several limitations, one of which is poor interobserver concordance among pathologists. Despite these limitations, clinical indications relying on PD-L1 CPS are increasing. In response, Korean gastrointestinal pathologists held a consensus meeting for the interpretation of PD-L1 CPS in gastric cancer. Eleven pathologists reviewed 20 PD-L1 slides with a CPS cutoff close to 5, stained with the 28-8 pharmDx assay, and determined the consensus scores. The issues observed in discrepant cases were discussed. In this review, we present cases of gastric cancer with consensus PD-L1 CPS. In addition, we briefly touch upon current practices and clinical issues associated with assays used for the assessment of PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Organ Preservation for Gastroesophageal Junction and Gastric Cancers: Ready for Primetime?
Winta Mehtsun, Lola Van Doosselaere, Ugwuji N. Maduekwe
American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning Analysis Based on Dual-energy CT-Derived Iodine Map for Predicting PD-L1 Expression in Gastric Cancer: A Multicenter Study
Lihong Chen, Yuncong Zhao, Xiaomin Tian, Deye Zeng, Yongxiu Tong, Haiping Xu, Yaru You, Caiming Weng, Sen Lin, Keru Chen, Yilin Chen, Yunjing Xue
Academic Radiology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Adjuvant immunotherapy in patients with resected gastric and oesophagogastric junction cancer following preoperative chemotherapy with high risk for recurrence (ypN+ and/or R1): European Organisation of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) 1707 VESTIG
F. Lordick, M.E. Mauer, G. Stocker, C.A. Cella, I. Ben-Aharon, G. Piessen, L. Wyrwicz, G. Al-Haidari, T. Fleitas-Kanonnikoff, V. Boige, R. Lordick Obermannová, U.M. Martens, C. Gomez-Martin, P. Thuss-Patience, V. Arrazubi, A. Avallone, K.K. Shiu, P. Artru
Annals of Oncology.2025; 36(2): 197. CrossRef - PD-L1 as a Biomarker in Gastric Cancer Immunotherapy
Yunjoo Cho, Soomin Ahn, Kyoung-Mee Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 177. CrossRef - PD-L1 importance in malignancies comprehensive insights into the role of PD-L1 in malignancies: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities
Mojdeh Soltani, Mohammad Abbaszadeh, Hamed Fouladseresht, Mark J. M. Sullman, Nahid Eskandari
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - CLDN18.2 expression in gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: prevalence, heterogeneity, and prognostic implications in Spanish patients
Carolina Martinez-Ciarpaglini, María Ortega, Sandra Pérez-Buira, Aitana Bolea, Beatriz Casado Guerra, Carmen Herencia Bellido, Paula Tornero Piñero, Dolores Naranjo-Hans, Brenda Palomar, Hernán Quiceno, Amanda Sardón Fernández, Ariadna Torner Calvo, Feder
Virchows Archiv.2025; 487(6): 1337. CrossRef - Distinct clinicopathological and survival profiles of CLDN18.2 and PD-L1 expression in advanced gastric cancer and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma
D.R. Castillo, M. Guo, P. Shah, M. Hazeltin, D. Tai, F. Al-Manaseer, S. Mlamba, D. Perez, S. Yeremian, S. Guzman, R. Mannan, C. Crook, C. Lau, N. Tawar, G. Brar, M. Raoof, Y. Woo, S.P. Wu, D. Li
ESMO Gastrointestinal Oncology.2025; 10: 100261. CrossRef - Best Practice PD-L1 Staining and Interpretation in Gastric Cancer Using PD-L1 IHC PharmDx 22C3 and PD-L1 IHC PharmDx 28-8 Assays, with Reference to Common Issues and Solutions
Soomin Ahn, Inwoo Hwang, Yuyeon Kim, Somin Lee, Yunjoo Cho, So Young Kang, Deok Geun Kim, Jeeyun Lee, Kyoung-Mee Kim
Biomedicines.2025; 13(11): 2824. CrossRef - Intraperitoneal immune microenvironment and efficacy of intraperitoneal chemotherapy in patients with gastric cancer and peritoneal metastasis
Tomoya Nakanishi, Motohiro Imano, Masashi Kohda, Hiroaki Kato, Naoko Kounami, Atsushi Yamada, Masuhiro Terada, Yoko Hiraki, Osamu Shiraishi, Atsushi Yasuda, Masayuki Shinkai, Takushi Yasuda
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - PD-L1 thresholds predict efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibition in first-line treatment of advanced gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. A systematic review and meta-analysis of seven phase III randomized trials
V. Formica, C. Morelli, L. Fornaro, S. Riondino, M. Rofei, E. Fontana, E.C. Smyth, M. Roselli, H.-T. Arkenau
ESMO Open.2024; 9(11): 103967. CrossRef
- Organ Preservation for Gastroesophageal Junction and Gastric Cancers: Ready for Primetime?
Newsletter
- What’s new in thyroid pathology 2024: updates from the new WHO classification and Bethesda system
- Andrey Bychkov, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):98-101. Published online March 13, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.06
- 27,292 View
- 2,057 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In line with the release of the 5th edition WHO Classification of Tumors of Endocrine Organs (2022) and the 3rd edition of the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (2023), the field of thyroid pathology and cytopathology has witnessed key transformations. This digest brings to the fore the refined terminologies, newly introduced categories, and contentious methodological considerations pivotal to the updated classification.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnosis and management of thyroid nodule
Suganya Sekar, Deepak Thomas Abraham
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2025; 32(5): 167. CrossRef - Impact of thyroid Bethesda category IV (follicular neoplasm) terminology unification on atypia of undetermined significance reporting patterns in thyroid fine-needle aspiration
Shirin Abbasi, Lorena Marcano-Bonilla, Syed Z. Ali
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Challenges, Prognostic Assessment, and Treatment Strategies in High-Grade Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
Chan Kwon Jung, Agnes Stephanie Harahap
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(6): 830. CrossRef - Cytologic and Clinicopathologic Features of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Prominent Hobnail Features on FNAC
Deepali Saxena, Ravi Hari Phulware, Prashant Durgapal, Arvind Kumar, Amit Kumar Tyagi
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2024; 76(5): 4885. CrossRef - FHL1: A novel diagnostic marker for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Yeting Zeng, Dehua Zeng, Xingfeng Qi, Hanxi Wang, Xuzhou Wang, Xiaodong Dai, Lijuan Qu
Pathology International.2024; 74(9): 520. CrossRef - Nouveautés en pathologie thyroïdienne : classification OMS 2022, système Bethesda 2023, biologie moléculaire et testing moléculaire
Mohamed Amine Bani, Sophie Moog, Voichita Suciu, Livia Lamartina, Abir Al Ghuzlan
Bulletin du Cancer.2024; 111(10): 10S5. CrossRef - Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(6): 265. CrossRef - Surgical and Pathological Challenges in Thyroidectomy after Thermal Ablation of Thyroid Nodules
Ting-Chun Kuo, Kuen-Yuan Chen, Hsiang-Wei Hu, Jie-Yang Jhuang, Ming-Tsan Lin, Chin-Hao Chang, Ming-Hsun Wu
Thyroid®.2024; 34(12): 1503. CrossRef
- Diagnosis and management of thyroid nodule
Original Article
- TERT mutations and aggressive histopathologic characteristics of radioiodine-refractory papillary thyroid cancer
- Ju Yeon Pyo, Yoon Jin Cha, SoonWon Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):310-320. Published online September 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.29
- 5,088 View
- 344 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Radioiodine (RI) ablation following thyroid-stimulating hormone suppression is an effective treatment for papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), typically leading to favorable outcomes. However, RI-refractory tumors exhibit aggressive behavior and poor prognoses. Recent studies highlight the role of genetic abnormalities in PTC signaling pathways, including the activation of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), and the correlation of mutations with adverse outcomes.
Methods
This study analyzed mutations in BRAF V600E and the TERT-promoter genes, comparing clinicopathological features between RI-refractory and RI-responsive PTCs. Among 82 RI-refractory patients, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues from initial surgeries were available for 26. Another 89 without distant metastasis over 5 years formed a matched RI-responsive control group.
Results
Histopathologically, RI-refractory PTCs showed increased frequencies of small tumor clusters without fibrovascular cores, hobnail features, and a high height-to-width ratio of tumor cells. These tumors were more likely to exhibit necrosis, mitosis, lymph node metastasis, extrathyroidal extension, and involvement of resection margins. TERT-promoter mutations were statistically significantly associated with these aggressive clinicopathologic features. Immunohistochemically, decreased expression of sodium iodide symporter and thyroglobulin stimulating hormone receptor proteins was common in RI-refractory PTCs, along with lower levels of oncogenic proteins such as vascular endothelial cell growth factor, vascular endothelial cell growth factor receptor 2, and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells. Total loss of PTEN expression was occasionally observed. In contrast, all cases tested positive for cytoplasmic β-catenin.
Conclusions
RI-refractory PTCs are linked to TERT mutations and exhibit specific aggressive histopathologic features, particularly in tumor centers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterizing thyroid carcinomas in the elderly: Histological subtypes and TERT promoter mutation analysis based on the latest WHO classification
Myoung Ju Koh, Songmi Noh, Jin Kyong Kim, Gi Jeong Kim
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2026; 80: 152578. CrossRef - Insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction in thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer
Stefano Iuliano, Maria Mirabelli, Stefania Giuliano, Antonio Brunetti
Current Opinion in Oncology.2026; 38(1): 1. CrossRef - Differentiated high-grade thyroid carcinoma (DHGTC): clinicopathological analysis of a new entity in a chilean center
Marlín Solórzano, Ignacio Fuentes, José Miguel González, Nicole Lustig, Lorena Mosso, Joel Falcón, Catalina Ruiz, Joaquín Viñambres, Rodolfo Cabello, Hernán González, Pablo H Montero, Francisco Cruz, Rodrigo Jaimovich, Juan Carlos Quintana, Antonieta Sola
Endocrine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics and outcome of pediatric and adult differentiated thyroid cancer with distant metastases
Ali S. Alzahrani, Lulu Alobaid, Eman Albasri, Afnan Hadadi, Abdulrhman Hakami, Fayha Abothenain, Deema Alturki, Najla Ewain, Ali Howaidi, Hindi Alhindi, Ghada Alskait, Yasser Aljufan, Shatha Alghaihb, Azzam Alkhalifah, Leenah AlAyoubi, Amani Abualnaja
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The ability of anexelekto (AXL) expression and TERT promoter mutation to predict radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Hasrayati Agustina, Tutik Nur Ayni, Yohana Azhar, Erwin Affandi Soeriadi, Bethy Suryawathy Hernowo
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathologic characteristics of papillary thyroid carcinoma, tall cell subtype and subtype with tall cell features, an institutional experience
Xueting Jin, Shunsuke Koga, Xiao Zhou, Niaz Z. Khan, Zubair W. Baloch
Human Pathology.2025; 161: 105867. CrossRef - Calcifying nested stromal-epithelial tumor of the liver: Report of two cases revealing novel WT1 mutation and distinct epigenetic features
Andrea Strakova-Peterikova, Franco Fedeli, Boris Rychly, Jiri Soukup, Michael Michal, Petr Martinek, Marian Grendar, Elaheh Mosaieby, Nikola Ptakova, Maryna Slisarenko, Michal Michal, Kvetoslava Michalova
Virchows Archiv.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Characterizing thyroid carcinomas in the elderly: Histological subtypes and TERT promoter mutation analysis based on the latest WHO classification
Case Study
- Uncommon granulomatous manifestation in Epstein-Barr virus–positive follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: a case report
- Henry Goh Di Shen, Yue Zhang, Wei Qiang Leow
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):133-138. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.27
- 4,134 View
- 351 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatic Epstein-Barr virus–positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma (EBV+ IFDCS) represents a rare form of liver malignancy. The absence of distinct clinical and radiological characteristics, compounded by its rare occurrence, contributes to a challenging diagnosis. Here, we report a case of a 54-year-old Chinese female with a background of chronic hepatitis B virus treated with entecavir and complicated by advanced fibrosis presenting with a liver mass found on her annual surveillance ultrasound. Hepatectomy was performed under clinical suspicion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Immunomorphologic characteristics of the tumor were consistent with EBV+ IFDCS with distinct non-caseating granulomatous inflammation. Our case illustrates the importance of considering EBV+ IFDCS in the differential diagnosis of hepatic inflammatory lesions. Awareness of this entity and its characteristic features is essential for accurately diagnosing and managing this rare neoplasm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mesenchymal Tumors of the Liver: An Update Review
Joon Hyuk Choi, Swan N. Thung
Biomedicines.2025; 13(2): 479. CrossRef - EBV-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma occurring in different organs: a case report and literature review
Wenhua Bai, Chunfang Hu, Zheng Zhu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Spleen EBV-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: a case report and literature review
Yi Xiao, Lanlan Li, Xiumei Zhan, Juner Xu, Yewu Chen, Qiuchan Zhao, Yinghao Fu, Xian Luo, Huadi Chen, Hao Xu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Epstein-Barr virus-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma of the liver: clinical features, imaging findings and potential diagnostic clues
Gui-Ling Huang, Man-Qian Huang, Yu-Ting Zhang, Hui-Ning Huang, Hong-Tao Liu, Xiao-Qing Pei
Abdominal Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Epstein‑Barr virus+ inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma with clonal immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangement: A case report and literature review
Qian Ye, Juan Zhao, Jiao He, Weishan Zhang
Oncology Letters.2025; 31(2): 1. CrossRef - Primary hepatic follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A case study and literature review
Junjie Zhu, Ying Liang, Li Zhang, Bingqi Li, Danfeng Zheng, Hangyan Wang
Journal of International Medical Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Mesenchymal Tumors of the Liver: An Update Review
Newsletter
- What’s new in neuropathology 2024: CNS WHO 5th edition updates
- Heather Smith, Jared T. Ahrendsen
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):346-349. Published online September 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.11
- 22,983 View
- 1,184 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The fifth edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Central Nervous System (CNS) Tumors was released in 2021, just five years following the updated fourth edition. Advanced molecular testing such as next-generation sequencing, RNA fusion analysis, and DNA methylation profiling has led to more precise grading and classification of pre-existing tumor types as well as the recognition of new ones. Herein, we outline the major updates of the 2021 WHO Classification of CNS tumors, with emphasis on the expanded molecular characterization of CNS tumors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bioinformatics insights into ACSL1 and ACSL5: prognostic and immune roles in low-grade glioma
Cheng Zhang, Zhonghua Lv, Hongsheng Liang, Fulan Hu, Haoran Bi
BMC Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Understanding of the Exosomes and Their Associated Biomolecules in the Glioblastoma Biology, Clinical Treatment, and Diagnosis
Aghdas Ramezani, Maryam Rahnama, Fatemeh Mahmoudian, Fatemeh Shirazi, Mahmoud Ganji, Shohreh Bakhshi, Bahman Khalesi, Zahra Sadat Hashemi, Saeed Khalili
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Utility of Intratumoral Susceptibility Signals in Adult Diffuse Gliomas: Tumor Grade Prediction and Correlation with Molecular Markers Within the WHO CNS5 (2021) Classification
José Ignacio Tudela Martínez, Victoria Vázquez Sáez, Guillermo Carbonell, Héctor Rodrigo Lara, Florentina Guzmán-Aroca, Juan de Dios Berna Mestre
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(11): 4004. CrossRef - Glioblastoma in Puerto Rico: A 21-year population-based study
Carlos E Calderon-Valero, Esteban Rivera, Odaly Balasquide, Alejandro E Cedeño-Moran, Aixa De Jesus, Miguel Mayol Del Valle
Neuro-Oncology Advances.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Brain Tumors, AI and Psychiatry: Predicting Tumor-Associated Psychiatric Syndromes with Machine Learning and Biomarkers
Matei Șerban, Corneliu Toader, Răzvan-Adrian Covache-Busuioc
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(17): 8114. CrossRef - Engineered bacteria/bacterial components strategy for glioma
Yan Zhu, Meilin Shen, Qi Chen, Huanghao Yang
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 525: 170539. CrossRef
- Bioinformatics insights into ACSL1 and ACSL5: prognostic and immune roles in low-grade glioma
Original Articles
- The spectrum of microvascular patterns in adult diffuse glioma and their correlation with tumor grade
- Soni , Vaishali Walke, Deepti Joshi, Tanya Sharma, Adesh Shrivastava, Amit Agrawal
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):127-133. Published online May 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.11
- 7,419 View
- 359 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Primary brain tumors constitute the leading cause of cancer-related mortality. Among them, adult diffuse gliomas are the most common type, affecting the cerebral hemispheres and displaying a diffuse infiltrative pattern of growth in the surrounding neuropil that accounts for about 80% of all primary intracranial tumors. The hallmark feature of gliomas is blood vessel proliferation, which plays an important role in tumor growth, tumor biological behavior, and disease outcome. High-grade gliomas exhibit increased vascularity, the worst prognosis, and lower survival rates. Several angiogenic receptors and factors are upregulated in glioblastomas and stimulate angiogenesis signaling pathways by means of activating oncogenes and/or down-regulating tumor-suppressor genes. Existing literature has emphasized that different microvascular patterns (MVPs) are displayed in different subtypes of adult diffuse gliomas.
Methods
We examined the distribution and biological characteristics of different MVPs in 50 patients with adult diffuse gliomas. Haematoxylin and eosin staining results, along with periodic acid–Schiff and CD34 dual-stained sections, were examined to assess the vascular patterns and correlate with different grades of diffuse glioma.
Results
The present observational study on adult diffuse glioma evaluated tumor grade and MVPs. Microvascular sprouting was the most common pattern, while a bizarre pattern (type 2) was associated with the presence of a high-grade glioma. Vascular mimicry was observed in 6% of cases, all of which were grade 4 gliomas.
Conclusions
This study supplements the role of neo-angiogenesis and aberrant vasculature patterns in the grading and progression of adult diffuse gliomas, which can be future targets for planning treatment strategies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unlocking therapeutic potential: Exploring nuclear receptors in brain cancer treatment
Sujitha Jayaprakash, Hiu Yan Lam, Ravichandran Vishwa, Bandari BharathwajChetty, Kenneth C-H Yap, Mohammed S. Alqahtani, Mohamed Abbas, Gautam Sethi, Alan Prem Kumar, Ajaikumar B. Kunnumakkara
Chinese Medical Journal.2025; 138(21): 2722. CrossRef - Uptake patterns of Adult-type Non-Enhanced diffuse gliomas on [11C] methionine positron emission tomography
Shoji Yasuda, Naoya Imai, Hirohito Yano, Yuka Ikegame, Soko Ikuta, Takashi Maruyama, Noriyuki Nakayama, Morio Kumagai, Yoshihiro Muragaki, Jun Shinoda, Tsuyoshi Izumo
Neuroradiology.2025; 67(10): 2611. CrossRef - Loss of Fibronectin Fiber Tension in Glioblastoma is Associated with Microvascular Proliferations and Immune Cell Infiltration
Michele Crestani, Isabel Gerber, Arnaud Mieville, Katrin Frauenknecht, Theoni Maragkou, Tibor Hortobagyi, Viola Vogel
Advanced Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - High ORC6 expression is a prognostic indicator of poor survival in glioma patients
Mengjie Wang, Song Feng, Chen Zhang, Feng Jin
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Consequences of Hypoxic Events, Necrosis, and Microvascular Density, in Astrocytoma IDH-Mutant, CNS WHO Grade 4
Cristian Ionut Orasanu, Madalina Bosoteanu, Sorin Vamesu, Raluca Ioana Voda, Anamaria Sincu, Mariana Deacu
Medical Sciences.2025; 14(1): 6. CrossRef - Association of PD-L1 expression with adverse pathological features in adult diffuse astrocytoma
Rania K. Elsaid, Maha M. Abuhashim, Sylvia A. Ashamallah, Khaled M. Abouelkhair, Marwa M. Zaki
Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.2025; 12(1): 526. CrossRef
- Unlocking therapeutic potential: Exploring nuclear receptors in brain cancer treatment
- Identification of invasive subpopulations using spatial transcriptome analysis in thyroid follicular tumors
- Ayana Suzuki, Satoshi Nojima, Shinichiro Tahara, Daisuke Motooka, Masaharu Kohara, Daisuke Okuzaki, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Eiichi Morii
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):22-28. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.21
- 4,999 View
- 273 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Follicular tumors include follicular thyroid adenomas and carcinomas; however, it is difficult to distinguish between the two when the cytology or biopsy material is obtained from a portion of the tumor. The presence or absence of invasion in the resected material is used to differentiate between adenomas and carcinomas, which often results in the unnecessary removal of the adenomas. If nodules that may be follicular thyroid carcinomas are identified preoperatively, active surveillance of other nodules as adenomas is possible, which reduces the risk of surgical complications and the expenses incurred during medical treatment. Therefore, we aimed to identify biomarkers in the invasive subpopulation of follicular tumor cells.
Methods
We performed a spatial transcriptome analysis of a case of follicular thyroid carcinoma and examined the dynamics of CD74 expression in 36 cases.
Results
We identified a subpopulation in a region close to the invasive area, and this subpopulation expressed high levels of CD74. Immunohistochemically, CD74 was highly expressed in the invasive and peripheral areas of the tumor.
Conclusions
Although high CD74 expression has been reported in papillary and anaplastic thyroid carcinomas, it has not been analyzed in follicular thyroid carcinomas. Furthermore, the heterogeneity of CD74 expression in thyroid tumors has not yet been reported. The CD74-positive subpopulation identified in this study may be useful in predicting invasion of follicular thyroid carcinomas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carbonic Anhydrase 12 as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for High‐Risk Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma
Masashi Tanida, Tsuyoshi Takashima, Shinichiro Tahara, Masaharu Kohara, Haruka Kanai, Masami Suzuki, Motoyuki Suzuki, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Ayana Suzuki, Shinya Sato, Daisuke Okuzaki, Satoshi Nojima, Takahiro Matsui, Hidenori Inohara, Eiichi Morii
Cancer Science.2026; 117(1): 257. CrossRef - An emerging role of CD74 in thyroid follicular cells in Hashimoto´s thyroiditis
Pablo Sacristán-Gómez, Ana Serrano-Somavilla, Nuria Sánchez de la Blanca, Andrea Álvarez-Rodríguez, Eduardo Martínez-Parra, Miguel Sampedro-Nuñez, Fernando Sebastián-Valles, Mónica Marazuela, Rebeca Martínez-Hernández
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2026; 194: 118945. CrossRef - Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Shanop Shuangshoti, Nakarin Kitkumthorn, Somboon Keelawat
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(1): 39. CrossRef - Spatial Transcriptomics in Thyroid Cancer: Applications, Limitations, and Future Perspectives
Chaerim Song, Hye-Ji Park, Man S. Kim
Cells.2025; 14(12): 936. CrossRef - A New Tool to Decrease Interobserver Variability in Biomarker Annotation in Solid Tumor Tissue for Spatial Transcriptomic Analysis
Sravya Palavalasa, Emily Baker, Jack Freeman, Aditri Gokul, Weihua Zhou, Dafydd Thomas, Wajd N. Al-Holou, Meredith A. Morgan, Theodore S. Lawrence, Daniel R. Wahl
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2025; 47(7): 531. CrossRef
- Carbonic Anhydrase 12 as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for High‐Risk Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma
Review
- Development of CytoAcademy: a new web- and mobile-based E-learning platform for cytopathologists and cytotechnologists by the Korean Society for Cytopathology in the post-pandemic era
- Ran Hong, Yosep Chong, Seung Wan Chae, Seung-Sook Lee, Gyungyub Gong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):261-264. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.02
- 4,864 View
- 286 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Since the late 1990s, online e-learning has offered unparalleled convenience and affordability, becoming increasingly popular among pathologists. Traditional learning theories have been successfully applied to web/mobile-based learning systems, with mobile technologies even enhancing conventional offline education. In cytopathology, hands-on microscope training has traditionally been paramount, complemented by real-case presentations and lectures. However, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic disrupted regular academic activities, making online e-learning platforms essential. We designed a web/mobile-based learning platform to enhance continued medical education in cytopathology at various levels, particularly during the era of COVID-19 and beyond. Since 2021, we have integrated curriculum materials, virtual education files, and whole-slide images (WSIs) of cytopathology, submitted from over 200 institutions across Korea, with the support of numerous instructors. We develop a new e-learning platform named “CytoAcademy” composed of a basic session for each organ and level across the range of morphologic findings; on-demand lectures to enhance cytopathologic knowledge; WSI archives that allow users to explore various histologically confirmed cases; and a self-assessment test to help organize diagnostic knowledge acquired through the web/mobile-friendly learning system. The platform provides not just an opportunity to achieve a correct diagnosis, but also a learning experience based on problem-solving point. Members interact, identify their deficiencies, and focus on specific educational materials. In this manner, all participants can actively engage in creating and maintaining knowledge and foster a proactive approach to learning.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(2): 146. CrossRef - Developing a smart and scalable tool for histopathological education—PATe 2.0
Lina Winter, Annalena Artinger, Hendrik Böck, Vignesh Ramakrishnan, Bruno Reible, Jan Albin, Peter J. Schüffler, Georgios Raptis, Christoph Brochhausen
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2026; 20: 100535. CrossRef - National quality assurance program using digital cytopathology: a 5-year digital transformation experience by the Korean Society for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Soon Auck Hong, Sung Soon Kim, Bo-Sung Kim, Younghee Choi, Yoon Jung Choi, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Soo Jin Jung, Hoon Kyu Oh, Seung-Sook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(5): 320. CrossRef - Integration of Digital Cytology in Quality Assurance Programs for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Maria Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Zaibo Li, Andrey Bychkov
Acta Cytologica.2025; 70(1): 126. CrossRef
- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Original Articles
- Clinicopathological implications of immunohistochemical expression of TBX21, CXCR3, GATA3, CCR4, and TCF1 in nodal follicular helper T-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified
- Bogyeong Han, Sojung Lim, Jeemin Yim, Young Keun Song, Jiwon Koh, Sehui Kim, Cheol Lee, Young A Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):59-71. Published online January 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.01.04
- 8,147 View
- 377 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The classification of nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) has evolved according to histology, cell-of-origin, and genetic alterations. However, the comprehensive expression pattern of follicular helper T-cell (Tfh) markers, T-cell factor-1 (TCF1), and Th1- and Th2-like molecules in nodal PTCL is unclear.
Methods
Eighty-two cases of nodal PTCL were classified into 53 angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphomas (AITLs)/nodal T-follicular helper cell lymphoma (nTFHL)-AI, 18 PTCLs-Tfh/nTFHL–not otherwise specified (NOS), and 11 PTCLs-NOS according to the revised 4th/5th World Health Organization classifications. Immunohistochemistry for TCF1, TBX21, CXCR3, GATA3, and CCR4 was performed.
Results
TCF1 was highly expressed in up to 68% of patients with nTFHL but also in 44% of patients with PTCL-NOS (p > .05). CXCR3 expression was higher in AITLs than in non-AITLs (p = .035), whereas GATA3 expression was higher in non-AITL than in AITL (p = .007) and in PTCL-Tfh compared to AITL (p = .010). Of the cases, 70% of AITL, 44% of PTCLTfh/ nTFHL-NOS, and 36% of PTCL-NOS were subclassified as the TBX21 subtype; and 15% of AITL, 38% of PTCL-Tfh/nTFHL-NOS, and 36% of PTCL-NOS were subclassified as the GATA3 subtype. The others were an unclassified subtype. CCR4 expression was associated with poor progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with PTCL-Tfh (p < .001) and nTFHL (p = .023). The GATA3 subtype showed poor overall survival in PTCL-NOS compared to TBX21 (p = .046) and tended to be associated with poor PFS in patients with non-AITL (p = .054).
Conclusions
The TBX21 subtype was more prevalent than the GATA3 subtype in AITL. The GATA3 subtype was associated with poor prognosis in patients with non-AITL and PTCL-NOS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- T-bet: biological functions, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic applications: a systematic review
Xiaowen Yang, Min Sun, Xinyi Tang, Xiaoyuan Zhang, Wenzhi Shen
Frontiers in Immunology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - CXCR Family and Hematologic Malignancies in the Bone Marrow Microenvironment
Yanquan Liu, Huanwen Tang
Biomolecules.2025; 15(5): 716. CrossRef - Diagnostic and therapeutic pathways for lymphoma patients: expert consensus through Nominal Group Technique and Delphi methodology
Attilio Guarini, Valentina Bozzoli, Sabino Ciavarella, Michele Cimminiello, Francesca Donatelli, Angelo Fama, Vincenza Fernanda Fesce, Vincenzo Fraticelli, Francesco Gaudio, Giuseppina Greco, Augusto Martellini, Francesca Merchionne, Rosanna Maria Miccoli
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Significance of TBX21 and GATA3 Subtype Classification in Indolent Adult T‐Cell Leukemia‐Lymphoma With Cutaneous Lesions
Kazuhiro Kawai, Youhei Uchida, Takuro Kanekura
The Journal of Dermatology.2025; 52(11): 1674. CrossRef
- T-bet: biological functions, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic applications: a systematic review
- Tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes evaluated using digital image analysis predict the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Yunjoo Cho, Jiyeon Lee, Bogyeong Han, Sang Eun Yoon, Seok Jin Kim, Won Seog Kim, Junhun Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):12-21. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.02
- 5,422 View
- 271 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The implication of the presence of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes (TIL-T) in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is yet to be elucidated. We aimed to investigate the effect of TIL-T levels on the prognosis of patients with DLBCL.
Methods
Ninety-six patients with DLBCL were enrolled in the study. The TIL-T ratio was measured using QuPath, a digital pathology software package. The TIL-T ratio was investigated in three foci (highest, intermediate, and lowest) for each case, resulting in TIL-T–Max, TIL-T–Intermediate, and TIL-T–Min. The relationship between the TIL-T ratios and prognosis was investigated.
Results
When 19% was used as the cutoff value for TIL-T–Max, 72 (75.0%) and 24 (25.0%) patients had high and low TIL-T–Max, respectively. A high TIL-T–Max was significantly associated with lower serum lactate dehydrogenase levels (p < .001), with patient group who achieved complete remission after RCHOP therapy (p < .001), and a low-risk revised International Prognostic Index score (p < .001). Univariate analysis showed that patients with a low TIL-T–Max had a significantly worse prognosis in overall survival compared to those with a high TIL-T–Max (p < .001); this difference remained significant in a multivariate analysis with Cox proportional hazards (hazard ratio, 7.55; 95% confidence interval, 2.54 to 22.42; p < .001).
Conclusions
Patients with DLBCL with a high TIL-T–Max showed significantly better prognosis than those with a low TIL-T–Max, and the TIL-T–Max was an independent indicator of overall survival. These results suggest that evaluating TIL-T ratios using a digital pathology system is useful in predicting the prognosis of patients with DLBCL. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Do Pre‐Treatment Biopsy Characteristics Predict Early Tumour Progression in Feline Diffuse Large B Cell Nasal Lymphoma Treated With Radiotherapy?
Valerie J. Poirier, Valeria Meier, Michelle Turek, Neil Christensen, Jacqueline Bowal, Matthew D. Ponzini, Stefan M. Keller
Veterinary and Comparative Oncology.2025; 23(1): 82. CrossRef - Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor Microenvironment and PD-L1 Expression Associations with Clinicopathological Features and Prognosis in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Yun-Li Xie, Long-Feng Ke, Wen-Wen Zhang, Fu Kang, Shu-Yi Lu, Chen-Yu Wu, Huan-Huan Zhu, Jian-Chao Wang, Gang Chen, Yan-Ping Chen
Blood and Lymphatic Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2025; Volume 15: 167. CrossRef - Metabolic-immune axis in the tumor microenvironment: a new strategy for prognostic assessment and precision therapy in DLBCL and FL
Chengqian Chen, Wei Guo, Haotian Wang, Luming Cao, Ou Bai
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrative analysis of a novel immunogenic PANoptosis‑related gene signature in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma for prognostication and therapeutic decision-making
Ming Xu, Ming Ruan, Wenhua Zhu, Jiayue Xu, Ling Lin, Weili Li, Weirong Zhu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Do Pre‐Treatment Biopsy Characteristics Predict Early Tumour Progression in Feline Diffuse Large B Cell Nasal Lymphoma Treated With Radiotherapy?
Review Article
- Multiple sclerosis: a practical review for pathologists
- Rachel A. Multz, Pouya Jamshidi, Jared T. Ahrendsen
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):203-213. Published online June 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.05.20
- 16,862 View
- 496 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an immune-mediated demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system. It is a chronic disorder resulting in neurologic dysfunction that is disseminated both in time (multiple discrete episodes) and space (involving multiple sites). Histologically, MS is characterized by localized loss of myelin with relative preservation of axons. This review will discuss the epidemiology, clinical, laboratory, radiologic, and pathologic features of multiple sclerosis, as well as briefly touch on the differential diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of the disease, especially as they relate to the pathologic interpretation of tissue specimens.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- White Matter in Crisis: Oligodendrocytes and the Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis
Mario García-Domínguez
Cells.2025; 14(18): 1408. CrossRef - Tumefactive demyelinating lesions: a case report and literature review
Raneem Jaki, Zyad Al-Frejat, Ziad Bitar
BMC Neurology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Liquerologia: Uma ferramenta no diagnóstico de esclerose múltipla e outras doenças neurodegenerativas e desmielinizantes
Laura Maria de Araújo Pereira, Talyta Valeria Siqueira do Monte Guedes, Rafaell Batista Pereira, Davi Abrantes Lucena Messias, Marfran José Cunha Urtiga, Davi Rodrigues Vieira, Samuel da Costa Chaves Trindade Martins, José Guedes da Silva Júnior
Research, Society and Development.2025; 14(12): e72141249815. CrossRef
- White Matter in Crisis: Oligodendrocytes and the Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis
Original Articles
- Low Ki-67 labeling index is a clinically useful predictive factor for recurrence-free survival in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Takashi Masui, Katsunari Yane, Ichiro Ota, Kennichi Kakudo, Tomoko Wakasa, Satoru Koike, Hirotaka Kinugawa, Ryuji Yasumatsu, Tadashi Kitahara
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):115-124. Published online February 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.08
- 5,577 View
- 247 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
We report a new risk stratification of invasive stage papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs) by combining invasive status, using extrathyroid invasion (Ex) status, and tumor growth speed using the Ki-67 labeling index (LI). Methods: We examined tumor recurrence in 167 patients with PTC who were surgically treated at the Kindai University Nara Hospital between 2010 and 2022. The patients were classified according to the degree of invasion [negative (Ex0) or positive (Ex1, Ex2, and Ex3)] and tumor growth speed expressed with Ki-67 LI, as low (<5%) or high (>5%). This study confirmed previous findings that the disease-free survival (DFS) rate in PTCs significantly differed between patients with a high and low Ki-67 index. Results: When combining Ex status (negative or positive) and Ki-67 proliferation status (low or high), the DFS rate of invasion in the negative, low Ki-67 LI group was only 1.1%, while that of invasion in the positive, high Ki-67 LI was 44.1%. This study reports for the first time that recurrence risks can be stratified accurately when combining carcinoma’s essential two features of extrathyroid invasion status and tumor growth speed. Conclusions: We believe the evidence for low tumor recurrence risk may contribute to use of more conservative treatment options for invasive-stage PTCs and help alleviate patient anxiety about tumor recurrence and death. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress on the Correlation between Three Biomarkers, Ki-67, CAIX and VEGF and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
锦容 马
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2025; 15(09): 326. CrossRef - Immunophenotypic Panel for Comprehensive Characterization of Aggressive Thyroid Carcinomas
Mihail Ceausu, Mihai Alin Publik, Dana Terzea, Carmen Adina Cristea, Dumitru Ioachim, Dana Manda, Sorina Schipor
Cells.2025; 14(19): 1554. CrossRef - High Ki-67 labeling index correlates with aggressive clinicopathological features in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective study
Defi Nurlia Erdian, Maria Francisca Ham, Dina Khoirunnisa, Agnes Stephanie Harahap
Thyroid Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research Progress on the Correlation between Three Biomarkers, Ki-67, CAIX and VEGF and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PLUNC downregulates the expression of PD-L1 by inhibiting the interaction of DDX17/β-catenin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Ranran Feng, Yilin Guo, Meilin Chen, Ziying Tian, Yijun Liu, Su Jiang, Jieyu Zhou, Qingluan Liu, Xiayu Li, Wei Xiong, Lei Shi, Songqing Fan, Guiyuan Li, Wenling Zhang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):68-83. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.27
- 3,790 View
- 140 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is characterized by high programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression and abundant infiltration of non-malignant lymphocytes, which renders patients potentially suitable candidates for immune checkpoint blockade therapies. Palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone (PLUNC) inhibit the growth of NPC cells and enhance cellular apoptosis and differentiation. Currently, the relationship between PLUNC (as a tumor-suppressor) and PD-L1 in NPC is unclear.
Methods
We collected clinical samples of NPC to verify the relationship between PLUNC and PD-L1. PLUNC plasmid was transfected into NPC cells, and the variation of PD-L1 was verified by western blot and immunofluorescence. In NPC cells, we verified the relationship of PD-L1, activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3), and β-catenin by western blot and immunofluorescence. Later, we further verified that PLUNC regulates PD-L1 through β-catenin. Finally, the effect of PLUNC on β-catenin was verified by co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP).
Results
We found that PLUNC expression was lower in NPC tissues than in paracancer tissues. PD-L1 expression was opposite to that of PLUNC. Western blot and immunofluorescence showed that β-catenin could upregulate ATF3 and PD-L1, while PLUNC could downregulate ATF3/PD-L1 by inhibiting the expression of β-catenin. PLUNC inhibits the entry of β-catenin into the nucleus. Co-IP experiments demonstrated that PLUNC inhibited the interaction of DEAD-box helicase 17 (DDX17) and β-catenin.
Conclusions
PLUNC downregulates the expression of PD-L1 by inhibiting the interaction of DDX17/β-catenin in NPC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Potential Role of SP-G and PLUNC in Tumor Pathogenesis and Wound Healing in the Human Larynx
Aurelius Scheer, Lars Bräuer, Markus Eckstein, Heinrich Iro, Friedrich Paulsen, Fabian Garreis, Martin Schicht, Antoniu-Oreste Gostian
Biomedicines.2025; 13(5): 1240. CrossRef - Role of DEAD/DEAH-box helicases in immunity, infection and cancers
Rex Devasahayam Arokia Balaya, Saptami Kanekar, Shreya Kumar, Richard K. Kandasamy
Cell Communication and Signaling.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - CHIP modulates Wnt/β-catenin signalling in colorectal cancer through proteasomal degradation of DDX17
Sunny Kumar, Sayani Ghosh, Malini Basu, Mrinal K. Ghosh
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2025; 1872(8): 120049. CrossRef
- The Potential Role of SP-G and PLUNC in Tumor Pathogenesis and Wound Healing in the Human Larynx
Reviews
- Breast fine-needle aspiration cytology in the era of core-needle biopsy: what is its role?
- Ahrong Kim, Hyun Jung Lee, Jee Yeon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):26-38. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.01
- Correction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2025;59(2):147
- 13,771 View
- 459 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) has long been recognized as a minimally invasive, cost-effective, and reliable diagnostic tool for breast lesions. However, with the advent of core-needle biopsy (CNB), the role of FNAC has diminished in some clinical settings. This review aims to re-evaluate the diagnostic value of FNAC in the current era, focusing on its complementary use alongside CNB, the adoption of new approaches such as the International Academy of Cytology Yokohama System, and the implementation of rapid on-site evaluation to reduce inadequate sample rates. Advances in liquid-based cytology, receptor expression testing, molecular diagnostics, and artificial intelligence are discussed, highlighting their potential to enhance the diagnostic accuracy of FNAC. Despite challenges, FNAC remains a valuable diagnostic method, particularly in low-resource settings and specific clinical scenarios, and its role continues to evolve with technology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Breast Lesions on Cytology Using International Academy of Cytology Yokohama Standardized Reporting System
Manish Jaiswal, Anurag Gupta, Tripti Verma, Pradyumn Singh, Rita Yadav, Akash Agarwal, Ashish Singhal, Nuzhat Husain, Shamrendra Narayan, Neha Singh
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(3): 184. CrossRef - Personalizing therapies over the course of hormone receptor‐positive/HER2‐negative metastatic breast cancer
Akshara Singareeka Raghavendra, Senthil Damodaran, Carlos H. Barcenas, Suzanne A. Fuqua, Rachel M. Layman, Debu Tripathy
CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Bulk-lysis protocols as a sensitive method for investigation of circulating CK19 cells in the peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer by flow cytometry
Daniella Serafin Couto Vieira, Laura Otto Walter, Maria Eduarda Cunha da Silva, Lisandra de Oliveira Silva, Heloísa Zorzi Costa, Chandra Chiappin Cardoso, Fernando Carlos de Lander Schmitt, Maria Cláudia Santos-Silva
Analytical Methods.2025; 17(23): 4771. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Breast Lesions on Cytology Using International Academy of Cytology Yokohama Standardized Reporting System
- Next step of molecular pathology: next-generation sequencing in cytology
- Ricella Souza da Silva, Fernando Schmitt
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):291-298. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.22
- 6,736 View
- 382 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The evolving landscape of precision oncology underscores the pivotal shift from morphological diagnosis to treatment decisions driven by molecular profiling. Recent guidelines from the European Society for Medical Oncology recomend the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) across a broader range of cancers, reflecting its superior efficiency and clinical value. NGS not only updates oncology testing by offering quicker, sample-friendly, and sensitive analysis but also reduces the need for multiple individual tests. Cytology samples, often obtained through less invasive methods, can yield high-quality genetic material suitable for molecular analysis. This article focuses on optimizing the use of cytology samples in NGS, and outlines their potential benefits in identifying actionable molecular alterations for targeted therapies across various solid tumors. It also addresses the need for validation studies and the strategies to incorporate or combine different types of samples into routine clinical practice. Integrating cytological and liquid biopsies into routine clinical practice, alongside conventional tissue biopsies, offers a comprehensive approach to tumor genotyping, early disease detection, and monitoring of therapeutic responses across various solid tumor types. For comprehensive biomarker characterization, all patient specimens, although limited, is always valuable.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The World Health Organization Reporting System for Lymph Node, Spleen, and Thymus Cytopathology: Part 1 – Lymph Node
Immacolata Cozzolino, Mats Ehinger, Maria Calaminici, Andrea Ronchi, Mousa A. Al-Abbadi, Helena Barroca, Beata Bode-Lesniewska, David F. Chhieng, Ruth L. Katz, Oscar Lin, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, Martha Bishop Pitman, Arvind Rajwanshi, Fernando C. Schmitt, Ph
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - The impact of cytological preparation techniques on RNA quality: A comparative study on smear samples
Cisel Aydin Mericoz, Gulsum Caylak, Elif Sevin Sanioglu, Zeynep Seçil Satilmis, Ayse Humeyra Dur Karasayar, Ibrahim Kulac
Cancer Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Reimagining cytopathology in the molecular era: Integration or fragmentation?
Sumanta Das, R. Naveen Kumar, Biswajit Dey, Pranjal Kalita
Cytojournal.2025; 22: 94. CrossRef
- The World Health Organization Reporting System for Lymph Node, Spleen, and Thymus Cytopathology: Part 1 – Lymph Node
Case Study
- Rhabdomyosarcoma of the skull with EWSR1 fusion and ALK and cytokeratin expression: a case report
- Hyeong Rok An, Kyung-Ja Cho, Sang Woo Song, Ji Eun Park, Joon Seon Song
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):255-260. Published online September 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.08.15
- 4,534 View
- 219 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) comprises of heterogeneous group of neoplasms that occasionally express epithelial markers on immunohistochemistry (IHC). We herein report the case of a patient who developed RMS of the skull with EWSR1 fusion and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and cytokeratin expression as cytomorphologic features. A 40-year-old man presented with a mass in his forehead. Surgical resection was performed, during which intraoperative frozen specimens were obtained. Squash cytology showed scattered or clustered spindle and epithelioid cells. IHC revealed that the resected tumor cells were positive for desmin, MyoD1, cytokeratin AE1/ AE3, and ALK. Although EWSR1 rearrangement was identified on fluorescence in situ hybridization, ALK, and TFCP2 rearrangement were not noted. Despite providing adjuvant chemoradiation therapy, the patient died of tumor progression 10 months after diagnosis. We emphasize that a subset of RMS can express cytokeratin and show characteristic histomorphology, implying the need for specific molecular examination.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rhabdomyosarcomas of Bone
Ahmed Shah, Andrew L. Folpe
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2025; 18(3): 503. CrossRef - Review of imaging modalities and radiological findings of calvarial lesions
Erkan Gökçe, Murat Beyhan
World Journal of Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Morphology of Telangiectatic Osteosarcoma Associated With Сystic Content: A Case Report
David Makaridze, Armaz Mariamidze, Tamuna Gvianishvili, Giulia Ottaviani , Liana Gogiashvili
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Rhabdomyosarcomas of Bone
Original Article
- Immunohistochemical expression in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies at a single center in Vietnam
- Dat Quoc Ngo, Si Tri Le, Khanh Hoang Phuong Phan, Thao Thi Phuong Doan, Linh Ngoc Khanh Nguyen, Minh Hoang Dang, Thien Thanh Ly, Thu Dang Anh Phan
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):174-181. Published online June 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.05.02
- 4,499 View
- 270 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The identification of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) requires a comprehensive analysis involving clinical manifestations and histological findings. This study aims to provide insights into the histopathological and immunohistochemical aspects of IIMs.
Methods
This retrospective case series involved 56 patients diagnosed with IIMs at the Department of Pathology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy at Ho Chi Minh City, from 2019 to 2023. The histology and immunohistochemical expression of HLA-ABC, HLA-DR, C5b-9, Mx1/2/3, and p62 were detected.
Results
We examined six categories of inflammatory myopathy, including immunemediated necrotizing myopathy (58.9%), dermatomyositis (DM; 23.2%), overlap myositis (8.9%), antisynthetase syndrome (5.4%), inclusion body myositis (IBM; 1.8%), and polymyositis (1.8%). The average age of the patients was 49.7 ± 16.1 years, with a female-to-male ratio of 3:1. Inflammatory cell infiltration in the endomysium was present in 62.5% of cases, perifascicular atrophy was found in 17.8%, and fiber necrosis was observed in 42 cases (75.0%). Rimmed vacuoles were present in 100% of cases in the IBM group. Immunohistochemistry showed the following positivity rates: HLA-ABC (89.2%), HLA-DR (19.6%), C5b-9 (57.1%), and Mx1/2/3 (10.7%). Mx1/2/3 expression was high in DM cases. p62 vacuole deposits were noted in the IBM case. The combination of membrane attack complex and major histocompatibility complex I helped detect IIMs in 96% of cases.
Conclusions
The diagnosis of IIMs and their subtypes should be based on clinical features and histopathological characteristics. Immunohistochemistry plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and differentiation of these subgroups. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluating the Diagnostic Potential of Myxovirus Resistance Protein 1 (MX1) and Myxovirus Resistance Protein 2 (MX2) As Biomarkers in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
Raghavee Neupane, Mustafa Haider, Perry Smith, Marc M Kesselman
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Rapidly Progressive Polymyositis With Vasculitis: The Pivotal Role of Histopathology in Diagnosis and Management
Amitha Venmanassery Karnalsingh, Arjun Karappilly Vijayan, Monica Roselin Edwin Peter, Dilan Davis
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Autoimmune Neuromuscular Disorders at a Molecular Crossroad: Linking Pathogenesis to Targeted Immunotherapy
Anca-Maria Florea, Dimela-Gabriela Luca, Eugenia Irene Davidescu, Bogdan-Ovidiu Popescu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(23): 11736. CrossRef
- Evaluating the Diagnostic Potential of Myxovirus Resistance Protein 1 (MX1) and Myxovirus Resistance Protein 2 (MX2) As Biomarkers in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
Case Study
- Malignant potential of neuroendocrine microtumor of the pancreas harboring high-grade transformation: lesson learned from a patient with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
- Jongwon Lee, Kyung Jin Lee, Dae Wook Hwang, Seung-Mo Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):91-97. Published online March 13, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.02.13
- 4,889 View
- 215 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pancreatic neuroendocrine microtumor (PNEMT) is a neuroendocrine tumor (NET) < 0.5 cm in diameter, and it is considered benign. We report a PNEMT with high-grade transformation (HGT). A man in his 60s with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome underwent surgical resection of a NET. A second sub-centimeter nodule with a nodule-in-nodule pattern was discovered. The 0.4 cm outer nodule contained clear columnar cells with round nuclei and indistinct nucleoli, while the 0.1 cm inner nodule had eosinophilic cells with an increased nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio, vesicular nuclei, and prominent nucleoli. Tumor cells in the outer and inner nodules were synaptophysin and chromogranin positive. Only the inner nodule was p53 positive, while the outer nodule was exclusively positive for carbonic anhydrase 9 and vimentin. The Ki-67 labeling indices for the outer and inner nodules were 2.1% (grade 1) and 44.3% (grade 3), respectively. This nodule was determined to be a PNEMT with HGT. Our findings suggest that a PNEMT may not always be benign and can undergo HGT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Decoding Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: Molecular Profiles, Biomarkers, and Pathways to Personalized Therapy
Linda Galasso, Federica Vitale, Gabriele Giansanti, Giorgio Esposto, Raffaele Borriello, Irene Mignini, Alberto Nicoletti, Lorenzo Zileri Dal Verme, Antonio Gasbarrini, Maria Elena Ainora, Maria Assunta Zocco
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(16): 7814. CrossRef - Pancreatic neuroendocrine microtumors in the elderly: A retrospective study using cadaveric pancreatic tissue
Ting Yang, Ke Ren, Xiang-Quan Chen, Taku Toriumi, Yutaro Natsuyama, Jun Li, Aoi Sukeda, Toshitaka Nagao, Shuang-Qin Yi
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Basis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
Alesia Maluchenko, Denis Maksimov, Zoia Antysheva, Julia Krupinova, Ekaterina Avsievich, Olga Glazova, Natalia Bodunova, Nikolay Karnaukhov, Ilia Feidorov, Diana Salimgereeva, Mark Voloshin, Pavel Volchkov
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(20): 11017. CrossRef
- Decoding Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: Molecular Profiles, Biomarkers, and Pathways to Personalized Therapy
Review
- Exploring histological predictive biomarkers for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy response in non–small cell lung cancer
- Uiju Cho, Soyoung Im, Hyung Soon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):49-58. Published online February 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.01.31
- 9,947 View
- 348 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Treatment challenges persist in advanced lung cancer despite the development of therapies beyond the traditional platinum-based chemotherapy. The early 2000s marked a shift to tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeting epidermal growth factor receptor, ushering in personalized genetic-based treatment. A further significant advance was the development of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), especially for non–small cell lung cancer. These target programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4, which enhanced the immune response against tumor cells. However, not all patients respond, and immune-related toxicities arise. This review emphasizes identifying biomarkers for ICI response prediction. While PD-L1 is a widely used, validated biomarker, its predictive accuracy is imperfect. Investigating tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, tertiary lymphoid structure, and emerging biomarkers such as high endothelial venule, Human leukocyte antigen class I, T-cell immunoreceptors with Ig and ITIM domains, and lymphocyte activation gene-3 counts is promising. Understanding and exploring additional predictive biomarkers for ICI response are crucial for enhancing patient stratification and overall care in lung cancer treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Machine learning methods for histopathological image analysis: Updates in 2024
Daisuke Komura, Mieko Ochi, Shumpei Ishikawa
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2025; 27: 383. CrossRef - Beyond single biomarkers: multi-omics strategies to predict immunotherapy outcomes in blood cancers
Mohammad Pirouzbakht, Soroosh Hamzeh, Hamed Soleimani Samarkhazan
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Temporal changes in tongue color during immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: a prospective observational study using digital tongue diagnosis
Eunbyul Cho, Woosu Choi, Jun Hyeok Lim, Ji Woong Son, Seung Hun Jang, Seung Hyeun Lee, Jong Gwon Choi, In-Jae Oh, Tae-Won Jang, Seong Hoon Yoon, Seung Joon Kim, Chang-Min Choi, Sung Yong Lee, Mi Mi Ko, Mi-Kyung Jeong
Oncology Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Machine learning methods for histopathological image analysis: Updates in 2024
Case Study
- Primary leiomyosarcoma of the bone: a case report
- Ala Abu-Dayeh, Samir Alhyassat
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):35-39. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.14
- 6,281 View
- 269 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary leiomyosarcoma of the bone is rare. Histologically, it resembles leiomyosarcoma of soft tissue. Given the rarity of this entity, its diagnosis should be made only after clinical studies and workup have excluded metastasis from other sites. Herein, we describe an additional case of primary bone leiomyosarcoma. We report a 32-year-old female patient, who presented with right knee pain and was found to have a right distal femur mass by imaging studies. Biopsy showed a neoplasm composed of fascicles of spindle cells, arranged in different patterns, with significant pleomorphism. The tumor cells were positive for smooth muscle actin, focally positive for desmin and H-caldesmon. No other masses in the body were detected by imaging studies. The diagnosis of leiomyosarcoma of the bone was rendered. Given the broad diagnostic differential of primary bone leiomyosarcoma, it is important to be aware of this rare bone tumor phenotype and of its histomorphologic and immunohistochemical features for an accurate diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Leiomyosarcoma of Bone: A Rare Case Series with Review of Literature
Jitin Goyal, Bineeta Parihar, Nitin Agarwal, Sulagna Manna, Anila Sharma, Sunil Kumar Puri
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Limb Leiomyosarcoma With Multifocal Musculoskeletal Soft Tissue Metastasis: A Case Report and Literature Review
Milad Haji Agha Bozorgi, Hoda Borooghani, Taghi Aghajanlou
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Chronic Ethanol Exposure Induces Early Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Premalignant Changes in Gingival Keratinocytes: An In Vitro Model of Very Early Oral Carcinogenesis
Martin Philipp Dieterle, Thorsten Steinberg, Ayman Husari, Pascal Tomakidi
Cells.2025; 14(23): 1887. CrossRef
- Primary Leiomyosarcoma of Bone: A Rare Case Series with Review of Literature
Newsletter
- What’s new in genitourinary pathology 2023: WHO 5th edition updates for urinary tract, prostate, testis, and penis
- Bonnie Choy, Maria Tretiakova, Debra L. Zynger
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):45-48. Published online December 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.12.11
- 11,670 View
- 912 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The 5th edition WHO Classification of Urinary and Male Genital Tumours (2022) introduced many significant changes relevant to urologic daily practice, mainly to renal tumors which was covered in the What’s New newsletter in September 2022. In this newsletter, we summarize the notable changes to bladder, prostate, testis, and penis based on the 5th edition of the WHO.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predicting variant histology in bladder cancer: the role of multiparametric MRI and vesical imaging-reporting and data system (VI-RADS)
Serdar Aslan, Merve Nur Tasdemir, Ertugrul Cakir, Ural Oguz, Birgul Tok
Abdominal Radiology.2025; 50(10): 4700. CrossRef - Pictorial review of multiparametric MRI in bladder urothelial carcinoma with variant histology: pearls and pitfalls
Yuki Arita, Sungmin Woo, Lisa Ruby, Thomas C. Kwee, Keisuke Shigeta, Ryo Ueda, Sunny Nalavenkata, Hiromi Edo, Kosuke Miyai, Jeeban Das, Pamela I. Causa Andrieu, Hebert Alberto Vargas
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 49(8): 2797. CrossRef - Oncological outcomes and prognostic implications of T1 histo-anatomic substaging in the management of high-Grade non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: results from a large single centre series
Marco Finati, Antonio Fanelli, Francesco Cinelli, Nicola Schiavone, Ugo Giovanni Falagario, Anna Ricapito, Nicola d’Altilia, Richard Naspro, Angelo Porreca, Felice Crocetto, Biagio Barone, Ciro Imbimbo, Carlo Bettocchi, Francesca Sanguedolce, Luigi Cormio
World Journal of Urology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Predicting variant histology in bladder cancer: the role of multiparametric MRI and vesical imaging-reporting and data system (VI-RADS)
Original Articles
- Thoracic aortic calcification as a predictor of coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hussein Nafakhi, Alaa Salah Jumaah, Akeel Abed Yasseen
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(3):161-170. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.03.05
- 7,549 View
- 173 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The relationship between coronary atherosclerosis (progression, outcome) and calcification in the thoracic aorta (TAC), particularly across its various segments, is complex and often shows conflicting associations in the literature. To address this debated and complex relationship, we aimed to evaluate how TAC and its segments correlate with the presence and severity of coronary artery disease (CAD).
Methods
We reviewed all articles published between January 1990 and September 2024 that examined the link between TAC and CAD and were indexed in PubMed, Scopus, or EMBASE. Using a random-effects model, we calculated pooled proportions, odds ratios, and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) to evaluate the association between TAC and CAD, with consideration of severity.
Results
The study included 17 studies with 8,187 participants, 2,775 of whom had CAD (1,059 with severe CAD), and 5,412 of whom did not. The pooled odds ratio of TAC in patients with CAD compared to that in those without was 3.874 (95% CI, 2.789 to 5.381). For severe CAD versus mild CAD, the odds ratio was 8.005 (95% CI, 2.611 to 24.542). Calcification of the aortic root (pooled proportion, 51%; 95% CI, 0.282 to 0.733) or descending aorta (pooled proportion, 53.4%; 95% CI, 0.341 to 0.718) had the strongest association with CAD compared to calcification of the arch or ascending aorta.
Conclusions
TAC is significantly associated with both the presence and severity of CAD. Calcification in the descending aorta and aortic root is more strongly linked to CAD than calcification in the arch or ascending aorta. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- International Liver Transplantation Society/Liver Intensive Care Group of Europe guidelines for cardiovascular assessment before liver transplantation
Emmanuel Weiss, Gonzalo Crespo, Alexandra Anderson, Gianni Biancofiore, Ryan Chadha, Jacek B. Cywinski, Andrea De Gasperi, James Findlay, Marc Giménez-Milà, Constantine Karvellas, Michael Kaufman, Ashish Malik, Marina Moguilevitch, Sher-Lu Pai, Koen Reynt
American Journal of Transplantation.2026; 26(2): 219. CrossRef - Segmental thoracic aorta calcification in diabetic patients: Relationship with coronary atherosclerosis burden
Wasan Kadhum Abbas, Abdulameer A. Al-Mosawi, Ali M. Al-Shirazi, Hussein Nafakhi, Hayder Nafakhi
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- International Liver Transplantation Society/Liver Intensive Care Group of Europe guidelines for cardiovascular assessment before liver transplantation
- Association study of TYMS gene expression with TYMS and ENOSF1 genetic variants in neoadjuvant chemotherapy response of gastric cancer
- Khadijeh Arjmandi, Iman Salahshourifar, Shiva Irani, Fereshteh Ameli, Mohsen Esfandbod
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):105-114. Published online February 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.05
- 3,513 View
- 145 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The present research was designed to study the associations between genetic variants of TYMS and ENOSF1 genes with TYMS and ENOSF1 gene expression in neoadjuvant chemotherapy response among patients with gastric cancer. Methods: Formalin-embedded and paraffin-fixed matched tumor and normal gastric cancer tissue samples from patients who received neoadjuvant 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) treatment were obtained. DNA and RNA were extracted for all samples. A 28-bp variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) at the 5' untranslated region of TYMS gene and rs2612091 and rs2741171 variants in the ENOSF1 gene were genotyped for normal tissue samples. The real-time polymerase chain reaction method was used to study the expression of ENOSF1 and TYMS genes in both normal and tumor tissues. Data were analyzed using REST 2000 and SPSS ver. 26.0 software programs. Results: A significant association between TYMS 2R3R VNTR genotypes and 5-FU therapy was found (p = .032). The 3R3R and 2R2R genotypes were significantly associated with increased and decreased survival time, respectively (p = .003). The 3R3R genotype was significantly associated with TYMS overexpression (p < .001). Moreover, a significant association was found between the rs2612091 genotype and treatment outcome (p = .017). Conclusions: This study highlights the impact of TYMS and ENOSF1 genes as predictive indicators for survival and response to 5-FU–based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in gastric cancer patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Innovative biomaterial strategies for mitigating radiotherapy toxicity: multidimensional mechanistic interventions of nano-microscale materials and hydrogels
Yifan Liu, Fengdi Jiang, Jie Song, Huaijin Qiao, Junlong Dai, Hao Bai, Shuyu Zhang
Coordination Chemistry Reviews.2026; 549: 217313. CrossRef - Mebendazole impairs the expression and function of enzymes in nucleotide metabolism pathways, leading to Selective Cytotoxicity, Cell Cycle Arrest, and Damage to Cell Morphology in Gastric Cancer
Emerson Lucena da Silva, Felipe Pantoja Mesquita, Pedro Victor da Rocha Lima, José Hélio de Araújo Filho, Francisco Laio de Oliveira, Ana Beatriz da Lima, Pedro Filho Noronha Souza, Raquel Carvalho Montenegro
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2026; 430: 111973. CrossRef
- Innovative biomaterial strategies for mitigating radiotherapy toxicity: multidimensional mechanistic interventions of nano-microscale materials and hydrogels
Reviews
- Professional biobanking education in Korea based on ISO 20387
- Jong Ok Kim, Chungyeul Kim, Sangyong Song, Eunah Shin, Ji-Sun Song, Mee Sook Roh, Dong-chul Kim, Han-Kyeom Kim, Joon Mee Kim, Yeong Jin Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):11-25. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.04
- 6,161 View
- 187 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To ensure high-quality bioresources and standardize biobanks, there is an urgent need to develop and disseminate educational training programs in accordance with ISO 20387, which was developed in 2018. The standardization of biobank education programs is also required to train biobank experts. The subdivision of categories and levels of education is necessary for jobs such as operations manager (bank president), quality manager, practitioner, and administrator. Essential training includes programs tailored for beginner, intermediate, and advanced practitioners, along with customized training for operations managers. We reviewed and studied ways to develop an appropriate range of education and training opportunities for standard biobanking education and the training of experts based on KS J ISO 20387. We propose more systematic and professional biobanking training programs in accordance with ISO 20387, in addition to the certification programs of the National Biobank and the Korean Laboratory Accreditation System. We suggest various training programs appropriate to a student’s affiliation or work, such as university biobanking specialized education, short-term job training at unit biobanks, biobank research institute symposiums by the Korean Society of Pathologists, and education programs for biobankers and researchers. Through these various education programs, we expect that Korean biobanks will satisfy global standards, meet the needs of users and researchers, and contribute to the advancement of science.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a big data platform for collecting and utilizing clinical information from the Korea Biobank Network
Yun Seon Im, Seol Whan Oh, Ki Hoon Kim, Wona Choi, In Young Choi
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Frozen section histopathology and preanalytical factors affecting nucleic acid integrity in biobanked fresh-frozen human cancer tissues
Soungeun Kim, Jaewon Kang, Boyeon Kim, Yoonjin Kwak, Hye Seung Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(6): 398. CrossRef
- Development of a big data platform for collecting and utilizing clinical information from the Korea Biobank Network
- Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cytology in pregnancy
- Ji-Young Kim, Jeong Yun Shim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):283-290. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.17
- 10,905 View
- 450 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cervical cancer screening during pregnancy presents unique challenges for cytologic interpretation. This review focuses on pregnancy-associated cytomorphological changes and their impact on diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical cancer. Pregnancy-induced alterations include navicular cells, hyperplastic endocervical cells, immature metaplastic cells, and occasional decidual cells or trophoblasts. These changes can mimic abnormalities such as koilocytosis, adenocarcinoma in situ, and high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, potentially leading to misdiagnosis. Careful attention to nuclear features and awareness of pregnancy-related changes are crucial for correct interpretation. The natural history of CIN during pregnancy shows higher regression rates, particularly for CIN 2, with minimal risk of progression. Management of abnormal cytology follows modified risk-based guidelines to avoid invasive procedures, with treatment typically deferred until postpartum. The findings reported in this review emphasize the importance of considering pregnancy status in cytological interpretation, highlight potential problems, and provide guidance on differentiating benign pregnancy-related changes from true abnormalities. Understanding these nuances is essential for accurate diagnosis and proper management of cervical abnormalities in pregnant women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The significance of biological samples from pregnant women in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Xue Mi, Maharjan Rashmi, Zangyu Pan, Di Wu, Jinwei Miao
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Oncologic and pregnancy outcomes of cervical high-grade intraepithelial lesions and delivery mode
Olga P. Matylevich, Ilya A. Tarasau, Sviatlana Y. Shelkovich, Aliaksandr F. Martsinkevich
Academia Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- The significance of biological samples from pregnant women in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Original Articles
- Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
- Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Shanop Shuangshoti, Nakarin Kitkumthorn, Somboon Keelawat
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):39-49. Published online October 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.14
- 4,504 View
- 330 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Although the criteria for follicular-pattern thyroid tumors are well-established, diagnosing these lesions remains challenging in some cases. In the recent World Health Organization Classification of Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Tumors (5th edition), the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma was reclassified as its own entity. It is crucial to differentiate this variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from low-risk follicular pattern tumors due to their shared morphological characteristics. Proteomics holds significant promise for detecting and quantifying protein biomarkers. We investigated the potential value of a protein biomarker panel defined by machine learning for identifying the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma, initially using formalin- fixed paraffin-embedded samples.
Methods
We developed a supervised machine-learning model and tested its performance using proteomics data from 46 thyroid tissue samples.
Results
We applied a random forest classifier utilizing five protein biomarkers (ZEB1, NUP98, C2C2L, NPAP1, and KCNJ3). This classifier achieved areas under the curve (AUCs) of 1.00 and accuracy rates of 1.00 in training samples for distinguishing the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from non-malignant samples. Additionally, we analyzed the performance of single-protein/gene receiver operating characteristic in differentiating the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from others within The Cancer Genome Atlas projects, which yielded an AUC >0.5.
Conclusions
We demonstrated that integration of high-throughput proteomics with machine learning can effectively differentiate the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from other follicular pattern thyroid tumors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in immunotherapy for thyroid malignancies: from molecular targets to clinical outcomes
Shuo Lv, Jinbao Wang, Guohao Chen, Yongshun Wang, Naiqing Liu
Frontiers in Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Misdiagnosed follicular adenoma with 11 year postoperative liver and lung metastases a case report and literature review
Kai-Li Yang, Heng-Tong Han, Shou-Hua Li, Xiao-Xiao Li, Ze Yang, Li-Bin Ma, Yong-Xun Zhao
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advances in immunotherapy for thyroid malignancies: from molecular targets to clinical outcomes
- Histopathologic classification and immunohistochemical features of papillary renal neoplasm with potential therapeutic targets
- Jeong Hwan Park, Su-Jin Shin, Hyun-Jung Kim, Sohee Oh, Yong Mee Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):321-330. Published online September 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.31
- 7,028 View
- 431 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Papillary renal cell carcinoma (pRCC) is the second most common histological subtype of renal cell carcinoma and is considered a morphologically and molecularly heterogeneous tumor. Accurate classification and assessment of the immunohistochemical features of possible therapeutic targets are needed for precise patient care. We aimed to evaluate immunohistochemical features and possible therapeutic targets of papillary renal neoplasms
Methods
We collected 140 papillary renal neoplasms from three different hospitals and conducted immunohistochemical studies on tissue microarray slides. We performed succinate dehydrogenase B, fumarate hydratase, and transcription factor E3 immunohistochemical studies for differential diagnosis and re-classified five cases (3.6%) of papillary renal neoplasms. In addition, we conducted c-MET, p16, c-Myc, Ki-67, p53, and stimulator of interferon genes (STING) immunohistochemical studies to evaluate their pathogenesis and value for therapeutic targets.
Results
We found that c-MET expression was more common in pRCC (classic) (p = .021) among papillary renal neoplasms and Ki-67 proliferation index was higher in pRCC (not otherwise specified, NOS) compared to that of pRCC (classic) and papillary neoplasm with reverse polarity (marginal significance, p = .080). Small subsets of cases with p16 block positivity (4.5%) (pRCC [NOS] only) and c-Myc expression (7.1%) (pRCC [classic] only) were found. Also, there were some cases showing STING expression and those cases were associated with increased Ki-67 proliferation index (marginal significance, p = .063).
Conclusions
Our findings suggested that there are subsets of pRCC with c-MET, p16, c-MYC, and STING expression and those cases could be potential candidates for targeted therapy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tissue-Based Biomarkers Important for Prognostication and Management of Genitourinary Tumors, Including Surrogate Markers of Genomic Alterations
Leonie Beauchamp, Shreeya Indulkar, Eric Erak, Mohammad Salimian, Andres Matoso
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2025; 18(1): 175. CrossRef - Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity: a case report and literature review
Diego Gonzalez, Kris Kokoneshi, Sam Kwon, Ryan Thomas Mathews, Ryan Michael Antar, Maher Ali, Abiye Kassa, Michael Whalen
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Tissue-Based Biomarkers Important for Prognostication and Management of Genitourinary Tumors, Including Surrogate Markers of Genomic Alterations
- Paricalcitol prevents MAPK pathway activation and inflammation in adriamycin-induced kidney injury in rats
- Amanda Lima Deluque, Lucas Ferreira de Almeida, Beatriz Magalhães Oliveira, Cláudia Silva Souza, Ana Lívia Dias Maciel, Heloísa Della Coletta Francescato, Cleonice Giovanini, Roberto Silva Costa, Terezila Machado Coimbra
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):219-228. Published online August 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.12
- 3,977 View
- 222 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway induces uncontrolled cell proliferation in response to inflammatory stimuli. Adriamycin (ADR)-induced nephropathy (ADRN) in rats triggers MAPK activation and pro-inflammatory mechanisms by increasing cytokine secretion, similar to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Activation of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) plays a crucial role in suppressing the expression of inflammatory markers in the kidney and may contribute to reducing cellular proliferation. This study evaluated the effect of pre-treatment with paricalcitol on ADRN in renal inflammation mechanisms.
Methods
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were implanted with an osmotic minipump containing activated vitamin D (paricalcitol, Zemplar, 6 ng/day) or vehicle (NaCl 0.9%). Two days after implantation, ADR (Fauldoxo, 3.5 mg/kg) or vehicle (NaCl 0.9%) was injected. The rats were divided into four experimental groups: control, n = 6; paricalcitol, n = 6; ADR, n = 7 and, ADR + paricalcitol, n = 7.
Results
VDR activation was demonstrated by increased CYP24A1 in renal tissue. Paricalcitol prevented macrophage infiltration in the glomeruli, cortex, and outer medulla, prevented secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-1β, increased arginase I and decreased arginase II tissue expressions, effects associated with attenuation of MAPK pathways, increased zonula occludens-1, and reduced cell proliferation associated with proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression. Paricalcitol treatment decreased the stromal cell-derived factor 1α/chemokine C-X-C receptor type 4/β-catenin pathway.
Conclusions
Paricalcitol plays a renoprotective role by modulating renal inflammation and cell proliferation. These results highlight potential targets for treating CKD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perirenal fat differs in patients with chronic kidney disease receiving different vitamin D-based treatments: a preliminary study
Ana Checa-Ros, Antonella Locascio, Owahabanun-Joshua Okojie, Pablo Abellán-Galiana, Luis D’Marco
BMC Nephrology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Attenuating amiodarone-induced lung toxicity by the vitamin D receptor activator paricalcitol in rats: targeting TLR4/NF-κB/HIF-1α and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways
Aamal G. El-Waseif, Mahmoud Elshal, Dalia H. El-Kashef, Nashwa M. Abu-Elsaad
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Perirenal fat differs in patients with chronic kidney disease receiving different vitamin D-based treatments: a preliminary study
Review
- Welcoming the new, revisiting the old: a brief glance at cytopathology reporting systems for lung, pancreas, and thyroid
- Rita Luis, Balamurugan Thirunavukkarasu, Deepali Jain, Sule Canberk
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):165-173. Published online July 15, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.06.11
- 4,698 View
- 279 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This review addresses new reporting systems for lung and pancreatobiliary cytopathology as well as the most recent edition of The Bethesda Reporting System for Thyroid Cytopathology. The review spans past, present, and future aspects within the context of the intricate interplay between traditional morphological assessments and cutting-edge molecular diagnostics. For lung and pancreas, the authors discuss the evolution of reporting systems, emphasizing the bridge between past directives and more recent collaborative efforts of the International Academy of Cytology and the World Health Organization in shaping universal reporting systems. The review offers a brief overview of the structure of these novel systems, highlighting their strengths and pinpointing areas that require further refinement. For thyroid, the authors primarily focus on the third edition of The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology, also considering the two preceding editions. This review serves as an invaluable resource for cytopathologists, offering a panoramic view of the evolving landscape of cytopathology reporting and pointing out the integrative role of the cytopathologist in an era of rapid diagnostic and therapeutic advancements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology: Insights Into the Insufficient/Inadequate/Non‐Diagnostic, Atypical and Suspicious for Malignancy Categories and How to Use Them
Zahra Maleki, Sule Canberk, Andrew Field
Cytopathology.2025; 36(5): 434. CrossRef - Reproducibility of the Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology (TBSRTC): An observational study of 100 patients
Kishori Moni Panda, Reena Naik, Mohd Ghouse Mohiddin
Indian Journal of Pathology and Oncology.2024; 11(4): 385. CrossRef
- WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology: Insights Into the Insufficient/Inadequate/Non‐Diagnostic, Atypical and Suspicious for Malignancy Categories and How to Use Them
Original Article
- Single umbilical artery and associated birth defects in perinatal autopsies: prenatal diagnosis and management
- Manushree Saxena, Bhagyashri Hungund
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):214-218. Published online July 9, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.03
- 16,509 View
- 435 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The umbilical cord forms the connection between the fetus and the placenta at the feto-maternal interface and normally comprises two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein. In some cases, only a single umbilical artery (SUA) is present. This study was conducted to evaluate associations between SUA and other congenital malformations discovered in perinatal autopsies and to ascertain the existence of preferential associations between SUA and certain anomalies.
Methods
We evaluated records of all fetuses sent for autopsy to the Department of Pathology during the 10-year period from 2013 through 2022 (n = 1,277). The data were obtained from the hospital’s pathology laboratory records. The congenital anomalies were grouped by organ or system for analysis and included cardiovascular, urinary tract, nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, musculoskeletal, and lung anomalies.
Results
A SUA was present in 8.61% of the autopsies. The gestational age of the affected fetuses ranged between 13 to 40 weeks. An SUA presented as an isolated single anomaly in 44 cases (3.4%). Of the 110 SUA cases, 60% had other congenital anomalies. There was a significant association between birth defects and SUAs (p < .001). Strong associations between SUA and urinary tract, lung, and musculoskeletal anomalies were observed.
Conclusions
A SUA is usually seen in association with other congenital malformations rather than as an isolated defect. Therefore, examination for associated anomalies when an SUA is detected either antenatally or postnatally is imperative. The findings of this study should be helpful in counseling expectant mothers and their families in cases of SUA. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Single Umbilical Artery with Symmetrical IUGR and Multiple Fetal Anomalies - An Interesting Case Report
Amulya Choudary Kotapati, Bhargavi Khandru, Vijayasree M.
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2025; : 10. CrossRef - Epidemiological and Histopathological Characteristics of Fetuses with Congenital Disorders: A Study in Greece
Despoina Nteli, Maria Nteli, Konstantinos Konstantinidis, Maria Ouzounidou, Paschalis Theotokis, Maria-Eleni Manthou, Iasonas Dermitzakis, Xeni Miliara, Chrysoula Gouta, Stamatia Angelidou, Dimosthenis Miliaras, Soultana Meditskou
Biology.2025; 14(6): 626. CrossRef
- Single Umbilical Artery with Symmetrical IUGR and Multiple Fetal Anomalies - An Interesting Case Report
Case Study
- Primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain with EML4::ALK fusion mimicking intra-axial glioma: a case report and brief literature review
- Eric Eunshik Kim, Chul-Kee Park, Koung Mi Kang, Yoonjin Kwak, Sung-Hye Park, Jae-Kyung Won
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):141-145. Published online May 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.04.12
- 4,920 View
- 211 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An aggressive subtype of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma occurs primarily inside the abdominal cavity, followed by a pulmonary localization. Most harbor anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangements, with RANBP2 and RRBP1 among the well-documented fusion partners. We report the second case of primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain, with a well-known EML4::ALK fusion. The case is notable for its intra-axial presentation that clinico-radiologically mimicked glioma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
Original Article
- Immunohistochemical expression of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in neuroblastoma and its relations with some clinical and histopathological features
- Thu Dang Anh Phan, Thao Quyen Nguyen, Nhi Thuy To, Thien Ly Thanh, Dat Quoc Ngo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):29-34. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.12.07
- 5,620 View
- 292 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) mutations have been identified as a prominent cause of some familial and sporadic neuroblastoma (NB). ALK expression in NB and its relationship with clinical and histopathological features remains controversial. This study investigated ALK expression and its potential relations with these features in NB.
Methods
Ninety cases of NB at the Department of Pathology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy at Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam from 01/01/2018 to 12/31/2021, were immunohistochemically stained with ALK (D5F3) antibody. The ALK expression and its relations with some clinical and histopathological features were investigated.
Results
The rate of ALK expression in NB was 91.1%. High ALK expression (over 50% of tumor cells were positive with moderate-strong intensity) accounted for 65.6%, and low ALK expression accounted for 34.4%. All the MYCN-amplified NB patients had ALK immunohistochemistry positivity, most cases had high ALK protein expression. The undifferentiated subtype of NB had a lower ALK-positive rate than the poorly differentiated and differentiated subtype. The percentages of ALK positivity were significantly higher in more differentiated histological types of NB (p = .024). There was no relation between ALK expression and: age group, sex, primary tumor location, tumor stage, MYCN status, clinical risk, Mitotic-Karyorrhectic Index, prognostic group, necrosis, and calcification.
Conclusions
ALK was highly expressed in NB. ALK expression was not related to several clinical and histopathological features. More studies are needed to elucidate the association between ALK expression and ALK gene status and to investigate disease progression, especially the oncogenesis of ALK-positive NB. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A humanized anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-directed antibody-drug conjugate with pyrrolobenzodiazepine payload demonstrates efficacy in ALK-expressing cancers
Alberto D. Guerra, Smita Matkar, Christina Acholla, Colleen Casey, Grant Li, Martina Mazzeschi, Khushbu Patel, Kateryna Krytska, Chuan Chen, Skye Balyasny, Joshua Kalna, Paul Kamitsuka, Mark Gerelus, Grace Polkosnik, David Groff, Apratim Mukherje, Cynthia
Nature Communications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Integration of ALK gene mutations and targeted therapies in pediatric high-risk neuroblastoma: advancements in precision oncology
Bhumika Bheemavarapu, Mohammad Khalil, Aseef Rehman, Saman Javid, FNU Cyrus, Sardar Noman Qayyum, Aasvi Gohil, Siraj Ul Muneer, Samim Noori
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2025; 87(10): 6470. CrossRef
- A humanized anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-directed antibody-drug conjugate with pyrrolobenzodiazepine payload demonstrates efficacy in ALK-expressing cancers
Reviews
- Diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases: from Averill A. Liebow to artificial intelligence
- Eunhee S. Yi, Paul Wawryko, Jay H. Ryu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):1-11. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.17
- 7,858 View
- 438 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Histopathologic criteria of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP)/idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) were defined over the years and endorsed by leading organizations decades after Dr. Averill A. Liebow first coined the term UIP in the 1960s as a distinct pathologic pattern of fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Novel technology and recent research on interstitial lung diseases with genetic component shed light on molecular pathogenesis of UIP/IPF. Two antifibrotic agents introduced in the mid-2010s opened a new era of therapeutic approaches to UIP/IPF, albeit contentious issues regarding their efficacy, side effects, and costs. Recently, the concept of progressive pulmonary fibrosis was introduced to acknowledge additional types of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases with the clinical and pathologic phenotypes comparable to those of UIP/IPF. Likewise, some authors have proposed a paradigm shift by considering UIP as a stand-alone diagnostic entity to encompass other fibrosing interstitial lung diseases that manifest a relentless progression as in IPF. These trends signal a pendulum moving toward the tendency of lumping diagnoses, which poses a risk of obscuring potentially important information crucial to both clinical and research purposes. Recent advances in whole slide imaging for digital pathology and artificial intelligence technology could offer an unprecedented opportunity to enhance histopathologic evaluation of interstitial lung diseases. However, current clinical practice trends of moving away from surgical lung biopsies in interstitial lung disease patients may become a limiting factor in this endeavor as it would be difficult to build a large histopathologic database with correlative clinical data required for artificial intelligence models.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Identification of early genes in the pathophysiology of fibrotic interstitial lung disease in a new model of pulmonary fibrosis
Nathan Hennion, Corentin Bedart, Léonie Vandomber, Frédéric Gottrand, Sarah Humez, Cécile Chenivesse, Jean-Luc Desseyn, Valérie Gouyer
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiological Insights into UIP Pattern: A Comparison Between IPF and Non-IPF Patients
Stefano Palmucci, Miriam Adorna, Angelica Rapisarda, Alessandro Libra, Sefora Fischetti, Gianluca Sambataro, Letizia Antonella Mauro, Emanuele David, Pietro Valerio Foti, Claudia Mattina, Corrado Spatola, Carlo Vancheri, Antonio Basile
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(12): 4162. CrossRef
- Identification of early genes in the pathophysiology of fibrotic interstitial lung disease in a new model of pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical practice recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing in patients with solid cancer: a joint report from KSMO and KSP
- Miso Kim, Hyo Sup Shim, Sheehyun Kim, In Hee Lee, Jihun Kim, Shinkyo Yoon, Hyung-Don Kim, Inkeun Park, Jae Ho Jeong, Changhoon Yoo, Jaekyung Cheon, In-Ho Kim, Jieun Lee, Sook Hee Hong, Sehhoon Park, Hyun Ae Jung, Jin Won Kim, Han Jo Kim, Yongjun Cha, Sun Min Lim, Han Sang Kim, Choong-Kun Lee, Jee Hung Kim, Sang Hoon Chun, Jina Yun, So Yeon Park, Hye Seung Lee, Yong Mee Cho, Soo Jeong Nam, Kiyong Na, Sun Och Yoon, Ahwon Lee, Kee-Taek Jang, Hongseok Yun, Sungyoung Lee, Jee Hyun Kim, Wan-Seop Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):147-164. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.01
- 9,455 View
- 496 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In recent years, next-generation sequencing (NGS)–based genetic testing has become crucial in cancer care. While its primary objective is to identify actionable genetic alterations to guide treatment decisions, its scope has broadened to encompass aiding in pathological diagnosis and exploring resistance mechanisms. With the ongoing expansion in NGS application and reliance, a compelling necessity arises for expert consensus on its application in solid cancers. To address this demand, the forthcoming recommendations not only provide pragmatic guidance for the clinical use of NGS but also systematically classify actionable genes based on specific cancer types. Additionally, these recommendations will incorporate expert perspectives on crucial biomarkers, ensuring informed decisions regarding circulating tumor DNA panel testing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apport de la génomique dans la prise en charge des cancers
Étienne Rouleau, Lucie Karayan-Tapon, Marie-Dominique Galibert, Alexandre Harlé, Isabelle Soubeyran
Revue Francophone des Laboratoires.2025; 2025(568): 67. CrossRef - The Redox–Adhesion–Exosome (RAX) Hub in Cancer: Lipid Peroxidation-Driven EMT Plasticity and Ferroptosis Defense with HNE/MDA Signaling and Lipidomic Perspectives
Moon Nyeo Park, Jinwon Choi, Rosy Iara Maciel de Azambuja Ribeiro, Domenico V. Delfino, Seong-Gyu Ko, Bonglee Kim
Antioxidants.2025; 14(12): 1474. CrossRef
- Apport de la génomique dans la prise en charge des cancers
Case Study
- Drug-induced phospholipidosis of the kidney suspected to be caused by atomoxetine
- Sung-Eun Choi, Kee Hyuck Kim, Minsun Jung, Jeong Hae Kie
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):124-128. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.10
- 1,480 View
- 126 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Drug-induced phospholipidosis (DIP) is characterized by intracellular accumulation of phospholipids with lamellar body formation secondary to drug-altered lipid metabolism, which can trigger inflammation and histopathological changes. Fabry disease and DIP both exhibit zebra bodies on electron microscopy, complicating differential diagnosis. A 17-year-old male with microscopic hematuria and proteinuria had received atomoxetine (40 mg) for 11 months to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Light microscopy showed one glomerulus with perihilar sclerosis and periglomerular fibrosis. Kidney biopsy revealed zebra bodies in podocytes, initially suggesting Fabry disease. However, α-galactosidase A enzyme activity was normal on tandem mass spectrometry. Next-generation sequencing of GLA identified only three benign variants. This represents the first reported case of atomoxetine-induced DIP. When zebra bodies are observed, clinicians should consider DIP caused by cationic amphiphilic drugs alongside Fabry disease. Atomoxetine meets the structural criteria for inducing DIP, and awareness of this potential complication is essential.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Atomoxetine
Reactions Weekly.2026; 2095(1): 19. CrossRef
- Atomoxetine
Original Articles
- National quality assurance program using digital cytopathology: a 5-year digital transformation experience by the Korean Society for Cytopathology
- Yosep Chong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Soon Auck Hong, Sung Soon Kim, Bo-Sung Kim, Younghee Choi, Yoon Jung Choi, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Soo Jin Jung, Hoon Kyu Oh, Seung-Sook Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):320-333. Published online September 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.27
- 3,494 View
- 106 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Digital cytopathology (DC) is emerging as a transformative approach in quality assurance programs (QAP), though its comprehensive evaluation remains limited. Since 2020, the Korean Society for Cytopathology has progressively incorporated DC into its national QAP, including digital proficiency testing (PT), sample adequacy testing (SAT), a customizable PT module, and a self-assessment module (SAM), aiming for full digital implementation by 2026. Methods: This 5-year study assessed diagnostic concordance between conventional and digital PT formats and analyzed participant feedback on service quality and digital image usability across PT, SAT, and SAM. Parallel testing was conducted during the transitional phase, and satisfaction was measured through structured surveys. Results: Participation in digital PT increased from 48 institutions in 2020 to 93 in 2024, while digital SAT participation rose from 29 to 71 between 2022 and 2024. In 2023, 56 institutions joined SAM. Diagnostic concordance rates were comparable between digital and conventional PTs (78.6%–84.6% vs. 82.0%–85.1%), including similar category C (major discordance) rates. Satisfaction with digital PT services and image quality exceeded 85%, and over 90% of institutions reported positive feedback on SAT and SAM. Over 80% were satisfied with the customizable PT module. Conclusions: DC is a reliable and effective modality for cytopathology QAP. It demonstrates diagnostic equivalence to conventional methods and high user satisfaction, supporting its broader implementation in national quality assurance frameworks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
- Frozen section histopathology and preanalytical factors affecting nucleic acid integrity in biobanked fresh-frozen human cancer tissues
- Soungeun Kim, Jaewon Kang, Boyeon Kim, Yoonjin Kwak, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):398-407. Published online September 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.22
- 5,371 View
- 207 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
In this study, we evaluated the effects of storage duration and ischemic time on nucleic acid quality of fresh-frozen tissue (FFT) from colon adenocarcinoma (COAD), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and renal cell carcinoma (RCC) collected at the Cancer Tissue Bank of Seoul National University Hospital. Methods: A total of 102 FFT samples were analyzed to compare DNA integrity number (DIN) and RNA integrity number (RIN) according to storage duration and ischemic time. Additionally, the effects of histopathologic features—such as tumor cell proportion, inflammatory cell infiltration, and stromal fibrosis—on nucleic acid quality were evaluated. Results: DIN and RIN remained stable overall even though the storage duration increased, with no statistically significant differences observed. In particular, there was almost no decrease in RNA quality in HCC and RCC samples, but in COAD samples, RIN tended to decrease slightly as the storage duration increased. No significant difference was confirmed between ischemic time and nucleic acid quality, but in COAD tissue, RNA quality variability tended to increase as the ischemic time increased. Furthermore, RIN increased as the tumor cell proportion increased, whereas inflammatory cell infiltration and extracellular mucin pool were identified as independent negative predictors of RIN. Conclusions: This study confirmed that nucleic acid integrity can be maintained even during long-term storage of FFT and demonstrated that histologic features are closely related to RNA quality. This study would contribute to the establishment of quality assessment and management standards for biobank FFT samples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
Zhiyong Liu, Jianhe Wu, Yuanwei Li, Qiang Lu, Yongjun Yang
BMC Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
Letter to the Editor
- Variation in mitotic counting and risk classification practices for gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a survey of pathologists in South Korea
- In Hye Song, Soomin Ahn, Jeong-Hyeon Jo, Young Soo Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):348-352. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.14
- 2,337 View
- 30 Download
- 1 Crossref
Newsletter
- What’s new in medical renal pathology 2025: Updates on podocytopathy and immunofluorescence staining in medical kidney
- Astrid Weins, Ibrahim Batal, Paola Romagnani, Geetika Singh, Rahul Raj, Nicole Andeen, Jonathan Zuckerman, Martina Uzzo, Mariam Priya Alexander, Anjali Satoskar
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):269-272. Published online July 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.19
- 6,082 View
- 364 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Diffuse podocytopathy, including minimal change disease and primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, is a common cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults and children. It is increasingly recognized to be autoimmune-mediated associated with anti-nephrin and other emerging anti-slit diaphragm antibodies, and can recur in the kidney allograft. Immunofluorescence is routinely used in evaluation of kidney biopsies, and updates include those on fibrillar diseases, monoclonal staining, lupus-like staining, and use of antibody KM55 in IgA-dominant glomerulonephritis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Opportunities and challenges in recurrent diffuse podocytopathy post-transplantation: the critical value of the definition
Rachel Nuccitelli, Amadea Toutoungis, Elena Martinelli, Simone Sanna-Cherchi, Astrid Weins, Heather K. Morris, Andrew S. Bomback, Ibrahim Batal
Frontiers in Immunology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Opportunities and challenges in recurrent diffuse podocytopathy post-transplantation: the critical value of the definition
Original Articles
- Pancreatic cancer in liquid-based cytology: cytological features and cell block utility from 254 fine-needle aspiration samples
- Jaeyong Min, Wookjin Oh, Baek-hui Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):249-261. Published online July 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.05.27
- 3,155 View
- 213 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Despite the increasing use of liquid-based cytology (LBC) for pancreatic cancer diagnosis, relatively few studies have directly examined such research. This study analyzed the cytopathological features of pancreatic cancer in LBC and demonstrated the utility of cell blocks in diagnosing pancreatic lesions. Methods: A retrospective review identified LBC from 254 pancreatic fine-needle aspirations (FNAs) (221 patients). FNAs were categorized into five subgroups based on cytopathological, clinical, and histopathological findings. Two pathologists evaluated cytological features in LBC samples, cell blocks, and tissue slides. Comparative analysis assessed differences between groups. Results: Compared to benign lesions, LBC of pancreatic cancer more frequently showed a necrotic background, intermediate to high cellularity, mixed architecture, nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio >0.8, anisonucleosis >4:1, irregular and thick nuclear membranes, multinucleated tumor cells, hyperchromatic nuclei, coarse to clumped chromatin, and a prominent single nucleolus. In cases of conventional pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, the palliative treatment subgroup showed a higher incidence of necrotic background than the resection subgroup. In the cell block analysis, tumor cells not identified in LBC slides were detected in 16 FNAs. Additionally, 13 FNAs contributed to differential diagnosis: ancillary tests aided diagnosis in 12 FNAs, while histopathological evaluation of the cell block slide alone was helpful in one case. Conclusions: The cytological features of pancreatic cancer in LBC are similar to those observed in conventional smears, with a necrotic background suggesting advanced (unresectable) disease. The cell block methodology minimizes tumor cell loss and facilitates differential diagnosis by enabling ancillary testing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytology and small biopsy diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Maria Pimenova, Matthew W. Rosenbaum
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2026; 43(2): 150992. CrossRef
- Cytology and small biopsy diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- AMACR is a highly sensitive and specific immunohistochemical marker for diagnosing prostate cancer on biopsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Johannes Cansius Prihadi, Stevan Kristian Lionardi, Nicolas Daniel Widjanarko, Steven Alvianto, Fransiskus Xaverius Rinaldi, Archie Fontana Iskandar
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):235-248. Published online July 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.04.16
- 7,001 View
- 228 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) is the preferred biomarker for distinguishing malignant from benign glands in prostate biopsies, showing high sensitivity and specificity for prostate cancer. A meta-analysis of immunohistochemistry (IHC) for AMACR is essential to further assess its diagnostic accuracy across diverse sample sources. Methods: A systematic search of databases including MEDLINE, ScienceDirect, ProQuest, Google Scholar, and the Cochrane Library was performed, focusing on studies of AMACR to diagnose prostate cancer, particularly in biopsy samples analyzed through IHC over the last 20 years. Quality of studies was assessed using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies 2 tool, followed by a meta-analysis of regions and subgroups to calculate summary estimates of diagnostic test accuracy. Results: In the final analysis, 37 studies, with a pooled size of 5,898 samples, were included from the examination of 94 full-text papers. Among them, 27 studies with similar sample sources and testing methodologies underwent meta-analysis, yielding a combined sensitivity estimate of 0.90 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.86 to 0.93) and specificity of 0.91 (95% CI, 0.83 to 0.95), both with significant heterogeneity (p < .01). The region beneath the hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.93 to 0.97), positive likelihood ratio was 9.6 (95% CI, 5.3 to 17.4), negative likelihood ratio was 0.11 (95% CI, 0.08 to 0.15), and diagnostic odds ratio was 88 (95% CI, 42 to 181). Conclusions: Our meta-analysis findings substantiate AMACR as a highly accurate tool for diagnosing prostate cancer, specifically in biopsy samples, via immunohistochemical staining. Further studies involving diverse samples are needed to enhance our understanding of the AMACR diagnostic accuracy in a range of clinical settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pathogenesis-Guided Biomarker Assessment: A Shift in Prostate Cancer Diagnostics
Jessica M. Logan, Victoria Malone, John J. O’Leary, Doug A. Brooks
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(24): 11786. CrossRef
- Pathogenesis-Guided Biomarker Assessment: A Shift in Prostate Cancer Diagnostics
- Primary Merkel cell carcinoma of the salivary gland: a clinicopathologic study of four cases with a review of literature
- Gyuheon Choi, Joon Seon Song, Hee Jin Lee, Gi Hwan Kim, Young Ho Jung, Yoon Se Lee, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(3):171-179. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.03.25
- 3,897 View
- 156 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Primary Merkel cell carcinoma of the salivary gland is currently not listed in the World Health Organization classification. However, cases of Merkel cell type neuroendocrine carcinomas of the salivary gland with perinuclear cytokeratin 20 positivity have been intermittently reported. We here investigated the clinicopathologic features of additional cases.
Methods
Data of four cases of Merkel cell type small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the salivary gland were retrieved. To confirm the tumors’ primary nature, clinical records and pathologic materials were reviewed. Optimal immunohistochemical staining was performed to support the diagnosis.
Results
All tumors were located in the parotid gland. Possibilities of metastasis were excluded in all cases through a meticulous clinicopathological review. Tumor histology was consistent with the diagnosis of small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Tumors’ immunohistochemical phenotypes were consistent with Merkel cell carcinoma, including Merkel cell polyomavirus large T antigen positivity in two of the four cases.
Conclusions
Merkel cell carcinomas can originate in salivary glands and are partly associated with Merkel cell polyomavirus infection as in cutaneous Merkel cell carcinomas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parotid intranodal metastasis of Merkel cell carcinoma: a rare case report
Tong Gao, Dengshun Wang, Hongwei Yu, Yu’e Wang, Haibin Lu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Parotid intranodal metastasis of Merkel cell carcinoma: a rare case report
- Categorizing high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma into clinically relevant subgroups using deep learning–based histomic clusters
- Byungsoo Ahn, Eunhyang Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):91-104. Published online February 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.23
- 5,388 View
- 254 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSC) exhibits significant heterogeneity, posing challenges for effective clinical categorization. Understanding the histomorphological diversity within HGSC could lead to improved prognostic stratification and personalized treatment approaches. Methods: We applied the Histomic Atlases of Variation Of Cancers model to whole slide images from The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset for ovarian cancer. Histologically distinct tumor clones were grouped into common histomic clusters. Principal component analysis and K-means clustering classified HGSC samples into three groups: highly differentiated (HD), intermediately differentiated (ID), and lowly differentiated (LD). Results: HD tumors showed diverse patterns, lower densities, and stronger eosin staining. ID tumors had intermediate densities and balanced staining, while LD tumors were dense, patternless, and strongly hematoxylin-stained. RNA sequencing revealed distinct patterns in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and energy metabolism, with upregulation in the HD, downregulation in the LD, and the ID positioned in between. Survival analysis showed significantly lower overall survival for the LD compared to the HD and ID, underscoring the critical role of mitochondrial dynamics and energy metabolism in HGSC progression. Conclusions: Deep learning-based histologic analysis effectively stratifies HGSC into clinically relevant prognostic groups, highlighting the role of mitochondrial dynamics and energy metabolism in disease progression. This method offers a novel approach to HGSC categorization. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Learning Disabilities in the 21st Century: Integrating Neuroscience, Education, and Technology for Better Outcomes
Syed Mohammed Basheeruddin Asdaq, Ahmad H. Alhowail, Syed Imam Rabbani, Naira Nayeem, Syed Mohammed Emaduddin Asdaq, Faiqa Nausheen
SAGE Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Learning Disabilities in the 21st Century: Integrating Neuroscience, Education, and Technology for Better Outcomes
Review
- Post-transplant liver biopsies: a concise and practical approach for beginners
- Mohamad Besher Ourfali, David Hirsch, Marianna Scranton, Tony El Jabbour
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):1-10. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.15
- 5,002 View
- 398 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Exposure to post-transplant liver biopsies varies among pathology residencies and largely depends on the institution's training program, particularly if the hospital has a liver transplant program. The interpretation of biopsies from transplanted livers presents its own set of challenges, even for those with a solid understanding of non-transplant medical liver biopsies. In this review, we aim to provide a succinct, step-by-step approach to help you interpret liver transplant biopsies. This article may be beneficial for residents interested in liver pathology, gastrointestinal and liver pathology fellows in the early stages of training, clinical gastroenterology and hepatology fellows, hepatologists and general pathologists who are curious about this niche.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Histological and Molecular Evaluation of Liver Biopsies: A Practical and Updated Review
Joon Hyuk Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(16): 7729. CrossRef
- Histological and Molecular Evaluation of Liver Biopsies: A Practical and Updated Review
Case Study
- Primary renal BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma in a female patient: case report
- Somang Lee, Binnari Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):84-90. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.30
- 5,168 View
- 179 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BCOR-rearranged sarcoma was classified by the World Health Organization in 2020 as a new subgroup of undifferentiated small round-cell sarcoma. It is known to occur very rarely in the kidney. This report presents the first case of a primary renal BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma in a 22-year-old woman. An 8-cm cystic mass was identified in the left kidney by abdominal pelvic computed tomography. Histopathologic examination revealed the mass to be composed of small round to oval or spindle cells with fibrous septa and a delicate vascular network. A BCOR::CCNB3 fusion was detected by next-generation sequencing–based molecular testing. BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma presents diagnostic difficulties, highlighting the importance of recognizing its histological features. Immunohistochemical markers are helpful for diagnosis, but genetic molecular testing is necessary for accurate diagnosis. These tumors have a very poor and aggressive prognosis, and an optimal therapeutic regimen has not yet been defined. Therefore, further studies are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Update on the management of BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma
Jungo Imanishi, Kenji Sato, Yoshinao Kikuchi, Asako Yamamoto, Shiori Watabe, Taisuke Matsuyama, Chiaki Sato, Hiroshi Kobayashi, Hirotaka Kawano
Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology.2025; 55(10): 1097. CrossRef
- Update on the management of BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma
Original Articles
- Fine needle aspiration cytology diagnoses of follicular thyroid carcinoma: results from a multicenter study in Asia
- Hee Young Na, Miyoko Higuchi, Shinya Satoh, Kaori Kameyama, Chan Kwon Jung, Su-Jin Shin, Shipra Agarwal, Jen-Fan Hang, Yun Zhu, Zhiyan Liu, Andrey Bychkov, Kennichi Kakudo, So Yeon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):331-340. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.12
- 6,480 View
- 267 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
This study was designed to compare diagnostic categories of thyroid fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) and incidence of thyroid tumors in the multi-institutional Asian series with a special focus on diagnostic category IV (suspicious for a follicular neoplasm) and follicular thyroid carcinomas (FTCs). Methods: Distribution of FNAC categories, incidence of thyroid tumors in resection specimens and cytologic diagnoses of surgically confirmed follicular adenomas (FAs) and FTCs were collected from 10 institutes from five Asian countries and were compared among countries and between FAs and FTCs. Results: The frequency of category IV diagnoses (3.0%) in preoperative FNAC were significantly lower compared to those in Western countries (10.1%). When comparing diagnostic categories among Asian countries, category IV was more frequent in Japan (4.6%) and India (7.9%) than in Taiwan (1.4%), Korea (1.4%), and China (3.6%). Similarly, incidence of FAs and FTCs in surgical resection specimens was significantly higher in Japan (10.9%) and India (10.1%) than in Taiwan (5.5%), Korea (3.0%), and China (2.5%). FTCs were more commonly diagnosed as category IV in Japan (77.5%) than in Korea (33.3%) and China (35.0%). Nuclear pleomorphism, nuclear crowding, microfollicular pattern, and dyshesive cell pattern were more common in FTCs compared with FAs. Conclusions: Our study highlighted the difference in FNAC diagnostic categories of FTCs among Asian countries, which is likely related to different reporting systems and thyroid cancer incidence. Cytologic features such as nuclear pleomorphism, nuclear crowding, microfollicular pattern, and dyshesive cell pattern were found to be useful in diagnosing FTCs more effectively. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Misdiagnosed follicular adenoma with 11 year postoperative liver and lung metastases a case report and literature review
Kai-Li Yang, Heng-Tong Han, Shou-Hua Li, Xiao-Xiao Li, Ze Yang, Li-Bin Ma, Yong-Xun Zhao
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Misdiagnosed follicular adenoma with 11 year postoperative liver and lung metastases a case report and literature review
- Diagnostic challenges in the assessment of thyroid neoplasms using nuclear features and vascular and capsular invasion: a multi-center interobserver agreement study
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Mutiah Mutmainnah, Maria Francisca Ham, Dina Khoirunnisa, Abdillah Hasbi Assadyk, Husni Cangara, Aswiyanti Asri, Diah Prabawati Retnani, Fairuz Quzwain, Hasrayati Agustina, Hermawan Istiadi, Indri Windarti, Krisna Murti, Muhammad Takbir, Ni Made Mahastuti, Nila Kurniasari, Nungki Anggorowati, Pamela Abineno, Yulita Pundewi Setyorini, Kennichi Kakudo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):299-309. Published online September 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.25
- Correction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2025;59(3):201
- 5,431 View
- 411 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The diagnosis of thyroid neoplasms necessitates the identification of distinct histological features. Various education/hospital centers located in cities across Indonesia likely result in discordances among pathologists when diagnosing thyroid neoplasms.
Methods
This study examined the concordance among Indonesian pathologists in assessing nuclear features and capsular and vascular invasion of thyroid tumors. Fifteen pathologists from different centers independently assessed the same 14 digital slides of thyroid tumor specimens. All the specimens were thyroid neoplasms with known BRAFV600E and RAS mutational status, from a single center. We evaluated the pre- and post-training agreement using the Fleiss kappa. The significance of the training was evaluated using a paired T-test.
Results
Baseline agreement on nuclear features was slight to fair based on a 3-point scoring system (k = 0.14 to 0.28) and poor to fair based on an eight-point system (k = –0.02 to 0.24). Agreements on vascular (κ = 0.35) and capsular invasion (κ = 0.27) were fair, whereas the estimated molecular type showed substantial agreement (κ = 0.74). Following the training, agreement using the eight-point system significantly improved (p = 0.001).
Conclusions
The level of concordance among Indonesian pathologists in diagnosing thyroid neoplasm was relatively poor. Consensus in pathology assessment requires ongoing collaboration and education to refine diagnostic criteria. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Dina Khoirunnisa, Salinah, Maria Francisca Ham
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 75: 152434. CrossRef
- Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Case Study
- Colorectal cancer with a germline BRCA1 variant inherited paternally: a case report
- Kyoung Min Kim, Min Ro Lee, Ae Ri Ahn, Myoung Ja Chung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):341-345. Published online September 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.08.14
- 7,411 View
- 308 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BRCA genes have well-known associations with breast and ovarian cancers. However, variations in the BRCA gene, especially germline variations, have also been reported in colorectal cancer (CRC). We present the case of a rectal cancer with a germline BRCA1 variation inherited from the paternal side. A 39-year-old male was admitted with rectal cancer. The patient underwent surgical resection and the pathologic diagnosis was adenocarcinoma. Next-generation sequencing was performed and a BRCA1 variant was detected. Reviewing the public database and considering the young age of the patient, the variant was suggested to be germline. The patient’s father had had prostate cancer and next-generation sequencing testing revealed an identical BRCA1 variant. In the BRCA cancer group, there is relatively little attention paid to male cancers. The accumulation of male CRC cases linked to BRCA variations may help clarify the potential pathological relationship between the two.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Aggressive Right-Sided Colon Cancer in a Young Adult: Triple-Whammy Mutations (POLE, KRAS, BRCA1/2) Highlight Emerging Genetic Associations
Ravi Patel, Ganesh Kumar, Yash Shah, Dushyant Singh Dahiya, Sumant Inamdar
ACG Case Reports Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Aggressive Right-Sided Colon Cancer in a Young Adult: Triple-Whammy Mutations (POLE, KRAS, BRCA1/2) Highlight Emerging Genetic Associations

 E-submission
E-submission













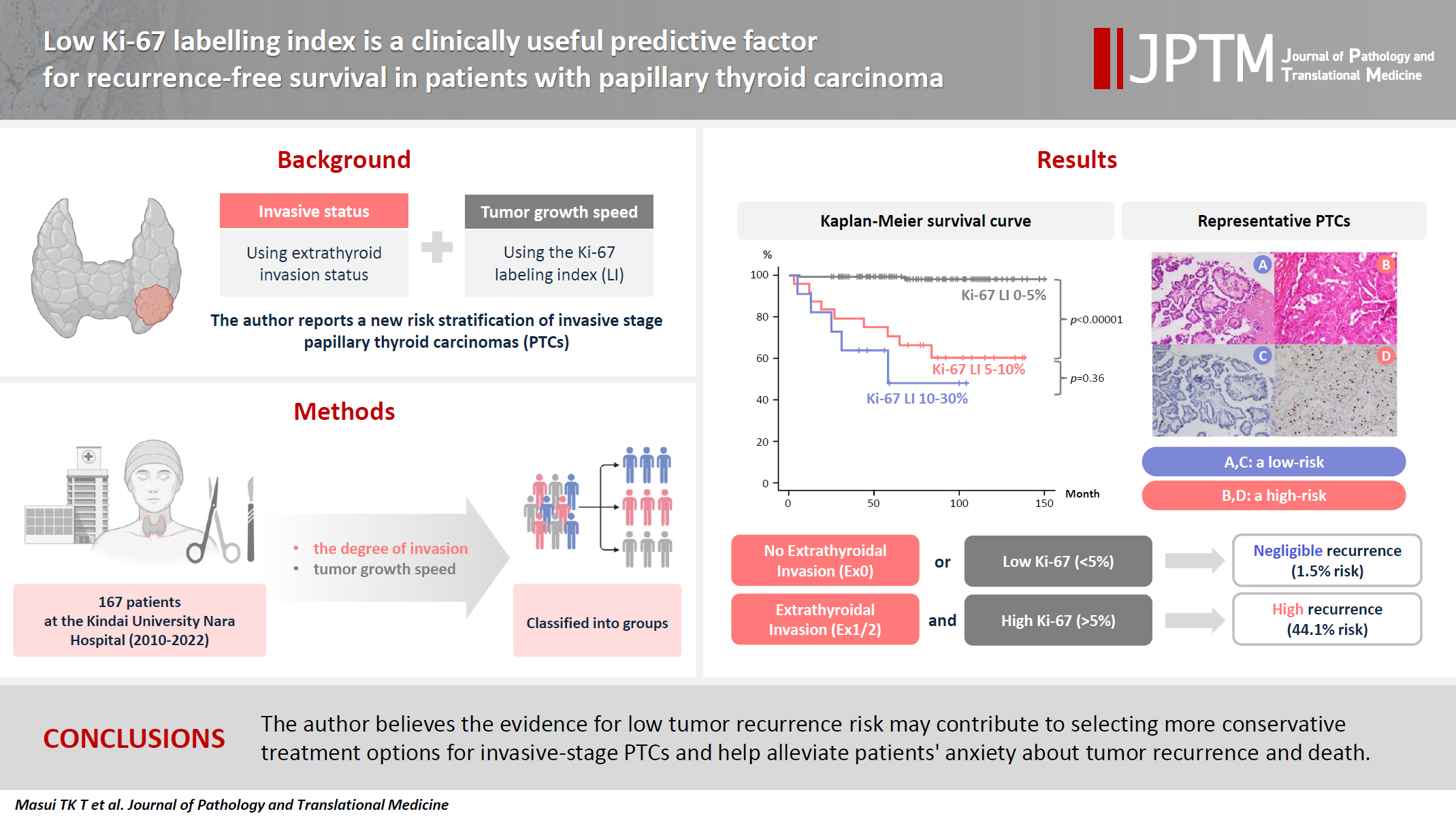





















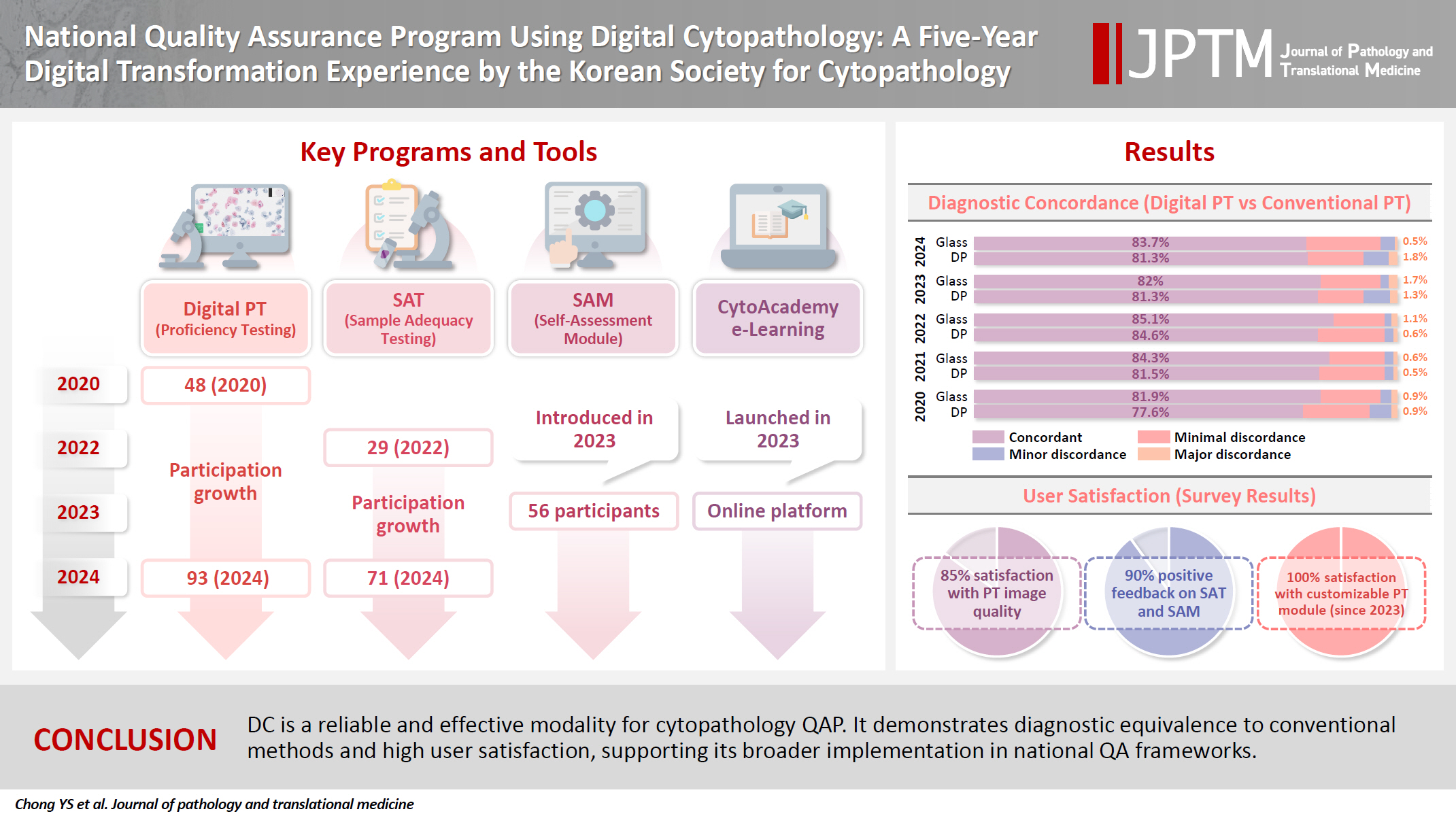








 First
First Prev
Prev



