Funded articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Funded articles
Original Article
- Clinicopathological and molecular mechanisms of CLDN18.2 in gastric cancer aggressiveness: a high-risk population study with multi-omics profiling
- Hengquan Wu, Mei Li, Gang Wang, Peiqing Liao, Peng Zhang, Luxi Yang, Yumin Li, Tao Liu, Wenting He
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):47-57. Published online January 5, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.11
- Funded: The Fundamental Research Funds for The Science and Technology Program of Gansu Province, International science and technology cooperation project of Gansu Provincial Science and Technology Department
- 2,001 View
- 180 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The tight junction protein claudin18.2 (CLDN18.2) has been implicated in poor prognosis and suboptimal immunotherapy response in gastric cancer (GC). This study investigates the clinicopathological relevance of CLDN18.2 expression and its association with molecular subtypes in GC patients from a high-incidence region, combining transcriptomic and proteomic approaches to explore how CLDN18.2 contributes to progression and metastasis.
Methods
A retrospective cohort of 494 GC patients (2019–2024) underwent immunohistochemical analysis for CLDN18.2, Epstein-Barr virus (Epstein–Barr virus–encoded RNA), p53, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and mismatch repair proteins (MLH1, MSH2, PMS2, and MSH6). CLDN18.2 positivity was defined as moderate to strong (2+/3+) membranous staining in ≥75% of tumor cells. Clinicopathological correlations, biomarker associations, and survival outcomes were evaluated. Transcriptomic and proteomic sequencing was performed to explore molecular mechanisms.
Results
CLDN18.2 positivity was observed in 26.9% (133/494) of gastric adenocarcinomas. CLDN18.2-positive tumors correlated with TNM stage (p = .003) and shorter overall survival (p = .018). No associations were identified with age, sex, HER2 status, microsatellite instability, or Epstein-Barr virus infection. Transcriptomic profiling revealed CLDN18.2-high tumors enriched in pathways involving cell junction disruption, signaling regulation, and immune modulation. Proteomic profiling showed that tumors with high CLDN18.2 were enriched in multiple mechanism-related pathways such as integrated metabolic reprogramming, cytoskeletal recombination, immune microenvironment dysregulation, and pro-survival signaling. These mechanisms may collectively contribute to tumor progression and metastasis.
Conclusions
CLDN18.2 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in GC patients. Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses demonstrate that CLDN18.2 promotes tumor progression and metastasis, underscoring its potential as an independent prognostic factor in regions with a high incidence of GC.
Review Article
- A comprehensive review of ossifying fibromyxoid tumor: insights into its clinical, pathological, and molecular landscape
- Kyriakos Chatzopoulos, Antonia Syrnioti, Mohamed Yakoub, Konstantinos Linos
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):6-19. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.02
- Funded: MSK NIH
- 2,254 View
- 117 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor (OFMT) is a rare mesenchymal neoplasm first described in 1989. It typically arises in the superficial soft tissues of the extremities as a slow-growing, painless mass. Histologically, it is commonly characterized by a multilobular architecture composed of uniform epithelioid cells embedded in a fibromyxoid matrix, often surrounded by a rim of metaplastic bone. While classic cases are readily identifiable, the tumor's histopathological heterogeneity can mimic a range of benign and malignant neoplasms, posing significant diagnostic challenges. Molecularly, most OFMTs harbor PHF1 rearrangements, commonly involving fusion partners such as EP400, MEAF6, or TFE3. This review underscores the importance of an integrated diagnostic approach- incorporating histopathological, immunohistochemical, and molecular data- to accurately classify OFMT and distinguish it from its mimics. Expanding awareness of its morphologic and molecular spectrum is essential for precise diagnosis, optimal patient management, and a deeper understanding of this enigmatic neoplasm.
Original Articles
- Significance of KM55 immunohistochemical staining in the diagnosis and prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Hoe In Jeong, Beom Jin Lim, Minsun Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):69-82. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.17
- Funded: The Korean Society of Pathologist
- 2,035 View
- 151 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) plays a crucial role in IgA nephropathy (IgAN). The monoclonal antibody KM55 has emerged as a simplified method for detecting Gd-IgA1; however, the clinicopathological significance of immunohistochemistry for Gd-IgA1 remains underexplored. This study evaluated the prognostic and clinicopathological significance of KM55 immunohistochemistry in IgAN. Methods: A total of 114 native kidney biopsies showing at least mild mesangial IgA positivity on immunofluorescence were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were categorized as having IgAN or non-IgAN diseases. The KM55 immunohistochemical staining was graded as 0, 1+, 2+, 3, or 4+. Data on Oxford classification, laboratory parameters, and renal outcomes were collected. Results: The IgAN group showed significantly higher KM55 scores than the non-IgAN group (median: 3 vs. 1; p < .001). IgAN cases were further stratified into KM55-high (≥3+, n = 38) and -low groups (≤2+, n = 37). The KM55-high group had significantly higher diastolic blood pressure, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, urine protein/creatinine ratio, and Oxford mesangial hypercellularity scores, along with lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and serum albumin. Cox analysis revealed significantly poorer outcomes in the KM55-high group for chronic kidney disease stage 4 (p = .015), end-stage renal disease (p = .024), and 75% eGFR decline (p = .016). Conclusions: Mesangial Gd-IgA1 deposition graded by KM55 immunohistochemistry may be a useful adjunct for IgAN diagnosis and a potential prognostic biomarker.
- Correlations and prognostic impacts of tumor spread through airspaces in surgically resected non–small cell lung cancer: a retrospective study from Jordan
- Ola Abu Al Karsaneh, Amani Al-Rousan, Sofian Al Shboul, Mohammed El-Sadoni, Anas Hayajneh, Moath Alrjoub, Sura Al-Rawabdeh, Tareq Saleh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):92-106. Published online January 9, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.15
- Funded: Hashemite University
- 2,047 View
- 119 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Spread through air spaces (STAS) has been identified as an invasion pattern in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This study evaluated the association between tumor STAS and various clinicopathological parameters of NSCLC, with emphasis on the prognostic role of STAS. Methods: We evaluated 96 cases of NSCLC for STAS. STAS-positive cases were graded according to the distance between the edge of the primary tumor and the furthest STAS, in millimeters, or the number of alveoli separating STAS from the tumor. Results: STAS was observed in 33 patients (34.4%). In 28 cases, STAS was located in airspaces >3 alveoli away from the primary tumor. In 18 cases, STAS was found in airspaces > 2.5 mm away from the edge of the primary tumor. Morphologically, 18 cases of STAS demonstrated a solid nest pattern, eight showed a micropapillary cluster pattern, and seven exhibited a single-cell pattern. In multivariate analysis, only high tumor grade (p = .001) was independently associated with STAS in NSCLC. The presence of STAS (p = .047), lymphovascular invasion (p = .001), positive surgical margin (p = .021), adenocarcinoma histology (p = .020), and postoperative therapy (p = .049) showed a statistically significant lower overall survival (OS). However, multivariate analyses showed that STAS is not an independent predictor of OS in NSCLC. In addition, STAS-positive cases with an extension of >2.5 mm had significantly lower disease-free survival (DFS) (p = .018). Conclusions: The findings demonstrated that STAS is independently associated with a higher tumor grade and appears to have an adverse impact on OS and DFS in the examined subpopulation.
- Frozen section histopathology and preanalytical factors affecting nucleic acid integrity in biobanked fresh-frozen human cancer tissues
- Soungeun Kim, Jaewon Kang, Boyeon Kim, Yoonjin Kwak, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):398-407. Published online September 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.22
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
- 5,839 View
- 208 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
In this study, we evaluated the effects of storage duration and ischemic time on nucleic acid quality of fresh-frozen tissue (FFT) from colon adenocarcinoma (COAD), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and renal cell carcinoma (RCC) collected at the Cancer Tissue Bank of Seoul National University Hospital. Methods: A total of 102 FFT samples were analyzed to compare DNA integrity number (DIN) and RNA integrity number (RIN) according to storage duration and ischemic time. Additionally, the effects of histopathologic features—such as tumor cell proportion, inflammatory cell infiltration, and stromal fibrosis—on nucleic acid quality were evaluated. Results: DIN and RIN remained stable overall even though the storage duration increased, with no statistically significant differences observed. In particular, there was almost no decrease in RNA quality in HCC and RCC samples, but in COAD samples, RIN tended to decrease slightly as the storage duration increased. No significant difference was confirmed between ischemic time and nucleic acid quality, but in COAD tissue, RNA quality variability tended to increase as the ischemic time increased. Furthermore, RIN increased as the tumor cell proportion increased, whereas inflammatory cell infiltration and extracellular mucin pool were identified as independent negative predictors of RIN. Conclusions: This study confirmed that nucleic acid integrity can be maintained even during long-term storage of FFT and demonstrated that histologic features are closely related to RNA quality. This study would contribute to the establishment of quality assessment and management standards for biobank FFT samples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
Zhiyong Liu, Jianhe Wu, Yuanwei Li, Qiang Lu, Yongjun Yang
BMC Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
- Modified plasma-thrombin method using patient-derived plasma for cell block preparation in endobronchial ultrasound–guided transbronchial fine-needle aspiration
- Xizhe Zhang, Chunli Tang, Yingying Gu, Zeyun Lin, Shiqi Tang, Anzi Tan, Mengshi Li, Zhucheng Chen, Yuying Chen, Shi-yue Li, Juhong Jiang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):434-443. Published online November 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.20
- Funded: National Natural Science Foundation of China, Open Project of the State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease
- 2,927 View
- 97 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The plasma-thrombin method, which uses expired blood bank plasma as an ancillary component, has been widely used in cell block (CB) preparation. However, the application of expired blood bank plasma raises concerns about nucleic acid contamination. This study investigated the feasibility of using patient-derived plasma as a substitute for blood bank plasma in the modified plasma-thrombin (MPT) method for CB preparation in endobronchial ultrasound–guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) samples. Methods: A prospective study was conducted to compare the adequacy of CB preparation between a previously used self-clotting (SC) method and the MPT method. The EBUS-TBNA specimens from each targeted lesion were divided into paired samples: one processed using the SC method and the other using the MPT method, substituting the blood bank plasma with patient-derived plasma. Results: A total of 82 paired EBUS-TBNA samples from 59 patients were analyzed. The diagnostic yield of the SC method and the MPT method was 86.6% and 97.6%, respectively. Among patients diagnosed with non–small cell lung cancer, the adequacy rate for molecular testing was 79.2% with the SC method and 91.7% with the MPT method. Conclusions: The MPT method significantly improved the cellular yield of EBUS-TBNA–derived CBs. Using patient-derived fresh plasma rather than expired blood bank plasma avoids a known contamination risk. The additional step modestly prolongs the procedure and introduces minimal risks by vein puncture. This approach is generally considered cost-effective.
- Diagnostic value of cytology in detecting human papillomavirus–independent cervical malignancies: a nation-wide study in Korea
- Hye-Ra Jung, Junyoung Shin, Chong Woo Yoo, Eun Na Kim, Cheol Lee, Kyeongmin Kim, Ho-chang Lee, Yonghee Lee, Ji Hye Kim, Soo Jin Jung, Yumin Chung, Joo Yeon Kim, Hye Eun Park, Tae Hoen Kim, Wonae Lee, Min-Sun Cho, Ran Hong, Yoon Jung Choi, Younghee Choi, Young Sub Lee, Sang-Ryung Lee, Myunghee Kang, Young Jin Seo, Seung-Sook Lee, Yoon-Jung Hwang, Hyun-Jung Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):444-452. Published online November 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.21
- Funded: The Korean Society for Cytopathology
- 3,866 View
- 138 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) independent cervical malignancies (HPV-IDCMs) have recently been classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) 5th edition. These malignancies have historically received limited attention due to their rarity and the potential for evasion of HPV-based screening.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 5,854 biopsy-confirmed cervical malignancies from 22 institutions over 3 years (July 2020–June 2023). Histologic classification followed the WHO guidelines. HPV independence was confirmed by dual negativity for p16 and HPV; discordant cases (p16-positive/HPV-negative) underwent additional HPV testing using paraffin-embedded tissue. Cytological results were matched sequentially to histological confirmation.
Results
The prevalence of HPV-IDCM was 4.4% (257/5,854) overall and was 3.6% (208/5,805 cases) among primary cervical malignancy. Patient age of HPV-IDCM was 29 to 89 years (median, 57.79). Its histologic subtypes included primary adenocarcinoma (n = 116), endometrial adenocarcinoma (n = 35), squamous cell carcinoma (n = 72), metastatic carcinoma (n = 14), carcinoma, not otherwise specified (n = 10), neuroendocrine carcinoma (n = 3), and others (n = 7). Among 155 cytology-histological matched cases, the overall and primary Pap test detection rates were 85.2% (132/155) and 83.2% (104/125), respectively. The interval between cytology and histologic confirmation extended up to 38 months.
Conclusions
HPV-IDCMs comprised 3.6% of primary cervical malignancies with a high detection rate via cytology (83.2%). These findings affirm the value of cytological screening, particularly in patients with limited screening history or at risk for HPV-independent lesions, and may guide future screening protocols.
- Unraveling the crucial role of CCL3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: bioinformatics and immunohistochemical insights
- Xiaopeng Guo, Zhen Sun, Ya Liang, Aoshuang Chang, Junjun Ling, Houyu Zhao, Xianlu Zhuo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):281-290. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.05.23
- Funded: Guizhou Science and Technology Project, Cultivation project of Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University
- 1,797 View
- 142 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
C-C motif chemokine ligand 3 (CCL3) is a crucial chemokine that plays a fundamental role in the immune microenvironment and is closely linked to the development of various cancers. Despite its importance, there is limited research regarding the expression and function of CCL3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Therefore, this study seeks to examine the expression of CCL3 and assess its clinical significance in NPC using bioinformatics analysis and experiments. Methods: The bioinformatics approach was employed to assess the expression and function of CCL3 in NPC. Subsequently, protein expression of CCL3 was detected in an NPC cohort using immunohistochemistry based on a tissue microarray. The relationship between CCL3 expression and clinical features was then investigated. Results: A total of 20 CCL3-related genes and 14 possible target genes were identified through bioinformatics analysis, many of which play crucial roles in pathways such as chemokine signaling pathway and transcriptional misregulation in cancer signaling pathways. CCL3 was found to be associated with drug resistance and various immune cell infiltrations. In NPC, CCL3 expression was significantly higher than normal controls, and high expression of CCL3 correlated with cervical lymph node metastasis, tumor recurrence, advanced clinical stage, and poor prognosis. Conclusions: CCL3 may be a key gene in the initiation and progression of NPC. It has the potential to serve as both a diagnostic biomarker and a therapeutic target for NPC.
- Evaluation of potential prognostic significance of JUNB in human prostate cancer: a bioinformatic and histopathological study
- Noha R. Noufal, Einas M. Yousef, Mohamed Taha
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):291-305. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.06
- Funded: Dar Al Uloom University
- 1,911 View
- 123 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Prostate cancer is one of the most common malignancies in males worldwide. Serum prostate-specific antigen is a frequently employed biomarker in the diagnosis and risk stratification of prostate cancer; however, it is known for its low predictive accuracy for disease progression. New prognostic biomarkers are needed to distinguish aggressive prostate cancer from low-risk disease. This study aimed to identify and validate potential prognostic biomarkers of prostate cancer. Methods: Two prostate cancer datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus were analyzed to identify differentially expressed genes between benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostatic carcinoma. Immunohistochemistry was used to evaluate the JUNB proto-oncogene, a subunit of the AP-1 transcription factor (JUNB), in 70 prostate cancer patients and 10 BPH samples. Results: Our findings showed that JUNB was significantly enriched in prostate cancer-related pathways and biological processes. JUNB expression was considerably higher in prostatic adenocarcinoma patients than in BPH patients. Regarding JUNB expression in prostate cancer cases, lower levels of JUNB expression were associated with higher grades of prostatic adenocarcinoma. Lower JUNB expression was associated with a higher risk of prostatic adenocarcinoma progression and shorter overall survival. Conclusions: These results suggest that JUNB is a promising prognostic biomarker and a potential tumor suppressor in prostate cancer.
- A single-institution demographic study of pathologically proven kidney disease in South Korea over the last 33 years
- Hyejin Noh, Jiyeon Kim, Yeong Jin Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):306-319. Published online September 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.18
- Funded: Korea Medical Device Development Fund, Ministry of Science and ICT, Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Ministry of Food and Drug Safety
- 2,027 View
- 91 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
To date, epidemiological studies on the entire spectrum of kidney disease based on pathology have been rarely reported. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on patients diagnosed with kidney disease at Seoul St. Mary's Hospital between 1991 and 2023. Results: Among 7,803 patients with native kidney disease, glomerular disease (70.3%) was the most common, followed by tubulointerstitial (15.1%) and vascular disease (8.8%). In kidney biopsy, glomerular disease (77.8%) showed the highest frequency, particularly in those under 20s (95.6%) (p = .013). Primary glomerulonephritis (GN) (72.8%) was the predominant glomerular disease, with IgA nephropathy (IgAN) (47.3%) being the most common one. Tubulointerstitial and vascular diseases increased with age, showing the highest prevalence in those over 60 years (p = .008 and p = .032, respectively). Glomerular disease was diagnosed at a younger age (39.7 ± 16.7 years) than tubulointerstitial (49.1 ± 16.2) and vascular (48.1 ± 15.3) diseases (p < .001). When glomerular diseases were classified morphologically, proliferative GN (57.9%) was the most common, followed by non-proliferative (39.6%) and sclerosing (1.6%). When classified by etiology, primary GN accounted for the most (72.8%), followed by secondary (19.3%) and hereditary GN (5.7%). In nephrectomy, tubulointerstitial disease (64.6%) was the most common. Those with a tubulointerstitial disease had a higher mean age than those with a glomerular disease (p < .001). In cases where nephrectomy was performed for glomerular diseases, IgAN (34.1%) was the most common diagnosis. Conclusions: Kidney disease has been increasing in South Korea for 33 years. Glomerular disease was the most common across all age groups, tubulointerstitial and vascular diseases increased over 60 years.
- National quality assurance program using digital cytopathology: a 5-year digital transformation experience by the Korean Society for Cytopathology
- Yosep Chong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Soon Auck Hong, Sung Soon Kim, Bo-Sung Kim, Younghee Choi, Yoon Jung Choi, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Soo Jin Jung, Hoon Kyu Oh, Seung-Sook Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):320-333. Published online September 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.27
- Funded: The Korean Society for Cytopathology, National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
- 3,730 View
- 107 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Digital cytopathology (DC) is emerging as a transformative approach in quality assurance programs (QAP), though its comprehensive evaluation remains limited. Since 2020, the Korean Society for Cytopathology has progressively incorporated DC into its national QAP, including digital proficiency testing (PT), sample adequacy testing (SAT), a customizable PT module, and a self-assessment module (SAM), aiming for full digital implementation by 2026. Methods: This 5-year study assessed diagnostic concordance between conventional and digital PT formats and analyzed participant feedback on service quality and digital image usability across PT, SAT, and SAM. Parallel testing was conducted during the transitional phase, and satisfaction was measured through structured surveys. Results: Participation in digital PT increased from 48 institutions in 2020 to 93 in 2024, while digital SAT participation rose from 29 to 71 between 2022 and 2024. In 2023, 56 institutions joined SAM. Diagnostic concordance rates were comparable between digital and conventional PTs (78.6%–84.6% vs. 82.0%–85.1%), including similar category C (major discordance) rates. Satisfaction with digital PT services and image quality exceeded 85%, and over 90% of institutions reported positive feedback on SAT and SAM. Over 80% were satisfied with the customizable PT module. Conclusions: DC is a reliable and effective modality for cytopathology QAP. It demonstrates diagnostic equivalence to conventional methods and high user satisfaction, supporting its broader implementation in national quality assurance frameworks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Review Article
- Central nervous system tumors with BCOR internal tandem duplications: a systematic review of clinical, radiological, and pathological features in 69 cases
- Ji Young Lee, Sung Sun Kim, Hee Jo Baek, Tae-Young Jung, Kyung-Sub Moon, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Kyung-Hwa Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):273-280. Published online September 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.23
- Funded: Chonnam National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute
- 3,868 View
- 188 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Central nervous system tumors with BCL6 corepressor (BCOR) internal tandem duplications (ITDs) constitute a rare, recently characterized pediatric neoplasm with distinct molecular and histopathological features. To date, 69 cases have been documented in the literature, including our institutional case. These neoplasms predominantly occur in young children, with the cerebellum representing the most frequent anatomical location. Radiologically, these tumors present as large, well-circumscribed masses frequently demonstrating necrosis, hemorrhage, and heterogeneous enhancement. Histologically, they are characterized by a monomorphic cellular population featuring ependymoma-like perivascular pseudorosettes, myxoid stroma, and elevated mitotic activity. Immunohistochemically, these tumors exhibit sparse glial fibrillary acidic protein expression while consistently demonstrating positive staining for vimentin and CD56. The defining molecular hallmark is a heterozygous ITD within exon 15 of the BCOR gene, with insertions ranging from 9 to 42 amino acids in length. BCOR immunohistochemistry reveals nuclear positivity in 97.9% of examined cases, although this finding is not pathognomonic for BCOR ITDs. This comprehensive review synthesizes data from all published cases of this novel tumor entity, providing a detailed analysis of clinical presentation, neuroimaging findings, histopathological features with differential diagnostic considerations, therapeutic approaches, and prognostic outcomes.
Original Articles
- Lessons learned from the first 2 years of experience with thyroid core needle biopsy at an Indonesian national referral hospital
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Maria Francisca Ham, Retno Asti Werdhani, Erwin Danil Julian, Rafi Ilmansyah, Chloe Indira Arfelita Mangunkusumso, Tri Juli Edi Tarigan
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(3):149-160. Published online April 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.02.19
- Funded: Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital
- 3,998 View
- 192 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Core needle biopsy (CNB) improves diagnostic accuracy by providing precise tissue sampling for histopathological evaluation, overcoming the limitation of inconclusive fine-needle aspiration results. This study evaluated the diagnostic performance of CNB in assessing thyroid nodules, with additional analysis of the benefits of BRAF V600E and RAS Q61R immunohistochemical (IHC) markers.
Methods
This retrospective study enrolled patients with thyroid nodules who underwent CNB at Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital, Jakarta, from July 2022 to July 2024. CNB diagnoses were classified using the Korean Thyroid Association Criteria. Diagnostic efficacy was evaluated for neoplastic and malignant lesions, both independently and with BRAF V600E and RAS Q61R IHC. The correlation between nodule size and postoperative diagnosis was also analyzed.
Results
A total of 338 thyroid nodule samples was included, and 52.7% were classified as CNB category II. In the 104 samples with postoperative diagnoses, category IV was the most prevalent (39.4%). CNB demonstrated a sensitivity of 74% and a specificity of 100% for neoplastic lesions and 23.8% sensitivity and 100% specificity for malignant lesions. Combining CNB with BRAF V600E and RAS Q1R IHC increased the sensitivity to 77% for neoplastic lesions and 28.8% for malignant lesions. Larger nodules (>3 cm) were significantly associated with neoplastic (p = .005) and malignant lesions (p = .004).
Conclusions
CNB performs well in identifying neoplastic lesions, with or without BRAF V600E and RAS Q61R IHC, but its low sensitivity for malignant lesions warrants caution. While CNB categories V–VI indicate malignancy, the possibility of malignancy in categories I–IV should not be overlooked.
- Diagnostic yield of fine needle aspiration with simultaneous core needle biopsy for thyroid nodules
- Mohammad Ali Hasannia, Ramin Pourghorban, Hoda Asefi, Amir Aria, Elham Nazar, Hojat Ebrahiminik, Alireza Mohamadian
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(3):180-187. Published online April 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.03.04
- Funded: Tehran University of Medical Sciences
- 11,881 View
- 244 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) is a widely utilized technique for assessing thyroid nodules; however, its inherent non-diagnostic rate poses diagnostic challenges. The present study aimed to evaluate and compare the diagnostic efficacy of FNA, core needle biopsy (CNB), and their combined application in the assessment of thyroid nodules.
Methods
A total of 56 nodules from 50 patients was analyzed using both FNA and simultaneous CNB. The ultrasound characteristics were categorized according to the American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data Systems classification system. The study compared the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of FNA, CNB, and the combination of the two techniques.
Results
The concordance between FNA and CNB was notably high, with a kappa coefficient of 0.837. The sensitivity for detecting thyroid malignancy was found to be 25.0% for FNA, 66.7% for CNB, and 83.3% for the combined FNA/CNB approach, with corresponding specificities of 84.6%, 97.4%, and 97.4%. The accuracy of the FNA/CNB combination was the highest at 94.1%.
Conclusions
The findings of this study indicate that both CNB and the FNA/CNB combination offer greater diagnostic accuracy for thyroid malignancy compared to FNA alone, with no significant complications reported. Integrating CNB with FNA findings may enhance management strategies and treatment outcomes for patients with thyroid nodules.
- Categorizing high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma into clinically relevant subgroups using deep learning–based histomic clusters
- Byungsoo Ahn, Eunhyang Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):91-104. Published online February 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.23
- Funded: Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Yonsei University College of Medicine
- 5,478 View
- 254 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSC) exhibits significant heterogeneity, posing challenges for effective clinical categorization. Understanding the histomorphological diversity within HGSC could lead to improved prognostic stratification and personalized treatment approaches. Methods: We applied the Histomic Atlases of Variation Of Cancers model to whole slide images from The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset for ovarian cancer. Histologically distinct tumor clones were grouped into common histomic clusters. Principal component analysis and K-means clustering classified HGSC samples into three groups: highly differentiated (HD), intermediately differentiated (ID), and lowly differentiated (LD). Results: HD tumors showed diverse patterns, lower densities, and stronger eosin staining. ID tumors had intermediate densities and balanced staining, while LD tumors were dense, patternless, and strongly hematoxylin-stained. RNA sequencing revealed distinct patterns in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and energy metabolism, with upregulation in the HD, downregulation in the LD, and the ID positioned in between. Survival analysis showed significantly lower overall survival for the LD compared to the HD and ID, underscoring the critical role of mitochondrial dynamics and energy metabolism in HGSC progression. Conclusions: Deep learning-based histologic analysis effectively stratifies HGSC into clinically relevant prognostic groups, highlighting the role of mitochondrial dynamics and energy metabolism in disease progression. This method offers a novel approach to HGSC categorization. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Learning Disabilities in the 21st Century: Integrating Neuroscience, Education, and Technology for Better Outcomes
Syed Mohammed Basheeruddin Asdaq, Ahmad H. Alhowail, Syed Imam Rabbani, Naira Nayeem, Syed Mohammed Emaduddin Asdaq, Faiqa Nausheen
SAGE Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Learning Disabilities in the 21st Century: Integrating Neuroscience, Education, and Technology for Better Outcomes
- Characteristics of RET gene mutations in Vietnamese medullary thyroid carcinoma patients: a single-center analysis
- Van Hung Pham, Quoc Thang Pham, Minh Nguyen, Hoa Nhat Ngo, Thao Thi Thu Luu, Nha Dao Thi Minh, Trâm Đặng, Anh Tu Thai, Hoang Anh Vu, Dat Quoc Ngo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):125-132. Published online March 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.01.18
- Funded: University of Medicine and Pharmacy
- 5,309 View
- 189 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The RET gene point mutation is the main molecular alteration involved in medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) tumorigenesis. Previous studies in Vietnam mainly consisted of case reports, with limited data on larger sample sizes. In this study, we investigated RET gene mutations in exons 10, 11, and 16 and analyzed clinicopathological features of a series of Vietnamese MTC patients. Methods: We collected 33 tissue samples from patients with MTC and analyzed RET mutations using the Sanger sequencing method. The relationship between hotspot RET mutations (exons 10, 11, 16) and clinicopathological features were investigated. Results: Among the 33 analyzed cases, 17 tumors (52%) harbored RET mutations in exon 10, 11, or 16. A total of 10 distinct genetic alterations were identified, including eight missense mutations and two short indels. Of these, seven were classified as pathogenic mutations based on previous publications, with p.M918T being the most frequent (4 cases), followed by p.C634R (3 cases) and p.C618R (3 cases). Mutations were significantly associated with specific histological patterns, such as the nested/insular pattern (p=.026), giant cells (p=.007), nuclear pleomorphism (p=.018), stippled chromatin (p=.044), and amyloid deposits (p=.024). No mutations were found in germline analyses, suggesting these were somatic alterations. Conclusions: Our results provided the first comprehensive analysis of RET mutations in Vietnamese MTC patients. The most frequent mutation was p.M918T, followed by p.C634R and p.C618R. Mutations in these three exons were linked to specific histopathological features. Information on mutational profiles of patients with MTC will further aid in the development of targeted therapeutics to ensure effective disease management.
- The combination of CDX2 expression status and tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte density as a prognostic factor in adjuvant FOLFOX-treated patients with stage III colorectal cancers
- Ji-Ae Lee, Hye Eun Park, Hye-Yeong Jin, Lingyan Jin, Seung Yeon Yoo, Nam-Yun Cho, Jeong Mo Bae, Jung Ho Kim, Gyeong Hoon Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):50-59. Published online October 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.26
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
- 3,997 View
- 286 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Colorectal carcinomas (CRCs) with caudal-type homeobox 2 (CDX2) loss are recognized to pursue an aggressive behavior but tend to be accompanied by a high density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). However, little is known about whether there is an interplay between CDX2 loss and TIL density in the survival of patients with CRC.
Methods
Stage III CRC tissues were assessed for CDX2 loss using immunohistochemistry and analyzed for their densities of CD8 TILs in both intraepithelial (iTILs) and stromal areas using a machine learning-based analytic method.
Results
CDX2 loss was significantly associated with a higher density of CD8 TILs in both intraepithelial and stromal areas. Both CDX2 loss and a high CD8 iTIL density were found to be prognostic parameters and showed hazard ratios of 2.314 (1.050–5.100) and 0.378 (0.175–0.817), respectively, for cancer-specific survival. A subset of CRCs with retained CDX2 expression and a high density of CD8 iTILs showed the best clinical outcome (hazard ratio of 0.138 [0.023–0.826]), whereas a subset with CDX2 loss and a high density of CD8 iTILs exhibited the worst clinical outcome (15.781 [3.939–63.230]).
Conclusions
Altogether, a high density of CD8 iTILs did not make a difference in the survival of patients with CRC with CDX2 loss. The combination of CDX2 expression and intraepithelial CD8 TIL density was an independent prognostic marker in adjuvant chemotherapy-treated patients with stage III CRC.
- Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
- Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Shanop Shuangshoti, Nakarin Kitkumthorn, Somboon Keelawat
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):39-49. Published online October 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.14
- Funded: Chulalongkorn University
- 4,636 View
- 331 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Although the criteria for follicular-pattern thyroid tumors are well-established, diagnosing these lesions remains challenging in some cases. In the recent World Health Organization Classification of Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Tumors (5th edition), the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma was reclassified as its own entity. It is crucial to differentiate this variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from low-risk follicular pattern tumors due to their shared morphological characteristics. Proteomics holds significant promise for detecting and quantifying protein biomarkers. We investigated the potential value of a protein biomarker panel defined by machine learning for identifying the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma, initially using formalin- fixed paraffin-embedded samples.
Methods
We developed a supervised machine-learning model and tested its performance using proteomics data from 46 thyroid tissue samples.
Results
We applied a random forest classifier utilizing five protein biomarkers (ZEB1, NUP98, C2C2L, NPAP1, and KCNJ3). This classifier achieved areas under the curve (AUCs) of 1.00 and accuracy rates of 1.00 in training samples for distinguishing the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from non-malignant samples. Additionally, we analyzed the performance of single-protein/gene receiver operating characteristic in differentiating the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from others within The Cancer Genome Atlas projects, which yielded an AUC >0.5.
Conclusions
We demonstrated that integration of high-throughput proteomics with machine learning can effectively differentiate the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from other follicular pattern thyroid tumors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in immunotherapy for thyroid malignancies: from molecular targets to clinical outcomes
Shuo Lv, Jinbao Wang, Guohao Chen, Yongshun Wang, Naiqing Liu
Frontiers in Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Misdiagnosed follicular adenoma with 11 year postoperative liver and lung metastases a case report and literature review
Kai-Li Yang, Heng-Tong Han, Shou-Hua Li, Xiao-Xiao Li, Ze Yang, Li-Bin Ma, Yong-Xun Zhao
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advances in immunotherapy for thyroid malignancies: from molecular targets to clinical outcomes
- Comparison of tissue-based and plasma-based testing for EGFR mutation in non–small cell lung cancer patients
- Yoon Kyung Kang, Dong Hoon Shin, Joon Young Park, Chung Su Hwang, Hyun Jung Lee, Jung Hee Lee, Jee Yeon Kim, JooYoung Na
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):60-67. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.01
- Funded: Pusan National University
- 5,197 View
- 202 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene mutation testing is crucial for the administration of tyrosine kinase inhibitors to treat non–small cell lung cancer. In addition to traditional tissue-based tests, liquid biopsies using plasma are increasingly utilized, particularly for detecting T790M mutations. This study compared tissue- and plasma-based EGFR testing methods.
Methods
A total of 248 patients were tested for EGFR mutations using tissue and plasma samples from 2018 to 2023 at Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital. Tissue tests were performed using PANAmutyper, and plasma tests were performed using the Cobas EGFR Mutation Test v2.
Results
All 248 patients underwent tissue-based EGFR testing, and 245 (98.8%) showed positive results. Of the 408 plasma tests, 237 (58.1%) were positive. For the T790M mutation, tissue biopsies were performed 87 times in 69 patients, and 30 positive cases (38.6%) were detected. Plasma testing for the T790M mutation was conducted 333 times in 207 patients, yielding 62 positive results (18.6%). Of these, 57 (27.5%) were confirmed to have the mutation via plasma testing. Combined tissue and plasma tests for the T790M mutation were positive in nine patients (13.4%), while 17 (25.4%) were positive in tissue only and 12 (17.9%) in plasma only. This mutation was not detected in 28 patients (43.3%).
Conclusions
Although the tissue- and plasma-based tests showed a sensitivity of 37.3% and 32.8%, respectively, combined testing increased the detection rate to 56.7%. Thus, neither test demonstrated superiority, rather, they were complementary.
Review
- Professional biobanking education in Korea based on ISO 20387
- Jong Ok Kim, Chungyeul Kim, Sangyong Song, Eunah Shin, Ji-Sun Song, Mee Sook Roh, Dong-chul Kim, Han-Kyeom Kim, Joon Mee Kim, Yeong Jin Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):11-25. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.04
- Funded: The Korean Society for Pathologists
- 6,309 View
- 188 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To ensure high-quality bioresources and standardize biobanks, there is an urgent need to develop and disseminate educational training programs in accordance with ISO 20387, which was developed in 2018. The standardization of biobank education programs is also required to train biobank experts. The subdivision of categories and levels of education is necessary for jobs such as operations manager (bank president), quality manager, practitioner, and administrator. Essential training includes programs tailored for beginner, intermediate, and advanced practitioners, along with customized training for operations managers. We reviewed and studied ways to develop an appropriate range of education and training opportunities for standard biobanking education and the training of experts based on KS J ISO 20387. We propose more systematic and professional biobanking training programs in accordance with ISO 20387, in addition to the certification programs of the National Biobank and the Korean Laboratory Accreditation System. We suggest various training programs appropriate to a student’s affiliation or work, such as university biobanking specialized education, short-term job training at unit biobanks, biobank research institute symposiums by the Korean Society of Pathologists, and education programs for biobankers and researchers. Through these various education programs, we expect that Korean biobanks will satisfy global standards, meet the needs of users and researchers, and contribute to the advancement of science.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a big data platform for collecting and utilizing clinical information from the Korea Biobank Network
Yun Seon Im, Seol Whan Oh, Ki Hoon Kim, Wona Choi, In Young Choi
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Frozen section histopathology and preanalytical factors affecting nucleic acid integrity in biobanked fresh-frozen human cancer tissues
Soungeun Kim, Jaewon Kang, Boyeon Kim, Yoonjin Kwak, Hye Seung Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(6): 398. CrossRef
- Development of a big data platform for collecting and utilizing clinical information from the Korea Biobank Network
Original Article
- PLUNC downregulates the expression of PD-L1 by inhibiting the interaction of DDX17/β-catenin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Ranran Feng, Yilin Guo, Meilin Chen, Ziying Tian, Yijun Liu, Su Jiang, Jieyu Zhou, Qingluan Liu, Xiayu Li, Wei Xiong, Lei Shi, Songqing Fan, Guiyuan Li, Wenling Zhang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):68-83. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.27
- Funded: National Natural Science Foundation of China, Hunan Province Natural Science Foundation
- 3,889 View
- 140 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is characterized by high programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression and abundant infiltration of non-malignant lymphocytes, which renders patients potentially suitable candidates for immune checkpoint blockade therapies. Palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone (PLUNC) inhibit the growth of NPC cells and enhance cellular apoptosis and differentiation. Currently, the relationship between PLUNC (as a tumor-suppressor) and PD-L1 in NPC is unclear.
Methods
We collected clinical samples of NPC to verify the relationship between PLUNC and PD-L1. PLUNC plasmid was transfected into NPC cells, and the variation of PD-L1 was verified by western blot and immunofluorescence. In NPC cells, we verified the relationship of PD-L1, activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3), and β-catenin by western blot and immunofluorescence. Later, we further verified that PLUNC regulates PD-L1 through β-catenin. Finally, the effect of PLUNC on β-catenin was verified by co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP).
Results
We found that PLUNC expression was lower in NPC tissues than in paracancer tissues. PD-L1 expression was opposite to that of PLUNC. Western blot and immunofluorescence showed that β-catenin could upregulate ATF3 and PD-L1, while PLUNC could downregulate ATF3/PD-L1 by inhibiting the expression of β-catenin. PLUNC inhibits the entry of β-catenin into the nucleus. Co-IP experiments demonstrated that PLUNC inhibited the interaction of DEAD-box helicase 17 (DDX17) and β-catenin.
Conclusions
PLUNC downregulates the expression of PD-L1 by inhibiting the interaction of DDX17/β-catenin in NPC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Potential Role of SP-G and PLUNC in Tumor Pathogenesis and Wound Healing in the Human Larynx
Aurelius Scheer, Lars Bräuer, Markus Eckstein, Heinrich Iro, Friedrich Paulsen, Fabian Garreis, Martin Schicht, Antoniu-Oreste Gostian
Biomedicines.2025; 13(5): 1240. CrossRef - Role of DEAD/DEAH-box helicases in immunity, infection and cancers
Rex Devasahayam Arokia Balaya, Saptami Kanekar, Shreya Kumar, Richard K. Kandasamy
Cell Communication and Signaling.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - CHIP modulates Wnt/β-catenin signalling in colorectal cancer through proteasomal degradation of DDX17
Sunny Kumar, Sayani Ghosh, Malini Basu, Mrinal K. Ghosh
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2025; 1872(8): 120049. CrossRef
- The Potential Role of SP-G and PLUNC in Tumor Pathogenesis and Wound Healing in the Human Larynx
Case Study
- Colorectal cancer with a germline BRCA1 variant inherited paternally: a case report
- Kyoung Min Kim, Min Ro Lee, Ae Ri Ahn, Myoung Ja Chung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):341-345. Published online September 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.08.14
- Funded: Biomedical Research Institute, Jeonbuk National University Hospital
- 7,548 View
- 308 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BRCA genes have well-known associations with breast and ovarian cancers. However, variations in the BRCA gene, especially germline variations, have also been reported in colorectal cancer (CRC). We present the case of a rectal cancer with a germline BRCA1 variation inherited from the paternal side. A 39-year-old male was admitted with rectal cancer. The patient underwent surgical resection and the pathologic diagnosis was adenocarcinoma. Next-generation sequencing was performed and a BRCA1 variant was detected. Reviewing the public database and considering the young age of the patient, the variant was suggested to be germline. The patient’s father had had prostate cancer and next-generation sequencing testing revealed an identical BRCA1 variant. In the BRCA cancer group, there is relatively little attention paid to male cancers. The accumulation of male CRC cases linked to BRCA variations may help clarify the potential pathological relationship between the two.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Aggressive Right-Sided Colon Cancer in a Young Adult: Triple-Whammy Mutations (POLE, KRAS, BRCA1/2) Highlight Emerging Genetic Associations
Ravi Patel, Ganesh Kumar, Yash Shah, Dushyant Singh Dahiya, Sumant Inamdar
ACG Case Reports Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Aggressive Right-Sided Colon Cancer in a Young Adult: Triple-Whammy Mutations (POLE, KRAS, BRCA1/2) Highlight Emerging Genetic Associations
Original Articles
- Histopathologic classification and immunohistochemical features of papillary renal neoplasm with potential therapeutic targets
- Jeong Hwan Park, Su-Jin Shin, Hyun-Jung Kim, Sohee Oh, Yong Mee Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):321-330. Published online September 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.31
- Funded: Korean Society of Pathologists
- 7,123 View
- 434 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Papillary renal cell carcinoma (pRCC) is the second most common histological subtype of renal cell carcinoma and is considered a morphologically and molecularly heterogeneous tumor. Accurate classification and assessment of the immunohistochemical features of possible therapeutic targets are needed for precise patient care. We aimed to evaluate immunohistochemical features and possible therapeutic targets of papillary renal neoplasms
Methods
We collected 140 papillary renal neoplasms from three different hospitals and conducted immunohistochemical studies on tissue microarray slides. We performed succinate dehydrogenase B, fumarate hydratase, and transcription factor E3 immunohistochemical studies for differential diagnosis and re-classified five cases (3.6%) of papillary renal neoplasms. In addition, we conducted c-MET, p16, c-Myc, Ki-67, p53, and stimulator of interferon genes (STING) immunohistochemical studies to evaluate their pathogenesis and value for therapeutic targets.
Results
We found that c-MET expression was more common in pRCC (classic) (p = .021) among papillary renal neoplasms and Ki-67 proliferation index was higher in pRCC (not otherwise specified, NOS) compared to that of pRCC (classic) and papillary neoplasm with reverse polarity (marginal significance, p = .080). Small subsets of cases with p16 block positivity (4.5%) (pRCC [NOS] only) and c-Myc expression (7.1%) (pRCC [classic] only) were found. Also, there were some cases showing STING expression and those cases were associated with increased Ki-67 proliferation index (marginal significance, p = .063).
Conclusions
Our findings suggested that there are subsets of pRCC with c-MET, p16, c-MYC, and STING expression and those cases could be potential candidates for targeted therapy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tissue-Based Biomarkers Important for Prognostication and Management of Genitourinary Tumors, Including Surrogate Markers of Genomic Alterations
Leonie Beauchamp, Shreeya Indulkar, Eric Erak, Mohammad Salimian, Andres Matoso
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2025; 18(1): 175. CrossRef - Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity: a case report and literature review
Diego Gonzalez, Kris Kokoneshi, Sam Kwon, Ryan Thomas Mathews, Ryan Michael Antar, Maher Ali, Abiye Kassa, Michael Whalen
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Tissue-Based Biomarkers Important for Prognostication and Management of Genitourinary Tumors, Including Surrogate Markers of Genomic Alterations
- Diagnostic challenges in the assessment of thyroid neoplasms using nuclear features and vascular and capsular invasion: a multi-center interobserver agreement study
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Mutiah Mutmainnah, Maria Francisca Ham, Dina Khoirunnisa, Abdillah Hasbi Assadyk, Husni Cangara, Aswiyanti Asri, Diah Prabawati Retnani, Fairuz Quzwain, Hasrayati Agustina, Hermawan Istiadi, Indri Windarti, Krisna Murti, Muhammad Takbir, Ni Made Mahastuti, Nila Kurniasari, Nungki Anggorowati, Pamela Abineno, Yulita Pundewi Setyorini, Kennichi Kakudo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):299-309. Published online September 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.25
- Correction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2025;59(3):201
- Funded: Universitas Indonesia
- 5,516 View
- 413 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The diagnosis of thyroid neoplasms necessitates the identification of distinct histological features. Various education/hospital centers located in cities across Indonesia likely result in discordances among pathologists when diagnosing thyroid neoplasms.
Methods
This study examined the concordance among Indonesian pathologists in assessing nuclear features and capsular and vascular invasion of thyroid tumors. Fifteen pathologists from different centers independently assessed the same 14 digital slides of thyroid tumor specimens. All the specimens were thyroid neoplasms with known BRAFV600E and RAS mutational status, from a single center. We evaluated the pre- and post-training agreement using the Fleiss kappa. The significance of the training was evaluated using a paired T-test.
Results
Baseline agreement on nuclear features was slight to fair based on a 3-point scoring system (k = 0.14 to 0.28) and poor to fair based on an eight-point system (k = –0.02 to 0.24). Agreements on vascular (κ = 0.35) and capsular invasion (κ = 0.27) were fair, whereas the estimated molecular type showed substantial agreement (κ = 0.74). Following the training, agreement using the eight-point system significantly improved (p = 0.001).
Conclusions
The level of concordance among Indonesian pathologists in diagnosing thyroid neoplasm was relatively poor. Consensus in pathology assessment requires ongoing collaboration and education to refine diagnostic criteria. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Dina Khoirunnisa, Salinah, Maria Francisca Ham
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 75: 152434. CrossRef
- Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Review
- Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):265-282. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.11
- Funded: Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 16,290 View
- 631 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the most common thyroid malignancy, characterized by a range of subtypes that differ in their cytologic features, clinical behavior, and prognosis. Accurate cytologic evaluation of PTC using fine-needle aspiration is essential but can be challenging due to the morphologic diversity among subtypes. This review focuses on the distinct cytologic characteristics of various PTC subtypes, including the classic type, follicular variant, tall cell, columnar cell, hobnail, diffuse sclerosing, Warthin-like, solid/trabecular, and oncocytic PTCs. Each subtype demonstrates unique nuclear features, architectural patterns, and background elements essential for diagnosis and differentiation from other thyroid lesions. Recognizing these distinct cytologic patterns is essential for identifying aggressive subtypes like tall cell, hobnail, and columnar cell PTCs, which have a higher risk of recurrence, metastasis, and poorer clinical outcomes. Additionally, rare subtypes such as diffuse sclerosing and Warthin-like PTCs present unique cytologic profiles that must be carefully interpreted to avoid diagnostic errors. The review also highlights the cytologic indicators of lymph node metastasis and high-grade features, such as differentiated high-grade thyroid carcinoma. The integration of molecular testing can further refine subtype diagnosis by identifying specific genetic mutations. A thorough understanding of these subtype-specific cytologic features and molecular profiles is vital for accurate diagnosis, risk stratification, and personalized management of PTC patients. Future improvements in diagnostic techniques and standardization are needed to enhance cytologic evaluation and clinical decision-making in thyroid cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
Adeel M. Ashraf, Faisal Hassan, Adrian A. Dawkins, Julie C. Dueber, Derek B. Allison, Thèrése J. Bocklage
Cytopathology.2026; 37(1): 108. CrossRef - Using a new type of visible light-based emission fluorescence microscope to identify the benign and malignant nature of thyroid tissue during the surgical process: Analysis of diagnostic results
Yu Miao, Liu Xiaowei, Li Muyang, Gao Jian, Chen Lu
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2026; 57: 105324. CrossRef - Clinical Behavior of Aggressive Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Retrospective Case–Control Study
Jovan Ilic, Nikola Slijepcevic, Katarina Tausanovic, Bozidar Odalovic, Goran Zoric, Marija Milinkovic, Branislav Rovcanin, Milan Jovanovic, Matija Buzejic, Duska Vucen, Boban Stepanovic, Sara Ivanis, Milan Parezanovic, Milan Marinkovic, Vladan Zivaljevic
Cancers.2026; 18(2): 345. CrossRef - Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Dina Khoirunnisa, Salinah, Maria Francisca Ham
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 75: 152434. CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shin Je Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyo
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - Structure-based molecular screening and dynamic simulation of phytocompounds targeting VEGFR-2: a novel therapeutic approach for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Shuai Wang, Lingqian Zhang, Wenjun Zhang, Xiong Zeng, Jie Mei, Weidong Xiao, Lijie Yang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shinje Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(3): 307. CrossRef - A Case of Warthin-Like Variant of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Amy Chow, Israa Laklouk
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Propensity score-matched analysis of the ‘2+2’ parathyroid strategy in total thyroidectomy with central neck dissection
Hao Gong, Simei Yao, Tianyuchen Jiang, Yi Yang, Yuhan Jiang, Zhujuan Wu, Anping Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytological Findings in Pediatric Thoracic Tumors: A Review of Diagnostic Insights and Pitfalls
Parikshaa Gupta, Pranab Dey
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef
- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
Original Articles
- Educational exchange in thyroid core needle biopsy diagnosis: enhancing pathological interpretation through guideline integration and peer learning
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):205-213. Published online July 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.06.24
- Funded: Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 5,324 View
- 299 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
While fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) plays an essential role in the screening of thyroid nodules, core needle biopsy (CNB) acts as an alternative method to address FNAC limitations. However, diagnosing thyroid CNB samples can be challenging due to variations in background and levels of experience. Effective training is indispensable to mitigate this challenge. We aim to evaluate the impact of an educational program on improving the accuracy of CNB diagnostics.
Methods
The 2-week observational program included a host mentor pathologist with extensive experience and a visiting pathologist. The CNB classification by The Practice Guidelines Committee of the Korean Thyroid Association was used for the report. Two rounds of reviewing the case were carried out, and the level of agreement between the reviewers was analyzed.
Results
The first-round assessment showed a concordance between two pathologists for 247 thyroid CNB specimens by 84.2%, with a kappa coefficient of 0.74 (indicating substantial agreement). This finding was attributed to the discordance in the use of categories III and V. After peer learning, the two pathologists evaluated 30 new cases, which showed an overall improvement in the level of agreement. The percentage of agreement between pathologists on thyroid CNB diagnosis was 86.7%, as measured by kappa coefficient of 0.80.
Conclusions
This educational program, consisting of guided mentorship and peer learning, can substantially enhance the diagnostic accuracy of thyroid CNB. It is useful in promoting consistent diagnostic standards and contributes to the ongoing development of global pathology practices. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lessons learned from the first 2 years of experience with thyroid core needle biopsy at an Indonesian national referral hospital
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Maria Francisca Ham, Retno Asti Werdhani, Erwin Danil Julian, Rafi Ilmansyah, Chloe Indira Arfelita Mangunkusumso, Tri Juli Edi Tarigan
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(3): 149. CrossRef
- Lessons learned from the first 2 years of experience with thyroid core needle biopsy at an Indonesian national referral hospital
- Artificial intelligence algorithm for neoplastic cell percentage estimation and its application to copy number variation in urinary tract cancer
- Jinahn Jeong, Deokhoon Kim, Yeon-Mi Ryu, Ja-Min Park, Sun Young Yoon, Bokyung Ahn, Gi Hwan Kim, Se Un Jeong, Hyun-Jung Sung, Yong Il Lee, Sang-Yeob Kim, Yong Mee Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):229-240. Published online August 9, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.13
- Funded: Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Asan Medical Center
- 4,726 View
- 278 Download
- 1 Web of Science
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Bladder cancer is characterized by frequent mutations, which provide potential therapeutic targets for most patients. The effectiveness of emerging personalized therapies depends on an accurate molecular diagnosis, for which the accurate estimation of the neoplastic cell percentage (NCP) is a crucial initial step. However, the established method for determining the NCP, manual counting by a pathologist, is time-consuming and not easily executable.
Methods
To address this, artificial intelligence (AI) models were developed to estimate the NCP using nine convolutional neural networks and the scanned images of 39 cases of urinary tract cancer. The performance of the AI models was compared to that of six pathologists for 119 cases in the validation cohort. The ground truth value was obtained through multiplexed immunofluorescence. The AI model was then applied to 41 cases in the application cohort that underwent next-generation sequencing testing, and its impact on the copy number variation (CNV) was analyzed.
Results
Each AI model demonstrated high reliability, with intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) ranging from 0.82 to 0.88. These values were comparable or better to those of pathologists, whose ICCs ranged from 0.78 to 0.91 in urothelial carcinoma cases, both with and without divergent differentiation/ subtypes. After applying AI-driven NCP, 190 CNV (24.2%) were reclassified with 66 (8.4%) and 78 (9.9%) moved to amplification and loss, respectively, from neutral/minor CNV. The neutral/minor CNV proportion decreased by 6%.
Conclusions
These results suggest that AI models could assist human pathologists in repetitive and cumbersome NCP calculations.
- Paricalcitol prevents MAPK pathway activation and inflammation in adriamycin-induced kidney injury in rats
- Amanda Lima Deluque, Lucas Ferreira de Almeida, Beatriz Magalhães Oliveira, Cláudia Silva Souza, Ana Lívia Dias Maciel, Heloísa Della Coletta Francescato, Cleonice Giovanini, Roberto Silva Costa, Terezila Machado Coimbra
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):219-228. Published online August 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.12
- Funded: Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superi-or, Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- 4,048 View
- 222 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway induces uncontrolled cell proliferation in response to inflammatory stimuli. Adriamycin (ADR)-induced nephropathy (ADRN) in rats triggers MAPK activation and pro-inflammatory mechanisms by increasing cytokine secretion, similar to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Activation of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) plays a crucial role in suppressing the expression of inflammatory markers in the kidney and may contribute to reducing cellular proliferation. This study evaluated the effect of pre-treatment with paricalcitol on ADRN in renal inflammation mechanisms.
Methods
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were implanted with an osmotic minipump containing activated vitamin D (paricalcitol, Zemplar, 6 ng/day) or vehicle (NaCl 0.9%). Two days after implantation, ADR (Fauldoxo, 3.5 mg/kg) or vehicle (NaCl 0.9%) was injected. The rats were divided into four experimental groups: control, n = 6; paricalcitol, n = 6; ADR, n = 7 and, ADR + paricalcitol, n = 7.
Results
VDR activation was demonstrated by increased CYP24A1 in renal tissue. Paricalcitol prevented macrophage infiltration in the glomeruli, cortex, and outer medulla, prevented secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-1β, increased arginase I and decreased arginase II tissue expressions, effects associated with attenuation of MAPK pathways, increased zonula occludens-1, and reduced cell proliferation associated with proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression. Paricalcitol treatment decreased the stromal cell-derived factor 1α/chemokine C-X-C receptor type 4/β-catenin pathway.
Conclusions
Paricalcitol plays a renoprotective role by modulating renal inflammation and cell proliferation. These results highlight potential targets for treating CKD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perirenal fat differs in patients with chronic kidney disease receiving different vitamin D-based treatments: a preliminary study
Ana Checa-Ros, Antonella Locascio, Owahabanun-Joshua Okojie, Pablo Abellán-Galiana, Luis D’Marco
BMC Nephrology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Attenuating amiodarone-induced lung toxicity by the vitamin D receptor activator paricalcitol in rats: targeting TLR4/NF-κB/HIF-1α and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways
Aamal G. El-Waseif, Mahmoud Elshal, Dalia H. El-Kashef, Nashwa M. Abu-Elsaad
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Perirenal fat differs in patients with chronic kidney disease receiving different vitamin D-based treatments: a preliminary study
Review
- Clinical practice recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing in patients with solid cancer: a joint report from KSMO and KSP
- Miso Kim, Hyo Sup Shim, Sheehyun Kim, In Hee Lee, Jihun Kim, Shinkyo Yoon, Hyung-Don Kim, Inkeun Park, Jae Ho Jeong, Changhoon Yoo, Jaekyung Cheon, In-Ho Kim, Jieun Lee, Sook Hee Hong, Sehhoon Park, Hyun Ae Jung, Jin Won Kim, Han Jo Kim, Yongjun Cha, Sun Min Lim, Han Sang Kim, Choong-Kun Lee, Jee Hung Kim, Sang Hoon Chun, Jina Yun, So Yeon Park, Hye Seung Lee, Yong Mee Cho, Soo Jeong Nam, Kiyong Na, Sun Och Yoon, Ahwon Lee, Kee-Taek Jang, Hongseok Yun, Sungyoung Lee, Jee Hyun Kim, Wan-Seop Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):147-164. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.01
- Funded: National Cancer Center, Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 9,568 View
- 498 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In recent years, next-generation sequencing (NGS)–based genetic testing has become crucial in cancer care. While its primary objective is to identify actionable genetic alterations to guide treatment decisions, its scope has broadened to encompass aiding in pathological diagnosis and exploring resistance mechanisms. With the ongoing expansion in NGS application and reliance, a compelling necessity arises for expert consensus on its application in solid cancers. To address this demand, the forthcoming recommendations not only provide pragmatic guidance for the clinical use of NGS but also systematically classify actionable genes based on specific cancer types. Additionally, these recommendations will incorporate expert perspectives on crucial biomarkers, ensuring informed decisions regarding circulating tumor DNA panel testing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apport de la génomique dans la prise en charge des cancers
Étienne Rouleau, Lucie Karayan-Tapon, Marie-Dominique Galibert, Alexandre Harlé, Isabelle Soubeyran
Revue Francophone des Laboratoires.2025; 2025(568): 67. CrossRef - The Redox–Adhesion–Exosome (RAX) Hub in Cancer: Lipid Peroxidation-Driven EMT Plasticity and Ferroptosis Defense with HNE/MDA Signaling and Lipidomic Perspectives
Moon Nyeo Park, Jinwon Choi, Rosy Iara Maciel de Azambuja Ribeiro, Domenico V. Delfino, Seong-Gyu Ko, Bonglee Kim
Antioxidants.2025; 14(12): 1474. CrossRef
- Apport de la génomique dans la prise en charge des cancers
Original Articles
- Immunohistochemical expression in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies at a single center in Vietnam
- Dat Quoc Ngo, Si Tri Le, Khanh Hoang Phuong Phan, Thao Thi Phuong Doan, Linh Ngoc Khanh Nguyen, Minh Hoang Dang, Thien Thanh Ly, Thu Dang Anh Phan
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):174-181. Published online June 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.05.02
- Funded: University of Medicine and Pharmacy at HoChi Minh City
- 4,561 View
- 270 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The identification of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) requires a comprehensive analysis involving clinical manifestations and histological findings. This study aims to provide insights into the histopathological and immunohistochemical aspects of IIMs.
Methods
This retrospective case series involved 56 patients diagnosed with IIMs at the Department of Pathology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy at Ho Chi Minh City, from 2019 to 2023. The histology and immunohistochemical expression of HLA-ABC, HLA-DR, C5b-9, Mx1/2/3, and p62 were detected.
Results
We examined six categories of inflammatory myopathy, including immunemediated necrotizing myopathy (58.9%), dermatomyositis (DM; 23.2%), overlap myositis (8.9%), antisynthetase syndrome (5.4%), inclusion body myositis (IBM; 1.8%), and polymyositis (1.8%). The average age of the patients was 49.7 ± 16.1 years, with a female-to-male ratio of 3:1. Inflammatory cell infiltration in the endomysium was present in 62.5% of cases, perifascicular atrophy was found in 17.8%, and fiber necrosis was observed in 42 cases (75.0%). Rimmed vacuoles were present in 100% of cases in the IBM group. Immunohistochemistry showed the following positivity rates: HLA-ABC (89.2%), HLA-DR (19.6%), C5b-9 (57.1%), and Mx1/2/3 (10.7%). Mx1/2/3 expression was high in DM cases. p62 vacuole deposits were noted in the IBM case. The combination of membrane attack complex and major histocompatibility complex I helped detect IIMs in 96% of cases.
Conclusions
The diagnosis of IIMs and their subtypes should be based on clinical features and histopathological characteristics. Immunohistochemistry plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and differentiation of these subgroups. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluating the Diagnostic Potential of Myxovirus Resistance Protein 1 (MX1) and Myxovirus Resistance Protein 2 (MX2) As Biomarkers in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
Raghavee Neupane, Mustafa Haider, Perry Smith, Marc M Kesselman
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Rapidly Progressive Polymyositis With Vasculitis: The Pivotal Role of Histopathology in Diagnosis and Management
Amitha Venmanassery Karnalsingh, Arjun Karappilly Vijayan, Monica Roselin Edwin Peter, Dilan Davis
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Autoimmune Neuromuscular Disorders at a Molecular Crossroad: Linking Pathogenesis to Targeted Immunotherapy
Anca-Maria Florea, Dimela-Gabriela Luca, Eugenia Irene Davidescu, Bogdan-Ovidiu Popescu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(23): 11736. CrossRef
- Evaluating the Diagnostic Potential of Myxovirus Resistance Protein 1 (MX1) and Myxovirus Resistance Protein 2 (MX2) As Biomarkers in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
- Clinicopathological implications of immunohistochemical expression of TBX21, CXCR3, GATA3, CCR4, and TCF1 in nodal follicular helper T-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified
- Bogyeong Han, Sojung Lim, Jeemin Yim, Young Keun Song, Jiwon Koh, Sehui Kim, Cheol Lee, Young A Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):59-71. Published online January 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.01.04
- Funded: Seoul National University, HUNKIM FAMILY CHARITABLE FOUNDATION
- 8,228 View
- 378 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The classification of nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) has evolved according to histology, cell-of-origin, and genetic alterations. However, the comprehensive expression pattern of follicular helper T-cell (Tfh) markers, T-cell factor-1 (TCF1), and Th1- and Th2-like molecules in nodal PTCL is unclear.
Methods
Eighty-two cases of nodal PTCL were classified into 53 angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphomas (AITLs)/nodal T-follicular helper cell lymphoma (nTFHL)-AI, 18 PTCLs-Tfh/nTFHL–not otherwise specified (NOS), and 11 PTCLs-NOS according to the revised 4th/5th World Health Organization classifications. Immunohistochemistry for TCF1, TBX21, CXCR3, GATA3, and CCR4 was performed.
Results
TCF1 was highly expressed in up to 68% of patients with nTFHL but also in 44% of patients with PTCL-NOS (p > .05). CXCR3 expression was higher in AITLs than in non-AITLs (p = .035), whereas GATA3 expression was higher in non-AITL than in AITL (p = .007) and in PTCL-Tfh compared to AITL (p = .010). Of the cases, 70% of AITL, 44% of PTCLTfh/ nTFHL-NOS, and 36% of PTCL-NOS were subclassified as the TBX21 subtype; and 15% of AITL, 38% of PTCL-Tfh/nTFHL-NOS, and 36% of PTCL-NOS were subclassified as the GATA3 subtype. The others were an unclassified subtype. CCR4 expression was associated with poor progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with PTCL-Tfh (p < .001) and nTFHL (p = .023). The GATA3 subtype showed poor overall survival in PTCL-NOS compared to TBX21 (p = .046) and tended to be associated with poor PFS in patients with non-AITL (p = .054).
Conclusions
The TBX21 subtype was more prevalent than the GATA3 subtype in AITL. The GATA3 subtype was associated with poor prognosis in patients with non-AITL and PTCL-NOS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- T-bet: biological functions, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic applications: a systematic review
Xiaowen Yang, Min Sun, Xinyi Tang, Xiaoyuan Zhang, Wenzhi Shen
Frontiers in Immunology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - CXCR Family and Hematologic Malignancies in the Bone Marrow Microenvironment
Yanquan Liu, Huanwen Tang
Biomolecules.2025; 15(5): 716. CrossRef - Diagnostic and therapeutic pathways for lymphoma patients: expert consensus through Nominal Group Technique and Delphi methodology
Attilio Guarini, Valentina Bozzoli, Sabino Ciavarella, Michele Cimminiello, Francesca Donatelli, Angelo Fama, Vincenza Fernanda Fesce, Vincenzo Fraticelli, Francesco Gaudio, Giuseppina Greco, Augusto Martellini, Francesca Merchionne, Rosanna Maria Miccoli
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Significance of TBX21 and GATA3 Subtype Classification in Indolent Adult T‐Cell Leukemia‐Lymphoma With Cutaneous Lesions
Kazuhiro Kawai, Youhei Uchida, Takuro Kanekura
The Journal of Dermatology.2025; 52(11): 1674. CrossRef
- T-bet: biological functions, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic applications: a systematic review
- TRPS1 expression in non-melanocytic cutaneous neoplasms: an immunohistochemical analysis of 200 cases
- Yi A. Liu, Phyu P. Aung, Yunyi Wang, Jing Ning, Priyadharsini Nagarajan, Jonathan L. Curry, Carlos A. Torres-Cabala, Doina Ivan, Victor G. Prieto, Qingqing Ding, Woo Cheal Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):72-80. Published online February 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.01.23
- Funded: University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
- 7,512 View
- 395 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Although trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1 (TRPS1) was initially thought to be highly sensitive and specific for carcinomas and mesenchymal tumors of mammary origin, more recent data suggest its expression is not limited to breast neoplasms but also can be seen in other cutaneous neoplasms, such as extramammary Paget disease and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in situ.
Methods
Two-hundred cases of non-melanocytic cutaneous neoplasm, including basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) (n = 41), SCCs (n = 35), Merkel cell carcinomas (MCCs) (n = 25), and adnexal neoplasms (n = 99), were tested for TRPS1 expression using a monoclonal anti- TRPS1 rabbit anti-human antibody.
Results
TRPS1 expression was present in almost all cases of SCC (94%), with a median H-score of 200, while it was either absent or only focally present in most BCCs (90%), with a median H-score of 5. The difference between BCCs and SCCs in H-score was significant (p < .001). All MCCs (100%) lacked TRPS1 expression. TRPS1 expression was frequently seen in most adnexal neoplasms, benign and malignant, in variable intensity and proportion but was consistently absent in apocrine carcinomas. All endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinomas (EMPSGCs) (100%, 6/6) showed diffuse and strong TRPS1 immunoreactivity, with a median H-score of 300, which was significantly different (p < .001) than that of BCCs.
Conclusions
Our study shows that TRPS1 may be an effective discriminatory marker for BCCs and SCCs. It also has a role in distinguishing BCCs from EMPSGCs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastatic Vulvar Paget's Disease Presenting in a Supraclavicular Lymph Node: A Diagnostic Challenge on Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
Thiri Htoo Aung, Neha Seth, Anam Khan, Kasturi Das
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1 (TRPS1) in breast pathology: diagnostic utility and pitfalls
Atif Ali Hashmi, Edi Brogi, Hannah Y. Wen
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Refining NTRK Fusion Detection in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Through Pan-TRK Immunohistochemistry and Histopathologic Features
Hyun Lee, Sue Youn Kim, Ji Min Park, Seung-Hyun Jung, Ozgur Mete, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma: Case report and literature review
Nan Guo, Zhenlin Fan, Yitong Chen, Qian Li, Limin Guo
European Journal of Ophthalmology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Updates on utility of immunohistochemistry in diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer
Hongxia Sun, Aysegul A. Sahin, Qingqing Ding
Human Pathology.2025; 162: 105821. CrossRef - Primary Cutaneous NUT Adnexal Carcinoma With BRD4::NUTM1 Fusion: A 19-Year Follow-Up
Elsayed Ibrahim, Richard K. Yang, Maria A. Gubbiotti, Victor G. Prieto, Woo Cheal Cho
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2025; 47(9): 731. CrossRef - Primary mucinous carcinoma of the skin with co-expression of TRPS1 and GATA3: a case report
Liling Song, Ning Zhu, Lei Jiang, Dong Gao, Guohua Yu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Algorithm for Secondary Extramammary Paget Disease from Institutional Cases and Literature Review
Salin Kiratikanon, Ayaka Fukui, Masahiro Hirata, Jakob M. T. Moran, Masakazu Fujimoto, Mai P. Hoang
Cancers.2025; 17(24): 4014. CrossRef - TRPS1 Expression Is Frequently Seen in a Subset of Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms and Tumors of Uncertain Differentiation: A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall
Moon Joo Kim, Yi A. Liu, Yunyi Wang, Jing Ning, Woo Cheal Cho
Dermatopathology.2024; 11(3): 200. CrossRef - TRPS1 expression in MPNST is correlated with PRC2 inactivation and loss of H3K27me3
Rossana Lazcano, Davis R. Ingram, Gauri Panse, Alexander J. Lazar, Wei-Lien Wang, Jeffrey M. Cloutier
Human Pathology.2024; 151: 105632. CrossRef - Syringocystadenoma Papilliferum-Like Features in Poroma: An Unusual Morphologic Pattern of Poroma or True Synchronous Occurrence of 2 Distinct Neoplasms?
Mouaz Alsawas, Fiorinda F. Muhaj, Phyu P. Aung, Priyadharsini Nagarajan, Woo Cheal Cho
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2024; 46(12): 871. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review of TRPS1 as a Diagnostic Immunohistochemical Marker for Primary Breast Carcinoma: Latest Insights and Diagnostic Pitfalls
Antonia-Carmen Georgescu, Tiberiu-Augustin Georgescu, Simona-Alina Duca-Barbu, Lucian Gheorghe Pop, Daniela Oana Toader, Nicolae Suciu, Dragos Cretoiu
Cancers.2024; 16(21): 3568. CrossRef - Expression of TRPS1 in Metastatic Tumors of the Skin: An Immunohistochemical Study of 72 Cases
Kassiani Boulogeorgou, Christos Topalidis, Triantafyllia Koletsa, Georgia Karayannopoulou, Jean Kanitakis
Dermatopathology.2024; 11(4): 293. CrossRef
- Metastatic Vulvar Paget's Disease Presenting in a Supraclavicular Lymph Node: A Diagnostic Challenge on Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
Review
- Exploring histological predictive biomarkers for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy response in non–small cell lung cancer
- Uiju Cho, Soyoung Im, Hyung Soon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):49-58. Published online February 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.01.31
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Education
- 10,068 View
- 348 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Treatment challenges persist in advanced lung cancer despite the development of therapies beyond the traditional platinum-based chemotherapy. The early 2000s marked a shift to tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeting epidermal growth factor receptor, ushering in personalized genetic-based treatment. A further significant advance was the development of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), especially for non–small cell lung cancer. These target programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4, which enhanced the immune response against tumor cells. However, not all patients respond, and immune-related toxicities arise. This review emphasizes identifying biomarkers for ICI response prediction. While PD-L1 is a widely used, validated biomarker, its predictive accuracy is imperfect. Investigating tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, tertiary lymphoid structure, and emerging biomarkers such as high endothelial venule, Human leukocyte antigen class I, T-cell immunoreceptors with Ig and ITIM domains, and lymphocyte activation gene-3 counts is promising. Understanding and exploring additional predictive biomarkers for ICI response are crucial for enhancing patient stratification and overall care in lung cancer treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Machine learning methods for histopathological image analysis: Updates in 2024
Daisuke Komura, Mieko Ochi, Shumpei Ishikawa
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2025; 27: 383. CrossRef - Beyond single biomarkers: multi-omics strategies to predict immunotherapy outcomes in blood cancers
Mohammad Pirouzbakht, Soroosh Hamzeh, Hamed Soleimani Samarkhazan
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Temporal changes in tongue color during immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: a prospective observational study using digital tongue diagnosis
Eunbyul Cho, Woosu Choi, Jun Hyeok Lim, Ji Woong Son, Seung Hun Jang, Seung Hyeun Lee, Jong Gwon Choi, In-Jae Oh, Tae-Won Jang, Seong Hoon Yoon, Seung Joon Kim, Chang-Min Choi, Sung Yong Lee, Mi Mi Ko, Mi-Kyung Jeong
Oncology Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Machine learning methods for histopathological image analysis: Updates in 2024
Original Articles
- Identification of invasive subpopulations using spatial transcriptome analysis in thyroid follicular tumors
- Ayana Suzuki, Satoshi Nojima, Shinichiro Tahara, Daisuke Motooka, Masaharu Kohara, Daisuke Okuzaki, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Eiichi Morii
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):22-28. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.21
- Funded: Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- 5,086 View
- 274 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Follicular tumors include follicular thyroid adenomas and carcinomas; however, it is difficult to distinguish between the two when the cytology or biopsy material is obtained from a portion of the tumor. The presence or absence of invasion in the resected material is used to differentiate between adenomas and carcinomas, which often results in the unnecessary removal of the adenomas. If nodules that may be follicular thyroid carcinomas are identified preoperatively, active surveillance of other nodules as adenomas is possible, which reduces the risk of surgical complications and the expenses incurred during medical treatment. Therefore, we aimed to identify biomarkers in the invasive subpopulation of follicular tumor cells.
Methods
We performed a spatial transcriptome analysis of a case of follicular thyroid carcinoma and examined the dynamics of CD74 expression in 36 cases.
Results
We identified a subpopulation in a region close to the invasive area, and this subpopulation expressed high levels of CD74. Immunohistochemically, CD74 was highly expressed in the invasive and peripheral areas of the tumor.
Conclusions
Although high CD74 expression has been reported in papillary and anaplastic thyroid carcinomas, it has not been analyzed in follicular thyroid carcinomas. Furthermore, the heterogeneity of CD74 expression in thyroid tumors has not yet been reported. The CD74-positive subpopulation identified in this study may be useful in predicting invasion of follicular thyroid carcinomas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carbonic Anhydrase 12 as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for High‐Risk Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma
Masashi Tanida, Tsuyoshi Takashima, Shinichiro Tahara, Masaharu Kohara, Haruka Kanai, Masami Suzuki, Motoyuki Suzuki, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Ayana Suzuki, Shinya Sato, Daisuke Okuzaki, Satoshi Nojima, Takahiro Matsui, Hidenori Inohara, Eiichi Morii
Cancer Science.2026; 117(1): 257. CrossRef - An emerging role of CD74 in thyroid follicular cells in Hashimoto´s thyroiditis
Pablo Sacristán-Gómez, Ana Serrano-Somavilla, Nuria Sánchez de la Blanca, Andrea Álvarez-Rodríguez, Eduardo Martínez-Parra, Miguel Sampedro-Nuñez, Fernando Sebastián-Valles, Mónica Marazuela, Rebeca Martínez-Hernández
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2026; 194: 118945. CrossRef - Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Shanop Shuangshoti, Nakarin Kitkumthorn, Somboon Keelawat
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(1): 39. CrossRef - Spatial Transcriptomics in Thyroid Cancer: Applications, Limitations, and Future Perspectives
Chaerim Song, Hye-Ji Park, Man S. Kim
Cells.2025; 14(12): 936. CrossRef - A New Tool to Decrease Interobserver Variability in Biomarker Annotation in Solid Tumor Tissue for Spatial Transcriptomic Analysis
Sravya Palavalasa, Emily Baker, Jack Freeman, Aditri Gokul, Weihua Zhou, Dafydd Thomas, Wajd N. Al-Holou, Meredith A. Morgan, Theodore S. Lawrence, Daniel R. Wahl
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2025; 47(7): 531. CrossRef
- Carbonic Anhydrase 12 as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for High‐Risk Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma
- Immunohistochemical expression of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in neuroblastoma and its relations with some clinical and histopathological features
- Thu Dang Anh Phan, Thao Quyen Nguyen, Nhi Thuy To, Thien Ly Thanh, Dat Quoc Ngo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):29-34. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.12.07
- Funded: University of Medicine and Pharmacy Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- 5,696 View
- 293 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) mutations have been identified as a prominent cause of some familial and sporadic neuroblastoma (NB). ALK expression in NB and its relationship with clinical and histopathological features remains controversial. This study investigated ALK expression and its potential relations with these features in NB.
Methods
Ninety cases of NB at the Department of Pathology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy at Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam from 01/01/2018 to 12/31/2021, were immunohistochemically stained with ALK (D5F3) antibody. The ALK expression and its relations with some clinical and histopathological features were investigated.
Results
The rate of ALK expression in NB was 91.1%. High ALK expression (over 50% of tumor cells were positive with moderate-strong intensity) accounted for 65.6%, and low ALK expression accounted for 34.4%. All the MYCN-amplified NB patients had ALK immunohistochemistry positivity, most cases had high ALK protein expression. The undifferentiated subtype of NB had a lower ALK-positive rate than the poorly differentiated and differentiated subtype. The percentages of ALK positivity were significantly higher in more differentiated histological types of NB (p = .024). There was no relation between ALK expression and: age group, sex, primary tumor location, tumor stage, MYCN status, clinical risk, Mitotic-Karyorrhectic Index, prognostic group, necrosis, and calcification.
Conclusions
ALK was highly expressed in NB. ALK expression was not related to several clinical and histopathological features. More studies are needed to elucidate the association between ALK expression and ALK gene status and to investigate disease progression, especially the oncogenesis of ALK-positive NB. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A humanized anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-directed antibody-drug conjugate with pyrrolobenzodiazepine payload demonstrates efficacy in ALK-expressing cancers
Alberto D. Guerra, Smita Matkar, Christina Acholla, Colleen Casey, Grant Li, Martina Mazzeschi, Khushbu Patel, Kateryna Krytska, Chuan Chen, Skye Balyasny, Joshua Kalna, Paul Kamitsuka, Mark Gerelus, Grace Polkosnik, David Groff, Apratim Mukherje, Cynthia
Nature Communications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Integration of ALK gene mutations and targeted therapies in pediatric high-risk neuroblastoma: advancements in precision oncology
Bhumika Bheemavarapu, Mohammad Khalil, Aseef Rehman, Saman Javid, FNU Cyrus, Sardar Noman Qayyum, Aasvi Gohil, Siraj Ul Muneer, Samim Noori
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2025; 87(10): 6470. CrossRef
- A humanized anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-directed antibody-drug conjugate with pyrrolobenzodiazepine payload demonstrates efficacy in ALK-expressing cancers
- Senescent tumor cells in colorectal cancer are characterized by elevated enzymatic activity of complexes 1 and 2 in oxidative phosphorylation
- Jun Sang Shin, Tae-Gyu Kim, Young Hwa Kim, So Yeong Eom, So Hyun Park, Dong Hyun Lee, Tae Jun Park, Soon Sang Park, Jang-Hee Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(6):305-314. Published online November 7, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.10.09
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Ajou University Hospital
- 7,389 View
- 317 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Cellular senescence is defined as an irreversible cell cycle arrest caused by various internal and external insults. While the metabolic dysfunction of senescent cells in normal tissue is relatively well-established, there is a lack of information regarding the metabolic features of senescent tumor cells.
Methods
Publicly available single-cell RNA-sequencing data from the GSE166555 and GSE178341 datasets were utilized to investigate the metabolic features of senescent tumor cells. To validate the single-cell RNA-sequencing data, we performed senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-Gal) staining to identify senescent tumor cells in fresh frozen colorectal cancer tissue. We also evaluated nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase–tetrazolium reductase (NADH-TR) and succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) activity using enzyme histochemical methods and compared the staining with SA-β-Gal staining. MTT assay was performed to reveal the complex 1 activity of the respiratory chain in in-vitro senescence model.
Results
Single-cell RNA-sequencing data revealed an upregulation in the activity of complexes 1 and 2 in oxidative phosphorylation, despite overall mitochondrial dysfunction in senescent tumor cells. Both SA-β-Gal and enzyme histochemical staining using fresh frozen colorectal cancer tissues indicated a high correlation between SA-β-Gal positivity and NADH-TR/SDH staining positivity. MTT assay showed that senescent colorectal cancer cells exhibit higher absorbance in 600 nm wavelength.
Conclusions
Senescent tumor cells exhibit distinct metabolic features, characterized by upregulation of complexes 1 and 2 in the oxidative phosphorylation pathway. NADH-TR and SDH staining represent efficient methods for detecting senescent tumor cells in colorectal cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Senescence, Aging and Disease Throughout the Gastrointestinal System
Sofia Ferreira-Gonzalez, Tomonori Matsumoto, Eiji Hara, Stuart J. Forbes
Gastroenterology.2025; 169(7): 1357. CrossRef - Cellular Aging and Senescence in Cancer: A Holistic Review of Cellular Fate Determinants
Muhammad Tufail, Yu-Qi Huang, Jia-Ju Hu, Jie Liang, Cai-Yun He, Wen-Dong Wan, Can-Hua Jiang, Hong Wu, Ning Li
Aging and disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-time assessment of relative mitochondrial ATP synthesis response against inhibiting and stimulating substrates (MitoRAISE)
Eun Sol Chang, Kyoung Song, Ji-Young Song, Minjung Sung, Mi-Sook Lee, Jung Han Oh, Ji-Yeon Kim, Yeon Hee Park, Kyungsoo Jung, Yoon-La Choi
Cancer & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Senescence, Aging and Disease Throughout the Gastrointestinal System
- Diagnostic proficiency test using digital cytopathology and comparative assessment of whole slide images of cytologic samples for quality assurance program in Korea
- Yosep Chong, Soon Auck Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh, Soo Jin Jung, Bo-Sung Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Ho-Chang Lee, Gyungyub Gong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):251-264. Published online August 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.07.17
- Funded: Korean Society for Cytopathology, National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
- 8,170 View
- 343 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The Korean Society for Cytopathology introduced a digital proficiency test (PT) in 2021. However, many doubtful opinions remain on whether digitally scanned images can satisfactorily present subtle differences in the nuclear features and chromatin patterns of cytological samples.
Methods
We prepared 30 whole-slide images (WSIs) from the conventional PT archive by a selection process for digital PT. Digital and conventional PT were performed in parallel for volunteer institutes, and the results were compared using feedback. To assess the quality of cytological assessment WSIs, 12 slides were collected and scanned using five different scanners, with four cytopathologists evaluating image quality through a questionnaire.
Results
Among the 215 institutes, 108 and 107 participated in glass and digital PT, respectively. No significant difference was noted in category C (major discordance), although the number of discordant cases was slightly higher in the digital PT group. Leica, 3DHistech Pannoramic 250 Flash, and Hamamatsu NanoZoomer 360 systems showed comparable results in terms of image quality, feature presentation, and error rates for most cytological samples. Overall satisfaction was observed with the general convenience and image quality of digital PT.
Conclusions
As three-dimensional clusters are common and nuclear/chromatin features are critical for cytological interpretation, careful selection of scanners and optimal conditions are mandatory for the successful establishment of digital quality assurance programs in cytology. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(2): 146. CrossRef - Sensitivity, Specificity, and Cost–Benefit Effect Between Primary Human Papillomavirus Testing, Primary Liquid‐Based Cytology, and Co‐Testing Algorithms for Cervical Lesions
Chang Gok Woo, Seung‐Myoung Son, Hye‐Kyung Hwang, Jung‐Sil Bae, Ok‐Jun Lee, Ho‐Chang Lee
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(1): 35. CrossRef - Integration of AI‐Assisted in Digital Cervical Cytology Training: A Comparative Study
Yihui Yang, Dongyi Xian, Lihua Yu, Yanqing Kong, Huaisheng Lv, Liujing Huang, Kai Liu, Hao Zhang, Weiwei Wei, Hongping Tang
Cytopathology.2025; 36(2): 156. CrossRef - National quality assurance program using digital cytopathology: a 5-year digital transformation experience by the Korean Society for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Soon Auck Hong, Sung Soon Kim, Bo-Sung Kim, Younghee Choi, Yoon Jung Choi, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Soo Jin Jung, Hoon Kyu Oh, Seung-Sook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(5): 320. CrossRef - Integration of Digital Cytology in Quality Assurance Programs for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Maria Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Zaibo Li, Andrey Bychkov
Acta Cytologica.2025; 70(1): 126. CrossRef - Quantitative Assessment of Focus Quality in Whole-Slide Imaging of Thyroid Liquid-Based Cytology Using Laplacian Variance
Chan Kwon Jung, Chankyung Kim, Sora Jeon, Andrey Bychkov
Endocrine Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of digital image slides for diagnosis in cervico-vaginal cytology
Francisco Tresserra, Gemma Fabra, Olga Luque, Miriam Castélla, Carla Gómez, Carmen Fernández-Cid, Ignacio Rodríguez
Revista Española de Patología.2024; 57(3): 182. CrossRef - Improved Diagnostic Accuracy of Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology with Artificial Intelligence Technology
Yujin Lee, Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Hongsik Park, Kwangil Yim, Kyung Jin Seo, Gisu Hwang, Dahyeon Kim, Yeonsoo Chung, Gyungyub Gong, Nam Hoon Cho, Chong Woo Yoo, Yosep Chong, Hyun Joo Choi
Thyroid®.2024; 34(6): 723. CrossRef
- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Case Study
- Diagnostic conundrums of schwannomas: two cases highlighting morphological extremes and diagnostic challenges in biopsy specimens of soft tissue tumors
- Chankyung Kim, Yang-Guk Chung, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):278-283. Published online August 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.07.13
- Funded: Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 5,886 View
- 267 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Schwannomas are benign, slow-growing peripheral nerve sheath tumors commonly occurring in the head, neck, and flexor regions of the extremities. Although most schwannomas are easily diagnosable, their variable morphology can occasionally create difficulty in diagnosis. Reporting pathologists should be aware that schwannomas can exhibit a broad spectrum of morphological patterns. Clinical and radiological examinations can show correlation and should be performed, in conjunction with ancillary tests, when appropriate. Furthermore, deferring a definitive diagnosis until excision may be necessary for small biopsy specimens and frozen sections. This report underscores these challenges through examination of two unique schwannoma cases, one predominantly cellular and the other myxoid, both of which posed significant challenges in histological interpretation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oral and maxillofacial schwannoma (OMSCH): An institutional study of 102 patients
Lingli Huang, Wenya Zhu, Qicheng Ye, Shengwen Liu, Hao Lu, Wenjun Yang, Wanlin Xu
Journal of Stomatology Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2026; 127(3): 102678. CrossRef - Plexiform Schwannoma Over the Anterior Chest Wall: A Clinicopathological Review
Debojyoti Sasmal, Saswata Barenya, Hinglaj Saha, Pankaj Kumar Halder
Amrita Journal of Medicine.2025; 21(2): 95. CrossRef - Giant Retroperitoneal Schwannoma: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Magdalena Alexieva, Evgeni V Mekov, Silvia Ivanova, Alexandrina Vlahova, Georgi Yankov
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Breast schwannoma: review of entity and differential diagnosis
Sandra Ixchel Sanchez, Ashley Cimino-Mathews
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(6): 353. CrossRef
- Oral and maxillofacial schwannoma (OMSCH): An institutional study of 102 patients
Original Article
- Establishing molecular pathology curriculum for pathology trainees and continued medical education: a collaborative work from the Molecular Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists
- Jiwon Koh, Ha Young Park, Jeong Mo Bae, Jun Kang, Uiju Cho, Seung Eun Lee, Haeyoun Kang, Min Eui Hong, Jae Kyung Won, Youn-La Choi, Wan-Seop Kim, Ahwon Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):265-272. Published online September 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.08.26
- Funded: Korean Society of Pathologists
- 5,721 View
- 208 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The importance of molecular pathology tests has increased during the last decade, and there is a great need for efficient training of molecular pathology for pathology trainees and as continued medical education.
Methods
The Molecular Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists appointed a task force composed of experienced molecular pathologists to develop a refined educational curriculum of molecular pathology. A 3-day online educational session was held based on the newly established structure of learning objectives; the audience were asked to score their understanding of 22 selected learning objectives before and after the session to assess the effect of structured education.
Results
The structured objectives and goals of molecular pathology was established and posted as a web-based interface which can serve as a knowledge bank of molecular pathology. A total of 201 pathologists participated in the educational session. For all 22 learning objectives, the scores of self-reported understanding increased after educational session by 9.9 points on average (range, 6.6 to 17.0). The most effectively improved items were objectives from next-generation sequencing (NGS) section: ‘NGS library preparation and quality control’ (score increased from 51.8 to 68.8), ‘NGS interpretation of variants and reference database’ (score increased from 54.1 to 68.0), and ‘whole genome, whole exome, and targeted gene sequencing’ (score increased from 58.2 to 71.2). Qualitative responses regarding the adequacy of refined educational curriculum were collected, where favorable comments dominated.
Conclusions
Approach toward the education of molecular pathology was refined, which would greatly benefit the future trainees. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Presence of RB1 or Absence of LRP1B Mutation Predicts Poor Overall Survival in Patients with Gastric Neuroendocrine Carcinoma and Mixed Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma
In Hye Song, Bokyung Ahn, Young Soo Park, Deok Hoon Kim, Seung-Mo Hong
Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 57(2): 492. CrossRef
- Presence of RB1 or Absence of LRP1B Mutation Predicts Poor Overall Survival in Patients with Gastric Neuroendocrine Carcinoma and Mixed Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma
Reviews
- A stepwise approach to fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes
- Yosep Chong, Gyeongsin Park, Hee Jeong Cha, Hyun-Jung Kim, Chang Suk Kang, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Seung-Sook Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):196-207. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.12
- Funded: Korean Society for Cytopathology
- 49,466 View
- 2,360 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - The cytological diagnosis of lymph node lesions is extremely challenging because of the diverse diseases that cause lymph node enlargement, including both benign and malignant or metastatic lymphoid lesions. Furthermore, the cytological findings of different lesions often resemble one another. A stepwise diagnostic approach is essential for a comprehensive diagnosis that combines: clinical findings, including age, sex, site, multiplicity, and ultrasonography findings; low-power reactive, metastatic, and lymphoma patterns; high-power population patterns, including two populations of continuous range, small monotonous pattern and large monotonous pattern; and disease-specific diagnostic clues including granulomas and lymphoglandular granules. It is also important to remember the histological features of each diagnostic category that are common in lymph node cytology and to compare them with cytological findings. It is also essential to identify a few categories of diagnostic pitfalls that often resemble lymphomas and easily lead to misdiagnosis, particularly in malignant small round cell tumors, poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinomas, and nasopharyngeal undifferentiated carcinoma. Herein, we review a stepwise approach for fine needle aspiration cytology of lymphoid diseases and suggest a diagnostic algorithm that uses this approach and the Sydney classification system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Critical Role of Ancillary Testing in Fine-Needle Aspiration of Lymph Nodes, Thymus, and Spleen
Diana A. Baptista, Helena Barroca, Fernando C. Schmitt
Acta Cytologica.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Development and Validation of Explainable Artificial Intelligence System for Automatic Diagnosis of Cervical Lymphadenopathy From Ultrasound Images
Ming Xu, Yubiao Yue, Zhenzhang Li, Yinhong Li, Guoying Li, Haihua Liang, Di Liu, Xiaohong Xu, Mohamadreza (Mohammad) Khosravi
International Journal of Intelligent Systems.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of the Sydney system for classification and reporting lymph node cytopathology: a retrospective analysis at a tertiary centre
Ashok Teja Kummari, Pramod Kumar Pamu, Krishna Kiran Ganna, Param Jyothi, Sadashivudu
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic approach to FNA biopsy of cystic lesions of the head and neck
Stefen Andrianus, Olivia Leung, Zubair Baloch
Cancer Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Applicability of Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Lymph Nodes Using WHO Reporting System: Comparison between Pediatric and Adult Brazilian Populations
Leonardo Fávaro Ficoto, Deolino João Camilo Júnior, Gustavo Resende Nora, Vitor Bonetti Valente, Daniel Galera Bernabé, José Cândido Caldeira Xavier-Júnior
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Intraoperative cytological assessment of sentinel lymph nodes in gynecologic cancer: diagnostic accuracy and limitations
O. V. Pankova, S. V. Vtorushin, M. V. Klimova, D. S. Pismenny, M. O. Ochirov, L. A. Kolomiets, V. M. Perelmuter
Siberian journal of oncology.2025; 24(5): 72. CrossRef - From smear to diagnosis: the impact of ancillary techniques in lymph node fine-needle cytology
Elisabetta Maffei, Giuseppe Di Motta, Angela D’Ardia, Riccardo Ruotolo, Valentina Giudice, Alessandro Caputo, Pio Zeppa
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytopathologic Diagnosis of Non-Neoplastic Inflammatory Disorders of Lymphoid Organs
Joy M. Hoang, Havva Gokce Terzioglu, Matthew L. Kleinjan, Tatjana Antic, Nalini Gupta, Manish Rohilla, Radhika Srinivasan, Arvind Rajwanshi, Eva M. Wojcik, Güliz A. Barkan, Mark A. Russell, Swati Mehrotra
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Immunocytochemical markers, molecular testing and digital cytopathology for aspiration cytology of metastatic breast carcinoma
Joshua J. X. Li, Gary M. Tse
Cytopathology.2024; 35(2): 218. CrossRef - Response to comment on “A stepwise approach to fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes”
Yosep Chong, Gyeongsin Park, Hee Jeong Cha, Hyun-Jung Kim, Chang Suk Kang, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Seung-Sook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(1): 43. CrossRef - Comment on “A stepwise approach to fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes”
Elisabetta Maffei, Valeria Ciliberti, Pio Zeppa, Alessandro Caputo
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(1): 40. CrossRef - The Incidence of Thyroid Cancer in Bethesda III Thyroid Nodules: A Retrospective Analysis at a Single Endocrine Surgery Center
Iyad Hassan, Lina Hassan, Nahed Balalaa, Mohamad Askar, Hussa Alshehhi, Mohamad Almarzooqi
Diagnostics.2024; 14(10): 1026. CrossRef - Efficiency of Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) in Relation to Tru-Cut Biopsy of Lateral Neck Swellings
Mohammed S Al Olaimat, Fahad S Al Qooz, Zaid R Alzoubi, Elham M Alsharaiah, Ali S Al Murdif, Mohammad O Alanazi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pitfalls in the Cytological Diagnosis of Nodal Hodgkin Lymphoma
Uma Handa, Rasheeda Mohamedali, Rajpal Singh Punia, Simrandeep Singh, Ranjeev Bhagat, Phiza Aggarwal, Manveen Kaur
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(12): 715. CrossRef - Rapid 3D imaging at cellular resolution for digital cytopathology with a multi-camera array scanner (MCAS)
Kanghyun Kim, Amey Chaware, Clare B. Cook, Shiqi Xu, Monica Abdelmalak, Colin Cooke, Kevin C. Zhou, Mark Harfouche, Paul Reamey, Veton Saliu, Jed Doman, Clay Dugo, Gregor Horstmeyer, Richard Davis, Ian Taylor-Cho, Wen-Chi Foo, Lucas Kreiss, Xiaoyin Sara J
npj Imaging.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Critical Role of Ancillary Testing in Fine-Needle Aspiration of Lymph Nodes, Thymus, and Spleen
- Reevaluating diagnostic categories and associated malignancy risks in thyroid core needle biopsy
- Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):208-216. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.20
- Funded: Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 7,506 View
- 269 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - As the application of core needle biopsy (CNB) in evaluating thyroid nodules rises in clinical practice, the 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules have officially recognized its value for the first time. CNB procures tissue samples preserving both histologic structure and cytologic detail, thereby supplying substantial material for an accurate diagnosis and reducing the necessity for repeated biopsies or subsequent surgical interventions. The current review introduces the risk of malignancy within distinct diagnostic categories, emphasizing the implications of noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features on these malignancy risks. Prior research has indicated diagnostic challenges associated with follicular-patterned lesions, resulting in notable variation within indeterminate diagnostic categories. The utilization of mutation-specific immunostaining in CNB enhances the accuracy of lesion classification. This review underlines the essential role of a multidisciplinary approach in diagnosing follicular-patterned lesions and the potential of mutation-specific immunostaining to strengthen diagnostic consensus and inform patient management decisions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lessons learned from the first 2 years of experience with thyroid core needle biopsy at an Indonesian national referral hospital
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Maria Francisca Ham, Retno Asti Werdhani, Erwin Danil Julian, Rafi Ilmansyah, Chloe Indira Arfelita Mangunkusumso, Tri Juli Edi Tarigan
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(3): 149. CrossRef - Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules Diagnosed as Follicular Neoplasm on Core Needle Biopsy
Byeong-Joo Noh, Won Jun Kim, Jin Yub Kim, Ha Young Kim, Jong Cheol Lee, Myoung Sook Shim, Yong Jin Song, Kwang Hyun Yoon, In-Hye Jung, Hyo Sang Lee, Wooyul Paik, Dong Gyu Na
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(4): 610. CrossRef - Diagnostic implication of thyroid spherules for cytological diagnosis of thyroid nodules
Heeseung Sohn, Kennichi Kakudo, Chan Kwon Jung
Cytopathology.2024; 35(3): 383. CrossRef - A Narrative Review of the 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guideline for Patients with Thyroid Nodules
Eun Kyung Lee, Young Joo Park, Chan Kwon Jung, Dong Gyu Na
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 61. CrossRef - The Diagnostic Role of Repeated Biopsy of Thyroid Nodules with Atypia of Undetermined Significance with Architectural Atypia on Core-Needle Biopsy
Hye Hyeon Moon, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Tae-Yon Sung, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jung Hwan Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(2): 300. CrossRef - Core needle biopsy for thyroid nodules assessment-a new horizon?
David D Dolidze, Serghei Covantsev, Grigorii M Chechenin, Natalia V Pichugina, Anastasia V Bedina, Anna Bumbu
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2024; 15(5): 580. CrossRef - Educational exchange in thyroid core needle biopsy diagnosis: enhancing pathological interpretation through guideline integration and peer learning
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(5): 205. CrossRef - A simplified four-tier classification for thyroid core needle biopsy
M. Paja, J. L. Del Cura, R. Zabala, I. Korta, Mª T. Gutiérrez, A. Expósito, A. Ugalde
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2024; 48(4): 895. CrossRef
- Lessons learned from the first 2 years of experience with thyroid core needle biopsy at an Indonesian national referral hospital
Original Articles
- Loss of aquaporin-1 expression is associated with worse clinical outcomes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study
- Seokhyeon Lee, Bohyun Kim, Minsun Jung, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):232-237. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.17
- Funded: College of Medicine, Seoul National University
- 4,985 View
- 171 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Aquaporin (AQP) expression has been investigated in various malignant neoplasms, and the overexpression of AQP is related to poor prognosis in some malignancies. However, the expression of AQP protein in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) has not been extensively investigated by immunohistochemistry with large sample size.
Methods
We evaluated the AQP expression in 827 ccRCC with immunohistochemical staining in tissue microarray blocks and classified the cases into two categories, high and low expression.
Results
High expression of aquaporin-1 (AQP1) was found in 320 cases (38.7%), but aquaporin-3 was not expressed in ccRCC. High AQP1 expression was significantly related to younger age, low TNM stage, low World Health Organization/International Society of Urologic Pathology nuclear grade, and absence of distant metastasis. Furthermore, high AQP1 expression was also significantly associated with longer overall survival (OS; p<.001) and progression-specific survival (PFS; p<.001) and was an independent predictor of OS and PFS in ccRCC.
Conclusions
Our study revealed the prognostic significance of AQP1 protein expression in ccRCC. These findings could be applied to predict the prognosis of ccRCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Loss of Aquaporin-1 in Tumor Cells Fosters Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Progression
César I. Gaspari, Carine Beaupere, Seth Richard, Estanislao Peixoto, Bouchra Lekbaby, Mirko Minini, Branko Dubravcic, Javier Vaquero, Marie Vallette, Ander Arbelaiz, Marion Janona, Corentin Louis, Pauline Le Gall, Cédric Coulouarn, Julieta Marrone, Juan E
The American Journal of Pathology.2026; 196(2): 428. CrossRef - Construction and validation of renal cell carcinoma tumor cell differentiation-related prognostic classification (RCC-TCDC): an integrated bioinformatic analysis and clinical study
Yifan Liu, Keqin Dong, Yuntao Yao, Bingnan Lu, Lei Wang, Guo Ji, Haoyu Zhang, Zihui Zhao, Xinyue Yang, Runzhi Huang, Wang Zhou, Xiuwu Pan, Xingang Cui
Annals of Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Assessment of Aquaporins in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: An In Silico Analysis
Vignesh Krishnasamy, Lalhmingliana, Nachimuthu Senthil Kumar
Current Biotechnology.2025; 14(2): 130. CrossRef - Targeting PLOD2 induces epithelioid differentiation and improves therapeutic response in sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma
Xiangyu Chen, Dongkui Xu, Yu Ji, Xichen Dong, Xiaomei Dong, Zihan Li, Jingyu Tan, Qianqian Sun, Huixian Xin, Ziwei Liu, Qing Deng, Tao Wen, Yanjun Jia, Xuhui Zhu, Jian Liu
Journal of Advanced Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Exosomal MiR-874 as a Potential Biomarker for Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
Amal F. Gharib, Saad S. Al-Shehri, Abdulraheem Almalki, Ayman Alhazmi, Mamdouh Allahyani, Ahmed Alghamdi, Amani A. Alrehaili, Maha M. Bakhuraysah, Althobaiti Naif Saad M., Weal H. Elsawy
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Loss of Aquaporin-1 in Tumor Cells Fosters Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Progression
- Expression of specific microRNAs in tissue and plasma in colorectal cancer
- Allan Fellizar, Vivencio Refuerzo, John Donnie Ramos, Pia Marie Albano
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(3):147-157. Published online May 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.02.19
- Funded: Commission on Higher Education, Philippine Association of Medical Technologists
- 11,760 View
- 603 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
MicroRNAs (miRNA/miR) play significant roles in the regulation of cell differentiation, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis. They become dysregulated during carcinogenesis and are eventually released into the circulation, enabling their detection in body fluids. Thus, this study compared the miRNA expression in tissue and plasma samples of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients and clinically healthy controls and determined miRNA expression as a potential CRC biomarker.
Methods
Using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), miR-21-5p, miR-29a-3p, miR-92a-3p, miR-135b-5p, miR-196b-5p, and miR-197-3p, expression was analyzed and compared between the malignant (n = 41) and the adjacent neoplasm free mucosal tissues (n = 41) of CRC patients. The findings were validated in plasma samples (n = 36) collected from the same CRC patients prior to surgery or any form of treatment and compared to plasma from their age and sex-matched controls (n = 36).
Results
MiR-21-5p, miR-29a-3p, miR-92a-3p, and miR- 196b-5p were upregulated and miR-135b-5p was downregulated in CRC malignant tissues compared to their expression in adjacent neoplasm-free tissue. This was further observed in the plasma of the same CRC cases compared to controls. MiR-92a-3p showed itself the most sensitive (0.93; p < .001) and most specific (0.95; p < .001) in detecting CRC in tissue. In plasma, miR-196b-5p was the most sensitive (0.97; p < .001) and specific (0.94; p < .001) in detecting CRC. Plasma miR-92a-3p and miR-196b-5p were the most sensitive (0.95; p < .001) and specific (0.94; p < .001) in the early detection of CRC.
Conclusions
Results show that specific miRNAs dysregulated in malignant tissues are released and can be detected in the circulation, supporting their potential as non-invasive biomarkers of CRC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Liquid biopsy for the management of gastrointestinal cancers
Zeinab Salehnia, Delsuz Rezaee, Sajad Ehtiati, Mohammad Bakhtiari, Mohammad Amin Khalilzad, Sajad Najafi
Clinica Chimica Acta.2026; 578: 120474. CrossRef - Differential Circulating miRNA Responses to PM Exposure in Healthy and Diabetes Mellitus Patients: Implications for Lung Cancer Susceptibility
Moe Thi Thi Han, Nichakorn Satitpornbunpot, Naoomi Tominaga, Saranta Freeouf, Khanittha Punturee, Chidchamai Kewchareonwong, Busayamas Chewaskulyong, Ganjana Lertmemongkolchai, Ratchada Cressey
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2026; 27(2): 613. CrossRef - Unlocking the power of non-coding RNAs: toward real-time cancer monitoring in precision oncology
Manon Chang, Thomas Papazyan, Elvire Pons-Tostivint, Delphine Fradin
Molecular Cancer.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Except for Robust Outliers, Rapamycin Increases Lesion Burden in a Murine Model of Cerebral Cavernous Malformations
Roberto J. Alcazar-Felix, Robert Shenkar, Christian R. Benavides, Akash Bindal, Abhinav Srinath, Ying Li, Serena Kinkade, Tatiana Terranova, Evon DeBose-Scarlett, Rhonda Lightle, Dorothy DeBiasse, Hanadi Almazroue, Diana Vera Cruz, Sharbel Romanos, Aditya
Translational Stroke Research.2025; 16(3): 859. CrossRef - miR-135b: A key role in cancer biology and therapeutic targets
Yingchun Shao, Shuangshuang Zhang, Yuxin Pan, Zhan Peng, Yinying Dong
Non-coding RNA Research.2025; 12: 67. CrossRef - The role of tumor-associated fibroblast-derived exosomes in chemotherapy resistance of colorectal cancer and its application prospect
Meichen Liu, Teng-zheng Li, Congcong Xu
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects.2025; 1869(6): 130796. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of MicroRNAs in Hemorrhagic Neurovascular Disease: Cerebral Cavernous Malformations as a Paradigm
Roberto J. Alcazar-Felix, Aditya Jhaveri, Javed Iqbal, Abhinav Srinath, Carolyn Bennett, Akash Bindal, Diana Vera Cruz, Sharbel Romanos, Stephanie Hage, Agnieszka Stadnik, Justine Lee, Rhonda Lightle, Robert Shenkar, Janne Koskimäki, Sean P. Polster, Romu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(8): 3794. CrossRef - microRNA-196b-5p expression in cancer tissues is closely associated with clinical and pathological characteristics and prognosis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Wei Liu, Xiaomin Lu, Changgang Yang, Fengjun Ji, Xiaodan Wu
Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of mir196a2 and mir146a polymorphisms and colorectal cancer risk: A meta-analysis
Zahraa isam jameel, Hanan Ali Kareem, Zahraa Mohammed Yahya, Ahmed Ali Hussein, zahraa abdel Kareem
Human Gene.2025; 45: 201448. CrossRef - Micro RNA in Colorectal Cancer—Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers—An Updated Review
Weronika Pająk, Jakub Kleinrok, Joanna Pec, Karolina Michno, Jan Wojtas, Miłosz Badach, Barbara Teresińska, Jacek Baj
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(17): 8615. CrossRef - MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer: A comparative analysis of circulating and tissue microRNA levels
Iulia Andreea Pelisenco, Bogdan Trandafir, Anastasia-Maria Dobre, Andrei-Daniel Dragne, Vlad Herlea, Andrei Marian Niculae, Catalin Vasilescu, Mihail Eugen Hinescu, Elena Milanesi, Maria Dobre
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of miRNAs Present in Cell- and Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles—Possible Biomarkers of Colorectal Cancer
Marzena Lenart, Izabela Siemińska, Rafał Szatanek, Anna Mordel, Antoni Szczepanik, Mateusz Rubinkiewicz, Maciej Siedlar, Monika Baj-Krzyworzeka
Cancers.2024; 16(13): 2464. CrossRef - The emerging role of blood-based biomarkers in early detection of colorectal cancer: A systematic review
Faris Shweikeh, Yuhao Zeng, Abdur Rahman Jabir, Erica Whittenberger, Saurav P. Kadatane, Yuting Huang, Mohamad Mouchli, Dani Ran Castillo
Cancer Treatment and Research Communications.2024; 42: 100872. CrossRef - The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Colorectal Cancer
Yujian Xia, Chaoran Yu, Ernest Johann Helwig, Yousheng Li
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HNRNPA2B1-Mediated MicroRNA-92a Upregulation and Section Acts as a Promising Noninvasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer
Yiling Li, Kexin Li, Xiaoying Lou, Yue Wu, Samuel Seery, Danfei Xu, Yuqing Pei, Benheng Qian, Yuxin Wu, Shuang Liang, Kui Wu, Wei Cui
Cancers.2023; 15(4): 1367. CrossRef - Role of salivary miRNAs in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal disorders: a mini-review of available evidence
Maria Oana Săsăran, Claudia Bănescu
Frontiers in Genetics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Role of Circulating Cell-Free RNA in the Development of Colorectal Cancer
Chau-Ming Kan, Xiao Meng Pei, Martin Ho Yin Yeung, Nana Jin, Simon Siu Man Ng, Hin Fung Tsang, William Chi Shing Cho, Aldrin Kay-Yuen Yim, Allen Chi-Shing Yu, Sze Chuen Cesar Wong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(13): 11026. CrossRef - Lynch Syndrome Biopathology and Treatment: The Potential Role of microRNAs in Clinical Practice
Serena Ascrizzi, Grazia Maria Arillotta, Katia Grillone, Giulio Caridà, Stefania Signorelli, Asad Ali, Caterina Romeo, Pierfrancesco Tassone, Pierosandro Tagliaferri
Cancers.2023; 15(15): 3930. CrossRef
- Liquid biopsy for the management of gastrointestinal cancers
- Clinicopathologic characterization of cervical metastasis from an unknown primary tumor: a multicenter study in Korea
- Miseon Lee, Uiree Jo, Joon Seon Song, Youn Soo Lee, Chang Gok Woo, Dong-Hoon Kim, Jung Yeon Kim, Sun Och Yoon, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(3):166-177. Published online May 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.04.12
- Funded: Korean Society of Pathologists
- 6,581 View
- 172 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Research regarding cervical metastasis from an unknown primary tumor (CUP) according to human papillomavirus (HPV) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) status in Korea has been sporadic and small-scale. This study aims to analyze and understand the characteristics of CUP in Korea according to viral and p16 and p53 status through a multicenter study.
Methods
Ninety-five cases of CUP retrieved from six hospitals in Korea between January 2006 and December 2016 were subjected to high-risk HPV detection (DNA in situ hybridization [ISH] or real-time polymerase chain reaction), EBV detection (ISH), and immunohistochemistry for p16 and p53.
Results
CUP was HPV-related in 37 cases (38.9%), EBV-related in five cases (5.3%), and unrelated to HPV or EBV in 46 cases (48.4%). HPV-related CUP cases had the best overall survival (OS) (p = .004). According to the multivariate analysis, virus-unrelated disease (p = .023) and longer smoking duration (p < .005) were prognostic factors for poor OS. Cystic change (p = .016) and basaloid pattern (p < .001) were more frequent in HPV-related cases, and lymphoepithelial lesion was frequent in EBV-related cases (p = .010). There was no significant association between viral status and p53 positivity (p = .341), smoking status (p = .728), or smoking duration (p = .187). Korean data differ from Western data in the absence of an association among HPV, p53 positivity, and smoking history.
Conclusions
Virus-unrelated CUP in Korea had the highest frequency among all CUP cases. HPV-related CUP is similar to HPV-mediated oropharyngeal cancer and EBVrelated CUP is similar to nasopharyngeal cancer in terms of characteristics, respectively. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Management of squamous cell carcinoma of unknown primary in the head and neck: current evidence-based diagnostic and treatment strategies
Marcel Kloppenburg, Matthias Santer, Lukas Schmutzler, Felix Johnson, Benedikt Hofauer, Teresa Steinbichler
memo - Magazine of European Medical Oncology.2026; 19(1): 45. CrossRef - Differenzierung von benignen und malignen Halszysten – eine diagnostische Herausforderung
Christina Sauter, Matthias Sand, Karim Plath, Michaela Maria Plath
Laryngo-Rhino-Otologie.2025; 104(05): 296. CrossRef - Unlocking the Hidden: Advancing Imaging Techniques in Diagnosing Cancers of Unknown Primary in the Head and Neck Region
Daniela Messineo, Filippo Valentini, Giovanni Francesco Niccolini, Federica Zoccali, Francesca Ripari, Enrico Marotta, Marcello Caratozzolo, Pasquale Frisina
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(4): 2194. CrossRef - Characterization of undifferentiated carcinoma of the salivary gland: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analyses in comparison with lymphoepithelial carcinoma
Sangjoon Choi, Gyuheon Choi, Hee Jin Lee, Joon Seon Song, Yoon Se Lee, Seung-Ho Choi, Kyung-Ja Cho
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(6): 361. CrossRef - Expansion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to assess the potential of adoptive cell therapy
Sangjoon Choi, Mofazzal Hossain, Hyun Lee, Jina Baek, Hye Seon Park, Chae-Lyul Lim, DoYeon Han, Taehyun Park, Jong Hyeok Kim, Gyungyub Gong, Mi-Na Kweon, Hee Jin Lee
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Management of squamous cell carcinoma of unknown primary in the head and neck: current evidence-based diagnostic and treatment strategies
- Current state of cytopathology residency training: a Korean national survey of pathologists
- Uiju Cho, Tae Jung Kim, Wan Seop Kim, Kyo Young Lee, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Hyun Joo Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(2):95-101. Published online March 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.01.06
- Funded: Korean Society for Cytopathology, Korea
- 4,074 View
- 82 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Although the Korean Society for Cytopathology has developed educational goals as guidelines for cytopathology education in Korea, there is still no systematic approach to cytopathology education status for pathology residents. Furthermore, satisfaction with cytopathology education and with the outcome of the current training/educational program has not been investigated in Korea. This study aimed to obtain comprehensive data on the current state of cytopathology education for residents and evaluate education outcomes.
Methods
An online survey was conducted in December 2020 for the board-certified pathologists and training residents registered as members of the Korean Society for Cytopathology. The questionnaire comprised questions that investigated the current status of cytopathology at each training institution, the degree of satisfaction with the work and education related to cytopathology, outcomes of cytopathology training, and educational accomplishments.
Results
Of the participants surveyed, 12.3% (132/1,075) completed the questionnaire, and 36.8% (32/87) of cytopathology residents participated. The mean overall satisfaction with cytopathology education was 3.1 points (on a 1- to 5-point scale, 5: very satisfied). The most frequent suggestion among the free description format responses was to expand educational opportunities, such as online education opportunities, outside of the individual institutions.
Conclusions
Our results showed that cytopathology training in Korea needs further improvement. We expect that this study will inform systematic training of competent medical personnel armed with broad cytopathology knowledge and strong problem-solving abilities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Artificial Intelligence–Assisted Daily Quality Control System for the Histologic Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Biopsies: A 1-Year Experience
Seung-Yeon Yoo, Yuri Hwang, Seokju Yun, Ok Hee Lee, Jiwook Jang, Youngjin Park, Tae Young Cho, Young Sin Ko
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2025; 149(7): 659. CrossRef
- Artificial Intelligence–Assisted Daily Quality Control System for the Histologic Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Biopsies: A 1-Year Experience
- Postmortem lung and heart examination of COVID-19 patients in a case series from Jordan
- Maram Abdaljaleel, Isra Tawalbeh, Malik Sallam, Amjad Bani Hani, Imad M. Al-Abdallat, Baheth Al Omari, Sahar Al-Mustafa, Hasan Abder-Rahman, Adnan Said Abbas, Mahmoud Zureigat, Mousa A. Al-Abbadi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(2):102-112. Published online March 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.01.30
- Funded: Deanship of Scientific Research at the University of Jordan
- 7,295 View
- 171 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has emerged as a pandemic for more than 2 years. Autopsy examination is an invaluable tool to understand the pathogenesis of emerging infections and their consequent mortalities. The aim of the current study was to present the lung and heart pathological findings of COVID-19–positive autopsies performed in Jordan.
Methods
The study involved medicolegal cases, where the cause of death was unclear and autopsy examination was mandated by law. We included the clinical and pathologic findings of routine gross and microscopic examination of cases that were positive for COVID-19 at time of death. Testing for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was confirmed through molecular detection by real-time polymerase chain reaction, serologic testing for IgM and electron microscope examination of lung samples.
Results
Seventeen autopsies were included, with male predominance (76.5%), Jordanians (70.6%), and 50 years as the mean age at time of death. Nine out of 16 cases (56.3%) had co-morbidities, with one case lacking such data. Histologic examination of lung tissue revealed diffuse alveolar damage in 13/17 cases (76.5%), and pulmonary microthrombi in 8/17 cases (47.1%). Microscopic cardiac findings were scarcely detected. Two patients died as a direct result of acute cardiac disease with limited pulmonary findings.
Conclusions
The detection of SARS-CoV-2 in postmortem examination can be an incidental or contributory finding which highlights the value of autopsy examination to determine the exact cause of death in controversial cases.
- The proteomic landscape shows oncologic relevance in cystitis glandularis
- Jun Yong Kim, Dohyun Han, Hyeyoon Kim, Minsun Jung, Han Suk Ryu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(1):67-74. Published online December 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.10.24
- Funded: Korean Society of Pathologists
- 5,791 View
- 177 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The relationship between cystitis glandularis (CG) and bladder malignancy remains unclear.
Methods
We identified the oncologic significance of CG at the molecular level using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis of 10 CG, 12 urothelial carcinoma (UC), and nine normal urothelium (NU) specimens. Differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) were identified based on an analysis of variance false discovery rate < 0.05, and their functional enrichment was analyzed using a network model, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis, and Gene Ontology annotation.
Results
We identified 9,890 proteins across all samples and 1,139 DEPs among the three entities. A substantial number of DEPs overlapped in CG/NU, distinct from UC. Interestingly, we found that a subset of DEP clusters (n = 53, 5%) was differentially expressed in NU but similarly between CG and UC. This “UC-like signature” was enriched for reactive oxygen species (ROS) and energy metabolism, growth and DNA repair, transport, motility, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and cell survival. Using the top 10 shortlisted DEPs, including SOD2, PRKCD, CYCS, and HCLS1, we identified functional elements related to ROS metabolism, development, and transport using network analysis. The abundance of these four molecules in UC/CG than in NU was consistent with the oncologic functions in CG.
Conclusions
Using a proteomic approach, we identified a predominantly non-neoplastic landscape of CG, which was closer to NU than to UC. We also confirmed a small subset of common DEPs in UC and CG, suggesting that altered ROS metabolism might imply potential cancerous risks in CG. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantitative proteomics and immunohistochemistry uncover NT5DC2 as a diagnostic biomarker for papillary urothelial carcinoma
Jun Yong Kim, Jae Seok Lee, Dohyun Han, Ilias P. Nikas, Hyeyoon Kim, Minsun Jung, Han Suk Ryu
Heliyon.2024; 10(15): e35475. CrossRef - KRT18 as a Novel Biomarker of Urothelial Papilloma while Evaluating Low-Grade Papillary Urothelial Neoplasms: Bi-Center Analysis
Minsun Jung, Bohyun Kim, Jae Seok Lee, Jun Yong Kim, Dohyun Han, Kwangsoo Kim, Sunah Yang, Eun Na Kim, Hyeyooon Kim, Ilias P. Nikas, Sohyeon Yang, Kyung Chul Moon, Hyebin Lee, Han Suk Ryu
Pathobiology.2024; : 1. CrossRef
- Quantitative proteomics and immunohistochemistry uncover NT5DC2 as a diagnostic biomarker for papillary urothelial carcinoma
Reviews
- Single-cell and spatial sequencing application in pathology
- Yoon-Seob Kim, Jinyong Choi, Sug Hyung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(1):43-51. Published online January 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.12.12
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea
- 10,752 View
- 412 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traditionally, diagnostic pathology uses histology representing structural alterations in a disease’s cells and tissues. In many cases, however, it is supplemented by other morphology-based methods such as immunohistochemistry and fluorescent in situ hybridization. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is one of the strategies that may help tackle the heterogeneous cells in a disease, but it does not usually provide histologic information. Spatial sequencing is designed to assign cell types, subtypes, or states according to the mRNA expression on a histological section by RNA sequencing. It can provide mRNA expressions not only of diseased cells, such as cancer cells but also of stromal cells, such as immune cells, fibroblasts, and vascular cells. In this review, we studied current methods of spatial transcriptome sequencing based on their technical backgrounds, tissue preparation, and analytic procedures. With the pathology examples, useful recommendations for pathologists who are just getting started to use spatial sequencing analysis in research are provided here. In addition, leveraging spatial sequencing by integration with scRNA-seq is reviewed. With the advantages of simultaneous histologic and single-cell information, spatial sequencing may give a molecular basis for pathological diagnosis, improve our understanding of diseases, and have potential clinical applications in prognostics and diagnostic pathology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trends and Challenges of the Modern Pathology Laboratory for Biopharmaceutical Research Excellence
Sílvia Sisó, Anoop Murthy Kavirayani, Suzana Couto, Birgit Stierstorfer, Sunish Mohanan, Caroline Morel, Mathiew Marella, Dinesh S. Bangari, Elizabeth Clark, Annette Schwartz, Vinicius Carreira
Toxicologic Pathology.2025; 53(1): 5. CrossRef - Single-cell RNA sequencing in osteosarcoma: applications in diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment
Christèle Asmar, Guy Awad, Marc Boutros, Simon Daccache, Alain Chebly, Catherine Alix-Panabières, Hampig-Raphael Kourié
Medical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterizing Stroke Clots Using Single‐Cell Sequencing
Daniela Renedo, Tanyeri Barak, Jonathan DeLong, Julian N. Acosta, Nanthiya Sujijantarat, Andrew Koo, Cyprien A. Rivier, Santiago Clocchiatti‐Tuozzo, Shufan Huo, Joseph Antonios, James Giles, Guido J. Falcone, Kevin N. Sheth, Ryan Hebert, Murat Gunel, Laur
Journal of the American Heart Association.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Spatial transcriptomics meets diabetic kidney disease: Illuminating the path to precision medicine
Dan-Dan Liu, Han-Yue Hu, Fei-Fei Li, Qiu-Yue Hu, Ming-Wei Liu, You-Jin Hao, Bo Li
World Journal of Diabetes.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Spatial Transcriptomics in Pancreatic Cancer: Current Insights and Future Directions
Jin Su Kim
Journal of Digestive Cancer Research.2025; 13(3): 288. CrossRef - Incorporating Novel Technologies in Precision Oncology for Colorectal Cancer: Advancing Personalized Medicine
Pankaj Ahluwalia, Kalyani Ballur, Tiffanie Leeman, Ashutosh Vashisht, Harmanpreet Singh, Nivin Omar, Ashis K. Mondal, Kumar Vaibhav, Babak Baban, Ravindra Kolhe
Cancers.2024; 16(3): 480. CrossRef - Potential therapeutic targets for hypotension in duchenne muscular dystrophy
Harshi Saxena, Neal L. Weintraub, Yaoliang Tang
Medical Hypotheses.2024; 185: 111318. CrossRef - The crosstalk role of CDKN2A between tumor progression and cuproptosis resistance in colorectal cancer
Xifu Cheng, Famin Yang, Yuanheng Li, Yuke Cao, Meng Zhang, Jiameng JI, Yuxiao Bai, Qing Li, Qiongfang Yu, Dian Gao
Aging.2024; 16(12): 10512. CrossRef - Enquête exclusive sur le psoriasis
Imrane Ben Moussa, Bienfait Abasi-Ali, Fatima-Zahra Afarhkhane, Inès Mountadir, Claire Deligne
médecine/sciences.2024; 40(6-7): 584. CrossRef - Mechanisms of radiation‐induced tissue damage and response
Lin Zhou, Jiaojiao Zhu, Yuhao Liu, Ping‐Kun Zhou, Yongqing Gu
MedComm.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative analysis of single-cell transcriptomic technologies in plants and animals
Vamsidhar Reddy Netla, Harshraj Shinde, Gulshan Kumar, Ambika Dudhate, Jong Chan Hong, Ulhas Sopanrao Kadam
Current Plant Biology.2023; 35-36: 100289. CrossRef - Fibroblasts – the cellular choreographers of wound healing
Samuel Knoedler, Sonja Broichhausen, Ruiji Guo, Ruoxuan Dai, Leonard Knoedler, Martin Kauke-Navarro, Fortunay Diatta, Bohdan Pomahac, Hans-Guenther Machens, Dongsheng Jiang, Yuval Rinkevich
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Trends and Challenges of the Modern Pathology Laboratory for Biopharmaceutical Research Excellence
- Perspectives on single-nucleus RNA sequencing in different cell types and tissues
- Nayoung Kim, Huiram Kang, Areum Jo, Seung-Ah Yoo, Hae-Ock Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(1):52-59. Published online January 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.12.19
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
- 24,682 View
- 477 Download
- 43 Web of Science
- 37 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Single-cell RNA sequencing has become a powerful and essential tool for delineating cellular diversity in normal tissues and alterations in disease states. For certain cell types and conditions, there are difficulties in isolating intact cells for transcriptome profiling due to their fragility, large size, tight interconnections, and other factors. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) is an alternative or complementary approach for cells that are difficult to isolate. In this review, we will provide an overview of the experimental and analysis steps of snRNA-seq to understand the methods and characteristics of general and tissue-specific snRNA-seq data. Knowing the advantages and limitations of snRNA-seq will increase its use and improve the biological interpretation of the data generated using this technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integrative Genomics Approach Identifies Glial Transcriptomic Dysregulation and Risk in the Cortex of Individuals With Alcohol Use Disorder
Anna S. Warden, Nihal A. Salem, Eric Brenner, Greg T. Sutherland, Julia Stevens, Manav Kapoor, Alison M. Goate, R. Dayne Mayfield
Biological Psychiatry.2026; 99(1): 34. CrossRef - Müller cell glutamine metabolism links photoreceptor and endothelial injury in diabetic retinopathy
Katia Corano Scheri, Yi-Wen Hsieh, Thomas Tedeschi, James B Hurley, Amani A Fawzi
Life Science Alliance.2026; 9(2): e202503434. CrossRef - Leveraging Single-Cell Technologies to Advance Understanding of Myocardial Disease
Robert S. Gardner, Nathan R. Tucker, Kaushik Amancherla
Circulation Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Single-cell and spatial omics: exploring hypothalamic heterogeneity
Muhammad Junaid, Eun Jeong Lee, Su Bin Lim
Neural Regeneration Research.2025; 20(6): 1525. CrossRef - Exploring the utility of snRNA-seq in profiling human bladder tissue: A comprehensive comparison with scRNA-seq
Briana Santo, Emily E. Fink, Alexandra E. Krylova, Yi-Chia Lin, Mohamed Eltemamy, Alvin Wee, Oliver Wessely, Byron H. Lee, Angela H. Ting
iScience.2025; 28(1): 111628. CrossRef - Applications and emerging challenges of single-cell RNA sequencing technology in tumor drug discovery
Lu Zhang, Yueying Yang, Jianjun Tan
Drug Discovery Today.2025; 30(2): 104290. CrossRef - Techniques and analytic workflow for spatial transcriptomics and its application to allergy and inflammation
Haihan Zhang, Matthew T. Patrick, Jingyu Zhao, Xintong Zhai, Jialin Liu, Zheng Li, Yiqian Gu, Joshua Welch, Xiang Zhou, Robert L. Modlin, Lam C. Tsoi, Johann E. Gudjonsson
Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.2025; 155(3): 678. CrossRef - Single-cell RNA sequencing in autoimmune diseases: New insights and challenges
Jialing Huang, Yuelin Hu, Shuqing Wang, Yuefang Liu, Xin Sun, Xin Wang, Hongsong Yu
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2025; 267: 108807. CrossRef - SGK1 drives hippocampal demyelination and diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction in mice
Ziying Jiang, Bin Liu, Tangsheng Lu, Xiaoxing Liu, Renjun Lv, Kai Yuan, Mengna Zhu, Xinning Wang, Shangbin Li, Song Xu, Xinyu Wang, Yifei Wang, Zhenfang Gao, Peiqing Zhao, Zongyong Zhang, Junwei Hao, Lin Lu, Qingqing Yin
Nature Communications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Unraveling cell–cell communication with NicheNet by inferring active ligands from transcriptomics data
Chananchida Sang-aram, Robin Browaeys, Ruth Seurinck, Yvan Saeys
Nature Protocols.2025; 20(6): 1439. CrossRef - A versatile and efficient method to isolate nuclei from low-input cryopreserved tissues for single-nuclei transcriptomics
Cristopher Segovia, Vincent Desrosiers, Fatemeh Khadangi, Karine Robitaille, Victoria Saavedra Armero, Myreille D’Astous, Gabriel Khelifi, Alain Bergeron, Samer Hussein, Maxime Richer, Yohan Bossé, Yves Fradet, Vincent Fradet, Steve Bilodeau
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of single-cell sequencing technology and its clinical implications in Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease: a narrative review
Zhonghao Chen, Jack Shi, Longfei Li
Advanced Technology in Neuroscience.2025; 2(1): 9. CrossRef - SGK1 upregulation in GFAP+ neurons in the frontal association cortex protects against neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury
Anbiao Wu, Guang Yang, Genyu Liu, Jiyan Zhang
Cell Death & Disease.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Expert recommendations to standardize transcriptomic analysis in inflammatory bowel disease clinical trials
Bryan Linggi, Salas Azucena, Boyd Steere, Bram Verstockt, Dahham Alsoud, David Casero, Dermot McGovern, Eileen Chan, Michelle I Smith, Federica Ungaro, Florian Rieder, Konrad Aden, Lisa M Shackelton, Luca Massimino, Markus Neurath, Matthieu Allez, Raja At
Journal of Crohn's and Colitis.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcriptional characterization of sepsis in a LPS porcine model
Ryan Neill
Molecular Genetics and Genomics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Single nuclear‐spatial transcriptomic sequencing reveals distinct puncture‐induced cell subpopulations in the intervertebral disc of a rat model
Guoyan Liang, Jing Tan, Chong Chen, Yuying Liu, Yongyu Ye, Xiaolin Pan, Qiujian Zheng, Yunbing Chang, Feng‐Juan Lyu
Clinical and Translational Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Harp: data harmonization for computational tissue deconvolution across diverse transcriptomics platforms
Zahra Nozari, Paul Hüttl, Jakob Simeth, Marian Schön, James A Hutchinson, Rainer Spang, Macha Nikolski
Bioinformatics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Transformation of an Olfactory Placode-Derived Cell into One with Stem Cell Characteristics by Disrupting Epigenetic Barriers
Ghazia Abbas, Rutesh Vyas, Joyce C. Noble, Brian Lin, Robert P. Lane
Cellular Reprogramming.2025; 27(4): 164. CrossRef - Altered Neuroinflammatory Transcriptomic Profile in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus Three Weeks After Lateral Fluid Percussion Injury in Rats
Anthony J. DeSana, Yara Alfawares, Roshni Khatri, Tracy M. Hopkins, Faith V. Best, Jennifer L. McGuire, Laura B. Ngwenya
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(18): 9140. CrossRef - Methodologies for Sample Multiplexing and Computational Deconvolution in Single‐Cell Sequencing
Yufei Gao, Weiwei Yin, Wei Hu, Wei Chen
Advanced Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A single-nucleus transcriptomic atlas of the adult Aedes aegypti mosquito
Olivia V. Goldman, Alexandra E. DeFoe, Yanyan Qi, Yaoyu Jiao, Shih-Che Weng, Brittney Wick, Leah Houri-Zeevi, Priyanka Lakhiani, Takeshi Morita, Jacopo Razzauti, Adriana Rosas-Villegas, Yael N. Tsitohay, Madison M. Walker, Ben R. Hopkins, Joshua X.D. Ang,
Cell.2025; 188(25): 7267. CrossRef - Leveraging single-cell RNA-seq in helminthology
Yi Mu, Chika P. Zumuk, Malcolm K. Jones, Pengfei Cai
Trends in Parasitology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Administration of a barcoded AAV capsid library to the putamen of non-human primates identifies variants with efficient retrograde transport
Yulia Dzhashiashvili, Jodi L. McBride, Emily Fabyanic, Xin Huang, Brian M. Kelly, Greglynn D. Walton-Gibbs, Vimala Vemireddi, Joan Wicks, Mohamad Nayal, Ariel A. Hippen, Zhenming Yu, Pichai Raman, Elizabeth Ramsburg, Marcus Davidsson, Esteban A. Engel, To
Molecular Therapy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Single-nucleus RNA sequencing resolves microenvironmental dynamics in brown/beige adipose tissue after bariatric surgery
Wei Wang, Yangxingyun Wang, Zhonghao Guo, Yao Lu, Wei Xie, Ruibin Li
Journal of Translational Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mapping the cellular landscape of Atlantic salmon head kidney by single cell and single nucleus transcriptomics
Adriana M.S. Andresen, Richard S. Taylor, Unni Grimholt, Rose Ruiz Daniels, Jianxuan Sun, Ross Dobie, Neil C. Henderson, Samuel A.M. Martin, Daniel J. Macqueen, Johanna H. Fosse
Fish & Shellfish Immunology.2024; 146: 109357. CrossRef - Single-cell and spatially resolved transcriptomics for liver biology
Ping Lin, Xi Yan, Siyu Jing, Yanhong Wu, Yiran Shan, Wenbo Guo, Jin Gu, Yu Li, Haibing Zhang, Hong Li
Hepatology.2024; 80(3): 698. CrossRef - Single-cell transcriptomics in thyroid eye disease
Sofia Ahsanuddin, Albert Y. Wu
Taiwan Journal of Ophthalmology.2024; 14(4): 554. CrossRef - Impaired cortical neuronal homeostasis and cognition after diffuse traumatic brain injury are dependent on microglia and type I interferon responses
Jonathan M. Packer, Chelsea E. Bray, Nicolas B. Beckman, Lynde M. Wangler, Amara C. Davis, Ethan J. Goodman, Nathaniel E. Klingele, Jonathan P. Godbout
Glia.2024; 72(2): 300. CrossRef - Adipose tissue macrophage heterogeneity in the single-cell genomics era
Haneul Kang, Jongsoon Lee
Molecules and Cells.2024; 47(2): 100031. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review on Circulating cfRNA in Plasma: Implications for Disease Diagnosis and Beyond
Pengqiang Zhong, Lu Bai, Mengzhi Hong, Juan Ouyang, Ruizhi Wang, Xiaoli Zhang, Peisong Chen
Diagnostics.2024; 14(10): 1045. CrossRef - Single-Cell Sequencing Technology in Ruminant Livestock: Challenges and Opportunities
Avery Lyons, Jocelynn Brown, Kimberly M. Davenport
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2024; 46(6): 5291. CrossRef - Single-Cell Transcriptomics Sheds Light on Tumor Evolution: Perspectives from City of Hope’s Clinical Trial Teams
Patrick A. Cosgrove, Andrea H. Bild, Thanh H. Dellinger, Behnam Badie, Jana Portnow, Aritro Nath
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(24): 7507. CrossRef - Integrated analysis of single-cell and bulk RNA-seq establishes a novel signature for prediction in gastric cancer
Fei Wen, Xin Guan, Hai-Xia Qu, Xiang-Jun Jiang
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2023; 15(7): 1215. CrossRef - Placental single cell transcriptomics: Opportunities for endocrine disrupting chemical toxicology
Elana R. Elkin, Kyle A. Campbell, Samantha Lapehn, Sean M. Harris, Vasantha Padmanabhan, Kelly M. Bakulski, Alison G. Paquette
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2023; 578: 112066. CrossRef - Analyzing alternative splicing in Alzheimer’s disease postmortem brain: a cell-level perspective
Mohammad-Erfan Farhadieh, Kamran Ghaedi
Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Single-nucleus transcriptome inventory of giant panda reveals cellular basis for fitness optimization under low metabolism
Shangchen Yang, Tianming Lan, Rongping Wei, Ling Zhang, Lin Lin, Hanyu Du, Yunting Huang, Guiquan Zhang, Shan Huang, Minhui Shi, Chengdong Wang, Qing Wang, Rengui Li, Lei Han, Dan Tang, Haimeng Li, Hemin Zhang, Jie Cui, Haorong Lu, Jinrong Huang, Yonglun
BMC Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Progress in research on tumor microenvironment-based spatial omics technologies
FANGMEI XIE, NAITE XI, ZEPING HAN, WENFENG LUO, JIAN SHEN, JINGGENG LUO, XINGKUI TANG, TING PANG, YUBING LV, JIABING LIANG, LIYIN LIAO, HAOYU ZHANG, YONG JIANG, YUGUANG LI, JINHUA HE
Oncology Research.2023; 31(6): 877. CrossRef
- Integrative Genomics Approach Identifies Glial Transcriptomic Dysregulation and Risk in the Cortex of Individuals With Alcohol Use Disorder
- A standardized pathology report for gastric cancer: 2nd edition
- Young Soo Park, Myeong-Cherl Kook, Baek-hui Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Dong-Wook Kang, Mi-Jin Gu, Ok Ran Shin, Younghee Choi, Wonae Lee, Hyunki Kim, In Hye Song, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Hee Sung Kim, Guhyun Kang, Do Youn Park, So-Young Jin, Joon Mee Kim, Yoon Jung Choi, Hee Kyung Chang, Soomin Ahn, Mee Soo Chang, Song-Hee Han, Yoonjin Kwak, An Na Seo, Sung Hak Lee, Mee-Yon Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(1):1-27. Published online January 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.12.23
- Funded: Patient-Centered Clinical Research Coordinating Center, Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 37,580 View
- 1,554 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - The first edition of ‘A Standardized Pathology Report for Gastric Cancer’ was initiated by the Gastrointestinal Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists and published 17 years ago. Since then, significant advances have been made in the pathologic diagnosis, molecular genetics, and management of gastric cancer (GC). To reflect those changes, a committee for publishing a second edition of the report was formed within the Gastrointestinal Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists. This second edition consists of two parts: standard data elements and conditional data elements. The standard data elements contain the basic pathologic findings and items necessary to predict the prognosis of GC patients, and they are adequate for routine surgical pathology service. Other diagnostic and prognostic factors relevant to adjuvant therapy, including molecular biomarkers, are classified as conditional data elements to allow each pathologist to selectively choose items appropriate to the environment in their institution. We trust that the standardized pathology report will be helpful for GC diagnosis and facilitate large-scale multidisciplinary collaborative studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- GAST-NET: A multi-modal and multi-task deep learning framework for preoperative prediction of perineural invasion and prognostic risk in gastric cancer
Shidi Miao, Hexiang Dong, Jinyang Feng, Yuyang Jiang, Mengzhuo Sun, Zengyao Liu, Qiujun Wang, Xuemei Ding, Ruitao Wang
International Journal of Medical Informatics.2026; 212: 106348. CrossRef - Spatial and Temporal Tumor Heterogeneity in Gastric Cancer: Discordance of Predictive Biomarkers
Hye Seung Lee
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 192. CrossRef - PD-L1 as a Biomarker in Gastric Cancer Immunotherapy
Yunjoo Cho, Soomin Ahn, Kyoung-Mee Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 177. CrossRef - Korean Gastric Cancer Association-Led Nationwide Survey on Surgically Treated Gastric Cancers in 2023
Dong Jin Kim, Jeong Ho Song, Ji-Hyeon Park, Sojung Kim, Sin Hye Park, Cheol Min Shin, Yoonjin Kwak, Kyunghye Bang, Chung-sik Gong, Sung Eun Oh, Yoo Min Kim, Young Suk Park, Jeesun Kim, Ji Eun Jung, Mi Ran Jung, Bang Wool Eom, Ki Bum Park, Jae Hun Chung, S
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 115. CrossRef - A Comprehensive and Comparative Review of Global Gastric Cancer Treatment Guidelines: 2024 Update
Sang Soo Eom, Keun Won Ryu, Hye Sook Han, Seong-Ho Kong
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 153. CrossRef - Korea, Japan, Europe, and the United States: Why are guidelines for gastric cancer different?
Emily E. Stroobant, Seong-Ho Kong, Maria Bencivenga, Takahiro Kinoshita, Tae-Han Kim, Takeshi Sano, Giovanni de Manzoni, Han-Kwang Yang, Yuko Kitagawa, Vivian E. Strong
Gastric Cancer.2025; 28(4): 559. CrossRef - Can the Japanese guidelines for endoscopic submucosal dissection be safely applied to Korean gastric cancer patients? A multicenter retrospective study based on the Korean Gastric Cancer Association nationwide survey
Hayemin Lee, Mi Ryeong Park, Junhyun Lee
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2025; 109(2): 81. CrossRef - Double optimal transport for differential gene regulatory network inference with unpaired samples
Mengyu Li, Bencong Zhu, Cheng Meng, Xiaodan Fan, Laura Cantini
Bioinformatics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Effect of Fibrin Glue on Bleeding after Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Tae-Se Kim, Tae-Jun Kim, Yang Won Min, Hyuk Lee, Byung-Hoon Min, Jun Haeng Lee, Poong-Lyul Rhee, Jae J. Kim
Gut and Liver.2025; 19(5): 677. CrossRef - Diagnostic accuracy of stereomicroscopy assessment of invasion depth in ex vivo specimens of early gastric cancer
Jing Wang, Lin Chang, Dong-Feng Niu, Yan Yan, Chang-Qi Cao, Shi-Jie Li, Qi Wu
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - SMMILe enables accurate spatial quantification in digital pathology using multiple-instance learning
Zeyu Gao, Anyu Mao, Yuxing Dong, Hannah Clayton, Jialun Wu, Jiashuai Liu, ChunBao Wang, Kai He, Tieliang Gong, Chen Li, Mireia Crispin-Ortuzar
Nature Cancer.2025; 6(12): 2025. CrossRef - Genomic and Transcriptomic Characterization of Gastric Cancer with Bone Metastasis
Sujin Oh, Soo Kyung Nam, Keun-Wook Lee, Hye Seung Lee, Yujun Park, Yoonjin Kwak, Kyu Sang Lee, Ji-Won Kim, Jin Won Kim, Minsu Kang, Young Suk Park, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Yun-Suhk Suh, Do Joong Park, Hyung Ho Kim
Cancer Research and Treatment.2024; 56(1): 219. CrossRef - Microscopic tumor mapping of post-neoadjuvant therapy pancreatic cancer specimens to predict post-surgical recurrence: A prospective cohort study
Yeshong Park, Yeon Bi Han, Jinju Kim, MeeYoung Kang, Boram Lee, Eun Sung Ahn, Saemi Han, Haeryoung Kim, Hee-Young Na, Ho-Seong Han, Yoo-Seok Yoon
Pancreatology.2024; 24(4): 562. CrossRef - Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Resectable Gastric Cancer: Analysis from a Western Academic Center
Elliott J. Yee, Danielle Gilbert, Jeffrey Kaplan, Sachin Wani, Sunnie S. Kim, Martin D. McCarter, Camille L. Stewart
Cancers.2024; 16(7): 1428. CrossRef - Interpretation of PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer: summary of a consensus meeting of Korean gastrointestinal pathologists
Soomin Ahn, Yoonjin Kwak, Gui Young Kwon, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Moonsik Kim, Hyunki Kim, Young Soo Park, Hyeon Jeong Oh, Kyoungyul Lee, Sung Hak Lee, Hye Seung Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(3): 103. CrossRef - Expression of claudin 18.2 in poorly cohesive carcinoma and its association with clinicopathologic parameters in East Asian patients
Moonsik Kim, Byung Woog Kang, Jihyun Park, Jin Ho Baek, Jong Gwang Kim
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 263: 155628. CrossRef - Clinicopathological analysis of claudin 18.2 focusing on intratumoral heterogeneity and survival in patients with metastatic or unresectable gastric cancer
T.-Y. Kim, Y. Kwak, S.K. Nam, D. Han, D.-Y. Oh, S.-A. Im, H.S. Lee
ESMO Open.2024; 9(12): 104000. CrossRef - Pathological Interpretation of Gastric Tumors in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Jung Yeon Kim
Journal of Digestive Cancer Research.2023; 11(1): 15. CrossRef - Histopathology of Gastric Cancer
Baek-hui Kim, Sung Hak Lee
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2023; 23(2): 143. CrossRef - Endoscopic submucosal dissection hands-on training with artificial mucosal layer EndoGEL
Tae-Se Kim, Jun Haeng Lee
Journal of Innovative Medical Technology.2023; 1(1): 5. CrossRef
- GAST-NET: A multi-modal and multi-task deep learning framework for preoperative prediction of perineural invasion and prognostic risk in gastric cancer

 E-submission
E-submission

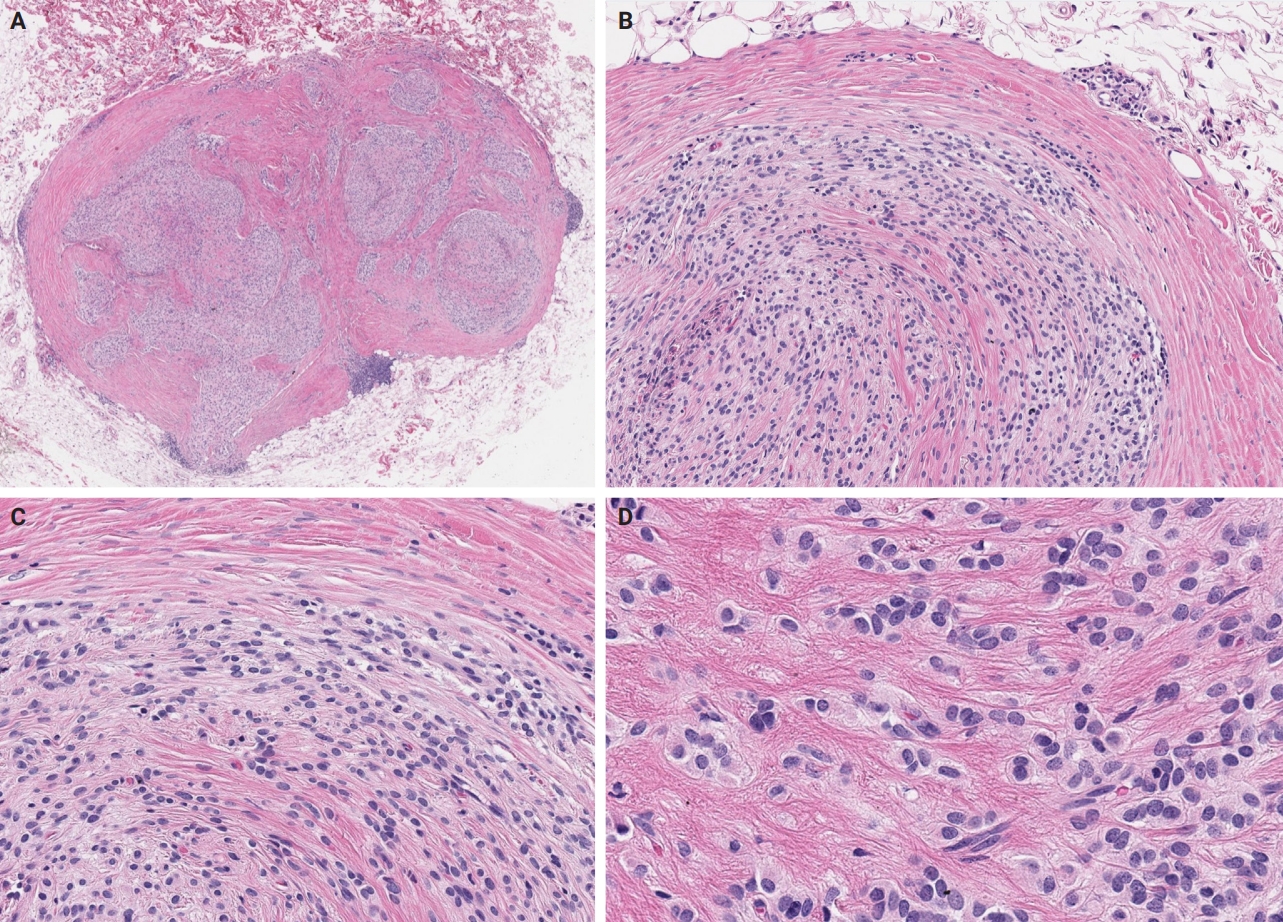
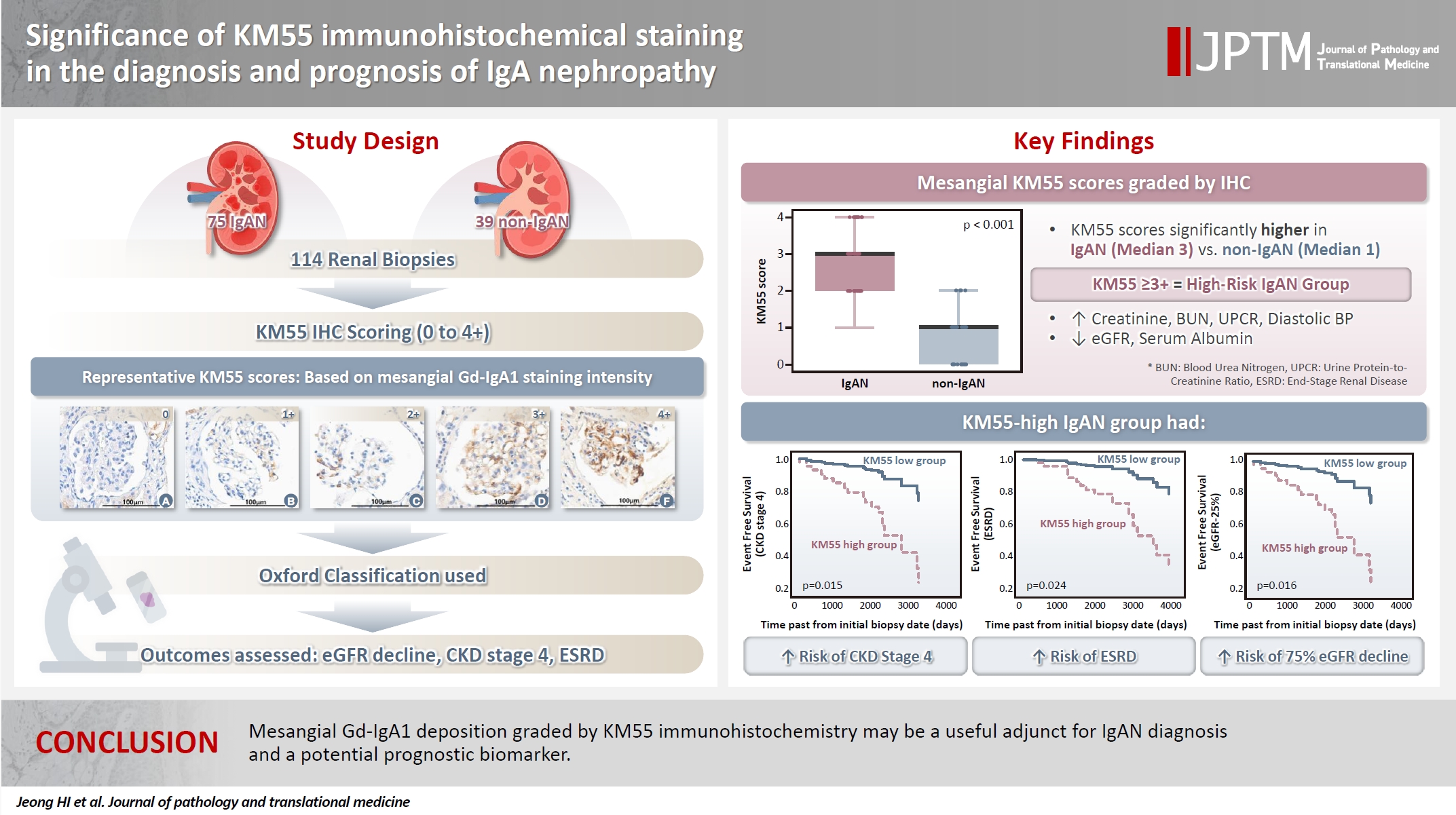
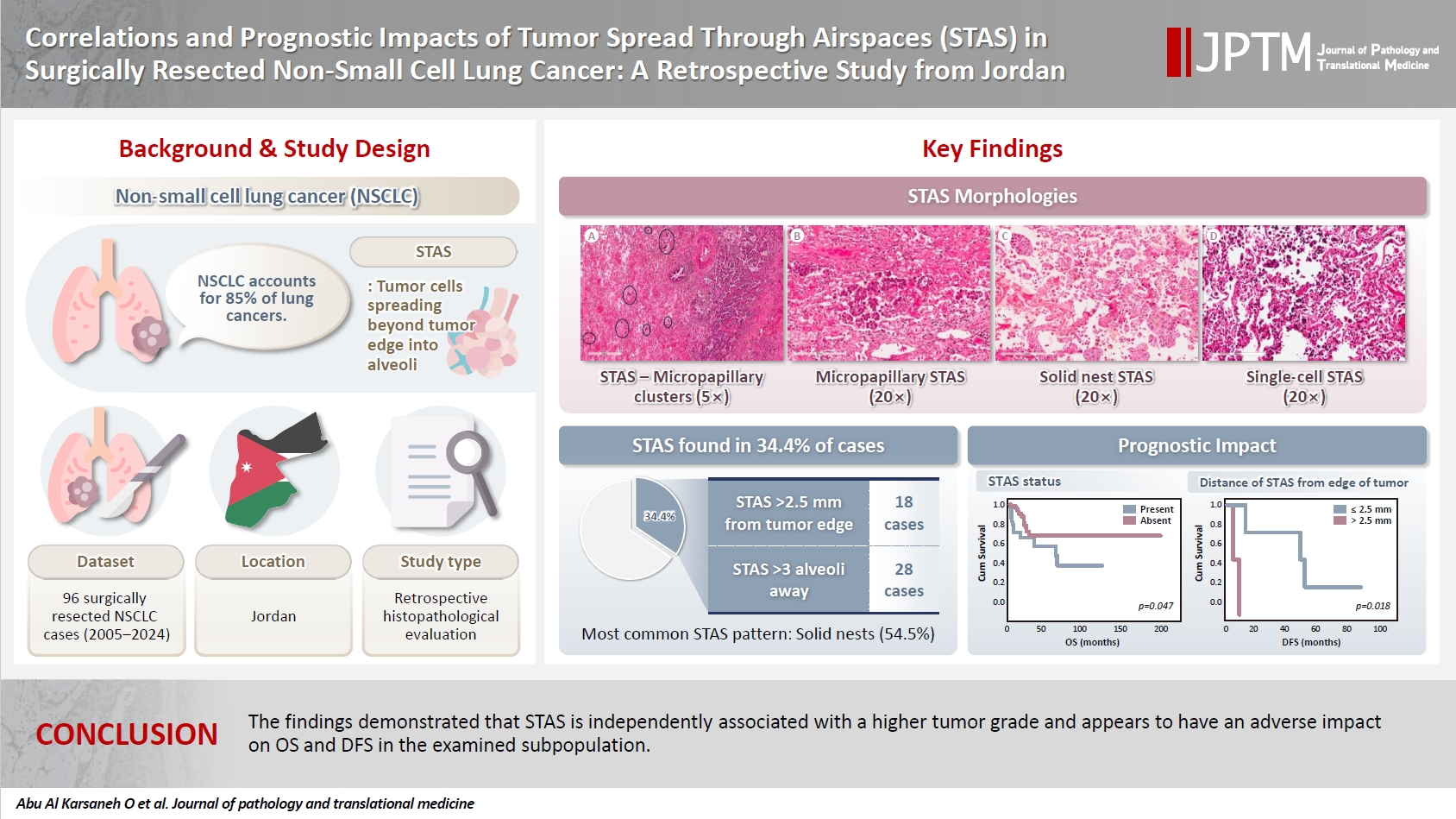
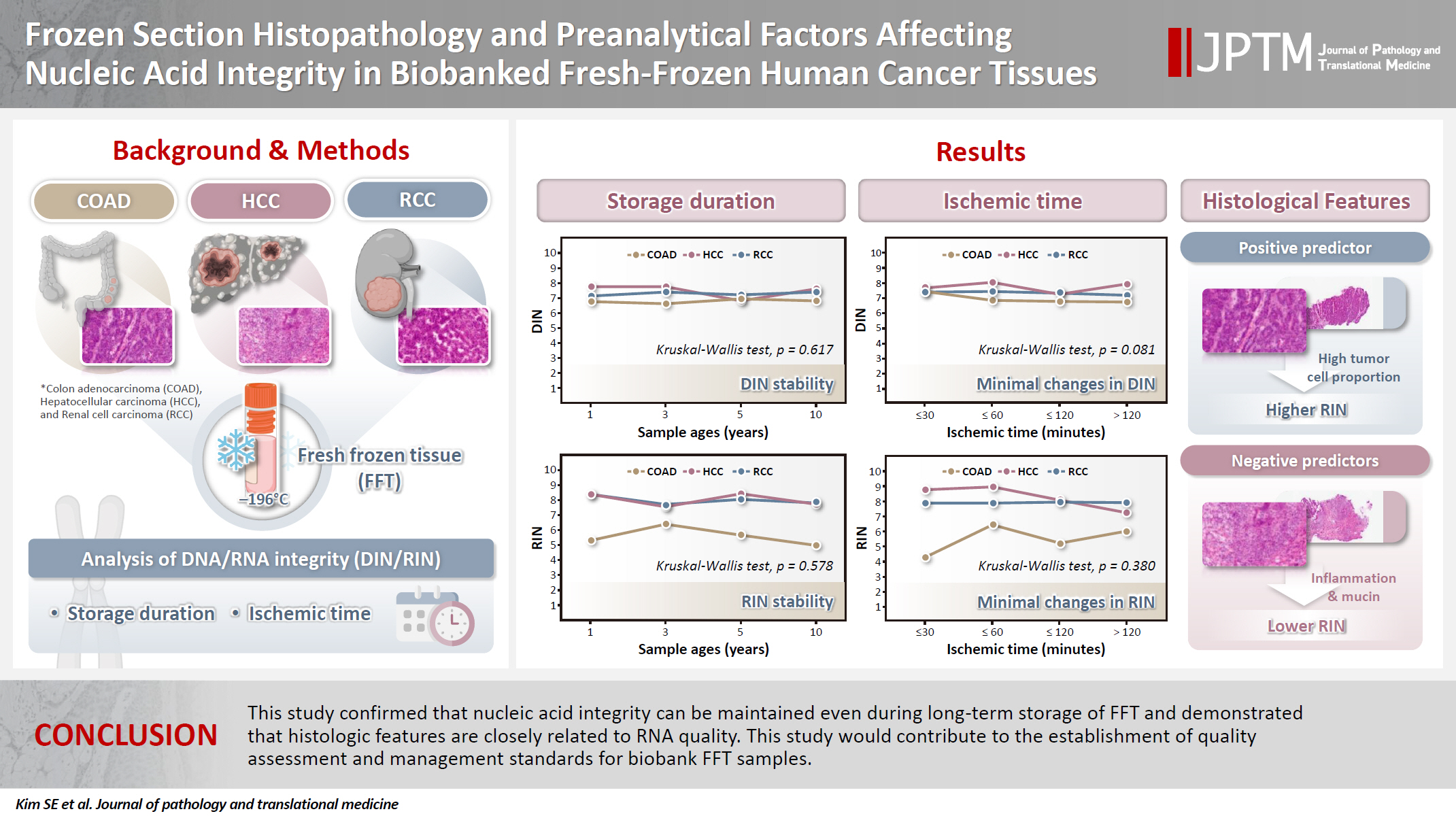



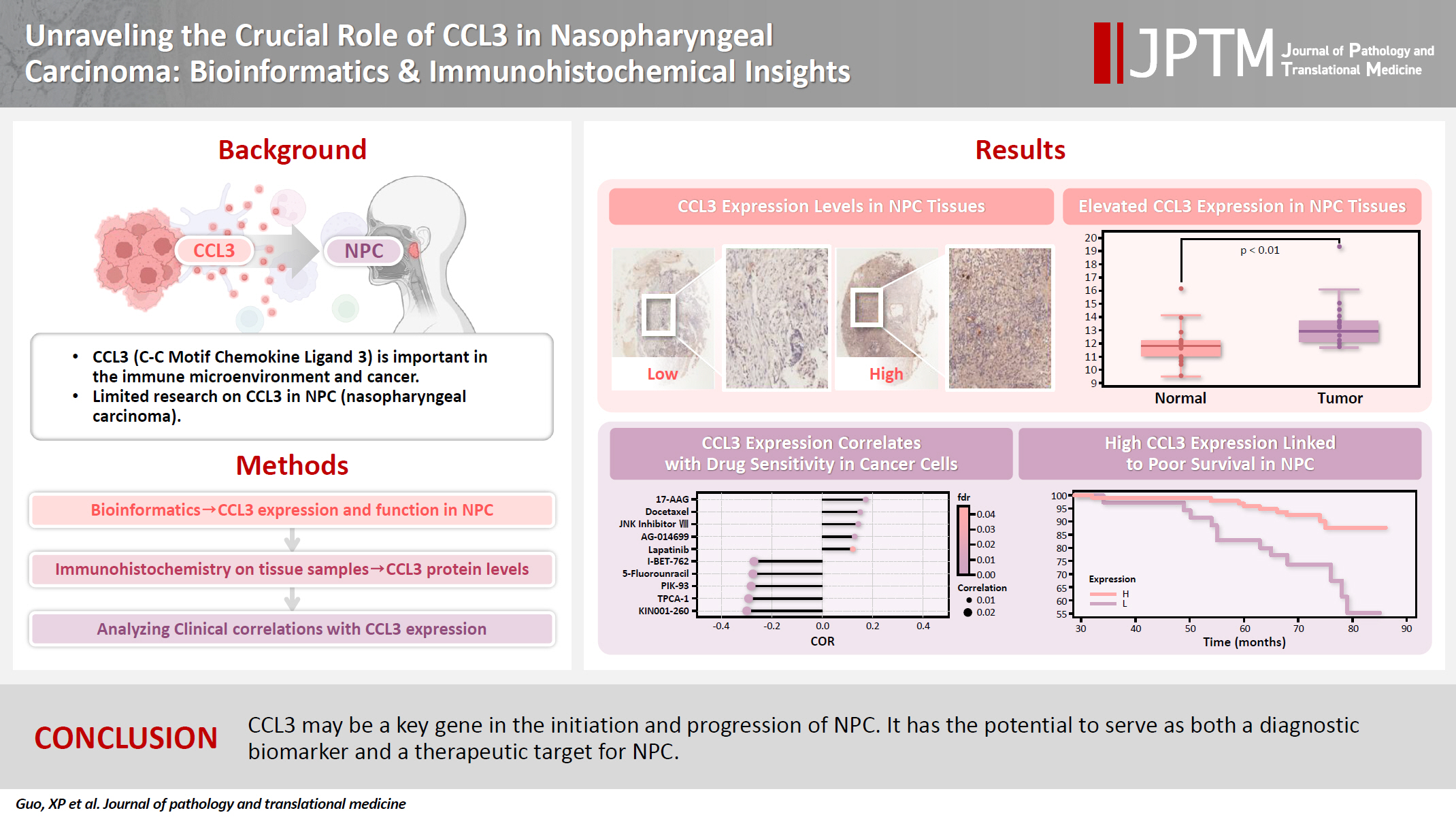
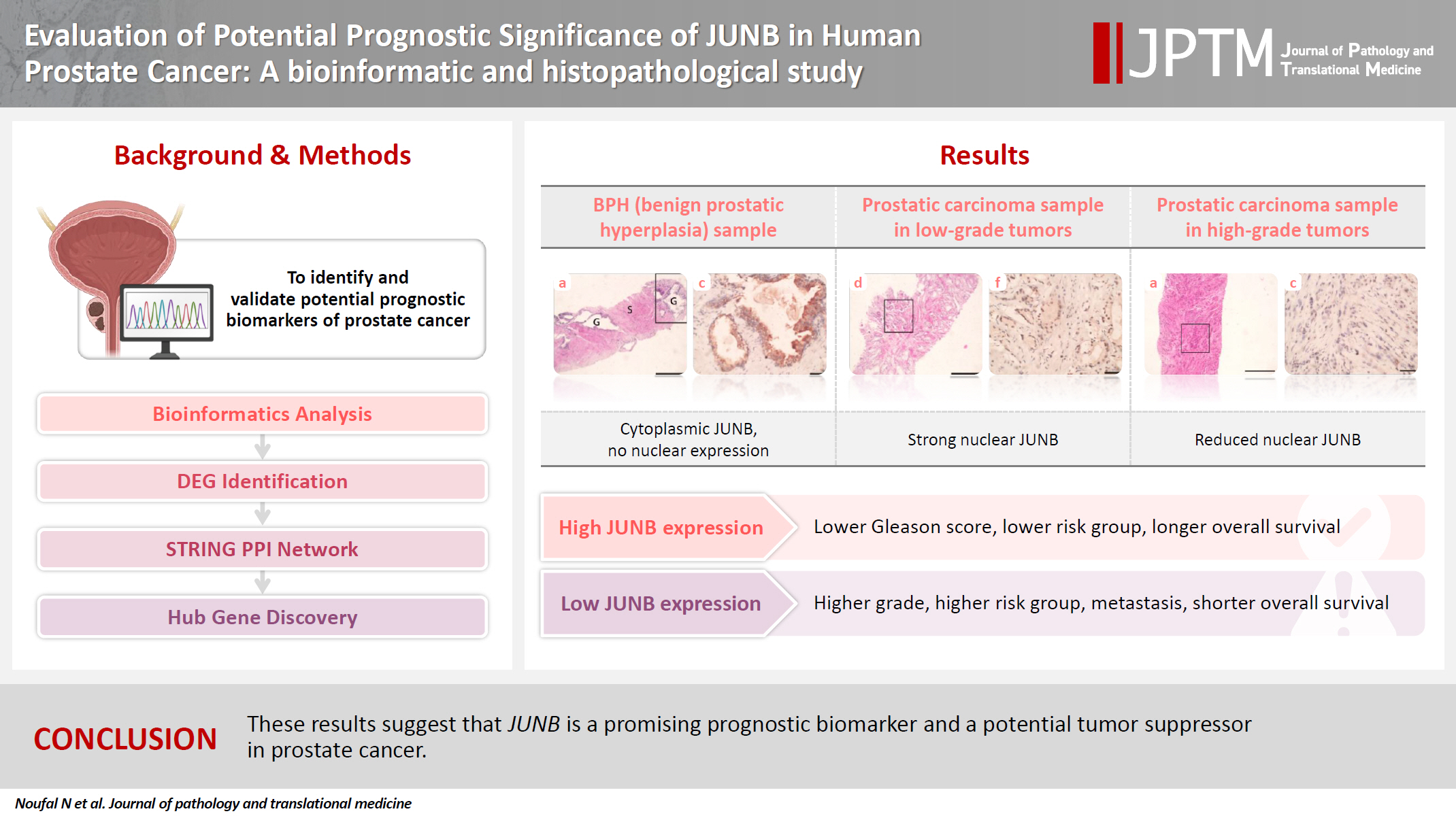
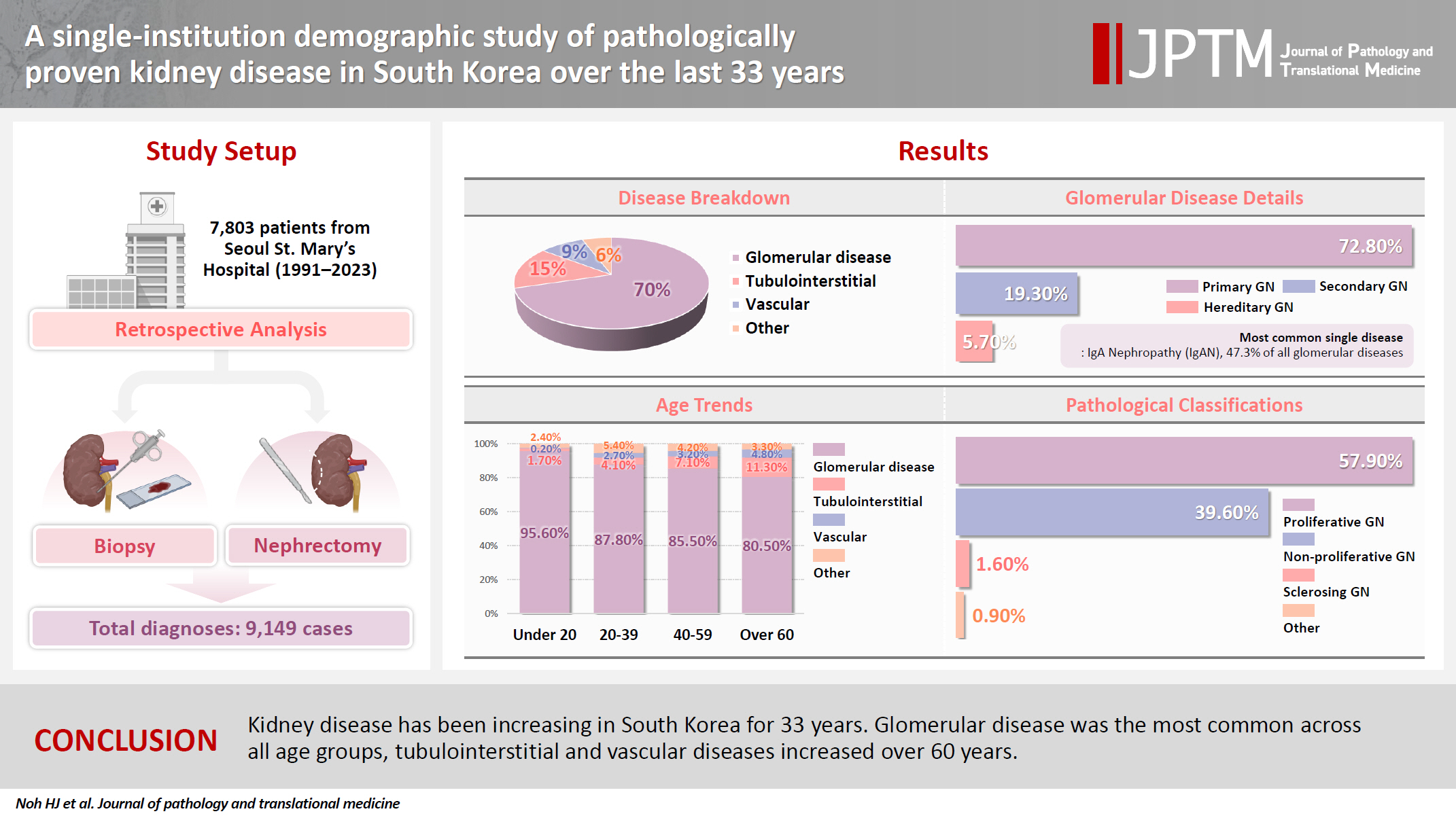
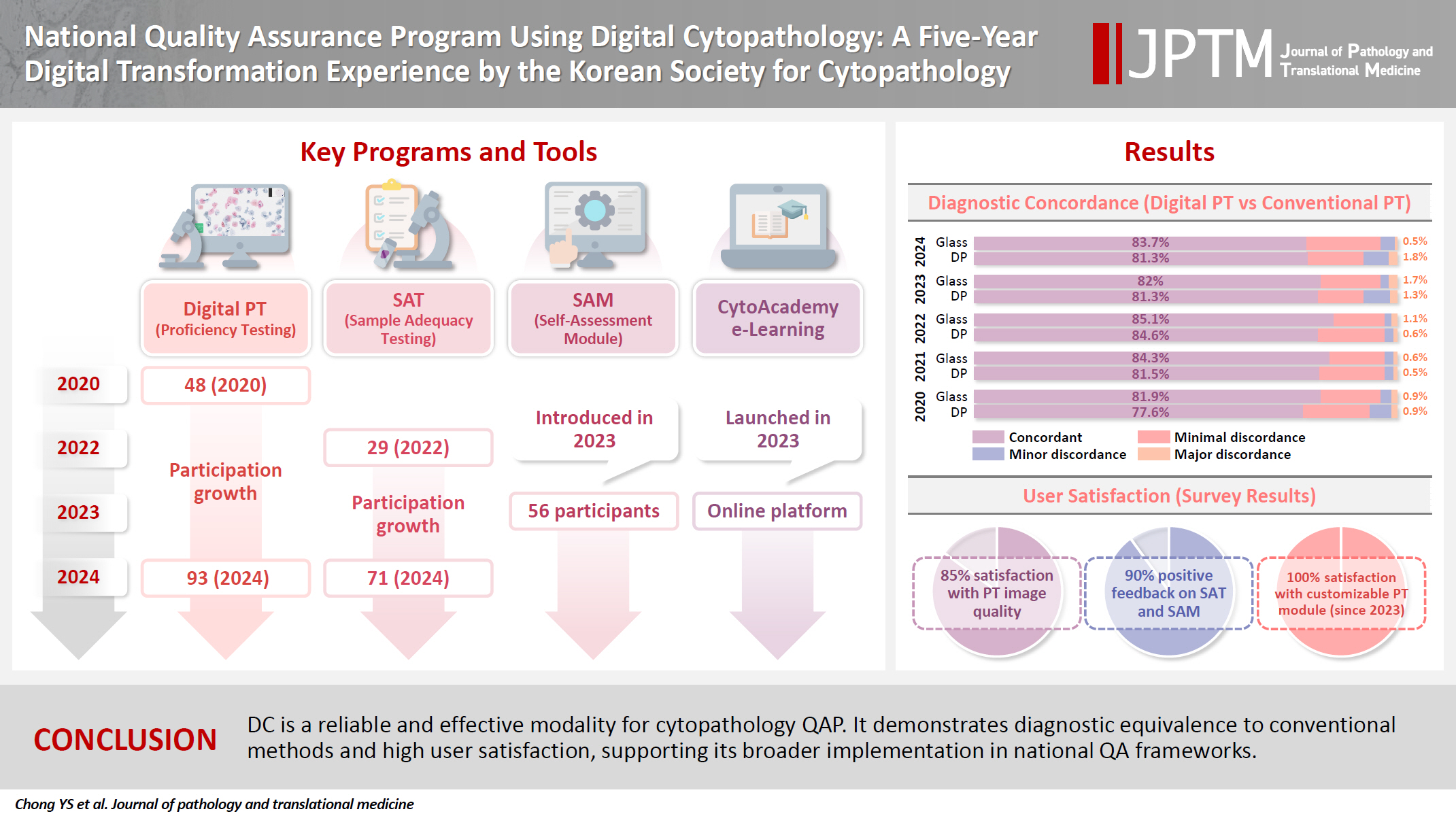

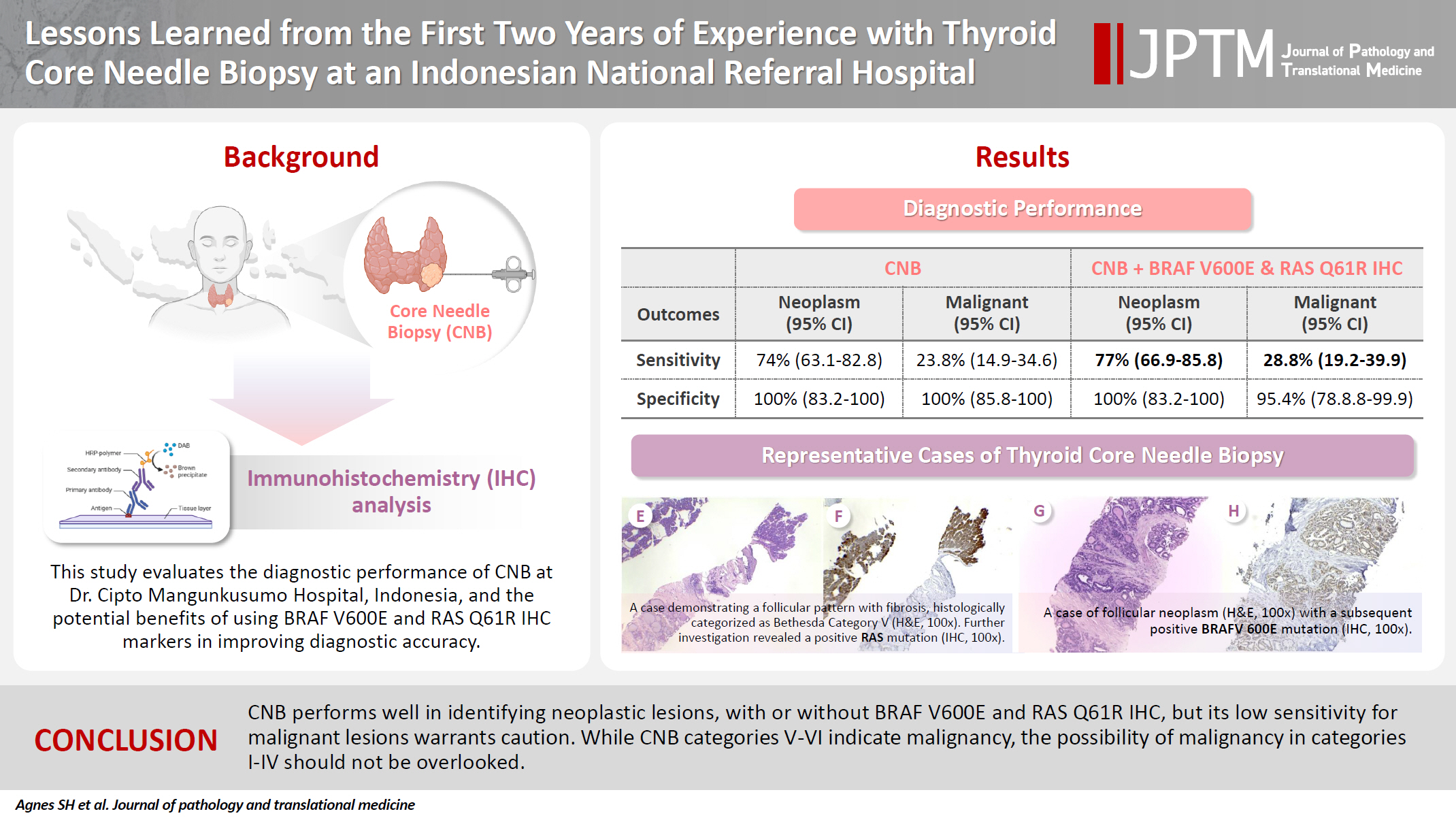
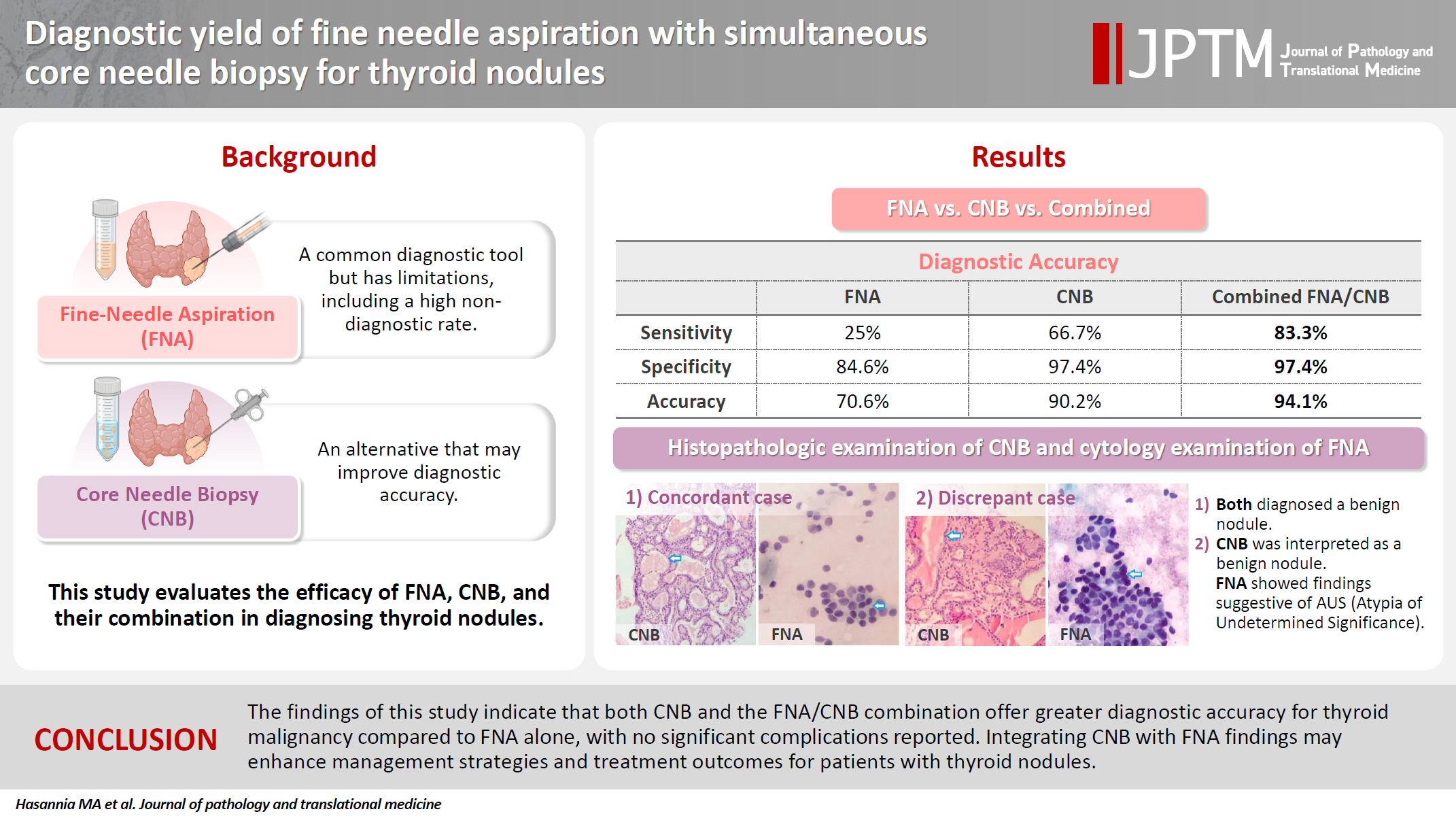
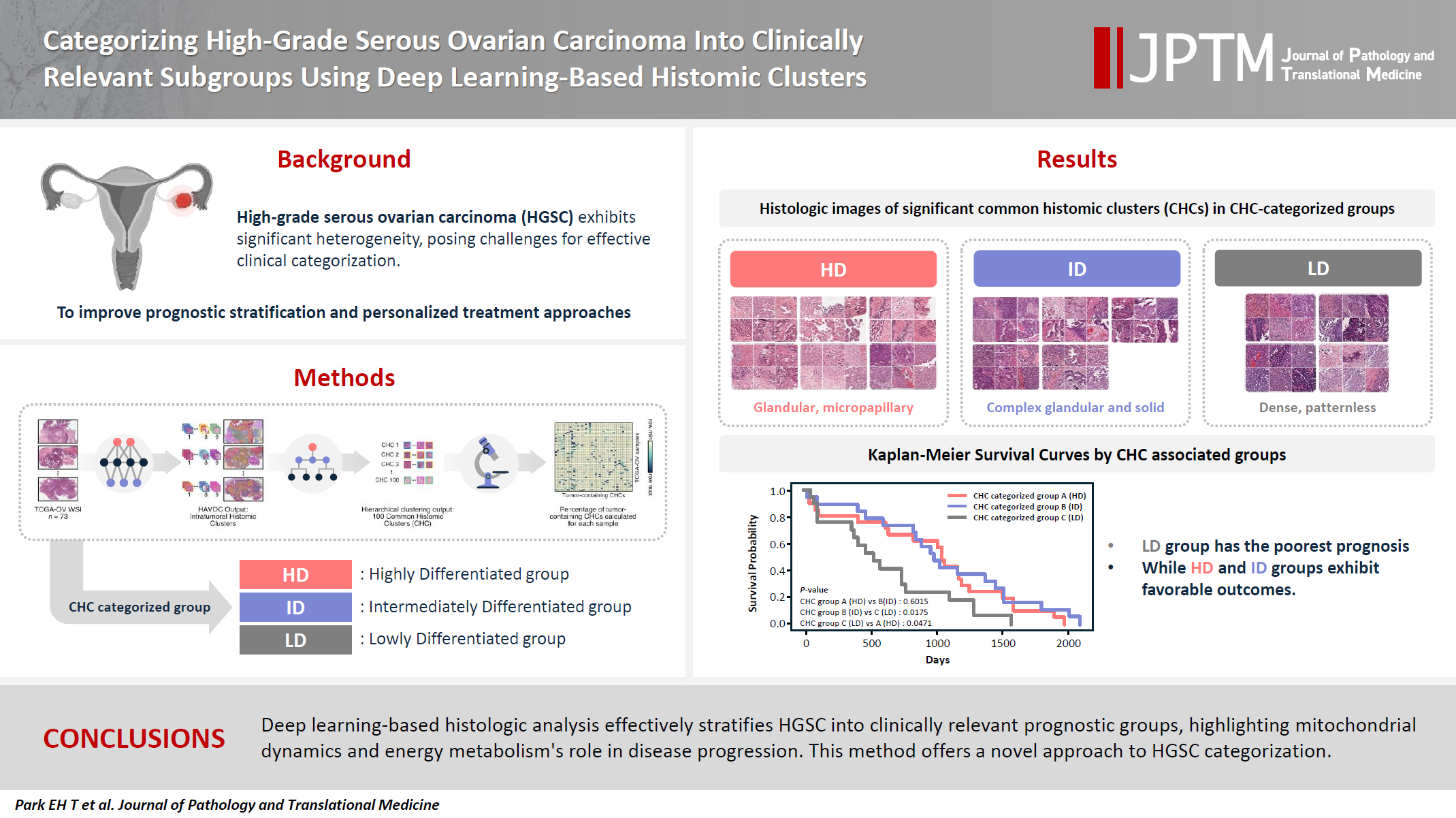




















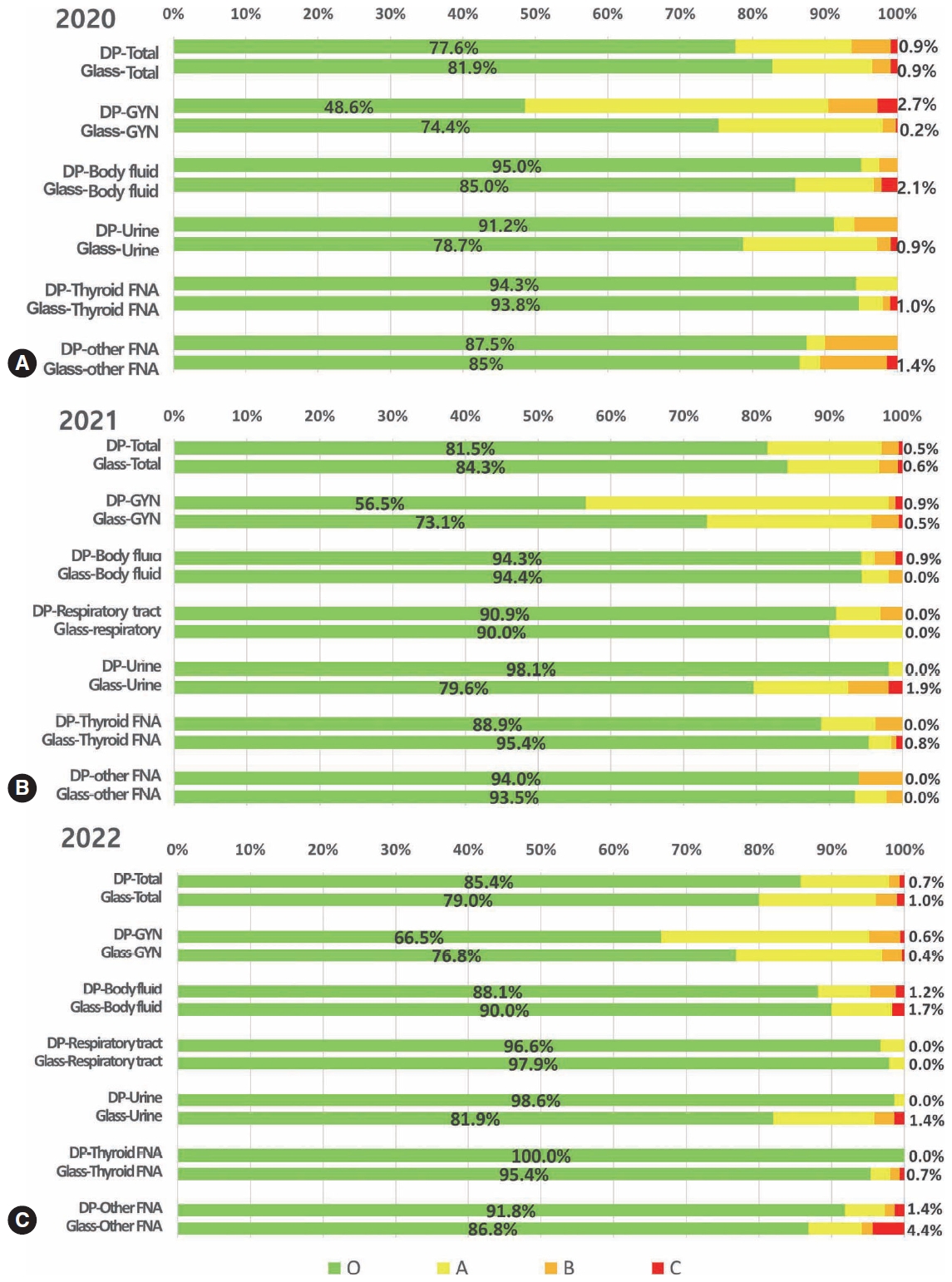












 First
First Prev
Prev



