Article category
- Page Path
- HOME > Article category > Article category
Original Articles
- Progastrin, annexin A2, and tumor-associated macrophages in gastric adenocarcinoma
- Konstantinos Christofidis, Rodanthi Fioretzaki, Stylianos Mavropoulos Papoudas, Nikolaos Charalampakis, Nikolaos Kavantzas, Dimitrios Schizas, Stratigoula Sakellariou
- Received September 13, 2025 Accepted December 19, 2025 Published online March 10, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.20 [Epub ahead of print]
- 111 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Gastric adenocarcinoma is a major cause of cancer mortality worldwide, and reliable biomarkers remain insufficient. This study investigates the immunohistochemical expression of progastrin (hPG) and annexin A2 (ANXA2) and the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages in gastric adenocarcinoma to explore their potential prognostic and biological significance. Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples from 60 patients with gastric adenocarcinoma (primary tumors, lymph node metastases, and non-tumoral gastric mucosa) and gastric biopsies from 23 healthy controls. The expression of hPG and ANXA2 was quantified using the H-score, and the CD163/human leukocyte antigen–DR (HLA-DR) ratio was used to represent macrophage polarization (M2/M1). Statistical analyses included non-parametric tests, Spearman correlations, Kaplan-Meier survival curves, and Cox proportional-hazards models. Results: ANXA2 expression was significantly elevated in cancer cells from primary tumors and lymph node metastases, compared with the non-tumoral gastric mucosa tissues and gastric mucosa tissues from healthy controls. ANXA2 expression increased with the tumor grade. High ANXA2 levels were associated with shorter overall and disease-free survival, but they did not have independent prognostic value. Although hPG expression correlated positively with ANXA2, it showed no significant prognostic association. The CD163/HLA-DR ratio increased with tumor progression and negatively correlated with ANXA2, but it did not influence survival outcomes. Conclusions: This study is the first to demonstrate the adverse prognostic impact of ANXA2 overexpression in gastric adenocarcinoma tissues from Caucasian patients. Our results suggest that ANXA2 might have utility as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target, if further large-scale studies validate and expand our findings.
- 3-Dimensional reconstruction reveals frequent intraluminal growth of submucosal veins in surgically resected pT1 colorectal cancers
- Jihyun Park, Mi-Ju Kim, Yeon Wook Kim, Byong-Wook Lee, Junyoung Shin, Jinho Shin, Chan-Gi Pack, Dong-Hoon Yang, Jihun Kim, In Ja Park, Ralph H. Hruban, Seung-Mo Hong
- Received September 24, 2025 Accepted December 19, 2025 Published online March 10, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.19 [Epub ahead of print]
- 107 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Although venous invasion (VI) is associated with distant metastasis and observed in >50% of pT2–4 colorectal cancers (CRCs), the role of VI in pT1 CRCs is not well-defined. Methods: Thirty-four surgically resected pT1 CRCs were reevaluated for 2-dimensional (2D) VI using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)–stained slides with additional elastic and desmin immunohistochemical staining (cohort A). Additionally, 27 pT1 CRCs without knowing VI status were selected for 3-dimensional (3D) VI evaluation only (cohort B). All 61 cases (cohorts A and B) were studied in 3D using tissue clearing. Results: VI was detected more commonly in 3D (17/34, 50.0%) than in 2D H&E slide evaluation (9/34, 26.5%, p = .047). When VI was identified in 3D (27/61, 44.3%), the most common phase was that of intraluminal growth (22/27, 81.5%), followed by intravasation (7/27, 25.9%) and extravasation (5/27, 18.5%). E-cadherin expression was characterized in 3D in foci of VI and varied in each phase of invasion. Conclusions: All three phases were observed in VI of pT1 CRCs. The extravasation of neoplastic cells from foci of VI in pT1 CRC suggests that VI could be a route of intratumoral spreading in a subset of pT1 CRCs.
- Can micro-CT distinguish between solid lung tumors? A comparative evaluation including solid adenocarcinoma, non-keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma, and carcinoid tumor
- Selim Sevim, Serpil Dizbay Sak, Kaan Orhan, Arda Buyuksungur, Duru Karasoy, Hilal Ozakinci, Ayten Kayi Cangir
- Received November 12, 2025 Accepted December 15, 2025 Published online March 10, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.16 [Epub ahead of print]
- 133 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Some pulmonary carcinomas display a solid pattern, and immunohistochemistry is commonly used for tumor differentiation. Micro–computed tomography (micro-CT), with its ability to produce detailed three-dimensional images using small voxel sizes, may offer additional insights. This study investigates whether three solid tumor types, solid adenocarcinoma (sAC), non-keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma, and carcinoid tumor (CaT), can be differentiated using micro-CT. Methods: Fifteen paraffin blocks, five for each type, were scanned with micro-CT (Skyscan 1275, Bruker). These images were compared to whole slide images (WSIs) of the same tumors. Consequently, tumoral (n = 74) and non-tumoral (n = 49) regions of interest (tumor ROIs [tROIs] and non-tumor ROIs [ntROIs]) were selected on the micro-CT images and evaluated in terms of certain structural variables (percent object volume, structure model index, structure thickness, structure linear density, connectivity, connectivity density, open porosity, closed porosity) to investigate whether tumors can be differentiated from normal parenchyma and from each other. Results: Although detailed images comparable to WSIs could not be obtained, it was considered an important advantage to be able to examine the entire depth of the paraffin blocks. tROIs and ntROIs could be distinguished based on all variables (p < .001). Additionally, sAC showed a notable difference from CaT in “percent object volume” (p = .011). Conclusions: With ongoing technological advancements, improving image quality without compromising tissue integrity will likely accelerate the adoption of micro-CT in pathology labs. Moreover, structural variables derived from micro-CT images may support differentiation among tumor types.
- Correlation between HER2 gene copy number and immunohistochemistry categories in HER2-negative breast cancer: diagnostic utility for differentiating HER2-null, ultralow, and low tumors
- Min Chong Kim, Young Kyung Bae
- Received September 1, 2025 Accepted November 7, 2025 Published online February 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.11.07 [Epub ahead of print]
- 290 View
- 34 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The recent recognition of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–low and HER2-ultralow breast cancers (BCs) has expanded the therapeutic relevance of HER2 testing in the antibody-drug conjugate era. However, the biological continuum of HER2 expression measured by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and its relationship with the HER2 gene copy number remain unclear. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 135 HER2-negative invasive BCs and reclassified them as HER2-null (IHC 0), HER2-ultralow (0+), or HER2-low (1+ or 2+ without amplification). HER2 gene copy number was determined using silver-enhanced in situ hybridization. Statistical analyses were performed to compare HER2 copy number among IHC categories and evaluate the discriminatory value of HER2 copy number for distinguishing IHC subgroups. Results: The mean HER2 copy number increased stepwise across IHC categories: 1.95 ± 0.54 (null), 2.03 ± 0.43 (ultralow), 2.25 ± 0.65 (low, 1+), and 3.29 ± 1.05 (low, 2+). Significant differences were observed between the ultralow and low groups (p = .003) and between the null and low groups (p < .001), but not between the null and ultralow groups or between the ultralow and 1+ groups. Conclusions: HER2 gene copy number was positively correlated with protein expression as reflected by IHC categories. Although HER2 gene copy number was statistically higher in HER2-low than in HER2-null tumors, the substantial overlap in copy number ranges likely limits its utility in distinguishing HER2-low from HER2- null BCs.
- Mutational status of non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP): molecular analysis should be performed for NIFTPs with nuclear score 3
- Ayaka Sako, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Michiko Matsuse, Miyoko Higuchi, Akira Miyauchi, Takashi Akamizu, Atsushi Kawakami, Norisato Mitsutake
- Received October 14, 2025 Accepted December 6, 2025 Published online February 23, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.06 [Epub ahead of print]
- 441 View
- 40 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The classification of non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) was introduced to prevent the overtreatment of indolent tumors that were formerly diagnosed as non-invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinomas (NIEFV-PTCs). Although NIFTP was initially estimated to account for 10%–20% of papillary thyroid carcinomas in Western populations, its incidence is substantially lower in Asian cohorts. However, a multi-institutional Japanese study revealed that 31.0% of tumors previously diagnosed as follicular adenomas (FAs) were reclassified as NIFTPs. NIFTP diagnosis requires a nuclear score (NS) of 2–3, and according to the recent World Health Organization criteria, molecular analysis is recommended, but not mandatory, to exclude high-risk subtypes, namely cases with the BRAFV600E mutation, particularly for NS3 tumors. Methods: We performed genetic analysis on 92 archival thyroid tumor samples, including 69 previously diagnosed as FA, of which 34 remained as FA upon re-evaluation (group A) and 35 were reclassified as NIFTP with NS2 (group B). Additional 23 tumors previously diagnosed as NIEFV-PTC were reclassified as NIFTP with NS3 (group C). Results: RAS mutations were detected in 8.8%, 34.3%, and 21.7% of the tumor samples in groups A, B, and C, respectively, whereas BRAF mutations were present in 43.5% of the tumor samples in group C only. Conclusions: These findings suggest the presence of two distinct tumor subsets within NIFTP-NS3, underscoring the need for routine molecular diagnostics in NIFTP-NS3 to facilitate appropriate clinical management.
- Multicenter evaluation of the PASS score as a negative predictive tool and the impact of inter-observer variability in pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma risk stratification
- Sungyeon Jung, Hye-Ri Shin, Su-Jin Shin, Hee Young Na, Soon-Won Hong, So Yeon Park, Chan Kwon Jung, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Young Lyun Oh, Jae-Kyung Won
- Received August 21, 2025 Accepted November 5, 2025 Published online February 23, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.11.05 [Epub ahead of print]
- 461 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The Pheochromocytoma of the Adrenal Gland Scaled Score (PASS) is widely used for risk stratification in pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma (PPGL), but its clinical utility is limited by inter-observer variability of its parameters and inconsistent predictive performance. Methods: We conducted a multicenter retrospective study of 1,518 patients with PPGL from five tertiary referral centers in Korea. Prognostic utility of PASS system was assessed using logistic regression, Kaplan-Meier analysis, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. Inter-observer variability was inferred by comparing area under the ROC curve (AUCs) across institutions. Simplified PASS systems were developed based on multivariable analysis of key histopathological parameters. Results: The PASS system was a significant predictor of adverse events and recurrence-free survival. Although the PASS system demonstrated only modest discriminative ability (AUC, 0.673), it showed a high negative predictive value (NPV, 0.885), supporting its usefulness as a screening tool for benign behavior. However, there was significant inter-institutional variability in PASS performance (AUC; range, 0.513 to 0.727; p < .05). The 3-factor Simple PASS, which incorporates necrosis, spindling, and mitotic figures, exhibited less inter-observer variation. The 4-factor Simple PASS, which adds vascular invasion to the 3-factor model, also showed reduced inter-observer variability and improved AUC and NPV compared to the original PASS system. Conclusions: In this multicenter cohort, the PASS system demonstrated high NPV and screening potential, but significant inter-observer variability remains a challenge. Simplification of the PASS system and enhanced pathologist training may improve reproducibility and clinical utility in PPGL risk stratification.
- Prevalence of HER2-ultralow breast cancer in South Korea: a multicenter study by reassessment of HER2-zero cases
- Min Chong Kim, Eun Yoon Cho, Hee Jin Lee, Ji Shin Lee, Jee Yeon Kim, Wan Seop Kim, Chungyeul Kim, Sun-Young Jun, Hye Jeong Choi, So Mang Lee, Ahrong Kim, Ji-Young Kim, Jeong Yun Shim, Gyungyub Gong, Young Kyung Bae
- Received September 17, 2025 Accepted October 21, 2025 Published online February 23, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.22 [Epub ahead of print]
- 452 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
This study aimed to determine the prevalence of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–ultralow breast cancer among cases initially classified as HER2 immunohistochemistry (IHC) 0 and assess interobserver variability in interpreting low-level HER2 expression. Methods: In this multicenter retrospective study, all invasive breast cancer cases diagnosed between January and December 2022 across 10 Korean institutions were retrieved. Institutional pathologists reexamined HER2 IHC slides originally reported as IHC 0 according to the 2018 American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guidelines and reclassified them as HER2-null (0), HER2-ultralow (0+), or HER2-low (1+). Slides from 10% of HER2-null and HER2-ultralow cases were digitized for central review and independently assessed by two pathologists, with discrepancies resolved by consensus. Results: Among 8,026 cases, 2,836 cases (35.5%) were initially reported as IHC 0. Upon re-review, 1,673 (59.0%), 1,139 (40.2%), and 24 (0.8%) cases were reclassified as HER2-null, HER2-ultralow, and HER2-low, respectively. The prevalence of HER2-ultralow breast cancer varied considerably across institutions (23.7%–78.1%). Central review of 268 digitized cases showed concordance in 193 cases (72.0%). Among the 75 discordant cases, 54 tumors (72.0%) were upgraded from HER2-null to HER2-ultralow, and 18 (24.0%) tumors were upgraded from HER2-ultralow to HER2-low. Furthermore, two tumors (2.7%) were downgraded from HER2-ultralow to HER2-null. Conclusions: Approximately 40% of cases initially categorized as IHC 0 were reclassified as HER2-ultralow. The substantial inter-institutional variability observed in interpreting low-level HER2 expression highlights the need for standardized training and quality assurance to ensure accurate identification of patients eligible for HER2-targeted antibody–drug conjugates.
Review Article
- The evolving role of TRPS1 in dermatopathology: insights from the past 4 years
- Mokhtar H. Abdelhammed, Woo Cheal Cho
- Received September 11, 2025 Accepted November 25, 2025 Published online January 29, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.11.25 [Epub ahead of print]
- 1,103 View
- 83 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Over the past 4 years, trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1 (TRPS1) has rapidly gained attention among practicing pathologists, with numerous studies emerging that both support and question its diagnostic utility. Initially regarded as a highly specific marker for tumors of mammary origin, TRPS1 is now recognized to have broader expression patterns, including in a variety of cutaneous neoplasms. This is likely due to embryologic parallels between breast tissue and skin adnexal structures, an overlap that was underappreciated in early investigations. Although TRPS1 lacks absolute specificity—even among cutaneous neoplasms—it can still offer meaningful diagnostic value when interpreted alongside conventional immunohistochemical markers and within the appropriate morphologic context. Noteworthy diagnostic applications include mammary Paget disease, primary extramammary Paget disease, rare adnexal neoplasms such as endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma and primary cutaneous NUT adnexal carcinoma, and cutaneous metastases from breast carcinoma. In this review, we present the most comprehensive and up-to-date evaluation of the utility and limitations of TRPS1 immunohistochemistry in dermatopathology. Our aim is to deepen understanding of this emerging marker and provide practical guidance on its optimal integration with established immunohistochemical panels to enhance diagnostic accuracy in routine practice.
Case Study
- Drug-induced phospholipidosis of the kidney suspected to be caused by atomoxetine
- Sung-Eun Choi, Kee Hyuck Kim, Minsun Jung, Jeong Hae Kie
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):124-128. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.10
- 1,653 View
- 142 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Drug-induced phospholipidosis (DIP) is characterized by intracellular accumulation of phospholipids with lamellar body formation secondary to drug-altered lipid metabolism, which can trigger inflammation and histopathological changes. Fabry disease and DIP both exhibit zebra bodies on electron microscopy, complicating differential diagnosis. A 17-year-old male with microscopic hematuria and proteinuria had received atomoxetine (40 mg) for 11 months to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Light microscopy showed one glomerulus with perihilar sclerosis and periglomerular fibrosis. Kidney biopsy revealed zebra bodies in podocytes, initially suggesting Fabry disease. However, α-galactosidase A enzyme activity was normal on tandem mass spectrometry. Next-generation sequencing of GLA identified only three benign variants. This represents the first reported case of atomoxetine-induced DIP. When zebra bodies are observed, clinicians should consider DIP caused by cationic amphiphilic drugs alongside Fabry disease. Atomoxetine meets the structural criteria for inducing DIP, and awareness of this potential complication is essential.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Atomoxetine
Reactions Weekly.2026; 2095(1): 19. CrossRef
- Atomoxetine
Editorial
- Advancing pathology through sixty volumes: reflections and future directions
- Chan Kwon Jung, So Yeon Park, Soon Won Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):1-5. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.08
- 2,443 View
- 25 Download
Original Article
- PSMA expression in hepatic colorectal cancer metastasis
- Eundong Park, Michel Kmeid, Xin Wang, Haiyan Qiu, Clifton G. Fulmer, Marcello P. Toscano, Nusret Bekir Subasi, Maciej Gracz, Hwajeong Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):107-123. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.20
- 1,534 View
- 108 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is expressed in the neovasculature of various malignancies, such as colorectal cancer (CRC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, PSMA expression in hepatic CRC metastasis has not been studied in detail. Methods: The PSMA expression in primary CRC and corresponding hepatic metastasis was evaluated by immunohistochemistry in a metastatic CRC cohort (n = 56), which was divided into subgroups according to treatment history and timing of metastasis. Demographic and histological characteristics of primary CRC were collected and their relationships with PSMA expression were examined. Additionally, the PSMA expression in resected HCC (n = 76) was compared with that of hepatic CRC metastasis. Results: In primary CRC, PSMA level showed a positive association with tumor size. Lower PSMA expression in hepatic metastasis was associated with higher primary CRC grade, advanced pTNM stage at the time of CRC resection, presence of tumor deposit, and unresectability of metastatic lesion. PSMA expression in primary CRC correlated with that in hepatic metastasis only in concurrent and untreated metastasis subgroup. PSMA expression in primary CRC and hepatic metastasis, regardless of treatment history and timing of metastasis, was not significantly different from that of HCC. Conclusions: Several adverse pathological features of primary CRC were associated with a lower PSMA expression in hepatic metastasis. PSMA expression in hepatic metastasis correlated with that of primary CRC only in concurrent and untreated subgroup. Primary HCC and hepatic CRC metastasis show comparable levels of PSMA expression.
Review Article
- A comprehensive review of ossifying fibromyxoid tumor: insights into its clinical, pathological, and molecular landscape
- Kyriakos Chatzopoulos, Antonia Syrnioti, Mohamed Yakoub, Konstantinos Linos
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):6-19. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.02
- 2,262 View
- 120 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor (OFMT) is a rare mesenchymal neoplasm first described in 1989. It typically arises in the superficial soft tissues of the extremities as a slow-growing, painless mass. Histologically, it is commonly characterized by a multilobular architecture composed of uniform epithelioid cells embedded in a fibromyxoid matrix, often surrounded by a rim of metaplastic bone. While classic cases are readily identifiable, the tumor's histopathological heterogeneity can mimic a range of benign and malignant neoplasms, posing significant diagnostic challenges. Molecularly, most OFMTs harbor PHF1 rearrangements, commonly involving fusion partners such as EP400, MEAF6, or TFE3. This review underscores the importance of an integrated diagnostic approach- incorporating histopathological, immunohistochemical, and molecular data- to accurately classify OFMT and distinguish it from its mimics. Expanding awareness of its morphologic and molecular spectrum is essential for precise diagnosis, optimal patient management, and a deeper understanding of this enigmatic neoplasm.
Original Articles
- Significance of KM55 immunohistochemical staining in the diagnosis and prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Hoe In Jeong, Beom Jin Lim, Minsun Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):69-82. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.17
- 2,048 View
- 154 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) plays a crucial role in IgA nephropathy (IgAN). The monoclonal antibody KM55 has emerged as a simplified method for detecting Gd-IgA1; however, the clinicopathological significance of immunohistochemistry for Gd-IgA1 remains underexplored. This study evaluated the prognostic and clinicopathological significance of KM55 immunohistochemistry in IgAN. Methods: A total of 114 native kidney biopsies showing at least mild mesangial IgA positivity on immunofluorescence were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were categorized as having IgAN or non-IgAN diseases. The KM55 immunohistochemical staining was graded as 0, 1+, 2+, 3, or 4+. Data on Oxford classification, laboratory parameters, and renal outcomes were collected. Results: The IgAN group showed significantly higher KM55 scores than the non-IgAN group (median: 3 vs. 1; p < .001). IgAN cases were further stratified into KM55-high (≥3+, n = 38) and -low groups (≤2+, n = 37). The KM55-high group had significantly higher diastolic blood pressure, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, urine protein/creatinine ratio, and Oxford mesangial hypercellularity scores, along with lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and serum albumin. Cox analysis revealed significantly poorer outcomes in the KM55-high group for chronic kidney disease stage 4 (p = .015), end-stage renal disease (p = .024), and 75% eGFR decline (p = .016). Conclusions: Mesangial Gd-IgA1 deposition graded by KM55 immunohistochemistry may be a useful adjunct for IgAN diagnosis and a potential prognostic biomarker.
- Correlations and prognostic impacts of tumor spread through airspaces in surgically resected non–small cell lung cancer: a retrospective study from Jordan
- Ola Abu Al Karsaneh, Amani Al-Rousan, Sofian Al Shboul, Mohammed El-Sadoni, Anas Hayajneh, Moath Alrjoub, Sura Al-Rawabdeh, Tareq Saleh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):92-106. Published online January 9, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.15
- 2,064 View
- 121 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Spread through air spaces (STAS) has been identified as an invasion pattern in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This study evaluated the association between tumor STAS and various clinicopathological parameters of NSCLC, with emphasis on the prognostic role of STAS. Methods: We evaluated 96 cases of NSCLC for STAS. STAS-positive cases were graded according to the distance between the edge of the primary tumor and the furthest STAS, in millimeters, or the number of alveoli separating STAS from the tumor. Results: STAS was observed in 33 patients (34.4%). In 28 cases, STAS was located in airspaces >3 alveoli away from the primary tumor. In 18 cases, STAS was found in airspaces > 2.5 mm away from the edge of the primary tumor. Morphologically, 18 cases of STAS demonstrated a solid nest pattern, eight showed a micropapillary cluster pattern, and seven exhibited a single-cell pattern. In multivariate analysis, only high tumor grade (p = .001) was independently associated with STAS in NSCLC. The presence of STAS (p = .047), lymphovascular invasion (p = .001), positive surgical margin (p = .021), adenocarcinoma histology (p = .020), and postoperative therapy (p = .049) showed a statistically significant lower overall survival (OS). However, multivariate analyses showed that STAS is not an independent predictor of OS in NSCLC. In addition, STAS-positive cases with an extension of >2.5 mm had significantly lower disease-free survival (DFS) (p = .018). Conclusions: The findings demonstrated that STAS is independently associated with a higher tumor grade and appears to have an adverse impact on OS and DFS in the examined subpopulation.
- Revisiting human sparganosis: a pathologic review from a single institution
- Jeemin Yim, Young A Kim, Jeong Hwan Park, Hye Eun Park, Hyun Beom Song, Ji Eun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):83-91. Published online January 9, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.14
- 1,591 View
- 93 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Sparganosis is a rare parasitic infection caused by Spirometra species. Although it was relatively common in the past, it is now often overlooked. In this study, we review cases diagnosed through histopathological examination at a single institution in recent years to raise awareness of this neglected parasitic disease. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed cases of human sparganosis identified in the pathology archives of a single institution in South Korea between 2004 and 2025. A comprehensive review was conducted, including demographic data, clinical features, lesion locations, imaging findings, exposure history (such as dietary habits), and histopathologic findings. Results: A total of 15 patients were identified, including 10 females and 5 males, with a mean age of 65.1 years. Lesions were most commonly located in the lower extremities and breast. Imaging findings were largely nonspecific, with ultrasonography being the most frequently used modality. In most cases, clinical suspicion of sparganosis was absent, and excision was performed under the impression of a benign or malignant tumor. Histologically, variably degenerated parasitic structures were identified within granulomatous inflammation. However, preserved features such as calcospherules and tegumental structures facilitated definitive diagnosis. Conclusions: This study underscores the importance of recognizing the characteristic histopathological features of sparganosis, which can allow for accurate diagnosis even in the absence of clinical suspicion. Although rare, sparganosis remains a relevant diagnostic consideration in endemic regions, particularly in East Asia.
- The significance of papillary architecture in the follow-up biopsies of patients with progestin-treated atypical endometrial hyperplasia
- Wangpan J. Shi, Oluwole Fadare
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):58-68. Published online January 8, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.12
- 1,605 View
- 161 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Follow-up biopsies in patients with progestin-treated atypical endometrial hyperplasia/endometrioid intraepithelial neoplasia (AH/EIN) may show papillary structures, the significance of which is unclear. Methods: The authors reviewed 253 serial specimens of 84 consecutive patients diagnosed with AH/EIN, inclusive of each patient's pre-progestin treatment sample and all post-treatment specimens. We assessed the predictive relationship between papillary architecture in a post-treatment biopsy and two study outcomes: AH/EIN or carcinoma in at least one sample subsequent to the one in which papillae were identified, and/or the last specimen received for that patient. Results: Papillae were identified in only 51.5% of pre-treatment samples but were present in at least one subsequent post-treatment sample for all patients. Post-treatment samples that exhibited papillae and no glandular crowding were associated with AH/EIN in at least one subsequent specimen in 39.7% (29/73) of cases, compared to 24.0% (6/25) in samples with neither papillae nor glandular crowding (p = .227) and 64.0% (16/25) in samples with concurrent gland crowding and papillae (p = .048). Univariate logistic regression analyses showed that the presence of papillae was not associated with study outcomes (odds ratio [OR], 0.99; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.49 to 1.99; p = .985), as compared with gland crowding (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.04 to 2.27; p = .031), or concurrent papillae and gland crowding (OR, 2.36; 95% CI, 1.01 to 5.52; p = .048). Conclusions: In post-treatment samples of progestin-treated AH/EIN, the presence of papillary architecture was not demonstrably associated with study outcomes independent of gland crowding, although the concurrent presence of both features may be significantly predictive.
- Clinicopathological and molecular mechanisms of CLDN18.2 in gastric cancer aggressiveness: a high-risk population study with multi-omics profiling
- Hengquan Wu, Mei Li, Gang Wang, Peiqing Liao, Peng Zhang, Luxi Yang, Yumin Li, Tao Liu, Wenting He
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):47-57. Published online January 5, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.11
- 2,015 View
- 182 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The tight junction protein claudin18.2 (CLDN18.2) has been implicated in poor prognosis and suboptimal immunotherapy response in gastric cancer (GC). This study investigates the clinicopathological relevance of CLDN18.2 expression and its association with molecular subtypes in GC patients from a high-incidence region, combining transcriptomic and proteomic approaches to explore how CLDN18.2 contributes to progression and metastasis.
Methods
A retrospective cohort of 494 GC patients (2019–2024) underwent immunohistochemical analysis for CLDN18.2, Epstein-Barr virus (Epstein–Barr virus–encoded RNA), p53, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and mismatch repair proteins (MLH1, MSH2, PMS2, and MSH6). CLDN18.2 positivity was defined as moderate to strong (2+/3+) membranous staining in ≥75% of tumor cells. Clinicopathological correlations, biomarker associations, and survival outcomes were evaluated. Transcriptomic and proteomic sequencing was performed to explore molecular mechanisms.
Results
CLDN18.2 positivity was observed in 26.9% (133/494) of gastric adenocarcinomas. CLDN18.2-positive tumors correlated with TNM stage (p = .003) and shorter overall survival (p = .018). No associations were identified with age, sex, HER2 status, microsatellite instability, or Epstein-Barr virus infection. Transcriptomic profiling revealed CLDN18.2-high tumors enriched in pathways involving cell junction disruption, signaling regulation, and immune modulation. Proteomic profiling showed that tumors with high CLDN18.2 were enriched in multiple mechanism-related pathways such as integrated metabolic reprogramming, cytoskeletal recombination, immune microenvironment dysregulation, and pro-survival signaling. These mechanisms may collectively contribute to tumor progression and metastasis.
Conclusions
CLDN18.2 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in GC patients. Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses demonstrate that CLDN18.2 promotes tumor progression and metastasis, underscoring its potential as an independent prognostic factor in regions with a high incidence of GC.
Newsletter
- What's new in molecular genetic pathology 2026: emerging biomarkers for personalized cancer therapies
- Umberto Maccio
- Received November 24, 2025 Accepted January 3, 2026 Published online January 3, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2026.01.03 [Epub ahead of print]
- 843 View
- 147 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - New and emerging biomarkers and current molecular assays for the most prevalent and lethal cancers worldwide—breast, lung, prostate, and colorectal cancer—are described. Notably, HER2-low breast cancer and HER2-mutated non-small cell lung cancer have recently been recognized as targetable entities. In addition, various tissue-based analyses are now available to assess prognosis and the risk of relapse in prostate cancer.
Review Article
- Solitary fibrous tumor: an updated review
- Joon Hyuk Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):20-46. Published online December 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.08
- 1,923 View
- 175 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) is a fibroblastic neoplasm characterized by a branching, thin-walled dilated staghorn-shaped (hemangiopericytoma-like) vasculature and a NAB2::STAT6 gene fusion. SFTs can occur in almost any anatomical location, including superficial and deep soft tissues, visceral organs, and bone. They most commonly occur in extrapleural locations, equally affect both sexes, and are typically present in adults. Although metastasis is rare, SFTs frequently show local recurrence. The diagnosis of SFTs is difficult because of their broad histological and morphological overlap with other neoplasms. An accurate diagnosis is important for guiding disease management and prognosis. Despite advances in molecular diagnostics and therapeutic strategies, the biological complexity and unpredictable clinical behavior of SFTs present significant challenges. This review provides an updated overview of SFT, with a focus on its molecular genetics, histopathological features, and diagnostic considerations.
Case Study
- Diagnostic challenge in Burkitt lymphoma of the mandible initially misdiagnosed as osteomyelitis: a case report
- Jiwon Do, Jin-Young Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):460-466. Published online November 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.18
- 2,786 View
- 100 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is a highly aggressive B-cell neoplasm that rarely involves the mandible in elderly without apparent immunodeficiency. We report a case of a 72-year-old male who presented with persistent mandibular pain following extraction of tooth #46. Initial imaging findings were consistent with incipient osteomyelitis, and the patient was treated with antibiotics. Despite treatment, pain persisted, and follow-up imaging revealed swelling and diffusion restriction in the lateral pterygoid muscle without evidence of a distinct mass. Biopsy revealed BL confirmed by immunohistochemistry: CD10+, BCL6+, c-MYC+, Ki-67 >95%, and negative for BCL2, MUM-1, and Epstein-Barr virus. Although c-MYC immunopositivity was demonstrated, fluorescence in situ hybridization for MYC rearrangement could not be performed due to limited tissue, representing a diagnostic limitation. Notably, the patient had no trismus despite deep muscle involvement, but complained of facial paresthesia and showed remote swelling in the scapular area during hospitalization. Systemic staging with imaging, cerebrospinal fluid cytology, and imaging revealed disseminated nodal and extranodal involvement including the central nervous system, corresponding to stage IV disease by Lugano classification. This case highlights the diagnostic challenge of distinguishing lymphoma from osteomyelitis and underscores the importance of considering malignancy in cases of refractory mandibular inflammation with atypical features.
Original Articles
- Diagnostic value of cytology in detecting human papillomavirus–independent cervical malignancies: a nation-wide study in Korea
- Hye-Ra Jung, Junyoung Shin, Chong Woo Yoo, Eun Na Kim, Cheol Lee, Kyeongmin Kim, Ho-chang Lee, Yonghee Lee, Ji Hye Kim, Soo Jin Jung, Yumin Chung, Joo Yeon Kim, Hye Eun Park, Tae Hoen Kim, Wonae Lee, Min-Sun Cho, Ran Hong, Yoon Jung Choi, Younghee Choi, Young Sub Lee, Sang-Ryung Lee, Myunghee Kang, Young Jin Seo, Seung-Sook Lee, Yoon-Jung Hwang, Hyun-Jung Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):444-452. Published online November 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.21
- 3,894 View
- 139 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) independent cervical malignancies (HPV-IDCMs) have recently been classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) 5th edition. These malignancies have historically received limited attention due to their rarity and the potential for evasion of HPV-based screening.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 5,854 biopsy-confirmed cervical malignancies from 22 institutions over 3 years (July 2020–June 2023). Histologic classification followed the WHO guidelines. HPV independence was confirmed by dual negativity for p16 and HPV; discordant cases (p16-positive/HPV-negative) underwent additional HPV testing using paraffin-embedded tissue. Cytological results were matched sequentially to histological confirmation.
Results
The prevalence of HPV-IDCM was 4.4% (257/5,854) overall and was 3.6% (208/5,805 cases) among primary cervical malignancy. Patient age of HPV-IDCM was 29 to 89 years (median, 57.79). Its histologic subtypes included primary adenocarcinoma (n = 116), endometrial adenocarcinoma (n = 35), squamous cell carcinoma (n = 72), metastatic carcinoma (n = 14), carcinoma, not otherwise specified (n = 10), neuroendocrine carcinoma (n = 3), and others (n = 7). Among 155 cytology-histological matched cases, the overall and primary Pap test detection rates were 85.2% (132/155) and 83.2% (104/125), respectively. The interval between cytology and histologic confirmation extended up to 38 months.
Conclusions
HPV-IDCMs comprised 3.6% of primary cervical malignancies with a high detection rate via cytology (83.2%). These findings affirm the value of cytological screening, particularly in patients with limited screening history or at risk for HPV-independent lesions, and may guide future screening protocols.
- Modified plasma-thrombin method using patient-derived plasma for cell block preparation in endobronchial ultrasound–guided transbronchial fine-needle aspiration
- Xizhe Zhang, Chunli Tang, Yingying Gu, Zeyun Lin, Shiqi Tang, Anzi Tan, Mengshi Li, Zhucheng Chen, Yuying Chen, Shi-yue Li, Juhong Jiang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):434-443. Published online November 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.20
- 2,951 View
- 97 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The plasma-thrombin method, which uses expired blood bank plasma as an ancillary component, has been widely used in cell block (CB) preparation. However, the application of expired blood bank plasma raises concerns about nucleic acid contamination. This study investigated the feasibility of using patient-derived plasma as a substitute for blood bank plasma in the modified plasma-thrombin (MPT) method for CB preparation in endobronchial ultrasound–guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) samples. Methods: A prospective study was conducted to compare the adequacy of CB preparation between a previously used self-clotting (SC) method and the MPT method. The EBUS-TBNA specimens from each targeted lesion were divided into paired samples: one processed using the SC method and the other using the MPT method, substituting the blood bank plasma with patient-derived plasma. Results: A total of 82 paired EBUS-TBNA samples from 59 patients were analyzed. The diagnostic yield of the SC method and the MPT method was 86.6% and 97.6%, respectively. Among patients diagnosed with non–small cell lung cancer, the adequacy rate for molecular testing was 79.2% with the SC method and 91.7% with the MPT method. Conclusions: The MPT method significantly improved the cellular yield of EBUS-TBNA–derived CBs. Using patient-derived fresh plasma rather than expired blood bank plasma avoids a known contamination risk. The additional step modestly prolongs the procedure and introduces minimal risks by vein puncture. This approach is generally considered cost-effective.
- E-cadherin expression and tumor-stroma ratio as prognostic biomarkers of peritoneal recurrence in advanced gastric cancer: a digital image analysis-based stratification study
- Somang Lee, Binnari Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):408-420. Published online November 6, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.27
- 2,812 View
- 114 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Gastric cancer remains a significant global health burden, with a high peritoneal recurrence rates after curative surgery. E-cadherin and the tumor-stroma ratio (TSR) have been proposed as prognostic indicators, but their combined prognostic utility remains unclear. Methods: This retrospective study included 130 patients with T3/T4a gastric cancer who underwent curative gastrectomy at Ulsan University Hospital between 2014 and 2019. Immunohistochemistry for E-cadherin and Vimentin was performed. Digital image analysis using QuPath’s object classifier quantified E-cadherin expression and TSR. Results: Low E-cadherin expression was associated with diffuse-type histology and advanced T stage. Low TSR was linked to younger age, female sex, and XELOX treatment. In Kaplan-Meier analysis, low TSR showed a non-significant trend toward higher peritoneal recurrence (p = .054), while low E-cadherin expression was significantly associated with increased peritoneal recurrence (p = .002). Combined biomarker analysis also revealed a significant difference in recurrence-free survival (RFS) among the four groups (p = .005); patients with both high TSR and high E-cadherin expression experienced the most favorable RFS. In multivariable analysis, E-cadherin expression remained the only independent predictor of peritoneal recurrence (high vs. low; hazard ratio, 0.348; 95% confidence interval, 0.149 to 0.816; p = .015). Conclusions: E-cadherin and TSR reflect distinct tumor biology such as epithelial integrity and stromal composition, and their combined evaluation improves prognostic stratification. Digital image analysis enhances reproducibility and objectivity, supporting their integration into clinical workflows.
- Spectrum of thyroiditis types: clinical, cytomorphological, and radiological findings
- Anam Singh, Indrajeet Kundu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):421-433. Published online November 6, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.13
- 3,513 View
- 180 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Thyroiditis encompasses a range of inflammatory conditions affecting the thyroid gland. Lymphocytic thyroiditis (LT) is a common form of thyroiditis, with acute suppuration of the thyroid, while tuberculous thyroiditis is relatively rare. Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) remains a safe and cost-effective tool for diagnosing thyroid-related diseases, especially when paired with ultrasound (US) and clinical examination. Methods: This is a cross-sectional study including 21 cases. The cases were reported as thyroiditis on US and FNAC, and the findings were correlated with patient clinical history, symptoms during presentation, and serological profiles. Results: The cases of thyroiditis encompassed the more common forms, LT and subacute granulomatous thyroiditis (SAT), as well as relatively rare forms like tuberculous thyroiditis and thyroid abscess. Cases of follicular neoplasms (FN) arising in the context of LT also are included in this study. The case of tuberculous thyroiditis presented as a bulky thyroid gland that appeared heterogeneous on US with extensive necrosis on FNAC. The cases of thyroid abscess and SAT presented with painful neck swellings, with granulomas in the latter cases. US features of LT showed an array of appearances ranging from pseudonodular to an atrophic thyroid gland. All cases of FN showed a lymphocytic background. Conclusions: Thyroiditis is a commonly encountered condition that needs to be sub-categorized accurately into acute, subacute, and chronic types for appropriate clinical management, as they can sometimes show overlapping features. Though rare, acute suppurative and tuberculous thyroiditis are often encountered and warrant immediate care and treatment.
Case Study
- Primary thyroid diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: fine needle aspiration and histological correlation
- Woo Sung Moon, Yong Tae Hong, Ae Ri Ahn
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):467-471. Published online November 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.28
- 2,829 View
- 107 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary thyroid lymphoma (PTL) is a rare type of cancer that arises within the thyroid gland, representing about 2%–8% of all thyroid malignancies. Fine-needle aspiration cytology is commonly used as the first-line diagnostic approach for thyroid nodules and can assist in identifying PTL when suggestive features are present. Herein, we report the case of a 59-year-old female patient who presented with a rapidly enlarging anterior neck mass over 20 days. Clinically, the case was challenging to distinguish from anaplastic thyroid carcinoma because of the sudden enlargement of the neck mass. However, pathological examination confirmed the diagnosis of primary thyroid diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Fine-needle aspiration cytology proved valuable in avoiding unnecessary surgical resection and guiding appropriate treatment. Additionally, we provide a brief review of the clinical and cytopathological features of primary thyroid lymphomas.
Review Article
- Breast schwannoma: review of entity and differential diagnosis
- Sandra Ixchel Sanchez, Ashley Cimino-Mathews
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):353-360. Published online November 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.12
- 3,326 View
- 165 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Schwannomas are benign peripheral nerve sheath tumors composed of Schwann cells, which uncommonly involve the breast. Most breast schwannomas are clinically present as a superficial palpable breast mass but may also be detected on screening mammography. Excision is the preferred treatment if symptomatic, and these are not known to recur. Histomorphology is similar to other anatomic sites: bland spindle cells with wavy nuclei, nuclear palisading (Verocay bodies), variably hypercellular (Antoni A) and hypocellular (Antoni B) areas, myxoid stroma, hyalinized vessels and variable cystic degeneration. Classic immunohistochemistry is diffuse and strong labeling for S100 and Sox10. Notable diagnostic pitfalls specific to the breast include myofibroblastoma, particularly the palisaded variant, and fascicular pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia.
Case Study
- Clinicopathological characteristics of digestive system angioleiomyomas: case report and literature review
- Georgios Kalliopitsas, Christos Topalidis, Constantine Halkias, Theodora Gkeka, Konstantinos Sapalidis, Triantafyllia Koletsa
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):453-459. Published online October 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.04
- 2,770 View
- 108 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Angioleiomyomas are benign soft tissue tumors originating from the vascular wall. Although angioleiomyomas mainly occur in extremities, followed by head, neck, and trunk, they can also be found throughout the digestive system and especially in the oral cavity. Herein, the fourth case of a rectal angioleiomyoma in the English literature is reported and the clinicopathological features of digestive system angioleiomyomas were investigated. In contrast to their soft tissue counterparts, digestive system angioleiomyomas mainly affect males at a slightly younger age. Angioleiomyomas are mainly asymptomatic and only rarely elicit pain. Clinicians consider angioleiomyomas infrequently and instead include more common soft tissue or epithelial tumors in their differential diagnosis. To prevent angiomyolipoma misdiagnosis, pathologists should exercise caution when examining an angioleiomyoma composed of adipose tissue, smooth muscle, and blood vessels. Pathologists, radiologists, and surgeons should be aware that angioleiomyomas can occur in the digestive system.
Newsletter
- What’s new in hematopathology 2025: myeloid neoplasms in the WHO 5th edition and ICC
- Barina Aqil
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):472-475. Published online October 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.24
- 9,918 View
- 357 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The previous edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of hematolymphoid neoplasms was published in 2008 and later revised in 2017. A new 5th edition of the WHO classification of hematolymphoid neoplasms was released in 2022. Additionally, the Clinical Advisory Committee developed the International Consensus Classification (ICC) of hematolymphoid tumors, which differs from the WHO classification in several key defining features as outlined below.
Original Articles
- Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor: clinicopathological analysis of 34 cases from Karachi, Pakistan
- Summaya Zafar, Sehar Sulaiman, Madeeha Nisar, Poonum Khan, Nasir Ud Din
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):390-397. Published online October 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.11
- 2,781 View
- 144 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor (AOT) is a benign slow-growing neoplasm of odontogenic epithelial origin that is relatively uncommon. Only a few studies have described its histological features. Hence, we aimed to describe the clinicopathological features of AOT in a cohort of patients. Methods: AOT cases diagnosed between 2009 and 2024 were searched electronically. Glass slides were retrieved from archives and were reviewed by two pathologists to record the associated morphological features. Other data including patient demographics and tumor site were collected by reviewing histopathology reports. Results: The age of patients ranged from 9 to 44 years (mean, 17.7 years), and most were female (55.9%). The maxilla (44.1%) was the most common tumor site. Histologically, a predominantly solid growth pattern (n = 34) accompanied by ducts with a cuboidal/columnar epithelial lining (n = 31), eosinophilic secretions (n = 31), calcifications (n = 31), lattice work pattern (n = 30), and cystic areas (n = 20) were observed. Less frequent features included calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor (CEOT)–like areas (n = 13), osteodentin (n = 6), association with impacted tooth (n = 3), mucin in tubules (n = 7), fibrocollagenous stroma (n = 6), mucin in ducts (n = 3) and ossifying fibroma-like areas (n = 6). The association of ducts with a cuboidal/columnar epithelial lining, lattice work pattern, calcifications, and eosinophilic secretions with gingival tumors was statistically significant (p ≤ .05). Additionally, tooth tumors were significantly associated with CEOT-like areas (p = .03). Conclusions: Our study confirms the trends in the clinicopathological features of AOT in previous case reports. Our results suggest that AOTs usually exhibit a predominantly solid pattern with duct-like spaces. Only a few cases with CEOT-like and ossifying fibroma-like areas were observed, similar to infrequent cases reported in the past.
- Clinicopathological implications of miR-3127 in melanoma
- Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Chau M. Bui, Vuong Gia Huy
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):371-381. Published online October 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.08
- 4,658 View
- 154 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Cutaneous melanoma is the most lethal of all skin cancers. Recent studies suggested that miR-3127 is dysregulated in multiple tumor types and has important roles in tumorigenesis and cancer progression, giving it potential as a prognostic biomarker. The aim of this study was to use bioinformatic analysis to assess miR-3127 expression and correlate expression patterns with disease course in patients with cutaneous melanoma. Methods: miRNA, mRNA sequencing, DNA methylation data, and clinical information of cutaneous melanoma cases were downloaded from the Human Cancer Atlas – Skin Cutaneous Melanoma (TCGA-SKCM). miR-3127 expression was classified into miR-3127–low and miR-3127–high clusters using maximally selected rank statistics. Results: Clustering analysis showed that high expression of miR-3127 (≥20.3 reads per million) was associated with worse progression-free (p < .001) and overall (p = .011) survival compared to low miR-3127 expression. More than five thousand differentially expressed genes between the two miR-3127 sample groups encoded cell differentiation markers, cytokines, growth factors, translocated cancer genes, and oncogenes. Pathway analysis revealed that miR-3127–high samples related to activity of proliferation, DNA repair, and ultraviolet response. Conclusions: The expression level of miR-3127 could act as a prognostic indicator for patients with melanoma.
- Attitudes toward artificial intelligence in pathology: a survey-based study of pathologists in northern India
- Manupriya Sharma, Kavita Kumari, Navpreet Navpreet, Sushma Bharti, Rajneesh Kumari
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):382-389. Published online October 2, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.10
- 5,344 View
- 187 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming pathology by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and workflow standardization. Despite its growing presence, AI adoption remains limited, particularly in resource-constrained settings like India. This study assessed the knowledge, awareness, and perceptions of AI among pathologists in Northern India. Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted among 138 practicing pathologists in Northern India between April and June 2024. A structured online questionnaire was used to collect data on demographics, AI awareness, self-reported knowledge, sources of AI education, technological proficiency, and interest in AI-related training programs. Data analysis included descriptive statistics and chi-square tests, with p < .05 considered statistically significant. Results: AI awareness was high (88.4%), with significant sex differences (93.5% in females vs. 78.3% in males, p = .008). However, formal AI training was limited (6.5%), and only 16.7% had used AI as a diagnostic tool. Academic pathologists were more likely to engage with AI literature than their non-academic counterparts (p = .003). Interest in AI workshops was strong (92.8%). Access to whole slide imaging (WSI) correlated with higher AI knowledge (p = .008), as did self-reported technological proficiency (p = .001). Conclusions: Despite high AI awareness among pathologists, significant gaps remain in training, infrastructure, and practical application. Expanding access to digital pathology tools like WSI and improving digital literacy could facilitate AI adoption. Structured educational programs and greater investment in digital infrastructure are crucial for integrating AI into pathology practice.
- National quality assurance program using digital cytopathology: a 5-year digital transformation experience by the Korean Society for Cytopathology
- Yosep Chong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Soon Auck Hong, Sung Soon Kim, Bo-Sung Kim, Younghee Choi, Yoon Jung Choi, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Soo Jin Jung, Hoon Kyu Oh, Seung-Sook Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):320-333. Published online September 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.27
- 3,762 View
- 107 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Digital cytopathology (DC) is emerging as a transformative approach in quality assurance programs (QAP), though its comprehensive evaluation remains limited. Since 2020, the Korean Society for Cytopathology has progressively incorporated DC into its national QAP, including digital proficiency testing (PT), sample adequacy testing (SAT), a customizable PT module, and a self-assessment module (SAM), aiming for full digital implementation by 2026. Methods: This 5-year study assessed diagnostic concordance between conventional and digital PT formats and analyzed participant feedback on service quality and digital image usability across PT, SAT, and SAM. Parallel testing was conducted during the transitional phase, and satisfaction was measured through structured surveys. Results: Participation in digital PT increased from 48 institutions in 2020 to 93 in 2024, while digital SAT participation rose from 29 to 71 between 2022 and 2024. In 2023, 56 institutions joined SAM. Diagnostic concordance rates were comparable between digital and conventional PTs (78.6%–84.6% vs. 82.0%–85.1%), including similar category C (major discordance) rates. Satisfaction with digital PT services and image quality exceeded 85%, and over 90% of institutions reported positive feedback on SAT and SAM. Over 80% were satisfied with the customizable PT module. Conclusions: DC is a reliable and effective modality for cytopathology QAP. It demonstrates diagnostic equivalence to conventional methods and high user satisfaction, supporting its broader implementation in national quality assurance frameworks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
- Frozen section histopathology and preanalytical factors affecting nucleic acid integrity in biobanked fresh-frozen human cancer tissues
- Soungeun Kim, Jaewon Kang, Boyeon Kim, Yoonjin Kwak, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):398-407. Published online September 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.22
- 5,884 View
- 208 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
In this study, we evaluated the effects of storage duration and ischemic time on nucleic acid quality of fresh-frozen tissue (FFT) from colon adenocarcinoma (COAD), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and renal cell carcinoma (RCC) collected at the Cancer Tissue Bank of Seoul National University Hospital. Methods: A total of 102 FFT samples were analyzed to compare DNA integrity number (DIN) and RNA integrity number (RIN) according to storage duration and ischemic time. Additionally, the effects of histopathologic features—such as tumor cell proportion, inflammatory cell infiltration, and stromal fibrosis—on nucleic acid quality were evaluated. Results: DIN and RIN remained stable overall even though the storage duration increased, with no statistically significant differences observed. In particular, there was almost no decrease in RNA quality in HCC and RCC samples, but in COAD samples, RIN tended to decrease slightly as the storage duration increased. No significant difference was confirmed between ischemic time and nucleic acid quality, but in COAD tissue, RNA quality variability tended to increase as the ischemic time increased. Furthermore, RIN increased as the tumor cell proportion increased, whereas inflammatory cell infiltration and extracellular mucin pool were identified as independent negative predictors of RIN. Conclusions: This study confirmed that nucleic acid integrity can be maintained even during long-term storage of FFT and demonstrated that histologic features are closely related to RNA quality. This study would contribute to the establishment of quality assessment and management standards for biobank FFT samples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
Zhiyong Liu, Jianhe Wu, Yuanwei Li, Qiang Lu, Yongjun Yang
BMC Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
Case Study
- Cytological characteristics of Müllerian adenosarcoma of the uterine corpus: a case report and literature review
- Junko Kuramoto, Chihiro Matsubara, Yasuko Sasamoto, Hitomi Tsukada, Shigemichi Hirose
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):340-347. Published online September 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.11
- 3,562 View
- 83 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Müllerian adenosarcoma of the uterus is a rare morphological variant of uterine sarcoma. Müllerian adenosarcoma has been described histologically, though it is rare in the cytological literature. This report describes the cytological findings of a case of adenosarcoma arising from the endometrium. The patient was a Japanese woman in her 40s. Endometrial cytological and histological findings were observed for 5 years, from the appearance of a polypoid lesion until adenosarcoma was suspected, and then hysterectomy was performed. Based on these longitudinal cytological and histological observations, it was possible to identify the cytological characteristics of adenosarcoma: decrease in the glandular-to-stromal ratio; increase in stromal cell density; and progression of stromal cell atypia. This case stresses the importance and usefulness of endometrial cytology in the identification of the sarcomatous component in adenosarcoma.
Original Article
- A single-institution demographic study of pathologically proven kidney disease in South Korea over the last 33 years
- Hyejin Noh, Jiyeon Kim, Yeong Jin Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):306-319. Published online September 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.18
- 2,034 View
- 91 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
To date, epidemiological studies on the entire spectrum of kidney disease based on pathology have been rarely reported. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on patients diagnosed with kidney disease at Seoul St. Mary's Hospital between 1991 and 2023. Results: Among 7,803 patients with native kidney disease, glomerular disease (70.3%) was the most common, followed by tubulointerstitial (15.1%) and vascular disease (8.8%). In kidney biopsy, glomerular disease (77.8%) showed the highest frequency, particularly in those under 20s (95.6%) (p = .013). Primary glomerulonephritis (GN) (72.8%) was the predominant glomerular disease, with IgA nephropathy (IgAN) (47.3%) being the most common one. Tubulointerstitial and vascular diseases increased with age, showing the highest prevalence in those over 60 years (p = .008 and p = .032, respectively). Glomerular disease was diagnosed at a younger age (39.7 ± 16.7 years) than tubulointerstitial (49.1 ± 16.2) and vascular (48.1 ± 15.3) diseases (p < .001). When glomerular diseases were classified morphologically, proliferative GN (57.9%) was the most common, followed by non-proliferative (39.6%) and sclerosing (1.6%). When classified by etiology, primary GN accounted for the most (72.8%), followed by secondary (19.3%) and hereditary GN (5.7%). In nephrectomy, tubulointerstitial disease (64.6%) was the most common. Those with a tubulointerstitial disease had a higher mean age than those with a glomerular disease (p < .001). In cases where nephrectomy was performed for glomerular diseases, IgAN (34.1%) was the most common diagnosis. Conclusions: Kidney disease has been increasing in South Korea for 33 years. Glomerular disease was the most common across all age groups, tubulointerstitial and vascular diseases increased over 60 years.
Letter to the Editor
- Variation in mitotic counting and risk classification practices for gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a survey of pathologists in South Korea
- In Hye Song, Soomin Ahn, Jeong-Hyeon Jo, Young Soo Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):348-352. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.14
- 2,435 View
- 32 Download
- 1 Crossref
Original Article
- Characterization of undifferentiated carcinoma of the salivary gland: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analyses in comparison with lymphoepithelial carcinoma
- Sangjoon Choi, Gyuheon Choi, Hee Jin Lee, Joon Seon Song, Yoon Se Lee, Seung-Ho Choi, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):361-370. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.07
- 3,171 View
- 286 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to reclassify a subset of poorly differentiated salivary gland carcinoma that do not conform to any entities of the current World Health Organization (WHO) classification into the category of undifferentiated carcinoma (UDC) because they lack specific histologic differentiation or immunophenotype. Methods: Cases of salivary gland carcinomas from Asan Medical Center (2002–2020) that did not fit any existing WHO classification criteria and were diagnosed as poorly differentiated carcinoma, high-grade carcinoma, or UDC, were retrospectively reviewed. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for p40, neuroendocrine markers, androgen receptor (AR), and gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in situ hybridization (ISH) were performed. Clinical data were collected from the electronic medical records. Results: Six salivary gland carcinomas did not align with any specific entities and lacked distinct differentiation. Two of six cases displayed lymphoepithelial carcinoma (LEC)-like morphology but were negative or showed negligible immunoreactivity for p40 and EBV ISH, distinguishing them from LEC of the salivary gland. Two cases showed strong AR positivity, suggesting a potential overlap with salivary duct carcinoma (SDC) but lacked classic SDC morphologies and GCDFP-15 expression. No cases expressed neuroendocrine markers. Conclusions: This study proposes reclassifying these poorly differentiated or high-grade salivary gland carcinomas as UDC based on their indeterminate differentiation and IHC profiles. This may lead to a clearer diagnostic category and enhance our understanding of these high-grade tumors.
Case Study
- Composite chronic lymphocytic leukemia and mantle cell lymphoma involving the bone marrow: a case report and literature review
- Roksolana Demianets, Susan O’Brien, Khosrow Mahdavi, Chenchen Niu, Sumayya Aslam, Truc Tran, Ying Zhang, Ashley Gamayo, Xiaohui Zhao, Sherif A. Rezk
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):334-339. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.02
- 2,700 View
- 143 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) is a clinically indolent lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by accumulation of mature B-cell lymphocytes. Given the common CD5 co-expression, mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is one of the most important entities in the differential diagnosis. MCL and CLL/SLL might exhibit overlapping morphologic and immunohistochemical features, making diagnosis particularly difficult in cases of composite lymphomas. Here, we present a unique case of composite lymphoma in an 86-year-old male, along with a literature review on the immunophenotypic variability of both MCL and CLL, which should always be confirmed with additional ancillary cytogenetic and molecular studies.
Original Articles
- Evaluation of potential prognostic significance of JUNB in human prostate cancer: a bioinformatic and histopathological study
- Noha R. Noufal, Einas M. Yousef, Mohamed Taha
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):291-305. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.06
- 1,916 View
- 124 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Prostate cancer is one of the most common malignancies in males worldwide. Serum prostate-specific antigen is a frequently employed biomarker in the diagnosis and risk stratification of prostate cancer; however, it is known for its low predictive accuracy for disease progression. New prognostic biomarkers are needed to distinguish aggressive prostate cancer from low-risk disease. This study aimed to identify and validate potential prognostic biomarkers of prostate cancer. Methods: Two prostate cancer datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus were analyzed to identify differentially expressed genes between benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostatic carcinoma. Immunohistochemistry was used to evaluate the JUNB proto-oncogene, a subunit of the AP-1 transcription factor (JUNB), in 70 prostate cancer patients and 10 BPH samples. Results: Our findings showed that JUNB was significantly enriched in prostate cancer-related pathways and biological processes. JUNB expression was considerably higher in prostatic adenocarcinoma patients than in BPH patients. Regarding JUNB expression in prostate cancer cases, lower levels of JUNB expression were associated with higher grades of prostatic adenocarcinoma. Lower JUNB expression was associated with a higher risk of prostatic adenocarcinoma progression and shorter overall survival. Conclusions: These results suggest that JUNB is a promising prognostic biomarker and a potential tumor suppressor in prostate cancer.
- Unraveling the crucial role of CCL3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: bioinformatics and immunohistochemical insights
- Xiaopeng Guo, Zhen Sun, Ya Liang, Aoshuang Chang, Junjun Ling, Houyu Zhao, Xianlu Zhuo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):281-290. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.05.23
- 1,810 View
- 142 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
C-C motif chemokine ligand 3 (CCL3) is a crucial chemokine that plays a fundamental role in the immune microenvironment and is closely linked to the development of various cancers. Despite its importance, there is limited research regarding the expression and function of CCL3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Therefore, this study seeks to examine the expression of CCL3 and assess its clinical significance in NPC using bioinformatics analysis and experiments. Methods: The bioinformatics approach was employed to assess the expression and function of CCL3 in NPC. Subsequently, protein expression of CCL3 was detected in an NPC cohort using immunohistochemistry based on a tissue microarray. The relationship between CCL3 expression and clinical features was then investigated. Results: A total of 20 CCL3-related genes and 14 possible target genes were identified through bioinformatics analysis, many of which play crucial roles in pathways such as chemokine signaling pathway and transcriptional misregulation in cancer signaling pathways. CCL3 was found to be associated with drug resistance and various immune cell infiltrations. In NPC, CCL3 expression was significantly higher than normal controls, and high expression of CCL3 correlated with cervical lymph node metastasis, tumor recurrence, advanced clinical stage, and poor prognosis. Conclusions: CCL3 may be a key gene in the initiation and progression of NPC. It has the potential to serve as both a diagnostic biomarker and a therapeutic target for NPC.
Review Article
- Central nervous system tumors with BCOR internal tandem duplications: a systematic review of clinical, radiological, and pathological features in 69 cases
- Ji Young Lee, Sung Sun Kim, Hee Jo Baek, Tae-Young Jung, Kyung-Sub Moon, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Kyung-Hwa Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):273-280. Published online September 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.23
- 3,877 View
- 188 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Central nervous system tumors with BCL6 corepressor (BCOR) internal tandem duplications (ITDs) constitute a rare, recently characterized pediatric neoplasm with distinct molecular and histopathological features. To date, 69 cases have been documented in the literature, including our institutional case. These neoplasms predominantly occur in young children, with the cerebellum representing the most frequent anatomical location. Radiologically, these tumors present as large, well-circumscribed masses frequently demonstrating necrosis, hemorrhage, and heterogeneous enhancement. Histologically, they are characterized by a monomorphic cellular population featuring ependymoma-like perivascular pseudorosettes, myxoid stroma, and elevated mitotic activity. Immunohistochemically, these tumors exhibit sparse glial fibrillary acidic protein expression while consistently demonstrating positive staining for vimentin and CD56. The defining molecular hallmark is a heterozygous ITD within exon 15 of the BCOR gene, with insertions ranging from 9 to 42 amino acids in length. BCOR immunohistochemistry reveals nuclear positivity in 97.9% of examined cases, although this finding is not pathognomonic for BCOR ITDs. This comprehensive review synthesizes data from all published cases of this novel tumor entity, providing a detailed analysis of clinical presentation, neuroimaging findings, histopathological features with differential diagnostic considerations, therapeutic approaches, and prognostic outcomes.
Newsletter
- What’s new in medical renal pathology 2025: Updates on podocytopathy and immunofluorescence staining in medical kidney
- Astrid Weins, Ibrahim Batal, Paola Romagnani, Geetika Singh, Rahul Raj, Nicole Andeen, Jonathan Zuckerman, Martina Uzzo, Mariam Priya Alexander, Anjali Satoskar
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):269-272. Published online July 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.19
- 6,354 View
- 378 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Diffuse podocytopathy, including minimal change disease and primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, is a common cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults and children. It is increasingly recognized to be autoimmune-mediated associated with anti-nephrin and other emerging anti-slit diaphragm antibodies, and can recur in the kidney allograft. Immunofluorescence is routinely used in evaluation of kidney biopsies, and updates include those on fibrillar diseases, monoclonal staining, lupus-like staining, and use of antibody KM55 in IgA-dominant glomerulonephritis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Opportunities and challenges in recurrent diffuse podocytopathy post-transplantation: the critical value of the definition
Rachel Nuccitelli, Amadea Toutoungis, Elena Martinelli, Simone Sanna-Cherchi, Astrid Weins, Heather K. Morris, Andrew S. Bomback, Ibrahim Batal
Frontiers in Immunology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Opportunities and challenges in recurrent diffuse podocytopathy post-transplantation: the critical value of the definition
Original Articles
- Pancreatic cancer in liquid-based cytology: cytological features and cell block utility from 254 fine-needle aspiration samples
- Jaeyong Min, Wookjin Oh, Baek-hui Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):249-261. Published online July 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.05.27
- 3,226 View
- 216 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Despite the increasing use of liquid-based cytology (LBC) for pancreatic cancer diagnosis, relatively few studies have directly examined such research. This study analyzed the cytopathological features of pancreatic cancer in LBC and demonstrated the utility of cell blocks in diagnosing pancreatic lesions. Methods: A retrospective review identified LBC from 254 pancreatic fine-needle aspirations (FNAs) (221 patients). FNAs were categorized into five subgroups based on cytopathological, clinical, and histopathological findings. Two pathologists evaluated cytological features in LBC samples, cell blocks, and tissue slides. Comparative analysis assessed differences between groups. Results: Compared to benign lesions, LBC of pancreatic cancer more frequently showed a necrotic background, intermediate to high cellularity, mixed architecture, nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio >0.8, anisonucleosis >4:1, irregular and thick nuclear membranes, multinucleated tumor cells, hyperchromatic nuclei, coarse to clumped chromatin, and a prominent single nucleolus. In cases of conventional pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, the palliative treatment subgroup showed a higher incidence of necrotic background than the resection subgroup. In the cell block analysis, tumor cells not identified in LBC slides were detected in 16 FNAs. Additionally, 13 FNAs contributed to differential diagnosis: ancillary tests aided diagnosis in 12 FNAs, while histopathological evaluation of the cell block slide alone was helpful in one case. Conclusions: The cytological features of pancreatic cancer in LBC are similar to those observed in conventional smears, with a necrotic background suggesting advanced (unresectable) disease. The cell block methodology minimizes tumor cell loss and facilitates differential diagnosis by enabling ancillary testing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytology and small biopsy diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Maria Pimenova, Matthew W. Rosenbaum
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2026; 43(2): 150992. CrossRef
- Cytology and small biopsy diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- AMACR is a highly sensitive and specific immunohistochemical marker for diagnosing prostate cancer on biopsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Johannes Cansius Prihadi, Stevan Kristian Lionardi, Nicolas Daniel Widjanarko, Steven Alvianto, Fransiskus Xaverius Rinaldi, Archie Fontana Iskandar
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):235-248. Published online July 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.04.16
- 7,149 View
- 231 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) is the preferred biomarker for distinguishing malignant from benign glands in prostate biopsies, showing high sensitivity and specificity for prostate cancer. A meta-analysis of immunohistochemistry (IHC) for AMACR is essential to further assess its diagnostic accuracy across diverse sample sources. Methods: A systematic search of databases including MEDLINE, ScienceDirect, ProQuest, Google Scholar, and the Cochrane Library was performed, focusing on studies of AMACR to diagnose prostate cancer, particularly in biopsy samples analyzed through IHC over the last 20 years. Quality of studies was assessed using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies 2 tool, followed by a meta-analysis of regions and subgroups to calculate summary estimates of diagnostic test accuracy. Results: In the final analysis, 37 studies, with a pooled size of 5,898 samples, were included from the examination of 94 full-text papers. Among them, 27 studies with similar sample sources and testing methodologies underwent meta-analysis, yielding a combined sensitivity estimate of 0.90 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.86 to 0.93) and specificity of 0.91 (95% CI, 0.83 to 0.95), both with significant heterogeneity (p < .01). The region beneath the hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.93 to 0.97), positive likelihood ratio was 9.6 (95% CI, 5.3 to 17.4), negative likelihood ratio was 0.11 (95% CI, 0.08 to 0.15), and diagnostic odds ratio was 88 (95% CI, 42 to 181). Conclusions: Our meta-analysis findings substantiate AMACR as a highly accurate tool for diagnosing prostate cancer, specifically in biopsy samples, via immunohistochemical staining. Further studies involving diverse samples are needed to enhance our understanding of the AMACR diagnostic accuracy in a range of clinical settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pathogenesis-Guided Biomarker Assessment: A Shift in Prostate Cancer Diagnostics
Jessica M. Logan, Victoria Malone, John J. O’Leary, Doug A. Brooks
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(24): 11786. CrossRef
- Pathogenesis-Guided Biomarker Assessment: A Shift in Prostate Cancer Diagnostics
- The Automatable Activity–Based Approach to Complexity Unit Scoring as a task-specific model approach to monetizing outcomes of pathology artificial intelligence solutions
- Stavros Pantelakos, Martha Nifora, Georgios Agrogiannis
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):225-234. Published online July 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.04.15
- 3,455 View
- 143 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Cost-containment policies are increasingly affecting decision-making in healthcare. In this context, the need for monetization of digital health interventions has been recently emphasized. Previous studies have attempted to extrapolate cost containment in conjunction with the implementation of digital pathology solutions mostly on the basis of operational cost savings or diagnostic error reduction. However, no study has attempted to link a wider spectrum of potential diagnostic tasks performed by artificial intelligence algorithms to financial figures.
Methods
Herein, we employ a workload measurement tool for the purpose of monetizing particular outcomes associated with the implementation of a pathology artificial intelligence solution. A hundred and thirty-two prostate core biopsy samples were encoded for workload using the Automatable Activity–Based Approach to Complexity Unit Scoring. Subsequently, avoided workload, full-time equivalent gains, and corresponding cost savings were calculated assuming full clinical deployment of a well-developed prostate cancer screening tool.
Results
For a fixed percentage of negative cores and a steady yearly workload of prostate core biopsies, the estimated total avoided workload amounted to 4,291 complexity units per year, with an average avoidance of 16.25 complexity units per ascension number. The calculated full-time equivalent gains were 0.12, whereas projected cost savings were as high as €2,402.34 per year or €0.55 per complexity unit, which in turn would yield an average of €8.93 per ascension number.
Conclusions
The Automatable Activity–Based Approach to Complexity Unit Scoring appears to be a suitable economic evaluation tool for assessing the possible implementation of task-specific artificial intelligence solutions in a given histopathology laboratory or group of laboratories, considering it is a task-specific workload measurement tool per design.
Review Articles
- Recent topics on thyroid cytopathology: reporting systems and ancillary studies
- Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Ayana Suzuki
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):214-224. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.04.18
- 4,215 View
- 297 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - As fine-needle aspiration techniques and diagnostic methodologies for thyroid nodules have continued to evolve and reporting systems have been updated accordingly, we need to be up to date with the latest information to achieve accurate diagnoses. However, the diagnostic approaches and therapeutic strategies for thyroid nodules vary across laboratories and institutions. Several differences exist between Western and Eastern practices regarding thyroid fine-needle aspiration. This review describes the reporting systems for thyroid cytopathology and ancillary studies. Updated reporting systems enhance the accuracy, consistency, and clarity of cytology reporting, leading to improved patient outcomes and management strategies. Although a single global reporting system is optimal, reporting systems tailored to each country is acceptable. In such cases, compatibility must be ensured to facilitate data sharing. Ancillary methods include liquid-based cytology, immunocytochemistry, biochemical measurements, flow cytometry, molecular testing, and artificial intelligence, all of which improve diagnostic accuracy. These methods continue to evolve, and cytopathologists should actively adopt the latest methods and information to achieve more accurate diagnoses. We believe this review will be useful to practitioners of routine thyroid cytology.
- Multiple sclerosis: a practical review for pathologists
- Rachel A. Multz, Pouya Jamshidi, Jared T. Ahrendsen
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):203-213. Published online June 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.05.20
- 17,509 View
- 507 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an immune-mediated demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system. It is a chronic disorder resulting in neurologic dysfunction that is disseminated both in time (multiple discrete episodes) and space (involving multiple sites). Histologically, MS is characterized by localized loss of myelin with relative preservation of axons. This review will discuss the epidemiology, clinical, laboratory, radiologic, and pathologic features of multiple sclerosis, as well as briefly touch on the differential diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of the disease, especially as they relate to the pathologic interpretation of tissue specimens.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- White Matter in Crisis: Oligodendrocytes and the Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis
Mario García-Domínguez
Cells.2025; 14(18): 1408. CrossRef - Tumefactive demyelinating lesions: a case report and literature review
Raneem Jaki, Zyad Al-Frejat, Ziad Bitar
BMC Neurology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Liquerologia: Uma ferramenta no diagnóstico de esclerose múltipla e outras doenças neurodegenerativas e desmielinizantes
Laura Maria de Araújo Pereira, Talyta Valeria Siqueira do Monte Guedes, Rafaell Batista Pereira, Davi Abrantes Lucena Messias, Marfran José Cunha Urtiga, Davi Rodrigues Vieira, Samuel da Costa Chaves Trindade Martins, José Guedes da Silva Júnior
Research, Society and Development.2025; 14(12): e72141249815. CrossRef
- White Matter in Crisis: Oligodendrocytes and the Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis
Case Studies
- Acquired aberrant partial CD3 expression in recurrent Epstein-Barr virus–negative solitary plasmacytoma of tonsil
- Chenchen Niu, Dong Ren, Truc Tran, Ashley Gamayo, Sherif Rezk, Xiaohui Zhao
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):262-268. Published online May 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.04.17
- 3,008 View
- 135 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The aberrant expression of specific T-cell maker CD3 in B-cell neoplasms can be a potential diagnostic pitfall leading to a misclassification of cell lineage. Here, we report a case of recurrent solitary plasmacytoma with new aberrant expression of CD3. The neoplastic plasma cells of the recurrent tumor were kappa restricted, positive for CD138, MUM1, negative for CD20, cyclin D1, and Epstein-Barr virus. CD79a was positive in majority of the tumor cells, except for a small focus which was strongly positive for CD3, but negative for other T-cell markers (CD2, CD5, CD7, CD4, and CD8) and CD56. The neoplastic plasma cells of the original tumor were negative for CD3. To the best of our knowledge, only one case of recurrent plasmacytoma with aberrant expression of CD3 has been published, which revealed disease progression in the recurrence. However, we did not observe morphologic evidence of disease progression in our case.
- Cytological features of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung: a case report
- Misa Takahashi, Seiya Homma, Chisato Setoguchi, Yoko Umezawa, Atsuhiko Sakamoto
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(3):195-200. Published online May 9, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.04.09
- 4,473 View
- 133 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) and adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) are generally treated as different lesions, depending on the differences in lesion size and histological findings. However, these differences are not absolute; thus, AAH and AIS are often difficult to distinguish. Moreover, whether AAH and AIS can be regarded as different lesions remains unknown because cytological specimens, especially those of AAH, are rare. In this study, we examined these uncommon cytological specimens and compared the cytological findings between AAH and AIS. We observed many common cytological features with no obvious differences between AAH and AIS. These findings suggest that these two distinct lesions can be grouped into a single category. Therefore, we propose creating a new cytological category.
Original Article
- Primary Merkel cell carcinoma of the salivary gland: a clinicopathologic study of four cases with a review of literature
- Gyuheon Choi, Joon Seon Song, Hee Jin Lee, Gi Hwan Kim, Young Ho Jung, Yoon Se Lee, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(3):171-179. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.03.25
- 3,966 View
- 157 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Primary Merkel cell carcinoma of the salivary gland is currently not listed in the World Health Organization classification. However, cases of Merkel cell type neuroendocrine carcinomas of the salivary gland with perinuclear cytokeratin 20 positivity have been intermittently reported. We here investigated the clinicopathologic features of additional cases.
Methods
Data of four cases of Merkel cell type small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the salivary gland were retrieved. To confirm the tumors’ primary nature, clinical records and pathologic materials were reviewed. Optimal immunohistochemical staining was performed to support the diagnosis.
Results
All tumors were located in the parotid gland. Possibilities of metastasis were excluded in all cases through a meticulous clinicopathological review. Tumor histology was consistent with the diagnosis of small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Tumors’ immunohistochemical phenotypes were consistent with Merkel cell carcinoma, including Merkel cell polyomavirus large T antigen positivity in two of the four cases.
Conclusions
Merkel cell carcinomas can originate in salivary glands and are partly associated with Merkel cell polyomavirus infection as in cutaneous Merkel cell carcinomas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parotid intranodal metastasis of Merkel cell carcinoma: a rare case report
Tong Gao, Dengshun Wang, Hongwei Yu, Yu’e Wang, Haibin Lu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Parotid intranodal metastasis of Merkel cell carcinoma: a rare case report

 E-submission
E-submission


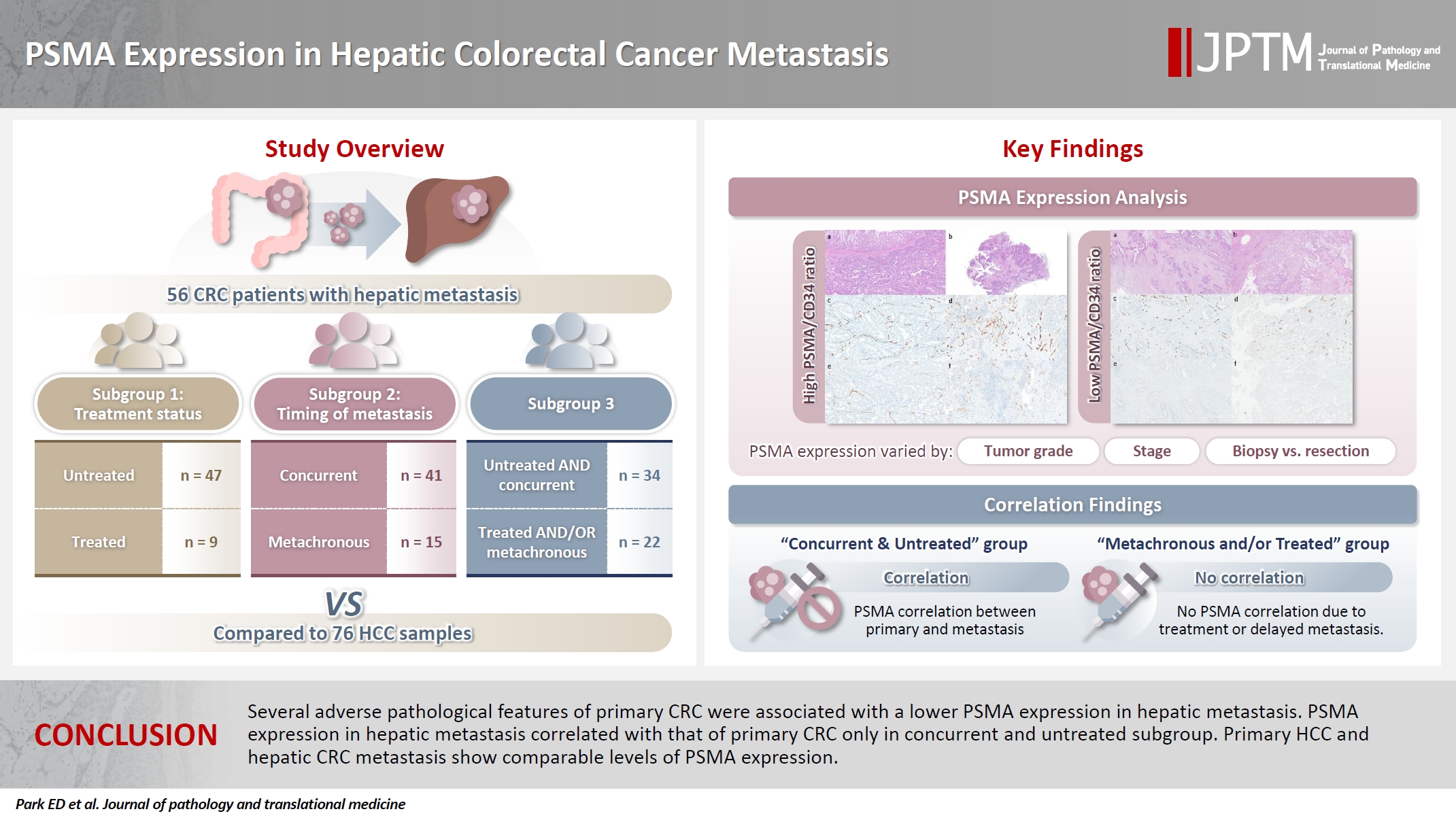
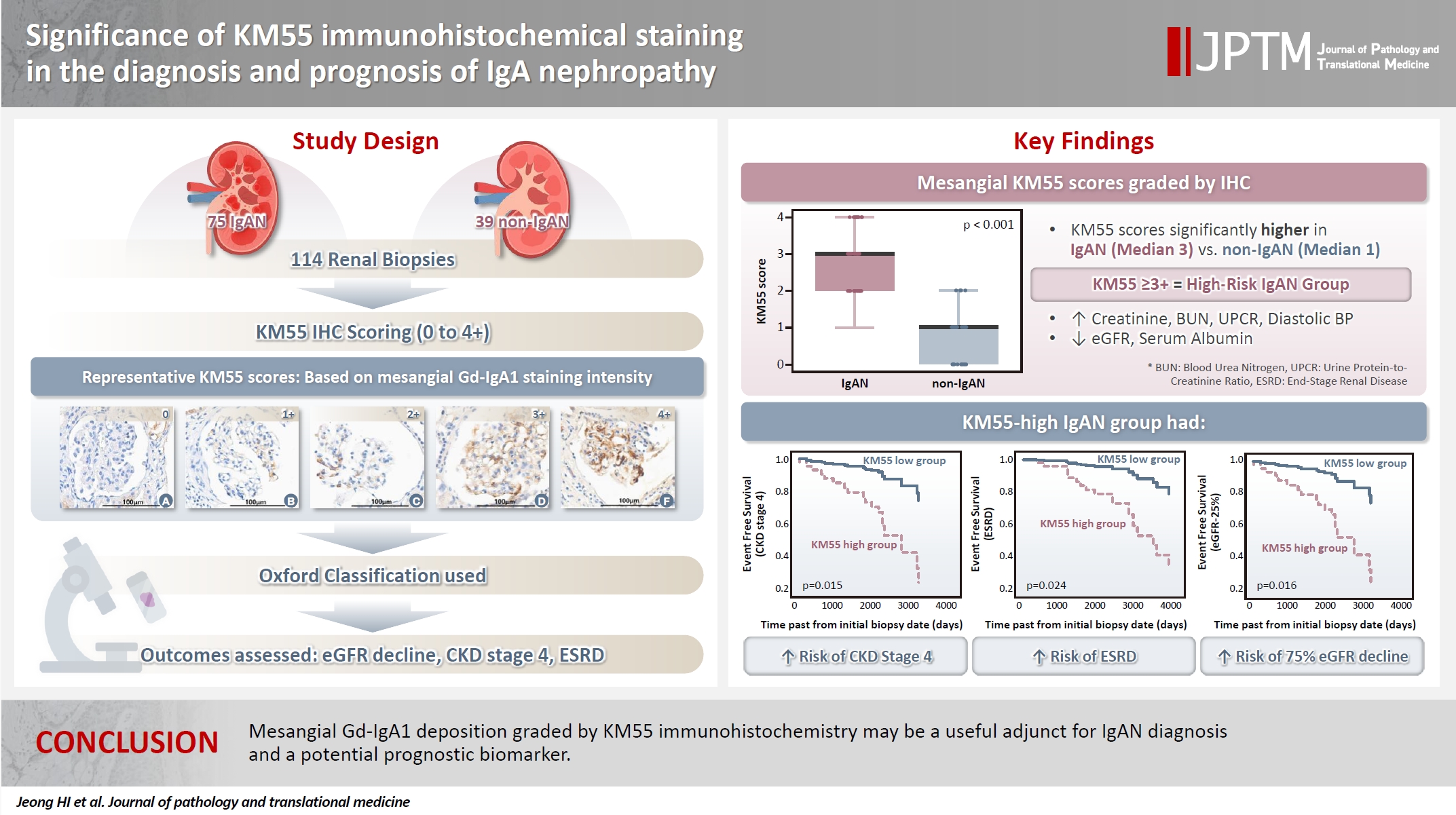
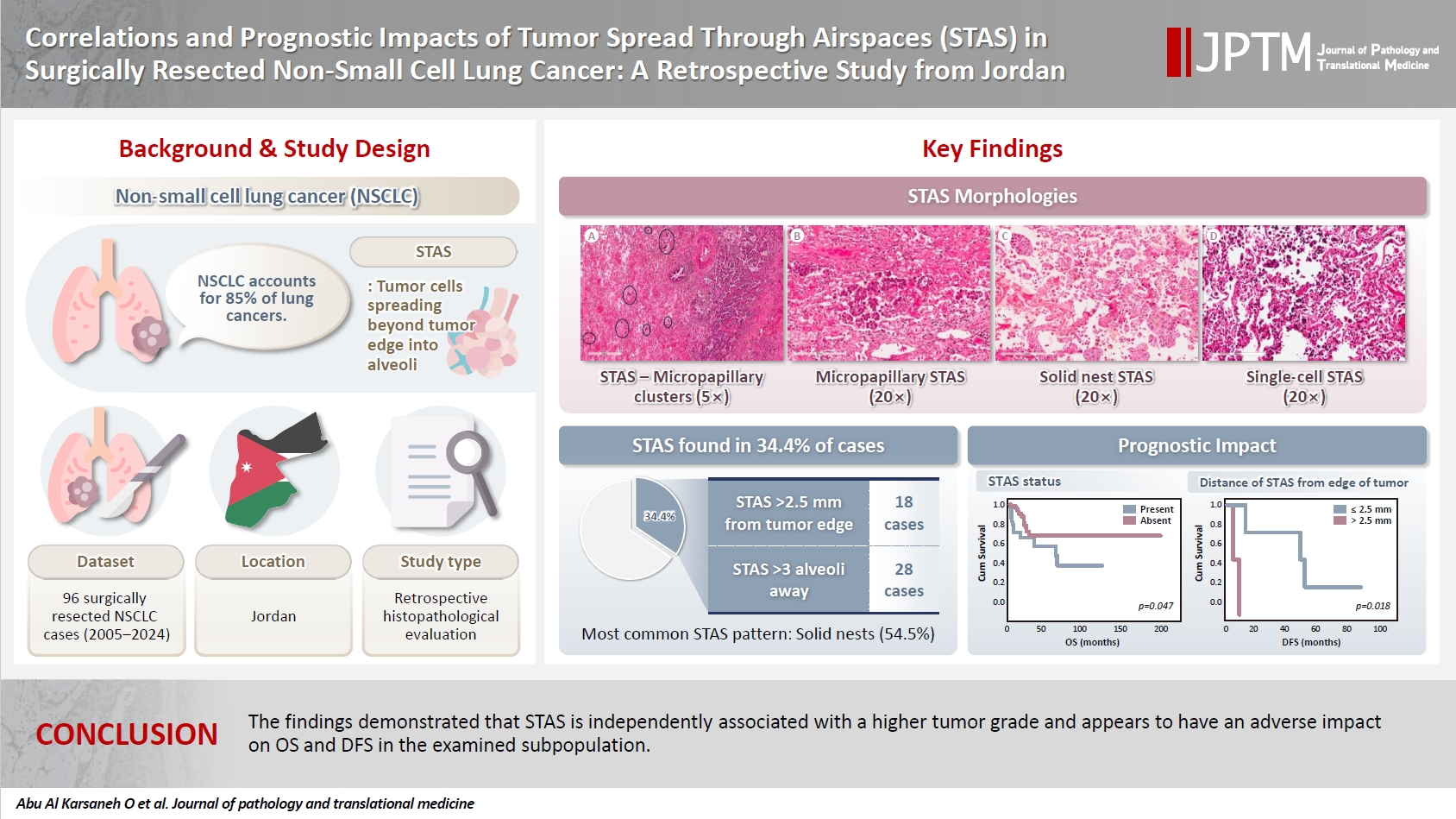








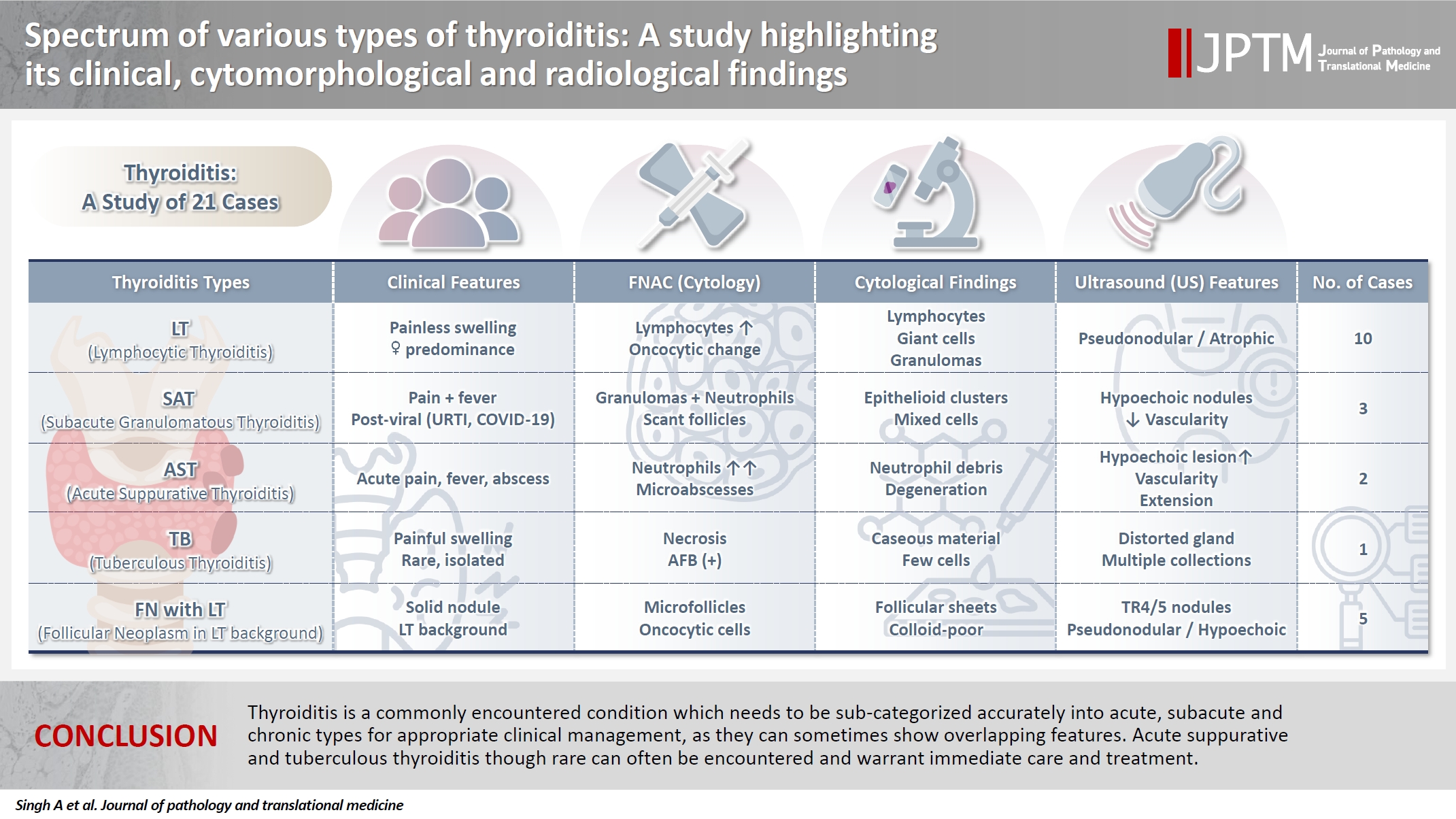
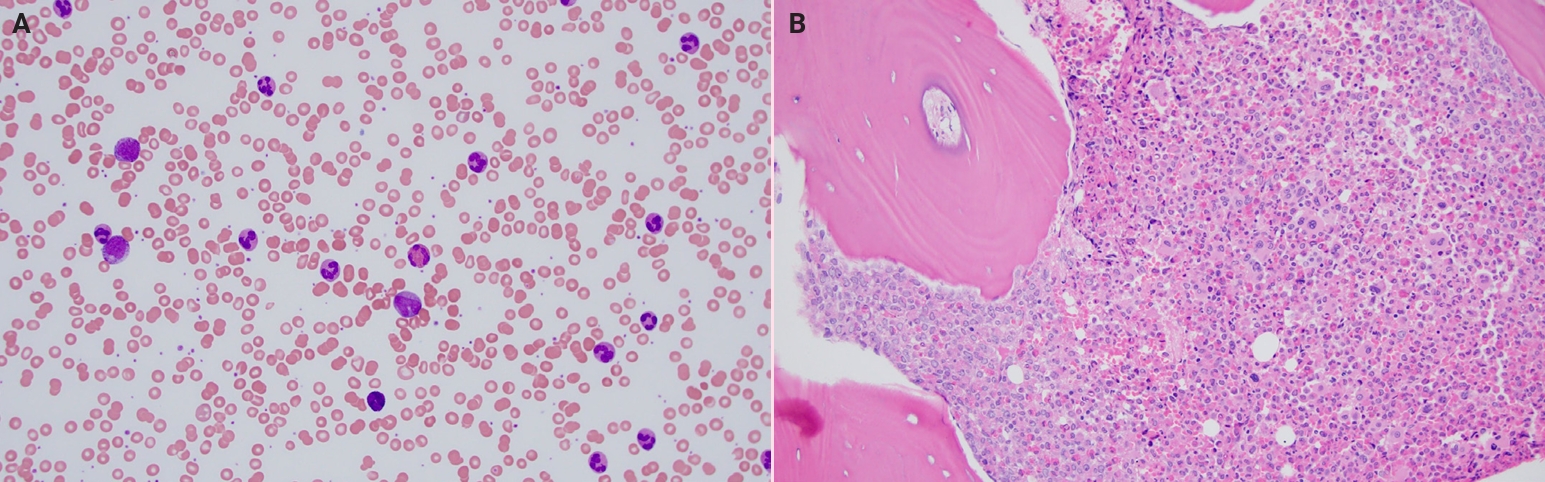
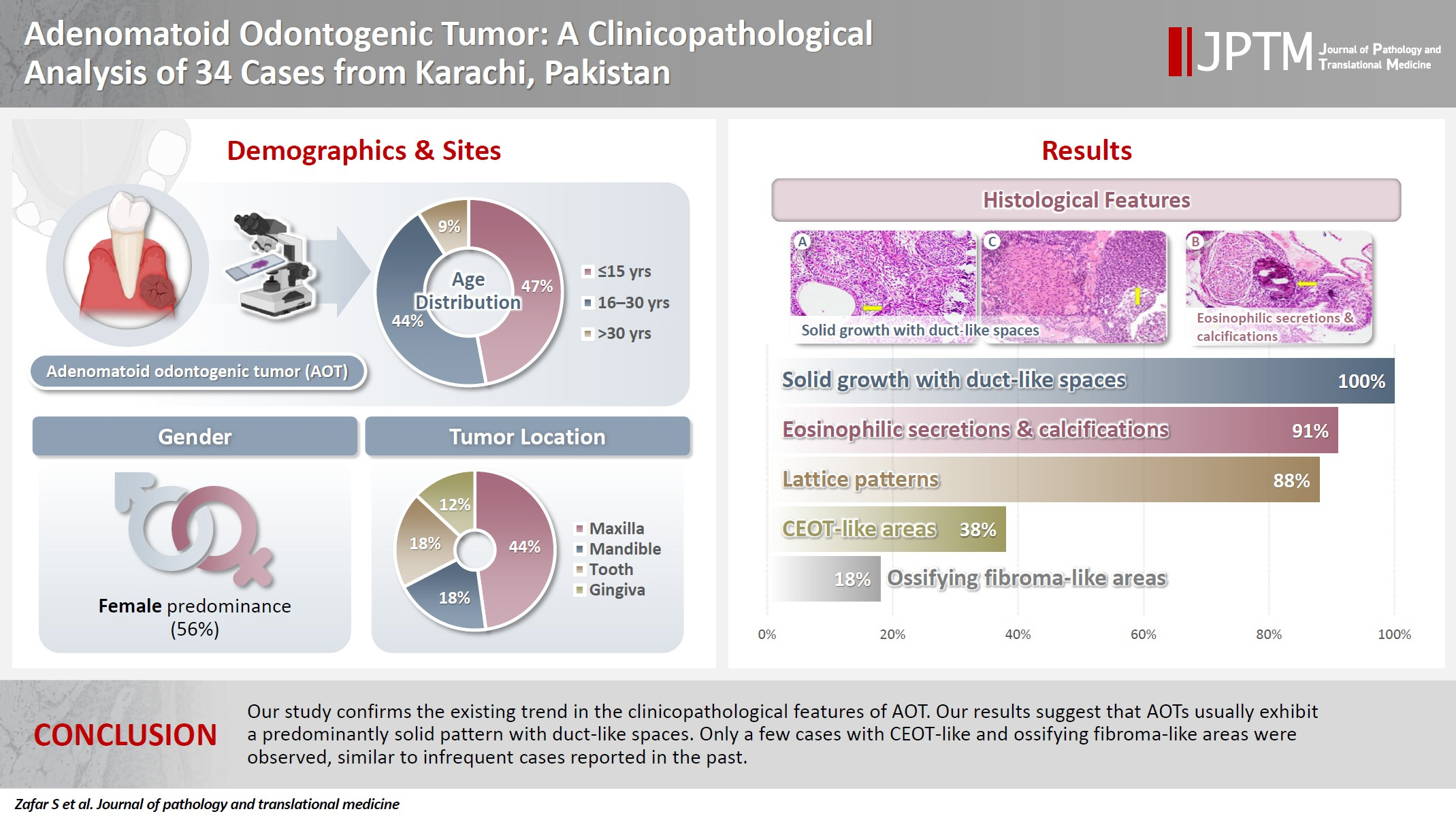
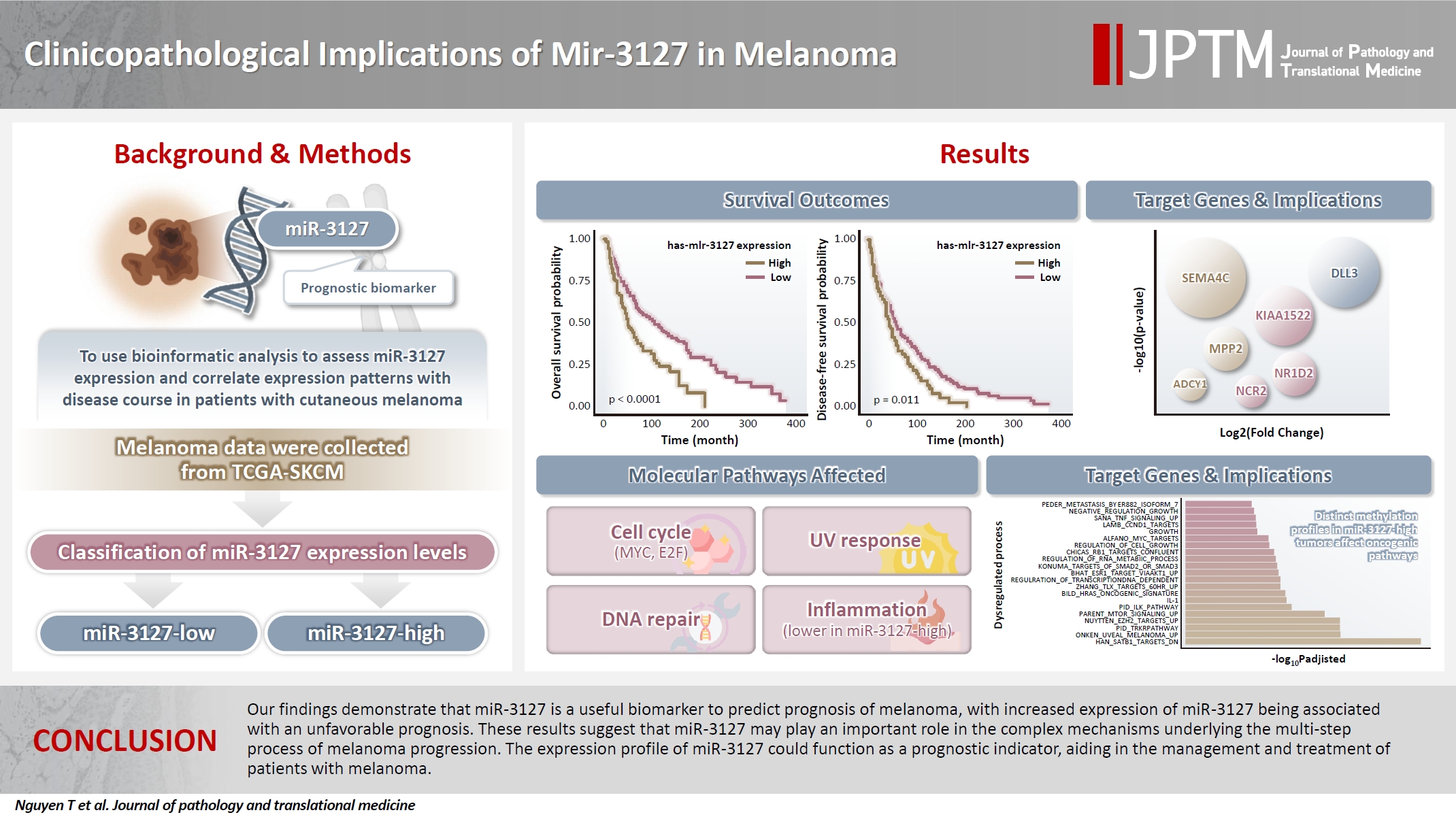

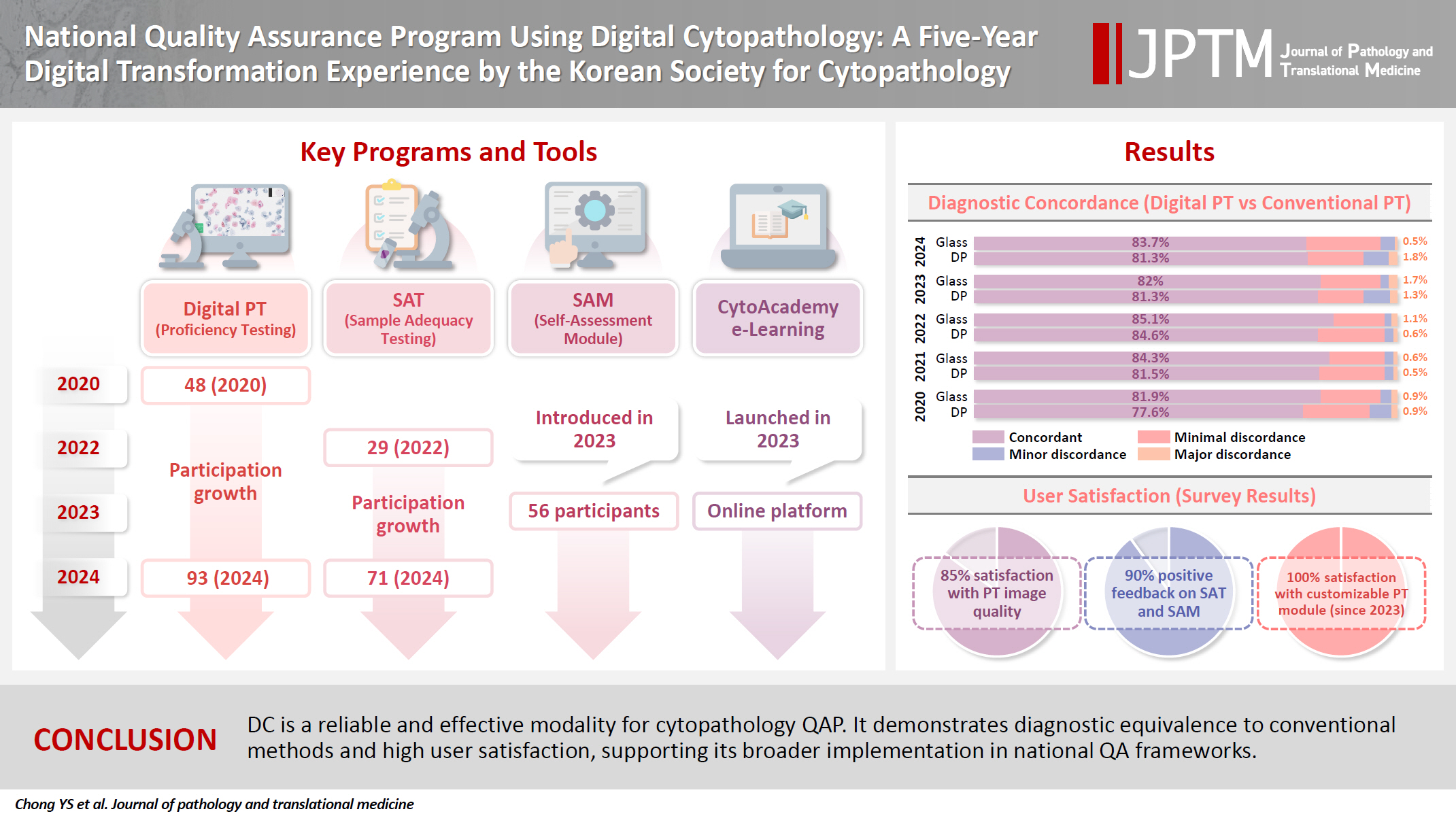
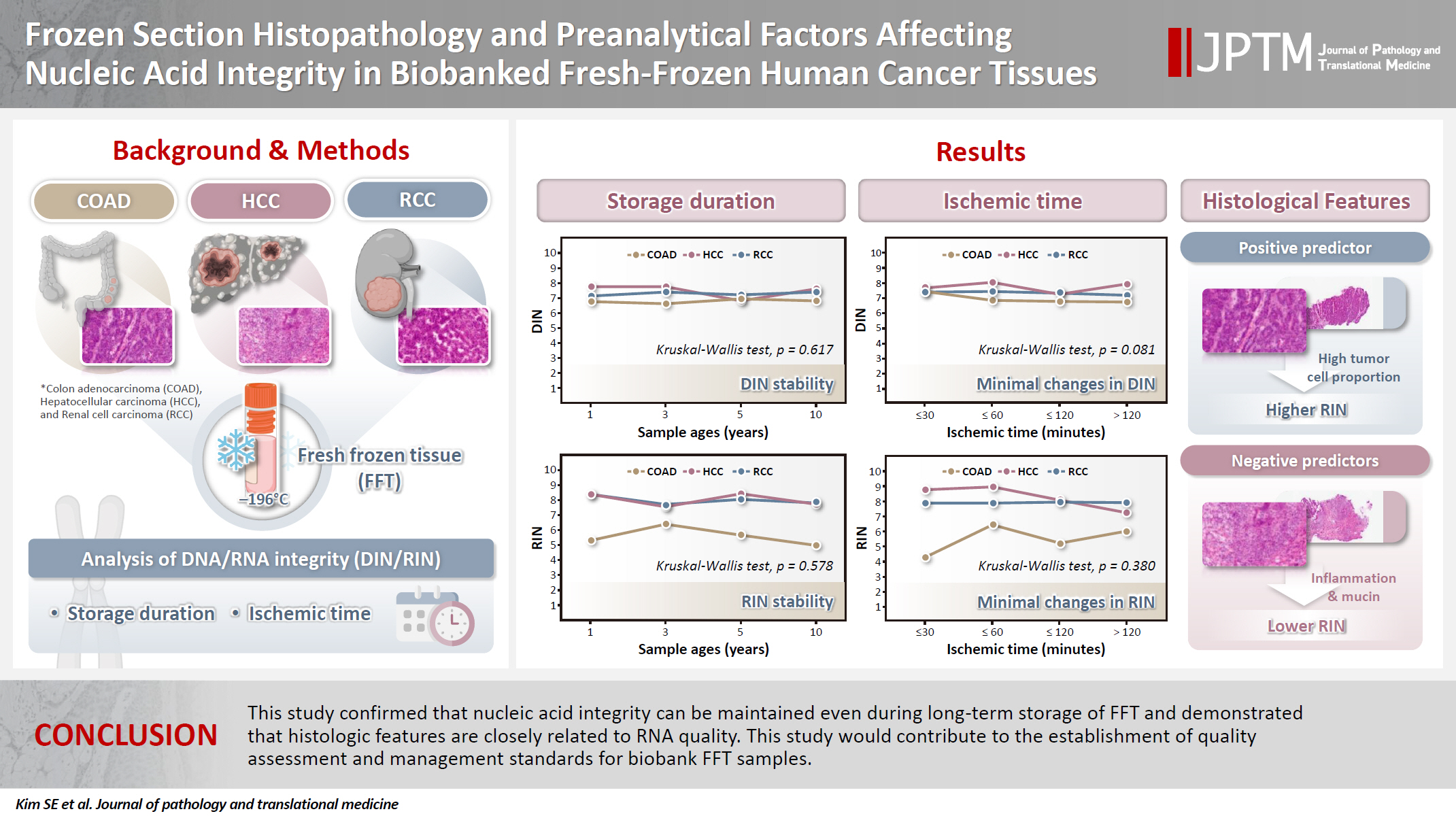
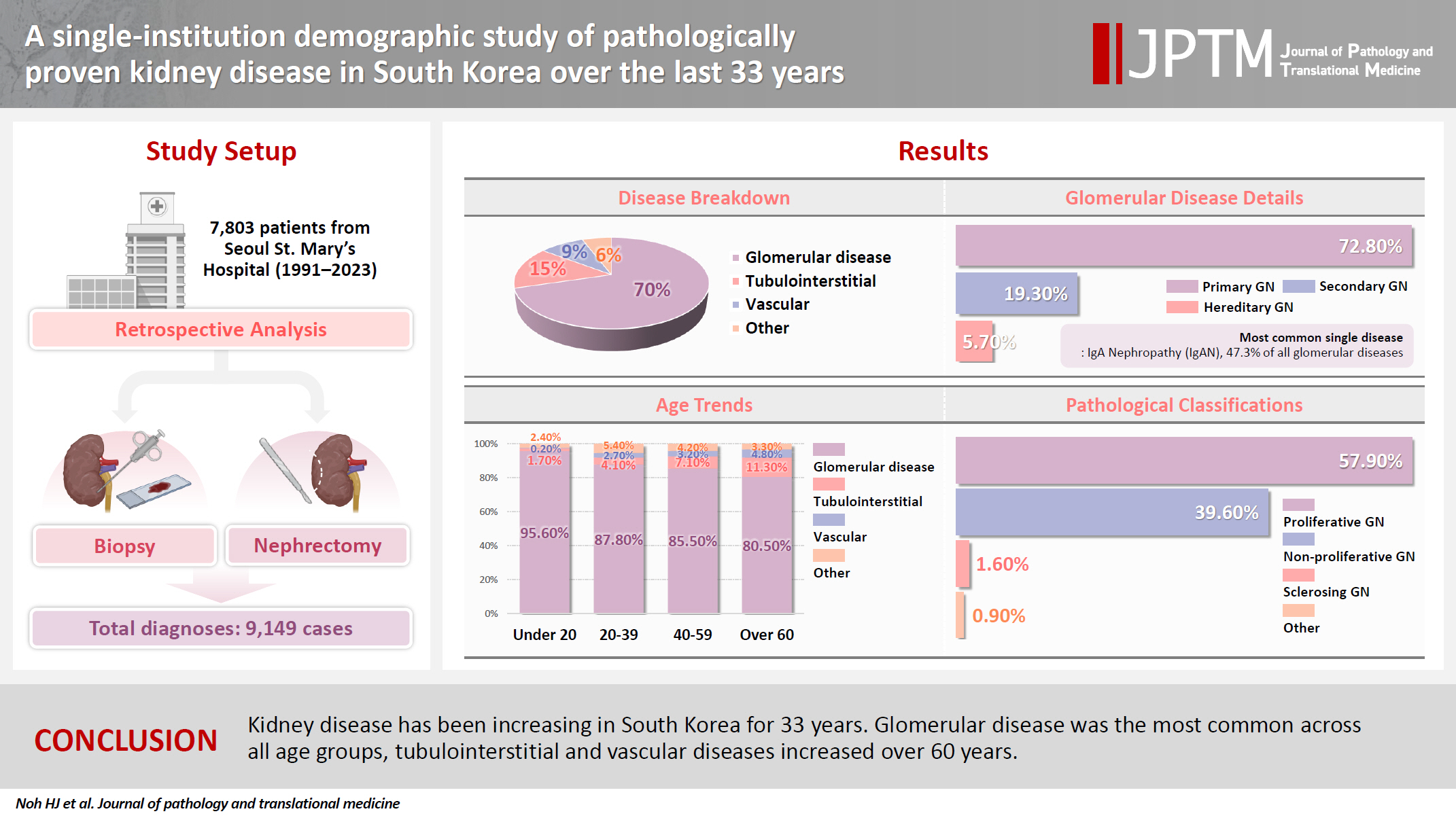
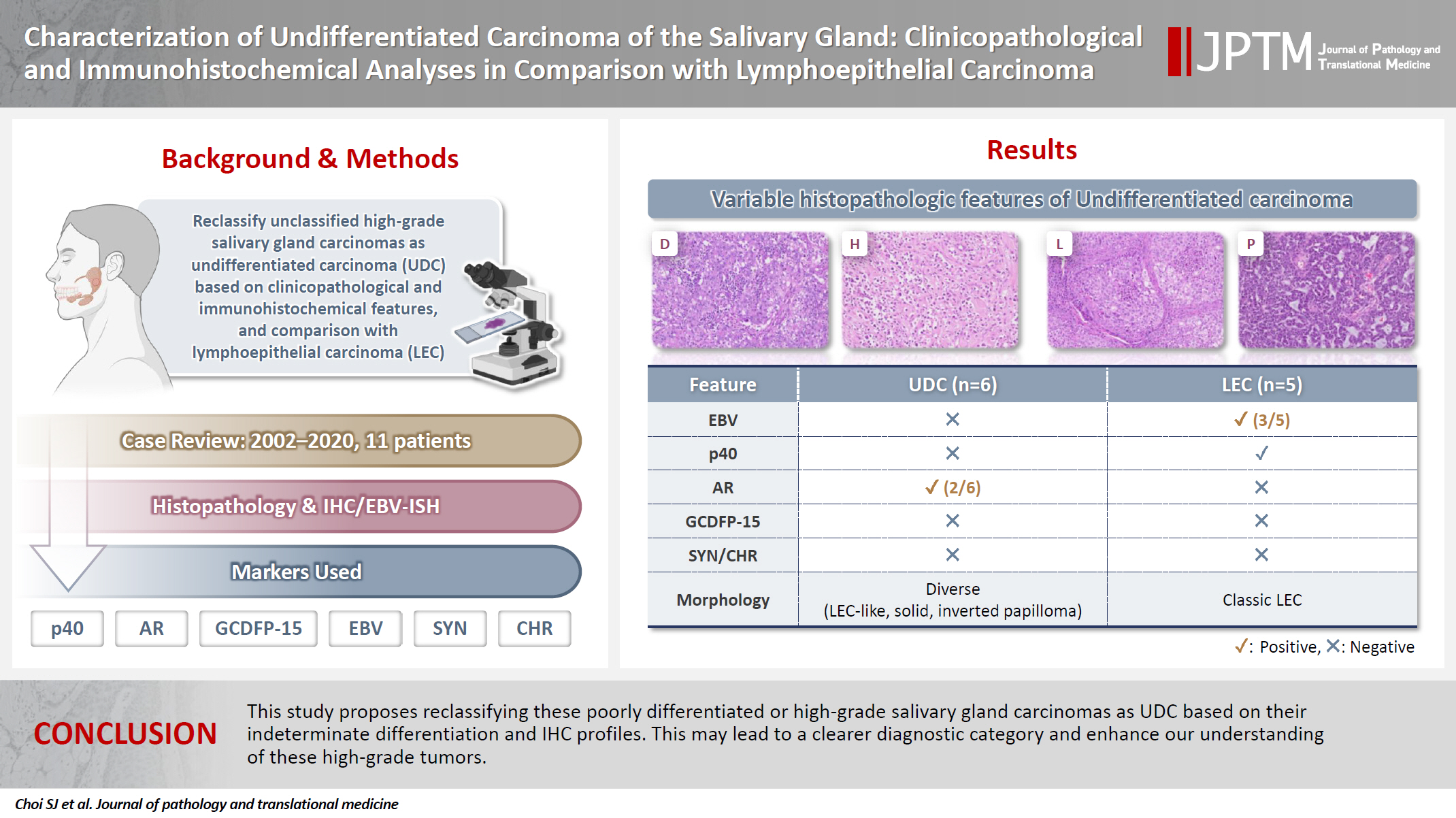
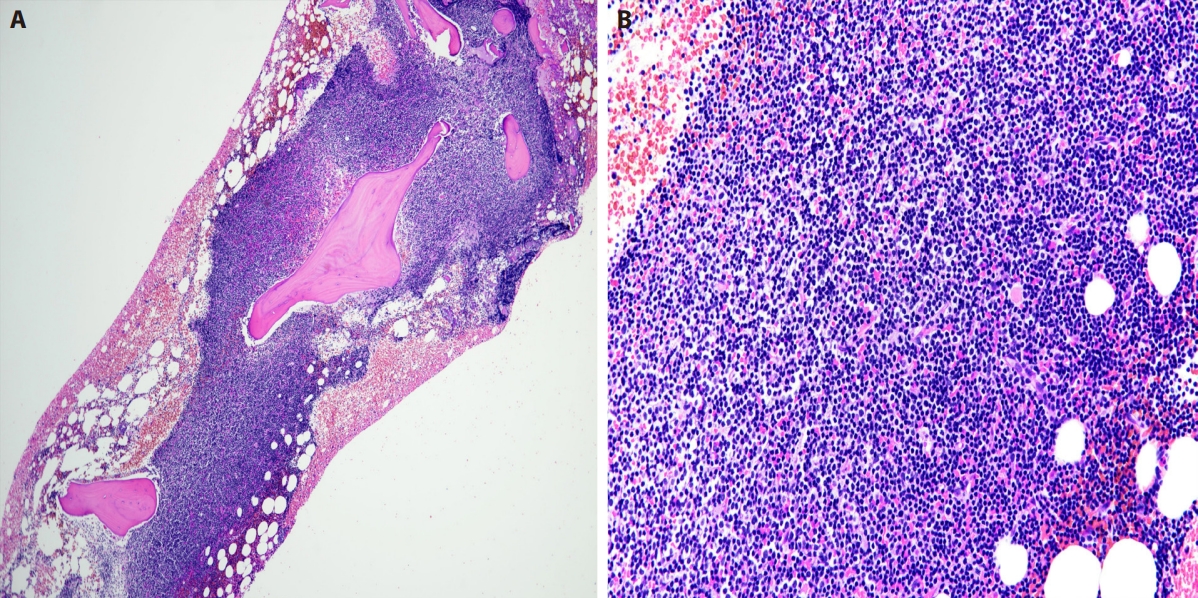
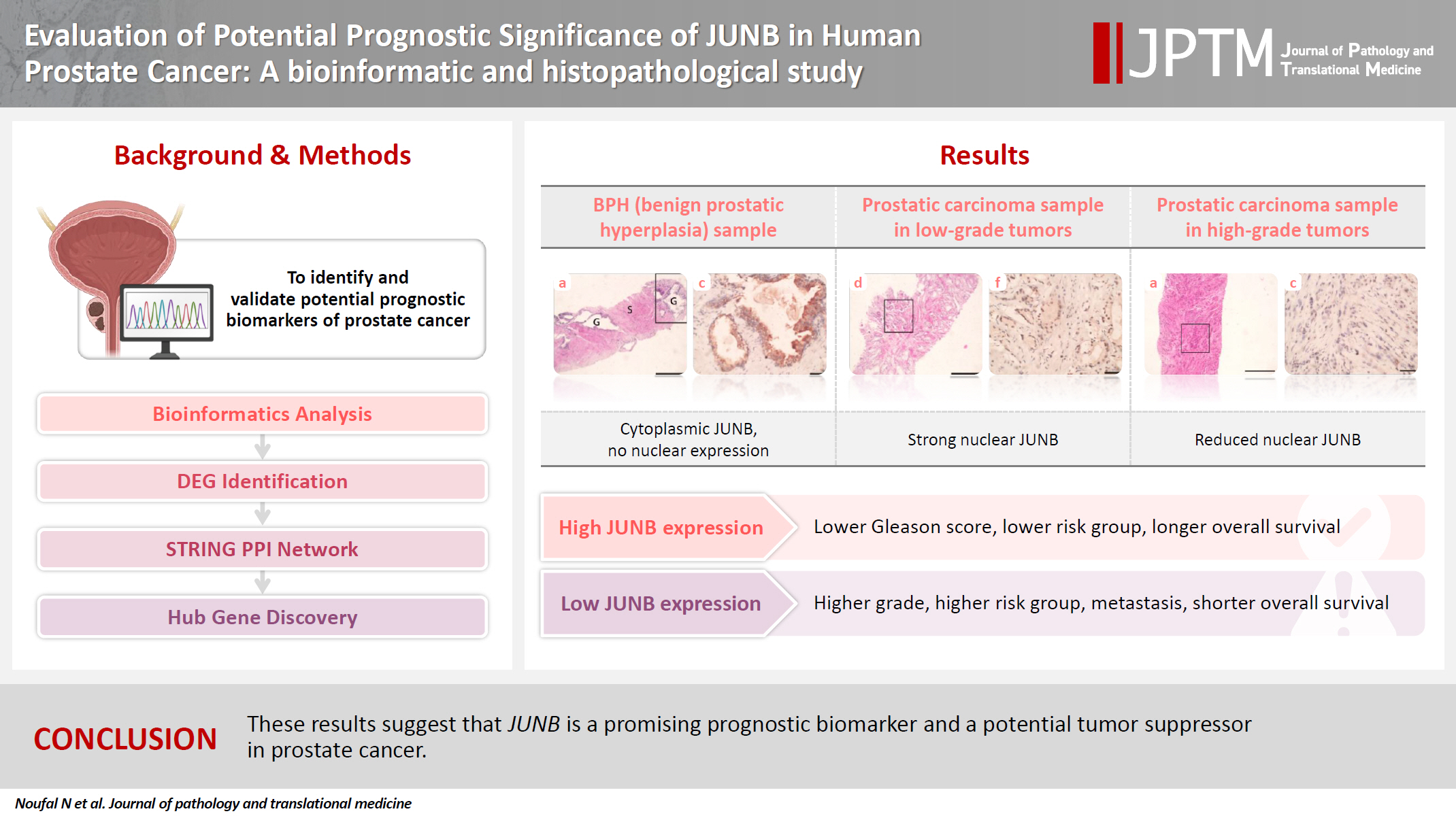
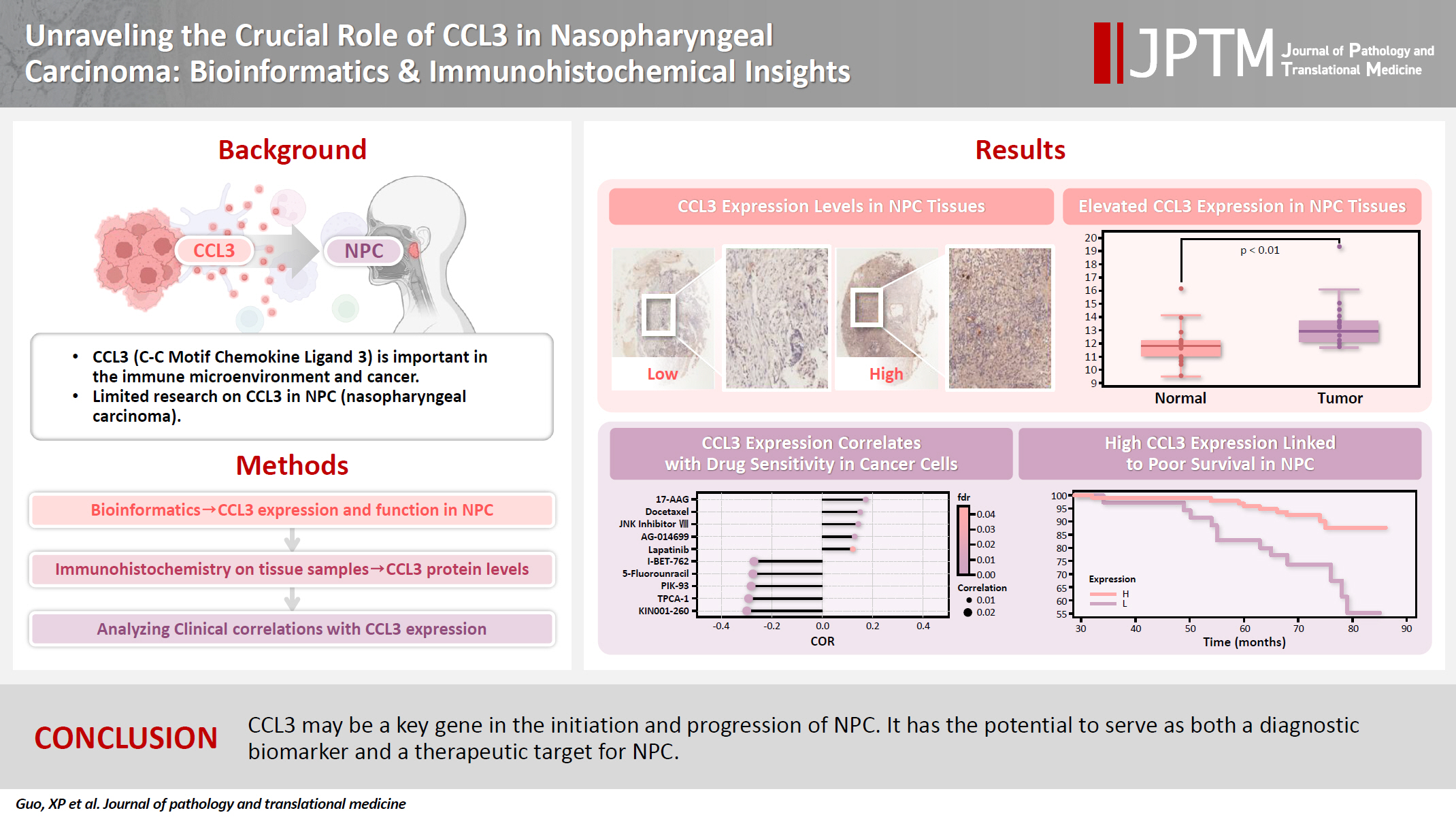







 First
First Prev
Prev



