Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Brief Case Reports
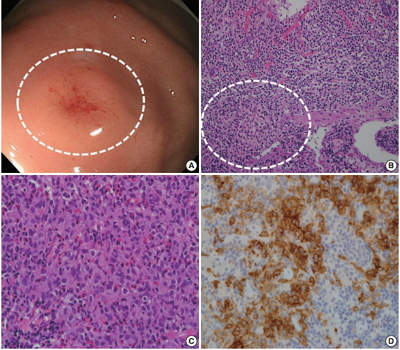
- Gastric Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis: Case Report and Review of the Literature
- So Jung Lee, Chung Su Hwang, Gi Young Huh, Chang Hun Lee, Do Youn Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(5):421-423. Published online June 9, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.05.19
- 11,295 View
- 73 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Isolated Adult Gastrointestinal Tract Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis—Report of Two Rare Patients with Review of Literature
Ekta Jain, Eric Ollila, Fatme Ghandour, Abrar Alghamdi, Samuel Borak, Sameer Al Diffalha
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025; 33(7): 1679. CrossRef - Gastric Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis is Easily Ignored or Misdiagnosed in Stomach Biopsy and Indicates a Poor Outcome in Multisystem Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
Yue Fan, Yang Liu, Haimin Xu, Lei Zhang, Fei Yuan, Hongmei Yi, Chaofu Wang
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Isolated Langerhans cell histiocytosis in the stomach of adults: four-case series and literature review
Jianmin Zhao, Yanlei Li, Yanlin Zhang, Xue Mei, Wei Liu, Yinghong Li
Journal of Hematopathology.2024; 17(2): 63. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes in Patients With Localized Gastric Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis: A Case Series
Tae-Se Kim, Soomin Ahn, Yang Won Min, Hyuk Lee, Jun Haeng Lee, Poong-Lyul Rhee, Jae J. Kim, Byung-Hoon Min
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2024; 24(2): 175. CrossRef - Isolated Langerhans cell histiocytosis of the stomach in adults: An analysis of clinicopathologic characteristics and molecular genetics
Ruinuan Wu, Yali Zhao, Xikang Wu, Huihui Gui, Xia Liu, Zhaohui Liu
Medicine.2024; 103(51): e40950. CrossRef - Unifocal Gastric Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis in a Child—A Unique Case to Remember
Bhaswati C. Acharyya, Mandira Roy, Hema Chakraborty
JPGN Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis with the Synchronous Invasion of Stomach and Colon in an Adult Patient: A Case Report
Seong Je Kim, Se In Hah, Ji Yoon Kwak, Jung Woo Choi, Hyun Chin Cho, Chang Yoon Ha, Woon Tae Jung, Ok Jae Lee, Chang Min Lee
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2022; 80(3): 149. CrossRef - Gastrointestinal Langerhans cell histiocytosis with unifocal, single‐system involvement in adults: Cases report and literature review
Li Wang, Fang Yang, Yong Ding, Lixia Lu, Haili Li, Yangyang Cui, Lu Lu, Xiaohan Shen, Rong Ge
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Upper Gastrointestinal Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis: A Report of 2 Adult Cases and a Literature Review
Yui Matsuoka, Yoshiki Iemura, Masakazu Fujimoto, Shinsuke Shibuya, Atsushi Yamada, Shigehiko Fujii, Toshihiro Kusaka, Takero Shindo, Sachiko Minamiguchi, Hironori Haga
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2021; 29(5): 550. CrossRef - Langerhans cell histiocytosis of the gastrointestinal tract
Aoife J. McCarthy, Madiha Emran Soofi, Imaad Mujeeb, Runjan Chetty
Diagnostic Histopathology.2018; 24(4): 154. CrossRef
- Isolated Adult Gastrointestinal Tract Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis—Report of Two Rare Patients with Review of Literature
- A Ciliated Cyst with Müllerian Differentiation Arising in the Posterior Mediastinum
- So Jung Lee, Chung Su Hwang, Do Youn Park, Gi Young Huh, Chang Hun Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(5):401-404. Published online October 27, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.5.401
- 9,581 View
- 80 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cyst of Hattori: literature review and case presentation
R. B. Berdnikov, K. A. Andryuschenko, N. S. Zavarov, E. M. Petrunina, A. V. Bazhenov, A. S. Romakhin
PULMONOLOGIYA.2025; 35(4): 553. CrossRef - Cyst of Hattori: A Rare Cyst in the Posterior Mediastinum
Matthew D. Turner, Elicia Goodale, Barry C. Gibney, Maria Cecilia D. Reyes
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2023; 31(4): 431. CrossRef - A large retroperitoneal Mullerian cyst: case report and review of the literature
Elena Parmentier, Jody Valk, Paul Willemsen, Caroline Mattelaer
Acta Chirurgica Belgica.2021; 121(4): 278. CrossRef - A case of resected Mullerian cyst in posterior mediastinum
Yoshiyuki Susaki, Noriyoshi Sawabata
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2020; 34(2): 137. CrossRef - Serosal Inclusion Cysts and Arteriovenous Fistulas in Paraprostatic Area of a Dog
Daisuke KOJIMA, Kyoko KOJIMA, Kazumi OTA, Yoshihiko KOJIMA
Journal of the Japan Veterinary Medical Association.2020; 73(9): 511. CrossRef - A surgical case of Mullerian cyst in the posterior mediastinum
Yusuke Kita, Yoshimasa Tokunaga, Taku Okamoto
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2019; 33(1): 68. CrossRef - CT and MRI characteristics for differentiating mediastinal Müllerian cysts from bronchogenic cysts
M. Kawaguchi, H. Kato, A. Hara, N. Suzui, H. Tomita, T. Miyazaki, H. Iwata, M. Matsuo
Clinical Radiology.2019; 74(12): 976.e19. CrossRef - A case of Mullerian cyst arising in the posterior mediastinum
Masahiro Adachi, Isao Sano, Shintaro Hashimoto, Ryoichiro Doi, Hideki Taniguchi, Kazuto Shigematsu
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2018; 32(6): 713. CrossRef - Two resected cases of Mullerian cyst in the posterior mediastinum
Shotaro Hashimoto, Masato Hisano, Masato Morimoto
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2018; 32(7): 818. CrossRef - Posterior mediastinal Müllerian cyst: a rare cause of pain in a young woman
Rebecca Weedle, Keith Conway, Igor Saftic, Alan Soo
Asian Cardiovascular and Thoracic Annals.2017; 25(6): 466. CrossRef
- Cyst of Hattori: literature review and case presentation
- Mediastinal Thymolipoma with Striated Myoid Cells: Report of a Peculiar Case
- Young Keum Kim, Nari Shin, Won Young Park, Do Youn Park, Gi Young Huh, Chang Hun Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(6):596-598. Published online December 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.6.596
- 8,793 View
- 45 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thymoangiolipoma: A rare case of mediastinal tumor with a brief review of literature
Shahin Hameed, Shehla Basheer Kollathodi, Jaseela Beevirakath Puthiyapuryil, Bindu Rajkumar
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2025; 68(4): 877. CrossRef - Thymoangiolipoma: A rare histologic variant of thymolipoma in a patient with myasthenia gravis
Mohammad Hossein Anbardar, Fatemeh Amirmoezi, Armin Amirian
Rare Tumors.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Thymic epithelial neoplasms with rhabdomyomatous component: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 7 cases
Neda Kalhor, Cesar A. Moran
Human Pathology.2019; 83: 100. CrossRef
- Thymoangiolipoma: A rare case of mediastinal tumor with a brief review of literature
Original Articles
- Molecular Biological Characteristics of Differentiated Early Gastric Cancer on the Basis of Mucin Expression.
- Nari Shin, Hye Yeon Kim, Woo Kyung Kim, Min Gyung Park, Kyung Bin Kim, Dong Hoon Shin, Kyung Un Choi, Jee Yeon Kim, Chang Hun Lee, Gi Young Huh, Mee Young Sol, Do Youn Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(1):69-78.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.1.69
- 4,716 View
- 23 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
It is clear that the biologic characteristics of gastric cancer are different on the basis of mucin phenotypes. However, there are unabated controversies on the exact biologic differences of mucin expression in gastric cancer.
METHODS
We analyzed various protein expressions and microsatellite instability (MSI) status based on mucin expression in 130 differentiated early gastric adenocarcinoma cases. Furthermore, we evaluated the genomic alternation in 10 selected differentiated early gastric adenocarcinoma cases using array based comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH).
RESULTS
Intestinal mucin predominant subtype showed significantly elevated p53 protein and caudal-related homeobox 2 expression, and delocalization of beta catenin expressions compared to the gastric mucin predominant subtype. On MSI status, the gastric mucin predominant subtype more frequently showed unstable status than the intestinal mucin predominant subtype. CGH study showed more frequent chromosomal gain and loss in the intestinal mucin predominant subtype than the gastric mucin predominant subtype, albeit without statistical significance. Interestingly, there were significant differences in chromosomal alternation between four mucin phenotypes.
CONCLUSIONS
Study results suggest possible different points of biologic behaviors in early differentiated gastric adenocarcinomas by mucin expression type. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mucin Expression in Gastric Cancer: Reappraisal of Its Clinicopathologic and Prognostic Significance
Dae Hwan Kim, Nari Shin, Gwang Ha Kim, Geum Am Song, Tae-Yong Jeon, Dong-Heon Kim, Gregory Y. Lauwers, Do Youn Park
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2013; 137(8): 1047. CrossRef - Microsatellite Instability Status in Gastric Cancer: A Reappraisal of Its Clinical Significance and Relationship with Mucin Phenotypes
Joo-Yeun Kim, Na Ri Shin, Ahrong Kim, Hyun-Jeong Lee, Won-young Park, Jee-Yeon Kim, Chang-Hun Lee, Gi-Young Huh, Do Youn Park
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(1): 28. CrossRef
- Mucin Expression in Gastric Cancer: Reappraisal of Its Clinicopathologic and Prognostic Significance
- Assessment of Apoptosis by M30 Immunoreactivity and the Relationship with the MSI status and the Clinicopathological Characteristics of Colorectal Carcinomas.
- Hyun Jeong Kang, Mee Young Sol, Do Youn Park, Soo Han Lee, Dong Hun Shin, Jee Yeon Kim, Kyung Un Choi, Hwal Woong Kim, Chang Hun Lee, Gi Young Huh
- Korean J Pathol. 2006;40(5):319-325.
- 2,293 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The monoclonal antibody M30 recognizes a neoepitope of cytokeratin 18 that's produced during the process of apoptosis, and it is reactive in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue. The detailed nature of apoptosis in colorectal cancer is unclear, especially in regard to the MSI status and the clinicopathologic factors. The purpose of this study was to elucidate the apoptosis assessed by M30 immunoreactivity in colorectal cancer and its relationship with the MSI status and the various clinicopathologic factors of colorectal cancers.
METHODS
101 colorectal cancers were classified according to levels of MSI as 12 MSI-H, 4 MSI-L and 85 MSS. Apoptosis was quantified by immunohistochemistry with using M30 CytoDEATH anti-body.
RESULTS
The apoptotic index assessed by M30 was significantly increased in the MSI-H and MSI-L colorectal cancer compared to that in the MSS colorectal cancer. Right sided colon cancer showed a significant higher apoptotic index than did the left sided colon cancer. There was also a tendency for decreased apoptosis in metastatic colorectal cancers (Duke's stage D). There was somewhat of an increase of apoptosis in colorectal cancers with mucinous carcinoma and medullary carcinoma, and also in the colorectal cancers with an increased TIL count, but this was not statistically significant.
CONCLUSION
M30 immunoreactivity is a valuable method to detect apoptosis in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue and it might explain that MSI-H colorectal cancer shows better clinical behavior than MSS colorectal cancer in regard to the increased apoptosis.

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



