Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Studies
- Rhabdomyosarcoma of the skull with EWSR1 fusion and ALK and cytokeratin expression: a case report
- Hyeong Rok An, Kyung-Ja Cho, Sang Woo Song, Ji Eun Park, Joon Seon Song
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):255-260. Published online September 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.08.15
- 4,231 View
- 218 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) comprises of heterogeneous group of neoplasms that occasionally express epithelial markers on immunohistochemistry (IHC). We herein report the case of a patient who developed RMS of the skull with EWSR1 fusion and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and cytokeratin expression as cytomorphologic features. A 40-year-old man presented with a mass in his forehead. Surgical resection was performed, during which intraoperative frozen specimens were obtained. Squash cytology showed scattered or clustered spindle and epithelioid cells. IHC revealed that the resected tumor cells were positive for desmin, MyoD1, cytokeratin AE1/ AE3, and ALK. Although EWSR1 rearrangement was identified on fluorescence in situ hybridization, ALK, and TFCP2 rearrangement were not noted. Despite providing adjuvant chemoradiation therapy, the patient died of tumor progression 10 months after diagnosis. We emphasize that a subset of RMS can express cytokeratin and show characteristic histomorphology, implying the need for specific molecular examination.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rhabdomyosarcomas of Bone
Ahmed Shah, Andrew L. Folpe
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2025; 18(3): 503. CrossRef - Review of imaging modalities and radiological findings of calvarial lesions
Erkan Gökçe, Murat Beyhan
World Journal of Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Morphology of Telangiectatic Osteosarcoma Associated With Сystic Content: A Case Report
David Makaridze, Armaz Mariamidze, Tamuna Gvianishvili, Giulia Ottaviani , Liana Gogiashvili
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Rhabdomyosarcomas of Bone
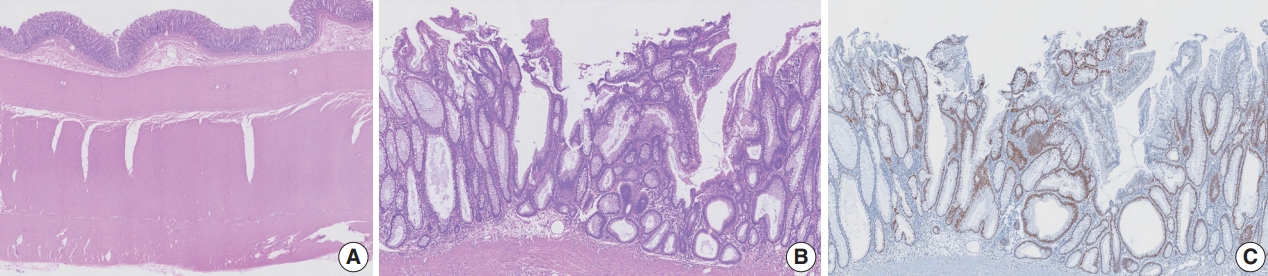
- Tubular adenoma arising in tubular colonic duplication: a case report
- Heonwoo Lee, Hyeong Rok An, Chan Wook Kim, Young Soo Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):198-200. Published online July 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.06.04
- 4,110 View
- 220 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Colonic duplication constitutes a rare congenital anomaly, characterized by the presence of hollow cystic or tubular structures exhibiting an epithelial-lined intestinal wall. Diagnostic challenges persist due to its low incidence and manifestation of nonspecific symptoms such as abdominal pain or constipation, resulting in a reluctance to pursue surgical resection. As associated malignancies in colonic duplication are rare, the inherent malignant potential of these anomalies remains undetermined. Additionally, despite reported instances of associated malignancies in colonic duplication, there is an absence of reports in the literature detailing tubular adenoma within these cases. The histologic features of the presented case are particularly noteworthy, situated at the precancerous stage, intimating potential progression towards adenocarcinoma within colonic duplication.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Low-grade mucinous neoplasm originating from intestinal duplication: a case report and review of the literature
Huihui Yin, Jie Yu, Yunzhao Chen
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Low-grade mucinous neoplasm originating from intestinal duplication: a case report and review of the literature

 E-submission
E-submission


 First
First Prev
Prev



