Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast
- Yunjeong Jang, Hera Jung, Han-Na Kim, Youjeong Seo, Emad Alsharif, Seok Jin Nam, Seok Won Kim, Jeong Eon Lee, Yeon Hee Park, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):95-102. Published online November 13, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.10.24
- 10,837 View
- 293 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Pure mucinous carcinoma (PMC) is a rare type of breast cancer, estimated to represent 2% of invasive breast cancer. PMC is typically positive for estrogen receptors (ER) and progesterone receptors (PR) and negative for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). The clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive PMC have not been investigated.
Methods
Pathology archives were searched for PMC diagnosed from January 1999 to April 2018. Clinicopathologic data and microscopic findings were reviewed and compared between HER2-positive PMC and HER2-negative PMC. We also analyzed the differences in disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival according to clinicopathologic parameters including HER2 status in overall PMC cases.
Results
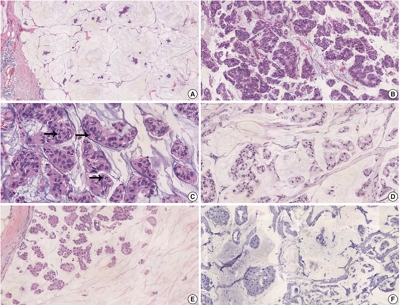
There were 21 HER2-positive cases (4.8%) in 438 PMCs. The average tumor size of HER2-positive PMC was 32.21 mm (± 26.55). Lymph node metastasis was present in seven cases. Compared to HER2-negative PMC, HER2-positive PMC presented with a more advanced T category (p < .001), more frequent lymph node metastasis (p = .009), and a higher nuclear and histologic grade (p < .001). Microscopically, signet ring cells were frequently observed in HER2-positive PMC (p < .001), whereas a micropapillary pattern was more frequent in HER2-negative PMC (p = .012). HER2-positive PMC was more frequently negative for ER (33.3% vs. 1.2%) and PR (28.6% vs. 7.2%) than HER2-negative PMC and showed a high Ki-67 labeling index. During follow-up, distant metastasis and recurrence developed in three HER2-positive PMC patients. Multivariate analysis revealed that only HER2-positivity and lymph node status were significantly associated with DFS.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that HER2-positive PMC is a more aggressive subgroup of PMC. HER2 positivity should be considered for adequate management of PMC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mucin‐producing breast lesions: a practical approach to diagnosis
Sunayana Misra, Mihir Gudi, Kimberly H Allison, Edi Brogi, Cecily Quinn, Hannah Y Wen, Puay Hoon Tan
Histopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological characteristics of mucinous breast cancer: a retrospective analysis of a 6-years study from national cancer center in Vietnam
Thi Huyen Phung, Thanh Tung Pham, Huu Thang Nguyen, Dinh Thach Nguyen, Thanh Long Nguyen, Thi Hoai Hoang
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 209(3): 667. CrossRef - Poor response of HER2-positive mucinous carcinomas of breast to neoadjuvant HER2-targeted therapy: A study of four cases
Min Han, Daniel Schmolze, Javier A. Arias-Stella, Christina H. Wei, Joanne Mortimer, Fang Fan
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 74: 152396. CrossRef - Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analysis of Mesonephric Marker Expression in Low-grade Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma
Yurimi Lee, Sangjoon Choi, Hyun-Soo Kim
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2024; 43(3): 221. CrossRef - Clinicopathological features and prognosis of mucinous breast carcinoma with a micropapillary structure
Beibei Yang, Menglu Shen, Bo Sun, Jing Zhao, Meng Wang
Thoracic Cancer.2024; 15(36): 2530. CrossRef - Pure Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
Cherie M Kuzmiak, Benjamin C Calhoun
Journal of Breast Imaging.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of circ-FOXO3 and miR-23a in radiosensitivity of breast cancer
Elahe Abdollahi, Hossein Mozdarani, Behrooz Z. Alizadeh
Breast Cancer.2023; 30(5): 714. CrossRef - On Ultrasonographic Features of Mucinous Carcinoma with Micropapillary Pattern
Wei-Sen Yang, Yang Li, Ya Gao
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2023; Volume 15: 473. CrossRef - Spectrum of Mucin-containing Lesions of the Breast: Multimodality Imaging Review with Pathologic Correlation
Janice N. Thai, Melinda F. Lerwill, Shinn-Huey S. Chou
RadioGraphics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Ovary: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Hyun Hee Koh, Eunhyang Park, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(2): 326. CrossRef - Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma of the Uterus: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Yurimi Lee, Kiyong Na, Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(5): 1102. CrossRef - Metastasis of the Mucionous adenocarcinoma of breast to the mandibular gingiva: Rare case report
Ivana Mijatov, Aleksandra Fejsa Levakov, Aleksandar Spasić, Jelena Nikolić, Saša Mijatov
Medicine.2022; 101(38): e30732. CrossRef - Endometrioid Carcinomas of the Ovaries and Endometrium Involving Endocervical Polyps: Comprehensive Clinicopathological Analyses
Jihee Sohn, Yurimi Lee, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(10): 2339. CrossRef - Serous Carcinoma of the Endometrium with Mesonephric-Like Differentiation Initially Misdiagnosed as Uterine Mesonephric-Like Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report with Emphasis on the Immunostaining and the Identification of Splice Site TP53 Mutation
Sangjoon Choi, Yoon Yang Jung, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(4): 717. CrossRef - HER2 positive mucinous carcinoma of breast with micropapillary features: Report of a case and review of literature
Dinesh Chandra Doval, Rupal Tripathi, Sunil Pasricha, Pankaj Goyal, Chaturbhuj Agrawal, Anurag Mehta
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2021; 25: 200531. CrossRef - Carcinoma mucosecretor de mama HER2-positivo, un caso clínico
A.M. González Aranda, E. Martínez Gómez, A. Santana Costa, F. Arnanz Velasco, M.H. González de Diego, A. Zapico Goñi
Clínica e Investigación en Ginecología y Obstetricia.2021; 48(4): 100685. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic features of unexpectedly HER2 positive breast carcinomas: An institutional experience
Carissa LaBoy, Kalliopi P. Siziopikou, Lauren Rosen, Luis Z. Blanco, Jennifer L. Pincus
Pathology - Research and Practice.2021; 222: 153441. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Differentiation of Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics Distinct from Those of Uterine Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma
Sujin Park, Go Eun Bae, Jiyoung Kim, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(8): 1450. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Corpus: Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analyses Using Markers for Mesonephric, Endometrioid and Serous Tumors
Hyunjin Kim, Kiyong Na, Go Eun Bae, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(11): 2042. CrossRef
- Mucin‐producing breast lesions: a practical approach to diagnosis
- Methylation and Immunoexpression of
p16INK4a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Primary Breast Cancer Tissue and Their Quantitativep16INK4a Hypermethylation in Plasma by Real-Time PCR - Jae Jun Lee, Eunkyung Ko, Junhun Cho, Ha Young Park, Jeong Eon Lee, Seok Jin Nam, Duk-Hwan Kim, Eun Yoon Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(6):554-561. Published online December 26, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.554
- 9,728 View
- 56 Download
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The
p16INK4a gene methylation has been reported to be a major tumorigenic mechanism.Methods We evaluated the methylation status of the
p16INK4a genes in 231 invasive breast cancer and 90 intraductal carcinoma specimens using a methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction and p16 protein expression using immunohistochemistry. The quantity of cell-free methylatedp16INK4a DNA in the plasma samples of 200 patients with invasive breast cancer was also examined using a fluorescence-based real-time polymerase chain reaction assay.Results The frequencies of
p16INK4a methylation in invasive and intraductal tumors were 52.8% (122/231) and 57.8% (52/90), respectively. The p16 protein was overexpressed in 145 of the 231 invasive carcinomas (62.8%) and 63 of the 90 intraductal carcinomas (70%). High p16 expression in invasive carcinomas correlated significantly with a high histologic grade, a negative estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor status, p53 immunoreactivity and high Ki-67 expression with immunohistochemistry. In addition, the methylation index ofp16INK4a was significantly higher in the cancer patients than the normal controls (p<0.001).Conclusions High p16 immunoreactivity correlated with a loss of differentiation in breast carcinomas and high frequency of
p16INK4a promoter methylation in both invasive and intraductal carcinomas, suggesting it may be involved in the pathogenesis of breast cancer.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Progress in epigenetic research of breast cancer: a bibliometric analysis since the 2000s
Hua Yang, Yu Fang, Haijuan Wang, Ting Lu, Qihua Chen, Hui Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Epigenetic Silencing of p16INK4a gene in Sporadic Breast Cancer
Satya P. Singh, Mallika Tewari, Alok K. Singh, Raghvendra R. Mishra, Hari S. Shukla
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2023; 14(4): 822. CrossRef - Pathogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Chia-Jung Li, Yen-Dun Tony Tzeng, Yi-Han Chiu, Hung-Yu Lin, Ming-Feng Hou, Pei-Yi Chu
Cancers.2021; 13(12): 2978. CrossRef - Mechanisms of resistance to estrogen receptor modulators in ER+/HER2− advanced breast cancer
Jin Zhang, Qianying Wang, Qing Wang, Jiangran Cao, Jiafu Sun, Zhengmao Zhu
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2020; 77(4): 559. CrossRef - Aberrantly Methylated cfDNA in Body Fluids as a Promising Diagnostic Tool for Early Detection of Breast Cancer
Igor Stastny, Pavol Zubor, Karol Kajo, Peter Kubatka, Olga Golubnitschaja, Zuzana Dankova
Clinical Breast Cancer.2020; 20(6): e711. CrossRef - Epigenetic modulation of BRCA‐1 and MGMT genes, and histones H4 and H3 are associated with breast tumors
Parisa Paydar, Gholamreza Asadikaram, Hamid Zeynali Nejad, Hamed Akbari, Moslem Abolhassani, Vahid Moazed, Mohammad Hadi Nematollahi, Ghasem Ebrahimi, Hossein Fallah
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2019; 120(8): 13726. CrossRef - The 9p21 locus: A potential therapeutic target and prognostic marker in breast cancer
Mahdi Rivandi, Mohammad‐Sadegh Khorrami, Hamid Fiuji, Soodabeh Shahidsales, Malihe Hasanzadeh, Mir Hadi Jazayeri, Seyed Mahdi Hassanian, Gordon A. Ferns, Nafiseh Saghafi, Amir Avan
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2018; 233(7): 5170. CrossRef - p16INK4a overexpression as a predictor of survival in ocular surface squamous neoplasia
Sheetal Chauhan, Seema Sen, Anjana Sharma, Seema Kashyap, Radhika Tandon, Mandeep S Bajaj, Neelam Pushker, Murugesan Vanathi, Shyam S Chauhan
British Journal of Ophthalmology.2018; 102(6): 840. CrossRef - Liquid biopsy prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis, cancer recurrence, and patient survival in breast cancer
Ju-Han Lee, Hoiseon Jeong, Jung-Woo Choi, Hwa Eun Oh, Young-Sik Kim
Medicine.2018; 97(42): e12862. CrossRef - EZH2 inhibition sensitizes tamoxifen‑resistant breast cancer cells through cell cycle regulation
Si Chen, Fan Yao, Qinghuan Xiao, Qiannan Liu, Yikun Yang, Xuejuan Li, Guanglie Jiang, Takayoshi Kuno, Yue Fang
Molecular Medicine Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Aberrant promoter methylation of cancer-related genes in human breast cancer
Liang Wu, Ye Shen, Xianzhen Peng, Simin Zhang, Ming Wang, Guisheng Xu, Xianzhi Zheng, Jianming Wang, Cheng Lu
Oncology Letters.2016; 12(6): 5145. CrossRef - Centrosome aberrations in human mammary epithelial cells driven by cooperative interactions between p16INK4a deficiency and telomere-dependent genotoxic stress
Daniel Domínguez, Purificación Feijoo, Aina Bernal, Amaia Ercilla, Neus Agell, Anna Genescà, Laura Tusell
Oncotarget.2015; 6(29): 28238. CrossRef - Relationships Betweenp16Gene Promoter Methylation and Clinicopathologic Features of Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of 27 Cohort Studies
Yan-Zhi Chen, Dan Liu, Yu-Xia Zhao, He-Tong Wang, Ya Gao, Ying Chen
DNA and Cell Biology.2014; 33(10): 729. CrossRef - Endocrine disruption of the epigenome: a breast cancer link
Kevin C Knower, Sarah Q To, Yuet-Kin Leung, Shuk-Mei Ho, Colin D Clyne
Endocrine-Related Cancer.2014; 21(2): T33. CrossRef - Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, p16 and p27, demonstrate different expression patterns in thymoma and thymic carcinoma
Mutsuko Omatsu, Toshiaki Kunimura, Tetsuya Mikogami, Akira Shiokawa, Atsuko Masunaga, Tomoko Nagai, Akihiko Kitami, Takashi Suzuki, Mitsutaka Kadokura
General Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.2014; 62(11): 678. CrossRef - Limoniastrum guyonianum aqueous gall extract induces apoptosis in human cervical cancer cells involving p16INK4A re-expression related to UHRF1 and DNMT1 down-regulation
Mounira Krifa, Mahmoud Alhosin, Christian D Muller, Jean-Pierre Gies, Leila Chekir-Ghedira, Kamel Ghedira, Yves Mély, Christian Bronner, Marc Mousli
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating tumor-related DNA in cancer patients
Diego M Marzese, Hajime Hirose, Dave S B Hoon
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2013; 13(8): 827. CrossRef - Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and trichostatin A synergistically inhibit human lymphoma cell proliferation through epigenetic modification of p16INK4a
DAN-SEN WU, JIAN-ZHEN SHEN, AI-FANG YU, HAI-YING FU, HUA-RONG ZHOU, SONG-FEI SHEN
Oncology Reports.2013; 30(6): 2969. CrossRef
- Progress in epigenetic research of breast cancer: a bibliometric analysis since the 2000s

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



