Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Colorectal epithelial neoplasm associated with gut-associated lymphoid tissue
- Yo Han Jeon, Ji Hyun Ahn, Hee Kyung Chang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(2):135-145. Published online January 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.11.06
- 9,719 View
- 255 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
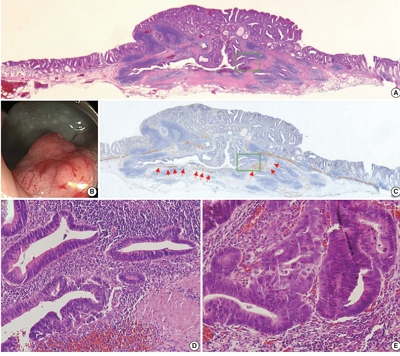
Colorectal epithelial neoplasm extending into the submucosal gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) can cause difficulties in the differential diagnosis. Regarding GALT-associated epithelial neoplasms, a few studies favor the term “GALT carcinoma” while other studies have mentioned the term “GALT-associated pseudoinvasion/epithelial misplacement (PEM)”.
Methods
The clinicopathologic characteristics of 11 cases of colorectal epithelial neoplasm associated with submucosal GALT diagnosed via endoscopic submucosal dissection were studied.
Results
Eight cases (72.7%) were in males. The median age was 59 years, and age ranged from 53 to 73. All cases had a submucosal tumor component more compatible with GALT-associated PEM. Eight cases (72.7%) were located in the right colon. Ten cases (90.9%) had a non-protruding endoscopic appearance. Nine cases (81.8%) showed continuity between the submucosal and surface adenomatous components. Nine cases showed (81.8%) focal defects or discontinuation of the muscularis mucosae adjacent to the submucosal GALT. No case showed hemosiderin deposits in the submucosa or desmoplastic reaction. No case showed single tumor cells or small clusters of tumor cells in the submucosal GALT. Seven cases (63.6%) showed goblet cells in the submucosa. No cases showed oncocytic columnar cells lining submucosal glands.
Conclusions
Our experience suggests that pathologists should be aware of the differential diagnosis of GALT-associated submucosal extension by colorectal adenomatous neoplasm. Further studies are needed to validate classification of GALT-associated epithelial neoplasms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Family adenomatous polyposis come across dome type adenocarcinoma: a case report and literature review
Ying-Ying Chang, Xiao-Long Zhang, Yao-Hui Wang, Ting-Sheng Ling
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiation-induced injury and the gut microbiota: insights from a microbial perspective
Qiaoli Wang, Guoqiang Xu, Ouying Yan, Shang Wang, Xin Wang
Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Family adenomatous polyposis come across dome type adenocarcinoma: a case report and literature review
Case Report
- Primary Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor (PEComa) of the Liver: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.
- Ji Hyun Ahn, Bang Hur
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45:S93-S97.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.S1.S93
- 5,420 View
- 46 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) is a mesenchymal tumor consisting of distinctive perivascular epithelioid cells, and is commonly detected in the uterus. The liver is an uncommon site for primary PEComa. In this study, we report a case of primary hepatic PEComa in a 36-year-old woman. Upon gross examination, the tumor was a well-defined, brownish solid mass, measuring 6.5x5.2x4.5 cm. Microscopically, the tumor consisted largely of epithelioid cells and some spindle cells with a clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm and a rich network of delicate capillaries in the stroma. With the exception of their relatively large size and microscopically sinusoidal infiltrative growth pattern, all other histopathologic features of the tumor were consistent with their being benign. The tumor cells were positive for human melanoma black-45 and smooth muscle actin, and negative for cytokeratin-cocktail and c-kit.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Liver Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor (PEComa): Case Report and Literature Review
Mindaugas Kvietkauskas, Austeja Samuolyte, Rokas Rackauskas, Raminta Luksaite-Lukste, Gintare Karaliute, Vygante Maskoliunaite, Ruta Barbora Valkiuniene, Vitalijus Sokolovas, Kestutis Strupas
Medicina.2024; 60(3): 409. CrossRef - Unresectable hepatic PEComa: a rare malignancy treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) followed by complete resection
Simon Kirste, Gian Kayser, Anne Zipfel, Anca-Ligia Grosu, Thomas Brunner
Radiation Oncology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): a case report with a review of literatures
Hyun Jin Son, Dong Wook Kang, Joo Heon Kim, Hyun Young Han, Min Koo Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2017; 23(1): 80. CrossRef - Malignant hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) – Case report and a brief review
Banerjee Abhirup, Kundalia Kaushal, Mehta Sanket, Nagarajan Ganesh
Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute.2015; 27(4): 239. CrossRef - Hepatic falciform ligament clear cell myomelanocytic tumor: A case report and a comprehensive review of the literature on perivascular epithelioid cell tumors
Zu-Sen Wang, Lin Xu, Lin Ma, Meng-Qi Song, Li-Qun Wu, Xuan Zhou
BMC Cancer.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving recognition of hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumor: Case report and literature review
Toshiya Maebayashi
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2015; 21(17): 5432. CrossRef - Primary perivascular epithelioid cell tumor of the liver: new case report and literature review
Hassania Ameurtesse, Laïla Chbani, Amal Bennani, Imane Toughrai, Nouhad Beggui, Imane Kamaoui, Hinde Elfatemi, Taoufik Harmouch, Afaf Amarti
Diagnostic Pathology.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): dynamic CT, MRI, ultrasonography, and pathologic features—analysis of 7 cases and review of the literature
Yan Tan, En-hua Xiao
Abdominal Radiology.2012; 37(5): 781. CrossRef
- Primary Liver Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor (PEComa): Case Report and Literature Review
Original Article
- Expression of Minichromosome Maintenance Protein 7 and Smad 4 in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus.
- Ji Hyun Ahn, Hee Kyung Chang
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(4):346-353.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.4.346
- 4,623 View
- 32 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Minichromosome maintenance protein 7 (MCM 7) performs a direct role in the initiation of DNA replication, which suggests that it may prove useful as a marker of cell proliferation. Smad 4 is a tumor suppressor gene that mediates the transforming growth factor beta pathway. The principal objective of this study was to characterize the expression of MCM 7 and Smad 4 and to analyze their relationship to clinicopathological parameters in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
METHODS
Expression levels of MCM 7 and Smad 4 were evaluated via immunohistochemistry on formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues from 67 cases of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
RESULTS
High levels of MCM 7 expression were detected in 53 cases (74.6%), and were associated with higher T stages (p = 0.030). Kaplan-Meier survival curves demonstrated that patients with higher levels of MCM 7 expression had poorer prognoses, although this association was not significant (p = 0.086). Loss of Smad 4 expression was noted in 18 cases (23.4%), and was not associated with clinicopathological characteristics, including MCM 7 expression, or prognosis.
CONCLUSIONS
MCM 7 expression is associated with the invasiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Altered expression of Smad 4 does not appear to have pathobiological significance in esophageal carcinoma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- scDiffCoAM: A complete framework to identify potential biomarkers for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using scRNA-Seq data analysis
Manaswita Saikia, Dhruba K Bhattacharyya, Jugal K Kalita
Journal of Biosciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical analysis of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and minichromosome maintenance complex component 7 in benign and malignant salivary gland tumors
Nafiseh Shamloo, Nasim Taghavi, Samane Ahmadi, Soudeh Shalpoush
Dental Research Journal.2022; 19(1): 17. CrossRef - Expression of Minichromosome Maintenance Proteins in Actinic Keratosis and Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Jelena Stojkovic-Filipovic, Dimitrije Brasanac, Martina Bosic, Novica Boricic, Branislav Lekic
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2018; 26(3): 165. CrossRef - Ki-67 protein predicts survival in oral squamous carcinoma cells: an immunohistochemical study
Verena Karla Monteiro LOPES, Adriana Souza de JESUS, Lucas Lacerda de SOUZA, Ligia Akiko Ninokata MIYAHARA, Douglas Magno GUIMARÃES, Helder Antônio Rebelo PONTES, Flavia Sirotheau Correa PONTES, Pedro Luiz de CARVALHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Expression of MCM2 in Nonmelanoma Epithelial Skin Cancers
Asmaa Gaber Abdou, Mohammed Gaber Abd Elwahed, Marwa Mohammed Serag El-dien, Dina Sharaf Eldien
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2014; 36(12): 959. CrossRef
- scDiffCoAM: A complete framework to identify potential biomarkers for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using scRNA-Seq data analysis

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



