Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- A single-institution demographic study of pathologically proven kidney disease in South Korea over the last 33 years
- Hyejin Noh, Jiyeon Kim, Yeong Jin Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):306-319. Published online September 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.18
- 1,680 View
- 86 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
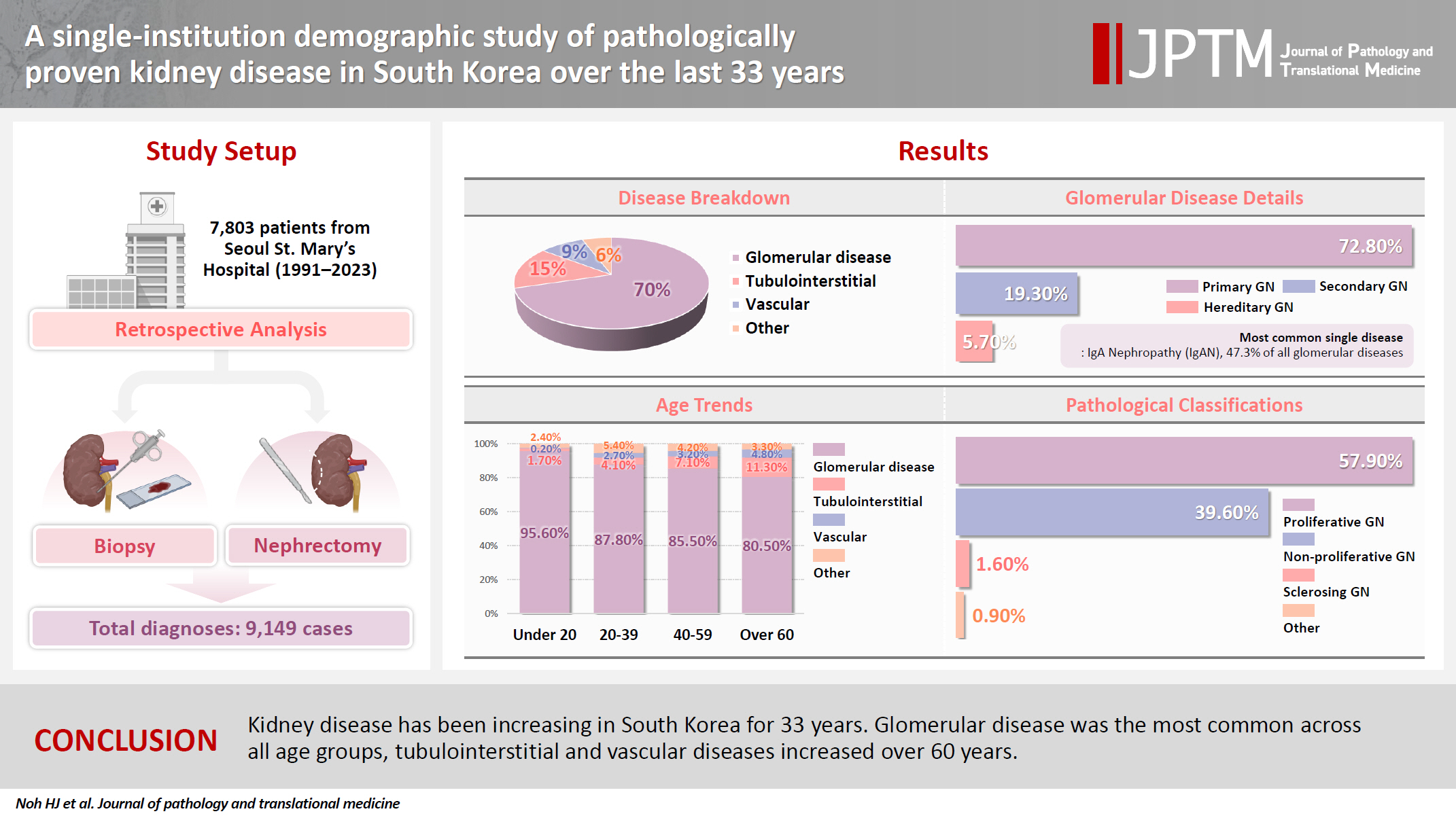
To date, epidemiological studies on the entire spectrum of kidney disease based on pathology have been rarely reported. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on patients diagnosed with kidney disease at Seoul St. Mary's Hospital between 1991 and 2023. Results: Among 7,803 patients with native kidney disease, glomerular disease (70.3%) was the most common, followed by tubulointerstitial (15.1%) and vascular disease (8.8%). In kidney biopsy, glomerular disease (77.8%) showed the highest frequency, particularly in those under 20s (95.6%) (p = .013). Primary glomerulonephritis (GN) (72.8%) was the predominant glomerular disease, with IgA nephropathy (IgAN) (47.3%) being the most common one. Tubulointerstitial and vascular diseases increased with age, showing the highest prevalence in those over 60 years (p = .008 and p = .032, respectively). Glomerular disease was diagnosed at a younger age (39.7 ± 16.7 years) than tubulointerstitial (49.1 ± 16.2) and vascular (48.1 ± 15.3) diseases (p < .001). When glomerular diseases were classified morphologically, proliferative GN (57.9%) was the most common, followed by non-proliferative (39.6%) and sclerosing (1.6%). When classified by etiology, primary GN accounted for the most (72.8%), followed by secondary (19.3%) and hereditary GN (5.7%). In nephrectomy, tubulointerstitial disease (64.6%) was the most common. Those with a tubulointerstitial disease had a higher mean age than those with a glomerular disease (p < .001). In cases where nephrectomy was performed for glomerular diseases, IgAN (34.1%) was the most common diagnosis. Conclusions: Kidney disease has been increasing in South Korea for 33 years. Glomerular disease was the most common across all age groups, tubulointerstitial and vascular diseases increased over 60 years.
- Renal Histologic Parameters Influencing Postoperative Renal Function in Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients
- Myoung Ju Koh, Beom Jin Lim, Kyu Hun Choi, Yon Hee Kim, Hyeon Joo Jeong
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(6):557-562. Published online December 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.6.557
- 7,636 View
- 45 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Pre-existing non-neoplastic renal diseases or lesions may influence patient renal function after tumor removal. However, its description is often neglected or omitted in pathologic reports. To determine the incidence and clinical significance of non-neoplastic lesions, we retrospectively examined renal tissues obtained during 85 radical nephrectomies for renal cell carcinoma.
Methods One paraffin-embedded tissue block from each case containing a sufficient amount of non-tumorous renal parenchyma was cut and processed with hematoxylin and eosin and periodic acid-Schiff methods. Non-neoplastic lesions of each histological compartment were semi-quantitatively and quantitatively evaluated.
Results Among the various histologic lesions found, tubular atrophy, arterial intimal thickening, and glomerulosclerosis were the most common (94.1%, 91.8%, and 88.2%, respectively). Glomerulosclerosis correlated with estimated glomerular filtration rate at the time of surgery, as well as at 1- and 5-years post-surgery (p=.0071), but tubulointerstitial fibrosis or arterial fibrous intimal thickening did not.
Post-hoc analysis revealed that glomerulosclerosis of more than 20% predicted post-operative renal function. However, its significance disappeared when gender and age were considered.Conclusions In conclusion, non-neoplastic lesions, especially with regard to glomerulosclerosis percentage, should be described in pathology reports to provide additional information on renal function decline.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diffusion kurtosis versus diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating clear cell renal cell carcinoma and renal angiomyolipoma with minimal fat: a comparative study
Yarong Lin, Wenrong Zhu, Qingqiang Zhu
Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI in differentiation of renal cell carcinoma subtypes
Amira R. Mahmoud, Nehad Fouda, Eman Mohamed Helmy, Ali Elsorougy
Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Chronic kidney damage pathology score for systematic assessment of the non-neoplastic kidney tissue and prediction of post-operative renal function outcomes
Yong Jia, Seyed M.M. Poor, Brenden Dufault, Vivian Lu, Jasmir G. Nayak, Deepak K. Pruthi, Ian W. Gibson
Human Pathology.2022; 124: 76. CrossRef - Value of intravoxel incoherent motion for differential diagnosis of renal tumors
Qingqiang Zhu, Wenrong Zhu, Jing Ye, Jingtao Wu, Wenxin Chen, Zhihua Hao
Acta Radiologica.2019; 60(3): 382. CrossRef - Conventional and Papillary Renal Cell Carcinomas and Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis in a Nephrectomy
Firas Al-Delfi, Guillermo A. Herrera
Pathology Case Reviews.2015; 20(6): 263. CrossRef
- Diffusion kurtosis versus diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating clear cell renal cell carcinoma and renal angiomyolipoma with minimal fat: a comparative study
- Experimental Study of the Progressive Glomerulosclerosis Induced by Long-term Administration of Puromycin Aminonucleoside in Rats.
- Mi Kyung Kim, Hyun Soon Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(1):1-10.
- 1,929 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pathogenetic mechanisms of progressive glomerulosclerosis are not clear. We studied the long-term(10 weeks) effects of puromycin aminonucleoside(PAN) in Sprague-Dawley rats with or without uninephrectomy(UN). Compared to rats with PAN injections only, rats with uninephrectomy and PAN injections showed significantly higher serum levels of urea nitrogen(153 +/- 155 mg/dl vs. 16 +/- 4 mg/dl, p<0.01), ceatinine(2.96 +/- 1.21 mg/dl vs. 0.92 +/- 0.36 mg/dl, p<0.01), cholesterol(466 +/- 125 mg/dl vs. 94 +/- 27 mg/dl, p<0.01), and triglyceride(337 +/- 237 mg/dl vs. 111 +/- 36 mg/dl, p<0.05) as well as increased amounts of proteinuria(428 +/- 90 mg/day vs. 136 +/- 130 mg/day, p<0.01). Lesions of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis(FSGS) were more frequently observed in rats with UN and PAN injections than rats with PAN infections only(39.5 +/- 17.2% vs. 4.3 +/- 4.7%, p<0.01). Ultrastructural examination of the glomeruli from rats with UN and PAN injections revealed severe epithelial cell changes including foot process effacement, vaculoar change or pseudocyst formation and focal detachment of epithelial cells from the underlying basement membrane. The results suggest that chronic nephrosis induced by PAN showed functional and morphologic features similar to those of human FSGS. Cytotoxic effect of PAN on the glomerular epithelial cells may be an initiating factor for the development of FSGS. which may be aggravated by some hemodynamic changes induced by uninephrectomy.

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



