Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Clinicopathologic Significance of Survivin Expression in Relation to CD133 Expression in Surgically Resected Stage II or III Colorectal Cancer
- Wanlu Li, Mi-Ra Lee, EunHee Choi, Mee-Yon Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):17-23. Published online December 15, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.09.23
- 11,364 View
- 176 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Cancer stem cells have been investigated as new targets for colorectal cancer (CRC) treatment. We recently reported that CD133+ colon cancer cells showed chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil through increased survivin expression and proposed the survivin inhibitor YM155 as an effective therapy for colon cancer in an in vitro study. Here, we investigate the relationship between survivin and CD133 expression in surgically resected CRC to identify whether the results obtained in our in vitro study are applicable to clinical samples.
Methods
We performed immunohistochemical staining for survivin and CD133 in surgically resected tissue from 187 stage II or III CRC patients. We also comparatively analyzed apoptosis according to survivin and CD133 expression using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling.
Results
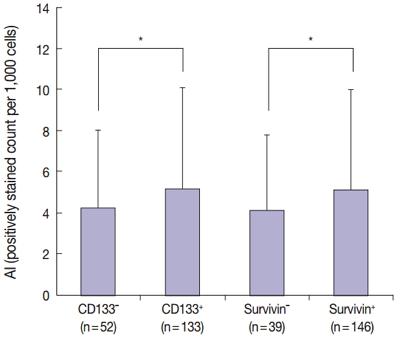
The results of the Mantel-Haenszel test established a linear association between nuclear survivin and CD133 expression (p = .018), although neither had prognostic significance, according to immunohistochemical expression level. No correlation was found between survivin expression and the following pathological parameters: invasion depth, lymph node metastasis, or histologic differentiation (p > .05). The mean apoptotic index in survivin+ and CD133+ tumors was higher than that in negative tumors: 5.116 ± 4.894 in survivin+ versus 4.103 ± 3.691 in survivin– (p = .044); 5.165 ± 4.961 in CD133+ versus 4.231 ± 3.812 in CD133– (p = .034).
Conclusions
As observed in our in vitro study, survivin expression is significantly related to CD133 expression. Survivin may be considered as a new therapeutic target for chemoresistant CRC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comprehensive review and in silico analysis of the role of survivin (BIRC5) in hepatocellular carcinoma hallmarks: A step toward precision
Nermin M. Mohamed, Rania Hassan Mohamed, John F. Kennedy, Mahmoud M. Elhefnawi, Nadia M. Hamdy
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2025; 311: 143616. CrossRef - Genetic Variants in BIRC5 (rs8073069, rs17878467, and rs9904341) Are Associated with Susceptibility in Mexican Patients with Breast Cancer: Clinical Associations and Their Analysis In Silico
María Renee Jiménez-López, César de Jesús Tovar-Jácome, Alejandra Palacios-Ramírez, Martha Patricia Gallegos-Arreola, Teresa Giovanna María Aguilar-Macedo, Rubria Alicia González-Sánchez, Efraín Salas-González, José Elías García-Ortiz, Clara Ibet Juárez-V
Genes.2025; 16(7): 786. CrossRef - Upregulation of EMR1 (ADGRE1) by Tumor-Associated Macrophages Promotes Colon Cancer Progression by Activating the JAK2/STAT1,3 Signaling Pathway in Tumor Cells
Rokeya Akter, Rackhyun Park, Soo Kyung Lee, Eun ju Han, Kyu-Sang Park, Junsoo Park, Mee-Yon Cho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(8): 4388. CrossRef - Antiapoptotic Gene Genotype and Allele Variations and the Risk of Lymphoma
Osama M. Al-Amer, Rashid Mir, Abdullah Hamadi, Mohammed I. Alasseiri, Malik A. Altayar, Waseem AlZamzami, Mamdoh Moawadh, Sael Alatawi, Hanan A. Niaz, Atif Abdulwahab A. Oyouni, Othman R. Alzahrani, Hanan E. Alatwi, Aishah E. Albalawi, Khalaf F. Alsharif,
Cancers.2023; 15(4): 1012. CrossRef - The Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications of the Chemoresistance Gene BIRC5 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Getinet M. Adinew, Samia Messeha, Equar Taka, Karam F. A. Soliman
Cancers.2022; 14(21): 5180. CrossRef - EMR1/ADGRE1 Expression in Cancer Cells Upregulated by Tumor-Associated Macrophages Is Related to Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer
Rokeya Akter, Kwangmin Kim, Hye Youn Kwon, Youngwan Kim, Young Woo Eom, Hye-mi Cho, Mee-Yon Cho
Biomedicines.2022; 10(12): 3121. CrossRef - Prognostic Significance of BIRC5/Survivin in Breast Cancer: Results from Three Independent Cohorts
Nina Oparina, Malin C. Erlandsson, Anna Fäldt Beding, Toshima Parris, Khalil Helou, Per Karlsson, Zakaria Einbeigi, Maria I. Bokarewa
Cancers.2021; 13(9): 2209. CrossRef - Obatoclax, a Pan-BCL-2 Inhibitor, Downregulates Survivin to Induce Apoptosis in Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells Via Suppressing WNT/β-catenin Signaling
Chi-Hung R. Or, Chiao-Wen Huang, Ching-Chin Chang, You-Chen Lai, Yi-Ju Chen, Chia-Che Chang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(5): 1773. CrossRef - M1 Macrophages Promote TRAIL Expression in Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells, Which Suppresses Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer by Increasing Apoptosis of CD133+ Cancer Stem Cells and Decreasing M2 Macrophage Population
Young Woo Eom, Rokeya Akter, Wanlu Li, Suji Lee, Soonjae Hwang, Jiye Kim, Mee-Yon Cho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(11): 3887. CrossRef - Emerging Importance of Survivin in Stem Cells and Cancer: the Development of New Cancer Therapeutics
Neerada Meenakshi Warrier, Prasoon Agarwal, Praveen Kumar
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports.2020; 16(5): 828. CrossRef - MMR-proficient and MMR-deficient colorectal cancer cells: 5-Fluorouracil treatment response and correlation to CD133 and MGMT expression
Jaime A. Oliver, Raúl Ortiz, Cristina Jiménez-Luna, Laura Cabeza, Gloria Perazzoli, Octavio Caba, Cristina Mesas, Consolación Melguizo, Jose Prados
Journal of Biosciences.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Survivin rs9904341 polymorphism significantly increased the risk of cancer: evidence from an updated meta-analysis of case–control studies
Abdolkarim Moazeni-Roodi, Saeid Ghavami, Mohammad Hashemi
International Journal of Clinical Oncology.2019; 24(4): 335. CrossRef - CRISPR-Cas9 mediated CD133 knockout inhibits colon cancer invasion through reduced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Wanlu Li, Mee-Yon Cho, Suji Lee, Mirae Jang, Junsoo Park, Rackhyun Park, Aamir Ahmad
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(8): e0220860. CrossRef - Diagnostic Approaches for Salivary Gland Tumors with Secretory and Microcystic Features
Ha Young Woo, Eun Chang Choi, Sun Och Yoon
Head and Neck Pathology.2018; 12(2): 237. CrossRef - MUC1‐ and Survivin‐based DNA Vaccine Combining Immunoadjuvants CpG and interleukin‐2 in a Bicistronic Expression Plasmid Generates Specific Immune Responses and Antitumour Effects in a Murine Colorectal Carcinoma Model
C. Liu, Y. Xie, B. Sun, F. Geng, F. Zhang, Q. Guo, H. Wu, B. Yu, J. Wu, X. Yu, W. Kong, H. Zhang
Scandinavian Journal of Immunology.2018; 87(2): 63. CrossRef - Activated STAT3 may participate in tumor progression through increasing CD133/survivin expression in early stage of colon cancer
Wanlu Li, Mi-Ra Lee, Taeyeong Kim, Young Wan Kim, Mee-Yon Cho
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2018; 497(1): 354. CrossRef - MiRNA-142-3p increases radiosensitivity in human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells by inhibiting the expression of CD133
Fang Yuan, Lu Liu, Yonghong Lei, Yi Hu
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - MLH1 enhances the sensitivity of human endometrial carcinoma cells to cisplatin by activating the MLH1/c-Abl apoptosis signaling pathway
Yue Li, Shihong Zhang, Yuanjian Wang, Jin Peng, Fang Fang, Xingsheng Yang
BMC Cancer.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Establishment of CMab-43, a Sensitive and Specific Anti-CD133 Monoclonal Antibody, for Immunohistochemistry
Shunsuke Itai, Yuki Fujii, Takuro Nakamura, Yao-Wen Chang, Miyuki Yanaka, Noriko Saidoh, Saori Handa, Hiroyoshi Suzuki, Hiroyuki Harada, Shinji Yamada, Mika K. Kaneko, Yukinari Kato
Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy.2017; 36(5): 231. CrossRef
- A comprehensive review and in silico analysis of the role of survivin (BIRC5) in hepatocellular carcinoma hallmarks: A step toward precision
- Alteration of Apoptosis-Related Proteins (Apaf-1, Caspase-9, Bcl-2, p53, and Survivin) According to Malignant Progression in Cutaneous Melanocytic Lesions.
- Yeo Ju Kang, Ji Han Jung, Kwnag Il Yim, Kyo Young Lee, Youn Soo Lee, Seok Jin Kang, Chang Suk Kang, Si Yong Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(3):247-253.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.3.247
- 4,006 View
- 34 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Apoptosis protease activating factor-1 (Apaf-1), caspase-9, Bcl-2, p53, and survivin are important factors in the pathway of apoptosis, but their clinicopathologic significance remains unclear in human cutaneous melanoma. We investigated the expression of these proteins and their clinical value in human cutaneous melanocytic lesions.
METHODS
We performed an immunohistochemical analysis to examine the expression and distribution of Apaf-1, caspase-9, Bcl-2, p53, and survivin in 36 cases of malignant melanoma (22 cases of primary melanoma and 14 cases of metastatic melanoma) and 41 cases of melanocytic nevus.
RESULTS
The expression of p53 was significantly higher in malignant melanoma than in melanocytic nevus (p<0.01), however the expressions of Apaf-1 and caspase-9 were significantly lower in malignant melanoma compared with melanocytic nevus (p<0.01 and p=0.027, respectively). Also, there was a significant difference for Bcl-2 staining between primary melanomas and metastatic lesions (p=0.004). Nuclear staining for survivin were absent in nevus, but were positive in 14 of 36 melanomas (p<0.01).
CONCLUSIONS
The altered expression of Apaf-1, caspase-9, p53, and survivin are considered to be related to malignant progression in human cutaneous melanocytic lesions. Loss of Bcl-2 can be considered as a prognostic marker of malignant melanomas.
- The Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 and Survivin in Urinary Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma.
- Tae Jung Jang, Kyung Seob Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(3):206-211.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.3.206
- 4,545 View
- 29 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to investigate the expressions of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and survivin in bladder transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) that has different clinicopathologic characteristics, and we also wanted to determine if a relation exists between the COX-2 and survivin expressions.
METHODS
The expressions of COX-2 and survivin were investigated in 80 bladder TCCs by performing immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS
The normal bladder mucosa did not express COX-2 and survivin. COX-2 immunopositivity and cytoplasmic survivin immunopositivity were seen in 48% and 30% of bladder tumors, respectively. The expressions of COX-2 and survivin were closely related to the differentiation, depth and recurrence of bladder TCC, and there was a significant correlation in topographic distribution of COX-2 and survivin immunopositivity. In addition, COX-2 and survivin were predominantly expressed at the invasive front of tumors.
CONCLUSIONS
This data suggest that COX-2 and survivin may be involved in the progression of bladder TCC, and there is a close correlation between the expressions of COX-2 and survivin. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of survivin and p27 expression as potential prognostic markers in urothelial cell carcinoma of urinary bladder in Egyptian patients
Noha Said Helal, Zeinab Omran, Mona Moussa
African Journal of Urology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Urinary Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma and its Association with Clinicopathological Characteristics
Hedieh Moradi Tabriz, Golrokh Olfati, Seyed Ali Ahmadi, Sudabeh Yusefnia
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2013; 14(8): 4539. CrossRef - High survivin expression in premalignant and malignant kidney lesions
Tahany M. Shams, Samaka M. Rehab, Mokhtar Metawea
Egyptian Journal of Pathology.2012; 32(1): 21. CrossRef - Reciprocal correlation between the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and E-cadherin in human bladder transitional cell carcinomas
Tae Jung Jang, Woo Heon Cha, Kyung Seob Lee
Virchows Archiv.2010; 457(3): 319. CrossRef
- Assessment of survivin and p27 expression as potential prognostic markers in urothelial cell carcinoma of urinary bladder in Egyptian patients
- Expression of Survivin According to Malignant Progression of Breast Lesions.
- Hyun Joo Choi, Ji Han Jung, Chan Kwon Jung, Jinyoung Yoo, Eun Jung Lee, Chang Suk Kang, Seok Jin Kang, Kyo Young Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(4):238-243.
- 2,185 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to examine the survivin expression pattern in benign lesions, atypical ductal hyperplasias (ADH), ductal carcinomas in situ (DCIS) and in invasive carcinomas of the breast and to evaluate the effect of expression of this marker on the malignant progression of breast cancers. In addition, the relationship between the expression of the marker and the clinicopathological characteristics for invasive carcinomas were investigated.
METHODS
Immunohistochemical staining using a tissue microarray method for survivin was performed for 103 benign lesions, 30 ADHs, 26 DCISs and 116 invasive carcinomas.
RESULTS
The expression of cytoplasmic survivin was higher for invasive carcinomas than for ADHs and DCISs (p<0.05). For breast invasive carcinomas, expression of cytoplasmic survivin significantly correlated with tumor size, lymph node metastasis and stage (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggest that overexpression of cytoplasmic survivin may be involved in the development of the late stage of breast malignancy, especially invasiveness. In breast invasive carcinomas, expression of survivin may be a useful indicator for the evaluation of patient prognosis.
- Expression of Survivin in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: Relationship to Tumor Biology and Prognosis in Surgically Treated Patients.
- Min Jung Jung, Bong Kwon Chun
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(3):151-157.
- 2,077 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Survivin, a novel member of inhibitor-of-apoptosis, is undetectable in most terminally differentiated nonproliferative adult tissue, but is overexpressed in some human malignancies. The survivin gene expression is repressed by binding of wild-type p53 with the survivin promotor. In this study, we investigated the prevalence of survivin expression, its association with p53 overexpression and proliferative index, and clinicopathological significance in non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLC).
METHODS
Immunohistochemical stainings were performed in 59 cases of primary NSCLC for survivin, p53 and Ki-67. Correlations between the survivin expression, p53 overexpression and Ki-67 labeling index were analyzed.
RESULTS
Survivin expression was detected in 47 carcinomas (80%) with nuclear immunoreactivity (56%). Survivin nuclear immunoreactivity revealed significantly worse prognosis in NSCLC patients (p=0.003), and correlated with lymph node metastasis (p=0.014), lymphovascular invasion (p=0.032), p53 overexpression, and Ki-67 labeling index (KI 24.2 +/- 6.9, p=0.045). Survivin expression was not correlated with histological type and pT status.
CONCLUSIONS
High incidence of survivin overexpression in NSCLC suggests that survivin is involved in lung carcinogenesis, and nuclear expression of survivin can be used as a poor prognostic predictor in NSCLC patients. Expression of mutant p53 seems to be a possible mechanism of survivin up-regulation in NSCLC.
- Survivin and Fas Ligand Expressions Are Correlated with Angiolymphatic Tumor Spread in Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma.
- Min Kyung Kim, Jin Hee Sohn, Mee Joo, Hanseung Kim, Sung Hye Park, Seong Hoe Park, Eo Jin Kim, Seoung Wan Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(5):320-325.
- 2,102 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) that originates from C cells comprises about 10% of all the malignant thyroid tumors. Activating mutations of the RET proto-oncogene have been found to be involved in the anti-apoptotic pathway of MTC that harbors the RET mutation. We investigated the correlation between the clinicopathologic parameters and the expressions of survivin, a novel anti-apoptotic molecule, and the other apoptosis-related proteins, and the known prognostic markers.
METHODS
Immunohistochemical staining was performed using antibodies for survivin, Fas, Fas ligand (FasL), bcl-2, calcitonin, CEA and cyclin A in 19 case of MTC; 10 sporadic MTCs, eight multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type 2A MTCs and one familial MTC (FMTC).
RESULTS
Survivin protein expression was found in five cases (26%) and this was correlated with the presence of angiolymphatic tumor emboli (p=0.019). FasL was expressed in 14 cases (74%) and it had correlation with the presence of lymph node metastases (p=0.029). The cyclin A-labeling indices were correlated with local invasiveness (p=0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Survivin and FasL might be involved in the lymphatic tumor spread of MTC.
- Expression of Survivin, HSP90, Bcl-2 and Bax Proteins in N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine-induced Rat Bladder Carcinogenesis.
- Sang Dae Lee, Sung Woong Park, Soon Auck Hong, Gui Young Kwon, Tae Jin Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2006;40(5):333-338.
- 2,199 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Survivin belongs to the inhibitor of apoptosis family, and it has recently been found to be expressed in most solid tumors. Therefore, its expression is suggested to have prognostic significance. However, no data are available concerning the significance of survivin for the carcinogenesis of bladder cancer.
METHODS
In order to induce urothelial tumor in the rat urinary bladder, 0.05% N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine (BBN) was administered to male Sprague-Dawley rats for 30 weeks. We used immunohistochemistry to investigate the expressions of survivin, HSP90, Bcl-2 and Bax in rat bladder carcinogenesis.
RESULTS
Urothelial cell hyperplasia, papilloma, non-invasive urothelial carcinoma and invasive urothelial carcinoma appeared at 5, 10, 20 and 30 weeks, respectively. The expressions of survivin and HSP90 increased sequentially from normal mucosa, hyperplasia, papilloma, non-invasive urothelial carcinoma to invasive urothelial carcinoma. The expressions of Bcl-2 and Bax did not increase, however the number of cases with more than 1 of Bcl-2/Bax expression ratio increased sequentially during the progression of urothelial lesion. The expression of survivin showed a statistically significant correlation with the expression of HSP90 and the Bcl-2/Bax expression ratio.
CONCLUSIONS
Our findings suggest that survivin may be involved in the carcinogenesis of rat bladder and its expression is correlated with the expression of HSP90 and the Bcl-2/Bax expression ratio.
- Vimentin and Survivin Expression Rates as Prognostic Factors in Medulloblastoma.
- Jae Yeon Seok, Se Hoon Kim, Yoon Hee Lee, Jieun Kwon, Tai Seung Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(2):87-94.
- 2,415 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
A medulloblastoma is a primitive neuroepithelial tumor of the cerebellum that occurs in children and metastasizes through the cerebrospinal fluid. It is highly malignant and invasive, and the 5-year survival rate is only 60%. Surgical resection techniques, radiation, and chemotherapy have improved the overall survival but the patients suffer life-long cognitive dysfunctions or endocrine abnormalities as the side effects of treatment. Therefore it is essential to identify prognostic markers to determine the appropriate treatment strategy in order to minimize the side effects.
METHODS
This study evaluated the immunohistochemical differentiation and survival rate with synaptophysin, glial fibrillary acidic protein, epithelial membrane antigen, vimentin and primitive neuroepithelial marker nestin of 55 paraffin-embedded medulloblastomas, using a tissue microarray. The expression of survivin, the apoptotic inhibitor, and the survival rate with regard to the proliferation index of Ki-67 were also investigated.
RESULTS
The group testing positive to vimentin, a mesenchymal differentiation marker, had a worse prognosis and there was a strong correlation between vimentin expression and nestin expression. Patients with a survivin expression rate >35% had a significantly poorer clinical course and there was a correlation between the survivin expression rate and Ki-67 expression rate.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, vimentin and survivin are negative prognostic markers in medulloblastomas.

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



