Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Characterization of undifferentiated carcinoma of the salivary gland: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analyses in comparison with lymphoepithelial carcinoma
- Sangjoon Choi, Gyuheon Choi, Hee Jin Lee, Joon Seon Song, Yoon Se Lee, Seung-Ho Choi, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):361-370. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.07
- 2,984 View
- 275 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
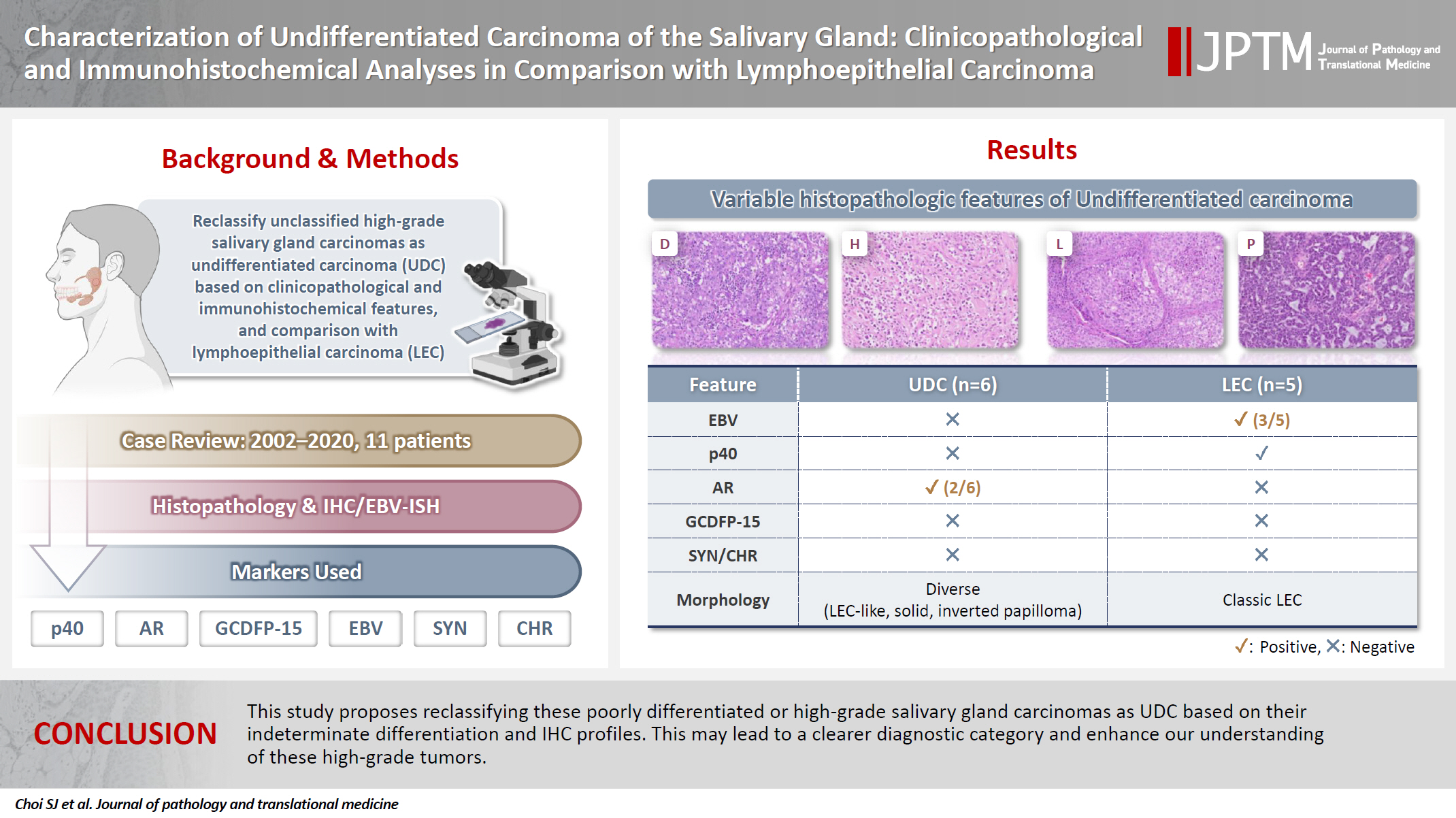
This study aimed to reclassify a subset of poorly differentiated salivary gland carcinoma that do not conform to any entities of the current World Health Organization (WHO) classification into the category of undifferentiated carcinoma (UDC) because they lack specific histologic differentiation or immunophenotype. Methods: Cases of salivary gland carcinomas from Asan Medical Center (2002–2020) that did not fit any existing WHO classification criteria and were diagnosed as poorly differentiated carcinoma, high-grade carcinoma, or UDC, were retrospectively reviewed. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for p40, neuroendocrine markers, androgen receptor (AR), and gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in situ hybridization (ISH) were performed. Clinical data were collected from the electronic medical records. Results: Six salivary gland carcinomas did not align with any specific entities and lacked distinct differentiation. Two of six cases displayed lymphoepithelial carcinoma (LEC)-like morphology but were negative or showed negligible immunoreactivity for p40 and EBV ISH, distinguishing them from LEC of the salivary gland. Two cases showed strong AR positivity, suggesting a potential overlap with salivary duct carcinoma (SDC) but lacked classic SDC morphologies and GCDFP-15 expression. No cases expressed neuroendocrine markers. Conclusions: This study proposes reclassifying these poorly differentiated or high-grade salivary gland carcinomas as UDC based on their indeterminate differentiation and IHC profiles. This may lead to a clearer diagnostic category and enhance our understanding of these high-grade tumors.
- Diagnostic Utility of the JAZF1/JJAZ1 Gene Fusion in Endometrial Stromal Sarcomas and Their Histologic Variants.
- Sang Ryung Lee, Joon Seon Song, Ga Hye Kim, Jene Choi, Hyung Kyoung Kim, Yonghee Lee, Kyu Rae Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(5):498-505.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.5.498
- 3,797 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The diagnosis of endometrial stromal sarcoma (ESS) is often difficult in cases showing diverse histological differentiation or in undifferentiated endometrial sarcoma (UES). Recently, JAZF1/JJAZ1 gene fusion has been described as a defining feature of low-grade ESS (LGESS). However, its prevalence is variably reported, and the diagnostic utility has rarely been examined for cases showing various histological differentiation.
METHODS
To test the diagnostic utility of JAZF1/JJAZ1 gene fusion in difficult cases, we compared the prevalence of the JAZF1/JJAZ1 fusion gene in LGESS with and without histological differentiation.
RESULTS
The JAZF1/JJAZ1 fusion transcript was detected in 18 of 21 LGESS (85.7%), including 14 classical LGESS (93%), four LGESS with diverse histological differentiation (67%), and two with UES (28.6%). Positive cases included two LGESS with sex cord-like differentiation, one with osseous differentiation, and two UES. LGESS showing smooth muscle differentiation revealed the fusion transcript only in the classic area. Direct sequencing analysis of two LGESS revealed a previously reported breakpoint at t(7;17)(p15;q21).
CONCLUSIONS
The JAZF1/JJAZ1 fusion gene was identified in a significant proportion of LGESS showing secondary histological differentiation except in cases with smooth muscle differentiation. Thus, this fusion gene may be useful to confirm the diagnosis in difficult cases of LGESS.
Case Report
- Pathologic Study of Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor: Report of 5 cases.
- Sook Nyo Lee, Jong Eun Joo, Dong Soo Suk, Hyung Dong Kim, Soo Hyu Kim, Jae Hong Sim, Je G Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 1989;23(3):331-341.
- 2,146 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) occuring in the brain (especially in the cereburm) of young individuals is a rare and highly malignant neoplasm. The authors analyzed 5 cases of primitive neuroectodermal tumor, operated from January 1986 to September 1987. They had characteristic clinical, radiologic and pathologic features. Patient's age ranged from 2 years to 14 years old (mean 8.2 years old) and there were 3 boys and 2 girls. They were rapidly growing tumor, with a brief duration of symptoms taking a rapidly progessive course. Computerized tomographic findings were characteristic, revealing the large, irregular, typically iso-to hyper-dense mass lesions with calcification and cystic or necrotic areas, and showing dense heterogeneous contrast enhancement of the mass in the cerebral hemisphere. Grossly all of the 5 cases showed hemorrhage and necrosis with sharp border and 2 cases showed calcification and cystic change grossly. Microscopically, they were predominantly composed of undifferentiated small dark cells with evidence of focal differentiation along glial and or neuronal lines. Four cases showed glial differentiation and three cases showed neuronal differentiation. Mesenchymal components were predominant in 3 cases.
Original Articles
- Primary Undifferentiated Carcinoma of the Endometrium with Small Cell and Trophoblastic Differentiation.
- Chul Hwan Kim, Seoung Hye Park, In Sun Kim, Seung Yong Paik
- Korean J Pathol. 1990;24(1):58-64.
- 2,141 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This report describes a very rare case of primary undifferentiated carcinoma of the endometrium with small cell and trophoblastic differentiation. The patient was 54-year-old woman with complaints of vaginal bleeding and palpable lower abdominal mass. The light microscopic findings revealed predominantly small cells with round nuclei, spindle cells, and large cells with hyperchromatic bizarre nuclei. Foci of syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells are scattered, especially in the hemorrhagic areas. Immunohistochemical stainging for neuron specific enolase and beta-hCG showed positive reactions to small cells and syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells, respectively. Argentaffin and argyrophil stains, however, showed negative reactions to small cells. The histogenesis of small cell undifferentiated carcinoma of the endometrium remains unclear; however, it may arise from epithelial precursors instead of neuroendocrine cells, and syncytiotrophoblastic cells may be differentiated or dedifferentiated from the undifferentiated carcinoma cells.
- Immunohistochemical and Ultrastructural Studies on the Histogenesis of Thyroid Undifferentiated Carcinoma.
- Myoung Ja Jeong, Woo Sung Moon, Young Hye Lee, Myoung Jae Kang, Ho Yeul Choi, Sang Ho Kim, Dong Geun Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(6):756-765.
- 2,014 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Histologic, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies were performed on 6 cases of undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma to study the histogenesis of the undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma, to determine the most useful markers for diagnosing these tumors and to investigate the nature of osteoclast-like giant cells rarely observed in these tumors. For the immuno-histochemical study, a panel of antibodies to epithelial (cocktailed keratin, low molecular weight keratin, CEA), mesenchymal(vimentin, desmin, actin, FVIIIRAg) endocrine(calcitonin, chromogranin), lymphocytic(LCA), histiocytic(alpha-l-ACT, alpha-1-AT, lysozyme, CD68), and Schwann cell(S-100 protein) markers were used. The following results were obtained; 1) Well differentiated carcinoma was associated with 2 cases of spindle cell type and 1 case of giant cell type of undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma and a transitional zone between the well differentiated and undifferentiated lesions was observed. 2) All of the examined cases expressed keratin, and 3 tumors expressed CEA. 3) All the mesenchymal markers, LCA, S-100 protein, calcitonin, and chromogranin were not expressed. Vimentin was coexpressed with keratin in 4 cases. 4) Osteoclast-like giant cells were observed in 1 case of spindle cell type. They expressed CD68 but not keratin. 5) Ultrastructural study revealed the desmosomes between the tumor cells and non-neoplastic, follicular, thyroid epithelial cells. The above results indicate that undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma originates from follicular epithelial cell, keratin is the most useful marker for diagnosis of this tumor, and the osteoclast-like giant cells are histiocytic in nature and reactive, rather than neoplastic.
- Immunohistochemical Study of Primary Large Cell Undifferentiated Carcinoma of the Lung.
- Hye Seung Han, Jeong Wook Seo, Eui Keun Ham
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(5):417-426.
- 2,224 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We performed a histopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 23 cases of surgically resected large cell undifferentiated carcinoma(LCUC) of the lung. The relative incidence of LCUC was 7.6% among the total resected cases of primary lung cancer over 7 years(1987-1993). The mean age of the patients was 56 years and 21 cases were male. The mean size of the mass was 5 cm and 11 cases were located peripherally. According to the histologic features, LCUC could be divided into three groups: squamous cell carcinoma-like(6 cases), adenocarcinoma-like(13 cases), and small cell carcinoma-like(4 cases) groups. The histologic differences were related to the variations of the immunohistochemical properties, but there were no differences in prognosis among these groups. Immunoreactivity to cytokeratin(CAM 5.2) was demonstrated in 22/23(96%). Carcinoembryonic antigen was positive in 13/23(57%). Neuron specific enolase and chromogranin were positive in 11/23(48%) and 5/23(22%), respectively. Vimentin was seen in 11/23(48%). From these observations, we could subclassify them by their immunologic phenotypes; exocrine features in 6/23(26%), neuroendocrine(NE) features in 4/23(17%), both exocrine and NE phenotypes in 7/23(30%), and 6 cases(26%) showed neither phenotype. The group with NE features showed a worse prognosis(P<0.05) and immunoreactivity for vimentin was also related to a worse prognosis(P<0.05). These findings imply that the immunohistochemical properties of LCUC are closely related to the histopathologic features. The groups, subdivided by histology and immunoreactivity, showed no prognostic difference except for the NE differentiation and reaction for vimentin.
- Undifferentiated Sarcoma of the Liver: Clinical and Pathologic Study of 9 Cases.
- Kyung Chul Moon, Chong Jai Kim, Je G Chi, Gyeong Hoon Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2003;37(1):50-57.
- 2,321 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Undifferentiated sarcoma of the liver (USL) is a rare malignant tumor that is found in children and young adults.
METHODS
We performed a clinicopathologic analysis of 9 cases (M:F=4:5) of USL using immunohistochemical staining for vimentin, desmin, -smooth muscle actin (SMA), CD68, CD117, S-100, cytokeratin, epithelial membrane antigen (EMA), and p53.
RESULTS
Grossly, the tumors were large, single, and well demarcated with areas of hemorrhage and necrosis. Microscopically, the tumors were composed of spindle to stellate cells and variable numbers of multinucleated giant cells with a myxoid background. The tumors had eosinophilic globules, small cystic spaces and fibrous pseudocapsule. Under immunohistochemical study, the tumor cells were positive for vimentin, CD68 and desmin, but negative for S-100 protein. p53 overexpression was noted in most cases, and four cases showed immunoreactivity for CD117. All patients received chemotherapy before or after the excision of the tumors. Two patients died during chemotherapy, but six patients survived without recurrence for 18, 35, 53, 57, 65 and 126 months after the initial diagnosis. The remaining one patient survived with recurrence for 20 months after the initial diagnosis.
CONCLUSION
Our cases showed unique pathological and immunohistochemical features similar to the cases of previous reports. In contrast to the previous reports, the outcome of our cases were not poor. Modern multimodal treatment including surgical resection combined with multiagent chemotherapy may contribute to the better prognoses.
- Immunohistochemical Application of Leukocyte Common Antigen and Epithelial Membrane Antigen in the Diagnosis of Large Cell Undifferentiated Tumors.
- Chan Hwan Kim, Sang Sook Lee, Chai Hong Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 1988;22(3):215-221.
- 2,052 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A total of 42 cases undifferentiated large cell tumors were stained by immunoperoxidase techniques using antibodies against leukocyte common antigen (LCA) and epithelial membrane antigen (EMA). In 18 of the 21 cases studied, initially diagnosed as malignant lymphoma or Hodgkin's disease, reactivity with monoclonal anti-LCA (and noreactivity with monoclonal anti-EMA)indicated that the tumor was a lymphomas. The remaining 3 cases gave the reverse reaction pattern and therefore were classified as carcinoma. One out of 16 cases diagnosed as undifferentiated carcinoma proved to be a case of mialignant lymphoma in 5 patients in whom the original diagnosis was uncertain, a definite diagnosis was possible in all cases and 3 of these proved to be large cell lymphoma; the remainders, undifferentiated carcinoma. It is suggested that the staining of undifferentiated human neoplasms using combinations of antibodies reactive with epithelial and lymphoid cells may result in much greater diagnostic accuracy.
Case Report
- Sinonasal Undifferentiated Carcinoma: A Case Report .
- Mi Kyung Shin, Yang Seok Chae
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1997;8(1):98-102.
- 2,091 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma(SNUC) is a distinct, relatively rare neoplasm arising in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses composed of undifferentiated epithelial cells and clinically characterized by a fulminant course. We report a case of SNUC in a 56-year old man who have had bilateral neck masses since one month ago before coming to our hospital. The paranasal computed tomography showed soft mass density in the left maxillary sinus and the nasal cavity with bone destruction in the anterior medial and the inferior maxillary sinus wall. This mass was extruded into the left orbital wall. Biopsy of the nasal mass and fine needle aspiration(FNA) of the neck mass were done. FNA revealed medium-sized neoplastic cells forming clusters or individually dispersed. Nuclei were round to oval, slightly to moderately pleomorphic, and hyperchromatic. Chromatin was finely granular, but occasionally was coarsely granular. Nucleoli varied from large to inconspicuous and the cytoplasm was scanty.
Original Article
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Extraskeletal Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma.
- Myoung Ja Chung, So Yeong Oh, Myoung Jae Kang, Dong Geun Lee, Ho Yeul Choi, Sang Ho Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1997;8(2):194-198.
- 2,067 View
- 27 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Extraskeletal mesenchymal chondrosarcoma is a relatively rare tumor and its cytologic findings have rarely been reported. We experienced a case of mesenchymal chondrosarcoma of soft tissue of the right lateral neck diagnosed by fine needle aspiration biopsy in a 59 year-old man. Cytologic findings showed two cell components. One was an undifferentiated, small cell component with moderate amount of cytoplasm and spindle nuclei. The second population was a chondroid component. These cytologic findings were diagnostic to mesenchymal chondrosarcoma.
Case Report
- Undifferentiated Gallbladder Carcinoma with Osteoclast-like Giant Cells: A Case Report.
- Yun Kyung Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(2):127-131.
- 2,037 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells (OGCs) is the least common type of gallbladder carcinoma. Here, the author presents a case of undifferentiated gallbladder carcinoma with OGCs in an 81-year-old male patient. Grossly, the tumor was a 10x7 cm sized, polypoid, lumen-filling mass with extensive hemorrhage and necrosis. Microscopically, the tumor was composed of pleomorphic ovoid to spindle cells admixed with numerous OGCs. There was a minute focus of mucosal dysplasia and carcinoma in situ. Immunohistochemically, the mononuclear cells were positive for cytokeratin, p53 and Ki-67, while the OGCs were negative for these markers but positive for CD68. These findings support an epithelial origin for the ovoid to spindle cells and the nonneoplastic reactive histiocytic lineage of the OGCs.

 E-submission
E-submission
 First
First Prev
Prev



