Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 51(5); 2017 > Article
-
Original Article
The Intraoperative Immunohistochemical Staining of CD56 and CK19 Improves Surgical Decision for Thyroid Follicular Lesions - Ju Yeon Pyo, Sung-eun Choi, Eunah Shin1, JaSeung Koo2, SoonWon Hong
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2017;51(5):463-470.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.05.25
Published online: August 2, 2017
Department of Pathology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
1Department of Pathology, CHA Gangnam Medical Center, CHA University, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Pathology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding Author SoonWon Hong, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 211 Eonju-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul 06273, Korea Tel: +82-2-2019-3540 Fax: +82-2-3463-2103 E-mail: soonwonh@yuhs.ac
© 2017 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
-
Background
- When differential diagnosis is difficult in thyroid follicular lesions with overlapping histological features, the immunohistochemical staining can help confirm the diagnosis. We aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of rapid immunohistochemical stains of CD56 and cytokeratin 19 on frozen sections of thyroid follicular lesion and explore the possible gains and limitations of the practice.
-
Methods
- Eighty-six nodules of 79 patients whose intraoperative frozen sections were selected as the control group, and 53 nodules of 48 patients whose intraoperative frozen sections were subject to rapid immunohistochemistry were selected as the study group.
-
Results
- Five nodules (6%) in the control group were diagnosed as follicular neoplasm and six nodules (7%) were deferred. In the study group, six nodules (11%) were follicular neoplasm and none were deferred. Three nodules (4%) in the control group showed diagnostic discrepancy between the frozen and permanent diagnoses, but none in the study group. The average turnaround time for the frozen diagnosis of the control group was 24 minutes, whereas it was 54 minutes for the study group.
-
Conclusions
- Intraoperative rapid immunohistochemical stains significantly decreased the diagnostic discrepancy in this study. Considering the adverse effects of indefinite frozen diagnosis or discrepancy with permanent diagnoses, the intraoperative rapid immunohistochemical stain can help to accurately diagnose and hence provide guidance to surgical treatment.
- Patients and nodules
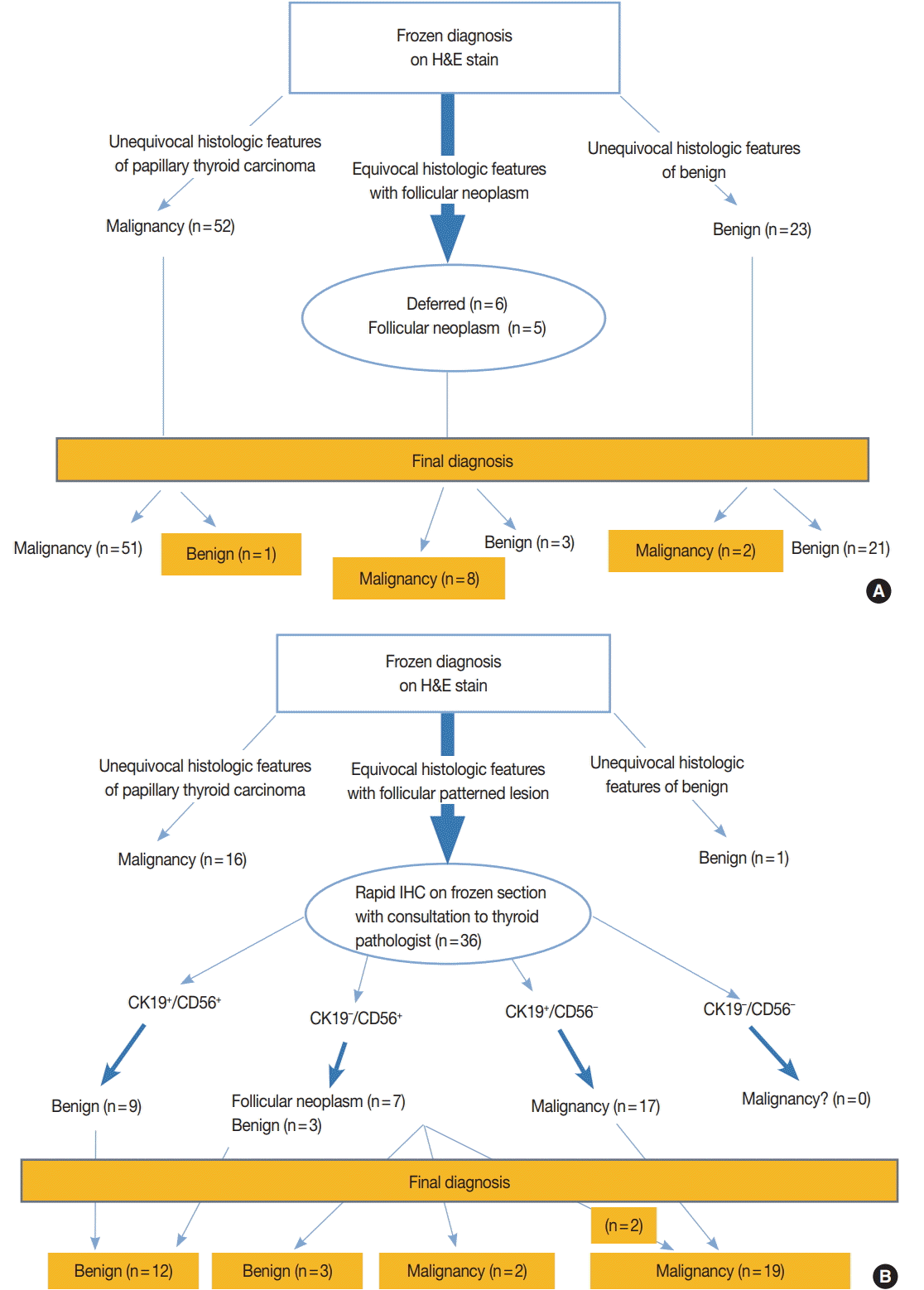
- Eighty-six nodules of 79 patients whose intraoperative frozen sections were not subject to IHC stains at all were selected as the control group (Fig. 1A) and 53 nodules of 48 patients whose intraoperative frozen sections could be subject to IHC stains if necessary were selected as the study group (Fig. 1B). For each group, the study duration was about a month. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Gangnam Severance Hospital with a waiver of informed consent (IRB No. 3-2015-0133).
- Rapid IHC stain
- Fresh frozen tissue in OCT compound was sectioned with Cryo-cut Microtome (Leica Biosystems, Newcastle Upon Tyne, UK) in 3–4 μm thickness, placed on silane coated slide, and let dry. The slide was then stained for rapid immunohistochemistry in LEICA BOND-III Autostainer using Bond Polymer Refine Detection kit (Leica Biosystems). Briefly, the dry slide was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 1 minute, immersed in peroxide block for 2 minutes to endogenous peroxidase blocking, washed and then applied with primary antibody for 4 minutes. After washing with Bond Wash solution, the slide was sequentially applied with post primary agent for 2 minutes and polymer for 2 minutes with washings in-between. The antibodies used were CK19 (1:80, RCK108, mouse monoclonal, DAKO, Carpinteria, CA, USA) and CD56 (1:50, 123C3, mouse monoclonal, DAKO). They were detected with 3,3’-diaminobenzidine (DAB) chromogen and DAB enhancer and counterstained with hematoxylin. The entire process takes roughly about 30 minutes.
- Microscopic evaluation
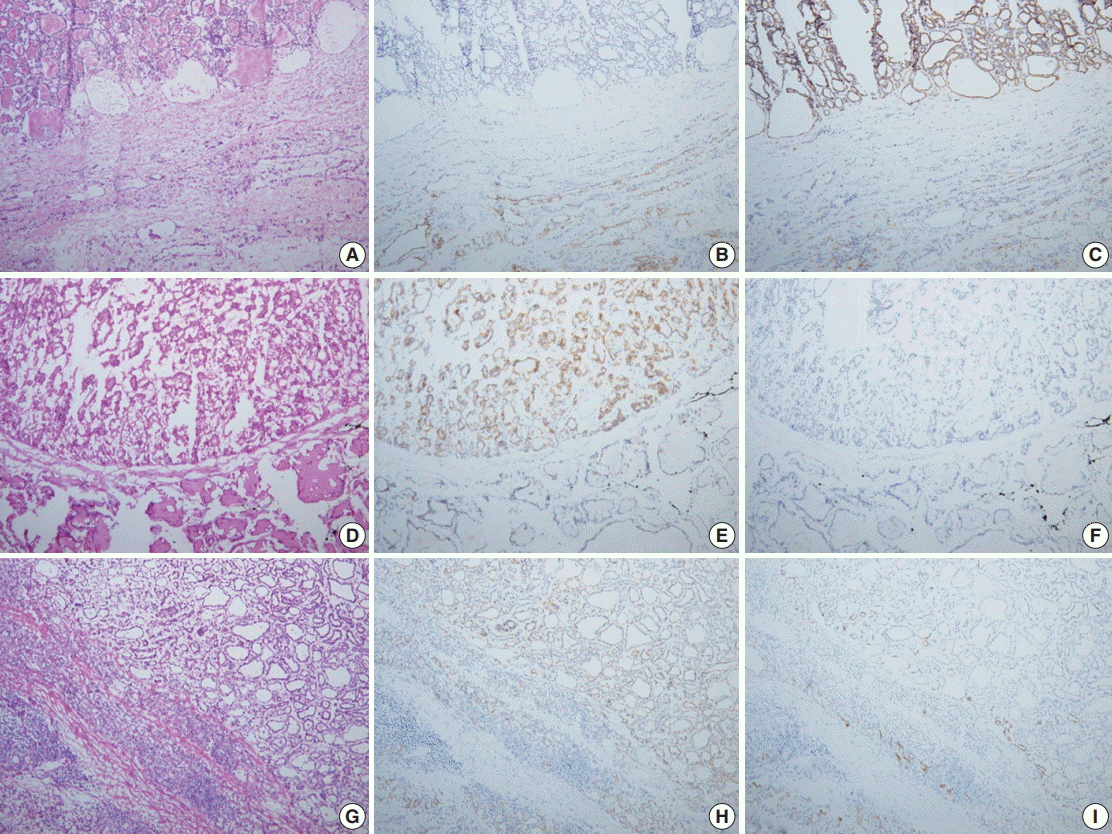
- Nodules of the control group were intraoperatively diagnosed based on the hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) findings alone and the total amount of time spent on the diagnosis, so-called turn-around time, was recorded. Nodules of the study group were subject to IHC stains for CD56 and CK19 only when the diagnosis could not be reached on H&E findings alone. When H&E findings were informative enough for definitive diagnosis, IHC stains were not performed and the turnaround time was recorded. According to El Demellawy et al. [11], membranous staining of follicular epithelial cells for CD56 (≥10% cut-off) was considered positive. As shown in the diagnostic algorithm of Fig. 1B, those lesions showing cytological features suspicious for, but not diagnostic of, papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) were subject to IHC stains, and PTC was diagnosed when the suspicious cells were CD56-negative and CK19-positive (Fig. 2A–C). When the suspicious cells were CD56-positive, however, the diagnosis of either follicular neoplasm (Fig. 2D–F) or adenomatous hyperplasia (Fig. 2G–I) was reached [11-13]. These diagnoses were based upon consultation to an experienced thyroid pathologist (S.W. Hong). The turnaround time was recorded after the IHC stains for the study group. For the control group, the frozen diagnoses were deferred when the histological or cytological features of the nodules were equivocal or when the histological features were suspicious of follicular neoplasm (Fig. 1A). The intraoperative diagnoses were classified as benign, malignant, follicular neoplasm, and deferred. The number of lesions showing discrepancy between the frozen diagnosis and permanent diagnosis and the type of discrepancy were evaluated in those that were not deferred in the intraoperative diagnosis. Final diagnoses on the permanent sections of the deferred lesions and those that were reported as follicular neoplasm intraoperatively were also evaluated.
- Statistical analysis
- The type of intraoperative diagnosis, the number of discrepancy between the frozen diagnosis and the final permanent diagnosis, and the turnaround time in the intraoperative diagnosis of the two groups were analyzed by Student’s t test and Fisher exact test. Statistical analysis of data was performed using the SPSS software ver. 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The p-value less than .05 were considered statistically significant.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
- Seventy-nine patients allocated to the control group consisted of 14 men and 65 women. Forty-eight patients in the study group consisted of eight men and 40 women. The clinicopathologic characteristics in two groups were tabulated (Table 1). There was no significant statistical difference in the distribution of gender and age between the two groups. A total of 84 nodules out of 86 in the control group (98%) were diagnosed within 40 minutes and only two nodules (2%) were diagnosed after 40 minutes. The turnaround time of 40 minutes was agreed to be a reasonable cutoff by the departments of pathology and surgery, considering the time required to construct one block of typical frozen section and the time required for rapid IHC. This is in line with the guidelines recommended by the Joint Commission of International Certification and the guidelines for quality management of the Korean Society of Pathologists. For frozen sections without immunostaining, the turnaround time was kept within 15 minutes to 20 minutes. The average turnaround time to diagnosis was 24 minutes for the control group. For the study group, 17 out of 53 nodules (32%) were diagnosed within 40 minutes and 36 nodules (68%) were diagnosed after 40 minutes (p<.000). The average turnaround time for the study group was 57 minutes (Table 1). As for the type of intraoperative frozen diagnosis, in 75 out of 86 nodules of the control group (87%) and 47 out of 53 nodules of the study group (89%), a clear definite diagnosis was possible. Five out of 86 nodules in the control group (6%) were diagnosed as follicular neoplasm, and six nodules (7%) were deferred. In contrast, six nodules out of 53 in the study group (11%) were diagnosed as follicular neoplasm, and none were deferred. There was no significant statistical difference in the distribution of intraoperative frozen diagnosis between the two groups (Table 1).
- With respect to the diagnostic discrepancy between frozen diagnosis and permanent diagnosis in the two groups, three nodules out of 75 (4%) in the control group showed discrepancy in the diagnosis; two cases were initially diagnosed as adenomatous hyperplasia and lymphocytic thyroiditis on frozen sections, and then as conventional PTC and noninvasive capsulated FVPTC on permanent sections (discrepancy rate, 0.087); and one nodule was initially diagnosed as conventional PTC on frozen section, and then as lymphocytic thyroiditis on permanent section (discrepancy rate, 0.019). None of the study group had discrepancy between the frozen and permanent diagnoses (discrepancy rate, 0). Although they are not classified as a discrepancy, six malignant nodules in the control group turned out to be different histologic types in permanent sections (Table 2). In the control group, two out of five follicular neoplasms on frozen section turned out to be FVPTC on permanent sections. In the study group, two out of six follicular neoplasms on frozen section were diagnosed as oncocytic variant PTC and noninvasive capsulated FVPTC on permanent sections, due to different nuclear features and IHC profiles on permanent sections (Table 3). Four out of six deferred nodules of the control group were revealed to be FVPTC on permanent diagnosis (malignancy rate, 0.667) (Table 4). Immunophenotypes of 36 nodules in the study group are summarized in Table 5. All of nine nodules (CK19+, CD56+) were immunohistochemically matched with benign on permanent diagnosis, and all of 15 nodules (CK19+, CD56–) were matched with conventional PTC. Two nodules which were initially diagnosed as follicular neoplasm due to the IHC staining results of CK19– and CD56+ were finally diagnosed as oncocytic variant PTC in one and FVPTC in the other; the IHC stain results were reversed to CK19+ and CD56– on permanent sections.
RESULTS
- Application of IHC to frozen sections can diminish critical diagnostic discrepancy between the intraoperative frozen diagnosis and subsequent permanent diagnosis. In our study, those that were not subject to IHC on frozen sections showed a diagnostic discrepancy in 4%, a change in histologic subtype of malignant nodules in 11%, and a diagnostic deferral in 7%. In those with a diagnostic discrepancy, for example, FVPTC was misdiagnosed as lymphocytic thyroiditis intraoperatively, lymphocytic thyroiditis was mistaken for conventional PTC, and conventional PTC was missed due to a sampling error. In addition, six out of 52 malignant nodules in the control group showed altered histological subtypes, but there was no difference in the 35 malignant nodules of the study group. Most of the deferred lesions and lesions of follicular neoplasm were finally diagnosed as capsulated FVPTC. However, those to which IHC was applied intraoperatively did not have any diagnostic discrepancy and none of them were deferred.
- With the introduction of FVPTC in 1977 [14], many cases previously thought to be follicular neoplasm were confirmed to be, in fact, FVPTC. This has led to a rather increased frequency of intraoperative pathologic consultation by frozen section in cases that had been preoperatively diagnosed as follicular neoplasm or reported to have some degree of nuclear atypia. Of course, these cases cannot be definitively diagnosed on frozen sections and they require meticulous sampling and ancillary IHC stain on permanent sections to reach definitive diagnosis [11-13]. To our knowledge, there has not yet been any report in thyroid lesions that employed the use of IHC in the intraoperative frozen diagnosis. Follicular neoplasm, by definition, cannot be a candidate for frozen diagnosis because its diagnosis depends on the histologic examination of the entire capsule of the mass [15]. However, as FVPTC has entered the diagnostic spectrum, a possible follicular neoplasm has also become a candidate for frozen diagnosis in order to rule out the possibility of FVPTC [16] which, in contrast to the follicular neoplasm, can be diagnosed on representative sections of the mass like other PTCs. At this point, we should note that considering the morphologic and gross features of FVPTC, there is always a hindrance of misinterpreting the microscopic appearance on frozen sections due to frozen artifacts [17]. In our institution, we have an experience of detecting micrometastasis in lymph nodes of breast cancer patients by applying IHC stain for cytokeratin on frozen sections [18]. With this previous experience, we applied IHC on frozen sections of the thyroid follicular lesions, expecting to distinguish between malignant and benign lesions intraoperatively and hence minimize the number of deferred or misdiagnosed lesions.
- Many antibodies are now being used in the diagnosis of FVPTC [11-13], but we chose CD56 and CK19 based on the integrated results of many antibodies and our accumulated experience heretofore. The combined results of CD56 negativity and CK19 positivity can maximize the diagnosis of PTC. Moreover, in contrast to HBME1, CK19 is often positive not only in PTC but also in adenomatous hyperplasia as well [11-13], and this has led us to integrate the staining patterns of the two antibodies in the differential diagnosis of follicular patterned lesions. In our study, we could definitely diagnose PTC and FVPTC in follicular patterned lesions showing atypical nuclear features with a constant IHC staining pattern of CK19+ and CD56–. On the other hand, we could avoid overdiagnosis by confirming an IHC staining pattern of CK19+ and CD56+ in benign follicular lesions such as lymphocytic thyroiditis, even with nuclear atypia.
- The study group showed a longer turnaround time, which was 33 minutes longer than that of the control group in average, and 68% of them took more than 40 minutes in the diagnosis. However, we should consider the total cost and psychological trauma of patients in the control group whose diagnoses were deferred (7%) or discrepant (4%). The time taken in IHC staining can be shortened to some extent although limited, but we expect to shorten the turnaround time more effectively if only we can decide with more speed whether the case in hand needs IHC on frozen section or not.
- Most of the nodules diagnosed as follicular neoplasm were finally diagnosed as FVPTC. Four out of five nodules of the control group were diagnosed as follicular carcinoma in one, hurthle cell carcinoma in one, and as encapsulated FVPTC in two nodules with or without capsular invasion. In contrast, only one out of six nodules diagnosed as follicular neoplasm in the study group was finally diagnosed as noninvasive encapsulated FVPTC after an additional IHC staining and further evaluation of permanent sections. The other nodule was diagnosed as oncocytic PTC after further evaluation of the remaining specimen.
- Deferred lesions or lesions of follicular neoplasm that are finally confirmed to be malignant on permanent sections need to undergo secondary surgical procedure or other additional treatment. As such, we should note that 80% of the follicular neoplasms and 67% of the deferred lesions in the control group were finally confirmed to be malignant, whereas 33% of the follicular neoplasms in the study group were finally confirmed to be malignant. In the control group, two patients diagnosed with follicular neoplasm underwent completion thyroidectomy and two times of radioiodine treatment. Three patients whose frozen diagnoses were deferred underwent additional radioiodine treatment. On the other hand, three patients in the study group, diagnosed as FVPTC (n=2) and lymphocytic thyroiditis (n=1), avoided secondary surgical procedure.
- We do have two nodules (3.7%) in the study group that could not be diagnosed even with the aid of IHC, which is only natural because patterns of immunoexpression in FVPTC can vary even in permanent sections [11-13]. But, if we consider the fact that the number escalates to six (7.0%) in the control group without the aid of IHC, we can safely say that the IHC can make a rather significant difference in the accuracy of frozen diagnosis in follicular patterned lesions. Therefore, we propose that if more specific antibodies are selected and applied, an intraoperative IHC stain on frozen sections can significantly improve the diagnostic accuracy in thyroid follicular lesions.
- In conclusion, although the significance of intraoperative IHC stain is somewhat compromised by longer turnaround time, it considerably diminishes the diagnostic discrepancy and inaccuracy. With consideration of the adverse effects of indefinite intraoperative diagnosis or discrepancy between the frozen and permanent diagnoses incurred on the patients, a development of more specific antibodies is necessary and their application to the intraoperative diagnosis of thyroid follicular lesions will further increase the diagnostic accuracy.
DISCUSSION
Acknowledgments
| Parameter | Control group | Study group | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (man:woman)a | 14:65 (18:82) | 8:40 (17:83) | 1.000b |
| Age, mean (range, yr)a | 49 (24–75) | 45 (24–68) | .258c |
| Man | 50 (32–75) | 54 (41–68) | |
| Woman | 47 (24–70) | 44 (24–64) | |
| Turnaround time (min)d | |||
| Mean | 24 | 57 | .000b |
| < 40 min | 84 (98) | 17 (32) | |
| ≥ 40 min | 2 (2) | 36 (68) | |
| Frozen diagnosisd | .149b | ||
| Benign | 23 (27) | 12 (23) | |
| AH | 20 (23) | 8 (15) | |
| LT | 3 (4) | 4 (7) | |
| Malignancy | 52 (60) | 35 (66) | |
| PTC, conventional | 43 (50) | 29 (55) | |
| FVPTC | 7 (8) | 4 (7) | |
| PTC, oncocytic variant | 1 (1) | 0 | |
| HC | 0 | 1 (2) | |
| FC | 1 (1) | 1 (2) | |
| Follicular neoplasm | 5 (6) | 6 (11) | |
| Deferred | 6 (7) | 0 |
Values are presented as number (%), unless otherwise indicated.
AH, adenomatous hyperplasia; LT, lymphocytic thyroiditis; PTC, papillary thyroid carcinoma; FVPTC, follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma; HC, Hurthle cell carcinoma; FC, follicular carcinoma, minimally invasive.
aNumber of patients: control (n = 79), study group (n = 48);
bFisher exact test;
ct test;
dNumber of nodules: control (n = 86), study group (n = 53).
AH, adenomatous hyperplasia; LT, lymphocytic thyroiditis; PTCc, papillary thyroid carcinoma, conventional; FVPTC, follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma; cap+, capsule present; inv-, no capsule invasion; inv+, capsule invasion present; cap-, no capsule; HC, Hurthle cell carcinoma; FC, follicular carcinoma, minimally invasive.
| FN at frozen diagnosis (No. of nodules) |
Permanent diagnosis (No. of nodules) |
Malignancy rate | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Follicular neoplasm |
Other |
||||||||||
|
Benign |
Malignant |
Total | AH | PTCo | FVPTC cap+, inv- | FVPTC cap+, inv+ | Total | ||||
| FA | HA | HC | FC | ||||||||
| Control group (n = 5) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 (60) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 (40) | 0.800 |
| Study group (n = 6) | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 (50) | 1 | 1a | 1a | 0 | 3 (50) | 0.333 |
Values are presented as number (%).
FN, follicular neoplasm; FA, follicular adenoma; HA, hurthle cell adenoma; HC, hurthle cell carcinoma; FC, follicular carcinoma, minimally invasive; AH, adenomatous hyperplasia; PTCo, oncocytic variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma; FVPTC, follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma; cap+, tumor capsule present; inv-, no capsule invasion; inv+, capsule invasion present.
aAlthough it showed CD56 positivity and cytokeratin 19 (CK19) negativity on rapid immunohistochemical stain of frozen section, focal loss of CD56 and focal reactivity of CK19 were revealed on permanent section of remained lesion.
FA, follicular adenoma; HA, hurthle cell adenoma; AH, adenomatous hyperplasia; PTCo, oncocytic variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma; FVPTC, follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma; cap+, tumor capsule present; inv-, no capsule invasion; inv+, capsule invasion present; HC, hurthle cell carcinoma; FC, follicular carcinoma, minimally invasive.
| Immunophenotype |
Permanent diagnosis (No. of nodules) |
Total No. of nodules (n = 36) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Benign (n = 15) |
Malignant (n = 21) |
|||||||||
| AH | LT | FA | HA | FC | HC | PTCc | PTCo | FVPTC | ||
| CK19+/CD56+ | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| CK19–/CD56+ | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| CK19+/CD56– | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 1a | 3a | 19 |
| CK19–/CD56– | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
AH, adenomatous hyperplasia; LT, lymphocytic thyroiditis; FA, follicular adenoma; HA, hurthle cell adenoma; FC, follicular carcinoma, minimally invasive; HC, hurthle cell carcinoma; PTCc, papillary thyroid carcinoma, conventional; PTCo, oncocytic variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma; FVPTC, follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinom.
aAlthough it showed CD56 positivity and cytokeratin 19 (CK19) negativity on rapid immunohistochemical stain of frozen section, focal loss of CD56 and focal reactivity of CK19 were revealed on permanent section of remained lesion.
- 1. Franssila KO, Ackerman LV, Brown CL, Hedinger CE. Follicular carcinoma. Semin Diagn Pathol 1985; 2: 101-22. PubMed
- 2. Posillico SE, Wilhelm SM, McHenry CR. The utility of frozen section examination for determining the extent of thyroidectomy in patients with a thyroid nodule and “atypia/follicular lesion of undetermined significance”. Am J Surg 2015; 209: 552-6. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Hirokawa M, Carney JA, Goellner JR, et al. Observer variation of encapsulated follicular lesions of the thyroid gland. Am J Surg Pathol 2002; 26: 1508-14. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Franc B, de la Salmonière P, Lange F, et al. Interobserver and intraobserver reproducibility in the histopathology of follicular thyroid carcinoma. Hum Pathol 2003; 34: 1092-100. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Lloyd RV, Erickson LA, Casey MB, et al. Observer variation in the diagnosis of follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 2004; 28: 1336-40. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Elsheikh TM, Asa SL, Chan JK, et al. Interobserver and intraobserver variation among experts in the diagnosis of thyroid follicular lesions with borderline nuclear features of papillary carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 2008; 130: 736-44. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Min HS, Kim JH, Ryoo I, Jung SL, Jung CK. The role of core needle biopsy in the preoperative diagnosis of follicular neoplasm of the thyroid. APMIS 2014; 122: 993-1000. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Na DG, Kim JH, Sung JY, et al. Core-needle biopsy is more useful than repeat fine-needle aspiration in thyroid nodules read as nondiagnostic or atypia of undetermined significance by the Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology. Thyroid 2012; 22: 468-75. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Hakala T, Kholová I, Sand J, Saaristo R, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P. A core needle biopsy provides more malignancy-specific results than fine-needle aspiration biopsy in thyroid nodules suspicious for malignancy. J Clin Pathol 2013; 66: 1046-50. ArticlePubMed
- 10. Asa SL. The role of immunohistochemical markers in the diagnosis of follicular-patterned lesions of the thyroid. Endocr Pathol 2005; 16: 295-309. ArticlePubMed
- 11. El Demellawy D, Nasr A, Alowami S. Application of CD56, P63 and CK19 immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis of papillary carcinoma of the thyroid. Diagn Pathol 2008; 3: 5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. de Matos LL, Del Giglio AB, Matsubayashi CO, de Lima Farah M, Del Giglio A, da Silva Pinhal MA. Expression of CK-19, galectin-3 and HBME-1 in the differentiation of thyroid lesions: systematic review and diagnostic meta-analysis. Diagn Pathol 2012; 7: 97.PubMedPMC
- 13. Nechifor-Boila A, Borda A, Sassolas G, et al. Immunohistochemical markers in the diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinomas: The promising role of combined immunostaining using HBME-1 and CD56. Pathol Res Pract 2013; 209: 585-92. ArticlePubMed
- 14. Chem KT, Rosai J. Follicular variant of thyroid papillary carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study of six cases. Am J Surg Pathol 1977; 1: 123-30. PubMed
- 15. LiVolsi VA, Baloch ZW. Follicular neoplasms of the thyroid: view, biases, and experiences. Adv Anat Pathol 2004; 11: 279-87. PubMed
- 16. Kesmodel SB, Terhune KP, Canter RJ, et al. The diagnostic dilemma of follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Surgery 2003; 134: 1005-12. ArticlePubMed
- 17. Lin HS, Komisar A, Opher E, Blaugrund SM. Follicular variant of papillary carcinoma: the diagnostic limitations of preoperative fine-needle aspiration and intraoperative frozen section evaluation. Laryngoscope 2000; 110: 1431-6. ArticlePubMed
- 18. Lee IK, Lee HD, Jeong J, et al. Intraoperative examination of sentinel lymph nodes by immunohistochemical staining in patients with breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 2006; 32: 405-9. ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- High-Contrast Facile Imaging with Target-Directing Fluorescent Molecular Rotors, the N3-Modified Thioflavin T Derivatives
Yuka Kataoka, Hiroto Fujita, Arina Afanaseva, Chioko Nagao, Kenji Mizuguchi, Yuuya Kasahara, Satoshi Obika, Masayasu Kuwahara
Biochemistry.2019; 58(6): 493. CrossRef - The diagnostic value of TROP-2, SLP-2 and CD56 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Xueyang Yang, Yifang Hu, He Shi, Chengzhou Zhang, Zhixiao Wang, Xiaoyun Liu, Huanhuan Chen, Lijuan Zhang, Dai Cui
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology.2018; 275(8): 2127. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure


Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
| Parameter | Control group | Study group | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (man:woman) |
14:65 (18:82) | 8:40 (17:83) | 1.000 |
| Age, mean (range, yr) |
49 (24–75) | 45 (24–68) | .258 |
| Man | 50 (32–75) | 54 (41–68) | |
| Woman | 47 (24–70) | 44 (24–64) | |
| Turnaround time (min) |
|||
| Mean | 24 | 57 | .000 |
| < 40 min | 84 (98) | 17 (32) | |
| ≥ 40 min | 2 (2) | 36 (68) | |
| Frozen diagnosis |
.149 |
||
| Benign | 23 (27) | 12 (23) | |
| AH | 20 (23) | 8 (15) | |
| LT | 3 (4) | 4 (7) | |
| Malignancy | 52 (60) | 35 (66) | |
| PTC, conventional | 43 (50) | 29 (55) | |
| FVPTC | 7 (8) | 4 (7) | |
| PTC, oncocytic variant | 1 (1) | 0 | |
| HC | 0 | 1 (2) | |
| FC | 1 (1) | 1 (2) | |
| Follicular neoplasm | 5 (6) | 6 (11) | |
| Deferred | 6 (7) | 0 |
| Frozen diagnosis (No. of nodules) | Permanent diagnosis (No. of nodules) |
Discrepancy rate | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign |
Malignant |
||||||||
| AH | LT | PTCc | FVPTC cap+, inv- | FVPTC cap+, inv+ | FVPTC cap- | HC | FC | ||
| Control group | |||||||||
| Benign (n = 23) | 0.087 | ||||||||
| AH | 19 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| LT | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Malignant (n = 52) | 0.019 | ||||||||
| PTCc | 0 | 1 | 38 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| FVPTC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 1 | |
| HC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| FC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Study group | |||||||||
| Benign (n = 12) | 0 | ||||||||
| AH | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| LT | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Malignant (n = 35) | 0 | ||||||||
| PTCc | 0 | 0 | 29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| FVPTC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| HC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| FC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| FN at frozen diagnosis (No. of nodules) | Permanent diagnosis (No. of nodules) |
Malignancy rate | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Follicular neoplasm |
Other |
||||||||||
| Benign |
Malignant |
Total | AH | PTCo | FVPTC cap+, inv- | FVPTC cap+, inv+ | Total | ||||
| FA | HA | HC | FC | ||||||||
| Control group (n = 5) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 (60) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 (40) | 0.800 |
| Study group (n = 6) | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 (50) | 1 | 1 |
1 |
0 | 3 (50) | 0.333 |
| Frozen diagnosis (deffered) | Permanent diagnosis (No. of nodules) |
Malignancy rate | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign (n = 2) |
Malignant (n = 4) |
||||||||
| FA | HA | AH | PTCo | FVPTC cap+, inv- | FVPTC cap+, inv+ | HC | FC | ||
| Control group | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.667 |
| Study group | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Immunophenotype | Permanent diagnosis (No. of nodules) |
Total No. of nodules (n = 36) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign (n = 15) |
Malignant (n = 21) |
|||||||||
| AH | LT | FA | HA | FC | HC | PTCc | PTCo | FVPTC | ||
| CK19+/CD56+ | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| CK19–/CD56+ | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| CK19+/CD56– | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 1 |
3 |
19 |
| CK19–/CD56– | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Values are presented as number (%), unless otherwise indicated. AH, adenomatous hyperplasia; LT, lymphocytic thyroiditis; PTC, papillary thyroid carcinoma; FVPTC, follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma; HC, Hurthle cell carcinoma; FC, follicular carcinoma, minimally invasive. Number of patients: control (n = 79), study group (n = 48); Fisher exact test; t test; Number of nodules: control (n = 86), study group (n = 53).
AH, adenomatous hyperplasia; LT, lymphocytic thyroiditis; PTCc, papillary thyroid carcinoma, conventional; FVPTC, follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma; cap+, capsule present; inv-, no capsule invasion; inv+, capsule invasion present; cap-, no capsule; HC, Hurthle cell carcinoma; FC, follicular carcinoma, minimally invasive.
Values are presented as number (%). FN, follicular neoplasm; FA, follicular adenoma; HA, hurthle cell adenoma; HC, hurthle cell carcinoma; FC, follicular carcinoma, minimally invasive; AH, adenomatous hyperplasia; PTCo, oncocytic variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma; FVPTC, follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma; cap+, tumor capsule present; inv-, no capsule invasion; inv+, capsule invasion present. Although it showed CD56 positivity and cytokeratin 19 (CK19) negativity on rapid immunohistochemical stain of frozen section, focal loss of CD56 and focal reactivity of CK19 were revealed on permanent section of remained lesion.
FA, follicular adenoma; HA, hurthle cell adenoma; AH, adenomatous hyperplasia; PTCo, oncocytic variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma; FVPTC, follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma; cap+, tumor capsule present; inv-, no capsule invasion; inv+, capsule invasion present; HC, hurthle cell carcinoma; FC, follicular carcinoma, minimally invasive.
AH, adenomatous hyperplasia; LT, lymphocytic thyroiditis; FA, follicular adenoma; HA, hurthle cell adenoma; FC, follicular carcinoma, minimally invasive; HC, hurthle cell carcinoma; PTCc, papillary thyroid carcinoma, conventional; PTCo, oncocytic variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma; FVPTC, follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinom. Although it showed CD56 positivity and cytokeratin 19 (CK19) negativity on rapid immunohistochemical stain of frozen section, focal loss of CD56 and focal reactivity of CK19 were revealed on permanent section of remained lesion.

 E-submission
E-submission




