Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 58(5); 2024 > Article
-
Original Article
Single umbilical artery and associated birth defects in perinatal autopsies: prenatal diagnosis and management -
Manushree Saxena
 , Bhagyashri Hungund
, Bhagyashri Hungund
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2024;58(5):214-218.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.03
Published online: July 9, 2024
Department of Pathology, KAHER’S Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Belagavi, India
- Corresponding Author: Bhagyashri Hungund, MD, Department of Pathology, KAHER’S Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Nehru Nagar, Belagavi 590010, Karnataka, India Tel: +91-9964318708, Fax: +91-0831-2470759, E-mail: Bhagya78h@gmail.com, Manushree.s444@gmail.com
© 2024 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
-
Background
- The umbilical cord forms the connection between the fetus and the placenta at the feto-maternal interface and normally comprises two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein. In some cases, only a single umbilical artery (SUA) is present. This study was conducted to evaluate associations between SUA and other congenital malformations discovered in perinatal autopsies and to ascertain the existence of preferential associations between SUA and certain anomalies.
-
Methods
- We evaluated records of all fetuses sent for autopsy to the Department of Pathology during the 10-year period from 2013 through 2022 (n = 1,277). The data were obtained from the hospital’s pathology laboratory records. The congenital anomalies were grouped by organ or system for analysis and included cardiovascular, urinary tract, nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, musculoskeletal, and lung anomalies.
-
Results
- A SUA was present in 8.61% of the autopsies. The gestational age of the affected fetuses ranged between 13 to 40 weeks. An SUA presented as an isolated single anomaly in 44 cases (3.4%). Of the 110 SUA cases, 60% had other congenital anomalies. There was a significant association between birth defects and SUAs (p < .001). Strong associations between SUA and urinary tract, lung, and musculoskeletal anomalies were observed.
-
Conclusions
- A SUA is usually seen in association with other congenital malformations rather than as an isolated defect. Therefore, examination for associated anomalies when an SUA is detected either antenatally or postnatally is imperative. The findings of this study should be helpful in counseling expectant mothers and their families in cases of SUA.
- The umbilical cord forms a stable connection between the fetus and the placenta at the feto-maternal interface [1]. The cord develops between the third and seventh week following conception and usually comprises two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein [2]. However, the presence of only a single umbilical artery (SUA) is the most common umbilical cord abnormality and occurs in 0.2%–1.2% of live newborns [3].
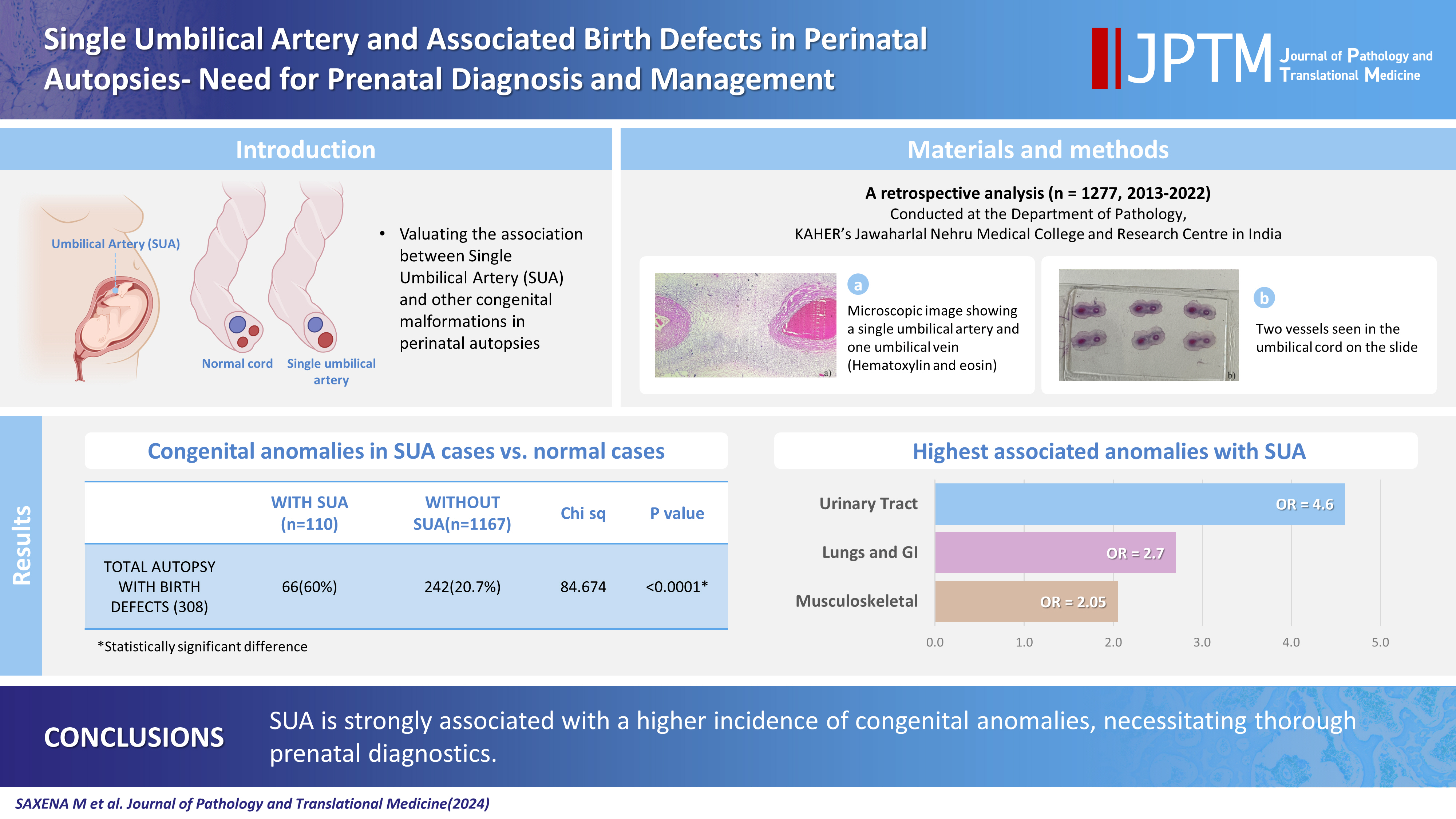
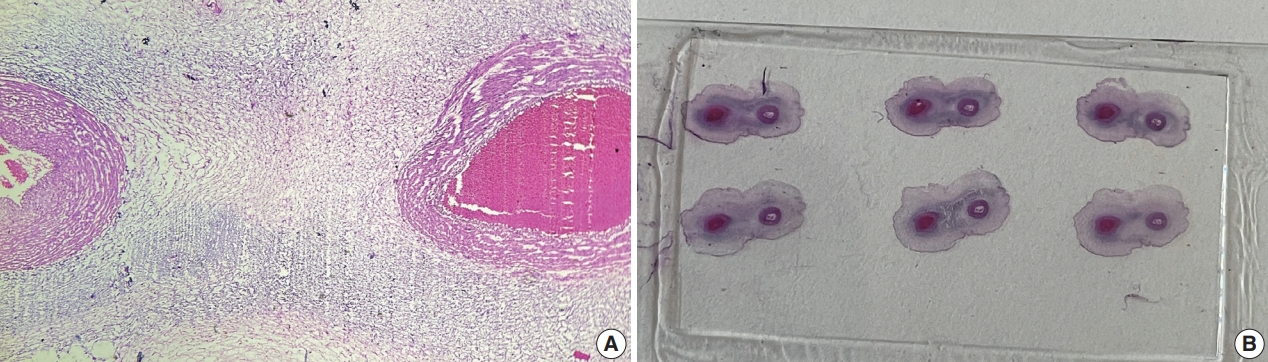
- The definitive diagnosis can be made histologically by the visualization of only two umbilical cord vessels. Prenatal diagnosis of SUA can be made using antenatal visualization of the umbilical cord using ultrasonography, especially with color Doppler flow imaging [1]. SUA incidence varies between studies and tends to be higher in aborted fetus and autopsy studies [4,5].
- Although its pathogenesis is not clearly understood, three theories have been put forth to explain the occurrence of SUA. One theory attributes SUA occurrence to primary agenesis of one artery, a second theory proposes atrophy or secondary atresia of a formerly normal umbilical artery as the cause, and the third theory implicates a persistent allantoic artery in the pathogenesis of SUA. From an embryological perspective, the second theory is the most plausible explanation [5].
- An SUA is more frequently encountered in conjunction with a wide variety of other anomalies instead of as an isolated SUA (iSUA) [6]. Although other malformations are present in 10%–27% of cases of SUA, documented findings lack consistency [4,7,8]. The reported incidences of SUA with and without associated comorbidities in live births, either at term or pre-term, vary substantially among studies [4,9-12]. The ability to predict poor perinatal outcome and presence of other congenital malformations is often questioned [13].
- Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the association between SUA and other congenital malformations at the time of perinatal autopsy and to ascertain the existence of any preferential associations between SUA and specific anomalies.
- Study design
- This was a retrospective study performed at Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College and Research Centre, Belagavi, India. We evaluated records of all fetuses sent for autopsy to the Department of Pathology during the 10-year period from 2013 through 2022 (n=1,277). The data were obtained from the hospital pathology laboratory records. The cases were either intrauterine deaths or abortions due to the detection of congenital anomalies. The presence of SUA was confirmed by histopathological examination of the umbilical cord (Fig. 1).
- Information on gestational age at delivery, twinning, sex, and the presence of significant congenital anomalies was reviewed. The congenital anomalies were grouped by organ or system for analysis and included cardiovascular, urinary tract, nervous system, gastrointestinal tract (GIT), musculoskeletal, and lung anomalies.
- Statistical analysis
- The odds ratio (OR) and chi-square test were used for data analysis using SPSS ver. 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). The OR and its 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were used to express the risk for incidence of a specific congenital abnormality related to SUA. The significance level was set at p<.05.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
- A SUA was found in 8.6% (110/1,277) of the autopsies. The gestational age of the fetuses ranged between 13 to 40 weeks. Three cases of SUA were twins; and, in each of these cases, the co-twin had three vessels. An iSUA was present in 44 cases (3.4%). Of the 110 cases with SUA, 60.0% (n=66) had other congenital anomalies. There was a significant association between birth defects and SUA cases (p<.001) (Table 1).
- The incidence of SUA was 4.5 times higher in malformed fetuses (21.4%, 66/308) than in fetuses without abnormalities (4.5%, 44/969).
- A strong association with SUA was seen for urinary tract, lung, GIT, and musculoskeletal anomalies. The most associated anomaly was urinary tract defect; this was 4.7 times more likely to occur in SUA cases (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 2.61 to 8.32; p<.001) (Table 2).
- Anomalies of the cardiovascular system (CVS) and central nervous system (CNS) did not show significant associations with SUA (p>.05).
- The congenital anomalies observed in the SUA group included 14 cases of anal atresia (12.7%), 12 cases of unilateral renal agenesis (10.9%), 11 cases of vertebral defects (10.0%), and 10 cases of anencephaly (9.0%). Other anomalies found along with SUA were eight cases of pulmonary hypoplasia (7.2%), six cases of diaphragmatic hernia (5.4%), six cases of sirenomelia sequence (5.4%), and six cases of multi-cystic dysplastic kidney (5.4%).
- The urinary tract defects found in the SUA cases in this study were unilateral renal agenesis (n=12), multi-cystic dysplastic kidney (n=6), hydronephrosis (n=5), horseshoe kidney (n=5), bilateral renal agenesis (n=4), urinary bladder agenesis (n=3) and congenital megacystitis (n=2). The lung defects included pulmonary hypoplasia (n=8) and congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (n=1). The gastrointestinal defects included anal atresia (n=14), diaphragmatic hernia (n=6), omphalocele (n=3), gastroschisis (n=2), and esophageal atresia (n=1). The musculoskeletal defects found were vertebral defects (n=11), sirenomelia (n=7), talipes equinovarus (n=4), cleft lip and/or palate (n=4), and phocomelia (n=1). CNS defects included anencephaly (n=10), meningomyelocele (n=5), congenital hydrocephalus (n=3), spina bifida (n=3), and encephalocele (n=2). CVS defects included ventricular septal defect (n=4), dextrocardia (n=4), tetralogy of Fallot (n=3), tricuspid atresia (n=1), coarctation of the aorta (n=1), and atrial septal defect (n=1).
- The results of our study showed 9.1% (10/110) of SUA cases had a VACTERL (vertebral anomalies-anal atresia-cardiac defects-tracheoesophageal fistula and/or esophageal atresia-renal anomalies-limb defects) association.
- Of the 110 cases of SUA, 58 were male, 42 were female and 10 had ambiguous genitalia. Ambiguous genitalia were seen in 10.6% of SUA cases as compared to 2.1% of double umbilical artery cases (Table 3).
RESULTS
- Estimates regarding malformations associated with SUA exhibit a marked degree of variation in different studies. This might be the result of different sampling sources and sample sizes or other methodological variations.
- Information on SUA and its association with congenital abnormalities has primarily originated from two sources: (1) abortions, fetal deaths, and terminations of fetuses with anomalies and (2) live births [4].
- Besides a less frequent association of congenital abnormalities with SUA, the incidence of SUA is lower in live births. Live births often show a reduced incidence and frequency of associated abnormalities because most of the affected fetuses have been aborted or terminated during pregnancy. This difference is highlighted by a meta-analysis of these data in which the incidence of SUA in the autopsy data sets approximates at 0.34%–7% and the associated anomalies at 0.25%–81.8% (generally 20%–25%) [14-18]. Additionally, there are temporal disparities between the studies that led to variations in the methods of detection and diagnosis.
- Our study found an incidence of SUA at perinatal autopsy of 8.61%, which is comparable to the Nayak et al. study’s [19] reported incidence of 7.9%.
- Congenital anomaly was observed in 60% of the SUA group, significantly higher than in the “non SUA” group. This was consistent with the findings of Froehlich and Fujikura in which 53% of SUA cases involved other malformations [20]. Lilja [8] reported a 4.3-times higher risk of associated abnormalities in SUA cases; our study revealed a threefold increase in the risk.
- In our study, urinary tract anomalies of varying severity were present in 35% of the SUA cases and indicated a strong association between urinary tract anomalies and SUA. This was consistent with most of the results reported by others [21-23]. This highlights the magnitude of urinary tract anomaly occurrence in these fetuses, but the pathogenesis and etiology of the association remain unclear.
- In our study, the congenital anomalies associated with SUA included anal atresia, unilateral renal agenesis, vertebral defects, and anencephaly in decreasing frequency. These findings were consistent with those of another study in which renal agenesis, imperforate anus, and vertebral defects were the most specific defects associated with SUA [24]. A population study from Norway also reported a strong association between SUA and gastrointestinal atresia [25].
- A study in mice showed that Hedgehog genes play a key role in the development of the feto-placental interface (arteries) and the visceral endoderm/hindgut [26]. This supplies a plausible explanation for the spectrum of malformations in the GIT associated with SUA in our study.
- Anomalies of the CVS and CNS did not show a significant association with SUA in our study. This finding agreed with an analysis of autopsied fetuses with SUA that showed lesions of the CNS and CVS are least frequent in SUA cases [22].
- Ambiguous genitalia were seen in 10.6% of SUA cases as compared to 2.1% of non-SUA cases in our study. This high occurrence in SUA cases could be due to the autopsy-based nature of this study; cases of ambiguous genitalia with other defects or chromosomal abnormalities may have been more likely to be detected prenatally and sent for autopsy. Therefore, the association cannot be directly attributed to SUA and should be tested in future studies.
- Our findings suggest that SUA detection should be accomplished as early as possible because of its association with other congenital malformations.
- One strength of the study was the large sample size. This is attributable to the referral nature of the hospital. Also, the detection of SUA in this study was highly sensitive and specific. This was achieved through histopathological examination of the umbilical cord in autopsied specimens.
- The typical drawbacks of retrospective research apply to this study as well. Since healthy and surviving infants were not part of the study sample, an extrapolation of the findings to the general population mandates population-based studies.
- We found an SUA in 8.61% of the perinatal autopsies. The overall prevalence of congenital anomalies in association with SUA was 60%, significantly greater than iSUA cases. Therefore, careful examination for other anomalies in SUA cases is imperative; detailed ultrasonography, echocardiography, and amniocentesis need to be used when an SUA is discovered during routine ultrasound. The findings of this study should be helpful for counseling expectant mothers and their families in cases of an SUA. We conclude that the identification of an SUA necessitates a thorough examination of the fetus for any other anomalies. Karyotyping for the detection of associated chromosomal abnormalities is a topic for future study.
DISCUSSION
Ethics Statement
All procedures performed in the current study were approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee (ref no. MCD/DOME/171 dated 19/04/2023). Formal written informed consent was not required; a waiver was obtained from the Institutional Ethics Committee because this was an autopsy-based study.
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets generated or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: MS, BH. Data curation: MS. Formal analysis: MS. Investigation: MS. Methodology: MS, BH. Project administration: BH, MS. Resources: MS. Software: MS. Supervision: BH. Validation: BH, MS. Visualization: MS. Writing—original draft: MS. Writing—review & editing: MS, BH. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Funding Statement
No funding to declare.
Acknowledgments
| SUA group (n = 66) | DUA group (n = 242) | Chi-square | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 23 (34.8) | 101 (41.7) | 10.343 | .005 |
| Male | 36 (54.6) | 136 (56.2) | ||
| Ambiguous | 7 (10.6) | 5 (2.1) |
- 1. Vrabie SC, Novac L, Manolea MM, Dijmarescu LA, Novac M, Siminel MA. Abnormalities of the umbilical cord. In: Tudorache S, ed. Congenital anomalies: from the embryo to the neonate. London: IntechOpen, 2017; 345-62.
- 2. Heil JR, Bordoni B. Embryology, umbilical cord [Internet]. Treasure Island: StatPearls Publishing, 2023 [cited 2024 Apr 4]. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32491422/.
- 3. Csecsei K, Kovacs T, Hinchliffe SA, Papp Z. Incidence and associations of single umbilical artery in prenatally diagnosed malformed, midtrimester fetuses: a review of 62 cases. Am J Med Genet 1992; 43: 524-30. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Thummala MR, Raju TN, Langenberg P. Isolated single umbilical artery anomaly and the risk for congenital malformations: a metaanalysis. J Pediatr Surg 1998; 33: 580-5. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Persutte WH, Hobbins J. Single umbilical artery: a clinical enigma in modern prenatal diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995; 6: 216-29. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Tulek F, Kahraman A, Taskin S, Ozkavukcu E, Soylemez F. Determination of risk factors and perinatal outcomes of singleton pregnancies complicated by isolated single umbilical artery in Turkish population. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc 2015; 16: 21-4. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Murphy-Kaulbeck L, Dodds L, Joseph KS, Van den Hof M. Single umbilical artery risk factors and pregnancy outcomes. Obstet Gynecol 2010; 116: 843-50. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Lilja M. Infants with single umbilical artery studied in a national registry. 3: a case control study of risk factors. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 1994; 8: 325-33. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Tasha I, Brook R, Frasure H, Lazebnik N. Prenatal detection of cardiac anomalies in fetuses with single umbilical artery: diagnostic accuracy comparison of maternal-fetal-medicine and pediatric cardiologist. J Pregnancy 2014; 2014: 265421.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 10. Burshtein S, Levy A, Holcberg G, Zlotnik A, Sheiner E. Is single umbilical artery an independent risk factor for perinatal mortality? Arch Gynecol Obstet 2011; 283: 191-4. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. Bombrys AE, Neiger R, Hawkins S, et al. Pregnancy outcome in isolated single umbilical artery. Am J Perinatol 2008; 25: 239-42. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Dagklis T, Defigueiredo D, Staboulidou I, Casagrandi D, Nicolaides KH. Isolated single umbilical artery and fetal karyotype. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2010; 36: 291-5. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Rittler M, Mazzitelli N, Fuksman R, de Rosa LG, Grandi C. Single umbilical artery and associated malformations in over 5500 autopsies: relevance for perinatal management. Pediatr Dev Pathol 2010; 13: 465-70. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Chow JS, Benson CB, Doubilet PM. Frequency and nature of structural anomalies in fetuses with single umbilical arteries. J Ultrasound Med 1998; 17: 765-8. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Abuhamad AZ, Shaffer W, Mari G, Copel JA, Hobbins JC, Evans AT. Single umbilical artery: does it matter which artery is missing? Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995; 173: 728-32. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Leung AK, Robson WL. Single umbilical artery: a report of 159 cases. Am J Dis Child 1989; 143: 108-11. ArticlePubMed
- 17. Tortora M, Chervenak FA, Mayden K, Hobbins JC. Antenatal sonographic diagnosis of single umbilical artery. Obstet Gynecol 1984; 63: 693-6. PubMed
- 18. Gossett DR, Lantz ME, Chisholm CA. Antenatal diagnosis of single umbilical artery: is fetal echocardiography warranted? Obstet Gynecol 2002; 100: 903-8. PubMed
- 19. Nayak SS, Shukla A, Girisha KM. Anomalies associated with single umbilical artery at perinatal autopsy. Indian Pediatr 2015; 52: 73-4. PubMed
- 20. Froehlich LA, Fujikura T. Follow-up of infants with single umbilical artery. Pediatrics 1973; 52: 6-13. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 21. Singh V, Patel R, Pradhan P. Single umbilical artery and associated hydronephrosis: a report of 2 cases. J Reprod Med 2004; 49: 136-8. PubMed
- 22. Heifetz SA. Single umbilical artery: a statistical analysis of 237 autopsy cases and review of the literature. Perspect Pediatr Pathol 1984; 8: 345-78. PubMed
- 23. Srinivasan R, Arora RS. Do well infants born with an isolated single umbilical artery need investigation? Arch Dis Child 2005; 90: 100-1. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Martinez-Payo C, Gaitero A, Tamarit I, Garcia-Espantaleon M, Iglesias Goy E. Perinatal results following the prenatal ultrasound diagnosis of single umbilical artery. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2005; 84: 1068-74. ArticlePubMed
- 25. Ebbing C, Kessler J, Moster D, Rasmussen S. Single umbilical artery and risk of congenital malformation: population-based study in Norway. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2020; 55: 510-5. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Rodriguez AM, Downs KM. Visceral endoderm and the primitive streak interact to build the fetal-placental interface of the mouse gastrula. Dev Biol 2017; 432: 98-124. ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Single Umbilical Artery with Symmetrical IUGR and Multiple Fetal Anomalies - An Interesting Case Report
Amulya Choudary Kotapati, Bhargavi Khandru, Vijayasree M.
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2025; : 10. CrossRef - Epidemiological and Histopathological Characteristics of Fetuses with Congenital Disorders: A Study in Greece
Despoina Nteli, Maria Nteli, Konstantinos Konstantinidis, Maria Ouzounidou, Paschalis Theotokis, Maria-Eleni Manthou, Iasonas Dermitzakis, Xeni Miliara, Chrysoula Gouta, Stamatia Angelidou, Dimosthenis Miliaras, Soultana Meditskou
Biology.2025; 14(6): 626. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure
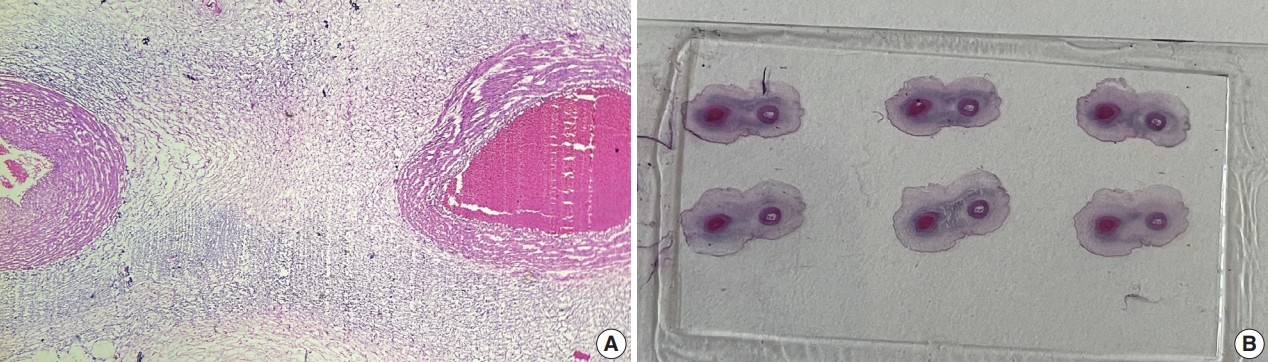

Fig. 1.
Graphical abstract
| With SUA (n = 110) | Without SUA (n = 1,167) | Chi-square | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total autopsy with birth defects (n = 308) | 66 (60.0) | 242 (20.7) | 84.674 | < .001 |
| Total autopsy without birth defects (n = 969) | 44 (40.0) | 925 (79.2) |
| Birth defect system | With SUA (n = 66) | Without SUA (n = 242) | OR (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNS | 23 (34.8) | 109 (45.0) | 0.653 (0.371–1.150) | .140 |
| Urinary tract | 39 (59) | 57 (23.5) | 4.688 (2.642–8.319) | < .001 |
| Lungs | 9 (13.6) | 13 (5.37) | 2.781 (1.133–6.828) | .026 |
| CVS | 14 (21.2) | 31 (12.8) | 1.833 (0.909–3.691) | .090 |
| Gastrointestinal | 16 (24.2) | 25 (10.3) | 2.778 (1.381–5.587) | .004 |
| Musculoskeletal | 27 (40.9) | 61 (25.2) | 2.054 (1.162–3.633) | .013 |
| SUA group (n = 66) | DUA group (n = 242) | Chi-square | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 23 (34.8) | 101 (41.7) | 10.343 | .005 |
| Male | 36 (54.6) | 136 (56.2) | ||
| Ambiguous | 7 (10.6) | 5 (2.1) |
Values are presented as number (%) unless otherwise indicated. SUA, single umbilical artery. p < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Values are presented as number (%) unless otherwise indicated. SUA, single umbilical artery; OR, odds ratio; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval; CNS, central nervous system; CVS, cardiovascular system. p < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Values are presented as number (%) unless otherwise indicated. SUA, single umbilical artery; DUA, double umbilical artery. p < .05 was considered statistically significant.

 E-submission
E-submission