Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 58(5); 2024 > Article
-
Original Article
Artificial intelligence algorithm for neoplastic cell percentage estimation and its application to copy number variation in urinary tract cancer -
Jinahn Jeong1
 , Deokhoon Kim1
, Deokhoon Kim1 , Yeon-Mi Ryu2
, Yeon-Mi Ryu2 , Ja-Min Park2
, Ja-Min Park2 , Sun Young Yoon2
, Sun Young Yoon2 , Bokyung Ahn1
, Bokyung Ahn1 , Gi Hwan Kim1
, Gi Hwan Kim1 , Se Un Jeong1,*
, Se Un Jeong1,* , Hyun-Jung Sung1
, Hyun-Jung Sung1 , Yong Il Lee1
, Yong Il Lee1 , Sang-Yeob Kim2
, Sang-Yeob Kim2 , Yong Mee Cho1
, Yong Mee Cho1
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2024;58(5):229-240.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.13
Published online: August 9, 2024
1Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Yong Mee Cho, MD, PhD, Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, 88 Olympic-ro 43-gil, Songpa-gu, Seoul 05505, Korea Tel: +82-2-3010-4560, Fax: +82-2-472-7898, E-mail: yongcho@amc.seoul.kr
- *Current address: Department of Pathology, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
© The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 4,651 Views
- 277 Download
Abstract
-
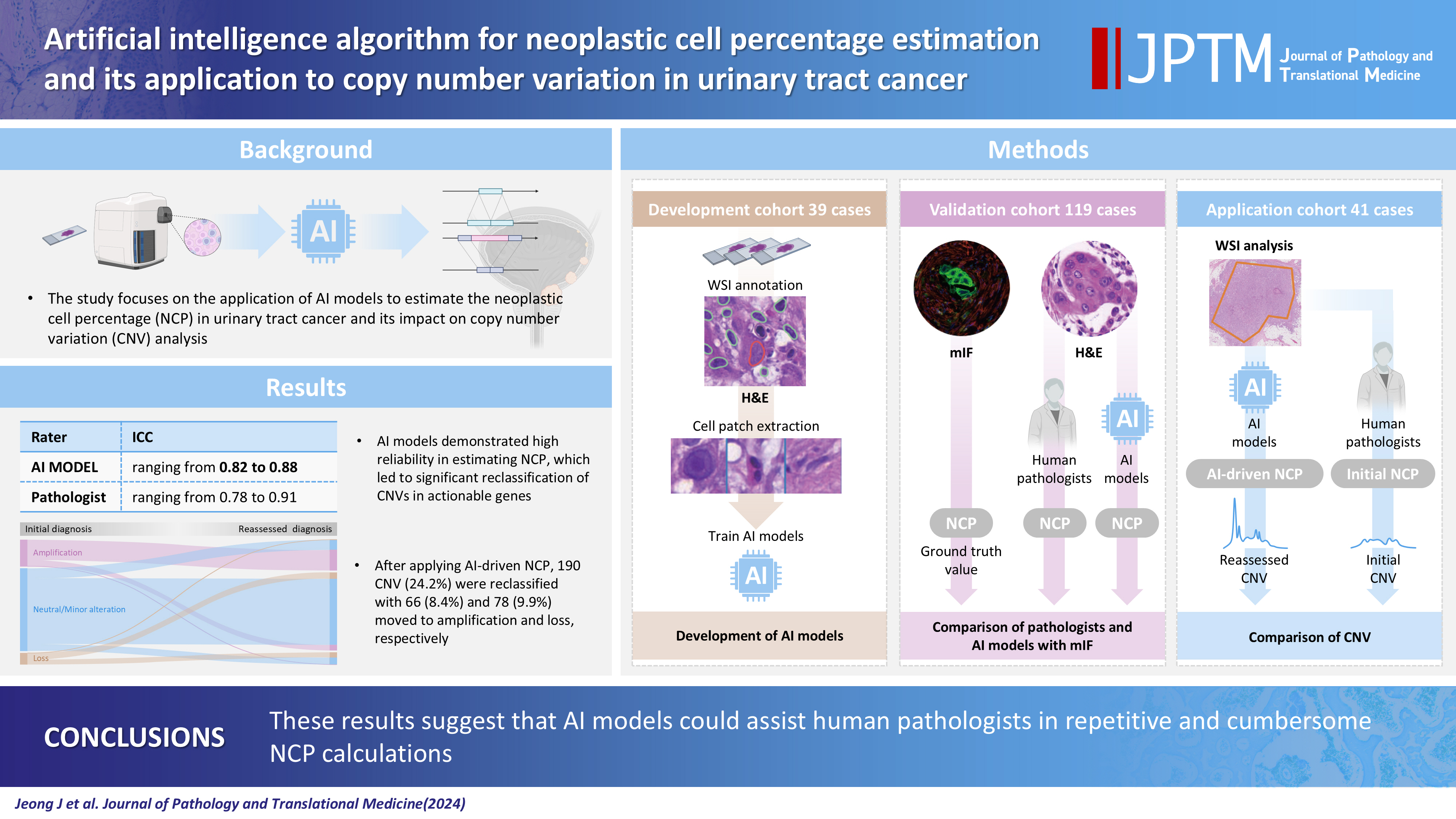
Background
- Bladder cancer is characterized by frequent mutations, which provide potential therapeutic targets for most patients. The effectiveness of emerging personalized therapies depends on an accurate molecular diagnosis, for which the accurate estimation of the neoplastic cell percentage (NCP) is a crucial initial step. However, the established method for determining the NCP, manual counting by a pathologist, is time-consuming and not easily executable.
-
Methods
- To address this, artificial intelligence (AI) models were developed to estimate the NCP using nine convolutional neural networks and the scanned images of 39 cases of urinary tract cancer. The performance of the AI models was compared to that of six pathologists for 119 cases in the validation cohort. The ground truth value was obtained through multiplexed immunofluorescence. The AI model was then applied to 41 cases in the application cohort that underwent next-generation sequencing testing, and its impact on the copy number variation (CNV) was analyzed.
-
Results
- Each AI model demonstrated high reliability, with intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) ranging from 0.82 to 0.88. These values were comparable or better to those of pathologists, whose ICCs ranged from 0.78 to 0.91 in urothelial carcinoma cases, both with and without divergent differentiation/ subtypes. After applying AI-driven NCP, 190 CNV (24.2%) were reclassified with 66 (8.4%) and 78 (9.9%) moved to amplification and loss, respectively, from neutral/minor CNV. The neutral/minor CNV proportion decreased by 6%.
-
Conclusions
- These results suggest that AI models could assist human pathologists in repetitive and cumbersome NCP calculations.
- Bladder cancer is one of the most highly mutated tumors with recurrent mutations, creating potential therapeutic targets in the majority (69%) of patients [1]. Recently, personalized treatments based on recurrent genetic alterations such as pan–fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitors targeting FGFR3 mutations and FGFR3/2 fusions have been emerging, where an accurate molecular diagnosis is a prerequisite for such personalized treatment [2]. In addition, several agents such as human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–targeting antibody-drug conjugates for HER2-overexpressing bladder cancer are under investigation in clinical trials with promising efficacy reported [3,4].
- Molecular tests such as targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) are widely used not only to define disease-associated genetic alterations for diagnostic purposes but also to find drug-associated clinically actionable targets for personalized medicine. As an initial step of NGS, an accurate assessment of the neoplastic cell percentage (NCP) is essential because solid tumors, including bladder cancer, contain a variable amount of non-neoplastic cells such as desmoplastic fibroblasts, inflammatory cells, vascular endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells. Depending on the NCP, an NGS test may proceed or be canceled for some specimens, especially those with a low tumor content near the cutoff level of the test. This is because NGS testing with insufficient neoplastic cells may lead to false negative results, even in the presence of a variant, when the test is conducted despite inadequate cellularity. Furthermore, an inappropriately assessed NCP produces noise and distorts the relationship between read counts, resulting in an inaccurate estimation of the copy number variation (CNV) in the NGS data [5].
- NCP, also referred to as normal cell contamination, is defined as the fraction of cancer cells in a tumor. Currently, NCP is determined by visual examination by pathologists of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained slides of tumor sections [6,7]. However, these pathologist estimates have limited accuracy and a wide range of interobserver variation [6,8]. To resolve this challenge, several in silico methods were developed by using genomic, epigenomic, or transcriptomic profiles. Although they appear to be accurate and bypass the effort of pathologists, these molecular estimates are obtained only after sequencing and analysis of the corresponding molecular tests has been completed. It has also been shown that there is poor concordance between pathologist and molecular estimates of NCP and limited concordance between genomic and transcriptomic derived estimates [8,9].
- In bladder cancer, the accurate measurement of NCP is a difficult task due to its wide range of histologic variation, including sarcomatous dedifferentiation, mucinous and glandular differentiation, significant inflammatory cell infiltration, etc. The lack of an easily applicable and reproducible cell counting method that can be used as the ground truth value has hampered the development of a method for NCP assessment. Multiplex immunofluorescence (mIF) has been developed to simultaneously assess multiple biomarkers and allows a quantitative assessment of the tumor microenvironment, which consists of various immune cells and stromal cells in addition to tumor cells. Therefore, we assumed that mIF could be used for phenotyping and counting tumor cells, stromal cells, and immune cells in bladder cancer to provide a ground truth value of NCP, which is a prerequisite for the development of an accurate method of NCP assessment.
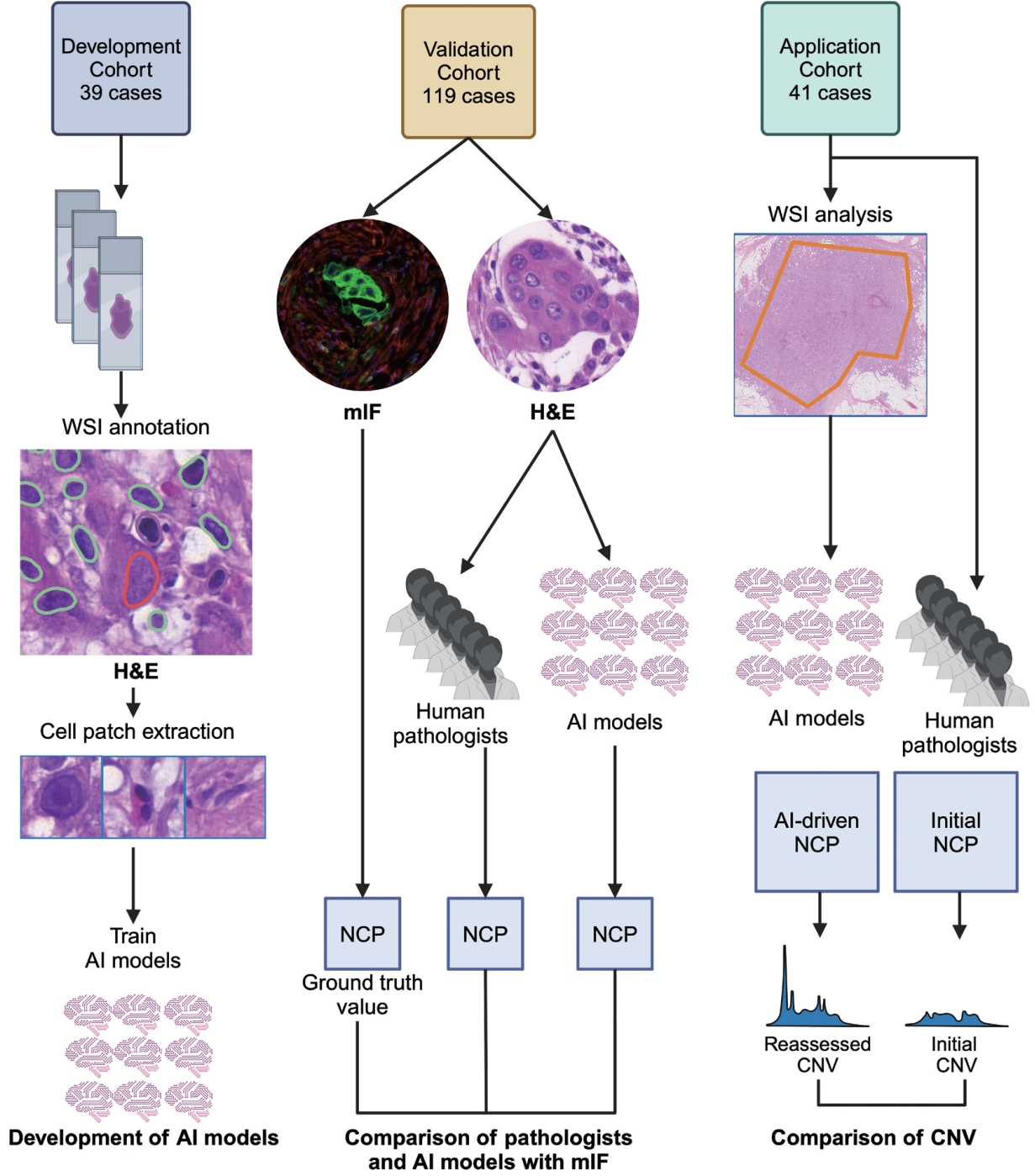
- Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a useful tool for quantitative and qualitative analyses of digital histopathology images [10]. AI-based quantitative image analysis has been reported to be able to estimate NCP in breast cancer and lung cancer, but not in urinary tract cancer [11-13]. In the present study, we developed AI models using digital images of urinary tract malignancies and convolutional neural network (CNN) models. The performance of the AI models was evaluated using mIF-driven NCP as ground truth values and compared to pathologists’ estimates. The impact of AI models on the CNV of actionable genes was analyzed in NGS cases. The workflow diagram of this study is shown in Fig. 1.
- Patients with urinary tract cancer
- It included patients with pathologically confirmed urinary tract malignancies treated at Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea with available clinical information and pathology materials, including H&E-stained slides and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue blocks. Three cohorts were established: a developmental cohort, a validation cohort, and an application cohort. For the developmental cohort, 39 cases were selected from 322 cases of invasive high-grade urothelial carcinoma diagnosed between March 2022 and August 2022 to create cell patches for the training of CNN models. The validation cohort consisted of 119 NGS cases, with samples collected between May 2019 and February 2022, to validate the trained CNN models on cases similar to those in the clinical setting. The application cohort consisted of 41 NGS cases, with samples collected between March 2022 and August 2022, to evaluate the impact of AI-driven NCPs on the CNV of actionable genes identified by NGS analysis.
- Tissue microarray construction
- Tissue microarrays (TMAs) were generated in the validation cohort with 1 mm-diameter cores from 10% neutrally buffered FFPE tumor blocks using a tissue microarrayer (Quick-Ray, Unitma Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea). To ensure that the TMA cores were representative of the validation cohort, three cores were collected from tumor areas that were representative of the histologic type and grade of each case, while attempting to avoid necrotic areas [7]. Different tumor locations (peripheral vs. central) were included, and an attempt was made to ensure that NCPs were evenly distributed by including tumor cells of different cell densities. To provide a negative control for AI-driven NCPs, areas without tumor cells were included.
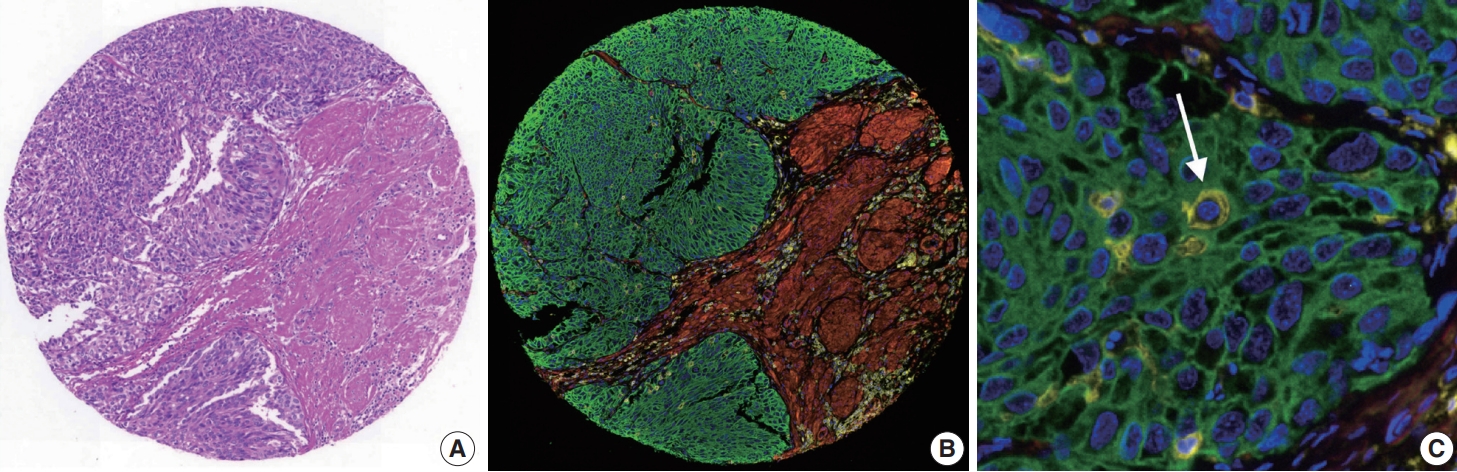
- Multiplex IF and multispectral imaging analysis
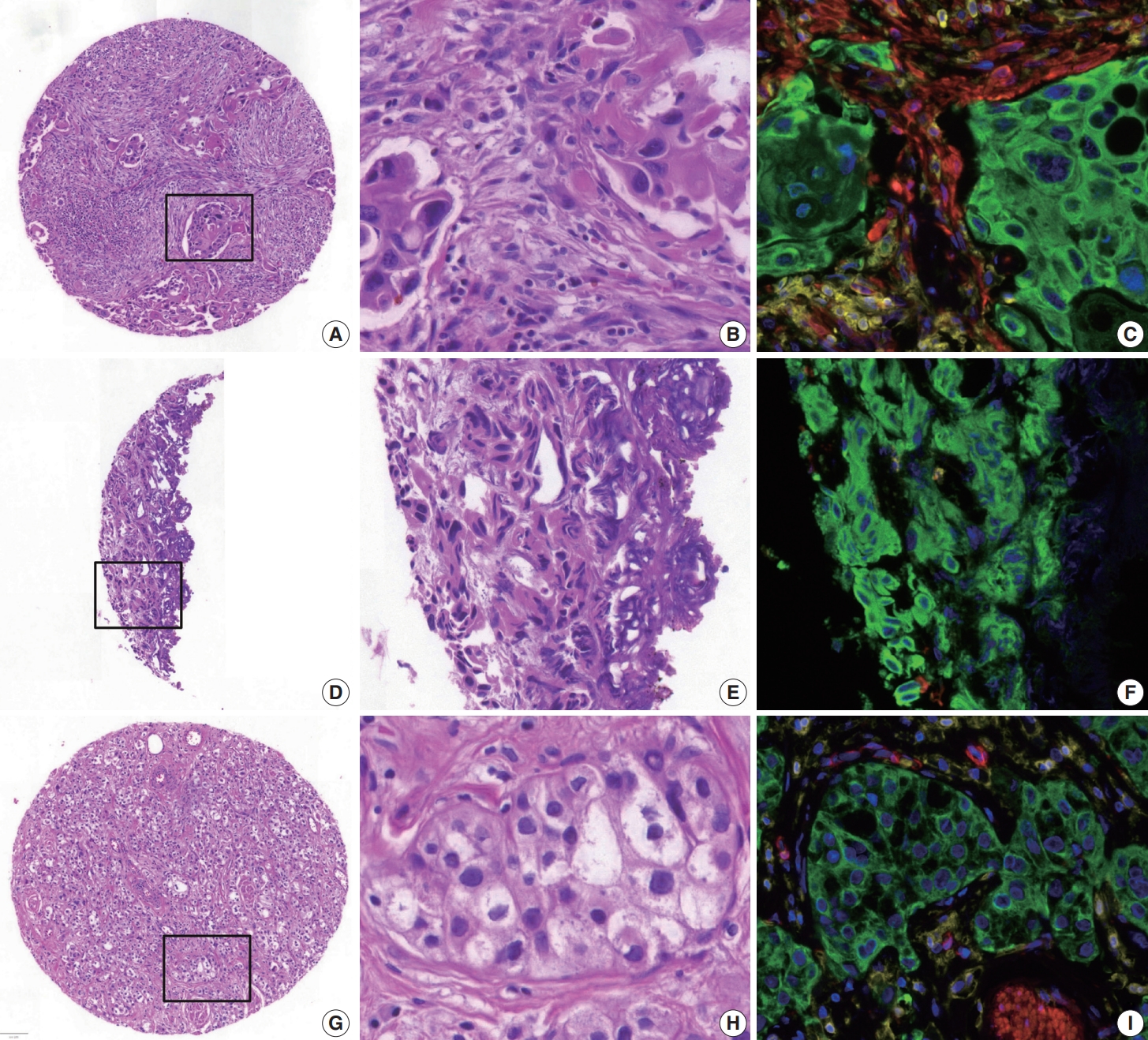
- Four-micron-thick tissue sections were cut from the TMA construct; and then transferred onto plus-charged slides. mIF was performed using a Leica Bond Rx Automated Stainer (Leica Biosystems, Nussloch, Germany) and Opal Polaris 7-Color Automated immunohistochemistry (IHC) Detection Kit (Akoya Biosciences, Marlborough, MA, USA) as previously described [14]. After sequential reactions, the tissue sections were counterstained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) for nuclear staining (62248, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and mounted with ProLong Gold antifade reagent (P36935, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The primary antibodies used in this study were CD45 (1:200, DAKO, Santa Clara, CA, USA) for immune cells, α-smooth muscle actin (SMA; 1:100, Zymed, San Francisco, CA, USA) for stromal cells, and pan-cytokeratin (CK; 1:300, Novus Biologicals, Littleton, CO, USA) for tumor cells with corresponding fluorophores for fluorescence signals Opal 570, Opal 690, and Opal 780, respectively. The multiplex-stained slides were scanned using a Vectra Polaris Automated Quantitative Pathology Imaging System (Akoya Biosciences), and the images were visualized with a Phenochart Whole Slide Viewer (Akoya Biosciences). Phenotyping of cellular components in the images was performed using inForm image analysis software and the phenoptr/phenoptrReports tissue analysis software packages (Akoya Biosciences). Based on the phenotyping, the mIF-driven NCP was calculated for each TMA core and used as the ground truth value.
- Whole-slide scanning
- H&E slides from the developmental and validation cohorts were scanned with a PANNORAMIC 250 Flash II scanner (3D HISTECH, Budapest, Hungary) at 40× magnification with 0.22 μm/pixel in a single layer. A Pathology Scanner SG300 (Philips, Best, The Netherlands) was used at 40× magnification with 0.25 μm/pixel in a single layer for the application cohort.
- Cell patch generation for CNN model training
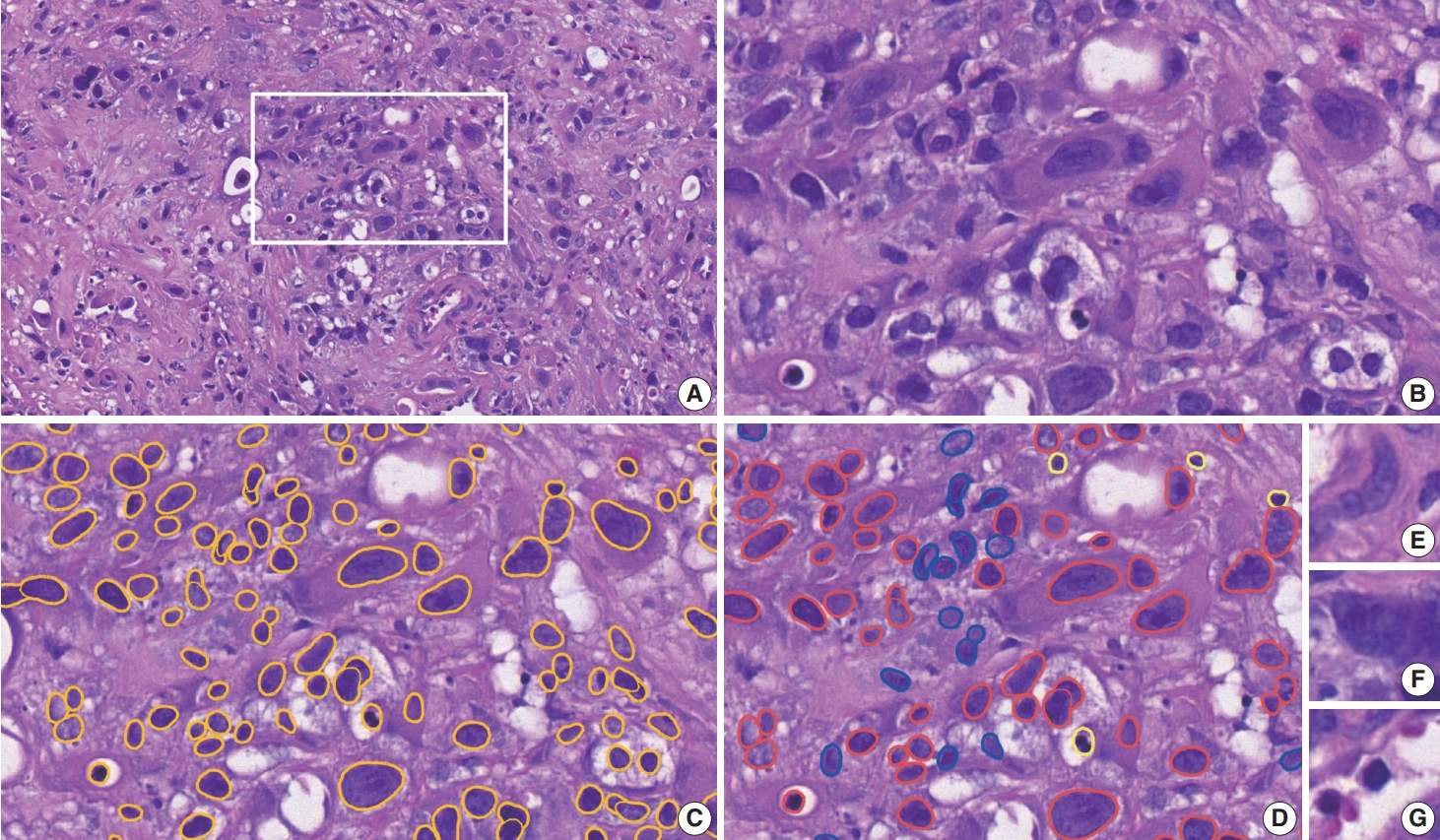
- Scanned slides were assessed using open-source digital pathology software, QuPath v. 3.4.2 [15]. The representative regions of interest, at least one per slide in the developmental cohort, were drawn by one (J.J.) of the authors. Cell nuclei were detected with star-convex polygons using the provided QuPath plugin to avoid incomplete segmentation of overlapping nuclei [16]. The detected cells were then manually classified into three classes: tumor cells, stromal cells, or immune cells. For each detected cell, 100×100 pixel image patches were obtained with their class labels. The extracted cell patches of the three classes were divided into the training set, tuning set, and test set, at a 7:2:1 ratio.
- CNN model training and performance metrics
- Cell patches in the training and tuning sets were transformed into tensors and augmented by Pytorch library ver. 1.12.1 [17]. Cell patches were provided to nine open-source CNN models provided by Pytorch. The models were AlexNet with five convolutional layers and three fully connected layers [18], VGG with 16 convolutional layers and three fully connected layers [19], ResNet with deep convolutional networks (50 layers) and residual learning [20], WideResNet with three increased width residual networks [21], EfficientNet with scaling of depth, width, and resolution [22], EfficientNet V2 optimized with training-aware neural architecture search and scaling [23], MobileNet V2 with inverted residual blocks [24], MobileNet V3 improved with network architecture search and tuning [25], and ShuffleNet V2 focused on direct metrics such as speed [26]. The Adam optimizer was adopted with default hyperparameters (β1=0.9; β2=0.999; ε=1.0×10-8) [27]. The Cross Entropy Loss function and Reduce LR On Plateau function were used as the loss function and learning rate scheduler, respectively. The batch size was set to 128 and the learning epoch was set to 80. The models were computed by two GPUs, RTX 3090 (NVIDIA, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
- The performance of the trained models was evaluated in the predetermined test set with the following parameters: sensitivity, specificity, precision, accuracy, and F1 score.
- Estimation of NCP by pathologists and AI models
- In the validation cohort, six pathologists with varying levels of expertise estimated the NCP of each core using H&E-stained digital images of the TMA construct. The pathologists included one uropathologist (Y.M.C.), two fellows (S.U.J. and B.A.), and three residents (G.H.K., H.J.S., and Y.I.L.). They were instructed to estimate each individual TMA core by eyeball measurement, not by counting cells individually. They provided NCP estimates on a 5% scale, ranging from 0% to 100%.
- To obtain AI-driven NCPs, the trained CNN models were applied on the H&E-stained digital images of the validation and application cohorts. The models classified the cells into three classes (tumor, stroma, or immune cells), and provided AI-driven NCP estimates of each TMA core in the validation cohort and each whole slide image in the application cohort.
- Performance comparison of pathologists and AI models
- The performance of pathologists and AI models in the validation cohort was evaluated by comparing them to mIF-driven NCP as the ground truth value using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) with ICC (2,1) as an individual estimator [28]. The ICC was interpreted as poor (<0.40), fair (0.40–0.59), good (0.60–0.74), and excellent (0.75–1.00) as previously proposed [29,30].
- Selecting significant inter-rater variation in the NCP assessment
- To identify TMA cores with significantly different NCP values between pathologists and AI models compared to the mIF, the mean absolute error (MAE) was calculated using the following formula for each TMA core in the validation cohort. The TMA cores with the top 20 MAE values for each group, pathologist and AI model, were selected for further analysis.
- (xi, AI-driven NCP or pathologist NCP; m, mIF-driven NCP; n, number of estimations)
- Copy number analysis
- The NextSeq 550Dx Sequencing System (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) and DNA-based targeted gene panel (OncoPanel AMC v4.3 panel) were used for NGS analysis as described previously [31-33]. The panel consisted of approximately 1.2 Mbp with 33524 probes targeting 382 genes [31-33]. The tumor area was macrodissected from FFPE tissue blocks and used for DNA extraction. The copy number (CN) analysis was conducted using CNVkit’s “batch” function [34]. The log2 ratio of the “cns” file in the analysis results had been utilized to calculate the estimated CN, using the NCP determined by a pathologist at initial diagnosis. The CN was re-evaluated by incorporating the AI-driven NCP.
- The estimated CN was classified into three groups according to the Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer (COSMIC) [35]. The criteria for CNV were as follows: amplification, total CN≥5; loss, total CN≤0; neutral/minor alteration, total CN, 2–4 [36]. The impact of AI-driven NCP on CNV was assessed on the 166 actionable genes for solid tumors listed at OncoKB, regardless of cancer type and level of evidence [37].
MATERIALS AND METHODS
- Patient cohorts
- In the developmental cohort, 39 cases were selected to include various subtypes, divergent differentiations, image artifacts, and commonly encountered specimen types for the training of CNN models on various pathologic features of urothelial carcinoma (Supplementary Table S1) [38]. Twenty-seven cases were pure invasive urothelial carcinoma. The remaining cases showed various histologic features, either single or in combination and included squamous (5 cases), sarcomatoid (3 cases), glandular (2 cases), small cell neuroendocrine (2 cases), microcystic (1 case), poorly differentiated (1 case), and micropapillary (2 cases) features (Table 1).
- In the validation cohort, in addition to 113 cases of invasive high-grade urothelial carcinoma, it contained collecting duct carcinoma (2 cases), urachal adenocarcinoma (2 cases), invasive squamous cell carcinoma (1 case), and non-invasive low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma (1 case). Fifty-seven cases of urothelial carcinoma were pure form and the others revealed various histologic features either isolated or in combination, including squamous (26 cases), micropapillary (24 cases), sarcomatoid (8 cases), nested (4 cases), giant cell (3 cases), glandular (2 cases), plasmacytoid (2 cases), and microcystic (2 cases) features (Table 1).
- In the application cohort, 21 cases were pure invasive urothelial carcinoma and the remaining revealed squamous (8 cases), micropapillary (4 cases), sarcomatoid (3 cases), plasmacytoid (2 cases), small cell neuroendocrine (2 cases), giant cell (1 case) features, either single or in combination (Table 1).
- Development of CNN models and their performance
- In the development cohort, a total of 291 regions of interest (median, 6; range, 1 to 22 per case) were selected, attempting to include various histologic features of urothelial carcinoma. A total of 133,941 cell patches were extracted, consisting of 76,330 tumor cell patches, 24,297 stromal cell patches, and 33,314 immune cell patches (Fig. 2). The image patches in the training and tuning sets were converted into tensors and subjected to augmentation techniques such as random flipping, rotation, and padding to increase the diversity of the images for the generalization of the CNN models (Supplementary Fig. S1). These augmented patches were then fed into the nine CNN models to train them to classify cell patches into the three specified classes.
- When the model performance was evaluated at the patch level using the test set, EfficientNet showed the highest sensitivity (0.94) and accuracy (0.87). AlexNet and VGG demonstrated low accuracy (0.55, each) and therefore were excluded from further analysis (Table 2).
- Calculation of mIF-driven NCP as the ground truth value
- In the TMA construct generated from the validation cohort, 335 cores were available for mIF staining of pan-cytokeratin, CD45, and SMA (Fig. 3). The proportion of cells with a single immunophenotype, positive for only one marker, was 89.4%. The most common double-positive immunophenotype was double-positivity for CD45 and SMA, accounting for 6.9% of the total cell count. This was followed by double-positivity for CK and SMA, accounting for 0.4% of the total cell count (Supplementary Table S2). Since only tumor cells were used to estimate NCP, not immune and stromal cells, it was calculated by dividing the number of cytokeratin-positive tumor cells by the total number of DAPI-positive cells. The median NCP of the TMA cores was 51% (range, 0% to 99%) (Supplementary Fig. S2). Fifteen cores contained no tumor cells and 71 cores contained an NCP less than 20%, which is the cutoff value generally considered adequate for reliable mutation detection in NGS testing. There were no significant differences in the mIF-driven NCP estimates between tumor locations, procedures, or histology subtypes (data not shown).
- Assessment of NCP by pathologists and AI models with comparison to mIF-driven NCP
- The pathologists estimated the NCP of the TMA cores from the validation cohort with excellent reliability. The ICC values were within a range of 0.78 to 0.91, with the uropathologist estimating NCP with the highest reliability, 0.91 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.89 to 0.93) (Table 3).
- AI models also estimated NCP with excellent reliability, with ICCs ranging from 0.83 to 0.88. The most reliable model was EfficientNet with an ICC of 0.88 (95% CI, 0.78 to 0.92) (Table 3). MobileNet V3 showed the lowest agreement with the mIF-driven NCP with an ICC of 0.82 (95% CI, 0.7 to 0.88) (Table 3).
- Performance comparison between AI models and pathologists
- In general, the AI models showed a higher level of agreement with the mIF-driven NCP than did the pathologists, although the one uropathologist had the highest agreement of all raters. Even the lowest AI model, MobileNet V3, had a higher or similar level of agreement than all but one of the pathologists (Table 3). When the distribution of NCP estimates by the six individual pathologists and seven AI models were assessed for each TMA core, pathologists’ NCP estimates were more variable in each range of NCP than AI-driven NCP estimates. However, the AI models tended to underestimate NCP when the mIF estimates were greater than 60% (Supplementary Fig. S3). They often misclassified neoplastic cells as stromal or immune cells when their nuclei became spindle-shaped or pyknotic due to degeneration, detachment from the epithelium, cauterization, and/or abundant cytoplasm. (Supplementary Table S3, Supplementary Fig. S4).
- Performance comparison between AI models and pathologists according to histological variation
- To evaluate the accuracy of NCP assessment according to histological variation, we divided the validation cohort into three groups: the pure form of urothelial carcinoma without divergent differentiation/subtype, urothelial carcinoma with divergent differentiation/subtype, and non-urothelial carcinoma, which included squamous cell carcinoma and urachal adenocarcinoma. The performance was measured against mIF-driven NCP (Supplementary Table S4).
- The estimation of NCP by pathologists was excellent with and without divergent differentiation/subtype (minimum ICC, 0.76 and 0.82, respectively), but the performance was decreased in non-urothelial carcinoma (minimum ICC, 0.61). The AI models demonstrated better or similar performance than the pathologists in cases of urothelial carcinoma, both with and without divergent differentiation/subtype (minimum ICC, 0.87 and 0.81, respectively). However, the performance of the AI models was markedly decreased in non-urothelial carcinoma cases, showing lower agreement (minimum ICC, 0.33) with mIF-driven NCP than those of pathologists (Supplementary Table S4).
- Analysis of highly discrepant cases in NCP estimation
- The top 20 TMA cores with high disagreement among pathologists showed abundant stroma (n=5), large tumor cells with abundant cytoplasm (n=4), cauterization artifact (n=2), dense infiltration of inflammatory cells (n=2), keratinization (n=1), and mucinous histology (n=1). Inaccurate assessment of mIF-driven NCP also resulted in high inter-pathologist discrepancies and was noted in cores with suboptimal cytokeratin staining (n=3), degeneration (n=1), and normal lung tissue (n=1).
- The top 20 TMA cores with high disagreement among the AI-models was noted in cores with cauterization (n=5), abundant stroma (n=3), spindling of tumor nuclei (n=3), dense infiltration of inflammatory cells (n=2), mucinous histology (n=2), hypocellular stroma (n=1), keratinization (n=1), and abundant cytoplasm of tumor cells (n=1). Inaccurate assessment of mIF-driven NCP was also noted in cores with suboptimal cytokeratin staining (n=2) (Fig. 4).
- Impact of AI-driven NCP estimation on CNV
- In the application cohort, a total of 785 CNVs (median, 16; range 1 to 120 per case) were reported at initial diagnosis with 173 amplifications (22.0%), 77 losses (9.8%), and 535 neutral/minor alterations (68.2%).
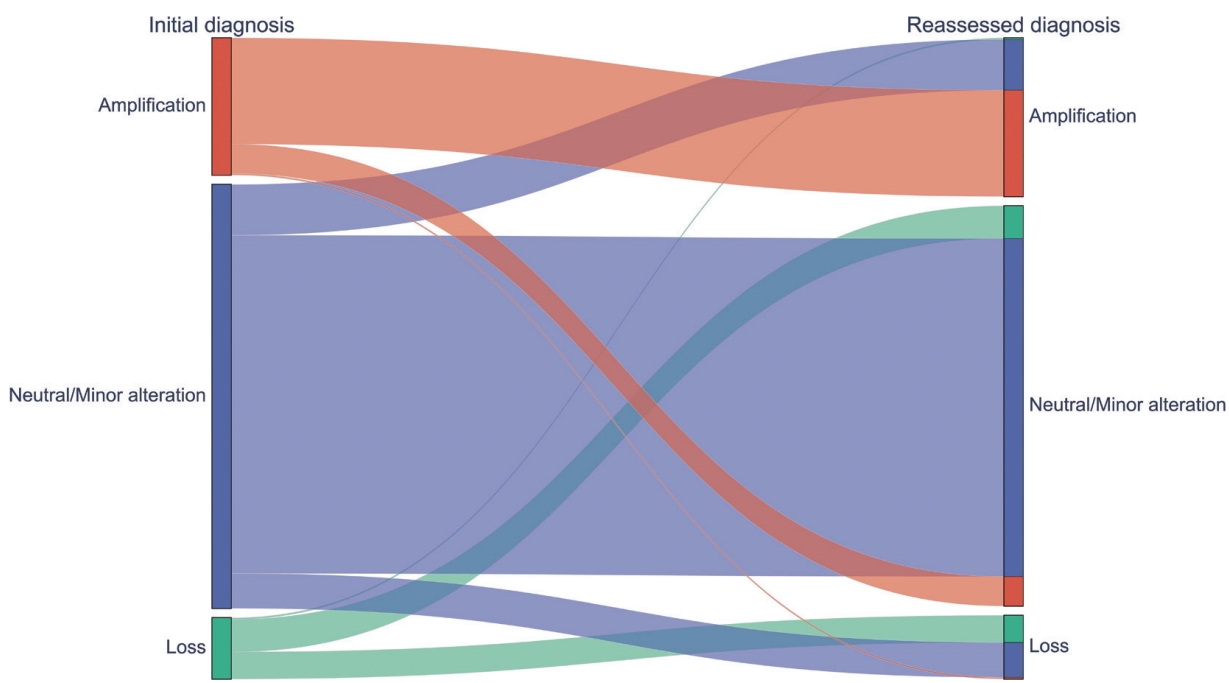
- AI-driven NCP was assessed using EfficientNet, which had the highest correlation with mIF. After applying the AI-driven NCP, 595 CNVs (75.8%) remained in the original groups and 190 (24.2%) were reclassified, resulting in 200 amplifications (25.5%), 80 losses (10.2%), and 505 neutral/minor alterations (64.3%). The 190 CNVs were reclassified into 66 amplifications (8.4%), 46 losses (5.9%), and 78 neutral/minor alterations (9.9%). Of note, 108 neutral/minor alterations (13.8%) at initial diagnosis were reclassified into either amplification (n=64, 8.2%) or loss (n=44, 5.6%) with the AI-driven NCPs, while neutral/minor alterations were reduced by 5.6%. Among the 77 CN losses at initial diagnosis, 41 (53.2%) were reclassified into neutral/minor alterations (Fig. 5, Supplementary Fig. S5).
- Among the reclassified 190 CNVs, 55 CNVs belonged to actionable genes with 16 CNVs reclassified to amplification from loss or neutral/minor alteration and 16 CNVs reclassified to loss from amplification or neutral/minor alteration. The genes of 16 CNVs had therapeutic drugs associated with the corresponding CNV.
RESULTS
- Here we report that AI models for NCP estimation in urinary tract cancer could be developed using open-source CNN models. The performance of the AI models was comparable to or better than that of pathologists. The application of the AI models reclassified a significant proportion of CNVs, with an increase of CN amplifications and losses and a decrease in neutral/minor CN alterations. In addition, we showed that mIF staining could be used to calculate NCP as a ground truth value for the development of AI models.
- Since the estimation of NCP is critical for accurate interpretation of NGS results, which are important for treatment decision making, it has been recommended that NCP estimation should be performed by the pathologist evaluating the case by selecting the area with the highest density of viable neoplastic cells and avoiding areas with inflammatory cells, necrosis, desmoplastic stroma, and mucus [7]. Since there is significant interpathologist variation in NCP estimates [39], innovative techniques such as in silico analysis and digital estimation have been developed to overcome this issue. However, in order to develop new technologies, accurate NCPs must be available for use as a ground truth value, but obtaining this ground truth value has been a challenge. There has been limited study using mIF to obtain ground truth values, while IHC was used to create a ground truth value generated by manual annotation of tumor cells with reference to immunostained slides with thyroid transcription factor-1and napsin A for NCP in lung cancer [40].
- Our study applied mIF as a new method for calculating NCP and used the mIF-driven estimates as a ground truth value, which is generally reliable but needs improvement. The cytoplasm stained for cytokeratin in tumor cells and CD45 in immune cells circumferentially surrounded the nuclei, so tumor cells and immune cells were easily immunophenotyped, but SMA staining was difficult to evaluate because the cell shapes were elongated and curved. Occasionally, cytoplasm outside the cross-section containing the nucleus interspersed between other cell types may appear as double/triple positive cells. In addition, cell types that cannot be defined by the three antibody types, such as neuronal cells, may be counted as unphenotyped cells. Nevertheless, the unphenotyped mesenchymal cells and double-positive cells for CD45 and ɑSMA did not affect NCP estimation because only cytokeratin-positive tumor cells among the total DAPI-positive nuclei were calculated for NCP estimation. The CK and SMA double-positive cells, which may represent myofibroblasts, were low at 0.4% of the total cell count with an insignificant impact on NCP. Suboptimal cytokeratin staining was noted in few TMA cores and resulted in inaccurate estimates of mIF-driven NCP, which needs to be improved by further development of the mIF technique and image analysis software. In addition, NCP assessment should be performed on a well-preserved representative viable tumor area, avoiding tissue degeneration and cauterization artifacts.
- After applying the AI-driven estimates in the application cohort, a significant proportion of cases were recategorized to have amplification or loss of CN on actionable target genes with a decrease of neutral/minor CN alteration, which would affect decision making for targeted drugs. It is worth noting that the majority of the CN loss at initial diagnosis was reclassified into the neutral/minor CN alteration group after applying AI-driven NCP estimates, implying that assigning CN loss should be cautious during CNV interpretation.
- As previously pointed out, a wide range of inter-pathologist variation was observed for samples with dense or scattered lymphocytic infiltrates or with mucinous stroma [39]. In addition, this study demonstrates that abundant stroma, cauterization and/or crush artifacts, and tumor cells with non-classic morphology, such as abundant cytoplasm and histologic subtypes, may lead to an inaccurate estimation of NCP and should be carefully evaluated.
- Although the AI models were developed using limited training data from the developmental cohort, they provided reliable estimates of NCP in the validation cohort with a larger number of cases and a more diverse range of histological features. The AI model could also be applied to the digital images with variations in the quality of H&E slides scanned by different whole slide image scanners in the application cohort. The developmental cohort consisted of invasive urothelial carcinoma cases and the AI models were not specifically trained on non-urothelial carcinoma cases such as mucinous adenocarcinoma. Nevertheless, the AI models showed fair to good reliability, although their performance was significantly reduced compared to urothelial carcinoma cases. This suggests that the models have a degree of generalizability across diverse tumor morphologies of urinary cancers. However, it is also worth noting that the AI model underestimated NCP in cases with a higher NCP, indicating a need for further improvement of the model, especially when tumor tissues contained cauterization artifacts, or neoplastic cells with spindled or pyknotic nuclei, or abundant cytoplasm. The AI models could be improved if they were been trained on a dataset containing more of these features. While the performance of older AI models such as AlexNet and VGG was less satisfactory in classifying tumor cell patches, newer AI models with various levels of computational resources and cognitive abilities performed similarly, with accuracies above 0.85, and none of them showed a particularly superior performance.
- This present study was associated with limitations, including its retrospective design and nature as a single-center study with a small number of cases. The uropathologist evaluation was excellent, but it is hard to generalize because it was only one person. In the future, these AI models need to be validated by a prospective multicenter study with a larger number of cases and participating pathologists. Further advances in mIF technology and in computational pathology will continue to increase the accuracy of AI models.
DISCUSSION
Supplementary Information
Ethics Statement
The Institutional Review Board of the Asan Medical Center, Republic of Korea (#2022-1558) approved this study. All of the clinical investigations were conducted in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Formal written informed consent was not required with a waiver by the appropriate IRB research ethics committee.
Availability of Data and Material
All raw data are available for researchers who reasonably request them from the corresponding author with approval of the institutional review boards.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: JJ, YMC. Formal analysis: JJ. Funding Acquisition: YMC. Methodology: JJ, DK. Resources: YMR, SYK, BA, GHK, SUJ, HJS, YIL, JMP, SYY. Supervision: YMC. Visualization: JJ. Writing—original draft preparation: JJ. Writing—review & editing: YMC. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Funding Statement
This study was supported by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (2019R1A2C1088246) and a grant (2023IP0052-1) from the Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
| Variable | Developmental cohort (n = 39) | Validation cohort (n = 119) | Application cohort (n = 41) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 30 (76.9) | 91 (76.5) | 30 (73.2) |
| Female | 9 (23.1) | 28 (23.5) | 11 (26.8) |
| Age (yr) | 72 (43–97) | 67.5 (35–90) | 68 (43–86) |
| Tumor location | |||
| Urinary bladder | 29 (74.4) | 52 (43.7) | 20 (48.8) |
| Renal pelvis | 4 (10.3) | 19 (16.0) | 11 (26.8) |
| Ureter | 6 (15.4) | 33 (27.7) | 8 (19.5) |
| Othersa | 0 | 15 (12.6) | 2 (4.9) |
| Procedure | |||
| Transurethral resection | 26 (66.7) | 23 (19.3) | 10 (24.4) |
| Curative surgeryb | 13 (33.3) | 86 (72.3) | 23 (56.1) |
| Endoscopic biopsy | 0 | 1 (0.8) | 8 (19.5) |
| Metastatectomyc | 0 | 9 (7.6) | 0 |
| 2022 WHO grade | |||
| Low | 0 | 1 (0.8) | 0 |
| High | 39 (100) | 113 (95.0) | 41 (100) |
| Histologic variation | |||
| None (pure form) | 27 (62.8) | 57 (47.9) | 21 (50) |
| Squamous | 5 (11.6) | 26 (21.8) | 8 (19.0) |
| Sarcomatoid | 3 (7.0) | 8 (6.7) | 3 (7.1) |
| Glandular | 2 (4.7) | 2 (1.7) | 0 |
| Small cell | 2 (4.7) | 0 | 2 (4.8) |
| Micropapillary | 2 (4.7) | 24 (20.2) | 4 (9.5) |
| Poorly differentiated | 1 (2.3) | 0 | 0 |
| Microcystic | 1 (2.3) | 2 (1.7) | 0 |
| Othersd | 0 | 9 (7.6) | 4 (9.5) |
| Nonurotheliale | 0 | 5 (4.2) | 0 |
Values are presented as median (range) or number (%).
WHO, World Health Organization.
aThis category includes urethra, regional lymph node, distant organ metastasis, and kidney (for collecting duct carcinoma);
bCurative surgery includes radical cystectomy, nephroureterectomy, distal ureterectomy, and partial cystectomy specimens;
cMetastectomy sites are lymph nodes, peritoneum, adrenal gland, and lung;
dIn the validation cohort, invasive urothelial carcinoma with nested (4 cases), giant cell (3 cases), and plasmacytoid (2 cases) features were included. In the application cohort, plasmacytoid (3 cases) and giant cell (1 case) features were included;
eNon-urothelial carcinoma includes collecting duct carcinoma, urachal adenocarcinoma, and pure squamous cell carcinoma cases.
- 1. Robertson AG, Kim J, Al-Ahmadie H, et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cell 2018; 174: 1033.PubMedPMC
- 2. Loriot Y, Necchi A, Park SH, et al. Erdafitinib in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2019; 381: 338-48. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Sheng X, Yan X, Wang L, et al. Open-label, multicenter, phase II study of RC48-ADC, a HER2-targeting antibody-drug conjugate, in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2021; 27: 43-51. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Patelli G, Zeppellini A, Spina F, et al. The evolving panorama of HER2-targeted treatments in metastatic urothelial cancer: a systematic review and future perspectives. Cancer Treat Rev 2022; 104: 102351.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Zare F, Dow M, Monteleone N, Hosny A, Nabavi S. An evaluation of copy number variation detection tools for cancer using whole exome sequencing data. BMC Bioinformatics 2017; 18: 286.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 6. Smits AJ, Kummer JA, de Bruin PC, et al. The estimation of tumor cell percentage for molecular testing by pathologists is not accurate. Mod Pathol 2014; 27: 168-74. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Dufraing K, van Krieken JH, De Hertogh G, et al. Neoplastic cell percentage estimation in tissue samples for molecular oncology: recommendations from a modified Delphi study. Histopathology 2019; 75: 312-9. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 8. Haider S, Tyekucheva S, Prandi D, et al. Systematic assessment of tumor purity and its clinical implications. JCO Precis Oncol 2020; 4: PO.20.00016.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Yadav VK, De S. An assessment of computational methods for estimating purity and clonality using genomic data derived from heterogeneous tumor tissue samples. Brief Bioinform 2015; 16: 232-41. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Baxi V, Edwards R, Montalto M, Saha S. Digital pathology and artificial intelligence in translational medicine and clinical practice. Mod Pathol 2022; 35: 23-32. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 11. Azimi V, Chang YH, Thibault G, et al. Breast cancer histopathology image analysis pipeline for tumor purity estimation. Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging 2017; 2017: 1137-40. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Lin S, Samsoondar JP, Bandari E, et al. Digital quantification of tumor cellularity as a novel prognostic feature of non-small cell lung carcinoma. Mod Pathol 2023; 36: 100055.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Amin MB. Histological variants of urothelial carcinoma: diagnostic, therapeutic and prognostic implications. Mod Pathol 2009; 22 Suppl 2: S96-118. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Ahn J, Jin M, Song E, et al. Immune profiling of advanced thyroid cancers using fluorescent multiplex immunohistochemistry. Thyroid 2021; 31: 61-7. ArticlePubMed
- 15. Bankhead P, Loughrey MB, Fernandez JA, et al. QuPath: open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 16878.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Schmidt U, Weigert M, Broaddus C, Myers G. Cell detection with star-convex polygons. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention - MICCAI 2018, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 11071; 2018 Sep 16-20; Granada, Spain.
- 17. Paszke A, Gross S, Massa F, et al. Pytorch: an imperative style, highperformance deep learning library. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32, NeurIPS 2019; 2019 Dec 8-14; Vancouver, BC, Canada.
- 18. Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vol. 1; 2012 Dec 3-6; Lake Tahoe, Nevada, CA, USA.
- 19. Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. Preprint arXiv at: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1409.1556 (2014). Article
- 20. He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); 2016 Jun 27-30; Las Vegas, NV, USA.
- 21. Zagoruyko S, Komodakis N. Wide residual networks. Preprint arXiv at: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1605.07146 (2016). Article
- 22. Tan M, Le Q. EfficientNet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR); 2019 Jun 9-15; Long Beach, CA, USA.
- 23. Tan M, Le Q. Efficientnetv2: smaller models and faster training. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR); 2021 Jul 18-24; Virtual Event.
- 24. Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, Zhmoginov A, Chen LC. Mobilenetv2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2018 Jun 18-23; Salt Lake City, UT, USA.
- 25. Howard A, Sandler M, Chen B, et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision; 2019 Oct 27-Nov 2; Seoul, Korea.
- 26. Ma N, Zhang X, Zheng HT, Sun J. Shufflenet v2: practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2018); 2018 Sep 8-14; Munich, Germany.
- 27. Kingma DP, Ba J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. Preprint arXiv at: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1412.6980 (2014). Article
- 28. Shrout PE, Fleiss JL. Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 1979; 86: 420-8. ArticlePubMed
- 29. Robert ME, Ruschoff J, Jasani B, et al. High interobserver variability among pathologists using combined positive score to evaluate PDL1 expression in gastric, gastroesophageal junction, and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol 2023; 36: 100154.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Cicchetti DV. Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psychol Assess 1994; 6: 284-90. Article
- 31. Kim JE, Chun SM, Hong YS, et al. Mutation burden and I index for detection of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer by targeted next-generation sequencing. J Mol Diagn 2019; 21: 241-50. ArticlePubMed
- 32. Kim M, Lee C, Hong J, et al. Validation and clinical application of ONCOaccuPanel for targeted next-generation sequencing of solid tumors. Cancer Res Treat 2023; 55: 429-41. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 33. Oh JH, Sung CO, Kim HD, Chun SM, Kim J. BRCA-mutated gastric adenocarcinomas are associated with chromosomal instability and responsiveness to platinum-based chemotherapy. J Pathol Transl Med 2023; 57: 323-31. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 34. Talevich E, Shain AH, Botton T, Bastian BC. CNVkit: genome-wide copy number detection and visualization from targeted DNA sequencing. PLoS Comput Biol 2016; 12: e1004873. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Tate JG, Bamford S, Jubb HC, et al. COSMIC: the catalogue of somatic mutations In cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 2019; 47: D941-7. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Zhao M, Zhao Z. Concordance of copy number loss and down-regulation of tumor suppressor genes: a pan-cancer study. BMC Genomics 2016; 17 Suppl 7: 532.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Suehnholz SP, Nissan MH, Zhang H, et al. Quantifying the expanding landscape of clinical actionability for patients with cancer. Cancer Discov 2024; 14: 49-65. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 38. Homeyer A, Geissler C, Schwen LO, et al. Recommendations on compiling test datasets for evaluating artificial intelligence solutions in pathology. Mod Pathol 2022; 35: 1759-69. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 39. Lhermitte B, Egele C, Weingertner N, et al. Adequately defining tumor cell proportion in tissue samples for molecular testing improves interobserver reproducibility of its assessment. Virchows Arch 2017; 470: 21-7. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 40. Sakamoto T, Furukawa T, Pham HH, et al. A collaborative workflow between pathologists and deep learning for the evaluation of tumour cellularity in lung adenocarcinoma. Histopathology 2022; 81: 758-69. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure






Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 4.
Fig. 5.
Graphical abstract
| Variable | Developmental cohort (n = 39) | Validation cohort (n = 119) | Application cohort (n = 41) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 30 (76.9) | 91 (76.5) | 30 (73.2) |
| Female | 9 (23.1) | 28 (23.5) | 11 (26.8) |
| Age (yr) | 72 (43–97) | 67.5 (35–90) | 68 (43–86) |
| Tumor location | |||
| Urinary bladder | 29 (74.4) | 52 (43.7) | 20 (48.8) |
| Renal pelvis | 4 (10.3) | 19 (16.0) | 11 (26.8) |
| Ureter | 6 (15.4) | 33 (27.7) | 8 (19.5) |
| Others |
0 | 15 (12.6) | 2 (4.9) |
| Procedure | |||
| Transurethral resection | 26 (66.7) | 23 (19.3) | 10 (24.4) |
| Curative surgery |
13 (33.3) | 86 (72.3) | 23 (56.1) |
| Endoscopic biopsy | 0 | 1 (0.8) | 8 (19.5) |
| Metastatectomy |
0 | 9 (7.6) | 0 |
| 2022 WHO grade | |||
| Low | 0 | 1 (0.8) | 0 |
| High | 39 (100) | 113 (95.0) | 41 (100) |
| Histologic variation | |||
| None (pure form) | 27 (62.8) | 57 (47.9) | 21 (50) |
| Squamous | 5 (11.6) | 26 (21.8) | 8 (19.0) |
| Sarcomatoid | 3 (7.0) | 8 (6.7) | 3 (7.1) |
| Glandular | 2 (4.7) | 2 (1.7) | 0 |
| Small cell | 2 (4.7) | 0 | 2 (4.8) |
| Micropapillary | 2 (4.7) | 24 (20.2) | 4 (9.5) |
| Poorly differentiated | 1 (2.3) | 0 | 0 |
| Microcystic | 1 (2.3) | 2 (1.7) | 0 |
| Others |
0 | 9 (7.6) | 4 (9.5) |
| Nonurothelial |
0 | 5 (4.2) | 0 |
| Model | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | Accuracy | F1-score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlexNet | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.71 |
| VGG | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.71 |
| EfficientNet | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.92 |
| EfficientNet V2 | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.91 |
| MobileNet V2 | 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.90 |
| MobileNet V3 | 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.90 |
| ResNet | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.91 |
| WideResNet | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.91 |
| ShuffleNet V2 | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.91 |
| Rater | ICC | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Pathologist | ||
| Uropathologist | 0.91 | 0.89–0.93 |
| Fellow 1 | 0.80 | 0.53–0.89 |
| Fellow 2 | 0.82 | 0.78–0.85 |
| Resident 1 | 0.78 | 0.72–0.83 |
| Resident 2 | 0.82 | 0.78–0.85 |
| Resident 3 | 0.81 | 0.73–0.86 |
| AI models | ||
| EfficientNet | 0.88 | 0.78–0.92 |
| EfficientNet V2 | 0.87 | 0.84–0.89 |
| MobileNet V2 | 0.87 | 0.85–0.90 |
| MobileNet V3 | 0.82 | 0.70–0.88 |
| ResNet | 0.86 | 0.76–0.91 |
| WideResNet | 0.85 | 0.80–0.88 |
| ShuffleNet V2 | 0.83 | 0.74–0.88 |
Values are presented as median (range) or number (%). WHO, World Health Organization. This category includes urethra, regional lymph node, distant organ metastasis, and kidney (for collecting duct carcinoma); Curative surgery includes radical cystectomy, nephroureterectomy, distal ureterectomy, and partial cystectomy specimens; Metastectomy sites are lymph nodes, peritoneum, adrenal gland, and lung; In the validation cohort, invasive urothelial carcinoma with nested (4 cases), giant cell (3 cases), and plasmacytoid (2 cases) features were included. In the application cohort, plasmacytoid (3 cases) and giant cell (1 case) features were included; Non-urothelial carcinoma includes collecting duct carcinoma, urachal adenocarcinoma, and pure squamous cell carcinoma cases.
CNN, convolutional neural network.
AI, artificial intelligence; NCP, neoplastic cell percentage; mIF, multiplex immunofluorescence; ICC, intraclass correlation coefficient; CI, confidence interval.

 E-submission
E-submission