Current issue
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Current issue
Editorial
- Advancing pathology through sixty volumes: reflections and future directions
- Chan Kwon Jung, So Yeon Park, Soon Won Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):1-5. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.08
- 1,819 View
- 14 Download
Review Articles
- A comprehensive review of ossifying fibromyxoid tumor: insights into its clinical, pathological, and molecular landscape
- Kyriakos Chatzopoulos, Antonia Syrnioti, Mohamed Yakoub, Konstantinos Linos
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):6-19. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.02
- 1,282 View
- 55 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor (OFMT) is a rare mesenchymal neoplasm first described in 1989. It typically arises in the superficial soft tissues of the extremities as a slow-growing, painless mass. Histologically, it is commonly characterized by a multilobular architecture composed of uniform epithelioid cells embedded in a fibromyxoid matrix, often surrounded by a rim of metaplastic bone. While classic cases are readily identifiable, the tumor's histopathological heterogeneity can mimic a range of benign and malignant neoplasms, posing significant diagnostic challenges. Molecularly, most OFMTs harbor PHF1 rearrangements, commonly involving fusion partners such as EP400, MEAF6, or TFE3. This review underscores the importance of an integrated diagnostic approach- incorporating histopathological, immunohistochemical, and molecular data- to accurately classify OFMT and distinguish it from its mimics. Expanding awareness of its morphologic and molecular spectrum is essential for precise diagnosis, optimal patient management, and a deeper understanding of this enigmatic neoplasm.
- Solitary fibrous tumor: an updated review
- Joon Hyuk Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):20-46. Published online December 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.08
- 1,195 View
- 90 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) is a fibroblastic neoplasm characterized by a branching, thin-walled dilated staghorn-shaped (hemangiopericytoma-like) vasculature and a NAB2::STAT6 gene fusion. SFTs can occur in almost any anatomical location, including superficial and deep soft tissues, visceral organs, and bone. They most commonly occur in extrapleural locations, equally affect both sexes, and are typically present in adults. Although metastasis is rare, SFTs frequently show local recurrence. The diagnosis of SFTs is difficult because of their broad histological and morphological overlap with other neoplasms. An accurate diagnosis is important for guiding disease management and prognosis. Despite advances in molecular diagnostics and therapeutic strategies, the biological complexity and unpredictable clinical behavior of SFTs present significant challenges. This review provides an updated overview of SFT, with a focus on its molecular genetics, histopathological features, and diagnostic considerations.
Original Articles
- Clinicopathological and molecular mechanisms of CLDN18.2 in gastric cancer aggressiveness: a high-risk population study with multi-omics profiling
- Hengquan Wu, Mei Li, Gang Wang, Peiqing Liao, Peng Zhang, Luxi Yang, Yumin Li, Tao Liu, Wenting He
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):47-57. Published online January 5, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.11
- 1,118 View
- 88 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The tight junction protein claudin18.2 (CLDN18.2) has been implicated in poor prognosis and suboptimal immunotherapy response in gastric cancer (GC). This study investigates the clinicopathological relevance of CLDN18.2 expression and its association with molecular subtypes in GC patients from a high-incidence region, combining transcriptomic and proteomic approaches to explore how CLDN18.2 contributes to progression and metastasis.
Methods
A retrospective cohort of 494 GC patients (2019–2024) underwent immunohistochemical analysis for CLDN18.2, Epstein-Barr virus (Epstein–Barr virus–encoded RNA), p53, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and mismatch repair proteins (MLH1, MSH2, PMS2, and MSH6). CLDN18.2 positivity was defined as moderate to strong (2+/3+) membranous staining in ≥75% of tumor cells. Clinicopathological correlations, biomarker associations, and survival outcomes were evaluated. Transcriptomic and proteomic sequencing was performed to explore molecular mechanisms.
Results
CLDN18.2 positivity was observed in 26.9% (133/494) of gastric adenocarcinomas. CLDN18.2-positive tumors correlated with TNM stage (p = .003) and shorter overall survival (p = .018). No associations were identified with age, sex, HER2 status, microsatellite instability, or Epstein-Barr virus infection. Transcriptomic profiling revealed CLDN18.2-high tumors enriched in pathways involving cell junction disruption, signaling regulation, and immune modulation. Proteomic profiling showed that tumors with high CLDN18.2 were enriched in multiple mechanism-related pathways such as integrated metabolic reprogramming, cytoskeletal recombination, immune microenvironment dysregulation, and pro-survival signaling. These mechanisms may collectively contribute to tumor progression and metastasis.
Conclusions
CLDN18.2 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in GC patients. Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses demonstrate that CLDN18.2 promotes tumor progression and metastasis, underscoring its potential as an independent prognostic factor in regions with a high incidence of GC.
- The significance of papillary architecture in the follow-up biopsies of patients with progestin-treated atypical endometrial hyperplasia
- Wangpan J. Shi, Oluwole Fadare
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):58-68. Published online January 8, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.12
- 871 View
- 70 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Follow-up biopsies in patients with progestin-treated atypical endometrial hyperplasia/endometrioid intraepithelial neoplasia (AH/EIN) may show papillary structures, the significance of which is unclear. Methods: The authors reviewed 253 serial specimens of 84 consecutive patients diagnosed with AH/EIN, inclusive of each patient's pre-progestin treatment sample and all post-treatment specimens. We assessed the predictive relationship between papillary architecture in a post-treatment biopsy and two study outcomes: AH/EIN or carcinoma in at least one sample subsequent to the one in which papillae were identified, and/or the last specimen received for that patient. Results: Papillae were identified in only 51.5% of pre-treatment samples but were present in at least one subsequent post-treatment sample for all patients. Post-treatment samples that exhibited papillae and no glandular crowding were associated with AH/EIN in at least one subsequent specimen in 39.7% (29/73) of cases, compared to 24.0% (6/25) in samples with neither papillae nor glandular crowding (p = .227) and 64.0% (16/25) in samples with concurrent gland crowding and papillae (p = .048). Univariate logistic regression analyses showed that the presence of papillae was not associated with study outcomes (odds ratio [OR], 0.99; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.49 to 1.99; p = .985), as compared with gland crowding (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.04 to 2.27; p = .031), or concurrent papillae and gland crowding (OR, 2.36; 95% CI, 1.01 to 5.52; p = .048). Conclusions: In post-treatment samples of progestin-treated AH/EIN, the presence of papillary architecture was not demonstrably associated with study outcomes independent of gland crowding, although the concurrent presence of both features may be significantly predictive.
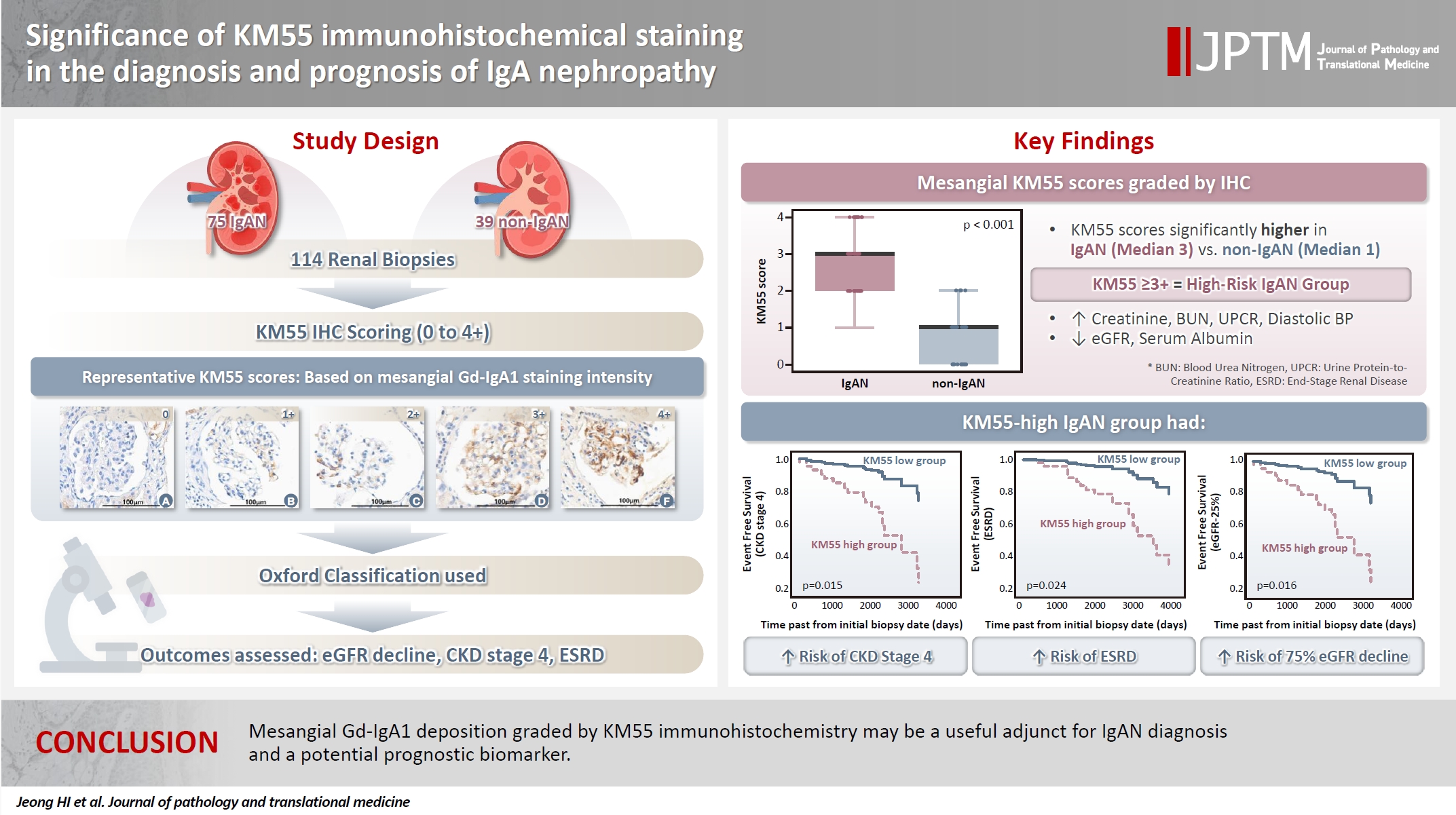
- Significance of KM55 immunohistochemical staining in the diagnosis and prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Hoe In Jeong, Beom Jin Lim, Minsun Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):69-82. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.17
- 1,147 View
- 67 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) plays a crucial role in IgA nephropathy (IgAN). The monoclonal antibody KM55 has emerged as a simplified method for detecting Gd-IgA1; however, the clinicopathological significance of immunohistochemistry for Gd-IgA1 remains underexplored. This study evaluated the prognostic and clinicopathological significance of KM55 immunohistochemistry in IgAN. Methods: A total of 114 native kidney biopsies showing at least mild mesangial IgA positivity on immunofluorescence were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were categorized as having IgAN or non-IgAN diseases. The KM55 immunohistochemical staining was graded as 0, 1+, 2+, 3, or 4+. Data on Oxford classification, laboratory parameters, and renal outcomes were collected. Results: The IgAN group showed significantly higher KM55 scores than the non-IgAN group (median: 3 vs. 1; p < .001). IgAN cases were further stratified into KM55-high (≥3+, n = 38) and -low groups (≤2+, n = 37). The KM55-high group had significantly higher diastolic blood pressure, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, urine protein/creatinine ratio, and Oxford mesangial hypercellularity scores, along with lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and serum albumin. Cox analysis revealed significantly poorer outcomes in the KM55-high group for chronic kidney disease stage 4 (p = .015), end-stage renal disease (p = .024), and 75% eGFR decline (p = .016). Conclusions: Mesangial Gd-IgA1 deposition graded by KM55 immunohistochemistry may be a useful adjunct for IgAN diagnosis and a potential prognostic biomarker.
- Revisiting human sparganosis: a pathologic review from a single institution
- Jeemin Yim, Young A Kim, Jeong Hwan Park, Hye Eun Park, Hyun Beom Song, Ji Eun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):83-91. Published online January 9, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.14
- 1,023 View
- 49 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Sparganosis is a rare parasitic infection caused by Spirometra species. Although it was relatively common in the past, it is now often overlooked. In this study, we review cases diagnosed through histopathological examination at a single institution in recent years to raise awareness of this neglected parasitic disease. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed cases of human sparganosis identified in the pathology archives of a single institution in South Korea between 2004 and 2025. A comprehensive review was conducted, including demographic data, clinical features, lesion locations, imaging findings, exposure history (such as dietary habits), and histopathologic findings. Results: A total of 15 patients were identified, including 10 females and 5 males, with a mean age of 65.1 years. Lesions were most commonly located in the lower extremities and breast. Imaging findings were largely nonspecific, with ultrasonography being the most frequently used modality. In most cases, clinical suspicion of sparganosis was absent, and excision was performed under the impression of a benign or malignant tumor. Histologically, variably degenerated parasitic structures were identified within granulomatous inflammation. However, preserved features such as calcospherules and tegumental structures facilitated definitive diagnosis. Conclusions: This study underscores the importance of recognizing the characteristic histopathological features of sparganosis, which can allow for accurate diagnosis even in the absence of clinical suspicion. Although rare, sparganosis remains a relevant diagnostic consideration in endemic regions, particularly in East Asia.
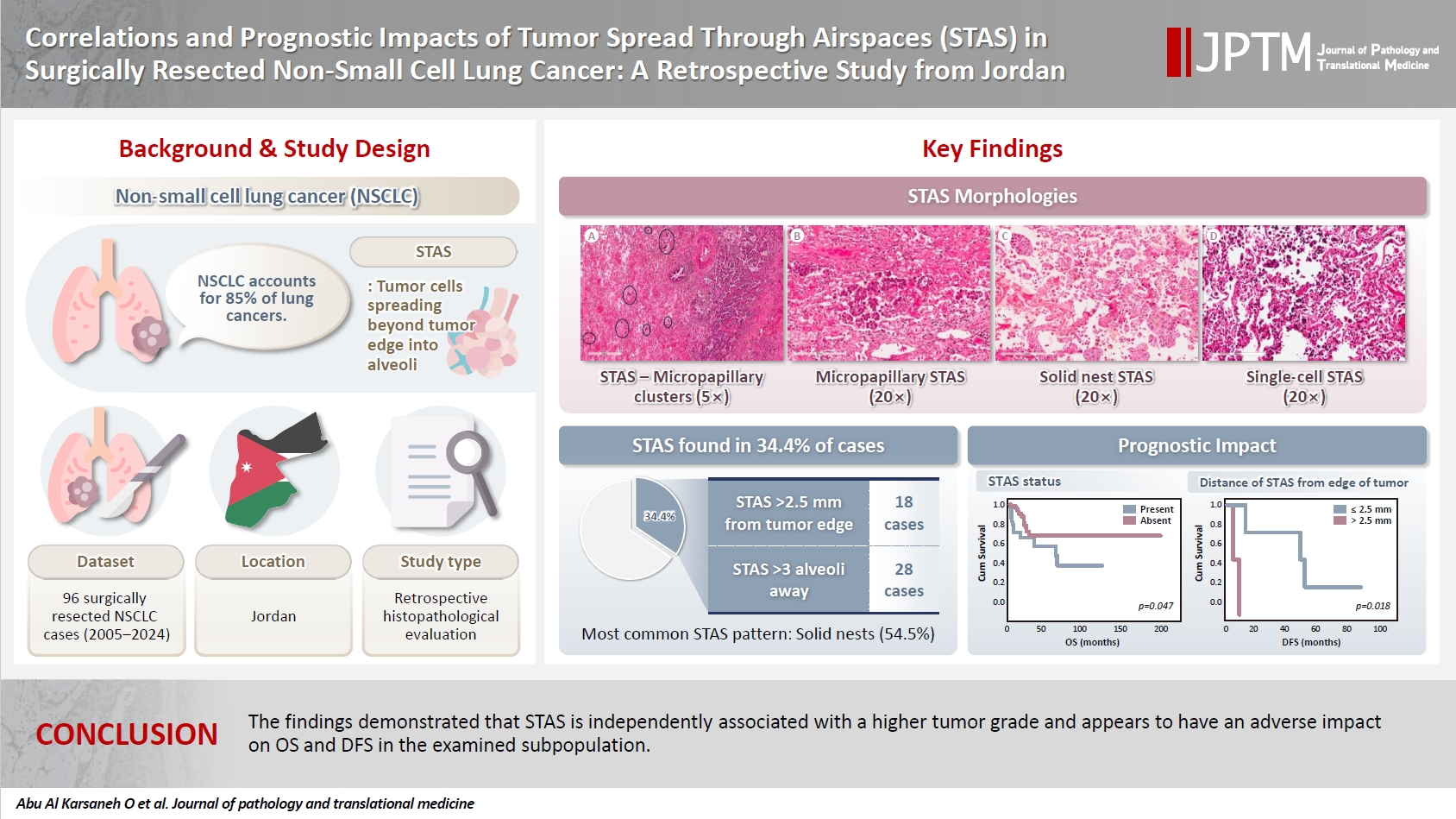
- Correlations and prognostic impacts of tumor spread through airspaces in surgically resected non–small cell lung cancer: a retrospective study from Jordan
- Ola Abu Al Karsaneh, Amani Al-Rousan, Sofian Al Shboul, Mohammed El-Sadoni, Anas Hayajneh, Moath Alrjoub, Sura Al-Rawabdeh, Tareq Saleh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):92-106. Published online January 9, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.15
- 1,147 View
- 60 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Spread through air spaces (STAS) has been identified as an invasion pattern in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This study evaluated the association between tumor STAS and various clinicopathological parameters of NSCLC, with emphasis on the prognostic role of STAS. Methods: We evaluated 96 cases of NSCLC for STAS. STAS-positive cases were graded according to the distance between the edge of the primary tumor and the furthest STAS, in millimeters, or the number of alveoli separating STAS from the tumor. Results: STAS was observed in 33 patients (34.4%). In 28 cases, STAS was located in airspaces >3 alveoli away from the primary tumor. In 18 cases, STAS was found in airspaces > 2.5 mm away from the edge of the primary tumor. Morphologically, 18 cases of STAS demonstrated a solid nest pattern, eight showed a micropapillary cluster pattern, and seven exhibited a single-cell pattern. In multivariate analysis, only high tumor grade (p = .001) was independently associated with STAS in NSCLC. The presence of STAS (p = .047), lymphovascular invasion (p = .001), positive surgical margin (p = .021), adenocarcinoma histology (p = .020), and postoperative therapy (p = .049) showed a statistically significant lower overall survival (OS). However, multivariate analyses showed that STAS is not an independent predictor of OS in NSCLC. In addition, STAS-positive cases with an extension of >2.5 mm had significantly lower disease-free survival (DFS) (p = .018). Conclusions: The findings demonstrated that STAS is independently associated with a higher tumor grade and appears to have an adverse impact on OS and DFS in the examined subpopulation.
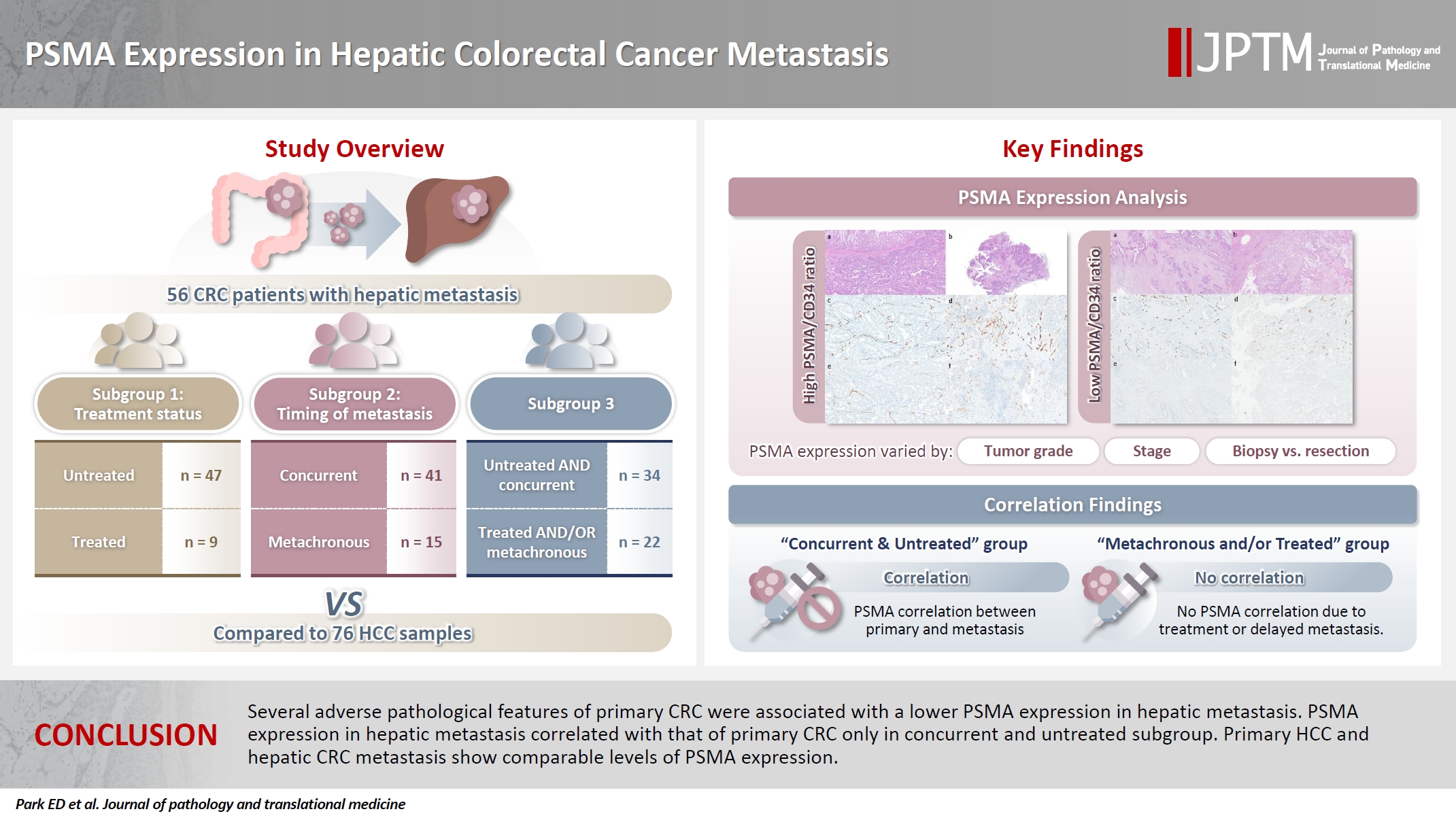
- PSMA expression in hepatic colorectal cancer metastasis
- Eundong Park, Michel Kmeid, Xin Wang, Haiyan Qiu, Clifton G. Fulmer, Marcello P. Toscano, Nusret Bekir Subasi, Maciej Gracz, Hwajeong Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):107-123. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.20
- 875 View
- 47 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is expressed in the neovasculature of various malignancies, such as colorectal cancer (CRC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, PSMA expression in hepatic CRC metastasis has not been studied in detail. Methods: The PSMA expression in primary CRC and corresponding hepatic metastasis was evaluated by immunohistochemistry in a metastatic CRC cohort (n = 56), which was divided into subgroups according to treatment history and timing of metastasis. Demographic and histological characteristics of primary CRC were collected and their relationships with PSMA expression were examined. Additionally, the PSMA expression in resected HCC (n = 76) was compared with that of hepatic CRC metastasis. Results: In primary CRC, PSMA level showed a positive association with tumor size. Lower PSMA expression in hepatic metastasis was associated with higher primary CRC grade, advanced pTNM stage at the time of CRC resection, presence of tumor deposit, and unresectability of metastatic lesion. PSMA expression in primary CRC correlated with that in hepatic metastasis only in concurrent and untreated metastasis subgroup. PSMA expression in primary CRC and hepatic metastasis, regardless of treatment history and timing of metastasis, was not significantly different from that of HCC. Conclusions: Several adverse pathological features of primary CRC were associated with a lower PSMA expression in hepatic metastasis. PSMA expression in hepatic metastasis correlated with that of primary CRC only in concurrent and untreated subgroup. Primary HCC and hepatic CRC metastasis show comparable levels of PSMA expression.
Case Study
- Drug-induced phospholipidosis of the kidney suspected to be caused by atomoxetine
- Sung-Eun Choi, Kee Hyuck Kim, Minsun Jung, Jeong Hae Kie
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):124-128. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.10
- 995 View
- 78 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Drug-induced phospholipidosis (DIP) is characterized by intracellular accumulation of phospholipids with lamellar body formation secondary to drug-altered lipid metabolism, which can trigger inflammation and histopathological changes. Fabry disease and DIP both exhibit zebra bodies on electron microscopy, complicating differential diagnosis. A 17-year-old male with microscopic hematuria and proteinuria had received atomoxetine (40 mg) for 11 months to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Light microscopy showed one glomerulus with perihilar sclerosis and periglomerular fibrosis. Kidney biopsy revealed zebra bodies in podocytes, initially suggesting Fabry disease. However, α-galactosidase A enzyme activity was normal on tandem mass spectrometry. Next-generation sequencing of GLA identified only three benign variants. This represents the first reported case of atomoxetine-induced DIP. When zebra bodies are observed, clinicians should consider DIP caused by cationic amphiphilic drugs alongside Fabry disease. Atomoxetine meets the structural criteria for inducing DIP, and awareness of this potential complication is essential.

 E-submission
E-submission







 First
First Prev
Prev



