Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Clinicopathologic Significance of Survivin Expression in Relation to CD133 Expression in Surgically Resected Stage II or III Colorectal Cancer
- Wanlu Li, Mi-Ra Lee, EunHee Choi, Mee-Yon Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):17-23. Published online December 15, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.09.23
- 11,266 View
- 176 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Cancer stem cells have been investigated as new targets for colorectal cancer (CRC) treatment. We recently reported that CD133+ colon cancer cells showed chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil through increased survivin expression and proposed the survivin inhibitor YM155 as an effective therapy for colon cancer in an in vitro study. Here, we investigate the relationship between survivin and CD133 expression in surgically resected CRC to identify whether the results obtained in our in vitro study are applicable to clinical samples.
Methods
We performed immunohistochemical staining for survivin and CD133 in surgically resected tissue from 187 stage II or III CRC patients. We also comparatively analyzed apoptosis according to survivin and CD133 expression using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling.
Results
The results of the Mantel-Haenszel test established a linear association between nuclear survivin and CD133 expression (p = .018), although neither had prognostic significance, according to immunohistochemical expression level. No correlation was found between survivin expression and the following pathological parameters: invasion depth, lymph node metastasis, or histologic differentiation (p > .05). The mean apoptotic index in survivin+ and CD133+ tumors was higher than that in negative tumors: 5.116 ± 4.894 in survivin+ versus 4.103 ± 3.691 in survivin– (p = .044); 5.165 ± 4.961 in CD133+ versus 4.231 ± 3.812 in CD133– (p = .034).
Conclusions
As observed in our in vitro study, survivin expression is significantly related to CD133 expression. Survivin may be considered as a new therapeutic target for chemoresistant CRC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comprehensive review and in silico analysis of the role of survivin (BIRC5) in hepatocellular carcinoma hallmarks: A step toward precision
Nermin M. Mohamed, Rania Hassan Mohamed, John F. Kennedy, Mahmoud M. Elhefnawi, Nadia M. Hamdy
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2025; 311: 143616. CrossRef - Genetic Variants in BIRC5 (rs8073069, rs17878467, and rs9904341) Are Associated with Susceptibility in Mexican Patients with Breast Cancer: Clinical Associations and Their Analysis In Silico
María Renee Jiménez-López, César de Jesús Tovar-Jácome, Alejandra Palacios-Ramírez, Martha Patricia Gallegos-Arreola, Teresa Giovanna María Aguilar-Macedo, Rubria Alicia González-Sánchez, Efraín Salas-González, José Elías García-Ortiz, Clara Ibet Juárez-V
Genes.2025; 16(7): 786. CrossRef - Upregulation of EMR1 (ADGRE1) by Tumor-Associated Macrophages Promotes Colon Cancer Progression by Activating the JAK2/STAT1,3 Signaling Pathway in Tumor Cells
Rokeya Akter, Rackhyun Park, Soo Kyung Lee, Eun ju Han, Kyu-Sang Park, Junsoo Park, Mee-Yon Cho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(8): 4388. CrossRef - Antiapoptotic Gene Genotype and Allele Variations and the Risk of Lymphoma
Osama M. Al-Amer, Rashid Mir, Abdullah Hamadi, Mohammed I. Alasseiri, Malik A. Altayar, Waseem AlZamzami, Mamdoh Moawadh, Sael Alatawi, Hanan A. Niaz, Atif Abdulwahab A. Oyouni, Othman R. Alzahrani, Hanan E. Alatwi, Aishah E. Albalawi, Khalaf F. Alsharif,
Cancers.2023; 15(4): 1012. CrossRef - The Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications of the Chemoresistance Gene BIRC5 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Getinet M. Adinew, Samia Messeha, Equar Taka, Karam F. A. Soliman
Cancers.2022; 14(21): 5180. CrossRef - EMR1/ADGRE1 Expression in Cancer Cells Upregulated by Tumor-Associated Macrophages Is Related to Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer
Rokeya Akter, Kwangmin Kim, Hye Youn Kwon, Youngwan Kim, Young Woo Eom, Hye-mi Cho, Mee-Yon Cho
Biomedicines.2022; 10(12): 3121. CrossRef - Prognostic Significance of BIRC5/Survivin in Breast Cancer: Results from Three Independent Cohorts
Nina Oparina, Malin C. Erlandsson, Anna Fäldt Beding, Toshima Parris, Khalil Helou, Per Karlsson, Zakaria Einbeigi, Maria I. Bokarewa
Cancers.2021; 13(9): 2209. CrossRef - Obatoclax, a Pan-BCL-2 Inhibitor, Downregulates Survivin to Induce Apoptosis in Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells Via Suppressing WNT/β-catenin Signaling
Chi-Hung R. Or, Chiao-Wen Huang, Ching-Chin Chang, You-Chen Lai, Yi-Ju Chen, Chia-Che Chang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(5): 1773. CrossRef - M1 Macrophages Promote TRAIL Expression in Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells, Which Suppresses Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer by Increasing Apoptosis of CD133+ Cancer Stem Cells and Decreasing M2 Macrophage Population
Young Woo Eom, Rokeya Akter, Wanlu Li, Suji Lee, Soonjae Hwang, Jiye Kim, Mee-Yon Cho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(11): 3887. CrossRef - Emerging Importance of Survivin in Stem Cells and Cancer: the Development of New Cancer Therapeutics
Neerada Meenakshi Warrier, Prasoon Agarwal, Praveen Kumar
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports.2020; 16(5): 828. CrossRef - MMR-proficient and MMR-deficient colorectal cancer cells: 5-Fluorouracil treatment response and correlation to CD133 and MGMT expression
Jaime A. Oliver, Raúl Ortiz, Cristina Jiménez-Luna, Laura Cabeza, Gloria Perazzoli, Octavio Caba, Cristina Mesas, Consolación Melguizo, Jose Prados
Journal of Biosciences.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Survivin rs9904341 polymorphism significantly increased the risk of cancer: evidence from an updated meta-analysis of case–control studies
Abdolkarim Moazeni-Roodi, Saeid Ghavami, Mohammad Hashemi
International Journal of Clinical Oncology.2019; 24(4): 335. CrossRef - CRISPR-Cas9 mediated CD133 knockout inhibits colon cancer invasion through reduced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Wanlu Li, Mee-Yon Cho, Suji Lee, Mirae Jang, Junsoo Park, Rackhyun Park, Aamir Ahmad
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(8): e0220860. CrossRef - Diagnostic Approaches for Salivary Gland Tumors with Secretory and Microcystic Features
Ha Young Woo, Eun Chang Choi, Sun Och Yoon
Head and Neck Pathology.2018; 12(2): 237. CrossRef - MUC1‐ and Survivin‐based DNA Vaccine Combining Immunoadjuvants CpG and interleukin‐2 in a Bicistronic Expression Plasmid Generates Specific Immune Responses and Antitumour Effects in a Murine Colorectal Carcinoma Model
C. Liu, Y. Xie, B. Sun, F. Geng, F. Zhang, Q. Guo, H. Wu, B. Yu, J. Wu, X. Yu, W. Kong, H. Zhang
Scandinavian Journal of Immunology.2018; 87(2): 63. CrossRef - Activated STAT3 may participate in tumor progression through increasing CD133/survivin expression in early stage of colon cancer
Wanlu Li, Mi-Ra Lee, Taeyeong Kim, Young Wan Kim, Mee-Yon Cho
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2018; 497(1): 354. CrossRef - MiRNA-142-3p increases radiosensitivity in human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells by inhibiting the expression of CD133
Fang Yuan, Lu Liu, Yonghong Lei, Yi Hu
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - MLH1 enhances the sensitivity of human endometrial carcinoma cells to cisplatin by activating the MLH1/c-Abl apoptosis signaling pathway
Yue Li, Shihong Zhang, Yuanjian Wang, Jin Peng, Fang Fang, Xingsheng Yang
BMC Cancer.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Establishment of CMab-43, a Sensitive and Specific Anti-CD133 Monoclonal Antibody, for Immunohistochemistry
Shunsuke Itai, Yuki Fujii, Takuro Nakamura, Yao-Wen Chang, Miyuki Yanaka, Noriko Saidoh, Saori Handa, Hiroyoshi Suzuki, Hiroyuki Harada, Shinji Yamada, Mika K. Kaneko, Yukinari Kato
Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy.2017; 36(5): 231. CrossRef
- A comprehensive review and in silico analysis of the role of survivin (BIRC5) in hepatocellular carcinoma hallmarks: A step toward precision
- Therapeutic Effects of Umbilical Cord Blood Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium on Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Rats
- Jae Chul Lee, Choong Ik Cha, Dong-Sik Kim, Soo Young Choe
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(6):472-480. Published online October 16, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.09.11
- Retraction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2016;50(4):325
- 16,747 View
- 82 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
Review
- Molecular Imaging in the Era of Personalized Medicine
- Kyung-Ho Jung, Kyung-Han Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(1):5-12. Published online January 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2014.10.24
- 15,449 View
- 212 Download
- 32 Web of Science
- 27 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clinical imaging creates visual representations of the body interior for disease assessment. The role of clinical imaging significantly overlaps with that of pathology, and diagnostic workflows largely depend on both fields. The field of clinical imaging is presently undergoing a radical change through the emergence of a new field called molecular imaging. This new technology, which lies at the intersection between imaging and molecular biology, enables noninvasive visualization of biochemical processes at the molecular level within living bodies. Molecular imaging differs from traditional anatomical imaging in that biomarkers known as imaging probes are used to visualize target molecules-of-interest. This ability opens up exciting new possibilities for applications in oncologic, neurological and cardiovascular diseases. Molecular imaging is expected to make major contributions to personalized medicine by allowing earlier diagnosis and predicting treatment response. The technique is also making a huge impact on pharmaceutical development by optimizing preclinical and clinical tests for new drug candidates. This review will describe the basic principles of molecular imaging and will briefly touch on three examples (from an immense list of new techniques) that may contribute to personalized medicine: receptor imaging, angiogenesis imaging, and apoptosis imaging.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ionic Cell Microscopy: A new modality for visualizing cells using microfluidic impedance cytometry and generative artificial intelligence
Mahtab Kokabi, Gulam M. Rather, Mehdi Javanmard
Biosensors and Bioelectronics: X.2025; 24: 100619. CrossRef - Multimodal imaging in cancer detection: the role of SPIONs and USPIONs as contrast agents for MRI, SPECT, and PET
Zahra Shaghaghi, Ramin Mansouri, Sahar Nosrati, Maryam Alvandi
Future Oncology.2025; 21(18): 2367. CrossRef - Supramolecular fluorescence biosensing based on macrocycles
Jia-Hong Tian, Haiqi Xu, Xin-Yue Hu, Dong-Sheng Guo
Supramolecular Materials.2024; 3: 100063. CrossRef - A non-invasive osteopontin-targeted phase changeable fluorescent nanoprobe for molecular imaging of myocardial fibrosis
Xueli Zhao, Yuze Qin, Bo Wang, Jiao Liu, Yueyue Wang, Kun Chen, Jia Zhao, Lanlan Zhang, Yuanming Wu, Liwen Liu
Nanoscale Advances.2024; 6(14): 3590. CrossRef - The Role of Molecular Imaging in Personalized Medicine
Suliman Salih, Aisyah Elliyanti, Ajnas Alkatheeri, Fatima AlYafei, Bashayer Almarri, Hasina Khan
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(2): 369. CrossRef - Development of a multifunctional platform for near-infrared imaging and targeted radionuclide therapy for tumors
Huihui He, Ke Li, Hang Li, Shiliang Zhu, Shuai Qin, Yong Mao, Jianguo Lin, Ling Qiu, Chunjing Yu
European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics.2023; 185: 107. CrossRef - Quantum Biotechnology
Nicolas P. Mauranyapin, Alex Terrasson, Warwick P. Bowen
Advanced Quantum Technologies.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Preparation Fe3O4@chitosan-graphene quantum dots nanocomposites for fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging
Kai Wang, Xiaoguang Xu, Yan Li, Mayifei Rong, Lifeng Wang, Liying Lu, Jian Wang, Fengwen Zhao, Bowen Sun, Yong Jiang
Chemical Physics Letters.2021; 783: 139060. CrossRef - Network Medicine: A Clinical Approach for Precision Medicine and Personalized Therapy in Coronary Heart Disease
Teresa Infante, Luca Del Viscovo, Maria Luisa De Rimini, Sergio Padula, Pio Caso, Claudio Napoli
Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis.2020; 27(4): 279. CrossRef - Nanodrug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer
Jonathan M. Pantshwa, Pierre P. D. Kondiah, Yahya E. Choonara, Thashree Marimuthu, Viness Pillay
Cancers.2020; 12(1): 213. CrossRef - Molecular imaging of the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor: opportunities beyond cancer
V. M. Baart, R. D. Houvast, L. F. de Geus-Oei, P. H. A. Quax, P. J. K. Kuppen, A. L. Vahrmeijer, C. F. M. Sier
EJNMMI Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - In vivo SPECT imaging of an 131I-labeled PM 2.5 mimic substitute
Dong-Hui Pan, Jie Sheng, Xin-Yu Wang, Qian-Huan Huang, Jun-Jie Yan, Li-Zhen Wang, Run-Ling Yang, Dong-Jian Shi, Yu-Ping Xu, Ming-Qing Chen
Nuclear Science and Techniques.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Optofluidics in bio-imaging applications
Sihui Chen, Rui Hao, Yi Zhang, Hui Yang
Photonics Research.2019; 7(5): 532. CrossRef - Nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond for nanoscale magnetic resonance imaging applications
Alberto Boretti, Lorenzo Rosa, Jonathan Blackledge, Stefania Castelletto
Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.2019; 10: 2128. CrossRef - Online molecular image repository and analysis system: A multicenter collaborative open-source infrastructure for molecular imaging research and application
Mahabubur Rahman, Hiroshi Watabe
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2018; 96: 233. CrossRef - Nε-Acryloyllysine Piperazides as Irreversible Inhibitors of Transglutaminase 2: Synthesis, Structure–Activity Relationships, and Pharmacokinetic Profiling
Robert Wodtke, Christoph Hauser, Gloria Ruiz-Gómez, Elisabeth Jäckel, David Bauer, Martin Lohse, Alan Wong, Johanna Pufe, Friedrich-Alexander Ludwig, Steffen Fischer, Sandra Hauser, Dieter Greif, M. Teresa Pisabarro, Jens Pietzsch, Markus Pietsch, Reik Lö
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2018; 61(10): 4528. CrossRef - Genomic Interventions in Medicine
Oluwadurotimi S Aworunse, Oluwatomiwa Adeniji, Olusola L Oyesola, Itunuoluwa Isewon, Jelili Oyelade, Olawole O Obembe
Bioinformatics and Biology Insights.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Restriction spectrum imaging: An evolving imaging biomarker in prostate MRI
Ryan L. Brunsing, Natalie M. Schenker-Ahmed, Nathan S. White, J. Kellogg Parsons, Christopher Kane, Joshua Kuperman, Hauke Bartsch, Andrew Karim Kader, Rebecca Rakow-Penner, Tyler M. Seibert, Daniel Margolis, Steven S. Raman, Carrie R. McDonald, Nikdokht
Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2017; 45(2): 323. CrossRef - Personalized medicine: a new option for nuclear medicine and molecular imaging in the third millennium
Orazio Schillaci, Nicoletta Urbano
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.2017; 44(4): 563. CrossRef - Nano-Magnetic Resonance Imaging (Nano-MRI) Gives Personalized Medicine a New Perspective
Lorenzo Rosa, Jonathan Blackledge, Albert Boretti
Biomedicines.2017; 5(1): 7. CrossRef - Optical nanoprobes for biomedical applications: shining a light on upconverting and near-infrared emitting nanoparticles for imaging, thermal sensing, and photodynamic therapy
E. Hemmer, P. Acosta-Mora, J. Méndez-Ramos, S. Fischer
Journal of Materials Chemistry B.2017; 5(23): 4365. CrossRef - Drug Discovery by Molecular Imaging and Monitoring Therapy Response in Lymphoma
Senthilkumar Kalimuthu, Ju Hye Jeong, Ji Min Oh, Byeong-Cheol Ahn
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2017; 18(8): 1639. CrossRef - Chemistry and engineering of cyclodextrins for molecular imaging
Wing-Fu Lai, Andrey L. Rogach, Wing-Tak Wong
Chemical Society Reviews.2017; 46(20): 6379. CrossRef - Prototypes of Lanthanide(III) Agents Responsive to Enzymatic Activities in Three Complementary Imaging Modalities: Visible/Near-Infrared Luminescence, PARACEST-, and T1-MRI
Jiefang He, Célia S. Bonnet, Svetlana V. Eliseeva, Sara Lacerda, Thomas Chauvin, Pascal Retailleau, Frederic Szeremeta, Bernard Badet, Stéphane Petoud, Éva Tóth, Philippe Durand
Journal of the American Chemical Society.2016; 138(9): 2913. CrossRef - Nanoparticles in practice for molecular-imaging applications: An overview
Parasuraman Padmanabhan, Ajay Kumar, Sundramurthy Kumar, Ravi Kumar Chaudhary, Balázs Gulyás
Acta Biomaterialia.2016; 41: 1. CrossRef - A new neuroinformatics approach to personalized medicine in neurology: The Virtual Brain
Maria I. Falcon, Viktor Jirsa, Ana Solodkin
Current Opinion in Neurology.2016; 29(4): 429. CrossRef - Targeted multimodal nano-reporters for pre-procedural MRI and intra-operative image-guidance
Joonseok Lee, Andrew C. Gordon, Hacksung Kim, Wooram Park, Soojeong Cho, Byeongdu Lee, Andrew C. Larson, Elena A. Rozhkova, Dong-Hyun Kim
Biomaterials.2016; 109: 69. CrossRef
- Ionic Cell Microscopy: A new modality for visualizing cells using microfluidic impedance cytometry and generative artificial intelligence
Original Articles
- Expression of DNA Topoisomerase II-alpha as a Proliferating Marker in Urothelial Carcinoma of Urinary Bladder based on World Health Organization/International Society of Urological Pathology Consensus Classification: A Correlation with Expression of Ki-67 and Apoptosis
- Tae Jin Lee, Dong Ki Lee, Eon Sub Park, Jae Hyung Yoo
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(5):305-313.
- 2,004 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
DNA topoisomerase II-alpha is linked with active cell proliferation in mammalian cells. The aim of this study was to examine the relationship between the expression of DNA topoisomerase II-alpha as a proliferating marker, and the expression of Ki-67 and apoptosis in urothelial carcinoma of urinary bladder based on World Health Organization/International Society of Urological Pathology (WHO/ISUP) consensus classification.
METHODS
73 urothelial carcinomas of the urinary bladder after transurethral resection and 25 carcinomas after radical cystectomy were investigated for histologic grading based on WHO and WHO/ISUP consensus classification. Formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissue of 98 specimens from 73 patients were immunohistochemically stained for DNA topoisomerase II-alpha and Ki-67, and in situ TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling method for evaluation of apoptotic cells was performed. For each case, a DNA topoisomerase II-alpha, Ki-67, and apoptotic indices were determined.
RESULTS
The histologic grades of 73 cases based on the WHO grading system were 21.9% (16 cases) in grade 1, 65.8% (48 cases) in grade 2, and 12.3% (9 cases). 5.5% (4 cases) of papillary neoplasm of low malignant potential, 47.9% (35 cases) of urothelial carcinoma of low grade, and 46.6% (34 cases) in urothelial carcinoma of high grade were reclassified using the WHO/ISUP consensus classification. Histologic grades based on two grading systems were correlated to invasion and stage (p<0.05). DNA topoisomerase II-alpha, Ki-67, and apoptotic indices were correlated to histologic grades based on two grading system and invasion. Also, the correlation of DNA topoisomerase II-alpha and Ki-67 indices, and DNA topoisomerase II-alpha and apoptotic indices were significant, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
DNA topoisomerase II-alpha appears to be an useful marker for assessing the proliferation potential of urothelial carcinoma of in the urinary bladder.
- Inhibitors of Apoptosis Proteins Expression and Their Prognostic Significance in Colorectal Carcinoma.
- Kyung Hwa Lee, Soong Lee, Hyeon Min Lee, Seung Chul Back, Sung Bum Cho, Jae Hyuk Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(4):397-405.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.4.397
- 4,539 View
- 22 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The expression of the inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) family has not been fully investigated in colorectal carcinomas. This study investigated IAP expression in colorectal carcinomas and assessed their prognostic significance.
METHODS
Livin, XIAP, and SMAC/DIABLO expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry in 159 colorectal carcinomas. Correlations between protein expression and clinicopathological features were evaluated. The survival data analysis was estimated according to the Kaplan-Meier method.
RESULTS
Increased expression of IAPs in cancer tissues compared to surrounding nonneoplastic counterparts was observed in 67 cases (42.1%) for Livin, 50 cases (31.4%) for XIAP, and 68 cases (42.8%) for SMAC. A significant correlation was found between Livin expression and tumor differentiation, and SMAC expression and tumor location. The recurrence-free and overall survival of patients with low Livin expression were inferior to those of patients with high Livin expression (p=0.054 and 0.095, respectively). High XIAP expression was significantly associated with shorter progression-free survival (p= 0.041).
CONCLUSIONS
Our study demonstrated that altered expression of IAP family members, including Livin, XIAP, and SMAC, is frequent in colorectal carcinoma. This result suggests that high Livin expression and low XIAP expression may be a favorable prognostic implication related to patient survival. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of the Current Impact of Inhibitors of Apoptosis Proteins and Their Repression in Cancer
Pierina Cetraro, Julio Plaza-Diaz, Alex MacKenzie, Francisco Abadía-Molina
Cancers.2022; 14(7): 1671. CrossRef
- A Review of the Current Impact of Inhibitors of Apoptosis Proteins and Their Repression in Cancer
- Prognostic Value of Phosphorylated Akt and Survivin Expression in Gastric Adenocarcinoma.
- Soong Lee, Yun Cheol Kim, Hyeon Min Lee, Ki Sang Lee, Byung Chul Shin, Hyung Seok Kim, Jae Hyuk Lee, Chang Soo Park, Kyung Hwa Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(3):252-258.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.3.252
- 4,710 View
- 22 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
pAkt (the phosphorylated form of the proto-oncogene protein c-akt) and survivin (human BIRC5 protein) are candidate apoptosis-related molecules that may be responsible for cancer progression. The aim of this study was to determine the expression of pAkt and survivin in malignant stomach neoplasm, and their value as prognostic indicators of cancer.
METHODS
The expression of pAkt and survivin in 144 cases of gastric cancer was detected by immunohistochemistry and compared with established clinicopathological parameters and prognosis of this disease.
RESULTS
Expression of pAkt showed significant correlations with depth of invasion, lymph node and distant metastasis, as well as the stage (p < 0.05 for all three correlations), but not with the Lauren classification. Survivin expression closely correlated with histological type, Lauren classification, depth of invasion, metastasis, and stage (p < 0.05 for all). The overall survival of patients with pAkt/survivin expression was inferior to that of patients with loss of pAkt/survivin expression. Cox multivariate analysis demonstrated a significant correlation between stage (p = 0.04), survivin expression (p = 0.02), and prognosis.
CONCLUSIONS
Patients with pAkt/survivin expression in gastric cancer are at increased risk of cancer-related mortality via the apoptosis resistance pathway. Expression of pAkt and survivin could be used as a prognostic indicator for gastric cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Transcriptome analysis reveals GPNMB as a potential therapeutic target for gastric cancer
Feifei Ren, Qitai Zhao, Bin Liu, Xiangdong Sun, Youcai Tang, Huang Huang, Lu Mei, Yong Yu, Hui Mo, Haibin Dong, Pengyuan Zheng, Yang Mi
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2020; 235(3): 2738. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Estrogen/Progesterone Receptor and Expression of mTOR/pAkt Proteins and the Analysis of Prognosis in Breast Cancer
Sun Wook Han, Moon Soo Lee, Sung Yong Kim, Gil Ho Kang, Zi Sun Kim, Cheol Wan Lim, Ji Hyun Lee, Hyun Ju Lee, Mee-Hye Oh, Min Hyuk Lee
Journal of Breast Disease.2013; 1(1): 8. CrossRef - Clinicopathological correlations of mTOR and pAkt expression in non-small cell lung cancer
Mee-Hye Oh, Hyun Ju Lee, Seol Bong Yoo, Xianhua Xu, Jae Sung Choi, Yong Hoon Kim, Seok Yeol Lee, Choon-Taek Lee, Sanghoon Jheon, Jin-Haeng Chung
Virchows Archiv.2012; 460(6): 601. CrossRef
- Transcriptome analysis reveals GPNMB as a potential therapeutic target for gastric cancer
- Expression of Survivin in Gastric Carcinoma and its Relation to Tumor Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis.
- Wan Sik Lee, Sung Bum Cho, Jong Sun Rew, Jae Hyuk Lee, Chang Soo Park, Young Eun Joo
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(4):329-334.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.4.329
- 4,135 View
- 43 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Survivin, a novel antiapoptotic gene has been linked with tumor development and progression in various human carcinomas including gastric carcinomas. The aim of this study was to evaluate the expression of survivin in gastric carcinoma and its correlation with tumor cell proliferation and apoptosis. METHODS: Expression of survivin was evaluated immunohistochemically in 84 surgically resected gastric carcinomas. Tumor cell apoptosis was evaluated with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP) nick-end labeling (TUNEL), and Ki-67 immunostaining was used for evaluation of tumor cell proliferation. RESULTS: Expression of survivin was noted in 53.6% of the gastric carcinomas, and was significantly associated with depth of invasion, status of lymph node metastasis or tumor stage (p=0.022, 0.034, 0.040, respectively). There was an inverse correlation between survivin expression and apoptotic index (p=0.015). But there was no significant correlation between survivin expression and Ki-67 labeling index (p=0.430). CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that survivin expression may contribute to tumor development and progression by inhibiting apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Significance of intracellular localization of survivin in cervical squamous cell lesions: Correlation with disease progression
SOO-AH KIM, RAN HONG
Oncology Letters.2014; 7(5): 1589. CrossRef
- Significance of intracellular localization of survivin in cervical squamous cell lesions: Correlation with disease progression
- Expression of P-glycoprotein and Apoptosis in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma.
- Ji Eun Kim, Young A Kim, Mee Soo Chang, Yunkyeong Jeon, JinHo Paik, Seon Og Yoon
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(4):317-320.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.4.317
- 3,878 View
- 74 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of malignant lymphoma which responds well to conventional chemotherapy. However, quite a few patients have a recurrence with more aggressive forms after completion of therapy. Multidrug resistance proteins (MRP) are related to this process in several ways such as cell cycle alteration and modulation of apoptosis. METHODS: We investigated the expression of P-glycoprotein (Gp), one of the well-known MRP, as well as apoptosis associated proteins in DLBCL. Immunohistochemical staining for Gp, p53, Bcl-2, Ki-67, active caspase 3 and FADD was done in forty DLBCL cases. The association between MRP and apoptosis associated proteins to clinical findings was also tested. RESULTS: Twenty-nine patients out of 40 (73%) with DLBCL were positive for Gp, and 26 cases (65%) had a strong positive for Gp. Gp expression was stronger in high-grade lesions than in low-grade lesions and was associated to Bcl-2 expression. However, we could not find an adverse impact of Gp expression on patients' overall survival or relapse free survival rate. CONCLUSIONS: Our study revealed a high frequency of expression for Gp in DLBCL with a possible relationship between the expressions of Gp to apoptosis associated proteins.
- Immunolocalization of the Apoptotic Inhibiting Protein (bcl-2) in Early Normal Pregnancy and Abortion.
- Jiae Lee, Jeong Wook Kim, Bum Chae Choi, Kwang Moon Yang, Young Youl Cho, Sung Ran Hong
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(1):48-52.
- 1,968 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The human placenta is an important organ in the maintenance of pregnancy, having functions in maturation and differentiation until the end of pregnancy. The bcl-2 protein is a proto-oncogene that prevents apoptosis and maintains cell survival. However, the mechanism through which bcl-2 inhibits apoptosis is unclear. The aims of this study are to localize bcl-2 at the placenta and to determine whether the expression of bcl-2 in early normal pregnancy is different from that of a missed abortion.
METHODS
Immunohistochemistry was performed for bcl-2 in formalin-fixed chorionic villi and decidual tissue collected from five early normal pregnancies and eleven missed abortions having histories of recurrent abortions during the first trimester.
RESULTS
The bcl-2 protein was observed in the syncytiotrophoblasts of chorionic villi and decidua in both the normal pregnancy and the missed abortion, and the expression of bcl-2 significantly increased in the missed abortion group (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
The bcl-2 may be necessary to maintain pregnancy through modulating the survival of the syncytiotrophoblast and decidua without affecting cell proliferation, and the increased bcl-2 expression is presumed to be a reparative process to the increased apoptotic activity.
- The Effects of Transforming Growth Factor beta1 on Apoptosis in Rat Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
- Young Euy Park, Young Hee Choi, Won Yo Lee, Jin Ja Park, Kyung Chan Choi, Hyung Shik Shin
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(2):71-79.
- 1,884 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Based upon the concept that carcinogenesis is associated with apoptosis, specific therapies designed to enhance the susceptibility of cancer cells to undergo apoptosis could be developed. Thus, in this paper, it was designed to investigate whether, using rat animal model with chemical-induced hepatocellular carcinoma, TGF-1 in vivo could induce apoptosis in cancer. The chemical hepatocarcinogenic procedure of Solt-Farber method was used on Sprague-Dawley rats. Experimental groups were divided into group A treated with the standard Solt-Farber regimen of diethylnitrosamine (DEN) and 2-Acetaminofluorene (AAF), group B TGF-, group C TGF-1, and group D adriamycin after hepatocellular carcinoma developed. For detection of apoptotic cells, apoptotic indices were examined by the in situ end DNA labelling method. The expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen was examined by immunohistochemical staining. Apoptosis of rat hepatocellular carcinoma cells increased significantly to 4.92+/-2.32/HPF in the group C compared with the control group (A) (2.54+/-1.13/HPF; P<0.05). Two distinctly different populations of proliferating hepatocellular carcinoma cells were identified. The cells at G1/S boundary (weak granular staining) increased to 15.75+/-6.19/HPF and 6.45+/-2.93/HPF in the groups C and D, respectively, but decreased to 2.42+/-2.06/HPF in the group B compared with the control group (A) (6.38+/-2.18/HPF; p<0.05). The cells at S phase (strong granular staining) increased to 3.37+/-2.69/HPF in the group B but decreased to 0.32+/-0.47/HPF in the group D (p<0.05). In conclusion, these results indicate that the TGF-1 may be used as an effective anticancer agent.
- Study on the Function of NAG-1 in Hepatocellular and Gastric Carcinoma Cells.
- Tae Jung Jang
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(4):244-251.
- 2,014 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug activated gene (NAG-1) has proapoptotic activities in the colon and also in gastric cancer cells that lack any endogenous COX-2 expression. Recent studies have suggested that the proa- poptotic activity of NAG-1 is cell type specific. I investigated the cell proliferation, invasiveness and apoptosis in Hep3B cells and SNU719 cells by determining the different expression levels of NAG-1. In addition, I examined the gene profile in the Hep3B cells that have a stable expression of NAG-1.
METHODS
SNU719 cells and several clones of Hep3B cells with a stable expression of NAG-1 were used. I reduced the expression level of NAG-1 via the RNAi method. An Agilent Human 22k microarray was used for studying the gene profile in Hep3B cells that had a stable expression of NAG-1.
RESULTS
The expression level of NAG-1 did not influence apoptosis, cell proliferation and invasiveness in Hep3B cells. There was no correlation between the reduction of the endogenous NAG-1 expression and cell proliferation, including invasiveness, in the SNU719 cells. However, a knocked-down NAG-1 expression protected against apoptosis in the SNU719 cells. The microarray analysis results showed that 0.25% (58/22,575) of the genes were induced or repressed more than three fold in the Hep3B cells that had a stable expression of NAG-1.
CONCLUSIONS
Proapoptotic activity of NAG-1 is found in gastric cancer cells, but not in hepatocellular cancer cells.
- A Study on the Expression of Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen and Apoptosis of the Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Human and Hepatitis B Virus X Transgenic Mice.
- Hyung Bae Moon, Dae Yeul Yu, Hyung Ryun Yoo, Byung Joon So, Kwon Mook Chae, Haak Cheol Kim, Ki Jung Yun, Won Cheol Han, Hyang Jeong Jo, Bo Yong Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(2):129-136.
- 2,029 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
This experiment was designed to study the cell kinetics of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in both hepatitis B virus X (HBx) transgenic mice and humans.
METHODS
The immunohistochemical stain of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay of apoptosis were used on formalin fixed-paraffin embedded tissues.
RESULTS
PCNA labeling indices (PCNA-LI) in the liver of HBx transgenic mice were markedly increased in HCC (11.3%) compare to the dysplastic areas (1.3%) and in the liver of non-transgenic littermates (0.1%). There was no significant difference of PCNA-LI in the dysplastic areas between HCC developed mice and non-HCC developed mice. Apoptosis labeling indices (Apoptosis-LI) in both the dysplastic areas and HCC of HBx transgenic mice were similar to those of non-transgenic littermates. PCNA-LI was markedly increased in human HCC (28.9%) compare to the background of HCC (2.9%) and the control liver (2.9%). Apoptosis-LI was decreased in human HCC (0.3%) compare to the background of HCC (0.4%) and the control liver (1.0%). Conclusion : There is a marked increase of cell proliferating activity in human HCC and in HCC of HBx transgenic mice, and there is a decrease of apoptosis in human HCC, but not in HCC of HBx transgenic mice.
- Cardiac Myocyte Cell Death in Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy in Rats.
- Soo Kyung Kim, Eun Sook Chang, Gee Youn Kwon
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(3):189-195.
- 2,435 View
- 289 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Although cardiac hypertrophy contributes to cardiac failure, the underlying mechanism has not yet been precisely determined. This study was planned in order to determine the pathogenesis of heart failure following cardiac hypertrophy induced by -adrenergic stimulation.
METHODS
The extent of cardiac hypertrophy was assessed after administrating isoproterenol (ISO, 5 mg/kg) intraperitoneally for 6 hours, 1, 3, 5, 7 and 10 days. The hematoxylin-eosin, Masson's trichrome and phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin stains along with immunohistochemical stainings for proliferating cell nuclear antigen and Ki-67 were performed in the paraffin-embedded left ventricle sections. Apoptosis was assessed by DNA laddering and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. TUNEL positive myocytes and some nonmyocytes appeared in the subepicardium at 6 hours after ISO administration. The localization of these cells was shifted to the subendocardium within 24 hours, and the TUNEL positive cells were seen throughout the myocardium on the 5th day after ISO treatment. Necrotic myocyte death occurred on the 3rd day of ISO administration in the subendocardium, and initial pericellular fibrosis was followed and increased thereafter, with replacement fibrosis accompanied by further necrotic myocyte cell death.
CONCLUSIONS
Our data showed that ISO treatment induced apoptotic myocyte death and superimposed necrotic myocyte death with subsequent fibrosis. The observed cardiac myocyte death may reflect myocardial dysfunction.
- The Role of MIB-1 Expression and Apoptosis in Experimental Crescentic Glomerulonephritis.
- Nam Hoon Kim, Wan Seop Kim, Jung Woo Noh, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(4):231-242.
- 2,066 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It has been postulated that programmed cell death via apoptosis may be critical for remodelling of glomeruli after inflammatory injury. To understand the regulatory mechanism of apoptosis in experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis (CGN), we examined the MIB-1 score (proliferation index, PI) and apoptotic index during the progression of experimental CGN to end-stage renal failure. CGN was induced in New Zealand White rabbits by administration of guinea pig anti-GBM IgG after sensitization with guinea pig IgG and their kidneys were analyzed for the development of crescents through sequential renal biopsies. Serum creatinine levels progressively increased in a time course until day 45. The PI in glomeruli, tubular epithelial cells, and interstitium progressively increased during the progression of experimental CGN. The mean numbers of MIB-1 positive intraglomerular nuclei (PI) were significantly correlated with degrees of crescent formation and the numbers of apoptotic cells in the glomeruli, tubules, and interstitium. Significant apoptosis was present from day 1 (15.8 10.16 cells/glomerular cross section) and increased in number with the proliferative lesions as glomerular inflammation continued. Moreover, apoptosis increased during the resolution of the glomerular inflammation, and many apoptotic cells were present in the sclerotic lesions in day 17 (18.6 12.99 cells/glomerular cross section). As glomerular inflammation subsided, cellular crescents progressed to fibrous crescents with a reduction of cellularity by day 45. On day 45, the glomerular PI and the numbers of apoptotic cells were markedly decreased. The correlations found in CGN between the creatinine level and the percentage of crescents, between the percentage of crescent and PI, and between the PI and number of apoptotic cells support the hypothesis that there is a change in the glomerular and tubulo-interstitial apoptosis under pathologic conditions. These findings indicate that apoptosis plays an essential role in the resolution of intra- and extraglomerular inflammation and in the elimination of glomerular cells within the sclerotic regions for progressive CGN. The regulation of the apoptotic phenomenon and increased PI during CGN may be important in the progression of glomerular inflammation and the development of pathologic glomerular sclerosis.
- Expression of bcl-2 Protein in Colorectal Adenoma and Adenocarcinoma and its Relationship with p53 and Apoptosis.
- Ae Ree Kim, Seong Jin Cho, Nam Hee Won, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(5):417-426.
- 1,929 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Either increased cellular proliferation or decreased death might result in an expansion of their numbers in the oncogenic process. Cellular apoptosis represents an autonomous suicide pathway that helps to restrict the cell number. However bcl-2 and mutant p53 inhibit programmed cell death. To determine whether the bcl-2 gene is activated during colorectal tumorigenesis and whether it has any relationship with p53 and apoptosis, we studied the expression of bcl-2 and p53 in the normal colonic mucosa, in the adenomatous polyps and in the adenocarcinomas using the immunohistochemical method. Also we evaluated the status of apoptosis using the in situ end labeling method. The bcl-2 immunoreactivity was restricted to the basal epithelial cells of all normal colonic mucosa and they were expressed in all adenomas and 86% of adenocarcinomas, especially in the superficial lesion of some tumors. Mutations of p53 were not found in the normal colonic mucosa, but they were present in dysplastic cells of adenomas (52%) and in cancer cells of the adenocarcinomas (47%). Apoptosis was confined to the tips of the normal colonic mucosa. It was more easily detected in the p53-positive adenomas than in the p53-negative adenomas (p=0.010). In the adenocarcinomas, the findings of apoptotic process are not related with p53 mutation (p=0.3) and bcl-2 expression (p=0.187). p53 and bcl-2 are probably one step of several apoptotic processes in the adenocarcinomas.
- Correlation Between the Frequency of Apoptotic Bodies and Gleason Scores in Prostatic Cancer.
- Hee Soo Yoon, Ho Jung Kim, Hea Soo Koo, Ok Kyung Kim, Sung Sook Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(5):462-469.
- 1,862 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Apoptosis (or programmed cell death) is defined by morphologic changes induced by a spectrum of physical and chemical agents. resulting in non-pathologic cell loss, which is relevant to a range of biological processes, including differentiation, development, maturation, and injury of cells as well as immunologic function. In this study, we examined the frequency of apoptotic bodies and mitoses (apoptotic and mitotic indices) in the tissue samples of 35 patients of prostatic carcinoma, which were grouped according to the Gleason scores, and 5 cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia. The indices were determined as the numbers of apoptotic and mitotic bodies per 100 tumor cells in hematoxylin eosin stained section. The apoptotic bodies were confirmed by the in situ nick end labelling method. The apoptotic and mitotic indices were observed more frequently in prostatic carcinoma than the benign hyperplastic prostatic tissues with a positive correlation between the frequency of apoptotic bodies and Gleason scores in prostatic cancer. In conclusion, an increased programmed cell death was correlated with the increasing malignant potential (higher Gleason scores) in prostatic cancer.
- Caspase 3 and Ki-67 Immunoreactivity and Its Correlation with Frequency of Apoptosis in Gastric Adenomas and Carcinomas.
- Jin Hee Sohn, Seoung Wan Chae, Kyung Chan Choi, Hyung Sik Shin
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(4):286-290.
- 2,083 View
- 27 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is under genetic control and is mediated by apoptosis-specific genes, certain oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Caspase 3, a group of cystein proteases, is involved in the induction of apoptosis and has been considered to be correlated with apoptosis. Therefore, we tried to define whether caspase 3 is expressed in gastric adenoma and carcinoma, and correlated with apoptosis.
METHODS
The apoptotic index and caspase 3 and Ki-67 immunoreactivity were observed in 25 gastric adenomas, 31 early gastric carcinomas (EGC) and 64 advanced gastric carcinomas (AGC) by in situ labelling and immunohistochemistry. RESULTS: The mean number of apoptotic bodies and caspase 3 immunoreactivity were significantly increased from adenoma through EGC to AGC. Ki-67 immunoreactivity was more increased in AGC than in adenoma and EGC. And the number of apoptotic bodies were positively correlated with caspase 3 and Ki-67 immunoreactivity, and caspase 3 immunoreactivity was negatively correlated with Ki-67 immunoreactivity even though they were statistically insignificant.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results suggest that caspase 3 activation is important for inducing apoptosis, and both caspase 3 and apoptosis are increased along the tumor progression.
- Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-1, MMP-3 Nitrotyrosine and Apoptosis in Articular Cartilage of Human Osteoarthritis.
- So Young Jin, Seong Su Kang, Dong Wha Lee, Soo Jae Yim, Yeo Hon Yun, Byung Ill Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(4):319-329.
- 2,299 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 and 3 are the most important degradating enzymes of the chondroid matrix. Chondrocytes may undergo apoptosis under various stimuli including nitric oxide (NO). We studied the expression rate and zone of MMP-1, MMP-3, nitrotyrosine, a marker of NO release, and apoptosis in the articular cartilage of human osteoarthritis.
METHODS
To investigate the role of nitrotyrosine and apoptosis in the degradation of the chondroid matrix in human osteoarthritis, immunohistochemistry was done for MMP-1, MMP-3, and nitrotyrosine; and the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated nick end labeling (TUNEL) method was performed for apoptosis using a total of 93 articular cartilages from 12 femoral heads and 17 knees obtained from total joint arthroplasty and 7 normal articular cartilages. RESULTS: In the normal control group, the expression rates for MMP-1, MMP-3, nitrotyrosine, and apoptosis were very low; and their expression zones were confined to the superficial layer of the articular cartilage. Their expression rates were low in the early stage of osteoarthritis and were moderate to high in the late stage (P<0.05). Their expression zones were confined to the superficial layer of the articular cartilage in the early stage of osteoarthritis and were expressed throughout the whole layer in the late stage and those of MMP-3 and nitrotyrosine were statistically significant (P<0.05). Their expression rates and zones were significantly correlated with the grade of osteoarthritis (P<0.05). Conclusion : The expression rate and zone of apoptosis and nitrotyrosine correlated well with those of MMP-1 and MMP-3. Therefore, NO and apoptosis may be related to the progression of human osteoarthritis.
- Correlation Between Neuronal Apoptosis and Expression of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase after Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia.
- Byoung Yuk Yi, Sung Kyoo Hwang, Ku Seong Kang, Hong Hua Quan, Young Mi Lee, Jung Wan Kim, Eun Kyoung Kwak, Ji Young Park, Yoon Kyung Sohn
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(6):364-371.
- 2,109 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Neuronal death in acute-phase cerebral ischemic injury is caused by necrosis. However, neuronal injury after reperfusion can be associated with apoptosis.
METHODS
We used Sprague-Dawley rats whose brains were reperfused after middle cerebral artery occlusion for either 30 min or 2 h. We examined a relationship between apoptosis and the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in the brain tissue from 3 h to 14 days after reperfusion in both groups.
RESULTS
TUNEL and iNOS positivity were closely related in both groups. The 2-h ischemia group exhibited increases in the amount of TUNEL and iNOS-positive cells for up to 3 days after reperfusion, at which the TUNEL and iNOS-positive cells decreased. The 30-min ischemia group exhibited peak positivity 24 h after reperfusion, followed by a similar decrease. iNOS mRNA expression peaked 3 h after reperfusion in the 30-min ischemia group, at which time it decreased. In the 2-h ischemia group, iNOS mRNA increased 3 h after reperfusion, peaked 24 h after reperfusion, and then decreased.
CONCLUSION
These results indicated the occurrence of delayed apoptosis in transient cerebral ischemia. Increased expression of iNOS is closely associated with this apoptosis, and oxygen free radical-producing materials, such as nitric oxide, may play an important role in the induction of this apoptosis.
- Relationship between Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), Apoptosis and Lymphocytic Infiltration in Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Rich Stroma.
- Tae Heon Kim, Mee Yon Cho, Sang Yeop Yi, Woo Hee Jung, Kwang Hwa Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(5):368-375.
- 2,183 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Gastric carcinoma with lymphoid rich stroma (GCLRS) is an undifferentiated gastric carcinoma with heavy lymphocytic infiltrate. In order to clarify the relationship between lymphocytic infiltration and apoptosis in gastric carcinoma, we investigated the association of apoptosis with apoptotic proteins and Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) expression in GCLRS.
METHODS
We performed immunohistochemical stains for bcl-2, bax and in situ hybridization for EBER (Epstein-Barr virus encoded RNA)-1 and the terminal deoxynucleaotidil transferase mediated dUTP-digoxigenin nick end labelling (TUNEL) technique using 47 out of 1635 gastric carcinoma cases.
RESULTS
The prevalence of GCLRS was 1.47% (24/1635). The prevalence of EBV involvement in GCLRS (79%, 19/24) was significantly higher than that of gastric carcinoma with lymphoid poor stroma (GCLPS) (8.7%, 2/23). The immunohistochemical stain for bcl-2 revealed negative expressions in all cases, but that of bax was positive for in all cases. bax was significantly correlated with the apototic index (P<0.05). There was no statistical significance between lymphocytic infiltration and apoptosis. The lymphocytic infiltration significantly correlated with the expression of EBV (P<0.05) but not with survival rate and apoptosis. However, most of the GCLRS displayed low clinical stages(stage IA, B), and we suggest that was a proper reason for a good prognosis.
CONCLUSIONS
These results support that EBV is associated with GCLRS, and there is no relationship between apoptosis and bcl-2, bax and prognosis. They also suggest that EBV infection play an important role in the gastric carcinogenesis.
- Expression of Fas/Fas Ligand and Its Relationship with Apoptosis in Chemically Induced Preneoplastic Lesions in Rat Liver.
- Hye Jin Lee, Do Youn Park, Kyung Un Choi, Jee Yeon Kim, Chang Hun Lee, Mee Young Sol, Kang Suek Suh
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(5):383-390.
- 2,077 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Apoptosis of hepatocytes plays a major role in experimental hepatocarcinogenesis of rats. But sequential change and localization of Fas and Fas ligand (FasL) in preneoplastic lesions and the relationship with apoptosis are not clearly elucidated.
METHODS
We investigated sequential change and localization of Fas/FasL and its relationship to apoptosis in preneoplastic lesions of chemical hepatocarcinogenesis in rats using northern blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase end labeling (TUNEL) assay.
RESULTS
We found that mRNA of Fas and Fas ligand increased for up to 42 days and 14 days after partial hepatectomy, respectively, and thereafter decreased with time. Fas protein was localized on the cytoplasm of hepatocytes of preneoplastic lesions, as well as on the cytoplasmic membrane of the adjacent liver parenchyme. Fas negative preneoplastic lesions were evident at 42 days after partial hepatectomy. FasL protein was found only in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes of preneoplastic lesions, instead of in the adjacent liver parenchyme. FasL-positive hepatocytes increased with time for up to 14 days after partial hepatectomy and therafter decreased. Also, TUNEL-positive apoptotic cells increased with time and were more numerous in the adjacent liver parenchyme than in the preneoplastic lesions.
CONCLUSIONS
It was suggested that Fas/FasL-mediated apoptosis might be one of the major mechanisms for controlling apoptotic cell death in the promotion stage of chemical hepatocarcinogenesis.
- The Spontaneously Occurred Apoptosis in Squamous Carcinoams of the Uterine Cervix.
- Chan Hwan Kim, Kwan Kyu Park, Kun Young Kwon, Sang Sook Lee, Eun Sook Chang
- Korean J Pathol. 1990;24(3):254-266.
- 1,847 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The apoptosis, a distinctive type of individual cell necrosis, has been considered to play a complementary but opposite role to mitosis in the regulation of animal cell populations. It can be initiated or inhibited by a variety of environmental stimuli, physiologically and pathologically. Apoptosis seems to appear in either non-neoplastic or neoplastic tissues, even malignant tumors in the state of untreatment or irradiation. This study was carried out to investigate the spontaneous occurrence of apoptosis in squamous carcinomas of the uterine cervix and its mechanisms. Light microscopically, noted were the condensation and fragmentation of individual tumor cells with formation of apoptotic bodies that were frequently phagocytosed by nearby intact tumor cells. They were commonly seen in the neighbourhood of coagulative necrosis. Electron microscopically (TEM and SEM), noted were nuclear condensation, margination toward the nuclear membrane and fragmentation of membrane-bounded apoptotic bodies that were well preserved. The intracellular apoptotic bodies were phagosomes and reduced to electron-dense lysosomal residual bodies. The conclusion obtained was as follow: Apoptosis was found in all cases of squamous carcinoma of the uterine cervix, of which the frequency was higher in tumors of poor differentiation than those of well to moderate differentiation. The process of the apoptosis is considered to pass through the step of formation of the apoptotic bodies, phagocytosis by adjoining tumor cells or histiocytes, and then degradation as lysosmal residual bodies.
- Apoptosis Induced by Adriamycin in HeLa Cells.
- Sun Young Kim, Sang Sook Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(5):433-442.
- 2,064 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was carried out to demonstrate the mode of ADR-induced cell death(apoptosis) on the light and electron microscopic features, to measure the apoptotic index dependent on various doses of ADR, to investigate the possible mechanism of apoptosis induced by ADR, and to evaluate ISNT method for the detection of DNA strand break. HeLa cells were treated with various doses of ADR 0.1~100.0 microgram/ml and observed under the light and transmission electron microscopes at 6 hours, 1 day and 3 days after ADR treatment. In addition, DNA strand breaks induced by ADR were detected in HeLa cells using the in situ nick translation(ISNT) method. The results were as follows: 1) The cell viability of HeLa cells decreased and the apoptotic index increased following exposure to ADR in a dose-dependent manner, resulting in about 44% of apoptotic index at 100.0 microgram/ml of ADR treatment. 2) Light microscopically, HeLa cells treated with ADR showed shrinkage or condensation of nucleus and cytoplasm. There were various unclear changes showing irregular, large, delineated masses of condensed chromatin abutting on the nuclear envelopes. Later stage of apoptosis revealed contracted and condensed cytoplasm with irregular cell membrane. Electron microscopically, margination of condensed chromatin, dilatation of endoplasmic reticulum under the plasma membrane, aggregation of cytoplasmic organelles with morphologically intact mitochondria, and irregular cell surface with blebbing were observed. 3) ISNT using biotinylated dUTP exhibited strong positive nuclear staining in HeLa cells treated with ADR. There was a marked response at 10.0~20.0 microgram/ml of ADR treatment. It is concluded from the above results that the death of HeLa cells induced by ADR was apoptotic in type based on light and electron microscopic appearance. The apoptotic index correlated with the increasing dose of ADR. ISNT with biotinylated dUTP led to visible evidence of DNA strand breaks following ADR treatment of HeLa cells. ISNT can be used for detection of DNA degradation, caused by activation of endogenous endonuclease, which is an early and specific characteristic of apoptosis.
- Apoptosis of Alveolar Cells in Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia: Application of Electron Microscopic Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase-Mediated dUTP-Biotin Nick End Labeling Method.
- Kyu Hun Kang, Sang Pyo Kim, Kun Young Kwon
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(6):496-505.
- 1,948 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Pneumocystis carinii (P. carinii) attaches to alveolar cells and causes injury to the epithelial cells by direct toxic effects or inhibition of epithelial growth and replication. Although respiratory cell damage or death is a common feature in P. carinii pneumonia, there has been little reports about expression of apoptosis of the lung tissue in the literatures.
METHODS
We examined expression of fibronectin and vitronectin in the interaction between P. carinii and alveolar cells, and in situ terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP biotin nick end-labeling (TUNEL) expression of apoptosis in the respiratory cells by immunohistochemistry and pre-embedding immunoelectron microscopy.
RESULTS
Light microscopic (LM) and electron microscopic (EM) immunohistochemical stains for the fibronectin and vitronectin showed strong expressions on the pellicles and tubular extensions of P. carinii and weak expression along the surfaces of type I alveolar cells. LM and EM TUNEL stains showed positive expression in the nuclei of alveolar cells, apoptotic bodies in the cytoplasm of alveolar macrophages and cellular debris in alveolar spaces.
CONCLUSIONS
P. carinii induces injury and apoptosis of alveolar cells after attachment of the organisms to host cells, and alveolar macrophages enhance the clearance of apoptotic bodies of alveolar cells as well as phagocytosis and degradation of P. carinii.
- Apoptosis in Renal Hypertrophy after Uninephrectomy in the Rats.
- Chan Pil Park, Jung Woo Noh, Joo Seob keum, Myung Sook Kim, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(6):513-523.
- 1,916 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Glomerular compensatory hypertrophy maintains decreased renal function after uninephrectomy (UNX). Proliferation and apoptosis of renal cells may be involved in hypertrophy.
METHODS
In small and large male Sprague-Dawley rats, contralateral kidneys were harvested 1, 7, 14 and 30 days after UNX. Apoptosis was assessed by the Tdt-mediated dUTP-digoxigenin nick end labelling method. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen and Fas ligand (FasL) expression was determined by immunohistochemically.
RESULTS
Morphometrically, glomerular hypertrophy was observed in both small and large rats after UNX, and it was more significant in the small rats. The glomerular proliferation index (PI) was gradually increased from day 7 but decreased on day 30 in the small rats. Glomerular PI was significantly increased from day 7 in large rats and peaked at day 14. Apoptotic cells in the glomeruli were slightly increased on day 1 and on day 7 in both groups of rats. The expression of FasL was gradually increased in the distal tubular epithelium in both groups.
CONCLUSIONS
These results demonstrate different profiles regarding the compensatory growth of the kidney, cell proliferation, and apoptosis during the period of compensatory hypertrophy in uninephrectomized rats of different weight and age. Apoptosis may play a role in regressing a number of proliferated cells during renal compensatory hypertrophy.
- Ki-67 Labelling Index and Bax Expression According to the Capsular Invasion in the Follicular Neoplasms of the Thyroid.
- Hee Kyung Kim, Dong Wha Lee, So Young Jin, Dong Won Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(6):531-535.
- 2,161 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
There have been a few studies concerning the differential diagnosis between follicular adenomas and minimally invasive follicular carcinomas, but it is difficult to exclude the possibility of minute capsular and/or vascular invasion throughout the capsular areas as a whole.
METHODS
We examined the diagnostic usefulness of Ki-67 labelling index and bax expression for the differential diagnosis of follicular adenomas and minimally invasive follicular carcinomas.
RESULTS
The result of immunohistochemical staining with Ki-67 and bax antibodies were analyzed in 58 cases of follicular neoplasms from 1996 to 1999. Of 58 cases, 35 were follicular adenomas and 23 were minimally invasive follicular carcinomas. The Ki-67 labelling index was significantly higher in minimally invasive follicular carcinoma of the thyroid (Ki-67 labelling index, 1.62+/-0.35%) than follicular adenoma (0.46+/-0.21%) (P<0.05). Of the follicular adenomas, Ki-67 labelling index of the tumor with 5 cm or more in diameter was 0.38+/-0.13%, while that of the tumor with less than 5 cm was 0.51+/-0.24%. Of the minimally invasive follicular carcinoma, Ki-67 labelling index of the tumor with 5 cm more was 1.30+/-0.07%, while that of the tumor with less than 5 cm was 1.65+/-0.37%. Diffuse bax expression was seen in 27 of 35 cases of follicular adenomas and 2 of 23 cases of minimally invasive follicular carcinoma (P<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Our findings suggest Ki-67 labelling index and the degree of bax expression are useful markers for the differential diagnosis between the follicular adenoma and the minimally invasive follicular carcinoma of the thyroid.
- Differentiation, Proliferative Index, and Caspase 3 Expression Rate in the Immunohistochemical Stains of Medulloblastoma as Prognostic Factors.
- Sung Eun Kim, Woo Ick Yang, Tai Seung Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(6):536-543.
- 1,952 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Medulloblastoma is a highly malignant neuroepithelial tumor of the childhood, less frequently, of adults, located in the posterior cranial fossa. It shows multiple lines of differentiation, expressing neuronal, glial, mesenchymal and ectodermal markers. The prognostic significance of cell differentiation has been studied, but received little agreement. In highly malignant tumors, very high proliferative index has been demonstrated. A major contributor to cell loss in medulloblastoma is reported to be apoptosis. In medulloblstoma, a linear relation between apoptotic index and proliferative index has not been convincingly demonstrated.
METHODS
We analyzed the immunohistochemical features, proliferative indices and apoptotic indices in medulloblastoma patients with regard to their clinical courses. Clinical features of 58 patients with medulloblastoma were reviewed. The presence of glial fibrillary acidic protein, synaptophysin, vimentin, and epithelial membrane antigen were examined with immunohistochemical method. The proliferative index (Ki-67) and caspase 3 expressing rate were calculated.
RESULTS
There was no significant correlation between the prognosis and the degree of cell differentiation. The positive correlation was noted between proliferative index and apoptotic index in a tumor mass.
CONCLUSIONS
Only proliferative index could be used as a prognostic factor.
- Abnormal Development and Apoptosis Observed in Brains of the Trisomy 16 Mouse.
- Eun youn Cho, Yeon Lim Suh, Je Geun Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(8):570-580.
- 1,962 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We have studied morphologic characteristics and apoptosis on the fetal brain of the trisomy 16 mouse, a model for human trisomy 21 syndrome. This study was based on serial sections of the whole brain from a sample of sixteen trisomy 16 mice and forty-six age-matched control littermates from embryonic day (ED) 12 to ED 18. Trisomy 16 brains showed a reduction of telencephalic size and abnormal cortical development. At ED 13 trisomy 16 and control brains appeared similar. By ED 14 difference in the cortical thickness and telencephalic growth became evident, and by ED 16 a marked size difference had developed between the trisomy 16 and control brains. By ED 18, however, the thickness of the trisomy 16 cortex had increased considerably and was not significantly different with respect to the thickness and cross-sectional areas of the pallium and its constituent cortical layers. The cell density of the trisomy 16 cortex had persistently decreased before ED 17, when the cell density of control and trisomy 16 corteces was similar within each layer. At ED 18 cell density of trisomy 16 cortex in each layer increased. There was inverse relationship between a number of TUNEL positive apoptotic cells and cell density in the trisomy 16 brains. Our results suggest that developmental abnormalities of the trisomy 16 brain indicated developmental delay of the telencephalon growth, which may be caused by apoptosis rather than by a proliferation defect.
- A Study of Apoptosis Induced by Microinjection of Cytochrome c Protein into Mouse 3T3 Fibroblast.
- Min Sup Lee, Gu Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(1):1-6.
- 1,777 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Microinjectors have been used for cell biology and development, and are useful for the study of cellular morphologic changes with response to the external milieu and intracellularly injected molecules.
METHODS
This study was performed to confirm the apoptotic changes induced by intracytoplasmic microinjection of cytochrome c (5 mg/mL) to mouse 3T3 fibroblasts with and without pretreatment of Ac-DEVD-CHO (100 mol/mL), and BSA (bovine serum albumin, 5 mg/mL) as a control, and evaluate the usefulness of microinjection as a method to study apoptosis pathways.
RESULTS
Mild focal cytoplasmic fragmentation was seen in the cells microinjected with cytochrome c as early as 10 min after the injection. Apoptotic morphology with apoptotic body formation was observed at 60 min after the injection, and then new apoptotic change of the injected cells was not seen. Cytochrome c-injected cells showed about 31% of apoptotic cells of the total injected cells 50-60 min after the injection. BSA-injected cells did not show apoptosis morphology at 50-60 min after the injections. Caspase-3 inhibitor, Ac-DEVD-CHO-treated cells with cytochrome c microinjection exhibited lower apoptosis indices (average apoptosis index; 11.5+/-8.6%) than non-treated cells of the inhibitor (average apoptosis index; 11.5+/-8.6%).
CONCLUSIONS
It was observed that intracellular microinjection of cytochromic c induced apoptosis which was inhibited by Ac-DEVD-CHO, although apoptotic cells were so easily detached that further study could not be performed. However it is thought that microinjection should be a method to study apoptosis and signal transduction with the molecular biological techniques currently available.
- Histomorphologic Changes of Small Intestinal Mucosa after Irradiation in Rats.
- Chan Hwan Kim, Eun Sook Chang, Keon Young Kwon, Kwan Kyu Park, Ok Bae Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(9):639-651.
- 1,966 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inadvertent application of ionizing radiation, a valuable tool in diagnostic radiology and radiotherapy, results in injury and death of adjacent normal cells, inducing gene mutations or even producing latent cancers. Captopril, an angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, has been reported to prevent the structural and functional changes in variable organs, such as lung and kidney, from radiation injury in different experimental animal models. An experiment was carried out to elucidate the radiation-induced histomorphologic changes of small intestine, especially jejunum, and to determine whether captopril can reduce or prevent the radiation-induced injuries in jejunum. Twenty-six healthy Sprague-Dawley rats were used. Experimental group (n=24) was divided into two large groups: the first one (n=16) was treated with two different single dose (9 Gy, 17 Gy) irradiation only and was sacrificed at 12 hours and at 8 weeks following irradiation; the second one (n=8) received captopril 500 mg/l per oral continuously after same doses of irradiation and was sacrificed at 8 weeks. The control group (n=2) was maintained on a stock diet in a same period of experimental group and sacrificed coincidentally. On light and electron microscopy, the 9 Gy and 17 Gy 12 hours groups revealed frequent apoptosis and necrosis but extremely decreased mitotic figures of the crypt cells. However, the 9 Gy and 17 Gy 8 weeks groups and the combined irradiation with captopril groups showed extremely reduced apoptosis and necrosis with increased mitotic figures. There was good correlation between experimental groups in apoptotic count and mitotic count (p<0.05). In the 9 Gy and 17 Gy 12 hours groups, the mucosal surface was focally or diffusely fragmented and the villi were slightly to moderately distorted. Collagen deposition was very mild and confined to the lower portion of the lamina propria. The 9 Gy and 17 Gy 8 weeks groups showed more severe mucosal surface fragmentation even with foci of erosion, short and distorted villi, and more intense collagen deposition. In contrast, the combined irradiation with captopril groups revealed complete regeneration of the mucosal surface epithelium and absent collagen deposition. These findings suggest that the acute radiation injuries to small intestine occur principally in the mucosal crypt cells. Captopril, the ACE inhibitor, might provide a useful intervention in the radiation injuries of intestinal mucosa.
- The Pattern of Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in Human Embryonic and Fetal Brain.
- Suk Jin Choi, Jung Ran Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(1):38-44.
- 2,137 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Cell proliferation and apoptosis account for the major morphogenetic mechanisms during development of the central nervous system. We investigated these processes in developing human brains.
METHODS
We examined human embryonic and fetal brains. Cell proliferation was analysed by classical histology and MIB-1 immunohistochemistry; cell death was investigated by the TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labelling method.
RESULTS
Most proliferating cells were observed in the ventricular zone (VZ) in the 3rd-10th week of gestational age (GA), and in both the VZ and the subventricular zone (SV) in the 19-24th week of GA. The proliferation index of the VZ was highest in the 8th week of GA and then decreased as the GA advanced. Apoptotic cells were observed in the VZ as early as the 5th week of GA. They were also observed in the intermediate zone in the 19-24th week of GA, although they were significantly lower in amount compared to that in the VZ and SV.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggest that apoptosis occurring early in the embryonic period is related to a cellular mechanism which selects and determines the cells that are committed to migration and differentiation during the development of the human brain.
- Mutational Analysis of Proapoptotic bcl-2 Family genes in Colon Carcinomas.
- Young Hwa Soung, Jong Woo Lee, Su Young Kim, Suk Woo Nam, Won Sang Park, Jung Young Lee, Nam Jin Yoo, Sug Hyung Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(3):168-171.
- 2,033 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Several lines of evidence have indicated that the deregulation of apoptosis is involved in the mechanisms of cancer development, and somatic mutations of the apoptosisrelated genes have been reported in human cancers. Members of the bcl-2 family proteins regulate the intrinsic apoptosis pathway mainly in the mitochondria. The aim of this study was to explore whether the somatic mutation of the proapoptotic bcl-2 family genes, one of the mechanisms that prolong the survival of cancer cells, occurred in colorectal carcinomas.
METHODS
In the current study, to detect the somatic mutations in the DNA sequences encoding the bcl-2 homology 3 (BH3) domain of the human bak, bid, bik, bim, PUMA, bcl-rambo, bcl-G, and bmf genes in 98 colon adenocarcinomas, we used polymerase chain reaction (PCR), single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP), and DNA sequencing.
RESULTS
The SSCP analysis detected no evidence of somatic mutations of the genes in the coding regions of the BH3 domain in the cancers.
CONCLUSIONS
The data presented here indicate that the proapoptotic bcl-2 family genes, bak, bid, bik, bim, PUMA, bcl-rambo, bcl-G and bmf may not be somatically mutated in human colorectal carcinomas, and suggest that the colorectal cancers may not utilize mutational events of these proapoptotic bcl-2 family genes in the mechanisms for evading apoptosis.
- Expression of Apoptosis, bcl-2, and PCNA in Uterine Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Invasive Carcinoma.
- Myoung Ja Chung, Kyu Yun Jang, Myoung Jae Kang, Dong Geen Lee, Byung Chan Oh
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(11):1180-1189.
- 2,262 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- This study was undertaken to know the extent of apoptosis, expression of bcl-2 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in uterine cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN; 15 cases) and invasive carcinoma (27 cases) and to evaluate them as a prognostic marker. Apoptosis was analysed by using the in situ apoptosis detection kit and bcl-2 and PCNA were detected by the immunohistochemical method. The results were as follows: Apoptotic indices (AI) in the invasive carcinoma (mean: 4.3) were 10-times higher than that in the CIN (mean: 0.43). Bcl-2 was expressed 60% of the cases in the dysplastic cells of the CIN II and CIN III, 33.3% of cases in the invasive carcinoma and not expressed in the CIN I except basal cells. The expression of the PCNA was increased by the grades of CIN and was strong in invasive carcinoma. The mean survival time of the patient with invasive carcinoma was significantly decreased in the higher AI index (above 4.3) than in the lower AI index (below 4.3). There was no significant correlation between the extent of apoptosis and the expression of bcl-2. According to the above results, AI are able to be used as an independent prognostic marker in the invasive cervical carcinoma, and bcl-2 and PCNA have an important role in the tumorigenesis of uterine cervical carcinoma.
- Relationship between HPV Infection and bcl-2 Protein Expression and Apoptosis in Invasive and In Situ Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix.
- Myoung Ja Chung, Kyu Yun Jang, Woo Sung Moon, Myoung Jae Kang, Dong Geun Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(9):702-708.
- 2,283 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Human papillomavirus (HPV) 16/18 is a causative agent of uterine cervical carcinoma. HPV 16/18 can alter cell cycle regulation through apoptosis. Bcl-2 is an important regulatory gene of apoptosis. A study was done to evaluate the relation between HPV 16/18 and bcl-2 and apoptosis in 21 cases of carcinoma in-situ (CIS), 5 cases of microinvasive carcinoma and 23 cases of invasive squamous cell carcinoma. HPV 16/18 was detected by hybrid capture system (HCS), bcl-2 protein by immunohistochemical method and apoptosis by using the hematoxylin-eosin stained slide. The results were as follows: Expression of the bcl-2 protein was 43% (9/21) in CIS and 26% (6/23) in invasive carcinoma. Expression of the bcl-2 protein was 42% (5/12) in CIS with HPV 16/18 infection, 44% in CIS without HPV 16/18 infection, 20% (2/10) in invasive carcinoma with HPV 16/18 infection and 31% (4/13) in invasive carcinoma without HPV 16/18 infection. Mean apoptotic index (mAI) was 3.36 in CIS, 5.23 in microinvasive and 6.25 in invasive carcinoma. mAI was 3.66 in CIS with HPV 16/18 infection, 2.86 in CIS without HPV 16/18 infection, 6.18 in invasive carcinoma with HPV 16/18 infection and 6.30 in invasive carcinoma without HPV 16/18 infection. Based on these results, we conclude that there are no correlation between HPV infection and bcl-2, and between HPV infection and apoptosis in invasive and in situ carcinoma of the uterine cervix, and apoptosis is increased according to tumor progression.
- The Expression of Bcl-2, Bax, Cytochrome C and Caspase-3 in Camptothecin-Induced Apoptosis of Mouse 3T3 Fibroblasts.
- Young Jun Ahn, Min Sup Lee, Gu Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(2):71-76.
- 2,350 View
- 52 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Camptothecin (CPT), which has been used for cancer treatment and apoptosis as an inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase I. We investigated the possibility that camptothecin induces anti-appoptotic bcl-2 and pro-apoptotic bax, cytochrome c and caspase-3.
METHODS
We performed immunocytochemical stains for bcl-2, bax and cytochrome c, and also performed westem blots for caspase-3 and the three proteins above using mouse 3T3 fibroblasts treated with CPT (0.5 microgram/mL). The immunostain for bcl-2 was done 12 hours after a microinjection of antisense oligomer to bcl-2 in the nuclei of the cells.
RESULTS
On immunocytochemistry, bcl-2 showed no expressions regardless of CPT treatment and microinjection of the antisense oligomer. The expression of cytochrome c was not changed before and after CPT treatment, and bax demonstrated weak or moderate expressions at 36 and 48 hours afte the treatment. There were no expressions at 0, 12, and 24 hours after CPT treatment. On westem blot, bcl-2 exhibited no expressions before and after CPT treatment. Expressions of ctyochrome c and caspase-3 increased after CPT treatment, and expressions of bax decreased 24 hours after CPT treatment followed by a tendency of increased expressions as time went by.
CONCLUSIONS
In the CPT-induced apoptosis of mouse 3T3 fibroblasts, CPT induced increased expressions of bax, cytochrome c and caspase-3 with no expressions of bcl-2, which are associated with the apoptosis pathway.
- An Analysis of p53, bcl-2 and Ki-67 Expressions, and Apoptosis in Rectal Cancer: Their Correlation with the Tumor Response after Preoperative Radiochemotherapy.
- Jinyoung Yoo, Su Zy Kim, Hyeon Min Cho, Sung Whan Kim, Hyung Min Chin, Jung Yong Lee, Jun Ki Kim, Seok Jin Kang, Chung Soo Chun, Chang Suk Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(4):222-228.
- 2,112 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
: Preoperative radiochemotherapy (RCT) has been administered for locally advanced rectal cancer to increase the therapeutic benefits, and to preserve the sphincter in low-lying tumors, however, tumor responses after RCT are variable. Methods : Apoptotic index (AI), and expressions of Ki-67, p53 and bcl-2 were analyzed in pretreatment biopsies from 69 patients with rectal cancer by immunohistochemistry. Tumor response was graded in surgically resected specimens by using a three-scale grading system: no response (NR), partial remission (PR) and complete remission (CR). Results : CR was identified in 19 cases (28%), PR in 24 cases (35%), and NR in 26 cases (38%) of 69 cases. p53 protein was expressed in 49 cases (71%), whereas bcl-2 was in 42 cases (61%). The pretreatment Ki-67 labeling index was 65.4+/-3.4%. The tumor response was not associated with any of these markers. Tumors with CR/PR showed a higher AI (0.84+/-.84%/0.66+/-.52%) than that of tumors with NR (0.58+/-0.54%). There was a significant correlation between tumor response and the histologic differentiation (p=0.008) or recurrence (p=0.039). Conclusions : The AI revealed a tendency to increase in tumors with CR/PR, while expressions of p53 and bcl-2, and Ki-67 labeling index had little direct association with tumor response.
- Immunohistochemical Study on the Expression of Bcl-2 and p53 Protein in Gastric Adenocarcinoma.
- Joon Hyuk Choi, Won Hee Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(12):1282-1290.
- 2,070 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was carried out to investigate the immunohistochemical expression of bcl-2 and p53 protein in the intestinal type and the diffuse type of gastric adenocarcinoma by Lauren's classification. A total of 100 cases, including 50 cases of the intestinal type and 50 cases of the diffuse type from paraffin embedded gastrectomy specimens, were immunohistochemically stained for bcl-2 and p53 protein. Bcl-2 protein was expressed in 38% (19/50) of intestinal type and 30% (15/50) of diffuse type. The incidence of bcl-2 protein expression was higher in the intestinal type than in the diffuse type, but no significant correlation was present (p>0.05). p53 protein was expressed in 68% (34/50) of the intestinal type and 60% (30/50) of the diffuse type. The incidence of p53 protein expression was higher in the intestinal type than in the diffuse type, but no significant correlation was present (p>0.05). And an expression of bcl-2 and p53 protein did not correlate with depth of invasion, lymph node meatastasis and TNM stage, respectively (p>0.05). These results suggest that bcl-2 and p53 gene alteration appear to play a more important role in the carcinogenesis of the intestinal type than the diffuse type. However, there is no significant difference between the intestinaPU: The Korean Society of Pathologistsl type and the diffuse type in bcl-2 and p53 protein expression.
- Taxol-induced Pathological Findings in Rat Small Intestine.
- Sun Hee Chang, Shi Nae Lee, Hee Soo Yoon, Min Sun Cho, Hea Soo Koo, Woon Sup Han
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(12):1291-1296.
- 2,176 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Taxol is an active chemotherapeutic agent against a variety of solid tumors and a potentially useful drug for augmenting the cytotoxic action of radiotherapy against certain cancers. Taxol blocks cells in the mitotic phase of cell cycle. The aim of this study was to define the in vivo response of rapidly dividing cells of the small intestinal mucosa to taxol. We studied the numbers of apoptotic and mitotic cells and the expression of bcl-2 and p53 in rat jejunal crypt cells at 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, and 24 hours and 3 and 5 days after intraperitoneal injection of taxol. Mitosis peaked at 2 and 4 hours and 12 and 16 hours. Apoptosis peaked at 16 hours and returned to normal after five days. The glands in crypts showed marked distortion with atypical lining cells after three days, which returned to normal at 5 days. bcl-2 expression was markedly decreased at 8 to 24 hours and subnormally recovered after three to five days. p53 showed no significant changes throughout. The histopathological changes in small intestine due to taxol were transient with complete recovery. bcl-2 expression was inversely corresponded to numbers of apoptosis. The changes were p53 independent. Further studies to understand the conditions that maximize the cell-cycle modulating effects of taxol cl-may greatly enhance its anti-tumor effectiveness.
- Expression of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase and Nitric Oxide Mediated Apoptosis in Neuronal PC12 Cells after Lipopolysaccharide/Tumor Necrosis Factor-/Interferon- Treatment.
- Jiyeon Kim, Jiyoung Kim, Kuseong Kang, Eunkyoung Kwak, Jiyoung Park, Taein Park, Yoonkyung Sohn
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(4):249-256.
- 1,942 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) has been detected in a number of pathologic conditions in the central nervous system. This study was investigated the patterns of iNOS expression in the neuronal PC12 cell and the effects of nitric oxide on the apoptosis of PC12 cells.
METHODS
The stimulating agents for induction of iNOS expression in PC12 cells were bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-), and interferon-gamma (IFN-).
RESULTS
The expression iNOS mRNA and protein in PC12 cells stimulated with LPS/TNF-/IFN- were profoundly increased. The expression of iNOS mRNA arose at 6 hours, peaked at 12 hours, and declined to 48 hours after LPS/TNF-/ IFN- treatment. iNOS protein was increased up to 24 hours in LPS/TNF-/IFN- treated PC12 cells while the expression of nNOS was unaffected. Accumulation of NO derivatives in the culture media was markedly increased at least at up to 48 hours after LPS/TNF-/IFN- treatment. The induction of iNOS expression and NO production in differentiated PC12 cells was correlated with apoptotic cell death judged by transmission electron microscopy and DNA fragmentation from the results of the Terminal deoxynucleotidyl-transferase-mediated dUDP biotin nick end-labeling (TUNEL) method. After treatment with NOS inhibitor, N-monomethylarginine (NMMA), a profound decrease in NO production by LPS/TNF-/IFN- treated PC12 cells was noted. And the LPS/TNF-/IFN- induced apoptosis was prevented by the NMMA treatment.
CONCLUSIONS
From the above results it is concluded that the expression of iNOS in differentiated PC12 cells is induced by the combined application of LPS, TNF-, and IFN-. And the apoptosis of cultured PC12 cells is mediated by iNOS-derived NO.
- Cytokine Expression on Microglial Proliferation and Apoptosis in Rat Lumbar Spinal Cord Following Unilateral Sciatic Nerve Transection.
- Sang Pyo Kim, Seung Il Suh, Young Rok Cho, Seung Che Cho, Seung Pil Kim, Jong Wook Park, Jyung Sik Kwak
- Korean J Pathol. 1998;32(2):94-103.
- 1,994 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was carried out to elucidate the cytokine mRNAs expression and morphological features according to a microglial proliferation and apoptosis in a rat lumbar spinal cord, after a right sciatic nerve transection. The control group was composed of 5 rats (Spraque-Dawley) and the experimental group was composed of 70 rats. On post operation day (pod) 1, 2, 3, 5, and 7 eight rats were sacrificed on those days. On pod 10 five rats were sacrificed as well as five rats sacrificed on post operation weeks 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. On light microscopy, activated microglia were often found in a perineuronal position around motoneurons in the ventral gray matter and more randomly distributed throughout the neuropil in the dorsal gray matter of lumbar spinal cord. GSA I-B4-positive microglia began to increase from 1 day after transection, and reached peak at 2~3 days and it persisted at 5~7 days and decreased thereafter. TUNEL-positive microglia was not observed in control group and began to increase from 5 days after transection and increased gradually until 3 weeks and decreased thereafter. On in situ RT-PCR, the positive signal for IL-1alpha and IL-6 mRNA was found mainly in the cytoplasm of the activated microglia and astrocytes at 1 day after transection and showed stronger signal at 3 days and decreased gradually until 10 days. TNF-alpha mRNA was detected 1 day after transection and remained for 7 days and localized to activated microglia as well as probably some astrocytes. The signal intensity of IL-1alpha and IL-6 mRNA was generally stronger than TNF-alpha mRNA. On transmission electron microscopy, there were chromatin condensation with margination toward nuclear membrane and condensation of cytoplasm at 3 days after transection. Apoptotic bodies were found after 5 days and increased gradually until 3 weeks. According to the above findings, it is concluded that apoptosis appears to be one mechanism by which activated microglia are gradually eliminated and cytokine expression seems to played an active role in the microglial turnover.
- Gender Differences in Expression of Apoptosis, p53, and Bcl-2 in Delayed Focal Cerebral Infarction in Rats.
- Hee Suk Jung, Seung Won Park, Sung Nam Hwang, Young Bak Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Byung Kuk Min, Jung Taik Kwon, Duck Young Choi, Jong Sik Suk
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(1):1-10.
- 2,121 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Apoptosis is a normal physiological process. Morphological studies have shown that cells die by physiological mechanisms after undergoing characteristic changes termed 'apoptosis' or 'programmed cell death'. Several genes were known to participate in the apoptotic process including p53 as a proapoptic gene and Bcl-2 as an antiapoptic gene. It was also known that there are certain gender differences in the cerebrovascular accidents and their effect on tissue damage. The purpose of this study is to evaluate how the apoptotic genes are expressed in delayed focal cerebral infarction and peri-infarct area in male and female adult rats by comparing the immunoexpression of p53 and Bcl-2 and p53:Bcl-2 ratio at delayed focal cerebral infarction between both sexes. In sixteen adult Spraugue-Dawley rats (nine males and seven females), the right MCA and both CCA were ligated for thirty minutes to make a delayed focal cerebral infarction in right frontal lobe. Their brains were taken at seventy two hours after the operation. And then the brains were prepared for immunohistochemical stains for apoptosis, p53 and Bcl-2 proteins. The infarction volume of male rats (11.3 mm3) was larger than that of female rats (7.3 mm3) (p<0.01). In male group, the width (micrometer2) of the apoptotic area (46.4 micrometer2) was significantly larger than those in female group (38.9 micrometer2) (p<0.005). The p53 : Bcl-2 ratio was significantly higher in male group (3.23) compared with female group (2.18) (p<0.01). As a result, the p53:Bcl-2 ratio seemed to be related to the gender differences in neuronal apoptosis after delayed focal cerebral infarction.
- Expression of p21, p53 and Ki-67, and Apoptosis in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma.
- Young Euy Park, Kyung Chan Choi, Jin Hee Sohn, Young Hee Choi, Hyung Sik Shin
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(5):296-304.
- 2,285 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The purpose of this study is to assess the roles of p21 protein, p53 protein, and Ki-67 expressions and apoptosis in colorectal tumorigenesis.
METHODS
Fifty-seven colorectal cancers and 15 villotubular adenomas were investigated by immunohistochemical staining for p21 protein, p53 protein, Ki-67, and in situ labeling of apoptotic cells. Clinicopathologic values (tumor size, histologic grade, Dukes stage, and lymph node metastasis) were compared with the incidence of expressions of p21 protein and p53 protein, index of Ki-67 expression, and apoptosis.
RESULTS
The incidence of p21 protein expression was decreased with lymph node metastasis (p<0.005), and that of p53 expression was increased with lymph node metastasis (p<0.005). There were no statistically significant correlations among the p21 protein or p53 protein expressions, tumor size, histologic grade and stage. The correlation between the Ki-67 labeling index and the clinicopathologic values was not statistically significant. The labeling index of apoptosis was increased with the Astler-Coller stage (p<0.05). Statistical analysis revealed a significant inverse correlation between the p21 protein and p53 protein expressions (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
It is suggested that p21 protein, p53 protein and the apoptotic labeling index are useful variables for the prognostic assessment of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Down-regulation of p21 protein expression may be associated with poor prognosis. Also, the expressions of p21 protein and p53 protein may play an important role in the tumorigenesis and progression of the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence.
- The Relation between Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis According to the Histologic Types in Chemically Induced Rat Mammary Tumorigenesis.
- Tae Jung Jang, Woo Hee Jung, Kwang Gil Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1998;32(3):174-185.
- 1,937 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Balancing the rates of cell proliferation and cell death is important in maintaining normal tissue homeostasis. The relationship among apoptosis, cell proliferation and factors influencing apoptosis according to the histologic types in chemically induced mammary tumorigenesis appears important in understanding the pathogenesis of breast carcinoma. In this study, we investigated alterations in the kinetics of cell proliferation and apoptosis during rat mammary tumorigenesis induced by 7, 12-dimethylbenzanthracene (DMBA) and we related these changes to the expressions of bcl-2, p53, and TGF-beta. Seven-week-old female Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into an experimental group (20 mg/ml DMBA by oral intubation) and a control group. The results were as follows. 1. In the experimental group, breast tumors occurred in twenty two of fifty nine rats(37.3%, 22/59), and the total number of tumors was 100 (4.5 2.0/rat). The histological classification was infiltrating ductal carcinomas (n=5), ductal carcinomas with focal invasion (n=10), intraductal carcinomas (n=36), adenomas accompanied with intraductal proliferation (n=35), intraductal proliferation (n=9), and adenomas (n=5); 2. The differentiation of terminal end bud into alveolar bud (AB) in the experimental group was significantly lower than that of the control group (p<0.05); 3. BrdU labeled tumor cells were mainly located at the peripheral portion of tumor cell nests. BrdU labeling indices were highest in ductal carcinomas, less pronounced in intraductal proliferation, and lowest in adenomas, whereas apoptosis levels were highest in adenomas, less pronounced in intraductal proliferation, and lowest in ductal carcinomas (p<0.05); 4. p53 protein was not expressed in any breast tumors. Although the expression of bcl-2 protein was highest in infiltrating and focal infiltrative ductal carcinomas (58.3%), compared with adenomas, intraductal proliferation, and intraductal carcinomas (p<0.05), the extent of its expression was less than 1% of all tumor cells; 5. TGF-beta was mainly expressed in the central portion of tumor cell nests rather than in peripheral portion, and TGF-beta immunoreactive tumor cells displayed good differentiation and did not reveal BrdU immunoreactivity. TGF-beta labeling index of infiltrating and focal infiltrative ductal carcinomas was significantly higher than that of intraductal carcinomas, intraductal proliferation, and adenomas (p<0.05). Based on these results, it is thought that high cell proliferation and the suppression of apoptosis are closely associated with DMBA-induced rat mammary carcinogenesis. However, the suppression of apoptosis is not related to p53 mutation, bcl-2, and TGF-beta. TGF-beta seems to be reversely related to tumor cell proliferation but closely associated with the progression of the tumor, especially an invasion of breast carcinomas.
- Melanosis Coli: Relation to Apoptosis in Pathogenesis.
- Sun Hee Sung, Hea Soo Koo, Woon Sup Han
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(7):570-575.
- 2,420 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Melanosis coli is characterized by a dark brownish discoloration of the colonic mucosa. Its pathogenesis is still unknown. Recently it was proposed that the apoptosis of mucosal epithelium due to habitual use of laxatives play an important role for induction of melanosis coli. We studied clinicopathologic aspects of 12 cases of melanosis coli and analysed the histochemical and immunohistochemical characteristics of them. Results are as follows. : Mean patient's age was 53.5, and the male:female ratio was 4:8. Nine patients had a history of constipation, and all of these had administrated various kinds of laxatives. The severity of discoloration was correlated with the duration of constipation and age. There was no difference of anatomical distribution in colon. Other remarkable mucosal lesions were not accompanied. On pathologic examination, all cases showed frequent yellow-brown pigment laden cells in lamina propria. These pigments were positive for periodic acid Schiff stains, Fontana Masson stains, and Victoria blue stains, however they were negative for prussian blue stain. On immunohistochemical stainings pigmented cells were positive for CD68, and negative for S-100 protein and neuron specific enolase. These results indicate that they are macrophages. On ultrastructural examination pigmented cytoplasms were filled with variable sized electron dense granules including irregulary round deformed membranous structures, lipid vacuoles. Apoptosis of mucosal epithelium was noted in 5 cases. These findings suggest that apoptosis is the significant pathologic process in the progression of some cases of melanosis coli.
- The Role of gadd and p53 Genes in Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Delay by Genotoxic Agents.
- Jung Young Lee, Jung Duk Lee, Seung Myung Dong, Eun Young Na, Min Sun Shin, Su Young Kim, Sug Hyung Lee, Won Sang Park, Nam Jin Yoo
- Korean J Pathol. 1998;32(4):239-247.
- 2,298 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The aim of this study was to investigate the relationships between the gadd genes expression and an apoptosis induction in two different growing cell types after treatments with cisplatin and methylmethan sulfonate (MMS). We have examined the kinetics and specificity of gadd45 and gadd153 expression following cisplatin and MMS treatments to HL-60 cells and primary cultured human kidney (HKN) cells. We have also determined an induction time of apoptosis by DNA fragmentation analysis and the presence of the cell cycle arrest by a flow cytometric measurement. The results were as follows. In non-adherent HL-60 cells, a typical ladder pattern was observed within 4 hours after treatments of 20 micrometer of cisplatin and 100 microgram/ml of MMS. At the same time while adherent HKN cells failed to exhibit a ladder pattern at even higher doses of genotoxic agents. Since HL-60 cells do not have p53 gene, these findings suggest the presence of a p53-independent apoptotic pathway. The increasing patterns of the mRNA levels of gadd45 and gadd153 varied with the type of genotoxic agents. In the case of MMS treatment, the induction was rapid and transient, regardless of the cell types. The mRNA level peaked at 4 hours after MMS treatment and markedly decreased after 12 hours. On the other hand, cisplatin-induced transcriptions of gadd45 and gadd153 continued to increase for at least 24 hours and reached a peak level at 48 hours after cisplatin treatment, regardless of the cell types. HL-60 cells revealed G2 arrest following 24 hours after cisplatin and MMS treatments. These findings suggest that the regulation mechanism of apoptosis between adherent and non-adherent cells, might be different and that gadd45 and gadd153 might have an important role in DNA repair rather than apoptosis. Also, the findings suggest that an expression pattern of gadd45 and gadd153 might be different according to the type of genotoxic agents.
- Lipopolysaccharide/Interferon-gamma Induced Nitric Oxide Production in C6 Glioma Cells: Modulation by Dexamethasone.
- Jong Heun Shin, Ku Seong Kang, Ji Yeoun Kim, Sun Zoo Kim, Ji Young Park, Eun Kyoung Kwak, Yoon Kyung Sohn
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(6):406-411.
- 2,192 View
- 42 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Glial cell-derived nitric oxide (NO), and its regulation has significant implications for central nervous system pathophysiology. The aim of the present study was to see the production of NO in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/interferon-gamma (IFN-)-treated C6 glioma cells and the effect of dexamethasone on NO production and apoptosis of LPS/IFN--treated C6 glioma cells.
METHODS
The apoptosis of LPS/IFN- treated C6 glioma cell was examined with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end-labeling (TUNEL) method and the production of NO in culture medium was measured. The expression of iNOS mRNA was examined by semi-quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The effect of the N-monomethyl L-arginine (NMMA) and dexamethasone on the apoptosis and NO production was also examined.
RESULTS
Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mRNA and NO production were markedly increased in LPS/IFN--treated C6 glioma cells. The expression of iNOS mRNA arose at 3 hours, peaked at 12 hours, and declined 24 hours after LPS/IFN--treatment. Accumulation of NO derivatives in the culture media was increased at least upto 48 hours after LPS/IFN-. The induction of iNOS expression and NO production in LPS/IFN--treated C6 cells was correlated with apoptotic cell death judged by TUNEL staining. After treatment of NMMA, one of the NOS inhibitors, NO production and apoptosis were markedly decreased. Dexamehasone treatment suppressed the NO production by concentration depenedent manner.
CONCLUSIONS
From the above results it is concluded that the LPS/IFN- induced apoptosis of C6 cells is mediated by iNOS-derived NO and NO production and apoptosis was suppressed by dexamethasone.
- Pulsating Magnetic Field Effects on in vitro Culture of Human Osteogenic Sarcoma Cell Lines.
- Hyo Sook Shin, Jin Young Lee, Suk Keun Lee, Sang Chul Park, Je G Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(3):169-180.
- 2,056 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to elucidate the biological effects of pulsating magnetic field in in vitro culture system we designed a pulsating magnetic apparatus using 120 Hertz, 24 Volt direct current. It can generate 63~225 Gauss in the experimental area of 90 mm petri dish, and has little thermal effect on the culture media in 37.5oC, 5% CO2. Human osteogenic sarcoma (HOS) cells were cultured in the pulsating magnetic field and the nuclear changes of cultured cells were observed routinely by hematoxylin staining, and apoptotic change was detected by ApopTag staining using both peroxidase and fluorescein labelings. Compared to the control group which formed well organized whorling pattern of HOS cell line in 3 days culture, the HOS cells cultured in the pulsating magnetic field for 12 hours or 24 hours grew irregularly and showed increased number of apoptotic cells. When the flow of pulsating magnetic field was interrupted by insertion of strong permanent magnetic bar (1000 Gauss, 5530 mm) beneath the petri dish during in vitro culture, the area of sparse pulsating magnetic field showed active proliferation and aggregation of HOS cells even in 24 hour exposure group. These data suggest that the pulsating magnetic field may play a role in inducing growth retardation and apoptosis of HOS cells. Furthermore, the hazardous effects of pulsating magnetic field can be lessened or nullified by the interruption of pulsating magnetic field with a strong permanent magnetic bar.
- Anticancer Effect and Apoptosis of All-trans-retinoic Acid on the Human Ovarian Epithelial Carcinoma Cell Lines.
- Jee Young Han, Woo Hee Jung, Tai Seung Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(3):225-234.
- 1,938 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ovarian carcinoma is a serious disease in women. Some reports revealed all-trans-retinoic acid (tRA) inhibited the proliferation of ovarian carcinoma cell lines and induced apoptosis. The aim of this study was to evaluate the anticancer and apoptotic effects of tRA and the expression of the retinoic acid receptor (RAR) alpha, beta, gamma, p53, bcl-2, and c-myc genes on the ovarian carcinoma cell lines, NIH OVCAR3 and SKOV3. In both cell lines, the proliferation of tumor cells was inhibited and characteristic morphologic patterns of apoptosis were shown after treatment of tRA. The number of apoptotic cells and the percentage of apoptosis were increased after treatment of tRA. The gel electrophoresis revealed the DNA ladder pattern in the NIH OVCAR3. Gene expressions were observed using northern blotting. There was no RARalpha expression in both cell lines. In NIH OVCAR3, there was no changes in the expression of RARbeta and bcl-2 gene. The RARgamma gene expression of tRA treated group was slightly increased, but p53 gene expression was decreased, and c-myc gene was not expressed. In SKOV3, the expressions of RARbeta, gamma, and p53 genes were increased and that of bcl-2 was decreased in the tRA treated group. There was no change in c-myc gene expression. These results suggest tRA has anticancer and apoptotic effect on both ovarian carcinoma cell lines. RARbeta, RARgamma, bcl-2, and p53 gene expressions were correlated with these effects of tRA on SKOV3 but not on NIH OVCAR3.
- Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes Using RNA Fingerprinting in Cell after DNA Damage.
- Jung Young Lee, Min Sun Shin, Seung Myung Dong, Eun Young Na, Su Young Kim, Sug Hyung Lee, Won Sang Park, Nam Jin Yoo
- Korean J Pathol. 1998;32(5):321-327.
- 1,937 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- RNA fingerprinting using on arbitrary primed polymerase chain reaction (RAP-PCR) was carried out to identify differentially expressed genes in HL-60 cell after treatment of methylmethane sulfonate (MMS). Twenty differentially expressed PCR products were cloned and analyzed. We have successfully obtained eight partial cDNA sequences by TA cloning method. Among these, six cDNAs were up-regulated and two cDNAs were down-regulated after the MMS treatment. Of these six up-regulated cDNAs, 3 cDNAs were equivalent to known genes in the GenBank/EMBL databases with 98~100% homology searched by BLAST program: genomic DNA fragment containing CpGg island (clone 26h8), Human Rev interacting protein-1 (RIP-1), and human zinc finger protein-4 (HZF4). The sequences of the three remaining cDNA were entirely new genes, but we didn't try to identify a full cDNA sequence. Two clones called KIAA0060 and KIAA0065, were down-regulated in HL-60 cells after the MMS treatment. These findings suggest that the RNA fingerprinting method using RAP-PCR is an effective method which can identify and separate the differentially expressed cDNAs and that the isolated cDNAs might involve in regulation mechanism of apoptosis and/or cell cycle delay, especially a p53-independent pathway, in the cells after DNA damage. But the nature of cDNAs that we have isolated remains to be elucidated.
- Castration-induced Apoptosis in the Rat Prostate.
- Ki Kwon Kim, Sang Sook Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1998;32(6):431-442.
- 2,144 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- This study was carried out to investigate the morphologic findings and process of castration-induced apoptosis in the rat prostate. The experimental group was treated with bilateral orchiectomy followed by sequential sacrifices at 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 days and 2, 3 weeks (6 rats, respectively). Ventral prostate was extirpated and examined by light microscopic and immunohistochemical, ultrastructural observation. Apoptotic index increased by 4 days after castration and decreased thereafter. ApopTag stain revealed brownish granular pattern in the nucleus of apoptotic cells. DNA fragmentation rate was 0.5% in the control group and began to increase by 1 day after castration and reached to 11.1% by 4 days and decreased thereafter. PCNA stain showed brownish granular pattern in the nucleus of some epithelial cells of the prostatic glands. PCNA labelling index was 2.4% in the control group and reached peak by 3 days after castration and decreased thereafter. Electron microscopically, there was chromatin condensation with margination toward the nuclear membrane by 1 day after castration. Also noted were condensation of cytoplasm, dilatation of RER and nuclear fragmentation. Apoptotic bodies were formed and phagocytosed by adjacent cells and some apoptotic bodies were found in the lumen of acini. Based on these results, it can be concluded that castration-induced prostatic involution is the result of apoptosis. Detection of DNA fragmentation with ApopTag is a more a accurate method to identify not only apoptotic body formation itself but also the previous step of apoptotic body formation. PCNA labelling index to identify the cellular proliferation seems to play an active role in the early step of apoptosis and be a good tool for investigation of apoptosis.

 E-submission
E-submission
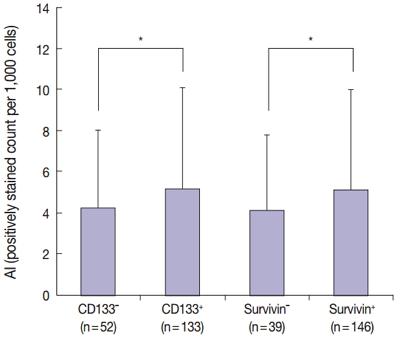

 First
First Prev
Prev



