Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Studies
- Primary carcinoid tumor in the external auditory canal
- Dong Hae Chung, Gyu Cheol Han, Na Rae Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(2):184-187. Published online November 13, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.11.07
- 9,289 View
- 167 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
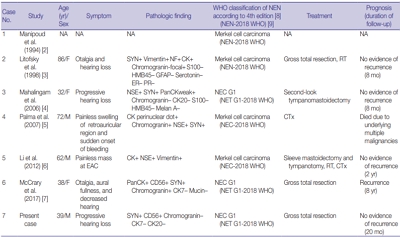
PDF - A 39-year-old man visited the department of otolaryngology due to an ongoing hearing disturbance that had lasted for 1 year. Temporal bone computed tomography revealed soft tissue density nearly obliterating the left external auditory canal (EAC). The mass was composed of sheets of round tumor cells containing moderate amounts of fine granular cytoplasm and salt and pepper chromatin. Neither mitosis nor necrosis was found. The Ki-67 proliferation index was less than 2%. Cells were positive for CD56 and synaptophysin but negative for chromogranin, cytokeratin (CK) 20, and CK7. Based on these findings, the tumor was diagnosed as a carcinoid tumor, well differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma, grade 1 (G1) according to current World Health Organization (WHO) classification of head and neck tumors; and a neuroendocrine tumor, G1 according to neuroendocrine neoplasm (NEN)-2018 WHO standard classification. He remained free of local recurrence and metastasis after 20 months of follow up. To date, only six cases of primary NENs in the EAC have been reported. Metastatic tumor should be included in the differential diagnoses. Because of its rarity, the prognosis and treatment have not yet been clarified.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- First Report on a Rare Poorly Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumour of the External Auditory Canal Involving Pinna
Akash Varshney, Amit Kumar Tyagi, Prashant Durgapal, Kajal Mahto, Akhilesh Chandra Yadav, Ankita Semwal
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2025; 77(4): 1922. CrossRef - Incidental finding of a neuroendocrine neoplasm in a suspected ear canal exostosis
Alexander Wieck Fjaeldstad, Gerda Elisabeth Villadsen, Gitte Dam, Stephen Jacques Hamilton-Dutoit, Thomas Winther Frederiksen
Otolaryngology Case Reports.2022; 22: 100394. CrossRef - 68Ga-DOTATATE Uptake in Well-Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumor of the External Auditory Canal
Özge Erol Fenercioğlu, Ediz Beyhan, Rahime Şahin, Mehmet Can Baloğlu, Tevfik Fikret Çermik
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2022; 47(8): e552. CrossRef
- First Report on a Rare Poorly Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumour of the External Auditory Canal Involving Pinna
- Nodular Fasciitis of External Auditory Canal
- Jihyun Ahn, Sunyoung Kim, Youngsil Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(5):394-396. Published online June 6, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.03.11
- 10,153 View
- 80 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nodular fasciitis is a pseudosarcomatous reactive process composed of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, and it is most common in the upper extremities. Nodular fasciitis of the external auditory canal is rare. To the best of our knowledge, less than 20 cases have been reported to date. We present a case of nodular fasciitis arising in the cartilaginous part of the external auditory canal. A 19-year-old man complained of an auricular mass with pruritus. Computed tomography showed a 1.7 cm sized soft tissue mass in the right external auditory canal, and total excision was performed. Histologic examination revealed spindle or stellate cells proliferation in a fascicular and storiform pattern. Lymphoid cells and erythrocytes were intermixed with tumor cells. The stroma was myxoid to hyalinized with a few microcysts. The tumor cells were immunoreactive for smooth muscle actin, but not for desmin, caldesmon, CD34, S-100, anaplastic lymphoma kinase, and cytokeratin. The patient has been doing well during the 1 year follow-up period.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nodular Fasciitis of the Nose and External Auditory Canal: Two Rare Case Reports
Wanjie Luo, Tianyu Ma, Siqi Wang, Xiaowei Qin, Li Jiang, Yuyao Wang, Tianhong Zhang
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathology Clinic: Nodular Fasciitis Involving the External Ear
Christina M. Yver, Michael A. Husson, Oren Friedman
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2023; 102(5): NP203. CrossRef - Nodular fasciitis of the external auditory canal: Clinical case report and review of the literature
Adrien Philippart, Jean-Christophe Degols, Jacques Vilain
Journal of Otology.2023; 18(4): 240. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of Nodular Fasciitis of Ear Region in Children: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Antonio Della Volpe, Paola Festa, Alfonso Maria Varricchio, Carmela Russo, Eugenio Maria Covelli, Delfina Bifano, Piera Piroli, Antonietta De Lucia, Arianna Di Stadio, Franco Ionna
Healthcare.2022; 10(10): 1962. CrossRef - A Case of Recurred Nodular Fasciitis in Supraauricular
Region
Dong-Jo Kim, Seong-Wook Choi, Chung-Su Hwang, Hyun-Min Lee
Journal of Clinical Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.2022; 33(4): 203. CrossRef
- Nodular Fasciitis of the Nose and External Auditory Canal: Two Rare Case Reports

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



