Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Frozen section histopathology and preanalytical factors affecting nucleic acid integrity in biobanked fresh-frozen human cancer tissues
- Soungeun Kim, Jaewon Kang, Boyeon Kim, Yoonjin Kwak, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):398-407. Published online September 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.22
- 4,929 View
- 206 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
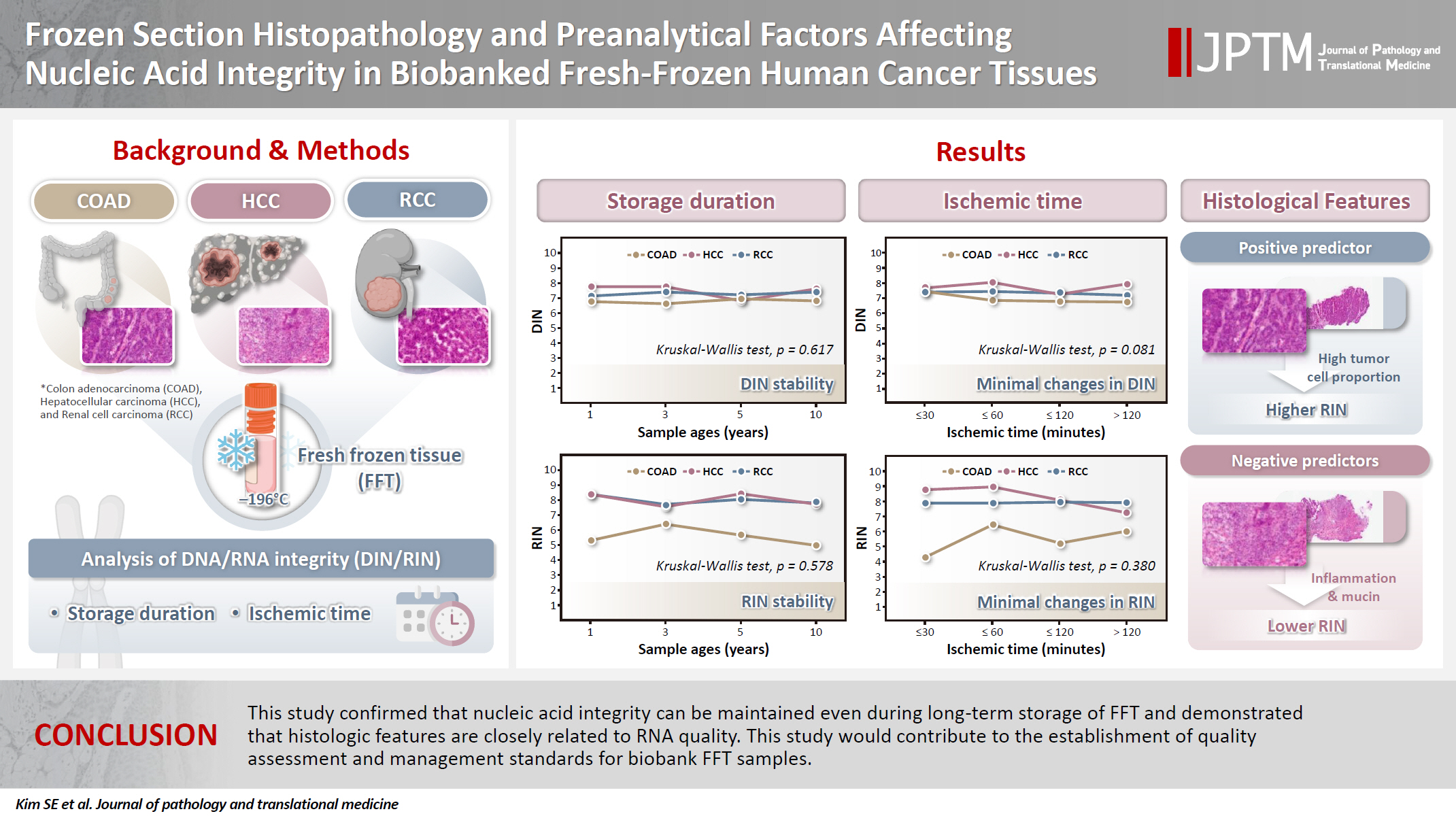
In this study, we evaluated the effects of storage duration and ischemic time on nucleic acid quality of fresh-frozen tissue (FFT) from colon adenocarcinoma (COAD), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and renal cell carcinoma (RCC) collected at the Cancer Tissue Bank of Seoul National University Hospital. Methods: A total of 102 FFT samples were analyzed to compare DNA integrity number (DIN) and RNA integrity number (RIN) according to storage duration and ischemic time. Additionally, the effects of histopathologic features—such as tumor cell proportion, inflammatory cell infiltration, and stromal fibrosis—on nucleic acid quality were evaluated. Results: DIN and RIN remained stable overall even though the storage duration increased, with no statistically significant differences observed. In particular, there was almost no decrease in RNA quality in HCC and RCC samples, but in COAD samples, RIN tended to decrease slightly as the storage duration increased. No significant difference was confirmed between ischemic time and nucleic acid quality, but in COAD tissue, RNA quality variability tended to increase as the ischemic time increased. Furthermore, RIN increased as the tumor cell proportion increased, whereas inflammatory cell infiltration and extracellular mucin pool were identified as independent negative predictors of RIN. Conclusions: This study confirmed that nucleic acid integrity can be maintained even during long-term storage of FFT and demonstrated that histologic features are closely related to RNA quality. This study would contribute to the establishment of quality assessment and management standards for biobank FFT samples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
Zhiyong Liu, Jianhe Wu, Yuanwei Li, Qiang Lu, Yongjun Yang
BMC Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
Case Study
- Diagnostic conundrums of schwannomas: two cases highlighting morphological extremes and diagnostic challenges in biopsy specimens of soft tissue tumors
- Chankyung Kim, Yang-Guk Chung, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):278-283. Published online August 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.07.13
- 5,685 View
- 266 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Schwannomas are benign, slow-growing peripheral nerve sheath tumors commonly occurring in the head, neck, and flexor regions of the extremities. Although most schwannomas are easily diagnosable, their variable morphology can occasionally create difficulty in diagnosis. Reporting pathologists should be aware that schwannomas can exhibit a broad spectrum of morphological patterns. Clinical and radiological examinations can show correlation and should be performed, in conjunction with ancillary tests, when appropriate. Furthermore, deferring a definitive diagnosis until excision may be necessary for small biopsy specimens and frozen sections. This report underscores these challenges through examination of two unique schwannoma cases, one predominantly cellular and the other myxoid, both of which posed significant challenges in histological interpretation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oral and maxillofacial schwannoma (OMSCH): An institutional study of 102 patients
Lingli Huang, Wenya Zhu, Qicheng Ye, Shengwen Liu, Hao Lu, Wenjun Yang, Wanlin Xu
Journal of Stomatology Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2026; 127(3): 102678. CrossRef - Plexiform Schwannoma Over the Anterior Chest Wall: A Clinicopathological Review
Debojyoti Sasmal, Saswata Barenya, Hinglaj Saha, Pankaj Kumar Halder
Amrita Journal of Medicine.2025; 21(2): 95. CrossRef - Giant Retroperitoneal Schwannoma: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Magdalena Alexieva, Evgeni V Mekov, Silvia Ivanova, Alexandrina Vlahova, Georgi Yankov
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Breast schwannoma: review of entity and differential diagnosis
Sandra Ixchel Sanchez, Ashley Cimino-Mathews
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(6): 353. CrossRef
- Oral and maxillofacial schwannoma (OMSCH): An institutional study of 102 patients
Original Article
- Contribution of cytologic examination to diagnosis of poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma
- Na Rae Kim, Jae Yeon Seok, Yoo Seung Chung, Joon Hyop Lee, Dong Hae Chung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(2):171-178. Published online February 5, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.12.03
- 8,955 View
- 208 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The cytologic diagnosis of poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma (PDTC) is difficult because it lacks salient cytologic findings and shares cytologic features with more commonly encountered neoplasms. Due to diverse cytologic findings and paucicellularity of PDTC, standardization of cytologic diagnostic criteria is limited. The purpose of this study is to investigate and recognize diverse thyroid findings of fine needle aspiration (FNA) cytology and frozen smear cytology in diagnosis of this rare but aggressive carcinoma.
Methods
The present study included six cases of FNA cytology and frozen smears of histologically diagnosed PDTCs.
Results
PDTC showed cytologic overlap with well-differentiated thyroid carcinomas (WDTCs). Five of six cases showed dedifferentiation arising from well differentiated thyroid carcinomas. Only one de novo PDTC showed highly cellular smears composed of discohesive small cells, high nuclear/cytoplasmic (N/C) ratio, prominent micronucleoli, and irregular nuclei. Retrospectively reviewed, these findings are highly suspicious for PDTC. Cytologic findings of nuclear atypia, pleomorphism, and irregularity were frequently found, whereas scattered small cells were seen only in the de novo case.
Conclusions
Heterogeneous cytologic findings of PDTCs are shared with those of WDTCs and contribute to difficult preoperative cytologic diagnoses. Most PDTCs show dedifferentiation from WDTCs. Albeit rare, de novo PDTC should be considered with cytology showing discohesive small cells with high N/C ratio. This will enable precise diagnosis and prompt treatment of this aggressive malignancy -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Plasma cells and plasmacytoid features in thyroid lesions
Qianqian Zhang, Angela Feraco, Belen Padial Urtueta, Elisabetta Merenda, Luisa Cioni, Alessia Piermattei, Patrizia Straccia, Federica Cianfrini, Antonino Mule, Liron Pantanowitz, Esther Diana Rossi
Virchows Archiv.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Practical and challenging issue in thyroid cytopathology
Qianqian Zhang, Belen Padial Urtueta, Elisabetta Merenda, Gabriele Rotondaro, Noemi Morelli, Alessia Piermattei, Patrizia Straccia, Federica Cianfrini, Angela Feraco, Alessia Granitto, Antonino Mule, Esther Diana Rossi
Human Pathology.2025; : 106019. CrossRef - Non-papillary thyroid carcinoma diagnoses in The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology categories V and VI: An institutional experience
Myunghee Kang, Na Rae Kim, Jae Yeon Seok
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2024; 71: 152263. CrossRef - Cytologic features of differentiated high‐grade thyroid carcinoma: A multi‐institutional study of 40 cases
Vanda F. Torous, Tikamporn Jitpasutham, Zubair Baloch, Richard L. Cantley, Darcy A. Kerr, Xiaoying Liu, Zahra Maleki, Ross Merkin, Vania Nosé, Liron Pantanowitz, Isabella Tondi Resta, Esther D. Rossi, William C. Faquin
Cancer Cytopathology.2024; 132(8): 525. CrossRef - An Unexpected Finding of Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma in a Toxic Thyroid Nodule
Kimberly Yuang, Huda Al-Bahadili, Alan Chang
JCEM Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Revisiting the cytomorphological features of poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a comparative analysis with indeterminate thyroid fine-needle aspiration samples
Yazeed Alwelaie, Ali Howaidi, Mohammed Tashkandi, Ahmad Almotairi, Hisham Saied, Moammar Muzzaffar, Doaa Alghamdi
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2023; 12(5): 331. CrossRef - Characterization of the genomic alterations in poorly differentiated thyroid cancer
Yeeun Lee, SeongRyeol Moon, Jae Yeon Seok, Joon-Hyop Lee, Seungyoon Nam, Yoo Seung Chung
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Plasma cells and plasmacytoid features in thyroid lesions
Case Study
- Frozen Cytology of Meningeal Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumor/Hemangiopericytoma
- Myunghee Kang, Na Rae Kim, Dong Hae Chung, Gie-Taek Yie
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(3):192-197. Published online April 11, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.03.20
- 8,030 View
- 160 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 51-year-old woman presented with severe dizziness. The brain magnetic resonance image revealed a 5.5 cm multiloculated mass with a thick rim in the left temporal lobe. Cytological examination of frozen diagnosis of the mass showed hypercellular sheets of round and rhabdoid cells in a hemorrhagic background, and two mitotic figures were observed. Histologically, the excised dura-based mass consisted of predominantly round cells with small foci of rhabdoid tumor cells in a pseudoalveolar pattern in a hemorrhagic background, and the cells showed nuclear positivity for signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 as well as frequent mitosis. The mass was diagnosed as a grade 3 solitary fibrous tumor (SFT)/hemangiopericytoma (HPC). The cytological diagnosis of SFT/HPC is challenging because of the heterogeneous cytological findings, such as histological heterogeneity, and because there are no standardized cytological criteria for malignant SFT/HPC. Cytological findings, such as singly scattered small cells, hypercellularity, rare ropy collagen, and round and rhabdoid cells with pseudoalveolar pattern, may assist in the diagnosis of malignant SFT/HPC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Rare Case of Cervical Solitary Fibrous Tumor in a Pediatric Patient: Case Report and Literature Review
Eleonora Becattini, Lorenzo Sgarbanti, Giuseppina Bevacqua, Valentina Grespi, Carlo Conti
NeuroSci.2025; 6(2): 49. CrossRef - Meningeal Solitary Fibrous Tumor: A Cytological Report With Emphasis on the Usefulness of Immunocytochemical Analysis for STAT6
Hiroyuki Okanishi, Mitsuaki Ishida, Naoto Kohno, Isako Kataoka, Mari Tomiuka, Mayumi Uragami, Shizuka Ono, Chihiro Deguchi, Reika Takeda, Yoshitaka Kurisu, Yoshinobu Hirose
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytologic features of mesenchymal, melanocytic and haematolymphoid tumours of the central nervous system and metastases
Carmen Bárcena, José A. Jiménez‐Heffernan
Cytopathology.2024; 35(5): 590. CrossRef - A Hemangiopericytoma in the External Auditory Canal: A Rare Clinical Presentation and Management
Vaibhavi Patil, Prasad Deshmukh, Sagar S Gaurkar , Ayushi Ghosh Moulic, Jasleen Kaur
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Scoring system for intraoperative diagnosis of intracranial schwannoma by squash cytology
Hirotaka Fujita, Takuma Tajiri, Tomohisa Machida, Nozomi Nomura, Suguru Toguchi, Hitoshi Itoh, Shinichiro Hiraiwa, Tomoko Sugiyama, Chie Inomoto, Masaaki Imai, Shinri Oda, Masami Shimoda, Naoya Nakamura
Cytopathology.2022; 33(2): 196. CrossRef - Occurrence of a solitary fibrous tumor adjacent to the resection bed of a high-grade meningioma: A case report
Coby Cunningham, Rocco Dabecco, Justin Davanzo
Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery.2021; 25: 101277. CrossRef - A case of solitary fibrous tumor arising in the meninge
Saori NAKANISHI, Naoto KURODA, Toshiko TAKAI, Mari KOJIMA, Misato OONOGI
The Journal of the Japanese Society of Clinical Cytology.2021; 60(4): 224. CrossRef - Intraoperative frozen cytology of intraosseous cystic meningioma in the sphenoid bone
Na Rae Kim, Gie-Taek Yie
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(6): 508. CrossRef
- A Rare Case of Cervical Solitary Fibrous Tumor in a Pediatric Patient: Case Report and Literature Review
Original Articles
- Intraoperative Frozen Cytology of Central Nervous System Neoplasms: An Ancillary Tool for Frozen Diagnosis
- Myunghee Kang, Dong Hae Chung, Na Rae Kim, Hyun Yee Cho, Seung Yeon Ha, Sangho Lee, Jungsuk An, Jae Yeon Seok, Gie-Taek Yie, Chan Jong Yoo, Sang Gu Lee, Eun Young Kim, Woo Kyung Kim, Seong Son, Sun Jin Sym, Dong Bok Shin, Hee Young Hwang, Eung Yeop Kim, Kyu Chan Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(2):104-111. Published online January 14, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.11.10
- 14,931 View
- 685 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Pathologic diagnosis of central nervous system (CNS) neoplasms is made by comparing light microscopic, immunohistochemical, and molecular cytogenetic findings with clinicoradiologic observations. Intraoperative frozen cytology smears can improve the diagnostic accuracy for CNS neoplasms. Here, we evaluate the diagnostic value of cytology in frozen diagnoses of CNS neoplasms.
Methods
Cases were selected from patients undergoing both frozen cytology and frozen sections. Diagnostic accuracy was evaluated.
Results
Four hundred and fifty-four cases were included in this retrospective single-center review study covering a span of 10 years. Five discrepant cases (1.1%) were found after excluding 53 deferred cases (31 cases of tentative diagnosis, 22 cases of inadequate frozen sampling). A total of 346 cases of complete concordance and 50 cases of partial concordance were classified as not discordant cases in the present study. Diagnostic accuracy of intraoperative frozen diagnosis was 87.2%, and the accuracy was 98.8% after excluding deferred cases. Discrepancies between frozen and permanent diagnoses (n = 5, 1.1%) were found in cases of nonrepresentative sampling (n = 2) and misinterpretation (n = 3). High concordance was observed more frequently in meningeal tumors (97/98, 99%), metastatic brain tumors (51/52, 98.1%), pituitary adenomas (86/89, 96.6%), schwannomas (45/47, 95.8%), high-grade astrocytic tumors (47/58, 81%), low grade astrocytic tumors (10/13, 76.9%), non-neoplastic lesions (23/36, 63.9%), in decreasing frequency.
Conclusions
Using intraoperative cytology and frozen sections of CNS tumors is a highly accurate diagnostic ancillary method, providing subtyping of CNS neoplasms, especially in frequently encountered entities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intraoperative Integrated Diagnostic System for Malignant Central Nervous System Tumors
Takahiro Hayashi, Kensuke Tateishi, Shinichiro Matsuyama, Hiromichi Iwashita, Yohei Miyake, Akito Oshima, Hirokuni Honma, Jo Sasame, Katsuhiro Takabayashi, Kyoka Sugino, Emi Hirata, Naoko Udaka, Yuko Matsushita, Ikuma Kato, Hiroaki Hayashi, Taishi Nakamur
Clinical Cancer Research.2024; 30(1): 116. CrossRef - A multicenter proof-of-concept study on deep learning-based intraoperative discrimination of primary central nervous system lymphoma
Xinke Zhang, Zihan Zhao, Ruixuan Wang, Haohua Chen, Xueyi Zheng, Lili Liu, Lilong Lan, Peng Li, Shuyang Wu, Qinghua Cao, Rongzhen Luo, Wanming Hu, Shanshan lyu, Zhengyu Zhang, Dan Xie, Yaping Ye, Yu Wang, Muyan Cai
Nature Communications.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in Neurosurgical Intraoperative Histology
Ali A. Mohamed, Emma Sargent, Cooper Williams, Zev Karve, Karthik Nair, Brandon Lucke-Wold
Tomography.2024; 10(5): 693. CrossRef - Unveiling the potential application of intraoperative brain smear for brain tumor diagnosis in low-middle-income countries: A comprehensive systematic review
Muhammad Shakir, Ahmed Altaf, Hawra Hussain, Syed Muhammad Aqeel Abidi, Zoey Petitt, Mahnoor Tariq, Ahmed Gilani, S. Ather Enam
Surgical Neurology International.2023; 14: 325. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Squash Smear Cytology Diagnosis and Radiological Diagnosis with Histopathology in Central Nervous System Lesions
B N Kumarguru, G Santhipriya, S Kranthi Kumar, R Ramesh Kumar, A S Ramaswamy, P Janakiraman
Journal of Cytology.2022; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - Intraoperative squash cytology provides a qualitative intraoperative diagnosis for cases in which frozen section yields a diagnosis of equivocal brain tumour
Hirotaka Fujita, Takuma Tajiri, Tomohisa Machida, Nozomi Nomura, Suguru Toguchi, Hitoshi Itoh, Shinichiro Hiraiwa, Tomoko Sugiyama, Masaaki Imai, Shinri Oda, Masami Shimoda, Naoya Nakamura
Cytopathology.2020; 31(2): 106. CrossRef - Intraoperative frozen cytology of intraosseous cystic meningioma in the sphenoid bone
Na Rae Kim, Gie-Taek Yie
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(6): 508. CrossRef - Use of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid for Confirmation of Lesional Biopsy Sample in Presumed High-Grade Glioma
Victoria L. Watson, Jeffrey W. Cozzens
World Neurosurgery.2019; 132: 21. CrossRef
- Intraoperative Integrated Diagnostic System for Malignant Central Nervous System Tumors
- The Intraoperative Immunohistochemical Staining of CD56 and CK19 Improves Surgical Decision for Thyroid Follicular Lesions
- Ju Yeon Pyo, Sung-eun Choi, Eunah Shin, JaSeung Koo, SoonWon Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(5):463-470. Published online August 2, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.05.25
- 11,856 View
- 157 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
When differential diagnosis is difficult in thyroid follicular lesions with overlapping histological features, the immunohistochemical staining can help confirm the diagnosis. We aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of rapid immunohistochemical stains of CD56 and cytokeratin 19 on frozen sections of thyroid follicular lesion and explore the possible gains and limitations of the practice. Methods: Eighty-six nodules of 79 patients whose intraoperative frozen sections were selected as the control group, and 53 nodules of 48 patients whose intraoperative frozen sections were subject to rapid immunohistochemistry were selected as the study group. Results: Five nodules (6%) in the control group were diagnosed as follicular neoplasm and six nodules (7%) were deferred. In the study group, six nodules (11%) were follicular neoplasm and none were deferred. Three nodules (4%) in the control group showed diagnostic discrepancy between the frozen and permanent diagnoses, but none in the study group. The average turnaround time for the frozen diagnosis of the control group was 24 minutes, whereas it was 54 minutes for the study group. Conclusions: Intraoperative rapid immunohistochemical stains significantly decreased the diagnostic discrepancy in this study. Considering the adverse effects of indefinite frozen diagnosis or discrepancy with permanent diagnoses, the intraoperative rapid immunohistochemical stain can help to accurately diagnose and hence provide guidance to surgical treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-Contrast Facile Imaging with Target-Directing Fluorescent Molecular Rotors, the N3-Modified Thioflavin T Derivatives
Yuka Kataoka, Hiroto Fujita, Arina Afanaseva, Chioko Nagao, Kenji Mizuguchi, Yuuya Kasahara, Satoshi Obika, Masayasu Kuwahara
Biochemistry.2019; 58(6): 493. CrossRef - The diagnostic value of TROP-2, SLP-2 and CD56 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Xueyang Yang, Yifang Hu, He Shi, Chengzhou Zhang, Zhixiao Wang, Xiaoyun Liu, Huanhuan Chen, Lijuan Zhang, Dai Cui
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology.2018; 275(8): 2127. CrossRef
- High-Contrast Facile Imaging with Target-Directing Fluorescent Molecular Rotors, the N3-Modified Thioflavin T Derivatives
- Quality Control Program for Fresh Frozen Tissue and Its Results of Chonbuk National University Hospital National Biobank of Korea.
- Shin Young Park, Hyun Ah Baek, Hyoung Jong Kwak, Sang Hyun Hong, Ho Sung Park, Kyu Yun Jang, Woo Sung Moon, Myoung Jae Kang, Dong Geun Lee, Myoung Ja Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(3):295-301.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.3.295
- 5,378 View
- 59 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Molecular tools for tissue profiling generally require collection of fresh frozen tissues (FFT) as sources of high-quality DNA and RNA. Nowadays, researchers carry out large-scale, multi-center studies and they request inter-institutional minimal intrinsic bias, some fundamental similarities, and the same standardized and validated procedures.
METHODS
This study reports standardized quality control procedure for fresh frozen tissue of the National Biobank of Korea.
RESULTS
The main procedures for quality control for FFT are as follows: records related to sample collection such as labeling of samples, transport temperature, lag time from excision of tissue to freezing, and sample size were reviewed for all fresh frozen samples. The stability of RNA and DNA in fresh frozen tissue was evaluated for 3% of collected samples and purity was assessed (ratio of the absorbance at 260 and 280 nm) as was integrity (agarose gel electrophoresis). Stained hematoxylin and eosin sections were reviewed by a pathologist to confirm the diagnosis and to assess how representative the frozen sample was.
CONCLUSIONS
We introduced that the quality-control criteria for fresh frozen tissue of the NBK. We expect that this study contributes to standardization of collection, storage, and quality control of fresh frozen tissue. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Cold Ischemia Time and Storage Period on DNA Quality and Biomarker Research in Biobanked Colorectal Cancer Tissues
Min Gyoung Pak, Mee Sook Roh
Kosin Medical Journal.2020; 35(1): 26. CrossRef
- Influence of Cold Ischemia Time and Storage Period on DNA Quality and Biomarker Research in Biobanked Colorectal Cancer Tissues
- Quality Assurance of Intraoperative Consultation Review Analysis of 2,392 frozen sections.
- Dong Hae Chung, Jae Hee Suh, On Ja Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(4):332-341.
- 2,716 View
- 48 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A retrospective quality assurance study of intraoperative consultation (frozen section) was carried out to assess the accuracy and to determine the reasons of discordance. Of 14,977 surgical pathology cases accessioned over a 6-month period in Asan Medical Center, frozen sections were done on 1,270 (8.5%) patients and 2,392 frozen sections (1.88 frozen sections/case) were performed. Discordance was noted in 106 cases (4.4%) and diagnosis was deferred in 26 cases (1.1%). All deferred cases were reviewed with the result of 53.8% justified and 46.2% unjustified. The discordant cases were divided into three categories as to their clinical significances: category A (no affect on patient care) 61.3%, B (minimal affect) 9.4%, and C (major affect) 29.2%. Of 31 category C cases, 7 cases were false positive and 24 cases were false negative. Misinterpretation (70.8%) was the leading cause of discordance, followed by sampling error (15.1%), failure to identify lesion (8.5%), and technical problem (5.7%). More than one-third (35.8%) of all discordances were of central nervous system cases. Total central nervous system cases were 403 (16.8%) with a significantly higher disordance rate (9.8%) and deferral rate (2.5%) in comparison to the other cases with 3.4% discordance rate and 0.8% deferral rate. There were 43 colorectal cancer cases of intraoperative consultation for adequacy of resectional margins. The surgical margins were between 0.4 cm and 28 cm (mean: 6.7 cm) away from the tumor and there was no tumor-positive case. The study indicates surgical pathology should 1) promote interpretative skills in cases involving minute fragments of neurosurgical cases, 2) defer the diagnosis and ask for more tissue on inadequate or inappropriate specimens and 3) give only gross opinions without unnecessary frozen section procedures in the event of simple, clear-cut cases.
- Usefulness of Frozen Section Examination of Core Needle Biopsy in the Breast Carcinoma.
- Yee Jeong Kim, Yi Kyeong Chun, Sung Ran Hong, Hy Sook Kim, Sung Su Kang, Ji Hyun Lee, Sung Kong Lee, Hye Sun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(3):163-166.
- 2,363 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Core needle biopsy (CNB) is widely used as the initial sampling method for breast cancer. And because frozen section (FS) diagnosis is rapid and reliable, we studied the diagnostic agreement between the diagnosis of FS of CNB and final diagnosis after surgery to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of the FS of CNB.
METHODS
Of 409 patients who were preoperatively diagnosed by FS of CNB and who underwent final surgery from 1996 through 2000, 24 cases were found to be ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and 385 cases invasive carcinoma (IC). The diagnoses of FS of CNB were compared with final diagnoses.
RESULTS
The diagnostic accuracy of carcinoma is 63.6% for DCIS and 86.9% for invasive carcinoma. Five cases (1.2%) could not be diagnosed because of material insufficiency for diagnosis. Twenty two cases (5.4%) were diagnosed as benign on FS, among which 20 (90.9%) were misdiagnosed by sampling error. Twenty seven cases (6.7%) were deferred on FS, 4 of these cases were DCIS, 5 were invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC), the rest displayed low nuclear grades or marked freezing artifacts.
CONCLUSIONS
The diagnostic accuracy of FS of CNB is very high except for cases of ILC and low grade DCIS. Considering the advantage of rapid evaluation, more definitive diagnosis, familiarity by pathologists and availability of ancillary study, FS of CNB is very useful method as the preoperative evaluation.
- Quality Assurance of Frozen Section Diagnosis An analysis of 5,273 consecutive cases .
- Sang Yong Song, Geunghwan Ahn
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(12):1182-1190.
- 2,578 View
- 43 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Quality assurance analysis of frozen section diagnosis is very important for the pathologists to improve the diagnostic ability and the quality of medical service. We analysed 5,273 consecutive cases of frozen section diagnosis which were done in Samsung Medical Center during 10 months from June 1, 1998 to March 31. 1999 with special reference to the discordance between frozen section diagnosis and final diagnosis. The concordance rate was 97.65%, discordance rate 1.34%, and deferred diagnosis (type 1) rate 1.01%. Category A (discordant diagnosis without any effect on the patients) was 53 cases (1.01%), category B (discordant diagnosis with minimal but no serious effect on the patients) was 10 cases (0.19%), and category C (discordant diagnosis with serious effect on the patients) was 8 cases (0.15%). Type 2 (discordant diagnosis by extra-pathologist problem) was 22 cases (0.42%) and type 3 (discordant diagnosis by pathologist problem) was 49 cases (0.93%). The most frequent causes of type 2 and 3 discordant diagnosis were presence of new lesions on deeper sections and the misinterpretation of lesions. Discordant diagnosis was noted in lymphoreticular system, central nervous system, thyroid, gastric resection margin, breast, female genital organs, intestine, hepatobiliary system, upper aerodigestive tract, urinary tract, lung, and soft tissue in descending order of frequency. Frozen section diagnosis was deferred in central nervous system, lymphoreticular system, gastric resection margin, female genital organs, thyroid, intestine, upper aerodigestive tract, lung, and soft tissue in descending order of frequency. The most important cause of discordant diagnosis was a misinterpretation of the lesions. Based on our results, a continuous and careful follow-up of quality assurance analysis of frozen section diagnosis and a share of experience of problematic cases are mandatory for the pathologists to improve the quality of medical services.

 E-submission
E-submission



 First
First Prev
Prev



