Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Study
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma Arising in a Huge Hepatocellular Adenoma with Bone Marrow Metaplasia
- Hyo Jeong Kang, Hui Jeong Jeong, So-Woon Kim, Eunsil Yu, Young-Joo Lee, So Yeon Kim, Jihun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(4):226-231. Published online December 27, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.11.12
- 8,541 View
- 152 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular adenoma (HCA) is the most common type of benign liver tumor, and its major complication is malignant transformation to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we report a case of HCC arising in HCA with bone marrow metaplasia in a 24-year-old Korean woman who presented with abdominal discomfort. A huge liver mass was found on abdominal ultrasonography. She underwent surgical hepatic resection, and the resected specimen was entirely involved by a 20-cm-sized tumor. Histological review revealed a well differentiated HCC arising from inflammatory HCA with β-catenin nuclear positivity and bone marrow metaplasia that contained hematopoietic cells. This case was unique because malignant transformation, inflammatory type HCA, β-catenin nuclear staining, and bone marrow metaplasia were simultaneously observed. Additionally, it should be noted that a large HCA with β-catenin activation can undergo malignant transformation and should be surgically resected in a timely manner.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adult Hepatocellular Carcinoma Coexisting with Extramedullary Hematopoiesis
Hirotsugu Noguchi, Michiyo Higashi, Ryo Desaki, Takashi Tasaki, Mari Kirishima, Ikumi Kitazono, Kazuhiro Tabata, Akihide Tanimoto
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2022; 30(3): 339. CrossRef - Spontaneous Occurrence of Various Types of Hepatocellular Adenoma in the Livers of Metabolic Syndrome-Associated Steatohepatitis Model TSOD Mice
Wenhua Shao, Orgil Jargalsaikhan, Mayuko Ichimura-Shimizu, Qinyi Cai, Hirohisa Ogawa, Yuko Miyakami, Kengo Atsumi, Mitsuru Tomita, Mitsuko Sutoh, Shunji Toyohara, Ryoji Hokao, Yasusei Kudo, Takeshi Oya, Koichi Tsuneyama
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(19): 11923. CrossRef - Bilateral Diffuse Nodular Pulmonary Ossification Mimicking Metastatic Disease in a Patient with Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Pattamon Sutthatarn, Cara E. Morin, Jessica Gartrell, Wayne L. Furman, Max R. Langham, Teresa Santiago, Andrew J. Murphy
Children.2021; 8(3): 226. CrossRef - Malignant transformation of liver fatty acid binding protein-deficient hepatocellular adenomas: histopathologic spectrum of a rare phenomenon
Juan Putra, Linda D. Ferrell, Annette S.H. Gouw, Valerie Paradis, Arvind Rishi, Christine Sempoux, Charles Balabaud, Swan N. Thung, Paulette Bioulac-Sage
Modern Pathology.2020; 33(4): 665. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma arising from hepatic adenoma in a young woman
Haythem Yacoub, Hela Kchir, Dhouha Cherif, Hajer Hassine, Slim Haouet, Asma Ayari, Habiba Mizouni, Saber Mannai, Mohamed Tahar Khalfallah, Nadia Maamouri
Clinical Case Reports.2020; 8(9): 1659. CrossRef - Metanephric adenoma with osseous metaplasia and bone marrow elements
Alessandro Pietro Aldera, Jeff John, Dharshnee Chetty, Dhirendra Govender
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2019; 17: 200316. CrossRef
- Adult Hepatocellular Carcinoma Coexisting with Extramedullary Hematopoiesis
Original Articles
- Protein Phosphatase Magnesium-Dependent 1δ (PPM1D) Expression as a Prognostic Marker in Adult Supratentorial Diffuse Astrocytic and Oligodendroglial Tumors
- Hui Jeong Jeong, Chang Gok Woo, Bora Lee, Shin Kwang Khang, Soo Jeong Nam, Jene Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(2):71-78. Published online October 18, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.10.21
- 8,759 View
- 201 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Protein phosphatase magnesium-dependent 1δ (PPM1D) is a p53-induced serine/ threonine phosphatase, which is overexpressed in various human cancers. A recent study reported that a mutation in the PPM1D gene is associated with poor prognosis in brainstem gliomas. In this study, we evaluated the utility of PPM1D as a prognostic biomarker of adult supratentorial diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial tumors.
Methods
To investigate PPM1D protein expression, mRNA expression, and copy number changes, immunohistochemistry, RNAscope in situ hybridization, and fluorescence in situ hybridization were performed in 84 adult supratentorial diffuse gliomas. We further analyzed clinical characteristics and overall survival (OS) according to PPM1D protein expression, and examined its correlation with other glioma biomarkers such as isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutation, and p53 expression.
Results
Forty-six cases (54.8%) were PPM1D-positive. PPM1D expression levels were significantly correlated with PPM1D transcript levels (p= .035), but marginally with PPM1D gene amplification (p=.079). Patients with high-grade gliomas showed a higher frequency of PPM1D expression than those with low-grade gliomas (p <.001). Multivariate analysis demonstrated that PPM1D expression (hazard ratio [HR], 2.58; p=.032), age over 60 years (HR, 2.55; p=.018), and IDH1 mutation (HR, 0.18; p=.002) were significantly independent prognostic factors; p53 expression had no prognostic significance (p=.986). The patients with tumor expressing PPM1D showed a shorter OS (p=.003). Moreover, patients with tumor harboring wild-type IDH1 and PPM1D expression had the worst OS (p<.001).
Conclusions
Our data suggest that a subset of gliomas express PPM1D; PPM1D expression is a significant marker of poor prognosis in adult supratentorial diffuse astrocytic and oligodendroglial tumors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characteristic analysis and identification of novel molecular biomarkers in elderly glioblastoma patients using the 2021 WHO Classification of Central Nervous System Tumors
Yaning Wang, Junlin Li, Yaning Cao, Wenlin Chen, Hao Xing, Xiaopeng Guo, Yixin Shi, Yuekun Wang, Tingyu Liang, Liguo Ye, Delin Liu, Tianrui Yang, Yu Wang, Wenbin Ma
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metal-dependent Ser/Thr protein phosphatase PPM family: Evolution, structures, diseases and inhibitors
Rui Kamada, Fuki Kudoh, Shogo Ito, Itsumi Tani, Jose Isagani B. Janairo, James G. Omichinski, Kazuyasu Sakaguchi
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2020; 215: 107622. CrossRef
- Characteristic analysis and identification of novel molecular biomarkers in elderly glioblastoma patients using the 2021 WHO Classification of Central Nervous System Tumors
- Diverse Immunoprofile of Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate with an Emphasis on the Prognostic Factors
- Se Un Jeong, Anuja Kashikar Kekatpure, Ja-Min Park, Minkyu Han, Hee Sang Hwang, Hui Jeong Jeong, Heounjeong Go, Yong Mee Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(5):471-481. Published online August 9, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.06.02
- 10,553 View
- 208 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
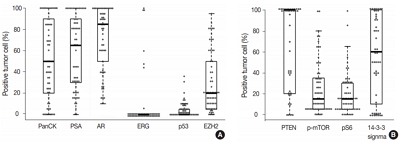
Ductal adenocarcinoma (DAC) of the prostate is an uncommon histologic subtype whose prognostic factors and immunoprofile have not been fully defined. Methods: To define its prognostic factors and immunoprofile, the clinicopathological features, including biochemical recurrence (BCR), of 61 cases of DAC were analyzed. Immunohistochemistry was performed on tissue microarray constructs to assess the expression of prostate cancer-related and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling-related proteins. Results: During the median follow-up period of 19.3 months, BCR occurred in 26 cases (42.6%). DAC demonstrated a wide expression range of prostate cancer-related proteins, including nine cases (14.8%) that were totally negative for pan-cytokeratin (PanCK) immunostaining. The mTOR signaling-related proteins also showed diverse expression. On univariate analysis, BCR was associated with high preoperative serum levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA), large tumor volume, predominant ductal component, high Gleason score (GS), comedo-necrosis, high tumor stage (pT), lymphovascular invasion, and positive surgical margin. High expressions of phospho-mTOR (p-mTOR) as well as low expressions of PSA, phospho-S6 ribosomal protein (pS6) and PanCK were associated with BCR. On multivariable analysis, GS, pT, and immunohistochemical expressions of PanCK and p-mTOR remained independent prognostic factors for BCR. Conclusions: These results suggest GS, pT, and immunohistochemical expressions of PanCK and p-mTOR as independent prognostic factors for BCR in DAC. Since DAC showed diverse expression of prostate cancer–related proteins, this should be recognized in interpreting the immunoprofile of DAC. The diverse expression of mTOR-related proteins implicates their potential utility as predictive markers for mTOR targeted therapy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermediate risk prostate tumors contain lethal subtypes
William L. Harryman, James P. Hinton, Rafael Sainz, Jaime M. C. Gard, John M. Ryniawec, Gregory C. Rogers, Noel A. Warfel, Beatrice S. Knudsen, Raymond B. Nagle, Juan J. Chipollini, Benjamin R. Lee, Belinda L. Sun, Anne E. Cress
Frontiers in Urology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - High GLUT1 membrane expression and low PSMA membrane expression in Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Intraductal Carcinoma of the prostate
Xingming Wang, Li Zhou, Lin Qi, Ye Zhang, Hongling Yin, Yu Gan, Xiaomei Gao, Yi Cai
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases.2024; 27(4): 720. CrossRef - Association of Lymphovascular Invasion with Biochemical Recurrence and Adverse Pathological Characteristics of Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jakub Karwacki, Marcel Stodolak, Andrzej Dłubak, Łukasz Nowak, Adam Gurwin, Kamil Kowalczyk, Paweł Kiełb, Nazar Holdun, Wojciech Szlasa, Wojciech Krajewski, Agnieszka Hałoń, Anna Karwacka, Tomasz Szydełko, Bartosz Małkiewicz
European Urology Open Science.2024; 69: 112. CrossRef - Impact of Epithelial Histological Types, Subtypes, and Growth Patterns on Oncological Outcomes for Patients with Nonmetastatic Prostate Cancer Treated with Curative Intent: A Systematic Review
Giancarlo Marra, Geert J.L.H. van Leenders, Fabio Zattoni, Claudia Kesch, Pawel Rajwa, Philip Cornford, Theodorus van der Kwast, Roderick C.N. van den Bergh, Erik Briers, Thomas Van den Broeck, Gert De Meerleer, Maria De Santis, Daniel Eberli, Andrea Faro
European Urology.2023; 84(1): 65. CrossRef - Impact of comedonecrosis on prostate cancer outcome: a systematic review
Kaveri T S Aiyer, Lisa J Kroon, Geert J L H van Leenders
Histopathology.2023; 83(3): 339. CrossRef - Survival after radical prostatectomy vs. radiation therapy in ductal carcinoma of the prostate
Francesco Chierigo, Marco Borghesi, Christoph Würnschimmel, Rocco Simone Flammia, Benedikt Horlemann, Gabriele Sorce, Benedikt Höh, Zhe Tian, Fred Saad, Markus Graefen, Michele Gallucci, Alberto Briganti, Francesco Montorsi, Felix K. H. Chun, Shahrokh F.
International Urology and Nephrology.2022; 54(1): 89. CrossRef - Defining Diagnostic Criteria for Prostatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma at Multiparametric MRI
Weranja K. B. Ranasinghe, Patricia Troncoso, Devaki Shilpa Surasi, Juan José Ibarra Rovira, Priya Bhosale, Janio Szklaruk, Andrea Kokorovic, Xuemei Wang, Mohamed Elsheshtawi, Miao Zhang, Ana Aparicio, Brian F. Chapin, Tharakeswara K. Bathala
Radiology.2022; 303(1): 110. CrossRef - Oncological outcomes of patients with ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate receiving radical prostatectomy or radiotherapy
Mengzhu Liu, Kun Jin, Shi Qiu, Pengyong Xu, Mingming Zhang, Wufeng Cai, Xiaonan Zheng, Lu Yang, Qiang Wei
Asian Journal of Urology.2021; 8(2): 227. CrossRef - Ductal Prostate Cancers Demonstrate Poor Outcomes with Conventional Therapies
Weranja Ranasinghe, Daniel D. Shapiro, Hyunsoo Hwang, Xuemei Wang, Chad A. Reichard, Mohamed Elsheshtawi, Mary F. Achim, Tharakeswara Bathala, Chad Tang, Ana Aparicio, Shi-Ming Tu, Nora Navone, Timothy C. Thompson, Louis Pisters, Patricia Troncoso, John W
European Urology.2021; 79(2): 298. CrossRef - Optimizing the diagnosis and management of ductal prostate cancer
Weranja Ranasinghe, Daniel D. Shapiro, Miao Zhang, Tharakeswara Bathala, Nora Navone, Timothy C. Thompson, Bradley Broom, Ana Aparicio, Shi-Ming Tu, Chad Tang, John W. Davis, Louis Pisters, Brian F. Chapin
Nature Reviews Urology.2021; 18(6): 337. CrossRef - A first case of ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate having characteristics of neuroendocrine phenotype with PTEN, RB1 and TP53 alterations
Hiroaki Kobayashi, Takeo Kosaka, Kohei Nakamura, Kazunori Shojo, Hiroshi Hongo, Shuji Mikami, Hiroshi Nishihara, Mototsugu Oya
BMC Medical Genomics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowing what’s growing: Why ductal and intraductal prostate cancer matter
Mitchell G. Lawrence, Laura H. Porter, David Clouston, Declan G. Murphy, Mark Frydenberg, Renea A. Taylor, Gail P. Risbridger
Science Translational Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrative Genomic Analysis of Coincident Cancer Foci Implicates CTNNB1 and PTEN Alterations in Ductal Prostate Cancer
Marc Gillard, Justin Lack, Andrea Pontier, Divya Gandla, David Hatcher, Adam G. Sowalsky, Jose Rodriguez-Nieves, Donald Vander Griend, Gladell Paner, David VanderWeele
European Urology Focus.2019; 5(3): 433. CrossRef - Genomic Characterization of Prostatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Identifies a High Prevalence of DNA Repair Gene Mutations
Michael T. Schweizer, Emmanuel S. Antonarakis, Tarek A. Bismar, Liana B. Guedes, Heather H. Cheng, Maria S. Tretiakova, Funda Vakar-Lopez, Nola Klemfuss, Eric Q. Konnick, Elahe A. Mostaghel, Andrew C. Hsieh, Peter S. Nelson, Evan Y. Yu, R. Bruce Montgomer
JCO Precision Oncology.2019; (3): 1. CrossRef
- Intermediate risk prostate tumors contain lethal subtypes

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



