Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- The Use of the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology in Korea: A Nationwide Multicenter Survey by the Korean Society of Endocrine Pathologists
- Mimi Kim, Hyo Jin Park, Hye Sook Min, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Chan Kwon Jung, Seoung Wan Chae, Hyun Ju Yoo, Yoo Duk Choi, Mi Ja Lee, Jeong Ja Kwak, Dong Eun Song, Dong Hoon Kim, Hye Kyung Lee, Ji Yeon Kim, Sook Hee Hong, Jang Sihn Sohn, Hyun Seung Lee, So Yeon Park, Soon Won Hong, Mi Kyung Shin
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):410-417. Published online June 14, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.04.05
- 12,766 View
- 228 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC) has standardized the reporting of thyroid cytology specimens. The objective of the current study was to evaluate the nationwide usage of TBSRTC and assess the malignancy rates in each category of TBSRTC in Korea.
Methods
Questionnaire surveys were used for data collection on the fine needle aspiration (FNA) of thyroid nodules at 74 institutes in 2012. The incidences and follow-up malignancy rates of each category diagnosed from January to December, 2011, in each institute were also collected and analyzed.
Results
Sixty out of 74 institutes answering the surveys reported the results of thyroid FNA in accordance with TBSRTC. The average malignancy rates for resected cases in 15 institutes were as follows: nondiagnostic, 45.6%; benign, 16.5%; atypical of undetermined significance, 68.8%; suspicious for follicular neoplasm (SFN), 30.2%; suspicious for malignancy, 97.5%; malignancy, 99.7%.
Conclusions
More than 80% of Korean institutes were using TBSRTC as of 2012. All malignancy rates other than the SFN and malignancy categories were higher than those reported by other countries. Therefore, the guidelines for treating patients with thyroid nodules in Korea should be revisited based on the malignancy rates reported in this study. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High Rates of Unnecessary Surgery for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules in the Absence of Molecular Test and the Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Molecular Test in an Asian Population: A Decision Analysis
Man Him Matrix Fung, Ching Tang, Gin Wai Kwok, Tin Ho Chan, Yan Luk, David Tak Wai Lui, Carlos King Ho Wong, Brian Hung Hin Lang
Thyroid®.2025; 35(2): 166. CrossRef - Inconclusive cytology results of fine-needle aspiration for thyroid nodules: the importance of strict guideline implementation
Sangwoo Cho, Kyunghwa Han, Jung Hyun Yoon, Vivian Youngjean Park, Miribi Rho, Jiyoung Yoon, Jin Young Kwak
Ultrasonography.2025; 44(4): 285. CrossRef - Improved Diagnostic Accuracy of Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology with Artificial Intelligence Technology
Yujin Lee, Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Hongsik Park, Kwangil Yim, Kyung Jin Seo, Gisu Hwang, Dahyeon Kim, Yeonsoo Chung, Gyungyub Gong, Nam Hoon Cho, Chong Woo Yoo, Yosep Chong, Hyun Joo Choi
Thyroid®.2024; 34(6): 723. CrossRef - Welcoming the new, revisiting the old: a brief glance at cytopathology reporting systems for lung, pancreas, and thyroid
Rita Luis, Balamurugan Thirunavukkarasu, Deepali Jain, Sule Canberk
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(4): 165. CrossRef - Fine needle aspiration cytology diagnoses of follicular thyroid carcinoma: results from a multicenter study in Asia
Hee Young Na, Miyoko Higuchi, Shinya Satoh, Kaori Kameyama, Chan Kwon Jung, Su-Jin Shin, Shipra Agarwal, Jen-Fan Hang, Yun Zhu, Zhiyan Liu, Andrey Bychkov, Kennichi Kakudo, So Yeon Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(6): 331. CrossRef - Predictors of Malignancy in Thyroid Nodules Classified as Bethesda Category III
Xiaoli Liu, Jingjing Wang, Wei Du, Liyuan Dai, Qigen Fang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk stratification of indeterminate thyroid nodules by novel multigene testing: a study of Asians with a high risk of malignancy
Chunfang Hu, Weiwei Jing, Qing Chang, Zhihui Zhang, Zhenrong Liu, Jian Cao, Linlin Zhao, Yue Sun, Cong Wang, Huan Zhao, Ting Xiao, Huiqin Guo
Molecular Oncology.2022; 16(8): 1680. CrossRef - CD56 Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Is Highly Dependent on the Histologic Subtype: A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall
Uiju Cho, Yourha Kim, Sora Jeon, Chan Kwon Jung
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2022; 30(5): 389. CrossRef - Malignancy rates in thyroid nodules: a long-term cohort study of 17,592 patients
M Grussendorf, I Ruschenburg, G Brabant
European Thyroid Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Subclassification of the Bethesda Category III (AUS/FLUS): A study of thyroid FNA cytology based on ThinPrep slides from the National Cancer Center in China
Huan Zhao, HuiQin Guo, LinLin Zhao, Jian Cao, Yue Sun, Cong Wang, ZhiHui Zhang
Cancer Cytopathology.2021; 129(8): 642. CrossRef - Effect of the Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm With Papillary-Like Nuclear Features (NIFTP) Nomenclature Revision on Indian Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Practice
Chanchal Rana, Pooja Ramakant, Divya Goel, Akanksha Singh, KulRanjan Singh, Suresh Babu, Anand Mishra
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2021; 156(2): 320. CrossRef - Comprehensive DNA Methylation Profiling Identifies Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers for Thyroid Cancer
Jong-Lyul Park, Sora Jeon, Eun-Hye Seo, Dong Hyuck Bae, Young Mun Jeong, Yourha Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Seon-Kyu Kim, Chan Kwon Jung, Yong Sung Kim
Thyroid.2020; 30(2): 192. CrossRef - Differences in surgical resection rate and risk of malignancy in thyroid cytopathology practice between Western and Asian countries: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Huy Gia Vuong, Hanh Thi Tuyet Ngo, Andrey Bychkov, Chan Kwon Jung, Trang Huyen Vu, Kim Bach Lu, Kennichi Kakudo, Tetsuo Kondo
Cancer Cytopathology.2020; 128(4): 238. CrossRef - Thyroid cancer among patients with thyroid nodules in Yemen: a three-year retrospective study in a tertiary center and a specialty clinic
Butheinah A. Al-Sharafi, Jamila A. AlSanabani, Ibraheem M. Alboany, Amani M. Shamsher
Thyroid Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Is Bethesda classification sufficient to predict thyroid cancer in endemic regions?
Gamze ÇITLAK, Bahar CANBAY TORUN
Journal of Surgery and Medicine.2020; 4(9): 794. CrossRef - Preoperative diagnostic categories of fine needle aspiration cytology for histologically proven thyroid follicular adenoma and carcinoma, and Hurthle cell adenoma and carcinoma: Analysis of cause of under- or misdiagnoses
Hee Young Na, Jae Hoon Moon, June Young Choi, Hyeong Won Yu, Woo-Jin Jeong, Yeo Koon Kim, Ji-Young Choe, So Yeon Park, Paula Soares
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0241597. CrossRef - Nuclear features of papillary thyroid carcinoma: Comparison of Core needle biopsy and thyroidectomy specimens
Jae Yeon Seok, Jungsuk An, Hyun Yee Cho, Younghye Kim, Seung Yeon Ha
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2018; 32: 35. CrossRef - Clinical utility of EZH1 mutations in the diagnosis of follicular-patterned thyroid tumors
Chan Kwon Jung, Yourha Kim, Sora Jeon, Kwanhoon Jo, Sohee Lee, Ja Seong Bae
Human Pathology.2018; 81: 9. CrossRef - The History of Korean Thyroid Pathology
Soon Won Hong, Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2018; 11(1): 15. CrossRef - Thyroid FNA cytology in Asian practice—Active surveillance for indeterminate thyroid nodules reduces overtreatment of thyroid carcinomas
K. Kakudo, M. Higuchi, M. Hirokawa, S. Satoh, C. K. Jung, A. Bychkov
Cytopathology.2017; 28(6): 455. CrossRef - Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology Practice in Korea
Yoon Jin Cha, Ju Yeon Pyo, SoonWon Hong, Jae Yeon Seok, Kyung-Ju Kim, Jee-Young Han, Jeong Mo Bae, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Yeejeong Kim, Kyueng-Whan Min, Soonae Oak, Sunhee Chang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(6): 521. CrossRef - Current Practices of Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration in Asia: A Missing Voice
Andrey Bychkov, Kennichi Kakudo, SoonWon Hong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(6): 517. CrossRef - Current Status of Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Practice in Thailand
Somboon Keelawat, Samreung Rangdaeng, Supinda Koonmee, Tikamporn Jitpasutham, Andrey Bychkov
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(6): 565. CrossRef
- High Rates of Unnecessary Surgery for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules in the Absence of Molecular Test and the Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Molecular Test in an Asian Population: A Decision Analysis
- Increased Expression of Thymosin β4 Is Independently Correlated with Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α (HIF-1α) and Worse Clinical Outcome in Human Colorectal Cancer
- Seung Yun Lee, Mee Ja Park, Hye Kyung Lee, Hyun Jin Son, Chang Nam Kim, Joo Heon Kim, Dong Wook Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):9-16. Published online October 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.08.23
- 12,007 View
- 163 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Thymosin β4 is a multi-functional hormone-like polypeptide, being involved in cell migration, angiogenesis, and tumor metastasis. This study was undertaken to clarify the clinicopathologic implications of thymosin β4 expression in human colorectal cancers (CRCs).
Methods
We investigated tissue sections from 143 patients with CRC by immunohistochemistry. In addition, we evaluated the expression patterns and the clinico-pathological significance of thymosin β4 expression in association with hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) expression in the CRC series.
Results
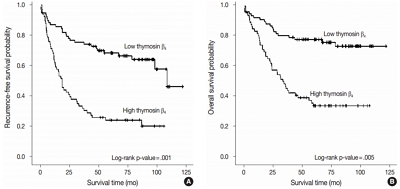
High expression of thymosin β4 was significantly correlated with lymphovascular invasion, invasion depth, regional lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, and TNM stage. Patients with high expression of thymosin β4 showed poor recurrence-free survival (p = .001) and poor overall survival (p = .005) on multivariate analysis. We also found that thymosin β4 and HIF-1α were overexpressed and that thymosin β4 expression increased in parallel with HIF-1α expression in CRC.
Conclusions
A high expression level of thymosin β4 indicates poor clinical outcomes and may be a useful prognostic factor in CRC. Thymosin β4 is functionally related with HIF-1α and may be a potentially valuable biomarker and possible therapeutic target for CRC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predicting the risk of lymph node metastasis in colon cancer: development and validation of an online dynamic nomogram based on multiple preoperative data
Longlian Deng, Lemuge Che, Haibin Sun, Riletu En, Bowen Ha, Tao Liu, Tengqi Wang, Qiang Xu
BMC Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Thymosin β4 Is an Endogenous Iron Chelator and Molecular Switcher of Ferroptosis
Joanna I. Lachowicz, Giusi Pichiri, Marco Piludu, Sara Fais, Germano Orrù, Terenzio Congiu, Monica Piras, Gavino Faa, Daniela Fanni, Gabriele Dalla Torre, Xabier Lopez, Kousik Chandra, Kacper Szczepski, Lukasz Jaremko, Mitra Ghosh, Abdul-Hamid Emwas, Mass
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(1): 551. CrossRef - Metal coordination of thymosin β4: Chemistry and possible implications
Joanna Izabela Lachowicz, Mariusz Jaremko, Lukasz Jaremko, Giuseppina Pichiri, Pierpaolo Coni, Marco Piludu
Coordination Chemistry Reviews.2019; 396: 117. CrossRef - Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhance Ovarian Cancer Growth and Metastasis by Increasing Thymosin Beta 4X-Linked Expression
Yijing Chu, Min You, Jingjing Zhang, Guoqiang Gao, Rendong Han, Wenqiang Luo, Tingting Liu, Jianxin Zuo, Fuling Wang
Stem Cells International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - An Investigation on the Therapeutic Effect of Thymosinβ4 and Its Expression Levels in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice
Kyung Sook Cho, Dong-Jin Kim, Bomee Shim, Jung Yeon Kim, Jun Mo Kang, Seon Hwa Park, Sang-Ho Lee, Hyung-In Yang, Kyoung Soo Kim
BioMed Research International.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in colorectal carcinoma
Ahmed M. Abd ElAziz, Hanan S. Abd ElHamid, Rasha R. Mostafa, Yousra R.A. Shalaby
Egyptian Journal of Pathology.2018; 38(1): 18. CrossRef
- Predicting the risk of lymph node metastasis in colon cancer: development and validation of an online dynamic nomogram based on multiple preoperative data
- The Stromal Overexpression of Decay Accelerating Factor (DAF/CD55) Correlates with Poor Clinical Outcome in Colorectal Cancer Patients.
- Tae Hwa Baek, Joo Heon Kim, Mee Ja Park, Hye Kyung Lee, Hyun Jin Son, Hyun Ki Soon, Chang Nam Kim, Che Myong Ko, Dong Wook Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(5):445-454.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.5.445
- 4,450 View
- 40 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Decay accelerating factor (DAF/CD55), regulates the complement system by accelerating decay of the C3 convertase, has been described in several malignancies, however, the clinicopathologic significance of CD55 and its receptor CD97 has not been fully investigated. We examined the expression patterns of both CD55 and CD97 and their association with clinicopathologic parameters in colorectal cancers (CRCs).
METHODS
Expression patterns of CD55 and CD97 in the stroma and tumor cells at tumor center and invasive front were examined in 130 CRCs, and their significance was statistically evaluated.
RESULTS
CD55-high stroma was correlated with tumor border (p=0.006) and invasion depth (p=0.013). CD55-high tumor cells at tumor center and invasive front were correlated with histologic grade, and CD55-high tumor cells at invasive front with tumor, node and metastasis (TNM) stage (p<0.05). CD97-high stroma was correlated with lymph node metastasis (p=0.016) and TNM stage (p=0.030). CD97-high tumor cells at tumor center and invasive front were correlated with tumor size and CD97-high tumor cells at tumor center with tumor border (p<0.05). Patients with CD55-high stroma showed poor overall and recurrence-free survival (p<0.05) in univariate analysis, and were independently associated with short recurrence-free survival (p=0.025) in multivariate analysis.
CONCLUSIONS
Stromal CD55 overexpression would be an indicator of adverse clinical outcome and a useful prognostic factor. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Non-canonical extracellular complement pathways and the complosome paradigm in cancer: a scoping review
Camila de Freitas Oliveira-Tore, Amarilis Giaretta de Moraes, Helena Musetti B. S. Plácido, Nathalia M. D. L. Signorini, Pamela Dias Fontana, Tatiane da Piedade Batista Godoy, Angelica Beate Winter Boldt, Iara de Messias
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Non-canonical extracellular complement pathways and the complosome paradigm in cancer: a scoping review
Case Report
- Langerhans Cell Sarcoma Arising in a Lymph Node: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.
- Dong Wook Kang, Hyun Jin Son, Tae Hwa Baek, Hye Kyung Lee, Joo Ryung Huh, Joo Heon Kim, Mee Ja Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(1):101-105.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.1.101
- 3,699 View
- 38 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report a case of Langerhans cell sarcoma presented as a solitary mass in the left supraclavicular area in a 31-year-old woman. Computed tomography revealed a relatively well-defined and lightly enhancing mass in the left supraclavicular area, measuring 5.5x4.5x3.2 cm. Excision was subsequently performed. Microscopically, the specimen consisted of an enlarged and partially effaced lymph node. Nests of different size composed of atypical tumor cells were located in the paracortex and the medulla of the lymph node. The tumor cells exhibited abundant eosinophilic or clear cytoplasm and displayed marked nuclear atypia and increased mitotic figures. Infiltration of many eosinophils was identified in the periphery and between the tumor cells. The tumor cells were reactive for CD1a and S100 protein. Ultrastructually, they were found to have Birbeck granules in the cytoplasm.
Original Article
- Pathologic Characteristics of Ovarian Hemorrhagic Polycyst in Estrogen Receptor-alpha (ERalpha) Knockout Mice and Roles of ERalpha in Hemorrhagic Polycyst.
- Hyun Jin Son, Joo Heon Kim, Hye Kyung Lee, Mee Ja Park, Dong Wook Kang, Che Myong Ko
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(4):376-383.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.4.376
- 3,924 View
- 53 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrinopathy causing anovulation in women of childbearing age. It has been well established that estrogen receptor-alpha knockout (ERalphaKO) mice display several pathologic ovarian phenotypes of PCOS. The aims of this study were to determine ovarian pathology in new ERalphaKO mice using a CreloxP approach and intra-ovarian ERalpha function as regulating key aspects of PCOS.
METHODS
ERalphaKO mice, which were deficient in exon 3 of the ERalpha gene, were used. Immunohistochemical studies were done on ovaries of control and ERalphaKO mice using antibodies specific to ERalpha, ERbeta, inhibin-alpha, and alpha-smooth muscle actin (SMA), as well as histochemical staining using Sudan black-B.
RESULTS
All ovaries of ERalphaKO mice were larger than control mouse ovaries and displayed a disrupted theca-interstitial tissue organization, multiple atretic follicles and multiple hemorrhagic cysts. None of the ERalphaKO mouse ovaries showed a corpus luteum. In addition, heavy deposition of Sudan black-B positive foamy cells was seen. The theca externa of preantral immature follicles and hemorrhagic cysts showed strong expression of alpha-SMA.
CONCLUSIONS
ERalphaKO mice show hemorrhagic polycystic ovaries and hyperplasia of the theca externa. This study demonstrates that the ERalpha is the functional key to the pathogenesis of PCOS.
Case Report
- Primary Synovial Sarcoma of the Kidney: A Case Report and Literature Review.
- Mee Ja Park, Tae Hwa Baek, Joo Heon Kim, Dong Wook Kang, Hye Kyung Lee, Hyun Jin Son
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(3):274-278.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.3.274
- 4,416 View
- 28 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Synovial sarcoma is a rare renal neoplasm that is not easy to diagnose unless SYT-SSX fusion transcripts are identified. We report here on a case of primary renal synovial sarcoma in a 35-year-old woman. A mass was discovered by accident in the lower part of the right kidney when ultrasonography was performed, and it was removed via radical nephrectomy. Grossly, the tumor was a homogeneously tan-brown soft mass that measured 4.5x3.2x3.0 cm, and it was encircled by a well-defined cystic space. The lesion exhibited hypercellularity of the oval or short spindle cells that were arranged in various solid sheets or intersecting fascicles. Immunohistochemically, the tumor showed diffuse positivity for vimentin, bcl-2 and CD99, and it showed focal positivity for epithelial membrane antigen. The SYT-SSX fusion transcripts were detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Synovial sarcoma should be considered in the differential diagnosis when a spindle cell neoplasm is encountered in the kidney.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Renal Synovial Sarcoma and Clinical and Pathological Findings: a Systematic Review
Leandro Blas, Javier Roberti
Current Urology Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Renal Synovial Sarcoma - A rare histology
Premkumar Krishnappa, Mohan keshavamurthy, Shakir Tabrez, Sreeharsha Harinatha, Mohan Balaiah Aswathaiya
Urology Case Reports.2020; 33: 101402. CrossRef
- Primary Renal Synovial Sarcoma and Clinical and Pathological Findings: a Systematic Review
Review
- Quality Control Program and Its Results of Korean Society for Cytopathologists.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Sung Nam Kim, Shin Kwang Khang, Chang Suk Kang, Hye Kyoung Yoon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2008;19(2):65-71.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3338/kjc.2008.19.2.65
- 3,556 View
- 23 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In Korea, the quality control(QC) program forcytopathology was introduced in 1995. The program consists of a checklist for the cytolopathology departments, analysis data on all the participating institutions' QC data, including the annual data on cytologic examinations, the distribution of the gynecological cytologic diagnoses, as based on The Bethesda System 2001, and the data on cytologic-histolgical correlation of the gynecological field, and an evaluation for diagnostic accuracy. The diagnostic accuracy program has been performed 3 times per year with using gynecological, body fluid and fine needle aspiration cytologic slides. We report here on the institutional QC data and the evaluation for diagnostic accuracy since 2004, and also on the new strategy for quality control and assurance in the cytologic field. The diagnostic accuracy results of both the participating institutions and the QC committee were as follows; Category 0 and A: about 94%, Category B: 4~5%, Category C: less than 2%. As a whole, the cytologic daignostic accuracy is relatively satisfactory. In 2008, on site evaluation for pathology and cytology laboratories, as based on the "Quality Assurance Program for Pathology Services" is now going on, and a new method using virtual slides or image files for determining the diagnostic accuracy will be performed in November 2008.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on the Workload of Cytotechnologists: Focus on Commercial Laboratories
Eun-Suk PARK
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2025; 57(2): 228. CrossRef - Diagnostic proficiency test using digital cytopathology and comparative assessment of whole slide images of cytologic samples for quality assurance program in Korea
Yosep Chong, Soon Auck Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh, Soo Jin Jung, Bo-Sung Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Ho-Chang Lee, Gyungyub Gong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(5): 251. CrossRef - Usefulness of p16INK4a Immunocytochemical staining for the Differentiation between Atrophy and ASCUS in Diagnosis of Uterine Cervical Cancer
Hye Ryoung Shin, Taekil Eom, Wan-Su Choi
Biomedical Science Letters.2023; 29(3): 144. CrossRef - Current status of cytopathology practice in Korea: impact of the coronavirus pandemic on cytopathology practice
Soon Auck Hong, Haeyoen Jung, Sung Sun Kim, Min-Sun Jin, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Younghee Choi, Gyungyub Gong, Yosep Chong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 361. CrossRef - Current status of cytopathology practices in Korea: annual report on the Continuous Quality Improvement program of the Korean Society for Cytopathology for 2018
Yosep Chong, Haeyoen Jung, Jung-Soo Pyo, Soon Won Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(4): 318. CrossRef - Continuous quality improvement program and its results of Korean Society for Cytopathology
Yoo-Duk Choi, Hoon-Kyu Oh, Su-Jin Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim, Yun-Kyung Lee, Bo-Sung Kim, Eun-Jeong Jang, Yoon-Jung Choi, Eun-Kyung Han, Dong-Hoon Kim, Younghee Choi, Chan-Kwon Jung, Sung-Nam Kim, Kyueng-Whan Min, Seok-Jin Yoon, Hun-Kyung Lee, Kyung Un Choi, Hye
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(3): 246. CrossRef - Current Status of and Perspectives on Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
Sung-Chul Lim, Chong Woo Yoo
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2019; 53(4): 210. CrossRef - Current Cytology Practices in Korea: A Nationwide Survey by the Korean Society for Cytopathology
Eun Ji Oh, Chan Kwon Jung, Dong-Hoon Kim, Han Kyeom Kim, Wan Seop Kim, So-Young Jin, Hye Kyoung Yoon
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(6): 579. CrossRef - Comparison of Unsatisfactory Samples from Conventional Smear versus Liquid-Based Cytology in Uterine Cervical Cancer Screening Test
Hoiseon Jeong, Sung Ran Hong, Seoung-Wan Chae, So-Young Jin, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Juhie Lee, Eun Kyung Kim, Sook Tai Ha, Sung Nam Kim, Eun-Jung Park, Jong Jae Jung, Sun Hee Sung, Sung-chul Lim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(3): 314. CrossRef - The Usefulness of p16INK4aImmunocytochemical Staining in ASC-H Patients
Kwang Il Yim, Yeo-Ju Kang, Tae Eun Kim, Gyeongsin Park, Eun Sun Jung, Yeong-Jin Choi, Kyo-Young Lee, Chang Seok Kang, Ahwon Lee
The Korean Journal of Pathology.2011; 45(3): 290. CrossRef
- A Study on the Workload of Cytotechnologists: Focus on Commercial Laboratories
Original Articles
- Histopathologic Study of Post-irradiation Specimen.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Kwang Min Lee, Dong Kyu Chung, Su Gon Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(6):593-600.
- 2,040 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The number of post-irradiated surgical specimen appears to have risen in recent years due to the increasing utiliz ation of radiotherapy for cancer patients. Radiation therapy damages cells by its effects on the deoxyribonucleic acid and the spectrum of injury ranges from acute self-limited lesion to irreversible chronic lesion. We reviewed 24 cases of post-irradiated specimen and thought that time interval is the main factor influencing the morphologic change. Within six weeks, the individual cytologic changes such as biz arre nuclei, altered nucleus/cytoplasm ratio, amphophilic and vacuolated cytoplasm are noted. Chronic injury resulting from progressive changes in the fibrovascular tissue of the radiated area occur in six months after the initial course of radiation and the vascular changes of intimal thickening and fibrosis, foamy histiocytes within media, periadventital fibrosis and chronic inflammatory cells infiltration are present. Althouhg above mentioned finding are not pathognomonic, we thought them quite constant nd reproducible characteristics of radiation injury.
- Availability of Toluidine Blue Stain in Body Fluid.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Myung Jin Joo, Kwang Min Lee, Eun Hee Lee, Sang In Sim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1999;10(1):7-11.
- 2,206 View
- 33 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We evaluated the availability of toluidine blue stain in body fluids, such as peritoneal and pleural fluid and urine. Nine hundreds specimens, i.e., 400 pleural and 400 peritoneal fluids and 100 urine samples, respectively, from Jan. 1995 to May 1996 were included. We obtained the result of high sensitivity and high specificity in toluidine blue stained body fluid in comparison with Papanicolaou stained result. Additionally, we found the diagnostically important crystals in chylothorax and some urine samples, which can not be seen in routine Papanicolaou stain. We thought the toluidine blue stain in body fluid is one of very useful diagnostic methods.
Case Report
- Elastofibroma: Report of a case.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Kwang Min Lee, Dong Kyu Chung, Eul Sam Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(6):635-637.
- 1,804 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Elastofibroma is a rare entity of slowly-growing, solid, ill-defined fibroblastic mass occurring almost exclusively in elderly persons and arising mainly from the connective tissue between the lower portion of the scapula and the chest wall. This entity has been considered to be a degenerative pseudo-neoplastic process caused by mechanical friction. We report an additional case of elastofibroma removed from the subscapular region of a 58-year-old woman. Microscopically the tumor was made up of a mixture of swollen eosinophilic collagen and elastic fibers occasionally associated with fibroblasts and mature fat cells. The elastic fibers showed a degenerated beaded appearance or were fragmented into small globules or droplets in a linear pattern.
Original Article
- Cryptosporidium Infection of Human Intestine: An Electron Microscopic Observation.
- Min Suk Kim, Yun Kyung Kang, Chul Jong Yoon, Mee Joo, Hye Kyung Lee, Jeong Gi Seo, Je G Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(2):121-127.
- 2,051 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Protozoa of the genus Cryptosporidium are small coccidian parasite known to infect the mucosal epithelium of a variety of animals including human, causing fatal course in immunodeficient patients as well as self-limited illness in healthy individuals. Various life cycle stages including trophozoite, meront, merozoite, gametocyte and oocyst in infected mucosa are a diagnostic feature. Electron microscopy (EM) provides sufficient findings for genus and species identification of this parasitic organism. The authors presented scanning and transmission EM findings of Cryptosporidium parvum infection in two children: one with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and the other without any evidence of immune compromise.
Case Reports
- Trichoblastic Carcinoma arising in Trichoblastoma: A Case Report.
- Kyung Jin Seo, Jinyoung Yoo, Seok Jin Kang, Ji Han Jung, Hye Kyung Lee, Kyo Young Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(4):274-277.
- 3,863 View
- 81 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Trichoblastic carcinoma is a rare malignant neoplasm of follicular germ cell origin; to the best of our knowledge, only six trichoblastic carcinomas arising in trichoblastomas have appeared on the literature. We recently experienced a trichoblastic carcinoma arising in a long standing trichoblastoma. A 68-year old woman came to the hospital with a chief complaint of an ulcerated nodule on her face. The nodule, 1.1x0.9 cm with an asymmetrical configuration, had been present and unchanged for more than 20 years, however, it grew suddenly with painful burning sensation. An excisional biopsy was performed and disclosed a deeply invasive, highgrade carcinoma, which consisted of cohesive epithelial cells arranged in irregular plump or germinative cell nests of various sizes. However, at the periphery of the tumor was a benign trichoblastoma surrounded by perifollicular sheath. We believe that the present case is a trichoblastic carcinoma developed via malignant transformation of pre-existing trichoblastoma.
- Ectopic Paragonimiasis Presented as Multiple Colonic and Liver Masses.
- Hye Sung Kim, Young Soo Lee, Yun Kyung Kang, Hye Kyung Lee, Jun Hee Kim, Hyuk Sang Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(4):357-360.
- 1,963 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ectopic paragonimiasis has been diagnosed in many organs such as the mesentery, ovary, pleura, central nervous system, subcutis and very rarely in the liver. However, simultaneous involvement of the colon and liver, which mimics colonic cancer with liver metastasis, is quite unusual, and to our knowledge has never been reported. Our case is a 63 year old woman who visited our hospital because of upper abdominal pain. Radiologically, space occupying lesions were detected in the transverse colon, mesocolon and left hepatic lobe. After the radical presection, they were proved to be an ectopic paragonimiasis forming multiple cavitary parasitic granulomas with Charcot-Leyden crystals and degenerating eggs.
Original Article
- Expression of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase-Associated Protein Phosphatase in Colorectal Carcinomas.
- Chang Nam Kim, Soo Young Kim, Jae Wha Kim, Dong Wook Kang, Hyun Jin Son, Hye Kyung Lee, Mee Ja Park, Joo Heon Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(6):367-372.
- 2,202 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Cyclin-dependent kinase-associated phosphatase (KAP) is a human dual-specificity protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates Cdk2 on threonine160 in a cyclin-dependent manner and that is known as an up-regulated molecule in some malignant tumors. We investigated the expression and clinicopathologic significance of KAP protein in relation to tumorigenesis of colorectal carcinoma.
METHODS
The expression patterns of KAP protein in tumor tissue were examined by reverse transcription-PCR and immunohistochemical staining.
RESULTS
An enhanced transcriptional level of KAP mRNA was observed in 11 out of 12 colorectal carcinoma specimens. Immunohistochemical examination showed that KAP protein was more highly expressed in the tumors than that in the adjacent non-neoplastic mucosal tissues for 52 of 102 colorectal cancer tissues. The statistical analysis showed that an increased level of KAP protein in the colorectal cancer tissues was inversely correlated with the histologic grade, tumor size and Duke's stage.
CONCLUSION
The present study suggests that alteration of KAP might play a role, at least in part, in the tumorigenicity of colorectal carcinoma through the mechanism of cell cycle regulation.
Case Reports
- Angiomyofibroblastoma of Vulva: A case report.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Myung Jin Joo, Kwang Min Lee, Dong Kyu Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(4):530-532.
- 1,937 View
- 35 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva is a rare mesenchymal tumor. It has been diagnostically confused with aggressive angiomyxoma which has a somewhat different clinical course and therapy. Herein we report a case of angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva in a 46-year-old female. Microscopically, there were alternating hypercellular and hypocelluar edematous zones in which abundant capillary blood vessels were irregularly distributed. Spindle, plump spindle, and oval stromal cells were concentrated around the blood vessels, or loosely dispersed in the hypocellular area. Immunohistochemically, the stromal cells were positive for desmin, vimentin, muscle-specific actin and weakly positive for S-100 protein. Ultrastructural studies showed well developed rough endoplasmic reticulum, abundant intermediate filaments, and pinocytic vesicles in the stromal cells.
- Intra-abdominal Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumor Diagnosed by Lymph Node Biopsy: A case report.
- Myung Jin Ju, Kwang Min Lee, Hye Kyung Lee, Dong Kyu Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(5):698-701.
- 1,967 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Intra-abdominal desmoplastic small round cell tumor has been described in the literature since 1989. It is characterized by the occurrence in ages less than 40 with male predominance, an intra-abdominal location, and small round to oval shaped tumor cells with divergent differentiation in the background of the desmoplastic stroma. We recently experienced this tumor in an inguinal lymph node of a 36-year-old man. It is suspected that it metastasized from a lower intra-abdominal tumor. Immunohistochemical stains for keratin, epithelial membrane antigen, vimentin, S-100 protein and neuron specific enolase were positive. This is the first documented case in Korea. Herein, we report on this tumor with a review of literature.
Original Article
- PTEN and p53 Mutations in Endometrial Carcinomas.
- Jae Sung Choi, Kwang Sun Suh, Heung Tae Noh, Yun Ee Rhee, Sun Young Na, Hye Kyung Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(1):1-8.
- 2,702 View
- 35 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Endometrial carcinomas are pathogenetically classified into two major types; endometrioid carcinoma (EC) and serous carcinoma (SC). The most frequently altered gene in EC is the PTEN tumor suppressor gene (TSG). SC is usually associated with mutations in the p53 TSG.
METHODS
To further determine the role of PTEN and p53 mutation in endometrial carcinogenesis, the analysis of 33 endometrial carcinomas, including 28 ECs and 5 SCs, for loss of heterozygosity (LOH) on 10q23 and for mutation in all 9 coding exons of PTEN and the 5-8 exons of p53, using SSCP-PCR methods was carried out.
RESULTS
LOH was detected in at least one marker in 12 (54.5%) of 22 ECs, but in only one (20.0%) of 5 SCs. Somatic PTEN mutations were detected in 10 (35.7%) of 28 ECs. PTEN was altered in 67.9% of ECs and in 20.0% of SCs, including those with 10q23 LOH. No PTEN mutations were found among the SCs. Somatic p53 mutations were detected in 2 (7.1%) of 28 ECs and 3 (60.0%) of 5 SCs.
CONCLUSIONS
PTEN gene alterations contribute to the pathogenesis of an endometrioid subtype of endometrial carcinoma, but not to the serous type. In contrast, p53 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of SCs.
Case Reports
- Cellular Schwannoma Arising in a Facial Nerve.
- Mee Joo, Hye Sung Kim, Yun Kyung Kang, Hye Kyung Lee, Jae Young Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(7):688-691.
- 2,039 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cellular schwaninoma is a variant of schwannoma, which is characterized by predominance of cellular Antoni A area, presence of mitotic activity, nuclear hyperchromasia, pleomorphism, and absence of Verocay body. These pathologic features often prompted a misdiagnosis of malignancy. However, the clinical outcome has indicated the benignity of the tumor. We have experienced a case of cellular schwannoma arising from right facial nerve with right hemifacial weakness and erosion of mastoid process. Grossly, it was a 3.5 x 3 cm sized and relatively well encapsulated mass with yellowish, friable cut surface. Microscopically, cellular growth with moderate cellular pleomorphism and some mitotic activity (5/40 HPFS, up to 2/HPF) were noted. Immunostaining for S-100 protein showed diffuse strong positive reaction.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytologic Findings of Thyroid Lymphoma: Report of Two Cases.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Jong Min Lee, Chang Suk Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2002;13(1):33-37.
- 2,098 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report two different types of thyroid lymphoma associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Both showed autoantibodies and were compatible with Hashimoto's thyroiditis according to their clinical backgrounds. A 76-year-old female noted a painless, rapidly growing mass in her neck which was diagnosed as diffuse non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, large cell type, after the fine needle aspiration cytology of the thyroid. She underwent chemo-radiotherapy and is free of the disease 10 months after diagnosis. The other patient, a 73-year-old female with a diffuse goiter, was diagnosed on fine needle aspiration cytology as having Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Three years later she developed a hard nodular growth in the both lobes of the thyroid. This was subjected to fine needle aspiration cytology and needle biopsy and was diagnosed as a MALT lymphoma. She refused any treatment and died 12 months after the diagnosis.
Original Articles
- Morphologic changes of postirradiated cervical cells in cervical cancer.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Kwang Min Lee, Dong Kyu Chung, Soo Kon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1993;4(2):87-92.
- 1,949 View
- 10 Download
- Usefulness of Cytologic Study of Intraoperative Suction Fluid in Brain Tumors.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Hyun Gjin Lee, Eun Hee Lee, Hee Jung Kim, Il Woo Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2002;13(2):66-69.
- 1,955 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In diagnosing a brain tumor, it is essential to obtain samples from many areas of the tumor. Although there are reports about the suitability of material obtained by cavitron ultrasonic surgical aspirator(CUSA), there is a paucity of reports regarding conventional intraoperative suction. This study was performed to evaluate the usefulness of the suction fluid and the effect of different hemolytic fixatives. Intraoperative suction fluid was obtained from 2 pituitary adenomas and 2 choroid plexus carcinomas. In two cases of mixed astro-oligodendroglioma, one of glioblastoma multiforme and 3 of meningioma, the fluid was collected by CUSA. Each sample was divided into four bottles for the different fixatives such as 0.1N HCl, 10% acetic acid, 95% alcohol, and no additive. All cases were evaluated by the both cytologic smear and cell block preparations, and were reviewed with concomitant histologic diagnosis. The result showed a good correlation between the cytologic study and the histologic diagnosis and 95% alcohol was found to be superior to other fixatives in cell preservation.
- Ultrastructural Observations on Human Primary Hepatocellular Carcinomas: Analysis of 35 Lobectomy Specimens.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Yong Il Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1986;20(4):442-452.
- 1,745 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The etiologic impacts in primary hepatocellular carcinoma among Koreans seem different from those in other countries with its high incidence and close association of hepatitis B virus infection and liver cirrhosis. A series of 35 lobectomy specimens of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was examined by means of electron microscopy to elucidate the general ultrastructural characteristics and to understand the morphogenesis of various histological growth patterns and cytologic features of HCC. 1) General cytological details of HCC were similar to those of non-neoplastic hepatocytes, but characterized by scantiness of subcellular organelles. Degree of cellular differentiation was not correlated with ultrastructural features of HCC. 2) Acinar pattern of HCC seemed to develop by either dilatation of central bile canaliculus or central cystic degeneration of microtrabecular growth, and clear cell group of HCC was expressed in abundance of glycogen particles and lipid droplets. 3) Intranuclear inclusions of HCC proved to be cytoplasmic herniations of tumor cells, and intracytoplasmic tubular arrays appeared to originate from the endoplasmic reticulum. 4) Hyaline globules seen in HCC corresponded to clumps of microfilamentous structures similar or identical to Mallory's hyalin.
- Results of Sputum Cytology in Diagnosis of Lung Cancer: Based on the Results Obtained for 16 months in Presbyterian Medical Center.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Kwang Min Lee, Dong Kyu Chung, Dae Song Kang, Kwi Wan Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1994;5(2):148-153.
- 2,011 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A prospective survey of sputum cytologic specimen was performed for 16 months from Jan. 1993 to Apr. 1994 in Presbyterian Medical Center. The purpose of this study is to find the positive rate of sputum cytology in the diagnosis of lung cancer and to correlate these results with tumor location and stage. Sputum cytologic specimen were received from 104 patients among 168 patients diagnosed as lung malignancy by histologic examination. Cytologic diagnosis of "suggestive of malignancy" was made in 61 patient(59%) and dysplasia in 9 patients(9%), atypia in 14 patients(13%), benign in 15 patients(14%) and inadequate specimen in 5 patients(5%), respectively. Among 84 patients beyond the cytologic diagnosis of atypia, 51 patients(61%) disclosed a central location, while 33patients(39%) showed peripheral lesions. All 54 patients diagnosed as suggestive of non-small cell carcinoma were stage III or over, and all 7 patients diagnosed as suggestive of small cell carcinoma were in advanced stage.
- Histopathological Differences between Silicone Granuloma and Paraffinoma.
- Yeon Mee Kim, Hye Kyung Lee, Hye Je Cho, Je Geun Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(5):427-436.
- 5,481 View
- 310 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - During the past two decades, silicone (polydimethylsiloxane) has become one of the most extensively applied biomaterials. Although pure silicone is relatively inert and usually causes only minimal tissue reactions, it has been reported to evoke a definite foreign body reaction. We studied five cases of silicone-induced granulomas in various sites; two in the breast, one in the breast and axillary lymph nodes, one in the subcutis of the abdomen, back and extremities and one in the eyeball, to illustrate the salient histopathologic features of reactions to silicone with particular emphasis to its differences from paraffin granuloma. For this, 17 paraffinomas were also studied. Tissue reaction to silicone liquid and gel was characterized by numerous round to oval empty cystic vacuoles, mild to moderate fat necrosis, foreign body reaction, a variable degree of mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltration and mild focal fibrosis. The cystic spaces were relatively uniform and showed a snow-man like appearance. In contrast to the silicone granulomas, the paraffinomas, also refered to as sclerosing lipogranulomas showed diffuse sclerosis and frequent calcification around the cystic vacuoles. The cystic spaces in paraffinomas were swiss cheese-like configuration, and the content of the cystic spaces was dirty and frequently calcified. However, there were certain similarities between these two types of granulomas particularly in the early phases of the reaction, therefore, the history of silicone injection or implant, is sometimes critical to the diagnosis of silicone granuloma. Despite great technologic advances in the manufacturing of prostheses and medical equipment, droplets and/or particles of silicone still escape into the body tissues in a variety of ways; therefores, the pathologist should always wonder whether the histologic reaction observed is due to silicone or to some other foreign material including paraffin.
Case Report
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising from Mature Cystic Teratoma of the Ovary: A report of three cases .
- Mee Joo, Han Nae Min, Yun Kyung Kang, Hye Kyung Lee, Young Chae Cho, Eung Soo Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(12):1211-1215.
- 2,406 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Malignant transformation develops in a little less than 2% of mature cystic teratomas. A wide variety of malignant tumors may arise within benign mature cystic teratomas, and the most common of these is squamous cell carcinoma, which account for 75~85%. In general, the tumors are in an advanced stage and the prognosis is poor as most patients die within a year. However, when the tumor is confined to the ovary, they have a good prognosis and the 5-year survival rate is 63~83%. We experienced three cases of squamous cell carcinoma arising in mature cystic teratoma. Two of the carcinomas occurred in postmenopausal women: 58-(case 1) and 66-(case 2) year-old, and were confined to the ovaries. They were alive 37 months and 18 months after the operation, respectively. The third case was a 45-year-old premenopausal woman who had an extraovarian extension of the tumor and early recurrence within two months. Histologically, cases 1 and 3 were conventional well to moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinomas and case 2 showed a well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with exuberant proliferating trichilemmal tumor-like areas.
Original Articles
- Histopathologic Findings & Expression of bcl-2 of the Endometrium Analysis of 1,000 consecutive biopsies of uterine bleeding .
- Hye Kyung Lee, Dong Geun Lee, Ho Lee, Sang In Shim
- Korean J Pathol. 1998;32(3):208-214.
- 1,953 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We evaluated 1,000 consecutive endometrial curettage samples obtained over a 30 month period. The clinico-pathologic correlation was analysed according to Hendrickson's five criteria based on the practical view. The causes of uterine bleeding in decreasing order of occurrence were as follows: 1) hormonal imbalance lesions (49.2%) encompassing glandular and stromal breakdown suggesting anovulatory bleeding, proliferative phase endometrium, and disordered proliferative endometrium, 2) pregnancy associated lesions (24.2%), 3) organic lesions (13.5%), 4) endometrial hyperplasia (6.9%), and 5) inadequate specimen (6.2%). According to age, pregnancy related lesions were most frequent in the third decade. In the fourth, fifth, and sixth decades, hormonal imbalance lesions were the most common cause. In approximately 30% of the samples, there were two or three morphologic patterns such as anovulatory bleeding with an endometrial polyp, postabortal bleeding with inflammation, and glandular-stromal dissociation with a polyp, which suggested there was a variable histologic morphology in the same disease spectrum. Using immunohistochemical techniques we studied the hormonal dependency of bcl-2 oncoprotein in anovulatory bleeding, endometrial hyperplasia, and proliferative endometrium. 70% of anovulatory bleeding specimens showed weak positivity in the epithelial cytoplasm, and all cases of endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma showed a strong positivity. These results suggest that there is a estrogenic hormonal dependency of apoptosis in the endometrium.
- Morphometric Analysis for Cytological Diagnosis of Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma.
- Jong Ok Kim, Bo Seong Yang, Hye Soo Kim, Jong Min Lee, Dong Ho Lee, So Young Shin, Chang Suk Kang, Hye Kyung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2006;17(2):116-119.
- 2,458 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer is generally based on the findings of intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions and nuclear grooves. Although anisokaryosis and poikilokaryosis, in papillary thyroid cancer, are not distinct when compared to other cancers, cytological examination can provide useful preoperative information. Our study evaluated the diagnostic role of computer-assisted image analysis for the pre-surgical assessment of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid aspirates from twenty female patients who were histologically confirmed to have both papillary carcinoma and benign nodules were studied. Different populations of 50 benign cells and 50 malignant cells were analyzed. Five morphometric parameters were selected for analysis: nuclear area, perimeter, maximum length, maximum width and intensity standard variation. The values obtained for papillary carcinomas were higher than the surrounding benign nodules as follows: nuclear area 63.5 vs. 36.1 (p=0.000), nuclear perimeter were 29.4 vs. 22.0 (p=0.000), maximum length 9.6 vs. 7.1 (p=0.000), maximum width 8.2 vs. 6.3 (p=0.000), the ratio between maximal length and maximal width 1.16 vs. 1.13 (p=0.000), the standard variation of intensity 14.9 vs. 15.9 (p=0.101) respectively. Therefore, morphometric information can be helpful for the differential cytological diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma.
- Promoting Effect of Aflatoxin B1 and D-Galactosamine on Development of Glutathione S-Transferase Positive Foci in Diethylnitrosamine-initiated Rat Liver.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Yong Il Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(4):389-398.
- 1,937 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The enhancing potential of anatoxin a (AFB1) and D-galactosamine (DGA) on development of preneoplastic glutathione S-transferase placental form positive (GST-P+) hepatic foci was examined using an in vivo mid-term assay system based on two-stage concept of hepatocarci-nogenesis. Rats were initially given a single dose (200 mg/kg) of diethylnitrosamine (DEN) intraperi-toneally, and thereafter. with an interval of 2 weeks, AFBl at a graded concentration (0.06, 0.012, 0.0024, 0.00048, and 0.000096 mg/kg i.g.) and DGA (100 mg/kg i.p.) were administered for 6 weeks and then sacrificed. All rats were subjected to a two-thirds partial hepatectomy to induce a potent growth stimulus to DEN-altered hepatocytes at the week 3. The modifying potential was scored by comparing the number and the area (mm2) per cm2 of GST-P+ foci in the liver with those of the corresponding control group given DEN alone. AFBl (at a graded concentration between 96 ng/kg and 60 microgram/kg) exerted a strong promoting effect oil induction of GST-P+ foci with both the number and the area. The logarithmic dose of AFBl and the potency to promote hepatocarcinogenesis were in dose-dependent relationship. DGA, a known necrogenic chemical to cause periportal necrosis and stimulate hepatocellular proliferation. also revealed the increase in the area of GST-P+ foci. although its enhancing potentia1 was 1ess profound than that of AFBl. The results suggest that DGA is also a useful proliferative stimulus m improve the medium-termdetection of unknown carcinogens.
- Cytologic Findings of Colon Lavage Fluid in Colon Cancer.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Myung Jin Joo, Kwang Min Lee, Dong Kyu Chung, Yong Woo Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1996;7(1):103-106.
- 1,983 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Although exfoliative colonic cytology for the diagnosis of colorectal cancer has been largely abandoned due to the widespread use of colonoscopy, some authors still insiston the usefulness of colon lavage fluid. We tried evaluating the diagnostic feasibility of colon lavage fluid cytology using an orally administered balanced electrolyte solution. We collected colon lavage fluids in 106 patients prior to colonoscopy and reviewed the slides. Cytologic examination revealed neoplastic cells in 7 of 16(44%) cases of endoscopically proven adenocarcinoma patients. Therefore, we think cytologic study of colon lavage fluid may be considered as one of the noninvasive diagnostic tools in colorectal cancer.
- Combined Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia and Miliary Tuberculosis in a Patient with AIDS.
- So Young Park, Hye Kyung Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(6):657-662.
- 2,286 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Patients with AIDS frequently present with pulmonary complications which are associated with a high mortality rate and infections are the most important cause of lung infiltrates. In addition to pneumonia caused by Pneumocystis carinii, which was noted in early reports of the syndrome, a variety of other severe pulmonary disorders may occur. Frequently more than one organism is found in a single patient and among these, combined infections of Pneumocystis carinii and cytomegalovirus are the most common. We experienced a case of combined Pneumosytis carinii and Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection as a pulmonary manifestation of AIDS in a 38-year-old man. In bronchoalveolar larvage, bronchial washing and brushing, and sputum smear specimens, Pneumocystis carinii organisms were recognized, especially in Gomori's methenamine silver stains. Transbronchial lung biopsy specimen revealed intra-alveolar frothy exudates composed of collections of Pneumocystis carinii organisms as well as several granulomas with central caseous necroses.
- Benign Epithelial Changes of Endometrium: Based on 450 hysterectomy specimens obtained from Jan. 1994 to Dec. 1994.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Myung Jin Joo, Kwang Min Lee, Dong Kyu Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(11):966-971.
- 2,186 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To evaluate the incidence and clinico-pathologic correlation of benign epithelial changes of endometrium, we tried to classify the changes into squamous cell change, ciliary change, eosinophilic cell change, papillary surface epithelial change, and mucinous cell change by the criteria of Hendrickson. Based on the 450 hysterectomy specimens obtained from Jan. 1994 to Dec. 1994 in PMC, the incidence of the cell changes was as follows: squamous cell change: 1.1%, eosinophilic cell change: 6.8%, mucinous cell change: 6.6%, ciliary change: 10.4%, papillary surface epithelial change: 16.4%. Squamous cell change was noted in severe endometritis or endometrial hyperplasia and papillary surface epithelial proliferation was mainly associated with plasma cell infiltration in adenomyosis or leiomyoma. Eosinophilic change and ciliary change were sometimes concomitantly found in dilated glands of the basal layer or in the invaded glands of adenomyosis. The results of this study suggested a correlation of benign epithelial changes with endometritis, adenomyosis, leiomyoma and dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
Case Report
- Accessory Hepatic Nodules: Histopathologic analysis of three cases.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Yong Il Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1985;19(1):97-101.
- 1,929 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This report deals with three cases of accessory hepatic nodules incidentally noted during operation. Two of them were found on the serosal surface of the gallbladder with no connection to the main body of the liver. The other case was in the greater omentum. All three cases were small oval shaped, measuring less than 1 cm in maximum dimension and were composed of histologically normal hepatic tissue and seemed to receive blood supply from the adjacent tissue through the capsular blood vessels. Presence of the fairly well retained intralobular mesenchymal component may reflect that accessory hepatic nodules develop after conjugation of hepatic diverticulum and septum transversum.
Original Article
- Biologic Significance of Hepatocyte Hepatitis B Core Antigen Expression in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection II.
- Hye Kyung Lee, Kwang Min Lee, Dong Kyu Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(4):355-359.
- 1,988 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Routine use of commercially available antisera against hepatitis B core antigen(HBcAg) has permitted a reevaluation of the histochemical distribution of the antigen in liver tissue. HBcAg, classically described almost exclusively in the nucleus, was found with a very high frequency in the cytoplasm of liver cells as well. To elucidate the biologic significance of HBcAg expression and its relation to the natural course of hepatitis B virus(HBV) infection, the patterns of activity in 33 needle liver biopsies of HBsAg carriers were analysed. A good correlation of liver HBcAg with disease activity was demonstrated. HBcAg was present in the hepatocyte nuclei(nHBcAg) or cytoplasm(cHBcAg), or in both(mixed). Pure nHBcAg was seen mainly in non-aggressive reactive liver tissue and cHBcAg was predominantly associated with chronic active hepatitis(95%). The results suggest that expression of HBcAg correlates with the liver pathology and the possibility of HBcAg to be an immunological target for T cell mediated hepatocyte damage.
Case Report
- Clear Cell Sarcoma of the Kidney: A case in 39 year old man.
- Hyun Ju Yoo, Yun Kyung Kang, Mee Joo, Hye Kyung Lee, Dae Woo Kim, Suk San Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(12):1138-1143.
- 2,451 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clear cell sarcoma of kidney(CCSK) is a rare pediatric neoplasm characterized by a predominating component of clear cells, a predilection for metastases to bone, and a poor prognosis. The incidence of CCSK peaks during the 2nd year of life and adult cases are very rare. We report a case of CCSK encountered in the right kidney of a 39-year-old man. Grossly, it was a lobulated mass showing infiltrative margin, measured 7x5.5x5cm and had a homogeneous gray-tan color with a soft, fish-flesh consistency. Microscopically, about half of the tumor revealed the classic pattern of CCSK, having tumor cell cords or nests separated by the characteristic alveolar capillary networks. The tumor cells had clear pale cytoplasm, bland looking round nuclei and inconspicuous nucleoli. The other half showed the epithelioid-trabecular pattern forming pseudorosette or cord-like structures. Immunohistochemically, there was only a focal positive reaction to vimentin. Ultrastructurally, the tumor cells showed the primitive nephrogenic mesenchymal differentiation such as electron lucent cytoplasm, a small amount of organelles, scanty heterochromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli, and a lack of flocculant basal lamina material around the cytoplasmic membrane. We consider that this is a case of CCSK occuring in the oldest patient ever reported, confirmed by both immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy.
Original Article
- Diffuse Neurofibromas: Clinicopathologic Analysis of 11 cases.
- So Young Park, Hye Kyung Lee, Se Min Baek
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(2):181-188.
- 2,047 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We reviewed surgical specimens from 11 patients with diffuse neurofibroma to define the specific clinicopathologic characteristics. Ten cases were cutaneous neurofibromas and one case was an uncommon gastrointestinal neurofibroma involving the rectum. The most frequent sites of involvement were the head and neck, especially the eyelids and the periorbital areas. They usually presented as a plaque-like elevation of the skin. They primarily occured in children and young adults and positive family histories of von Recklinghausen's neurofibromatosis were obtained in 45.4%. Pathologically, the involved skin & rectum were diffusely thickened by an infiltrative growing mass, showing proliferation of short fusiform cells in the uniform matrix of fine fibrillary collagen. The characteristic prominence of Wagner-Meissner bodies (45.4%) suggests they could be associated with pathogenesis of diffuse neurofibroma. On the basis of these findings, we could confirm diffuse neurofibroma to be a distinct form of neurofibroma.

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



