Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- National quality assurance program using digital cytopathology: a 5-year digital transformation experience by the Korean Society for Cytopathology
- Yosep Chong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Soon Auck Hong, Sung Soon Kim, Bo-Sung Kim, Younghee Choi, Yoon Jung Choi, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Soo Jin Jung, Hoon Kyu Oh, Seung-Sook Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):320-333. Published online September 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.27
- 2,707 View
- 102 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
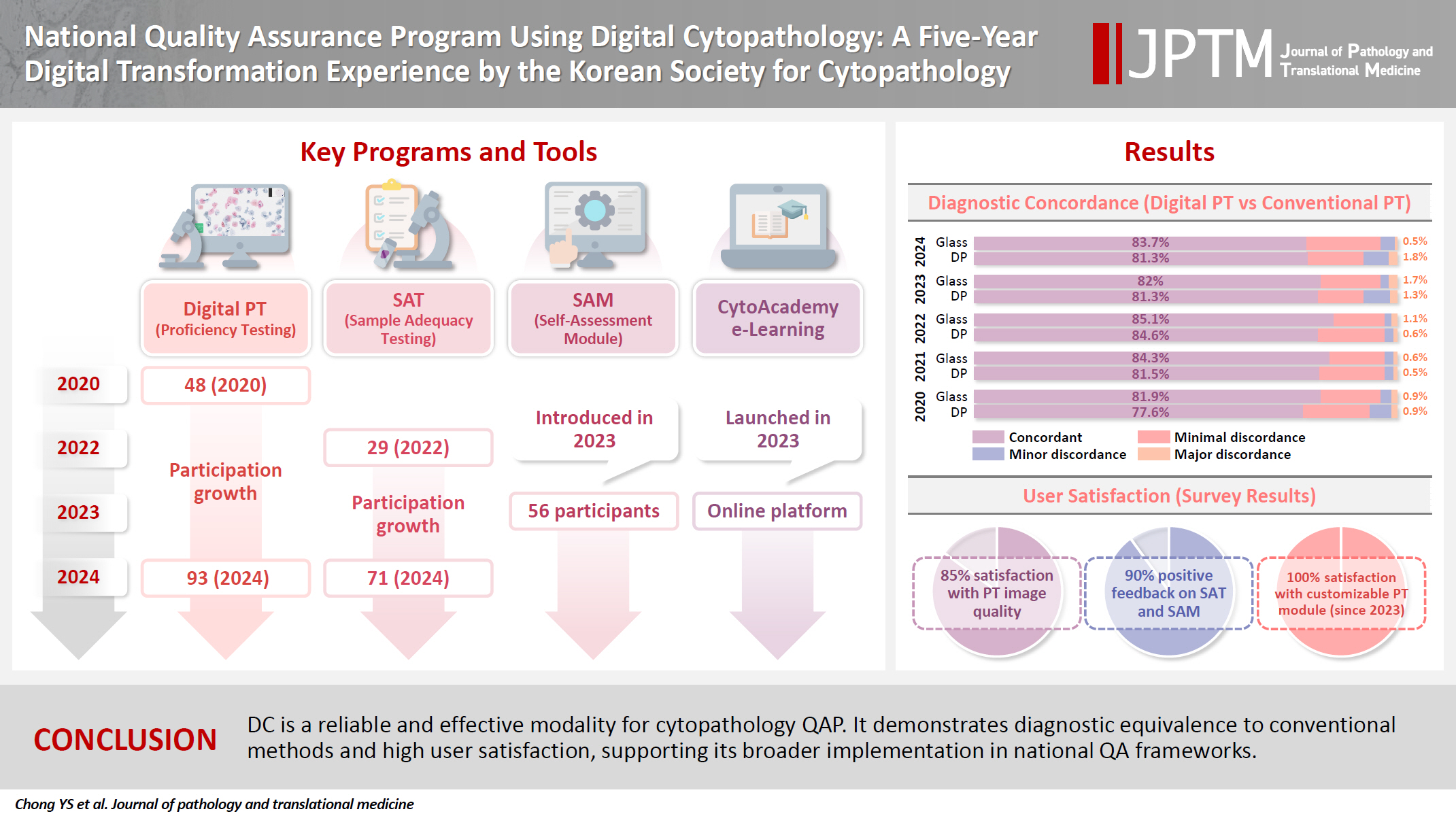
Digital cytopathology (DC) is emerging as a transformative approach in quality assurance programs (QAP), though its comprehensive evaluation remains limited. Since 2020, the Korean Society for Cytopathology has progressively incorporated DC into its national QAP, including digital proficiency testing (PT), sample adequacy testing (SAT), a customizable PT module, and a self-assessment module (SAM), aiming for full digital implementation by 2026. Methods: This 5-year study assessed diagnostic concordance between conventional and digital PT formats and analyzed participant feedback on service quality and digital image usability across PT, SAT, and SAM. Parallel testing was conducted during the transitional phase, and satisfaction was measured through structured surveys. Results: Participation in digital PT increased from 48 institutions in 2020 to 93 in 2024, while digital SAT participation rose from 29 to 71 between 2022 and 2024. In 2023, 56 institutions joined SAM. Diagnostic concordance rates were comparable between digital and conventional PTs (78.6%–84.6% vs. 82.0%–85.1%), including similar category C (major discordance) rates. Satisfaction with digital PT services and image quality exceeded 85%, and over 90% of institutions reported positive feedback on SAT and SAM. Over 80% were satisfied with the customizable PT module. Conclusions: DC is a reliable and effective modality for cytopathology QAP. It demonstrates diagnostic equivalence to conventional methods and high user satisfaction, supporting its broader implementation in national quality assurance frameworks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
- Current status of cytopathology practice in Korea: impact of the coronavirus pandemic on cytopathology practice
- Soon Auck Hong, Haeyoen Jung, Sung Sun Kim, Min-Sun Jin, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Younghee Choi, Gyungyub Gong, Yosep Chong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(6):361-369. Published online October 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.09.21
- 4,850 View
- 105 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The Continuous Quality Improvement program for cytopathology in 2020 was completed during the coronavirus pandemic. In this study, we report the result of the quality improvement program.
Methods
Data related to cytopathology practice from each institute were collected and processed at the web-based portal. The proficiency test was conducted using glass slides and whole-slide images (WSIs). Evaluation of the adequacy of gynecology (GYN) slides from each institution and submission of case glass slides and WSIs for the next quality improvement program were performed.
Results
A total of 214 institutions participated in the annual cytopathology survey in 2020. The number of entire cytopathology specimens was 8,220,650, a reduction of 19.0% from the 10,111,755 specimens evaluated in 2019. Notably, the number of respiratory cytopathology specimens, including sputum and bronchial washing/ brushing significantly decreased by 86.9% from 2019, which could be attributed to the global pandemic of coronavirus disease. The ratio of cases with atypical squamous cells to squamous intraepithelial lesions was 4.10. All participating institutions passed the proficiency test and the evaluation of adequacy of GYN slides.
Conclusions
Through the Continuous Quality Improvement program, the effect of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic, manifesting with a reduction in the number of cytologic examinations, especially in respiratory-related specimen has been identified. The Continuous Quality Improvement Program of the Korean Society for Cytopathology can serve as the gold standard to evaluate the current status of cytopathology practice in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on the Workload of Cytotechnologists: Focus on Commercial Laboratories
Eun-Suk PARK
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2025; 57(2): 228. CrossRef - Integration of Digital Cytology in Quality Assurance Programs for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Maria Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Zaibo Li, Andrey Bychkov
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - National quality assurance program using digital cytopathology: a 5-year digital transformation experience by the Korean Society for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Soon Auck Hong, Sung Soon Kim, Bo-Sung Kim, Younghee Choi, Yoon Jung Choi, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Soo Jin Jung, Hoon Kyu Oh, Seung-Sook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(5): 320. CrossRef - Commercially Available Artificial Intelligence Solutions for Gynaecologic Cytology Screening and Their Integration Into Clinical Workflow
Yosep Chong, Andrey Bychkov
Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A stepwise approach to fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes
Yosep Chong, Gyeongsin Park, Hee Jeong Cha, Hyun-Jung Kim, Chang Suk Kang, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Seung-Sook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(4): 196. CrossRef - Diagnostic proficiency test using digital cytopathology and comparative assessment of whole slide images of cytologic samples for quality assurance program in Korea
Yosep Chong, Soon Auck Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh, Soo Jin Jung, Bo-Sung Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Ho-Chang Lee, Gyungyub Gong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(5): 251. CrossRef
- A Study on the Workload of Cytotechnologists: Focus on Commercial Laboratories
- Analysis of PAX8 immunohistochemistry in lung cancers: a meta-analysis
- Jae Han Jeong, Nae Yu Kim, Jung-Soo Pyo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(4):300-309. Published online July 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.06.08
- 9,335 View
- 154 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
In this meta-analysis, we aimed to evaluate the PAX8 immunohistochemical expressions in primary lung cancers and metastatic cancers to the lung.
Methods
We identified and reviewed relevant articles from the PubMed databases. Ultimately, 18 articles were included in this meta-analysis. PAX8 expression rates were analyzed and compared between primary and metastatic lung cancers.
Results
The PAX8 expression rate in primary lung cancers was 0.042 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.025 to 0.071). PAX8 expression rates of small cell (0.129; 95% CI, 0.022 to 0.496) and non-small cell carcinomas of the lung (0.037; 95% CI, 0.022 to 0.061) were significantly different (p=.049 in a meta-regression test). However, the PAX8 expression rates of adenocarcinoma (0.013; 95% CI, 0.006 to 0.031) and squamous cell carcinoma (0.040; 95% CI, 0.016 to 0.097) were not significantly different. PAX8 expression rates of metastatic carcinomas to the lung varied, ranging from 1.8% to 94.9%. Metastatic carcinomas from the lung to other organs had a PAX8 expression rate of 6.3%. The PAX8 expression rates of metastatic carcinomas from the female genital organs, kidneys, and thyroid gland to the lung were higher than those of other metastatic carcinomas.
Conclusions
Primary lung cancers had a low PAX8 expression rate regardless of tumor subtype. However, the PAX8 expression rates of metastatic carcinomas from the female genital organs, kidneys, and thyroid were significantly higher than those of primary lung cancers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical significance of lncRNA PAX8-AS1 and miR-96-5p in non-small cell lung cancer
Qiaoling Ying, Hui Xu, Xiaojiao Wu, Hang Fang, Jingjing Shi, Hangcheng Pan
Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Lung Metastatic Recurrence as Carcinosarcoma from Ovarian Mesonephric-Like Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report
Kaito Nakama, Masayuki Ota, Takanori Aihara, Satoko Kageyama, Jun-ichiro Ikeda
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The TTF-1 and Napsin A Trap: Metastatic Endometrial Carcinoma Masquerading as Lung Primary
Carmen Alfonso-Rosa, Jesús Machuca-Aguado, Ana María Montaña-Ramírez, Francisco Javier Rubio-Garrido
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic value of PAX8 in small cell lung cancer
Fengyun Tao, Hangyan Zhu, Jiayun Xu, Yanan Guo, Xin Wang, Lei Shao, Deng Pan, Guosheng Li, Rong Fang
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e28251. CrossRef - Cystic primary squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid
Sakurako Harada‐Kagitani, Yusuke Kouchi, Yoshiki Shinomiya, Takuto Hiramoto, Tomoyuki Arai, Toyoyuki Hanazawa, Kiyotaka Onodera, Kaito Nakama, Takanori Aihara, Masayuki Ota, Jun‐Ichiro Ikeda, Takashi Kishimoto
Pathology International.2024; 74(5): 292. CrossRef - The combination of p16 and Rb expression pattern is helpful to predict high-risk HPV infection and the primary site in lymph node metastases of squamous cell carcinoma
Ryosuke Kuga, Hidetaka Yamamoto, Fumiya Narutomi, Misa Suzuki, Rina Jiromaru, Takahiro Hongo, Kazuhisa Hachisuga, Nobuko Yasutake, Kiyoko Kato, Takashi Nakagawa, Yoshinao Oda
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 263: 155642. CrossRef - Mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix with a prominent spindle cell component
Yingying Fan, Ying He, Liang Sun, Tianmin Liu, Yangmei Shen
Oncology Letters.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunocytochemistry of effusions: Processing and commonly used immunomarkers
Vinod B. Shidham, Beata Janikowski
Cytojournal.2022; 19: 6. CrossRef - Significance analysis of PAX8 expression in endometrial carcinoma
Shan Hu, Hua Gan, Fengmei Yang
Medicine.2022; 101(42): e31159. CrossRef
- Clinical significance of lncRNA PAX8-AS1 and miR-96-5p in non-small cell lung cancer
- Current status of cytopathology practices in Korea: annual report on the Continuous Quality Improvement program of the Korean Society for Cytopathology for 2018
- Yosep Chong, Haeyoen Jung, Jung-Soo Pyo, Soon Won Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(4):318-331. Published online April 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.02.26
- 7,186 View
- 118 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The Korean Society for Cytopathology has conducted the Continuous Quality Improvement program for cytopathology laboratories in Korea since 1995. In 2018 as part of the program, an annual survey of cytologic data was administered to determine the current status of cytopathology practices in Korea. Methods: A questionnaire was administered to 211 cytopathology laboratories. Individual laboratories submitted their annual statistics regarding cytopathology practices, diagnoses of gynecologic samples, inadequacy rates, and gynecologic cytology-histology correlation review (CHCR) data for 2018. In addition, proficiency tests and sample adequacy assessments were conducted using five consequent gynecologic slides. Results: Over 10 million cytologic exams were performed in 2018, and this number has almost tripled since this survey was first conducted in 2004 (compounded annual growth rate of 7.2%). The number of non-gynecologic samples has increased gradually over time and comprised 24% of all exams. The overall unsatisfactory rate was 0.14%. The ratio of the cases with atypical squamous cells to squamous intraepithelial lesions accounted for up to 4.24. The major discrepancy rate of the CHCR in gynecologic samples was 0.52%. In the proficiency test, the major discrepancy rate was approximately 1%. In the sample adequacy assessment, a discrepancy was observed in 0.1% of cases. Conclusions: This study represents the current status of cytopathology practices in Korea, illustrating the importance of the Continuous Quality Improvement program for increasing the accuracy and credibility of cytopathologic exams as well as developing national cancer exam guidelines and government projects on the prevention and treatment of cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Commercially Available Artificial Intelligence Solutions for Gynaecologic Cytology Screening and Their Integration Into Clinical Workflow
Yosep Chong, Andrey Bychkov
Cytopathology.2026; 37(1): 24. CrossRef - Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(2): 146. CrossRef - Sensitivity, Specificity, and Cost–Benefit Effect Between Primary Human Papillomavirus Testing, Primary Liquid‐Based Cytology, and Co‐Testing Algorithms for Cervical Lesions
Chang Gok Woo, Seung‐Myoung Son, Hye‐Kyung Hwang, Jung‐Sil Bae, Ok‐Jun Lee, Ho‐Chang Lee
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(1): 35. CrossRef - A Study on the Workload of Cytotechnologists: Focus on Commercial Laboratories
Eun-Suk PARK
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2025; 57(2): 228. CrossRef - Integration of Digital Cytology in Quality Assurance Programs for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Maria Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Zaibo Li, Andrey Bychkov
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - National quality assurance program using digital cytopathology: a 5-year digital transformation experience by the Korean Society for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Soon Auck Hong, Sung Soon Kim, Bo-Sung Kim, Younghee Choi, Yoon Jung Choi, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Soo Jin Jung, Hoon Kyu Oh, Seung-Sook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(5): 320. CrossRef - Diagnostic proficiency test using digital cytopathology and comparative assessment of whole slide images of cytologic samples for quality assurance program in Korea
Yosep Chong, Soon Auck Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh, Soo Jin Jung, Bo-Sung Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Ho-Chang Lee, Gyungyub Gong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(5): 251. CrossRef - Recent Application of Artificial Intelligence in Non-Gynecological Cancer Cytopathology: A Systematic Review
Nishant Thakur, Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2022; 14(14): 3529. CrossRef - Re-Increasing Trends in Thyroid Cancer Incidence after a Short Period of Decrease in Korea: Reigniting the Debate on Ultrasound Screening
Chan Kwon Jung, Ja Seong Bae, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 816. CrossRef - Current status of cytopathology practice in Korea: impact of the coronavirus pandemic on cytopathology practice
Soon Auck Hong, Haeyoen Jung, Sung Sun Kim, Min-Sun Jin, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Younghee Choi, Gyungyub Gong, Yosep Chong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 361. CrossRef
- Commercially Available Artificial Intelligence Solutions for Gynaecologic Cytology Screening and Their Integration Into Clinical Workflow
- Response to Comment on “Prognostic Role of Claudin-1 Immunohistochemistry in Malignant Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis”
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Nae Yu Kim, Won Jin Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(6):412-414. Published online November 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.09.27
- 5,210 View
- 64 Download
- Prognostic Role of Claudin-1 Immunohistochemistry in Malignant Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Nae Yu Kim, Won Jin Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(3):173-179. Published online March 5, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.02.03
- 8,564 View
- 167 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Although the correlation between low claudin-1 expression and worse prognosis has been reported, details on the prognostic implications of claudin-1 expression in various malignant tumors remain unclear. The present study aimed to elucidate the prognostic roles of claudin- 1 immunohistochemistry (IHC) in various malignant tumors through a meta-analysis.
Methods
The study included 2,792 patients from 22 eligible studies for assessment of the correlation between claudin-1 expression and survival rate in various malignant tumors. A subgroup analysis based on the specific tumor and evaluation criteria of claudin-1 IHC was conducted.
Results
Low claudin-1 expression was significantly correlated with worse overall survival (OS) (hazard ratio [HR], 1.851; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.506 to 2.274) and disease-free survival (DFS) (HR, 2.028; 95% CI, 1.313 to 3.134) compared to high claudin-1 expression. Breast, colorectal, esophageal, gallbladder, head and neck, and lung cancers, but not cervical, liver or stomach cancers, were significantly correlated with worse OS. Breast, colorectal, esophageal, and thyroid cancers with low claudin-1 expression were associated with poorer DFS. In the lower cut-off subgroup (< 25.0%) with respect to claudin-1 IHC, low claudin-1 expression was significantly correlated with worse OS and DFS.
Conclusions
Taken together, low claudin-1 IHC expression is significantly correlated with worse survival in various malignant tumors. More detailed criteria for claudin-1 IHC expression in various malignant tumors are needed for application in daily practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expression and Targeted Application of Claudins Family in Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases
Fangqian Du, Yuwei Xie, Shengze Wu, Mengling Ji, Bingzi Dong, Chengzhan Zhu
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2024; Volume 11: 1801. CrossRef - The Significance of Relative Claudin Expression in Odontogenic Tumors
Ekarat Phattarataratip, Kraisorn Sappayatosok
Head and Neck Pathology.2020; 14(2): 480. CrossRef - Claudin-1 upregulation is associated with favorable tumor features and a reduced risk for biochemical recurrence in ERG-positive prostate cancer
Simon Kind, Franziska Büscheck, Doris Höflmayer, Claudia Hube-Magg, Martina Kluth, Maria Christina Tsourlakis, Stefan Steurer, Till S. Clauditz, Andreas M. Luebke, Eike Burandt, Waldemar Wilczak, Andrea Hinsch, David Dum, Sören Weidemann, Christoph Fraune
World Journal of Urology.2020; 38(9): 2185. CrossRef - Characterisation of endogenous Claudin‐1 expression, motility and susceptibility to hepatitis C virus in CRISPR knock‐in cells
Camille M.H. Clément, Maika S. Deffieu, Cristina M. Dorobantu, Thomas F. Baumert, Nilda Vanesa Ayala‐Nunez, Yves Mély, Philippe Ronde, Raphael Gaudin
Biology of the Cell.2020; 112(5): 140. CrossRef - Comment on “Prognostic Role of Claudin-1 Immunohistochemistry in Malignant Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis”
Bolin Wang, Yan Huang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2019; 53(6): 411. CrossRef
- Expression and Targeted Application of Claudins Family in Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases
- Prognostic Role of Metastatic Lymph Node Ratio in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Kyungseek Chang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(5):331-338. Published online August 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.08.07
- 9,197 View
- 131 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The aim of this study is to elucidate the clinicopathological significances, including the prognostic role, of metastatic lymph node ratio (mLNR) and tumor deposit diameter in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) through a retrospective review and meta-analysis.
Methods
We categorized the cases into high (≥ 0.44) and low mLNR (< 0.44) and investigated the correlations with clinicopathological parameters in 64 PTCs with neck level VI lymph node (LN) metastasis. In addition, meta-analysis of seven eligible studies was used to investigate the correlation between mLNR and survival.
Results
Among 64 PTCs with neck level VI LN metastasis, high mLNR was found in 34 PTCs (53.1%). High mLNR was significantly correlated with macrometastasis (tumor deposit diameter ≥ 0.2 cm), extracapsular spread, and number of metastatic LNs. Based on linear regression test, mLNR was significantly increased by the largest LN size but not the largest metastatic LN (mLN) size. High mLNR was not correlated with nuclear factor κB or cyclin D1 immunohistochemical expression, Ki-67 labeling index, or other pathological parameters of primary tumor. Based on meta-analysis, high mLNR significantly correlated with worse disease-free survival at the 5-year and 10-year follow-up (hazard ratio [HR], 4.866; 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.527 to 6.714 and HR, 5.769; 95% CI, 2.951 to 11.275, respectively).
Conclusions
Our data showed that high mLNR significantly correlated with worse survival, macrometastasis, and extracapsular spread of mLNs. Further cumulative studies for more detailed criteria of mLNR are needed before application in daily practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The application of a clinical-multimodal ultrasound radiomics model for predicting cervical lymph node metastasis of thyroid papillary carcinoma
Chang Liu, Shangjie Yang, Tian Xue, Qian Zhang, Yanjing Zhang, Yufang Zhao, Guolin Yin, Xiaohui Yan, Ping Liang, Liping Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Predictive Value of a Nomogram Based on Ultrasound Radiomics, Clinical Factors, and Enhanced Ultrasound Features for Central Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Lei Gao, Xiuli Wen, Guanghui Yue, Hui Wang, Ziqing Lu, Beibei Wu, Zhihong Liu, Yuming Wu, Dongmei Lin, Shijian Yi, Wei Jiang, Yi Hao
Ultrasonic Imaging.2025; 47(2): 93. CrossRef - Lymph Node Metastasis Ratio: Prognostic Significance in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Ana Rita Ferreira, Diogo Ramalho, Daniela Martins, Andreia Amado, Susana Graça, Carlos Soares, Bela Pereira, Maria João Oliveira, Manuel Oliveira, Antónia Póvoa
Indian Journal of Surgery.2025; 87(6): 1047. CrossRef - CD105 (Endoglin) Expression as a Prognostic Marker in Aggressive Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
İlker Çordan, Tuğba Günler
Clinical Endocrinology.2025; 103(4): 596. CrossRef - Application and subgroup analysis of competing risks model based on different lymph node staging systems in differentiated thyroid cancer
Zhe Xu Cao, Jiang Sheng Huang, Ming Ming Wang
Updates in Surgery.2024; 76(5): 1927. CrossRef - Цитологічне прогнозування агресії раку щитоподібної залози як новий перспективний напрямок у клінічній тиреоїдології
H.V. Zelinska
Endokrynologia.2024; 29(4): 363. CrossRef - Thyroglobulin expression, Ki-67 index, and lymph node ratio in the prognostic assessment of papillary thyroid cancer
Helene Lindfors, Marie Karlsen, Ellinor Karlton, Jan Zedenius, Catharina Larsson, Catharina Ihre Lundgren, C. Christofer Juhlin, Ivan Shabo
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidental Node Metastasis as an Independent Factor of Worse Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Renan Aguera Pinheiro, Ana Kober Leite, Beatriz Godoi Cavalheiro, Evandro Sobroza de Mello, Luiz Paulo Kowalski, Leandro Luongo Matos
Cancers.2023; 15(3): 943. CrossRef - A High-Quality Nomogram for Predicting Lung Metastasis in Newly Diagnosed Stage IV Thyroid Cancer: A Population-Based Study
WenYi Wang, JiaJing Liu, XiaoFan Xu, LiQun Huo, XuLin Wang, Jun Gu
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lymph Node Ratio Predicts Recurrence in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Low Lymph Node Yield
Il Ku Kang, Joonseon Park, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, Kwangsoon Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(11): 2947. CrossRef - Superiority of metastatic lymph node ratio over number of node metastases and TNM/AJCC N classification in predicting cancer‐specific survival in medullary thyroid cancer
Andreas Machens, Kerstin Lorenz, Frank Weber, Henning Dralle
Head & Neck.2022; 44(12): 2717. CrossRef - Value of Combining Clinical Factors, Conventional Ultrasound, and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Features in Preoperative Prediction of Central Lymph Node Metastases of Different Sized Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas
Yanfang Wang, Fang Nie, Guojuan Wang, Ting Liu, Tiantian Dong, Yamin Sun
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 3403. CrossRef - Atypical Histiocytoid Cells and Multinucleated Giant Cells in Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of the Thyroid Predict Lymph Node Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Ji Eun Choi, Ja Seong Bae, Dong-Jun Lim, So Lyung Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
Cancers.2019; 11(6): 816. CrossRef - Patients Aged ≥55 Years With Stage T1-2N1M1 Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Should Be Downstaged in the Eighth Edition AJCC/TNM Cancer Staging System
Zeming Liu, Sichao Chen, Yihui Huang, Di Hu, Min Wang, Wei Wei, Chao Zhang, Wen Zeng, Liang Guo
Frontiers in Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Implication of Metastatic Lymph Node Ratio in Colorectal Cancers: Comparison Depending on Tumor Location
Jung-Soo Pyo, Young-Min Shin, Dong-Wook Kang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(11): 1812. CrossRef
- The application of a clinical-multimodal ultrasound radiomics model for predicting cervical lymph node metastasis of thyroid papillary carcinoma
- Detection of Tumor Multifocality Is Important for Prediction of Tumor Recurrence in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Retrospective Study and Meta-Analysis
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Guhyun Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(4):278-286. Published online June 6, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.03.29
- 12,061 View
- 111 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The clinicopathological characteristics and conclusive treatment modality for multifocal papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (mPTMC) have not been fully established.
Methods
A retrospective study, systematic review, and meta-analysis were conducted to elucidate the clinicopathological significance of mPTMC. We investigated the multiplicity of 383 classical papillary thyroid microcarcinomas (PTMCs) and the clinicopathological significance of incidental mPTMCs. Correlation between tumor recurrence and multifocality in PTMCs was evaluated through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Results
Tumor multifocality was identified in 103 of 383 PTMCs (26.9%). On linear regression analysis, primary tumor diameter was significantly correlated with tumor number (R2=0.014, p=.021) and supplemental tumor diameter (R2=0.117, p=.023). Of 103 mPTMCs, 61 (59.2%) were non-incidental, with tumor detected on preoperative ultrasonography, and 42 (40.8%) were diagnosed (incidental mPTMCs) on pathological examination. Lymph node metastasis and higher tumor stage were significantly correlated with tumor multifocality. However, there was no difference in nodal metastasis or tumor stage between incidental and non-incidental mPTMCs. On meta-analysis, tumor multifocality was significantly correlated with tumor recurrence in PTMCs (odds ratio, 2.002; 95% confidence interval, 1.475 to 2.719, p<.001).
Conclusions
Our results show that tumor multifocality in PTMC, regardless of manner of detection, is significantly correlated with aggressive tumor behavior. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Stratification in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Clinical Features Predicting Multifocality, Lymph Node Metastasis, and Recurrence – A Retrospective Cohort Study
Chih-Chieh Hsu, Chun-Yi Tsai, Li-Ching Lin, Shang-Yu Wang, Chun-Nan Yeh, Miaw-Jene Liou, Szu-Tah Chen
Cancer Management and Research.2026; Volume 18: 1. CrossRef - Clinical Impact of Multifocality and Bilaterality on Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Merima Goran, Marko Buta, Srdjan Nikolic, Nada Santrac, Nikola Jeftic, Nevena Savkovic, Jovan Raketic, Zoran Kozomara, Natasa Medic-Milijic, Ana Cvetkovic, Saska Pavlovic, Ivan Markovic
Diagnostics.2026; 16(2): 208. CrossRef - A machine learning model utilizing Delphian lymph node characteristics to predict contralateral central lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a prospective multicenter study
Jia-ling He, Yu-zhao Yan, Yan Zhang, Jin-sui Li, Fei Wang, Yi You, Wei Liu, Ying Hu, Ming-Hao Wang, Qing-wen Pan, Yan Liang, Ming-shijing Ren, Zi-wei Wu, Kai You, Yi Zhang, Jun Jiang, Peng Tang
International Journal of Surgery.2025; 111(1): 360. CrossRef - Retrospective comparison of individual risk factors hemithyroidectomy and thyroidectomy in patients with papillary carcinoma of the thyroid gland in combination with autoimmune thyroiditis
E. V. Ryabchenko
Head and Neck Tumors (HNT).2023; 12(4): 71. CrossRef - Individual risk factors for recurrence after hemithyroidectomy and thyroidectomy in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma in the presence of autoimmune thyroiditis
E.V. Ryabchenko
P.A. Herzen Journal of Oncology.2023; 12(3): 20. CrossRef - The value of total tumor diameter in unilateral multifocal papillary thyroid carcinoma: a propensity score matching analysis
Zhu-juan Wu, Bao-ying Xia, Zi-wei Chen, Hao Gong, Munire Abuduwaili, Zhi-chao Xing, An-ping Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Negative Histopathological Prognostic Factors Affecting Morbidity in T1 Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
Mine Araz, Elgin Özkan, Pınar Gunduz, Cigdem Soydal, N. Özlem Küçük, K. Metin Kır
Cancer Biotherapy and Radiopharmaceuticals.2022; 37(1): 56. CrossRef - Total tumor diameter is a better indicator of multifocal papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis
Ke-cheng Jiang, Bei Lin, Yu Zhang, Ling-qian Zhao, Ding-cun Luo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between lipotoxicity and risk of extrathyroidal extension in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Changlin Li, Haixia Guan, Qiao He, Yishen Zhao, Nan liang, Jiao Zhang, Gianlorenzo Dionigi, Hui Sun
Endocrine.2021; 74(3): 646. CrossRef - Multifocality and Progression of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma During Active Surveillance
Ryuta Nagaoka, Aya Ebina, Kazuhisa Toda, Tomoo Jikuzono, Marie Saitou, Masaomi Sen, Hiroko Kazusaka, Mami Matsui, Keiko Yamada, Hiroki Mitani, Iwao Sugitani
World Journal of Surgery.2021; 45(9): 2769. CrossRef - Correlation of ThyroSeq Results with Surgical Histopathology in Cytologically Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules
Patrick D. Chin, Catherine Y. Zhu, Dipti P. Sajed, Gregory A. Fishbein, Michael W. Yeh, Angela M. Leung, Masha J. Livhits
Endocrine Pathology.2020; 31(4): 377. CrossRef - Application of Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis and Management of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Huang, MD Kun, Liu, MD Ji-Bin
ADVANCED ULTRASOUND IN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY.2020; 4(4): 284. CrossRef - Analysis of Malignant Thyroid Neoplasms with a Striking Rise of Papillary Microcarcinoma in an Endemic Goiter Region
Alka Mary Mathai, K. Preetha, S. Valsala Devi, Sam Vicliph, Raja Pradeep, Aqib Shaick
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2019; 71(S1): 121. CrossRef - The first postoperative-stimulated serum thyroglobulin is a prognostic factor for thyroid microcarcinomas
Isabela de Oliveira Amui, José Vicente Tagliarini, Emanuel C. Castilho, Mariângela de Alencar Marques, Yoshio Kiy, José Eduardo Corrente, Gláucia M.F.S. Mazeto
Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology.2019; 85(1): 37. CrossRef - Surgical management of follicular thyroid carcinoma in children and adolescents: A study of 30 cases
Claudio Spinelli, Leonardo Rallo, Riccardo Morganti, Valentina Mazzotti, Alessandro Inserra, Giovanni Cecchetto, Maura Massimino, Paola Collini, Silvia Strambi
Journal of Pediatric Surgery.2019; 54(3): 521. CrossRef - The role of prophylactic central compartment lymph node dissection in elderly patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: a multicentric study
Claudio Gambardella, Renato Patrone, Francesco Di Capua, Chiara Offi, Claudio Mauriello, Guglielmo Clarizia, Claudia Andretta, Andrea Polistena, Alessandro Sanguinetti, Pietrogiorgio Calò, Giovanni Docimo, Nicola Avenia, Giovanni Conzo
BMC Surgery.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Cervical Lymph Node Metastases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma, in the Central and Lateral Compartments, in Children and Adolescents: Predictive Factors
C. Spinelli, F. Tognetti, S. Strambi, R. Morganti, M. Massimino, P. Collini
World Journal of Surgery.2018; 42(8): 2444. CrossRef - Active Surveillance for Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Challenges and Prospects
Shuai Xue, Peisong Wang, Zachary A. Hurst, Yi Seok Chang, Guang Chen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparison of lobectomy and total thyroidectomy in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a retrospective individual risk factor-matched cohort study
Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Suyeon Park, Mijin Kim, Dong Eun Song, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
European Journal of Endocrinology.2017; 176(4): 371. CrossRef - Total thyroidectomy may be more reasonable as initial surgery in unilateral multifocal papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a single-center experience
Shuai Xue, Peisong Wang, Jia Liu, Guang Chen
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Lack of Efficacy of Radioiodine Remnant Ablation for Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Verification Using Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting
Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Suyeon Park, Mijin Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Minkyu Han, Dong Eun Song, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Jin-Sook Ryu, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2017; 24(9): 2596. CrossRef - Radioactive Iodine Ablation Decrease Recurrences in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma with Lateral Lymph Node Metastasis in Chinese Patients
Shuai Xue, Peisong Wang, Jia Liu, Guang Chen
World Journal of Surgery.2017; 41(12): 3139. CrossRef - The Prognostic Value of Tumor Multifocality in Clinical Outcomes of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Fei Wang, Xiaolong Yu, Xiaopei Shen, Guangwu Zhu, Yueye Huang, Rengyun Liu, David Viola, Rossella Elisei, Efisio Puxeddu, Laura Fugazzola, Carla Colombo, Barbara Jarzab, Agnieszka Czarniecka, Alfred K Lam, Caterina Mian, Federica Vianello, Linwah Yip, Gar
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2017; 102(9): 3241. CrossRef - Evaluation of surgical results of micropapillary thyroid cancers according to tumor size and focality
Bekir Uçan, Muhammed Erkam Sencar, Muhammed Kızılgül, Mustafa Özbek, İlknur Öztürk Ünsal, Erman Çakal
Ortadoğu Tıp Dergisi.2017; 9(3): 123. CrossRef - Contrastive study of two screening criteria for active surveillance in patients with low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a retrospective analysis of 1001 patients
Kai Qian, Kai Guo, Xiaoke Zheng, Tuanqi Sun, Duanshu Li, Yi Wu, Qinghai Ji, Zhuoying Wang
Oncotarget.2017; 8(39): 65836. CrossRef - 10.1016/j.bjorlp.2018.01.005
CrossRef Listing of Deleted DOIs.2000;[Epub] CrossRef
- Risk Stratification in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Clinical Features Predicting Multifocality, Lymph Node Metastasis, and Recurrence – A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Core Needle Biopsy Is a More Conclusive Follow-up Method Than Repeat Fine Needle Aspiration for Thyroid Nodules with Initially Inconclusive Results: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Guhyun Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(3):217-224. Published online April 14, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.02.15
- 12,843 View
- 118 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study investigated the appropriate management of thyroid nodules with prior non-diagnostic or atypia of undetermined significance/follicular lesion of undetermined significance (AUS/FLUS) through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
This study included 4,235 thyroid nodules from 26 eligible studies. We investigated the conclusive rate of follow-up core needle biopsy (CNB) or repeat fine needle aspiration (rFNA) after initial fine needle aspiration (FNA) with non-diagnostic or AUS/FLUS results. A diagnostic test accuracy (DTA) review was performed to determine the diagnostic role of the follow-up CNB and to calculate the area under the curve (AUC) on the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve.
Results
The conclusive rates of follow-up CNB and rFNA after initial FNA were 0.879 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.801 to 0.929) and 0.684 (95% CI, 0.627 to 0.736), respectively. In comparison of the odds ratios of CNB and rFNA, CNB had more frequent conclusive results than rFNA (odds ratio, 5.707; 95% CI, 2.530 to 12.875). Upon subgroup analysis, follow-up CNB showed a higher conclusive rate than rFNA in both initial non-diagnostic and AUS/FLUS subgroups. In DTA review of followup CNB, the pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.94 (95% CI, 0.88 to 0.97) and 0.88 (95% CI, 0.84 to 0.91), respectively. The AUC for the SROC curve was 0.981, nearing 1.
Conclusions
Our results show that CNB has a higher conclusive rate than rFNA when the initial FNA produced inconclusive results. Further prospective studies with more detailed criteria are necessary before follow-up CNB can be applied in daily practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic yield of fine needle aspiration with simultaneous core needle biopsy for thyroid nodules
Mohammad Ali Hasannia, Ramin Pourghorban, Hoda Asefi, Amir Aria, Elham Nazar, Hojat Ebrahiminik, Alireza Mohamadian
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(3): 180. CrossRef - Comparison of Diagnostic Yield Between Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology and Core Needle Biopsy in the Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodule
Yeongrok Lee, Myung Jin Ban, Do Hyeon Kim, Jin-Young Kim, Hyung Kwon Byeon, Jae Hong Park
Diagnostics.2025; 15(20): 2566. CrossRef - Repeatedly non-diagnostic thyroid nodules: the experience of two thyroid clinics
Filippo EGALINI, Mattia ROSSI, Chiara MELE, Yanina LIZET CASTILLO, Francesca MALETTA, Barbara PULIGHEDDU, Ezio GHIGO, Ruth ROSSETTO GIACCHERINO, Loredana PAGANO, Mauro PAPOTTI
Minerva Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology vs. Core Needle Biopsy for Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective, Experimental Study Using Surgical Specimen
Hyuk Kwon, Jandee Lee, Soon Won Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Jin Young Kwak, Jung Hyun Yoon
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2022; 83(3): 645. CrossRef - Comparison of Core Needle Biopsy and Repeat Fine-Needle Aspiration in Avoiding Diagnostic Surgery for Thyroid Nodules Initially Diagnosed as Atypia/Follicular Lesion of Undetermined Significance
Leehi Joo, Dong Gyu Na, Ji-hoon Kim, Hyobin Seo
Korean Journal of Radiology.2022; 23(2): 280. CrossRef - Diagnostic performance of core needle biopsy as a first‐line diagnostic tool for thyroid nodules according to ultrasound patterns: Comparison with fine needle aspiration using propensity score matching analysis
Hye Shin Ahn, Inyoung Youn, Dong Gyu Na, Soo Jin Kim, Mi Yeon Lee
Clinical Endocrinology.2021; 94(3): 494. CrossRef - Usage and Diagnostic Yield of Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology and Core Needle Biopsy in Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Literature Published by Korean Authors
Soon-Hyun Ahn
Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology.2021; 14(1): 116. CrossRef - 2021 Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System and Imaging-Based Management of Thyroid Nodules: Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology Consensus Statement and Recommendations
Eun Ju Ha, Sae Rom Chung, Dong Gyu Na, Hye Shin Ahn, Jin Chung, Ji Ye Lee, Jeong Seon Park, Roh-Eul Yoo, Jung Hwan Baek, Sun Mi Baek, Seong Whi Cho, Yoon Jung Choi, Soo Yeon Hahn, So Lyung Jung, Ji-hoon Kim, Seul Kee Kim, Soo Jin Kim, Chang Yoon Lee, Ho K
Korean Journal of Radiology.2021; 22(12): 2094. CrossRef - Malignancy rate of Bethesda category III thyroid nodules according to ultrasound risk stratification system and cytological subtype
Won Sang Yoo, Hwa Young Ahn, Hye Shin Ahn, Yun Jae Chung, Hee Sung Kim, Bo Youn Cho, Mirinae Seo, Jae Hoon Moon, Young Joo Park
Medicine.2020; 99(2): e18780. CrossRef - 2019 Practice guidelines for thyroid core needle biopsy: a report of the Clinical Practice Guidelines Development Committee of the Korean Thyroid Association
Chan Kwon Jung, Jung Hwan Baek, Dong Gyu Na, Young Lyun Oh, Ka Hee Yi, Ho-Cheol Kang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(1): 64. CrossRef - Laser Ablation Versus Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Non-Functioning Thyroid Nodules: Six-Month Results of a Randomized, Parallel, Open-Label, Trial (LARA Trial)
Roberto Cesareo, Claudio Maurizio Pacella, Valerio Pasqualini, Giuseppe Campagna, Mario Iozzino, Andrea Gallo, Angelo Lauria Pantano, Roberto Cianni, Claudio Pedone, Paolo Pozzilli, Chiara Taffon, Anna Crescenzi, Silvia Manfrini, Andrea Palermo
Thyroid.2020; 30(6): 847. CrossRef - Diagnostic Efficacy and Safety of Core Needle Biopsy as a First-Line Diagnostic Method for Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Cohort Study
Min Ji Hong, Dong Gyu Na, Hunkyung Lee
Thyroid.2020; 30(8): 1141. CrossRef - Is thyroid core needle biopsy a valid compliment to fine-needle aspiration?
Liron Pantanowitz, Lester D.R. Thompson, Xin Jing, Esther Diana Rossi
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2020; 9(5): 383. CrossRef - A Monocentric Retrospective Study about the Correlation between Histology and Cytology of Thyroid Indeterminate Nodules Classified as TIR 3A and TIR 3B, according to 2014 Italian Consensus for Classification and Reporting of Thyroid Cytology
Francesco Quaglino, Giulia Arnulfo, Sergio Sandrucci, Claudio Rossi, Valentina Marchese, Roberto Saracco, Stefano Guzzetti, Stefano Taraglio, Enrico Mazza
Advances in Medicine.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Nuclear features of papillary thyroid carcinoma: Comparison of Core needle biopsy and thyroidectomy specimens
Jae Yeon Seok, Jungsuk An, Hyun Yee Cho, Younghye Kim, Seung Yeon Ha
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2018; 32: 35. CrossRef - Statement and Recommendations on Interventional Ultrasound as a Thyroid Diagnostic and Treatment Procedure
Christoph F. Dietrich, Thomas Müller, Jörg Bojunga, Yi Dong, Giovanni Mauri, Maija Radzina, Manjiri Dighe, Xin-Wu Cui, Frank Grünwald, Andreas Schuler, Andre Ignee, Huedayi Korkusuz
Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology.2018; 44(1): 14. CrossRef - Role of core needle biopsy as a first-line diagnostic tool for thyroid nodules: a retrospective cohort study
Min Ji Hong, Dong Gyu Na, Soo Jin Kim, Dae Sik Kim
Ultrasonography.2018; 37(3): 244. CrossRef - Core Needle Biopsy of the Thyroid: 2016 Consensus Statement and Recommendations from Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology
Dong Gyu Na, Jung Hwan Baek, So Lyung Jung, Ji-hoon Kim, Jin Yong Sung, Kyu Sun Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jung Hee Shin, Yoon Jung Choi, Eun Ju Ha, Hyun Kyung Lim, Soo Jin Kim, Soo Yeon Hahn, Kwang Hwi Lee, Young Jun Choi, Inyoung Youn, Young Joong Kim, Hye Sh
Korean Journal of Radiology.2017; 18(1): 217. CrossRef - Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration versus core needle biopsy: comparison of post-biopsy hematoma rates and risk factors
In Hye Chae, Eun-Kyung Kim, Hee Jung Moon, Jung Hyun Yoon, Vivian Y. Park, Jin Young Kwak
Endocrine.2017; 57(1): 108. CrossRef - The Role of Core Needle Biopsy for Thyroid Nodules with Initially Indeterminate Results on Previous Fine-Needle Aspiration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
C.H. Suh, J.H. Baek, C. Park, Y.J. Choi, J.H. Lee
American Journal of Neuroradiology.2017; 38(7): 1421. CrossRef
- Diagnostic yield of fine needle aspiration with simultaneous core needle biopsy for thyroid nodules
- MUC2 Expression Is Correlated with Tumor Differentiation and Inhibits Tumor Invasion in Gastric Carcinomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Guhyun Kang, Dong-Hoon Kim, Kyungeun Kim, In-Gu Do, Dong Hyun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(3):249-256. Published online May 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.03.27
- 10,112 View
- 72 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
While MUC2 is expressed in intestinal metaplasia and malignant lesions, the clinico-pathological significance of MUC2 expression is not fully elucidated in gastric carcinoma (GC). Methods: The present study investigated the correlation between MUC2 expression and clinico-pathological parameters in 167 human GCs. In addition, to confirm the clinicopathological significance of MUC2 expression, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis in 1,832 GCs. Results: MUC2 expression was found in 58 of 167 GCs (34.7%). MUC2-expressing GC showed lower primary tumor (T), regional lymph node (N), and tumor node metastasis (TNM) stages compared with GCs without MUC2 expression (p=.001, p=.001, and p=.011, respectively). However, MUC2 expression was not correlated with Lauren’s classification and tumor differentiation. In meta-analysis, MUC2 expression was significantly correlated with differentiation and lower tumor stage (odds ratio [OR], 1.303; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.020 to 1.664; p = .034 and OR, 1.352; 95% CI, 1.055 to 1.734; p = .017, respectively) but not with Lauren’s classification, pN stage, or pTNM stage. Conclusions: MUC2 expression was correlated with a lower tumor depth and lower lymph node metastasis in our study; the meta-analysis showed a correlation of MUC2 expression with tumor differentiation and lower tumor depth. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of mucin family members expression in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis
Shunda Wang, Yongrun Mu, Jianwei Zhang, Chengfeng Wang
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic gastrointestinal markers in primary lung cancer and pulmonary metastases
Karina Malmros, Andreas Lindholm, Halla Vidarsdottir, Karin Jirström, Björn Nodin, Johan Botling, Johanna S. M. Mattsson, Patrick Micke, Maria Planck, Mats Jönsson, Johan Staaf, Hans Brunnström
Virchows Archiv.2024; 485(2): 347. CrossRef - Gastric epithelial histology and precancerous conditions
Hang Yang, Wen-Juan Yang, Bing Hu
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2022; 14(2): 396. CrossRef - COX-2 strengthens the effects of acid and bile salts on human esophageal cells and Barrett esophageal cells
Shen Jiangang, Kang Nayoung, Wang Hongfang, Li Junda, Chen Li, Bai Xuefeng, Li Mingsong
BMC Molecular and Cell Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative genomic analysis of primary tumors and paired brain metastases in lung cancer patients by whole exome sequencing: a pilot study
Pascale Tomasini, Fabrice Barlesi, Sophie Gilles, Isabelle Nanni-Metellus, Riccardo Soffietti, Emilie Denicolai, Eric Pellegrino, Emilie Bialecki, L’Houcine Ouafik, Philippe Metellus
Oncotarget.2020; 11(50): 4648. CrossRef - A High Ki67/BCL2 Index Could Predict Lower Disease-Free and Overall Survival in Intestinal-Type Gastric Cancer
Kyueng-Whan Min, Dong-Hoon Kim, Byoung Kwan Son, Dong Hyun Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Jinwon Seo, Sang Bong Ahn, Yun Ju Jo, Young Sook Park, Junghoon Ha
European Surgical Research.2017; 58(3-4): 158. CrossRef
- Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of mucin family members expression in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis
- Traumatic Bowel Perforation and Inguinal Hernia Masking a Mesenteric Calcifying Fibrous Tumor
- Dong Hyun Kim, Kyueng-Whan Min, Dong-Hoon Kim, Seoung Wan Chae, Jin Hee Sohn, Jung-Soo Pyo, Sung-Im Do, Kyungeun Kim, Hyun Joo Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(3):267-269. Published online May 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.03.20
- 9,437 View
- 51 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A rare cause of small intestinal obstruction in children: a case report of calcifying fibrous tumor
Zesheng Yang, Xiaoying Xie, Shicheng Wang, Weijun Xu, Guanghua Pei, Jun Wan
BMC Pediatrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Calcifying Fibrous Tumor
Angeliki Chorti, Theodossis S. Papavramidis, Antonios Michalopoulos
Medicine.2016; 95(20): e3690. CrossRef
- A rare cause of small intestinal obstruction in children: a case report of calcifying fibrous tumor
- Extranodal Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma with Rapid Growth in Parapharynx: A Case Report
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Guhyun Kang, Sung-Im Do, Seoung Wan Chae, Kyungeun Kim, Sang Hyuk Lee, Yoon-La Choi, Joon Hyuk Choi, Jin Hee Sohn, Dong-Hoon Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(3):306-310. Published online June 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.3.306
- 8,508 View
- 54 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma (FDCS) is a rare malignancy arising from the antigen-presenting cells in the lymph node and extranodal tissue. We describe a 31-year-old male patient who presented with a swelling of the left parapharynx. The radiologic findings showed a 4.7×4.5×1.9 cm-sized, ill-defined mass in the left parapharyngeal space. A fine-needle aspiration cytology was performed and it showed scattered, irregular, cohesive clusters of tumor cells with a spindle-to-ovoid shape with irregular contours in a background of lymphocytes. Based on these findings, a diagnosis of spindle cell neoplasm was made. The surgically resected tumor was composed of elongated, ovoid or polygonal cells showing positive immunohistochemistry for CD21, CD23, and CD35. Postoperatively, the residual tumor was observed to undergo a rapidly growth. There is an overlap in the cytologic and histologic findings between FDCS of the parapharynx and other tumors. Pathologists should therefore be aware of its characteristics not only to provide an accurate diagnosis but also to recommend the appropriate clinical management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extranodal Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma of the Head and Neck Region: A Clinicopathological Study of 7 Cases
Nasir Ud Din, Zubair Ahmad, Shabina Rahim, Karen Fritchie, Muhammad Usman Tariq, Arsalan Ahmed
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2023; 31(6): 1067. CrossRef - Cytomorphology of follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: a report of 7 cases with an emphasis on the diagnostic challenges
Cody Weimholt, Jalal B. Jalaly, Cedric Bailey
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2023; 12(3): 229. CrossRef - Follicular dendritic cells
Seham A. Abd El‐Aleem, Entesar Ali Saber, Neven M. Aziz, Hani El‐Sherif, Asmaa M. Abdelraof, Laiche Djouhri
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2022; 237(4): 2019. CrossRef - Clinicopathological characteristics of extranodal follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A report of two cases
Xing Zhao, Dayong Sun, Gang Zhang
Oncology Letters.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytological diagnosis of follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A case report and review of literature
A. Dutta, P. Arun, P. Roy, I. Arun
Cytopathology.2018; 29(5): 461. CrossRef - Follicular dendritic cells and related sarcoma
Fabio Facchetti, Luisa Lorenzi
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2016; 33(5): 262. CrossRef - Extranodal follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A clinicopathological report of four cases and a literature review
RUI-FEN WANG, WEI HAN, LEI QI, LI-HUI SHAN, ZHENG-CAI WANG, LI-FENG WANG
Oncology Letters.2015; 9(1): 391. CrossRef - Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma of Parapharyngeal Space: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Turki Al-Hussain, Muhammad Saleem, Suresh Babu Velagapudi, Mohammad Anas Dababo
Head and Neck Pathology.2015; 9(1): 135. CrossRef - Clinical and pathological features of head and neck follicular dendritic cell sarcoma
Ji Li, Min-Li Zhou, Shui-Hong Zhou
Hematology.2015; 20(10): 571. CrossRef
- Extranodal Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma of the Head and Neck Region: A Clinicopathological Study of 7 Cases

 E-submission
E-submission





 First
First Prev
Prev



