Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Low Ki-67 labeling index is a clinically useful predictive factor for recurrence-free survival in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Takashi Masui, Katsunari Yane, Ichiro Ota, Kennichi Kakudo, Tomoko Wakasa, Satoru Koike, Hirotaka Kinugawa, Ryuji Yasumatsu, Tadashi Kitahara
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):115-124. Published online February 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.08
- 5,571 View
- 246 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
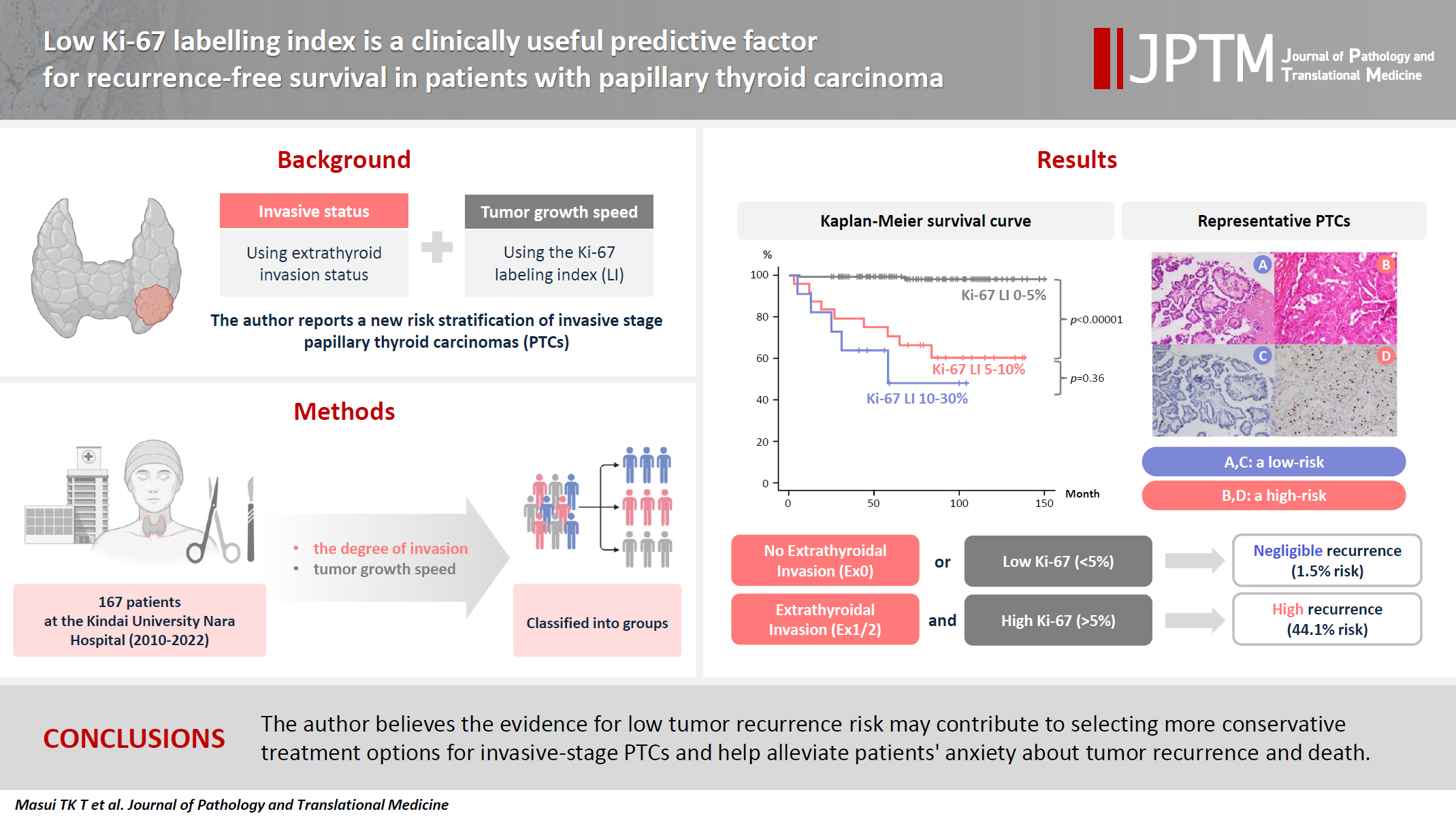
We report a new risk stratification of invasive stage papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs) by combining invasive status, using extrathyroid invasion (Ex) status, and tumor growth speed using the Ki-67 labeling index (LI). Methods: We examined tumor recurrence in 167 patients with PTC who were surgically treated at the Kindai University Nara Hospital between 2010 and 2022. The patients were classified according to the degree of invasion [negative (Ex0) or positive (Ex1, Ex2, and Ex3)] and tumor growth speed expressed with Ki-67 LI, as low (<5%) or high (>5%). This study confirmed previous findings that the disease-free survival (DFS) rate in PTCs significantly differed between patients with a high and low Ki-67 index. Results: When combining Ex status (negative or positive) and Ki-67 proliferation status (low or high), the DFS rate of invasion in the negative, low Ki-67 LI group was only 1.1%, while that of invasion in the positive, high Ki-67 LI was 44.1%. This study reports for the first time that recurrence risks can be stratified accurately when combining carcinoma’s essential two features of extrathyroid invasion status and tumor growth speed. Conclusions: We believe the evidence for low tumor recurrence risk may contribute to use of more conservative treatment options for invasive-stage PTCs and help alleviate patient anxiety about tumor recurrence and death. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress on the Correlation between Three Biomarkers, Ki-67, CAIX and VEGF and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
锦容 马
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2025; 15(09): 326. CrossRef - Immunophenotypic Panel for Comprehensive Characterization of Aggressive Thyroid Carcinomas
Mihail Ceausu, Mihai Alin Publik, Dana Terzea, Carmen Adina Cristea, Dumitru Ioachim, Dana Manda, Sorina Schipor
Cells.2025; 14(19): 1554. CrossRef - High Ki-67 labeling index correlates with aggressive clinicopathological features in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective study
Defi Nurlia Erdian, Maria Francisca Ham, Dina Khoirunnisa, Agnes Stephanie Harahap
Thyroid Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research Progress on the Correlation between Three Biomarkers, Ki-67, CAIX and VEGF and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Reducing Effect of Angiotensin-1 Converting Enzyme Inhibitor (Captopril) in Fibrosis of Radiation Induced Lung Injury.
- Kun Young Kwon, Hae Ra Jung, Sun Young Kwon, Jin Hee Kim, Ok Bae Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(3):145-156.
- 2,182 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The captopril reduces radiation induced lung injury and fibrosis. We designed a study to evaluate the antifibrogenic effect of Captopril in radiation induced lung injury.
METHODS
Fifty Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into radiation group (I) (n=30) and radiation plus captopril group (II) (n=15). The rats were sacrificed at 12 hours and 11 weeks after radiation. We examined light microscopic, immunohistochemical and electron microscopic features in each groups.
RESULTS
In Group I, the lungs showed acute lung injury at 12 h. The lungs showed patchy fibrosis with collagen deposits at 11 weeks. The severity of the alveolar injury and fibrosis was correlated with radiation doses. The Group II showed less severe lung fibrosis than Group I. The mean numbers of mast cells and myofibroblasts of Group II were lower than Group I (p< 0.05). The TNF-alpha and TGF-beta were higher expressed according to radiation doses in Group I, and less prominent in Group II. Ultrastructurally, the alveolar cell injury and fibrosis were less severe in Group II. The TUNEL stains showed higher expressions according to radiation doses in Group I, and expressed in Group II.
CONCLUSIONS
The captopril decreases the number of mast cells and myofibroblasts, reduces collagen deposition and apoptosis of alveolar cells in rat lungs after radiation, and so reduces the degree of pulmonary injury and fibrosis.
- Computerization of Microscope Slide Labelling.
- Dong Sug Kim, Dae Hong Suh
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(7):628-634.
- 1,702 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The automation in surgical pathology, particularly in the reporting and encoding system using personal computers has been greatly improved in recent years, but the computerization of microscope slide labelling has not been improved. The authors have developed database program for slide labelling using FoxPro 2.5 and FoxBASE SCOUNIX 2.1.2: For I year during trial an effect has been put forward to simplify and organize the labelling work in routine surgical pathology. The program is now become easily applicable to the labelling work without disturbing the normal flow in a pathology laboratory. It is possible to get information concerning how many paraffin blocks and H&E slides have been made, as well as what kind of special stains have been requested for each case. The authors think that the computerization of labelling work in routine surgical pathology is a fairly easy task, and this should simplify the labelling work at a lower cost, diminish the workload of a typist or technician, and indirect information concerning the workload in a pathology laboratory can be calculated.
- Apoptosis of Alveolar Cells in Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia: Application of Electron Microscopic Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase-Mediated dUTP-Biotin Nick End Labeling Method.
- Kyu Hun Kang, Sang Pyo Kim, Kun Young Kwon
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(6):496-505.
- 1,995 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Pneumocystis carinii (P. carinii) attaches to alveolar cells and causes injury to the epithelial cells by direct toxic effects or inhibition of epithelial growth and replication. Although respiratory cell damage or death is a common feature in P. carinii pneumonia, there has been little reports about expression of apoptosis of the lung tissue in the literatures.
METHODS
We examined expression of fibronectin and vitronectin in the interaction between P. carinii and alveolar cells, and in situ terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP biotin nick end-labeling (TUNEL) expression of apoptosis in the respiratory cells by immunohistochemistry and pre-embedding immunoelectron microscopy.
RESULTS
Light microscopic (LM) and electron microscopic (EM) immunohistochemical stains for the fibronectin and vitronectin showed strong expressions on the pellicles and tubular extensions of P. carinii and weak expression along the surfaces of type I alveolar cells. LM and EM TUNEL stains showed positive expression in the nuclei of alveolar cells, apoptotic bodies in the cytoplasm of alveolar macrophages and cellular debris in alveolar spaces.
CONCLUSIONS
P. carinii induces injury and apoptosis of alveolar cells after attachment of the organisms to host cells, and alveolar macrophages enhance the clearance of apoptotic bodies of alveolar cells as well as phagocytosis and degradation of P. carinii.
- The Pattern of Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in Human Embryonic and Fetal Brain.
- Suk Jin Choi, Jung Ran Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(1):38-44.
- 2,178 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Cell proliferation and apoptosis account for the major morphogenetic mechanisms during development of the central nervous system. We investigated these processes in developing human brains.
METHODS
We examined human embryonic and fetal brains. Cell proliferation was analysed by classical histology and MIB-1 immunohistochemistry; cell death was investigated by the TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labelling method.
RESULTS
Most proliferating cells were observed in the ventricular zone (VZ) in the 3rd-10th week of gestational age (GA), and in both the VZ and the subventricular zone (SV) in the 19-24th week of GA. The proliferation index of the VZ was highest in the 8th week of GA and then decreased as the GA advanced. Apoptotic cells were observed in the VZ as early as the 5th week of GA. They were also observed in the intermediate zone in the 19-24th week of GA, although they were significantly lower in amount compared to that in the VZ and SV.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggest that apoptosis occurring early in the embryonic period is related to a cellular mechanism which selects and determines the cells that are committed to migration and differentiation during the development of the human brain.
- Expression of Surfactant-D Protein and TNF-alpha in the Interaction of Pneumocystis Carinii and Alveolar Macrophages in Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia.
- Kun Young Kwon, Kwan Kyu Park, Chang Kwon Park, Young June Jeon, Eun Sook Chang
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(9):684-694.
- 1,887 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Alveolar macrophages participate in the host defense against P. carinii, but the mechanisms in degradation and clearance of the organism from lung has not been well established. We observed the transmission and scanning electron microscopic features and evaluated the expression of TNF-alpha and Surfactant-D in the interaction of P. carinii with alveolar macrophages. Expression of TNF-alpha and Surfactant-D in the experimentally induced P. carinii pneumonia in rat was examined by immunohistochemistry and immunoelectron microscopy. Electron microscopically, the alveolar macrophages phagocytized trophozoites and cysts of P. carinii micro-organisms. Immunohistochemically TNF-alpha was strongly expressed in the cytoplasms of alveolar macrophages. Postembedding immunogold labeling for Surfactant-D protein was expressed on the pellicles of trophozoites and cysts, P. carinii micro-organisms in the cytoplasms of macrophages, free floating surfactant materials and multilamellar bodies of type II epithelial cells. We conclude that alveolar macrophages interacted with P. carinii micro-organisms respond with increased expression of TNF-alpha. TNF-alpha may bind to P. carinii and exert a direct toxic effect upon the micro-organisms. Surfactant-D protein may augment binding of P. carinii to the alveolar macrophages and enhance the clearance of the micro-organisms.
- Proliferative Activity of Thyroid Lesions Evaluated by Mitotic Count and Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA).
- Hwa Sook Jeong, Geon Kook Lee, Hyung Geun Song, Ro hyun Sung
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(12):1297-1307.
- 2,090 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To evaluate the clinical and histopathological significance of the proliferative activity in neoplastic and non-neoplastic thyroid lesions, we analyzed the mitotic count and the proliferating cell nuclear antigen labeling index (PCNA-LI) by immunohistochemistry as the proliferation- related markers. In this study included were surgically removed normal thyroid tissue (27 cases), adenomatous goiter (15 cases), Hashimoto's thyroiditis (5 cases), follicular adenoma (13 cases), follicular carcinoma (7 cases), papillary carcinoma (44 cases), poorly differentiated carcinoma (2 cases) and undifferentiated carcinoma (3 cases). The median PCNA-LI was 0 in normal thyroid tissue, 0.5 in adenomatous goiter, 6.2 in Hashimoto's thyroiditis, 1.2 in follicular adenoma, 4.8 in follicular carcinoma, 8.5 in papillary carcinoma, 60.8 in poorly differentiated carcinoma, and 55.2 in undifferentiated carcinoma (p=0.0001). Although PCNA-LI was exceptionally high in Hashimoto's thyroiditis, it was suggested that PCNA-LI could be used as a marker differentiating benign lesions from malignant neoplasm. Also, it could differentiate follicular adenoma from follicular carcinoma. Except clinical stage (p=0.0397), PCNA-LI was not related with sex, size, histologic subtype, and lymph node metastasis in papillary carcinoma. The presence of mitosis differentiated the neoplastic thyroid lesions from the non-neoplastic lesions (p<0.05), however, it could not divide benign and malignant neoplasm. These results suggest that an evaluation of the proliferative activity can help to differentiate the thyroid lesions. In addition, there was no significant correlation between the value of PCNA-LI and the presence of mitosis. It can be recommended to evaluate both the mitotic count and the PCNA-LI for determining the proliferative activity of the thyroid lesions.
- Correlation of Clinical Stage and Presumptive Prognostic Factors in Renal Cell Carcinoma.
- Jin Ye Yoo, Hye Jae Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(11):1061-1066.
- 1,991 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Renal cell carcinoma is the most common primary cancer of the kidney. The tumor stage is a reliable prognostic marker in renal cell carcinoma which is significantly associated with patient survival. But assessment of other prognostic factors has produced varying and often conflicting results. We reevaluated the significance of varied prognostic parameters in 33 cases of renal cell carcinoma; clinical stage, cell type, histologic pattern, DNA ploidy, Ki-67 labeling index, and bcl-2 oncoprotein expression. We could not statistically prove that DNA ploidy and bcl-2 expression were related to any examined parameters. Cell type was not related to clinical stage nor nuclear grade but there was a significant correlation (p=0.002) between cell type and histologic pattern. Nuclear grade (p=0.007) and Ki-67 labeling index (p=0.036) were significantly related to clinical stage, suggesting their value as complementary prognostic markers for renal cell carcinoma.
- Correlation of Histologic Findings of Ovarian Epithelial Tumors with Expression of Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen and Flow Cytometric DNA Analysis.
- Sang Yeop Yi, Soon Hee Jung, Kwang Gil Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(1):68-76.
- 1,880 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The prognosis of malignant ovarian tumor is poorer than that of borderline malignant ovarian tumor, Therefore an accurate diagnosis and estimation of the biologic behavior of the tumor are necessary for proper management of the patient. The histologic investigation of the tumor may provide information on the estimation of the malignant potential of tumor cells, but it may be a questionable method because of the subjective determination of tumor grade. Quantification of proliferative activity of tumor cells may play a role as an objective method to provide an estimation of the malignant potential of tumor cells. An evaluation of histologic findings was done on 84 cases of ovarian mucinous and serous tumors that were surgically resected and diagnosed during the period from January 1981 through July 1992. The proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCN A) labelling index estimated from the immunohistochemical stain for PCN A and the Sphase fraction and porliferative index obtained from flow cytometric DN A analysis were assessed each other with histologic findings. The results are as follows: The presence of aneuploidy in malignant tumors was statistically significant as compared with benign tumors. The borderline malignant tumors showed no significant difference between the number of diploidy and aneuploidy. The PCNA labelling index, S-phase fraction and proliferative index tended to increase as the histologic grade of tumors went up. They were higher in malignant tumors than in others. The PCN A labelling index, S-phase fraction and proliferative index were higher in tumors with aneuploidy than in those with diploidy. In contrast to borderline malignant tumors, the PCNA labelling index in malignant tumors revealed a significant relation with the mitotic index. The S-phase fraction and proliferative index showed, in malignant tumors, a close correlation with the architectural grade and nucleolar grade, but not in borderline malignant tumors. Considering these results, the presence of aneuploidy, PCNA label.
- The prognostic significance of tumor angiogenesis, proliferating cell nuclear antigen(PCNA), and the Ki-67 index in carcinoma of the uterine cervix.
- Chan Pil Park, Seung Yon Lee, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(1):1-14.
- 2,053 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Angiogenesis, the induction of new capillaries and venules, is associated with tumor growth. This study was designed to determine whether cervical carcinomas are angiogenic, and to investigate whether tumor angiogenesis can serve as a prognostic factor in cervical carcinoma. Surgical specimens of 47 cervical carcinomas were immunohistochemically stained specifically for endothelial cells with factor VIII-related antigen to identify all vessels. Microvessels were counted from photographs of 200x microscopic fields. In addition, thirty-seven cases were studied by immunohistochemical means using the monoclonal antibodies for PCNA and for Ki-67 to determine tumor cell proliferation rates in cervical carcinomas. The microvessel count(MVC), the PCNA labelling index, and the Ki-67 index were calculated and compared with known prognostic factors and disease free survival rates in cervical carcinomas. A wide range in the MVC count(range 12-100 mean=38.2+/-19.2), the PCNA labeling index(8-69% mean=33.6+/-15.2%), and in the extent of Ki-67 staining(0-43% mean=10.3+/-10.5%) was observed, indicating considerable variation of tumor angiogenic activity and tumor growth rates. This study showed statistically significant correlations in disease free survival rates with both lymph node status and the microvessel count. However, there was no significant difference in disease free survival rates between tumor stage, age, the PCNA labelling index, and the Ki-67 index.

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



