Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Study
- Drug-induced phospholipidosis of the kidney suspected to be caused by atomoxetine
- Sung-Eun Choi, Kee Hyuck Kim, Minsun Jung, Jeong Hae Kie
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):124-128. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.10
- 555 View
- 60 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Drug-induced phospholipidosis (DIP) is characterized by intracellular accumulation of phospholipids with lamellar body formation secondary to drug-altered lipid metabolism, which can trigger inflammation and histopathological changes. Fabry disease and DIP both exhibit zebra bodies on electron microscopy, complicating differential diagnosis. A 17-year-old male with microscopic hematuria and proteinuria had received atomoxetine (40 mg) for 11 months to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Light microscopy showed one glomerulus with perihilar sclerosis and periglomerular fibrosis. Kidney biopsy revealed zebra bodies in podocytes, initially suggesting Fabry disease. However, α-galactosidase A enzyme activity was normal on tandem mass spectrometry. Next-generation sequencing of GLA identified only three benign variants. This represents the first reported case of atomoxetine-induced DIP. When zebra bodies are observed, clinicians should consider DIP caused by cationic amphiphilic drugs alongside Fabry disease. Atomoxetine meets the structural criteria for inducing DIP, and awareness of this potential complication is essential.
Original Article
- Significance of KM55 immunohistochemical staining in the diagnosis and prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Hoe In Jeong, Beom Jin Lim, Minsun Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):69-82. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.17
- 622 View
- 47 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) plays a crucial role in IgA nephropathy (IgAN). The monoclonal antibody KM55 has emerged as a simplified method for detecting Gd-IgA1; however, the clinicopathological significance of immunohistochemistry for Gd-IgA1 remains underexplored. This study evaluated the prognostic and clinicopathological significance of KM55 immunohistochemistry in IgAN. Methods: A total of 114 native kidney biopsies showing at least mild mesangial IgA positivity on immunofluorescence were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were categorized as having IgAN or non-IgAN diseases. The KM55 immunohistochemical staining was graded as 0, 1+, 2+, 3, or 4+. Data on Oxford classification, laboratory parameters, and renal outcomes were collected. Results: The IgAN group showed significantly higher KM55 scores than the non-IgAN group (median: 3 vs. 1; p < .001). IgAN cases were further stratified into KM55-high (≥3+, n = 38) and -low groups (≤2+, n = 37). The KM55-high group had significantly higher diastolic blood pressure, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, urine protein/creatinine ratio, and Oxford mesangial hypercellularity scores, along with lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and serum albumin. Cox analysis revealed significantly poorer outcomes in the KM55-high group for chronic kidney disease stage 4 (p = .015), end-stage renal disease (p = .024), and 75% eGFR decline (p = .016). Conclusions: Mesangial Gd-IgA1 deposition graded by KM55 immunohistochemistry may be a useful adjunct for IgAN diagnosis and a potential prognostic biomarker.
Case Study
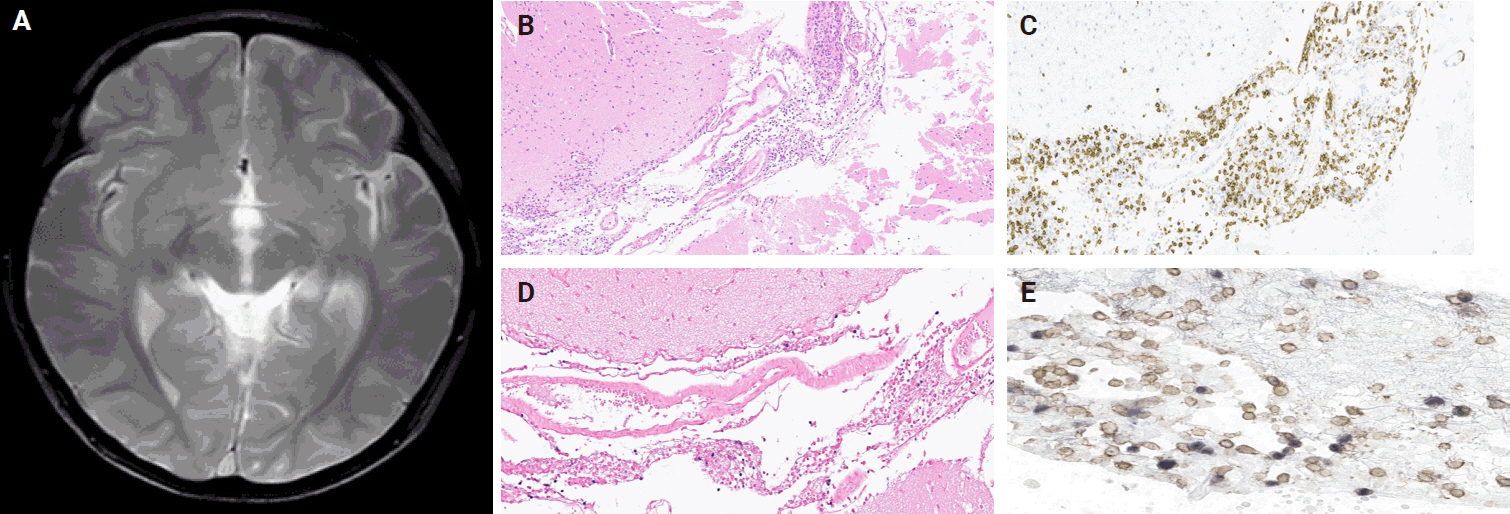
- Histopathological characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–associated encephalitis and colitis in chronic active EBV infection
- Betty A Kasimo, James J Yahaya, Sun Och Yoon, Se Hoon Kim, Minsun Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(3):188-194. Published online April 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.02.21
- 4,002 View
- 165 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Chronic active Epstein-Barr virus (CAEBV) can induce complications in various organs, including the brain and gastrointestinal tract. A 3-year-old boy was referred to the hospital with a history of fever and seizures for 15 days. A diagnosis of encephalitis based on computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging findings and clinical correlation was made. Laboratory tests showed positive serology for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and negative for Rotavirus antigen and IgG and IgM antibodies for cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, and varicella zoster virus, respectively. Abdominal CT showed diffuse wall thickening with fluid distension of small bowel loops, lower abdomen wall thickening, and a small amount of ascites. The biopsy demonstrated positive Epstein-Barr encoding region in situ hybridization in cells within the crypts and lamina propria. The patient was managed with steroids and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). This case showed histopathological characteristics of concurrent EBV-associated encephalitis and colitis in CAEBV infection. The three-step strategy of immunosuppressive therapy, chemotherapy, and allogeneic HSCT should be always be considered for prevention of disease progression.
Original Articles
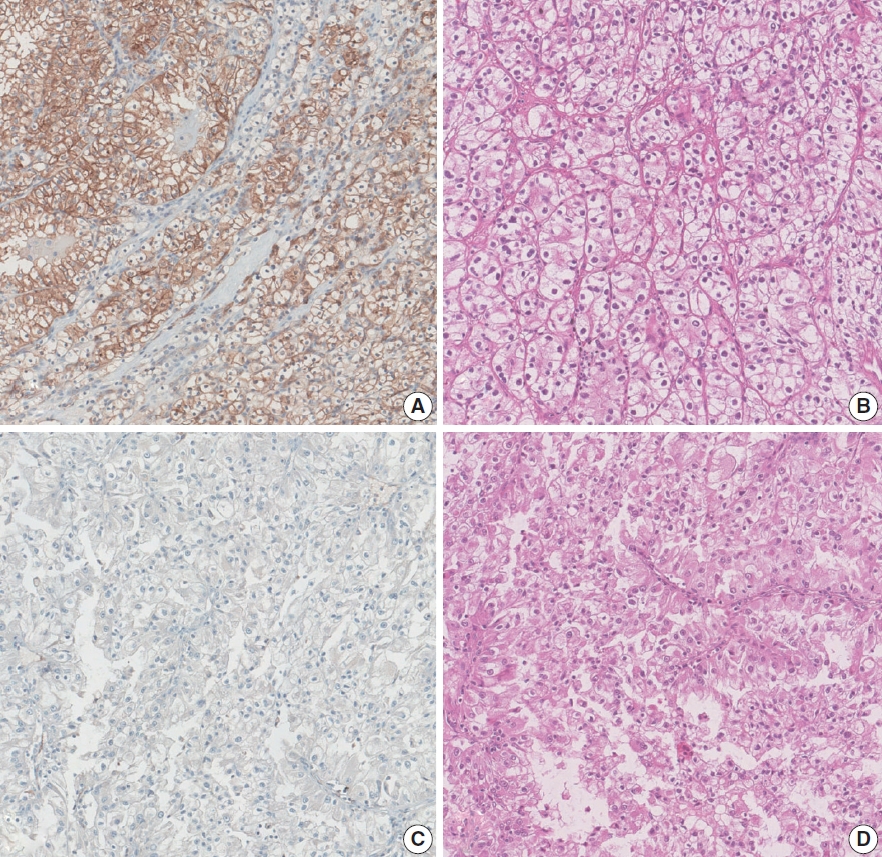
- Loss of aquaporin-1 expression is associated with worse clinical outcomes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study
- Seokhyeon Lee, Bohyun Kim, Minsun Jung, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):232-237. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.17
- 4,684 View
- 171 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Aquaporin (AQP) expression has been investigated in various malignant neoplasms, and the overexpression of AQP is related to poor prognosis in some malignancies. However, the expression of AQP protein in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) has not been extensively investigated by immunohistochemistry with large sample size.
Methods
We evaluated the AQP expression in 827 ccRCC with immunohistochemical staining in tissue microarray blocks and classified the cases into two categories, high and low expression.
Results
High expression of aquaporin-1 (AQP1) was found in 320 cases (38.7%), but aquaporin-3 was not expressed in ccRCC. High AQP1 expression was significantly related to younger age, low TNM stage, low World Health Organization/International Society of Urologic Pathology nuclear grade, and absence of distant metastasis. Furthermore, high AQP1 expression was also significantly associated with longer overall survival (OS; p<.001) and progression-specific survival (PFS; p<.001) and was an independent predictor of OS and PFS in ccRCC.
Conclusions
Our study revealed the prognostic significance of AQP1 protein expression in ccRCC. These findings could be applied to predict the prognosis of ccRCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Loss of Aquaporin-1 in Tumor Cells Fosters Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Progression
César I. Gaspari, Carine Beaupere, Seth Richard, Estanislao Peixoto, Bouchra Lekbaby, Mirko Minini, Branko Dubravcic, Javier Vaquero, Marie Vallette, Ander Arbelaiz, Marion Janona, Corentin Louis, Pauline Le Gall, Cédric Coulouarn, Julieta Marrone, Juan E
The American Journal of Pathology.2026; 196(2): 428. CrossRef - Construction and validation of renal cell carcinoma tumor cell differentiation-related prognostic classification (RCC-TCDC): an integrated bioinformatic analysis and clinical study
Yifan Liu, Keqin Dong, Yuntao Yao, Bingnan Lu, Lei Wang, Guo Ji, Haoyu Zhang, Zihui Zhao, Xinyue Yang, Runzhi Huang, Wang Zhou, Xiuwu Pan, Xingang Cui
Annals of Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Assessment of Aquaporins in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: An In Silico Analysis
Vignesh Krishnasamy, Lalhmingliana, Nachimuthu Senthil Kumar
Current Biotechnology.2025; 14(2): 130. CrossRef - Targeting PLOD2 induces epithelioid differentiation and improves therapeutic response in sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma
Xiangyu Chen, Dongkui Xu, Yu Ji, Xichen Dong, Xiaomei Dong, Zihan Li, Jingyu Tan, Qianqian Sun, Huixian Xin, Ziwei Liu, Qing Deng, Tao Wen, Yanjun Jia, Xuhui Zhu, Jian Liu
Journal of Advanced Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Exosomal MiR-874 as a Potential Biomarker for Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
Amal F. Gharib, Saad S. Al-Shehri, Abdulraheem Almalki, Ayman Alhazmi, Mamdouh Allahyani, Ahmed Alghamdi, Amani A. Alrehaili, Maha M. Bakhuraysah, Althobaiti Naif Saad M., Weal H. Elsawy
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Loss of Aquaporin-1 in Tumor Cells Fosters Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Progression
- The proteomic landscape shows oncologic relevance in cystitis glandularis
- Jun Yong Kim, Dohyun Han, Hyeyoon Kim, Minsun Jung, Han Suk Ryu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(1):67-74. Published online December 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.10.24
- 5,334 View
- 177 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The relationship between cystitis glandularis (CG) and bladder malignancy remains unclear.
Methods
We identified the oncologic significance of CG at the molecular level using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis of 10 CG, 12 urothelial carcinoma (UC), and nine normal urothelium (NU) specimens. Differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) were identified based on an analysis of variance false discovery rate < 0.05, and their functional enrichment was analyzed using a network model, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis, and Gene Ontology annotation.
Results
We identified 9,890 proteins across all samples and 1,139 DEPs among the three entities. A substantial number of DEPs overlapped in CG/NU, distinct from UC. Interestingly, we found that a subset of DEP clusters (n = 53, 5%) was differentially expressed in NU but similarly between CG and UC. This “UC-like signature” was enriched for reactive oxygen species (ROS) and energy metabolism, growth and DNA repair, transport, motility, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and cell survival. Using the top 10 shortlisted DEPs, including SOD2, PRKCD, CYCS, and HCLS1, we identified functional elements related to ROS metabolism, development, and transport using network analysis. The abundance of these four molecules in UC/CG than in NU was consistent with the oncologic functions in CG.
Conclusions
Using a proteomic approach, we identified a predominantly non-neoplastic landscape of CG, which was closer to NU than to UC. We also confirmed a small subset of common DEPs in UC and CG, suggesting that altered ROS metabolism might imply potential cancerous risks in CG. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantitative proteomics and immunohistochemistry uncover NT5DC2 as a diagnostic biomarker for papillary urothelial carcinoma
Jun Yong Kim, Jae Seok Lee, Dohyun Han, Ilias P. Nikas, Hyeyoon Kim, Minsun Jung, Han Suk Ryu
Heliyon.2024; 10(15): e35475. CrossRef - KRT18 as a Novel Biomarker of Urothelial Papilloma while Evaluating Low-Grade Papillary Urothelial Neoplasms: Bi-Center Analysis
Minsun Jung, Bohyun Kim, Jae Seok Lee, Jun Yong Kim, Dohyun Han, Kwangsoo Kim, Sunah Yang, Eun Na Kim, Hyeyooon Kim, Ilias P. Nikas, Sohyeon Yang, Kyung Chul Moon, Hyebin Lee, Han Suk Ryu
Pathobiology.2024; : 1. CrossRef
- Quantitative proteomics and immunohistochemistry uncover NT5DC2 as a diagnostic biomarker for papillary urothelial carcinoma

 E-submission
E-submission



 First
First Prev
Prev



