Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast
- Yunjeong Jang, Hera Jung, Han-Na Kim, Youjeong Seo, Emad Alsharif, Seok Jin Nam, Seok Won Kim, Jeong Eon Lee, Yeon Hee Park, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):95-102. Published online November 13, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.10.24
- 10,725 View
- 293 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Pure mucinous carcinoma (PMC) is a rare type of breast cancer, estimated to represent 2% of invasive breast cancer. PMC is typically positive for estrogen receptors (ER) and progesterone receptors (PR) and negative for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). The clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive PMC have not been investigated.
Methods
Pathology archives were searched for PMC diagnosed from January 1999 to April 2018. Clinicopathologic data and microscopic findings were reviewed and compared between HER2-positive PMC and HER2-negative PMC. We also analyzed the differences in disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival according to clinicopathologic parameters including HER2 status in overall PMC cases.
Results
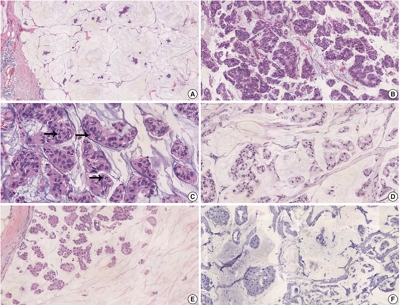
There were 21 HER2-positive cases (4.8%) in 438 PMCs. The average tumor size of HER2-positive PMC was 32.21 mm (± 26.55). Lymph node metastasis was present in seven cases. Compared to HER2-negative PMC, HER2-positive PMC presented with a more advanced T category (p < .001), more frequent lymph node metastasis (p = .009), and a higher nuclear and histologic grade (p < .001). Microscopically, signet ring cells were frequently observed in HER2-positive PMC (p < .001), whereas a micropapillary pattern was more frequent in HER2-negative PMC (p = .012). HER2-positive PMC was more frequently negative for ER (33.3% vs. 1.2%) and PR (28.6% vs. 7.2%) than HER2-negative PMC and showed a high Ki-67 labeling index. During follow-up, distant metastasis and recurrence developed in three HER2-positive PMC patients. Multivariate analysis revealed that only HER2-positivity and lymph node status were significantly associated with DFS.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that HER2-positive PMC is a more aggressive subgroup of PMC. HER2 positivity should be considered for adequate management of PMC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mucin‐producing breast lesions: a practical approach to diagnosis
Sunayana Misra, Mihir Gudi, Kimberly H Allison, Edi Brogi, Cecily Quinn, Hannah Y Wen, Puay Hoon Tan
Histopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological characteristics of mucinous breast cancer: a retrospective analysis of a 6-years study from national cancer center in Vietnam
Thi Huyen Phung, Thanh Tung Pham, Huu Thang Nguyen, Dinh Thach Nguyen, Thanh Long Nguyen, Thi Hoai Hoang
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 209(3): 667. CrossRef - Poor response of HER2-positive mucinous carcinomas of breast to neoadjuvant HER2-targeted therapy: A study of four cases
Min Han, Daniel Schmolze, Javier A. Arias-Stella, Christina H. Wei, Joanne Mortimer, Fang Fan
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 74: 152396. CrossRef - Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analysis of Mesonephric Marker Expression in Low-grade Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma
Yurimi Lee, Sangjoon Choi, Hyun-Soo Kim
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2024; 43(3): 221. CrossRef - Clinicopathological features and prognosis of mucinous breast carcinoma with a micropapillary structure
Beibei Yang, Menglu Shen, Bo Sun, Jing Zhao, Meng Wang
Thoracic Cancer.2024; 15(36): 2530. CrossRef - Pure Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
Cherie M Kuzmiak, Benjamin C Calhoun
Journal of Breast Imaging.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of circ-FOXO3 and miR-23a in radiosensitivity of breast cancer
Elahe Abdollahi, Hossein Mozdarani, Behrooz Z. Alizadeh
Breast Cancer.2023; 30(5): 714. CrossRef - On Ultrasonographic Features of Mucinous Carcinoma with Micropapillary Pattern
Wei-Sen Yang, Yang Li, Ya Gao
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2023; Volume 15: 473. CrossRef - Spectrum of Mucin-containing Lesions of the Breast: Multimodality Imaging Review with Pathologic Correlation
Janice N. Thai, Melinda F. Lerwill, Shinn-Huey S. Chou
RadioGraphics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Ovary: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Hyun Hee Koh, Eunhyang Park, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(2): 326. CrossRef - Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma of the Uterus: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Yurimi Lee, Kiyong Na, Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(5): 1102. CrossRef - Metastasis of the Mucionous adenocarcinoma of breast to the mandibular gingiva: Rare case report
Ivana Mijatov, Aleksandra Fejsa Levakov, Aleksandar Spasić, Jelena Nikolić, Saša Mijatov
Medicine.2022; 101(38): e30732. CrossRef - Endometrioid Carcinomas of the Ovaries and Endometrium Involving Endocervical Polyps: Comprehensive Clinicopathological Analyses
Jihee Sohn, Yurimi Lee, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(10): 2339. CrossRef - Serous Carcinoma of the Endometrium with Mesonephric-Like Differentiation Initially Misdiagnosed as Uterine Mesonephric-Like Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report with Emphasis on the Immunostaining and the Identification of Splice Site TP53 Mutation
Sangjoon Choi, Yoon Yang Jung, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(4): 717. CrossRef - HER2 positive mucinous carcinoma of breast with micropapillary features: Report of a case and review of literature
Dinesh Chandra Doval, Rupal Tripathi, Sunil Pasricha, Pankaj Goyal, Chaturbhuj Agrawal, Anurag Mehta
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2021; 25: 200531. CrossRef - Carcinoma mucosecretor de mama HER2-positivo, un caso clínico
A.M. González Aranda, E. Martínez Gómez, A. Santana Costa, F. Arnanz Velasco, M.H. González de Diego, A. Zapico Goñi
Clínica e Investigación en Ginecología y Obstetricia.2021; 48(4): 100685. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic features of unexpectedly HER2 positive breast carcinomas: An institutional experience
Carissa LaBoy, Kalliopi P. Siziopikou, Lauren Rosen, Luis Z. Blanco, Jennifer L. Pincus
Pathology - Research and Practice.2021; 222: 153441. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Differentiation of Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics Distinct from Those of Uterine Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma
Sujin Park, Go Eun Bae, Jiyoung Kim, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(8): 1450. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Corpus: Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analyses Using Markers for Mesonephric, Endometrioid and Serous Tumors
Hyunjin Kim, Kiyong Na, Go Eun Bae, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(11): 2042. CrossRef
- Mucin‐producing breast lesions: a practical approach to diagnosis
- Size of Non-lepidic Invasive Pattern Predicts Recurrence in Pulmonary Mucinous Adenocarcinoma: Morphologic Analysis of 188 Resected Cases with Reappraisal of Invasion Criteria
- Soohyun Hwang, Joungho Han, Misun Choi, Myung-Ju Ahn, Yong Soo Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):56-68. Published online October 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.09.17
- 12,315 View
- 237 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
We reviewed a series of 188 resected pulmonary mucinous adenocarcinomas (MAs) to clarify the prognostic significance of lepidic and non-lepidic patterns.
Methods
Non-lepidic patterns were divided into bland, non-distorted acini with uncertain invasiveness (pattern 1), unequivocal invasion into stroma (pattern 2), or invasion into alveolar spaces (pattern 3).
Results
The mean proportion of invasive patterns (patterns 2 and 3) was lowest in small (≤ 3 cm) tumors, and gradually increased in intermediate (> 3 cm and ≤ 7 cm) and large (> 7 cm) tumors (8.4%, 34.3%, and 50.1%, respectively). Adjusted T (aT) stage, as determined by the size of invasive patterns, was positively correlated with adverse histologic and clinical features including older age, male sex, and ever smokers. aTis tumors, which were exclusively composed of lepidic pattern (n = 9), or a mixture of lepidic and pattern 1 (n = 40) without any invasive patterns, showed 100% disease- free survival (DFS). The aT1mi tumors, with minimal (≤ 5 mm) invasive patterns (n = 63), showed a 95.2% 5-year DFS, with recurrences (n = 2) limited to tumors greater than 3 cm in total size (n = 23). Both T and aT stage were significantly associated with DFS; however, survival within the separate T-stage subgroups was stratified according to the aT stage, most notably in the intermediatestage subgroups. In multivariate analysis, the size of invasive patterns (p = .020), pleural invasion (p < .001), and vascular invasion (p = .048) were independent predictors of recurrence, whereas total size failed to achieve statistical significance (p = .121).
Conclusions
This study provides a rationale for histologic risk stratification in pulmonary MA based on the extent of invasive growth patterns with refined criteria for invasion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Distinct Recurrence Pattern and Survival Outcomes of Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Lung: The Potential Role of Local Therapy in Intrapulmonary Spread
Dong Woog Yoon, Soohyun Hwang, Tae Hee Hong, Yoon-La Choi, Hong Kwan Kim, Yong Soo Choi, Jhingook Kim, Young Mog Shim, Jong Ho Cho
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2024; 31(1): 201. CrossRef - Pulmonary invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma
Wei‐Chin Chang, Yu Zhi Zhang, Andrew G Nicholson
Histopathology.2024; 84(1): 18. CrossRef - Micropapillary Pattern in Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Lung: Comparison With Invasive Non-Mucinous Adenocarcinoma
Hui He, Lue Li, Yuan-yuan Wen, Li-yong Qian, Zhi-qiang Yang
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 32(5): 926. CrossRef - Radiological and clinical features of screening-detected pulmonary invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma
Dae Hyeon Kim, So Young Bae, Kwon Joong Na, Samina Park, In Kyu Park, Chang Hyun Kang, Young Tae Kim
Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery.2022; 34(2): 229. CrossRef - Micropapillary Pattern in Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Lung: Comparison with Invasive Non-Mucinous Adenocarcinoma
Hui He, Yuanyuan Wen, Liyong Qian, Zhiqiang Yang
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimal method for measuring invasive size that predicts survival in invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung
Tomonari Oki, Keiju Aokage, Shogo Nomura, Kenta Tane, Tomohiro Miyoshi, Norihiko Shiiya, Kazuhito Funai, Masahiro Tsuboi, Genichiro Ishii
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2020; 146(5): 1291. CrossRef - Prognostic Impact of Histopathologic Features in Pulmonary Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinomas
Wei-Chin Chang, Yu Zhi Zhang, Eric Lim, Andrew G Nicholson
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2020; 154(1): 88. CrossRef
- Distinct Recurrence Pattern and Survival Outcomes of Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Lung: The Potential Role of Local Therapy in Intrapulmonary Spread
Case Report
- Mucinous Adenocarcinoma in a Horseshoe Kidney.
- Man Hoon Han, Sang Chul Nam, Bup Wan Kim, Ghil Suk Yoon
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(1):60-62.
- 1,939 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report here on a case of mucinous adenocarcinoma that probably originated in the renal pelvis of a horseshoe kidney. A 61-year-old woman presented with a palpable mass in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen, and this mass had been present for several months. Computed tomography (CT) revealed a left renal pelvic tumor in the horseshoe kidney. Grossly, a 10x9x8 cm unilocular cystic mass filled with chocolate colored mucinous fluid was seen. A connection between the cystic mass and the renal pelvis was demonstrated on retrograde pyelography. Microscopically, the cyst contained anaplastic columnar mucosecretory epithelial cells. Some atypical cell clusters were freely floating in the mucinous lakes. The histopathological findings were consistent with mucinous adenocarcinoma. In addition, glandular metaplasia was noted in the cystic wall. Immunohistochemical assessment of the pelvic adenocarcinoma revealed the positive expressions of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and cytokeratin 20 (CK20) and a weak positive expression of cytokeratin 7 (CK7).
Original Article
- Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of Anal Ducts.
- Young Ha Oh, Wan Seop Kim, Eun Kyung Hong, Moon Hyang Park, Jung Dal Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(9):843-850.
- 2,422 View
- 44 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Anal duct carcinoma is a rare tumor, and accounts for less than 5 percent of all anal cancers, which typically present a long-standing perianal fistulas. Some authors suggest that the fistulous tracts are congenital duplications of the lower end of the hind gut lined by rectal mucosa which is prone to malignant change to mucinous adenocarcinoma. It is usually a well differentiated mucinous (colloid) adenocarcinoma. The prognosis after wide excision of the rectum is relatively good. Since 1985, we have had three cases of anal duct carcinoma with well differentiated mucinous adenocarcinoma involving the posterior wall of the anus. Two patients had a long history of perianal fistula with mucinous discharge. There was no spread to the regional lymph node except one patient who had regional lymph node metastasis, and post-operative chemotherapy and radiation therapy were then given. All patients have no evidence of any recurrent problem at 16 months to 3 years following the surgical treatment. Because of their rarity and the failure of recognition at an early stage, we are presenting three cases to emphasize the characteristic features of this insidious, slow-growing carcinoma.
Case Report
- Heterotopic Enchondral Ossification in Metastatic Colonic Adenocarcinoma: A case report .
- So Yeon Park, Yong Il Kim, Woo Ho Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(7):531-533.
- 1,999 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Calcification and ossification of colon cancer is frequently encountered, especially in the mucinous carcinoma. However, cartilage formation or enchondral ossification has rarely been described in human colon cancer. This report describes a case of a 59-year-old man with retroperitoneal metastasis of mucinous adenocarcinoma of colon, which showed a widespread heterotopic ossification through membranous or enchondral ossification. The ossification appeared in apposition to tumor cell nests and in the organized mucin pool. In our knowledge, this is the first case showing enchondral ossification in gastrointestinal carcinoma in Korea.
Original Article
- Ovarian Mucinous Adenocarcinoma Associated with Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Cervix.
- Kye Hyun Kwon, Jeong Ja Kwak, So Young Jin, Dong Wha Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(2):244-247.
- 2,885 View
- 45 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - When coexistence of carcinoma with similar histologic type is present in female genital tract, it is difficult to differentiate independent primary tumor from metastasis. Most of them are endometrial and ovarian tumors, but coexistence of uterine cervical and ovarian tumor with similar histologic type is rare. We experienced an independent primary tumor of ovarian mucinous cystadenocarcinoma associated with mucinous adenocarcinoma of uterine cervix. The patient was a 50-year-old woman. She had a lower abdominal mass which was detected as a huge cyst on ultrasonography. Although the ovarian lesions were bilateral, features that preferred to consider independent primary tumor are listed as; absence of lymphatic or vascular invasion, absence of ovarian surface implant, superficial invasion of cervical tumor, absence of tumor in abdominal cavity, and disease free follow-up after removal of the tumor.

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



