Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Artificial intelligence algorithm for neoplastic cell percentage estimation and its application to copy number variation in urinary tract cancer
- Jinahn Jeong, Deokhoon Kim, Yeon-Mi Ryu, Ja-Min Park, Sun Young Yoon, Bokyung Ahn, Gi Hwan Kim, Se Un Jeong, Hyun-Jung Sung, Yong Il Lee, Sang-Yeob Kim, Yong Mee Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):229-240. Published online August 9, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.13
- 4,405 View
- 276 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Bladder cancer is characterized by frequent mutations, which provide potential therapeutic targets for most patients. The effectiveness of emerging personalized therapies depends on an accurate molecular diagnosis, for which the accurate estimation of the neoplastic cell percentage (NCP) is a crucial initial step. However, the established method for determining the NCP, manual counting by a pathologist, is time-consuming and not easily executable.
Methods
To address this, artificial intelligence (AI) models were developed to estimate the NCP using nine convolutional neural networks and the scanned images of 39 cases of urinary tract cancer. The performance of the AI models was compared to that of six pathologists for 119 cases in the validation cohort. The ground truth value was obtained through multiplexed immunofluorescence. The AI model was then applied to 41 cases in the application cohort that underwent next-generation sequencing testing, and its impact on the copy number variation (CNV) was analyzed.
Results
Each AI model demonstrated high reliability, with intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) ranging from 0.82 to 0.88. These values were comparable or better to those of pathologists, whose ICCs ranged from 0.78 to 0.91 in urothelial carcinoma cases, both with and without divergent differentiation/ subtypes. After applying AI-driven NCP, 190 CNV (24.2%) were reclassified with 66 (8.4%) and 78 (9.9%) moved to amplification and loss, respectively, from neutral/minor CNV. The neutral/minor CNV proportion decreased by 6%.
Conclusions
These results suggest that AI models could assist human pathologists in repetitive and cumbersome NCP calculations.
- Diverse Immunoprofile of Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate with an Emphasis on the Prognostic Factors
- Se Un Jeong, Anuja Kashikar Kekatpure, Ja-Min Park, Minkyu Han, Hee Sang Hwang, Hui Jeong Jeong, Heounjeong Go, Yong Mee Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(5):471-481. Published online August 9, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.06.02
- 10,735 View
- 208 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
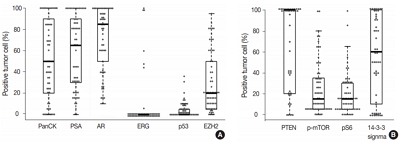
Ductal adenocarcinoma (DAC) of the prostate is an uncommon histologic subtype whose prognostic factors and immunoprofile have not been fully defined. Methods: To define its prognostic factors and immunoprofile, the clinicopathological features, including biochemical recurrence (BCR), of 61 cases of DAC were analyzed. Immunohistochemistry was performed on tissue microarray constructs to assess the expression of prostate cancer-related and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling-related proteins. Results: During the median follow-up period of 19.3 months, BCR occurred in 26 cases (42.6%). DAC demonstrated a wide expression range of prostate cancer-related proteins, including nine cases (14.8%) that were totally negative for pan-cytokeratin (PanCK) immunostaining. The mTOR signaling-related proteins also showed diverse expression. On univariate analysis, BCR was associated with high preoperative serum levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA), large tumor volume, predominant ductal component, high Gleason score (GS), comedo-necrosis, high tumor stage (pT), lymphovascular invasion, and positive surgical margin. High expressions of phospho-mTOR (p-mTOR) as well as low expressions of PSA, phospho-S6 ribosomal protein (pS6) and PanCK were associated with BCR. On multivariable analysis, GS, pT, and immunohistochemical expressions of PanCK and p-mTOR remained independent prognostic factors for BCR. Conclusions: These results suggest GS, pT, and immunohistochemical expressions of PanCK and p-mTOR as independent prognostic factors for BCR in DAC. Since DAC showed diverse expression of prostate cancer–related proteins, this should be recognized in interpreting the immunoprofile of DAC. The diverse expression of mTOR-related proteins implicates their potential utility as predictive markers for mTOR targeted therapy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermediate risk prostate tumors contain lethal subtypes
William L. Harryman, James P. Hinton, Rafael Sainz, Jaime M. C. Gard, John M. Ryniawec, Gregory C. Rogers, Noel A. Warfel, Beatrice S. Knudsen, Raymond B. Nagle, Juan J. Chipollini, Benjamin R. Lee, Belinda L. Sun, Anne E. Cress
Frontiers in Urology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - High GLUT1 membrane expression and low PSMA membrane expression in Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Intraductal Carcinoma of the prostate
Xingming Wang, Li Zhou, Lin Qi, Ye Zhang, Hongling Yin, Yu Gan, Xiaomei Gao, Yi Cai
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases.2024; 27(4): 720. CrossRef - Association of Lymphovascular Invasion with Biochemical Recurrence and Adverse Pathological Characteristics of Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jakub Karwacki, Marcel Stodolak, Andrzej Dłubak, Łukasz Nowak, Adam Gurwin, Kamil Kowalczyk, Paweł Kiełb, Nazar Holdun, Wojciech Szlasa, Wojciech Krajewski, Agnieszka Hałoń, Anna Karwacka, Tomasz Szydełko, Bartosz Małkiewicz
European Urology Open Science.2024; 69: 112. CrossRef - Impact of Epithelial Histological Types, Subtypes, and Growth Patterns on Oncological Outcomes for Patients with Nonmetastatic Prostate Cancer Treated with Curative Intent: A Systematic Review
Giancarlo Marra, Geert J.L.H. van Leenders, Fabio Zattoni, Claudia Kesch, Pawel Rajwa, Philip Cornford, Theodorus van der Kwast, Roderick C.N. van den Bergh, Erik Briers, Thomas Van den Broeck, Gert De Meerleer, Maria De Santis, Daniel Eberli, Andrea Faro
European Urology.2023; 84(1): 65. CrossRef - Impact of comedonecrosis on prostate cancer outcome: a systematic review
Kaveri T S Aiyer, Lisa J Kroon, Geert J L H van Leenders
Histopathology.2023; 83(3): 339. CrossRef - Survival after radical prostatectomy vs. radiation therapy in ductal carcinoma of the prostate
Francesco Chierigo, Marco Borghesi, Christoph Würnschimmel, Rocco Simone Flammia, Benedikt Horlemann, Gabriele Sorce, Benedikt Höh, Zhe Tian, Fred Saad, Markus Graefen, Michele Gallucci, Alberto Briganti, Francesco Montorsi, Felix K. H. Chun, Shahrokh F.
International Urology and Nephrology.2022; 54(1): 89. CrossRef - Defining Diagnostic Criteria for Prostatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma at Multiparametric MRI
Weranja K. B. Ranasinghe, Patricia Troncoso, Devaki Shilpa Surasi, Juan José Ibarra Rovira, Priya Bhosale, Janio Szklaruk, Andrea Kokorovic, Xuemei Wang, Mohamed Elsheshtawi, Miao Zhang, Ana Aparicio, Brian F. Chapin, Tharakeswara K. Bathala
Radiology.2022; 303(1): 110. CrossRef - Oncological outcomes of patients with ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate receiving radical prostatectomy or radiotherapy
Mengzhu Liu, Kun Jin, Shi Qiu, Pengyong Xu, Mingming Zhang, Wufeng Cai, Xiaonan Zheng, Lu Yang, Qiang Wei
Asian Journal of Urology.2021; 8(2): 227. CrossRef - Ductal Prostate Cancers Demonstrate Poor Outcomes with Conventional Therapies
Weranja Ranasinghe, Daniel D. Shapiro, Hyunsoo Hwang, Xuemei Wang, Chad A. Reichard, Mohamed Elsheshtawi, Mary F. Achim, Tharakeswara Bathala, Chad Tang, Ana Aparicio, Shi-Ming Tu, Nora Navone, Timothy C. Thompson, Louis Pisters, Patricia Troncoso, John W
European Urology.2021; 79(2): 298. CrossRef - Optimizing the diagnosis and management of ductal prostate cancer
Weranja Ranasinghe, Daniel D. Shapiro, Miao Zhang, Tharakeswara Bathala, Nora Navone, Timothy C. Thompson, Bradley Broom, Ana Aparicio, Shi-Ming Tu, Chad Tang, John W. Davis, Louis Pisters, Brian F. Chapin
Nature Reviews Urology.2021; 18(6): 337. CrossRef - A first case of ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate having characteristics of neuroendocrine phenotype with PTEN, RB1 and TP53 alterations
Hiroaki Kobayashi, Takeo Kosaka, Kohei Nakamura, Kazunori Shojo, Hiroshi Hongo, Shuji Mikami, Hiroshi Nishihara, Mototsugu Oya
BMC Medical Genomics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowing what’s growing: Why ductal and intraductal prostate cancer matter
Mitchell G. Lawrence, Laura H. Porter, David Clouston, Declan G. Murphy, Mark Frydenberg, Renea A. Taylor, Gail P. Risbridger
Science Translational Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrative Genomic Analysis of Coincident Cancer Foci Implicates CTNNB1 and PTEN Alterations in Ductal Prostate Cancer
Marc Gillard, Justin Lack, Andrea Pontier, Divya Gandla, David Hatcher, Adam G. Sowalsky, Jose Rodriguez-Nieves, Donald Vander Griend, Gladell Paner, David VanderWeele
European Urology Focus.2019; 5(3): 433. CrossRef - Genomic Characterization of Prostatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Identifies a High Prevalence of DNA Repair Gene Mutations
Michael T. Schweizer, Emmanuel S. Antonarakis, Tarek A. Bismar, Liana B. Guedes, Heather H. Cheng, Maria S. Tretiakova, Funda Vakar-Lopez, Nola Klemfuss, Eric Q. Konnick, Elahe A. Mostaghel, Andrew C. Hsieh, Peter S. Nelson, Evan Y. Yu, R. Bruce Montgomer
JCO Precision Oncology.2019; (3): 1. CrossRef
- Intermediate risk prostate tumors contain lethal subtypes
- Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: Subclassification into Basal, Ductal, and Mixed Subtypes Based on Comparison of Clinico-pathologic Features and Expression of p53, Cyclin D1, Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor, p16, and Human Papillomavirus
- Kyung-Ja Cho, Se Un Jeong, Sung Bae Kim, Sang-wook Lee, Seung-Ho Choi, Soon Yuhl Nam, Sang Yoon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):374-380. Published online June 8, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.03.03
- 21,358 View
- 484 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma (BSCC) is a rare variant of squamous cell carcinoma with distinct pathologic characteristics. The histogenesis of BSCC is not fully understood, and the cancer has been suggested to originate from a totipotent primitive cell in the basal cell layer of the surface epithelium or in the proximal duct of secretory glands.
Methods
Twenty-six cases of head and neck BSCC from Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, reported during a 14-year-period were subclassified into basal, ductal, and mixed subtypes according to the expression of basal (cytokeratin [CK] 5/6, p63) or ductal markers (CK7, CK8/18). The cases were also subject to immunohistochemical study for CK19, p53, cyclin D1, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and p16 and to in situ hybridization for human papillomavirus (HPV), and the results were clinico-pathologically compared.
Results
Mixed subtype (12 cases) was the most common, and these cases showed hypopharyngeal predilection, older age, and higher expression of CK19, p53, and EGFR than other subtypes. The basal subtype (nine cases) showed frequent comedo-necrosis and high expression of cyclin D1. The ductal subtype (five cases) showed the lowest expression of p53, cyclin D1, and EGFR. A small number of p16- and/or HPV-positive cases were not restricted to one subtype. BSCC was the cause of death in 19 patients, and the average follow-up period for all patients was 79.5 months. Overall survival among the three subtypes was not significantly different.
Conclusions
The results of this study suggest a heterogeneous pathogenesis of head and neck BSCC. Each subtype showed variable histology and immunoprofiles, although the clinical implication of heterogeneity was not determined in this study. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Histopathological variants of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: A multicenter study in Latin America
Heitor Albergoni Silveira, Karina Helen Martins, Ana Lia Anbinder, Thais Aguiar Santos, Elton Fernandes Barros, Pollianna Muniz Alves, Cassiano Francisco Weege Nonaka, Ana Terezinha Marques Mesquita, Matheus Henrique Lopes Dominguete, Rafael Rodrigues Dia
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2026; 80: 152565. CrossRef - HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer: epidemiology, molecular biology and clinical management
Matt Lechner, Jacklyn Liu, Liam Masterson, Tim R. Fenton
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology.2022; 19(5): 306. CrossRef - Neoadjuvant treatment combined with planned endoscopic surgery in locally advanced sphenoid sinus basaloid squamous cell carcinoma
Yinghong Zhang, Suqing Tian, Yali Du, Qiang Zuo, Li Zhu, Furong Ma
Medicine: Case Reports and Study Protocols.2022; 3(6): e0044. CrossRef - Cetuximab and paclitaxel combination therapy for recurrent basaloid squamous cell carcinoma in the ethmoid sinus
Satoshi Koyama, Kazunori Fujiwara, Tsuyoshi Morisaki, Taihei Fujii, Yosuke Nakamura, Takahiro Fukuhara, Hiromi Takeuchi
Auris Nasus Larynx.2021; 48(6): 1189. CrossRef - Constitutive Hedgehog/GLI2 signaling drives extracutaneous basaloid squamous cell carcinoma development and bone remodeling
Marina Grachtchouk, Jianhong Liu, Mark E Hutchin, Paul W Harms, Dafydd Thomas, Lebing Wei, Aiqin Wang, Donelle Cummings, Lori Lowe, Jonathan Garlick, James Sciubba, Arul M Chinnaiyan, Monique E Verhaegen, Andrzej A Dlugosz
Carcinogenesis.2021; 42(8): 1100. CrossRef - Conjunctival ‘mucoepidermoid carcinoma’ revisited: a revision of terminology, based on morphologic, immunohistochemical and molecular findings of 14 cases, and the 2018 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Eye
Hardeep S. Mudhar, Tatyana Milman, Paul J.L. Zhang, Carol L. Shields, Ralph C. Eagle, Sara E. Lally, Jerry A. Shields, Sachin M. Salvi, Paul A. Rundle, Jennifer Tan, Ian G. Rennie
Modern Pathology.2020; 33(7): 1242. CrossRef - Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma with adenoid cystic‐like features of the head and neck region: A report of two cases
Kimihide Kusafuka, Haruna Yagi, Satoshi Baba, Hiroshi Inagaki, Chinatsu Tsuchiya, Kazuki Hirata, Aya Muramatsu, Makoto Suzuki, Kazumori Arai, Tadashi Terada
Pathology International.2020; 70(10): 767. CrossRef - Association study of cell cycle proteins and human papillomavirus in laryngeal cancer in Chinese population
Lifang Cui, Congling Qu, Honggang Liu
Clinical Otolaryngology.2019; 44(3): 323. CrossRef - Liver metastatic basaloid squamous cell carcinoma with negative expression of pancytokeratin: a case report and literature review
Linxiu Liu, Xuemin Xue, Liyan Xue
Diagnostic Pathology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma at the Floor of the Mouth and Mandible: A Case Report
Jun-Sang Lee, Uk-Kyu Kim, Dae-Seok Hwang, Jun-Ho Lee, Hong-Seok Choi, Na-Rae Choi, Mi Heon Ryu, Gyoo Cheon Kim
The Korean Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2019; 43(5): 197. CrossRef - p53 and p16 expression in oral cavity squamous cell and basaloid squamous cell carcinoma
Allisson Filipe Lopes Martins, Carlos Henrique Pereira, Marília Oliveira Morais, Paulo Otávio Carmo Souza, Lucas Borges Fleury Fernandes, Aline Carvalho Batista, Elismauro Francisco Mendonça
Oral Cancer.2018; 2(1-2): 7. CrossRef - Expression and role of EGFR, cyclin�D1 and KRAS in laryngocarcinoma tissues
Xinsheng Lin, Guofeng Wen, Shuangle Wang, Hangui Lu, Chuangwei Li, Xin Wang
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Histopathological variants of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: A multicenter study in Latin America

 E-submission
E-submission


 First
First Prev
Prev



