Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Study
- Inconspicuous longitudinal tears of the intracranial vertebral artery in traumatic basal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Seongho Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(2):179-183. Published online November 8, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.10.15
- 10,209 View
- 208 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
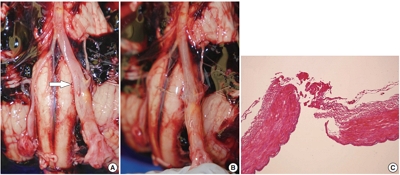
PDF - Blunt force trauma to the head or neck region can cause traumatic basal subarachnoid hemorrhage (TBSAH), which can result in rapid loss of consciousness and death; however, detecting such a vascular injury is difficult. Posterior neck dissection was performed to investigate the bleeding focus in TBSAH cases 2018 and 2019. In all four cases, autopsies revealed a longitudinal tear in the midsection of the vertebral artery’s intracranial portion. The midportion of the intracranial vertebral artery appears to be most vulnerable to TBSAH. Interestingly, three of the cases showed only a vaguely visible longitudinal fissure in the artery without a grossly apparent tear; rupture was confirmed by microscopic examination. Longitudinal fissures of the intracranial vertebral artery, which are difficult to identify without detailed examination, may be overlooked in some cases of TBSAH. Thus, careful gross and microscopic examination of the vertebral artery is recommended in cases of TBSAH.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Traumatic vertebrobasilar pseudoaneurysms: diagnostic pitfalls on CT angiography with forensic implications — two case reports
Numfon Tweeatsani, Kana Unuma, Yukiko Uemura, Hirotaro Iwase, Yohsuke Makino
Emergency Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ginseng Extract Ginsenoside Rg1 on Mice with Intracerebral Injury
Zixin Zhuang, Jinman Chen, Hao Xu, Yongjun Wang, Qianqian Liang
Chinese Medicine and Culture.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Traumatic vertebrobasilar pseudoaneurysms: diagnostic pitfalls on CT angiography with forensic implications — two case reports
Case Report
- Polycystic Kidney Disease Presenting as Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Due to Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm: An Autopsy Case.
- Yoo Duk Choi, Han Young Lee, Youn Shin Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2006;40(6):469-471.
- 7,973 View
- 89 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a hereditary disorder characterized by multiple expanding cysts in both kidneys, and they ultimately destroy the renal parenchyma and cause renal failure. Intracranial aneurysms are found in approximately 10% to 15% of ADPKD patients. Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) from a ruptured intracranial aneurysm is a frequent complication in patients with ADPKD and it makes up a considerable proportion of the causes of death in this group of patients. We report here an autopsy case of polycystic kidney disease that was morphologically identical to ADPKD, and the patients had presented after death with SAH due to a ruptured cerebral aneurysm.

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



