Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review
- Standardization of the pathologic diagnosis of appendiceal mucinous neoplasms
- Dong-Wook Kang, Baek-hui Kim, Joon Mee Kim, Jihun Kim, Hee Jin Chang, Mee Soo Chang, Jin-Hee Sohn, Mee-Yon Cho, So-Young Jin, Hee Kyung Chang, Hye Seung Han, Jung Yeon Kim, Hee Sung Kim, Do Youn Park, Ha Young Park, So Jeong Lee, Wonae Lee, Hye Seung Lee, Yoo Na Kang, Younghee Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(4):247-264. Published online July 8, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.05.28
- 14,023 View
- 944 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
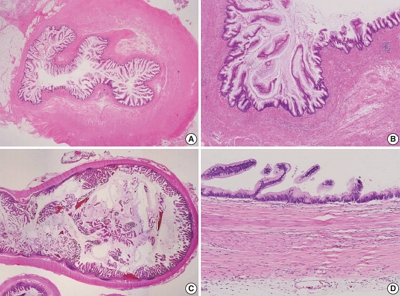
Supplementary Material - Although the understanding of appendiceal mucinous neoplasms (AMNs) and their relationship with disseminated peritoneal mucinous disease have advanced, the diagnosis, classification, and treatment of AMNs are still confusing for pathologists and clinicians. The Gastrointestinal Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists (GPSG-KSP) proposed a multicenter study and held a workshop for the “Standardization of the Pathologic Diagnosis of the Appendiceal Mucinous Neoplasm” to overcome the controversy and potential conflicts. The present article is focused on the diagnostic criteria, terminologies, tumor grading, pathologic staging, biologic behavior, treatment, and prognosis of AMNs and disseminated peritoneal mucinous disease. In addition, GPSG-KSP proposes a checklist of standard data elements of appendiceal epithelial neoplasms to standardize pathologic diagnosis. We hope the present article will provide pathologists with updated knowledge on how to handle and diagnose AMNs and disseminated peritoneal mucinous disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intrasplenic metastasis of appendiceal low-grade mucinous neoplasm – A case report and review of the literature
P. Meister, J. Rawitzer, M. Reschke, H.A. Baba, U. Neumann, M. Kaths
Current Problems in Cancer: Case Reports.2025; 18: 100364. CrossRef - Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding Secondary to Appendiceal Mucinous Neoplasm: A Report of Two Cases and a Review of the Literature
Jesús Omar Soto Llanes, Samanta Kin Dosal Limón, Ana Jimena Iberri Jaime, Mario Zambrano Lara, Billy Jiménez Bobadilla
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting Survival in Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Appendix: Demographics, Disease Presentation, and Treatment Methodology
Paul H. McClelland, Stephanie N. Gregory, Shirley K. Nah, Jonathan M. Hernandez, Jeremy L. Davis, Andrew M. Blakely
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2024; 31(9): 6237. CrossRef - Histoséminaire biopsies péritonéales tumorales. Néoplasies mucineuses appendiculaires
Peggy Dartigues
Annales de Pathologie.2024; 44(4): 274. CrossRef - Histoséminaire biopsies péritonéales tumorales. Cas no 2
Peggy Dartigues
Annales de Pathologie.2024; 44(4): 245. CrossRef - A Case of Low-Grade Appendiceal Mucinous Neoplasm: The Role of Preoperative Imaging and Surgical Technique in Achieving Favorable Outcomes
Daniel A Meza-Martinez, Yeudiel Suro Santos, Samantha J Andrade-Ordoñez, Julio A Palomino-Payan, Brando J Fematt-Rodriguez
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidental Appendiceal Mucinous Neoplasm Found During Appendectomy in a 15-Year-Old Patient: A Case Report
Fernando Aguilar-Ruiz, Kevin Joseph Fuentes-Calvo, Sara Fernanda Arechavala-Lopez, Irving Fuentes-Calvo, Luis F Arias-Ruiz
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Uncovering the Hidden Threat: Ileocolic Intussusception in an Adult With Appendicular Tumor
Mrunal Panchal, Shishir Kumar, Khushboo Jha, Kaushik Saha, Abhijit Kundu
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Low-Grade Appendiceal Mucinous Neoplasm vs. Appendiceal Diverticulum: Distinction with Histomorphologic Features
Cevriye Cansiz Ersöz, Siyar Ersöz, Berna Savas, Arzu Ensari
Gastrointestinal Disorders.2024; 6(4): 905. CrossRef - Appendiceal perforation secondary to endometriosis with intestinal metaplasia: A case report
Minghua Wang, Jing Liu, Boxin Hu, Simin Wang, Ping Xie, Ping Li
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary and secondary tumors of the peritoneum: key imaging features and differential diagnosis with surgical and pathological correlation
Javier Miguez González, Francesc Calaf Forn, Laura Pelegrí Martínez, Pilar Lozano Arranz, Rafael Oliveira Caiafa, Jordi Català Forteza, Lina Maria Palacio Arteaga, Ferrán Losa Gaspà, Isabel Ramos Bernadó, Pedro Barrios Sánchez, Juan Ramón Ayuso Colella
Insights into Imaging.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Muzinöse Tumoren des Peritoneums
Anne Kristin Fischer, Andrea Tannapfel, Alexander Quaas
Die Chirurgie.2023; 94(10): 823. CrossRef - Landscape of Genetic Mutations in Appendiceal Cancers
Marian Constantin, Cristina Mătanie, Livia Petrescu, Alexandra Bolocan, Octavian Andronic, Coralia Bleotu, Mihaela Magdalena Mitache, Sorin Tudorache, Corneliu Ovidiu Vrancianu
Cancers.2023; 15(14): 3591. CrossRef - Delivery of an Incidental Appendiceal Mucinous Neoplasm
Madison Bowles, Jessica Y Ng, Hajir Nabi
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Unearthing novel fusions as therapeutic targets in solid tumors using targeted RNA sequencing
Sungbin An, Hyun Hee Koh, Eun Sol Chang, Juyoung Choi, Ji-Young Song, Mi-Sook Lee, Yoon-La Choi
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Intrasplenic metastasis of appendiceal low-grade mucinous neoplasm – A case report and review of the literature
Original Article
- Image-Guided Fine Needle Cytology with Aspiration Versus Non-Aspiration in Retroperitoneal Masses: Is Aspiration Necessary?
- Rajiv Kumar Misra, Shaila Mitra, Rishav Kumar Jain, Shilpa Vahikar, Archana Bundela, Purak Misra
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(2):129-135. Published online March 12, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.01.28
- 8,714 View
- 67 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
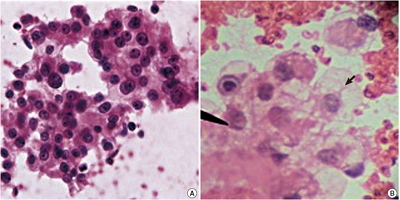
Although using fine needle cytology with aspiration (FNC-A) for establishing diagnoses in the retroperitoneal region has shown promise, there is scant literature supporting a role of non-aspiration cytology (FNC-NA) for this region. We assessed the accuracy and reliability of FNC-A and FNC-NA as tools for preoperative diagnosis of retroperitoneal masses and compared the results of both techniques with each other and with histopathology. Methods: Fifty-seven patients with retroperitoneal masses were subjected to FNC-A and FNC-NA. Smears were stained with May-Grunwald Giemsa and hematoxylin and eosin stain. An individual slide was objectively analysed using a point scoring system to enable comparison between FNC-A and FNC-NA. Results: By FNC-A, 91.7% accuracy was obtained in cases of retroperitoneal lymph node lesions followed by renal masses (83.3%). The diagnostic accuracy of other sites by FNC-A varied from 75.0%–81.9%. By FNC-NA, 93.4% diagnostically accurate results were obtained in the kidney, followed by 75.0% in adrenal masses. The diagnostic accuracy of other sites by FNC-NA varied from 66.7%–72.8%. Conclusions: Although both techniques have their own advantages and disadvantages, FNC-NA may be a more efficient adjuvant method of sampling in retroperitoneal lesions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comparison of cytologic quality in fine‐needle specimens obtained with and without aspiration from superficial lymph nodes in the dog
V. Karakitsou, M. M. Christopher, E. Meletis, P. Kostoulas, D. Pardali, C. K. Koutinas, M. E. Mylonakis
Journal of Small Animal Practice.2022; 63(1): 16. CrossRef - A comparison of cytological quality between fine‐needle aspiration and non‐aspiration techniques for obtaining ultrasound‐guided samples from canine and feline lymph nodes
James Whitlock, Olivier Taeymans, Paola Monti
Veterinary Record.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A randomised controlled comparison of aspiration and non-aspiration fine-needle techniques for obtaining ultrasound-guided cytological samples from canine livers
K.L. Fleming, E.J. Howells, E.J. Villiers, T.W. Maddox
The Veterinary Journal.2019; 252: 105372. CrossRef - Minimally invasive biopsy in retroperitoneal tumors (Review)
Radu Marcu, Camelia Diaconu, Traian Constantin, Bogdan Socea, Florentina Ionita‑Radu, Dan Mischianu, Ovidiu Bratu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - For diagnosis of liver masses, fine-needle aspiration versus needle core biopsy: which is better?
Liye Suo, Ruby Chang, Vijayalakshmi Padmanabhan, Shilpa Jain
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2018; 7(1): 46. CrossRef - Fine needle aspiration in retroperitoneal lesions
Parikshaa Gupta, Arvind Rajwanshi, Raje Nijhawan, Radhika Srinivasan, Nalini Gupta, Uma Nahar Saikia, Pranab Dey
APMIS.2017; 125(1): 16. CrossRef
- A comparison of cytologic quality in fine‐needle specimens obtained with and without aspiration from superficial lymph nodes in the dog
Case Reports
- Mature Teratoma in the Adrenal Gland.
- Eun Jung Cha
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45:S98-S100.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.S1.S98
- 3,355 View
- 42 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A teratoma is a germ-cell tumor composed of tissue components representing derivatives of three germ layers. A teratoma in the region of adrenal gland is a rare retroperitoneal tumor. We now report a case of a primary adrenal teratoma. A 38-year-old woman presented with an incidentally detected adrenal mass. The computed tomography scan revealed a 9x8x7.5 cm fat density mass with calcification in the left adrenal gland. The surgically resected tumor was round and well circumscribed and the adrenal gland was present at the periphery of the tumor. The cut surface contained fat tissue and a hair containing cyst. Microscopically, the tumor consisted of adipose tissue, hair, skin appendage, nerve, muscle bundle and bone.
- Retroperitoneal Synovial Sarcoma: A case report.
- Seoung Wan Chae, Jung Weon Shim, Hye Kyung Ahn, Min Chul Lee, Young Euy Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(4):540-542.
- 1,664 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Synovial sarcoma most commonly affects the extremities, especially the lower thigh and knee region. However, a smaller number develops in a central or axial distribution, an area which encompasses the trunk, orofacial, cervical and parapharyngeal regions. The retroperitoneum is an extremely unusual site and has never been recorded in the literature as primary a site for synovial sarcoma. We investigated a case of retroperitoneal synovial sarcoma in a 40-year-old woman. The specimen consisted of fragmented large bulky multinodular masses separated by slit-like spaces. The tumor was 130 gm in weight. Microscopically, the tumor was composed of nests of plump ovoid to polygonal shaped cells and bundles of spindle shaped cells, which had vesicular nuclei and a small amount of cytoplasm. In some areas, there were cleft like spaces and pseudoglandular structures lined by flat or cuboidal cells. Myxoid change, collagen deposition, foci of calcification and osseous metaplasia were also present. Immunohistochemically, the polygonal cells and some of the spindle cells reacted positively for keratin. The spindle cells, especially in the perivascular area were positive for vimentin. S-100 protein and GFAP were negative in both type of cells.
Original Articles
- Papillary and Solid Epithelial Neoplasm of the Pancreas with Multiple Metastases.
- Duck Hwan Kim, Youn Ju Kim, Seung Eun Yang, Sung Suk Paeng, Hee Jin Chang, Jung Il Suh
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(3):272-275.
- 1,616 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Papillary and solid epithelial neoplasm is a rare pancreatic tumor of low-grade malignancy. We report a case of a 23 year old female having solid and papillary neoplasm of the pancreatic tail with mutiple omental and peritoneal metastases. Microscopically, the main tumor showed typical histologic findings including solid and papillary areas with cystic change. But the metastasizing nodules were largely solid and the tumor cells demonstrated increased nuclear pleomorphism, hyperchromasia and an increased mitotic rate. The tumor cells contained considerable amount of intracellular and extracellular eosinophilic inclusions which were ultrastructually zymogen-like granules. These inclusions were more frequently found in the metastatic nodules. By flow cytometric study, the tumor was hyperdiploid. The DNA index was not significant.
- Differential Diagnosis of Ovarian Mucinous, Serous, and Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma in Peritoneal Washing Cytology .
- Shi Nae Lee, In Ae Park
- Korean J Cytopathol. 2000;11(2):83-88.
- 2,619 View
- 74 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study presents the cytologic features of peritoneal washings, with particular emphasis on the cytologic discrimination among serous, mucinous, and endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the ovary. We selected histologically confirmed 27 cases of peritoneal washing : 8 cases of serous cystadenocarcinomas, 5 cases of mucinous cystadenocarcinomas, and 14 cases of endometrioid adenocarcinomas. The most frequent cytologic pattern of three tumors was clusters. Ball pattern was found in serous cystadenocarcinoma(36%) and acinar pattern in endometrioid adenocarcinoma (36%). Mucinous adenocarcinoma showed mucoid background(100%) and endometrioid adenocarcinoma revealed inflammatory background(43%). The cytoplasmic vacuoles were noted in 80%, 13%, and 43% of mucinous, serous, and endometrioid adenocarcinoma, respectively. The endometrioid adenocarcinoma showed prominent nucleoli(64%). In conclusion, the cytologic findings of mucinous cystadenocarcinoma were different from that of serous and endometrioid carcinomas, such as mucoid background, abundant cytoplasm with vacuolated cytoplasm, and peripherally located cytoplasm. Although endometrioid carcinoma showed acinar pattern and prominent nucleoli, the differential diagnosis between serous cystadenocarcinoma and endometrioid adenocarcinoma in peritoneal washing cytology was not always possible.
Case Reports
- Secondary Oxalosis Involving the Epididymis.
- Sangkyum Kim, Kwanggi Lee, Namhoon Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(2):100-102.
- 1,658 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Secondary oxalosis in the epididymis is a rare complication among patients who have undergone hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. This case report presents secondary oxalosis confirmed via a clinicoradiological-pathologic process-in combination with clinical symptoms, ultrasonographic findings, cytologic findings in urine, and surgical pathological diagnosis.
- Giant Retroperitoneal Lipomatous Angiomyolipoma Simulating Liposarcoma: A Brief Case Report.
- Dakeun Lee, Joungho Han, Sung Joo Kim, Dongil Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(6):406-408.
- 1,706 View
- 28 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Extrarenal retroperitoneal angiomyolipomas (AML) are extremely rare, therefore they may present a diagnostic challenge. In this paper, the authors describe a case of a huge retroperitoneal AML in a 49-year-old woman who presented with sudden abdominal pain. Computed tomography revealed the presence of a large, round, fatty mass in the retroperitoneal space, which was easily removed by surgery. The mass was well encapsulated and dark yellow on the cut surface. Microscopically, the tumor was exclusively composed of adipose tissue with frequent multivacuolated, lipoblast-like cells masquerading as well differentiated liposarcoma. In addition, there were many clear, epithelioid cells present, especially around the small blood vessels, which were reactive for HMB-45 and smooth muscle actin.
- Low-grade Immature Teratoma of the Ovary with Gliomatosis Peritonei: A case report.
- Jin Young Yoo, Sang In Shim
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(3):322-324.
- 1,610 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Immature teratoma accounts for less than I percent of all ovarian teratomas and occurs commonly in young individuals, the peak incidence being in the second decade. It contains a variable mixture of mature and immature tissues in which neuroectodermal elements almost always predominate. Gliomatosis peritonei, miliary implants of mature glial tissues on the peritoneum or omentum, is an infrequently reported complication of mature or immature ovarian teratomas. We describe the first case in Korea of a 12-year-old girl with an immature teratoma and numerous glial peritoneal implants.
In Vitro
- Ovarian Serous Borderline Tumors with Peritoneal Implants: A clinicopathologic and flow cytometric DNA analysis of 5 cases.
- Kyu Rae Kim, Kwang Yul Cha, Soon Hee Jung, Woo Hee Jung, Dong Hee Choi, Jong Wook Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(2):143-151.
- 2,049 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Five cases of ovarian serous borderline tumor associated with multiple peritoneal implants were analysed. The age of 5 patients ranged from 34 to 45(mean: 39) years at the time of diagnosis. Two patients presented with secondary infertility underwent hyperstimulation of the ovary under the in vitro fertilization program. One patient was presented with abdominal pain and the remaining two with lower abdominal mass accompanied by abdominal pain. Serous surface papilloma of borderline malignancy, involving one or both ovaries, was present in all 5 cases and papillary serous cystic tumor of borderline malignancy was associated simultaneously in one or both ovaries in all cases. Marked adhesions between the pelvic organs, and multiple granularities and nodularities of the omentum and peritoneum were noted. Microscopically, the peritoneal lesions were composed of noninvasive implants of tumor cells and pasmmoma bodies on the surface of entire pelvic and abdominal organs. Flow cytometric analysis of nuclear DNA content from paraffin-embedded tissue fo primary ovarian tumor classified as aneuploidy in 3 cases and as diploidy in 2 cases. The DNA index of the aneuploid tumors ranged from 1.21 to 1.37. Four patients underwent hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and partial omentectomy in which two were followed by chemotherapy and one case underwent bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy.
Original Article
- Disseminated Deciduosis Peritonei.
- Moon Hyang Park, Chan Kum Park, Jung Dal Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1988;22(2):159-163.
- 1,591 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Gross deciduosis in pregnancy is rare. A case of disseminated deciduosis peritonei studied by light and transmission electron microscopy is reported. The pathogenesis of deciduosis peritonei and relationship with leiomyomatosis peritonealis disseminata are discussed in view of the present findings and those previously reported.

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



