Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 49(5); 2015 > Article
-
Review
Cytology Specimen Management, Triage and Standardized Reporting of Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsies of the Pancreas - Won Jae Yoon, Martha Bishop Pitman1,2
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2015;49(5):364-372.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.07.19
Published online: August 10, 2015
Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
1Department of Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
2Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- Corresponding Author Martha Bishop Pitman, MD Department of Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, 55 Fruit Street, Boston, MA 02114, USA Tel: +1-617-726-3185 Fax: +1-617-724-6564 E-mail: mpitman@mgh.harvard.edu
© 2015 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- Abstract
- CLINICAL INDICATIONS FOR SAMPLING
- TECHNIQUES OF CYTOLOGY SPECIMEN SAMPLING
- SPECIMEN TRIAGE AND PROCESSING
- RAPID ON-SITE EVALUATION
- PROCESSING OF ASPIRATES FROM SOLID MASSES
- CYSTIC LESIONS
- BIOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS
- MOLECULAR ANALYSIS
- STANDARDIZED REPORTING OF PANCREATICOBILIARY CYTOLOGY
- SUMMARY
- NOTES
- REFERENCES
Abstract
- The recent advances in pancreas cytology specimen sampling methods have enabled a specific cytologic diagnosis in most cases. Proper triage and processing of the cytologic specimen is pivotal in making a diagnosis due to the need for ancillary testing in addition to cytological evaluation, which is especially true in the diagnosis of pancreatic cysts. Newly proposed terminology for pancreaticobiliary cytology offers a standardized language for reporting that aims to improve communication among patient caregivers and provide for increased flexibility in patient management. This review focuses on these updates in pancreas cytology for the optimal evaluation of solid and cystic lesions of the pancreas.
- Pancreas cytology specimen sampling is indicated when the information obtained by specimen sampling has the potential to affect the patient management. This includes (1) differentiating benign from malignant lesions; (2) staging of cancer; and (3) diagnosis of malignancy before chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy [2,3].
CLINICAL INDICATIONS FOR SAMPLING
- Techniques of pancreas cytology specimen sampling include percutaneous computed tomography- or ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration (FNA), endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)–guided brush cytology of the pancreatic duct, and the distal common bile duct, and endoscopic ultrasound–guided FNA (EUS-FNA) [4]. ERCP-guided specimen sampling is rarely used, as the yield of exfoliative cytology from the aspirated pancreatic juice is low, and the risk of pancreatitis from ductal brushing is significant [4]. Compared to EUS-FNA, percutaneous FNA suffers from lower diagnostic yield in pancreatic tumors with diameter less than 3 cm [5], and is suggested to have higher complication rates [6]. Currently, EUS-FNA is considered to be the first-line technique when sampling of a suspected pancreatic cancer is indicated [7].
- EUS-FNA of solid pancreatic lesions is performed using linear echoendoscopes. Doppler imaging is used to identify and avoid blood vessels when passing the needle into the lesion [8]. Lesions in the head/uncinate process of the pancreas are accessed via transduodenal approach; lesions in the body or the tail of the pancreas are accessed via a transgastric route [4]. Selection of appropriate EUS needles is based on the vascularity of the target lesion, difficulty in accessing the lesion, and the type of specimen needed for the diagnosis [4]. For cytology, simple aspiration needles of 22- or 25-gauge are used [9]. A recent meta-analysis concluded that the EUS-FNA using 25-gauge needles are more sensitive than that using 22-gauge needles for diagnosis of pancreatic malignancy [10]. Histologic samples may be obtained by standard 19-gauge and 22-gauge FNA needles. Recently, 19-gauge and 22-gauge core biopsy needles have become available [11]. Core needle biopsies are often critical in procuring sufficient tissue for a specific diagnosis, which is especially true for diseases dependent on some tissue architecture such as autoimmune pancreatitis, or morphologically similar tumors distinguished by immunohistochemical studies such as neuroendocrine neoplasms, acinar cell carcinoma and solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms [12].
- When the lesion is identified, the needle, occluded by a stylet, is placed into the target lesion with one quick thrust. Once the lesion is placed into the solid lesion, the stylet is removed, and the needle is moved to and fro within the lesion with or without application of suction [4]. Use of a stylet is very important as it minimizes gastrointestinal contamination of the specimen which can cause significant diagnostic difficulty [13]. Using fanning technique during needle handling enables sampling from multiple areas within the lesion and increases the yield of cytology [14]. Multiple needle passes are usually needed for diagnosis [15].
- After each needle pass in EUS-FNA of solid masses, the procured material is expelled onto glass slides. Core particles are placed in formalin solution. Smears are prepared on glass slides and fixed in ethanol, or air-dried. In the case of EUS-FNA of pancreatic cystic lesions, the procedure is similar to that of solid pancreatic lesions except that direct smears are not made. All fluid should be aspirated using suction with one needle pass [16], and any solid component separately aspirated. Direct smears should be made of this aspirate, which could be evaluated onsite if so desired. Antibiotics are used to minimize the risk of cyst infection [17].
- Tumor cell seeding following EUS-FNA has been reported anecdotally, but relative to the number of biopsies performed, the rate is very low. Seeding of neoplastic mucinous cysts is of particular concern in Asian countries; however, a recent study has shown that there is no difference in peritoneal seeding or pseudomyxoma peritonei in patients who did and did not have EUS-FNA prior to resection [18].
TECHNIQUES OF CYTOLOGY SPECIMEN SAMPLING
- Specimen aspirated from the pancreas can be prepared using direct smears, cytospins (Thermo-Shandon Instruments, Asheville, NC, USA), liquid based preparations—ThinPrep (Hologic Corporation, Marlborough, MA, USA) or SurePath Prep (Becton-Dickinson, Burlington, NC, USA), and as formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue (cellblocks and core biopsies). The preparation technique used will depend on the type of lesion, and the preferences of the laboratory and pathologists assessing the samples. In order to perform a rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) at the time of biopsy, direct smears will have to be made.
SPECIMEN TRIAGE AND PROCESSING
- The purpose of ROSE is to ensure that the FNA is adequately cellular for diagnosis and that the tissue aspirated is appropriately prepared and triaged for diagnosis. ROSE has been shown to be beneficial for solid mass lesions of the pancreas [19-22], but since ROSE does not direct repeat biopsies of a cystic lesion, and the aspirated cyst fluid is usually so scant, ROSE is not recommended for cystic lesions that produce liquid cystic fluid. If the cyst has a solid component, it is separately sampled with direct smears made for cytological analysis.
RAPID ON-SITE EVALUATION
- The best method of processing specimen from FNAs of solid masses is with direct smears, as long as good direct smears can be made (see below). Processing specimen for cellblock preparation is recommended even if core biopsies are also planned as not all core biopsies are representative. Specimen in paraffin provides small tissue fragments for cytohistological evaluation and provides readily accessible tissue for immunohistochemical and molecular studies, which may be essential for an accurate and specific diagnosis. A dedicated biopsy pass can be triaged for microbiologic cultures, electron microscopy, and flow cytometric analysis [12].
- Direct smears
- Direct smears are made from aspirates that is solid enough to be smeared, which may include some aspirates from thick cyst contents. Direct smears may be air-dried or fixed with an alcohol based fixative. Air-dried smears are stained with a Romanowsky stain, such as Diff-Quik, which provides details of the cytoplasmic features and background mesenchymal elements. Fixed smears are stained with either a standard Papanicolaou stain or hematoxylin and eosin stain, which provides nuclear details. Regardless of the stain used, all require good quality smears for accurate interpretation. The person responsible for making the smears should have proper training.
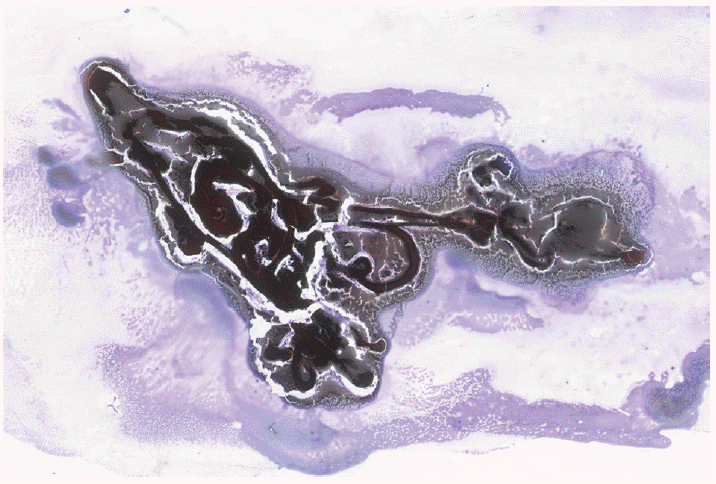
- Prior to expressing the aspirate onto slides to make the direct smears, the outside of the needle should be wiped clean of contaminating cells and mucus from the gastrointestinal tract. Aspirated specimen should be spread across the slide in a relatively thin layer with an even distribution, and without crush, air-drying or obscuring artifact. A poorly prepared smear may not be interpretable, or worse, may lead to a false-positive or false-negative interpretation. Critical to an optimal smear is to remove needle casts of clotted specimen from the slides, which are expressed as “worms” of clotted specimen and which may contain valuable specimen (Fig. 1). All such specimen clots should be gently lifted from the glass slide with the tip of a needle and placed in formalin for cellblock preparation.
- Liquid based preparations
- The two most common liquid based cytology (LBC) methods include ThinPrep (Hologic Inc., Marlborough, MA, USA) and SurePath (Becton-Dickinson, Burlington, NC, USA). The proprietary alcohol-based fixatives (Cytolyt [Hologic Corp., Marlborough, MA, USA] for ThinPrep and Cytorich Red [Becton-Dickinson, Burlington, NC, USA] for SurePath) reduce the potentially obscuring background elements such as blood and inflammation. Extracellular mucin, however, will be diluted and attenuated making morphological interpretation challenging. For this reason as well as the inability to perform biochemical testing, LBC is not recommended for cyst fluids. For solid masses, however, a liquid-based preparation is far more desirable than poorly prepared direct smears with artifact.
- Formalin-fixed paraffin embedded specimen
- Needle rinsings after expression of the aspirate on the slide coupled with a dedicated biopsy for rinsing only, often provide specimen for cellblock preparation. The cellular content of needle rinsing fluid is spun down into a cell button, which is then fixed in formalin and processed as a routine histology specimen (Fig. 2).
- There are different methods of agglutinating the cells. A common method is the plasma-thrombin clot method using outdated plasma from a blood bank. This method suspends the cells in a fibrin clot, which is wrapped in tissue paper and processed. Other methods include the HistoGel technique (Thermo Scientific Richard-Allan Scientific HistoGel, Kalamazoo, MI, USA) and the collodion bag technique (Mavidon, Nailsea, Somert, UK or Macron Fine Chemicals of Avantor Performance Materials Inc., Center Valley, PA, USA), both of which are more labor intensive, but which may be better for very scant specimens. An automated cellblock method is the Cellient Automated Cell Block System (Hologic Inc., Bedford, MA, USA) which creates a paraffin-embedded cell block by using vacuum filtration to deposit a layer of cells on a filter and then infiltrate those cells with processing reagents and paraffin.
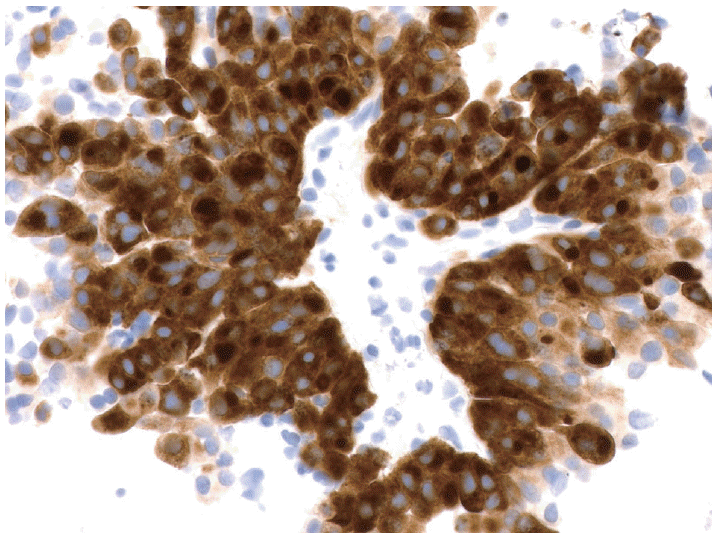
- Larger core biopsies which can be handled with forceps are processed using standard histotechnology techniques. All such core biopsies should be wrapped with tissue paper around a cardboard protector to prevent loss through the cassette during processing. If the core biopsy sample is small and fragmented, it should be handled as a cellblock. Having specimen fixed in formalin is an invaluable adjunct to cytological evaluation of a mass lesion. This is especially true for diseases dependent on some histologic architecture such as autoimmune pancreatitis, or morphologically similar tumors which are distinguished by immunohistochemical studies such as neuroendocrine neoplasms, acinar cell carcinoma and solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms. Secondarily cystic solid neoplasms, such a neuroendocrine tumors are dependent on cytology, and in many cases on the immunohistochemical staining that supports the neuroendocrine nature of the cells, for a specific diagnosis since biochemical analysis and molecular analysis are noncontributory [23,24]. So in addition to the simple hematoxylin and eosin stained sections from the cell-block, additional sections of the tissue can be used for ancillary testing including immunohistochemical stains and molecular analysis (Fig. 3) [12].
PROCESSING OF ASPIRATES FROM SOLID MASSES
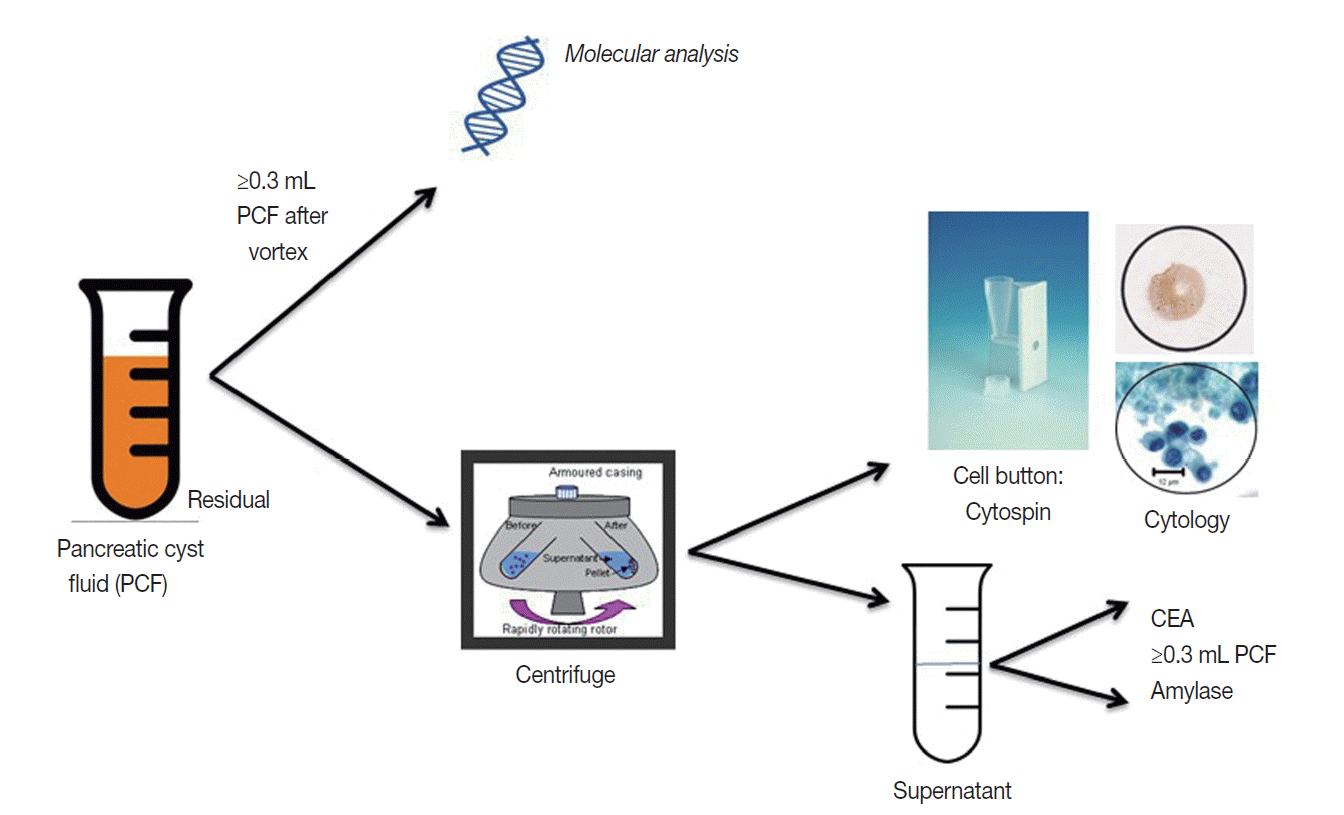
- The triage of cyst fluid for testing is volume dependent. Cyst fluid should always remain fresh and unfixed and sent to the cytology lab for processing. Fig. 4 outlines the cyst fluid triage protocol developed at the Massachusetts General Hospital. Cyst fluid is triaged to address two specific clinical questions that directly impact patient management: (1) is the cyst mucinous? and (2) is the cyst high-risk by cytology [25]?
- Very small quantities of cyst fluid (<0.5 mL) are typically too scant in cellularity to make cytology a meaningful test. However, if imaging features are characteristic of an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN), then the remaining clinical question is whether there is cytological evidence of a high-risk lesion warranting resection. As such, all of the cyst fluid should be sent for cytological analysis. If, however, the primary question is whether the cyst is mucinous or non-mucinous, fluid should be triaged to carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) or, if prior testing demonstrated a non-elevated CEA, molecular analysis [26].
- Cyst fluids measuring more than 0.5 mL offer sufficient volume for multiple ancillary tests (see below).
- Cytospin
- A cytospin is a cell concentration method of processing and is the best method for fresh cyst fluid and scantily cellular aspirates. High cellular samples need to be diluted. Cytospin preparations maintain the integrity of background elements such as mucin and necrosis. Once the pancreatic cyst fluid is centrifuged to create a cell button and the supernatant is sent for biochemical analysis, the cell button is resuspended and processed as a cytospin to create a cytological slide for routine staining.
CYSTIC LESIONS
- The supernatant cyst fluid following centrifugation is submitted to the chemistry laboratory for CEA and/or amylase testing. At least 0.3 mL of fluid is usually needed for each assay. If volume is scant, CEA generally takes priority over amylase. If there is sufficient fluid, both assays are performed.
- Carcinoembryonic antigen
- CEA has been shown to be the most reliable and accurate test for a mucinous cyst compared to mucin stains and cytology [27]. The CEA immunoassay uses the sandwich antibody method. The measured CEA value of a patient’s sample can vary depending on the testing procedure used so each laboratory must validate the assay for normal and abnormal ranges. Cut-off levels affect sensitivity and specificity. At a level of 192 ng/mL CEA has an overall accuracy of up to 80% (specificity of 84% and sensitivity of 75%) [28]. Raising the cut off value improves specificity at the expense of sensitivity. At a level of 800 ng/mL, the specificity is 98% but sensitivity is 48% [29]. Serous cystadenomas and pseudocysts typically have CEA levels lower than 0.5 ng/mL. However, elevations of CEA may be seen in pseudocysts and other non-mucinous cysts such as lymphoepithelial cysts [30], and non-neoplastic mucinous cysts such as gastrointestinal duplication cysts [31]. In addition, CEA is not always elevated in a mucinous cyst so a low CEA level may be supportive of a non-mucinous cyst, but should not be interpreted as diagnostic of a non-mucinous cyst. CEA levels also do not correlate with malignancy.
- Amylase
- Amylase testing uses an enzymatic colorimetric assay to quantify α-amylase. The utility of amylase analysis in cyst fluid is to support the clinical and cytological diagnosis of a pseudocyst or serous cystadenoma. Pseudocysts should always have a high amylase level, usually in the 1000’s due to the destruction of pancreatic acinar tissue, and serous cystadenomas consistently demonstrate low amylase levels [32]. A low amylase level (<250 U/L) in a pseudocyst is very unlikely [29]. Amylase levels are highly variable in mucinous cysts and do not distinguish between IPMN and mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN) [27,33].
BIOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS
- Mutational analysis is not routinely used for diagnosis or prognosis of solid pancreatic masses, but is extremely valuable in the diagnosis of pancreatic cysts [26,34-38]. Most epithelial neoplasms are readily diagnosed using routine cytology with or without immunohistochemical analysis. Molecular mutations are typically not sufficiently specific to establish a malignant diagnosis since precursor lesions such as pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) demonstrate some of the same mutations as invasive adenocarcinoma. The model of progressive and cumulative mutations from normal pancreas to PanIN to carcinoma has been established with the sequential accumulation of alterations in the KRAS and TP53 genes and loss of the CDKN2A and/or SMAD4 tumor suppressor genes [39]. Immunohistochemical stains of tissue in cellblocks can analyze for upregulation of P53 and loss of SMAD4 by staining for the protein products of these genes.
- For cysts, however, molecular analysis of DNA from the few cells or supernatant fluid is very valuable. Molecular testing is performed on a homogenized aliquot of cyst fluid typically at least 0.3 mL in volume. The DNA present in the sample may or may not be representative of the cells evaluated by cytology; in other words, the cytology may not demonstrate neoplastic cells, but the molecular analysis demonstrates a KRAS mutation [26,37,40,41]. Whatever DNA is present in the sample is analyzed, whether it is from cells in the sample or free DNA in the cyst fluid. As such, the presence of a mutation is a true positive result, but the absence of a mutation may very likely represent a false-negative result. Detection of KRAS/GNAS/RNF43 mutations are highly specific for determining that the cyst is mucinous, and may preclude the need for repeat testing if CEA is not elevated to support the clinical impression of a mucinous cyst from imaging [26,41]. Detection of mutations late in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence such as in TP53, p16/CDKN2A, and SMAD4 may add weight to an indeterminate (atypical or suspicious) cytological interpretation. Table 1 outlines the molecular profiles useful in the evaluation of pancreatic cysts.
MOLECULAR ANALYSIS
- The Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology has proposed a standardized terminology scheme for reporting pancreaticobiliary cytology with six categories (Table 2) [1]. New and somewhat controversial is the category “neoplastic” that is divided into clearly “benign” neoplasms and “other” neoplasms. The “other” category includes a wide variety of lesions ranging from premalignant mucinous cysts to low-grade potentially malignant and low-grade malignant neoplasms. This standardized terminology and nomenclature system aims to provide intra- and interdepartmental guidance for diagnosis, and one that correlates the diagnosis to our current understanding of the lesion’s biological behavior and management recommendations.
- Category I. Non-diagnostic
- A cytology specimen is non-diagnostic when it fails to provide any diagnostic or useful information about the solid or cystic lesion sampled. The clinical and imaging context should be taken into consideration when assessing whether a sample is adequate. Thick extracellular mucin without epithelial cells is not non-diagnostic, for example. Thin cyst fluid with an elevated CEA level above a validated cut-off level supporting a mucinous cyst is also not non-diagnostic despite the absence of an epithelial cell component [27-29]. In contrast, cyst fluid without lesional epithelium, scant thin extracellular mucin which could be gastrointestinal contamination, and a CEA level below the established cut-off level supporting a mucinous cyst is a nondiagnostic specimen.
- Category II. Negative (for malignancy)
- When an FNA contains adequate cellular and/or extracellular tissue to evaluate or define a lesion that is identified on imaging, it can be classified as negative (for malignancy). Whenever possible a specific diagnosis should be given, for example, chronic pancreatitis or lymphoepithelial cyst [42]. Benign pancreaticobiliary tissue in the setting of vague fullness and no discrete mass also qualifies as a negative interpretation. A negative interpretation with a descriptive diagnosis implies that the sample is adequately cellular and that no cytological atypia is present.
- Category III. Atypical
- When cells display cellular changes inconsistent with normal or reactive cellular changes, and that are insufficiently atypical or characteristic to make a diagnosis of a neoplasm or to be suspicious for a high-grade malignancy, then the atypical category is appropriate. Aspirates with cytological findings suggestive but not diagnostic of a low-grade neoplasm such as a neuroendocrine tumor or solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm due to insufficient specimen for confirmation of a specific diagnosis belong in the atypical category. Brushing cytology yielding atypical biliary epithelium remains in this category since premalignant lesions of the biliary tract have not been as well defined with correlative management algorithms.
- Category IV. Neoplastic
- Aspirates diagnostic of a benign neoplasm belong in this interpretation category, for example, serous cystadenoma, neuroendocrine microadenoma, and lymphangioma.
- Pre-malignant neoplasms such as IPMN or MCN with low, intermediate, or high-grade dysplasia, and potentially malignant or low-grade malignant neoplasms such as well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms belong in this category.
- The rationale for this proposed category relates the desire to standardize and correlate the cytological nomenclature with the 2010 World Health Organization (WHO) terminology classification that maintains the nomenclature for both neuroendocrine tumors and solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms as “neoplasms” rather than carcinomas, and to take into consideration the increasingly conservative management approaches for many of the lesions [43].
- These “other” neoplasms are either pre-invasive, potentially malignant, or low-grade malignant neoplasms, which should be distinguished from aggressive, high-grade malignancies such as ductal adenocarcinoma. All of the tumors in this category are clearly neoplastic, and even though some are low-grade malignant, the heading “Neoplastic: other” is an accurate and reasonable generic term that accurately reflects the pre-operative cytological terminology and does not define the neoplasm as benign or malignant. The cytological categories of “atypical” and “suspicious for malignancy” connote an indeterminate interpretation and do not relate the detection of a neoplasm, which could lead to unnecessary repeat biopsy.
- The cytological interpretation of a neuroendocrine tumor, not otherwise specified indicates a well-differentiated neoplasm. The term “carcinoma” is reserved for high-grade neoplasms (G3), typically with a small cell carcinoma or large cell undifferentiated carcinoma morphology. Although it is now widely accepted that well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors have malignant potential [44], many are very slow growing and even curable if caught at an early stage, and some are detected incidentally in asymptomatic, elderly patients who may be better served with conservative observation than surgical intervention. To distinguish these low-grade neoplasms from highly aggressive malignant neoplasms and to offer management flexibility in elderly patients with small, asymptomatic tumors where the risk to benefit ratio of surgery is high compared to conservative management, neuroendocrine tumors are placed in this category rather than the malignant category. Convincing a patient with a malignant cytology report that conservative management of their incidental 1-cm-sized neuroendocrine tumor is the best option for them is virtually impossible.
- Solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm is a low-grade malignancy but with a small local recurrence rate and low metastatic potential [45]. For these reasons coupled with the fact that the tumor is called a “neoplasm” and not carcinoma, it is included in this Neoplastic: other category.
- The pre-malignant mucinous cysts of the pancreas, IPMNs and MCNs, are lined by low, intermediate, or high-grade dysplasia; malignancy requires an invasive component. Atypia less than overtly malignant is included in this category of ‘Neoplastic: other’. Distinguishing the atypia in these cysts is challenging using a four-tiered system, and it is not always possible to distinguish high-grade dysplasia from carcinoma, or intermediate-grade dysplasia from high-grade dysplasia. A two-tiered system of low-grade (low-grade and intermediate-grade dysplasia) and high-grade (high-grade dysplasia or adenocarcinoma) epithelial atypia provides the best information for clinical management [46-49].
- Category V. Suspicious (for malignancy)
- A specimen is suspicious for malignancy when the quality and/or quantity of the cellular atypia are insufficient for a malignant interpretation. This category generally refers to pancreatic adenocarcinoma since most malignancies in the pancreas are ductal adenocarcinoma, but this category is used for all high-grade, aggressive malignancies. The suspicious category is also used for aspirates that include high-grade neoplasms in the differential diagnosis, e.g., acinar cell carcinoma or pancreatoblastoma, but insufficient tissue for confirmatory ancillary studies is not available.
- Category VI. Positive or malignant
- This category includes high-grade, aggressive tumors such as pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its variants, cholangiocarcinoma, acinar cell carcinoma, high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma (small cell and large cell), pancreatoblastoma, lymphomas, sarcomas and metastases to the pancreas.
STANDARDIZED REPORTING OF PANCREATICOBILIARY CYTOLOGY
IVA. Neoplastic: benign
IVB. Neoplastic: other
- Pancreatic cytology is an accurate method of evaluating solid and cystic lesions in the pancreas. Accuracy, however, requires a multidisciplinary and multimodal approach where the cytological features are interpreted in the context of the clinical, imaging and ancillary testing information available. Adequate tissue procurement, processing and triage are vital steps in ensuring that the tissue is sufficient for a diagnosis, and standardized terminology ensures that the language used to report the findings in a single coherent, integrated report is understood by all caregivers involved in the management of the patient.
SUMMARY

- 1. Pitman MB, Centeno BA, Ali SZ, et al. Standardized terminology and nomenclature for pancreatobiliary cytology: the Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology guidelines. Diagn Cytopathol 2014; 42: 338-50. ArticlePubMed
- 2. Mekky MA, Abbas WA. Endoscopic ultrasound in gastroenterology: from diagnosis to therapeutic implications. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20: 7801-7. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. Adler D, Max Schmidt C, Al-Haddad M, et al. Clinical evaluation, imaging studies, indications for cytologic study, and preprocedural requirements for duct brushing studies and pancreatic FNA: the Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology recommendations for pancreatic and biliary cytology. Diagn Cytopathol 2014; 42: 325-32. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Brugge W, Dewitt J, Klapman JB, et al. Techniques for cytologic sampling of pancreatic and bile duct lesions. Diagn Cytopathol 2014; 42: 333-7. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Volmar KE, Vollmer RT, Jowell PS, Nelson RC, Xie HB. Pancreatic FNA in 1000 cases: a comparison of imaging modalities. Gastrointest Endosc 2005; 61: 854-61. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Okasha HH, Naga MI, Esmat S, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration versus percutaneous ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration in diagnosis of focal pancreatic masses. Endosc Ultrasound 2013; 2: 190-3. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Dumonceau JM, Polkowski M, Larghi A, et al. Indications, results, and clinical impact of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided sampling in gastroenterology: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy 2011; 43: 897-912. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Wiersema MJ, Vilmann P, Giovannini M, Chang KJ, Wiersema LM. Endosonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy: diagnostic accuracy and complication assessment. Gastroenterology 1997; 112: 1087-95. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Lee JH, Stewart J, Ross WA, Anandasabapathy S, Xiao L, Staerkel G. Blinded prospective comparison of the performance of 22-gauge and 25-gauge needles in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of the pancreas and peri-pancreatic lesions. Dig Dis Sci 2009; 54: 2274-81. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 10. Madhoun MF, Wani SB, Rastogi A, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of 22-gauge and 25-gauge needles in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of solid pancreatic lesions: a meta-analysis. Endoscopy 2013; 45: 86-92. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Panic N, Larghi A. Techniques for endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 2014; 24: 83-107. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Layfield LJ, Ehya H, Filie AC, et al. Utilization of ancillary studies in the cytologic diagnosis of biliary and pancreatic lesions: the Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology guidelines for pancreatobiliary cytology. Diagn Cytopathol 2014; 42: 351-62. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Pitman M. Pancreas. In: Bibbo M, Wilbur DC, eds. Comprehensive cytopathology. London: Elsevier, 2014; 751-73.
- 14. Bang JY, Magee SH, Ramesh J, Trevino JM, Varadarajulu S. Randomized trial comparing fanning with standard technique for endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of solid pancreatic mass lesions. Endoscopy 2013; 45: 445-50. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Jenssen C, Dietrich CF. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy and trucut biopsy in gastroenterology: an overview. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2009; 23: 743-59. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Brugge WR. The role of EUS in the diagnosis of cystic lesions of the pancreas. Gastrointest Endosc 2000; 52(6 Suppl): S18-22. ArticlePubMed
- 17. Lee LS, Saltzman JR, Bounds BC, Poneros JM, Brugge WR, Thompson CC. EUS-guided fine needle aspiration of pancreatic cysts: a retrospective analysis of complications and their predictors. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005; 3: 231-6. ArticlePubMed
- 18. Yoon WJ, Daglilar ES, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Mino-Kenudson M, Pitman MB, Brugge WR. Peritoneal seeding in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas patients who underwent endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration: the PIPE Study. Endoscopy 2014; 46: 382-7. ArticlePubMed
- 19. Olson MT, Ali SZ. Cytotechnologist on-site evaluation of pancreas fine needle aspiration adequacy: comparison with cytopathologists and correlation with the final interpretation. Acta Cytol 2012; 56: 340-6. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 20. Iglesias-Garcia J, Dominguez-Munoz JE, Abdulkader I, et al. Influence of on-site cytopathology evaluation on the diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) of solid pancreatic masses. Am J Gastroenterol 2011; 106: 1705-10. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 21. Collins BT, Murad FM, Wang JF, Bernadt CT. Rapid on-site evaluation for endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy of the pancreas decreases the incidence of repeat biopsy procedures. Cancer Cytopathol 2013; 121: 518-24. ArticlePubMed
- 22. da Cunha Santos G, Ko HM, Saieg MA, Geddie WR. “The petals and thorns” of ROSE (rapid on-site evaluation). Cancer Cytopathol 2013; 121: 4-8. ArticlePubMed
- 23. Yoon WJ, Daglilar ES, Pitman MB, Brugge WR. Cystic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: endoscopic ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration characteristics. Endoscopy 2013; 45: 189-94. ArticlePubMed
- 24. Morales-Oyarvide V, Yoon WJ, Ingkakul T, et al. Cystic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: the value of cytology in preoperative diagnosis. Cancer Cytopathol 2014; 122: 435-44. ArticlePubMed
- 25. Pitman MB. Pancreatic cyst fluid triage: a critical component of the preoperative evaluation of pancreatic cysts. Cancer Cytopathol 2013; 121: 57-60. PubMed
- 26. Jones M, Zheng Z, Wang J, et al. Impact of next-generation sequencing on the clinical impression of pancreatic cysts. Gastrointest Endosc 2015 Aug 5 [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2015.06.047.
- 27. Cizginer S, Turner BG, Bilge AR, Karaca C, Pitman MB, Brugge WR. Cyst fluid carcinoembryonic antigen is an accurate diagnostic marker of pancreatic mucinous cysts. Pancreas 2011; 40: 1024-8. ArticlePubMed
- 28. Brugge WR, Lewandrowski K, Lee-Lewandrowski E, et al. Diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms: a report of the cooperative pancreatic cyst study. Gastroenterology 2004; 126: 1330-6. ArticlePubMed
- 29. van der Waaij LA, van Dullemen HM, Porte RJ. Cyst fluid analysis in the differential diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions: a pooled analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2005; 62: 383-9. ArticlePubMed
- 30. Raval JS, Zeh HJ, Moser AJ, et al. Pancreatic lymphoepithelial cysts express CEA and can contain mucous cells: potential pitfalls in the preoperative diagnosis. Mod Pathol 2010; 23: 1467-76. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 31. Johnston J, Wheatley GH 3rd, El Sayed HF, Marsh WB, Ellison EC, Bloomston M. Gastric duplication cysts expressing carcinoembryonic antigen mimicking cystic pancreatic neoplasms in two adults. Am Surg 2008; 74: 91-4. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 32. Lewandrowski KB, Southern JF, Pins MR, Compton CC, Warshaw AL. Cyst fluid analysis in the differential diagnosis of pancreatic cysts. A comparison of pseudocysts, serous cystadenomas, mucinous cystic neoplasms, and mucinous cystadenocarcinoma. Ann Surg 1993; 217: 41-7. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Moparty B, Pitman MB, Brugge WR. Pancreatic cyst fluid amylase is not a marker to differentiate IPMN from MCN. Gastrointest Endosc 2007; 65: AB303.Article
- 34. Khalid A, Zahid M, Finkelstein SD, et al. Pancreatic cyst fluid DNA analysis in evaluating pancreatic cysts: a report of the PANDA study. Gastrointest Endosc 2009; 69: 1095-102. ArticlePubMed
- 35. Shen J, Brugge WR, Dimaio CJ, Pitman MB. Molecular analysis of pancreatic cyst fluid: a comparative analysis with current practice of diagnosis. Cancer 2009; 117: 217-27. PubMed
- 36. Wu J, Matthaei H, Maitra A, et al. Recurrent GNAS mutations define an unexpected pathway for pancreatic cyst development. Sci Transl Med 2011; 3: 92ra66.Article
- 37. Nikiforova MN, Khalid A, Fasanella KE, et al. Integration of KRAS testing in the diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions: a clinical experience of 618 pancreatic cysts. Mod Pathol 2013; 26: 1478-87. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 38. Amato E, Molin MD, Mafficini A, et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing of cancer genes dissects the molecular profiles of intraductal papillary neoplasms of the pancreas. J Pathol 2014; 233: 217-27. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 39. Hruban RH, Goggins M, Parsons J, Kern SE. Progression model for pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6: 2969-72. PubMed
- 40. Finkelstein SD, Bibbo M, Loren DE, et al. Molecular analysis of centrifugation supernatant fluid from pancreaticobiliary duct samples can improve cancer detection. Acta Cytol 2012; 56: 439-47. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 41. Wu J, Jiao Y, Dal Molin M, et al. Whole-exome sequencing of neoplastic cysts of the pancreas reveals recurrent mutations in components of ubiquitin-dependent pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011; 108: 21188-93. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Pitman MB, Centeno BA, Ali SZ, et al. Standardized terminology and nomenclature for pancreatobiliary cytology: The Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology Guidelines. Cytojournal 2014; 11(Suppl 1): 3.Article
- 43. Kuo EJ, Salem RR. Population-level analysis of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors 2 cm or less in size. Ann Surg Oncol 2013; 20: 2815-21. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 44. Klimstra DS. Pathology reporting of neuroendocrine tumors: essential elements for accurate diagnosis, classification, and staging. Semin Oncol 2013; 40: 23-36. ArticlePubMed
- 45. Kloppel G, Hruban R, Klimstra D, et al. Solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas. In: Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND, eds. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. 4th ed. Sterling: Stylus Publishing, 2010; 327-30.
- 46. Pitman MB, Centeno BA, Daglilar ES, Brugge WR, Mino-Kenudson M. Cytological criteria of high-grade epithelial atypia in the cyst fluid of pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Cancer Cytopathol 2014; 122: 40-7. ArticlePubMed
- 47. Pitman MB, Centeno BA, Genevay M, Fonseca R, Mino-Kenudson M. Grading epithelial atypia in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fineneedle aspiration of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: an international interobserver concordance study. Cancer Cytopathol 2013; 121: 729-36. ArticlePubMed
- 48. Pitman MB, Genevay M, Yaeger K, et al. High-grade atypical epithelial cells in pancreatic mucinous cysts are a more accurate predictor of malignancy than “positive” cytology. Cancer Cytopathol 2010; 118: 434-40. ArticlePubMed
- 49. Pitman MB, Lewandrowski K, Shen J, Sahani D, Brugge W, Fernandez-del Castillo C. Pancreatic cysts: preoperative diagnosis and clinical management. Cancer Cytopathol 2010; 118: 1-13. PubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue sampling: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technical and Technology Review
Antonio Facciorusso, Marianna Arvanitakis, Stefano Francesco Crinò, Carlo Fabbri, Adele Fornelli, John Leeds, Livia Archibugi, Silvia Carrara, Jahnvi Dhar, Paraskevas Gkolfakis, Beate Haugk, Julio Iglesias Garcia, Bertrand Napoleon, Ioannis S. Papanikolao
Endoscopy.2025; 57(04): 390. CrossRef - Imaging of pancreatic serous cystadenoma and common imitators
Camila Lopes Vendrami, Nancy A. Hammond, David J. Escobar, Zachary Zilber, Meaghan Dwyer, Courtney C. Moreno, Pardeep K. Mittal, Frank H. Miller
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 49(10): 3666. CrossRef - “Evolving Trends in Pancreatic Cystic Tumors: A 3-Decade Single-Center Experience With 1290 Resections”
Jorge Roldán, Jon M. Harrison, Motaz Qadan, Louisa Bolm, Taisuke Baba, William R. Brugge, Brenna W. Casey, Kumar Krishnan, Mari Mino-Kenudson, Martha B. Pitman, Avinash Kambadakone, Cristina R. Ferrone, Andrew L. Warshaw, Keith D. Lillemoe, Carlos Fernánd
Annals of Surgery.2023; 277(3): 491. CrossRef - Role of fluorescence confocal microscopy for rapid evaluation of EUS fine-needle biopsy sampling in pancreatic solid lesions
Serena Stigliano, Anna Crescenzi, Chiara Taffon, Francesco Covotta, Cesare Hassan, Giulio Antonelli, Martina Verri, Dario Biasutto, Roberto Mario Scarpa, Francesco Maria Di Matteo
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2021; 94(3): 562. CrossRef - Towards optimal pancreatic cyst fluid management: the need for standardisation
Giacomo Puppa, Yann Christinat, Thomas Alexander McKee
Gut.2019; 68(10): 1906. CrossRef - It is necessary to exam bottom and top slide smears of EUS-FNA for pancreatic cancer
Jong-chan Lee, Haeryoung Kim, Hyoung Woo Kim, Jongchan Lee, Kyu-hyun Paik, Jingu Kang, Jin-Hyeok Hwang, Jaihwan Kim
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2018; 17(6): 553. CrossRef - Rationale and feasibility of mucin expression profiling by qRT-PCR as diagnostic biomarkers in cytology specimens of pancreatic cancer
Milosz Wiktorowicz, Damian Mlynarski, Radoslaw Pach, Romana Tomaszewska, Jan Kulig, Piotr Richter, Marek Sierzega
Pancreatology.2018; 18(8): 977. CrossRef - Variations in cancer centers’ use of cytology for the diagnosis of unresectable pancreatic cancer in the National Cancer Data Base
Ted Gansler, Stacey A. Fedewa, Chun Chieh Lin, Ahmedin Jemal, Elizabeth M. Ward
Cancer Cytopathology.2016; 124(11): 791. CrossRef - Pancreatic Cytopathology
Jennifer A. Collins, Syed Z. Ali, Christopher J. VandenBussche
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2016; 9(4): 661. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure




Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 4.
| Genetic change | Associated lesions |
|---|---|
| KRAS mutation | IPMN, MCN, and PanIN, all grades |
| GNAS mutation | IPMN, all grades |
| RNF43 mutation | IPMN and MCN, all grades |
| P16/CDKN2A loss | IPMN, MCN, and PanIN, all grades |
| TP53 mutation | IPMN, MCN, and PanIN, high-grade |
| SMAD4 loss | IPMN, MCN, and PanIN, high-grade |
| VHL mutation | Serous cystadenoma |
| CTNNB1 mutation | Solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm |
| I. Nondiagnostic |
| II. Negative (for malignancy) |
| III. Atypical |
| IV. Neoplastic |
| A. Benign |
| Serous cystadenoma |
| Neuroendocrine microadenoma |
| Lymphangioma |
| B. Other |
| Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (low, intermediate and high-grade dysplasia) |
| Mucinous cystic neoplasm (low, intermediate and high-grade dysplasia) |
| Well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor |
| Solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm |
| V. Suspicious (for malignancy) |
| VI. Positive/Malignant |
| Ductal adenocarcinoma and variants |
| High-grade (G3) neuroendocrine carcinoma |
| Acinar cell carcinoma |
| Pancreatoblastoma |
| Lymphoma |
| Metastases |
IPMN, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; MCN, mucinous cystic neoplasm; PanIN, pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia.

 E-submission
E-submission






