Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 50(6); 2016 > Article
-
Review
Immunohistochemistry for Pathologists: Protocols, Pitfalls, and Tips - So-Woon Kim, Jin Roh, Chan-Sik Park,
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2016;50(6):411-418.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.08.08
Published online: October 13, 2016
Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, 88 Olympic-ro, 43-gil, Songpa-gu, Seoul 05505, Korea
- Corresponding Author Chan-Sik Park, MD Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, 88 Olympic-ro, 43-gil, Songpa-gu, Seoul 05505, Korea Tel: +82-2-3010-5838 Fax: +82-2-472-7898 E-mail: csikpark@amc.seoul.kr
© 2016 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is an important auxiliary method for pathologists in routine diagnostic work as well as in basic and clinical research including exploration of biomarkers, as IHC allows confirmation of target molecule expressions in the context of microenvironment. Although there has been a considerable progress in automation and standardization of IHC, there are still many things to be considered in proper optimization and appropriate interpretation. In this review, we aim to provide possible pitfalls and useful tips for practicing pathologists and residents in pathology training. First, general procedure of IHC is summarized, followed by pitfalls and tips in each step and a summary of troubleshooting. Second, ways to an accurate interpretation of IHC are discussed, with introduction to general quantification and analysis methods. This review is not intended to provide complete information on IHC, but to be used as a basic reference for practice and publication.
- There are many critical steps in performing IHC. These include proper handling of the specimen, appropriate fixation, paraffin block preparation, antigen retrieval, selection and preparation of antibody and reagents, incubation, washing, and counterstaining [2]. The advent of automated IHC machines has improved reliability and reproducibility of IHC, particularly in clinical setting [3]. On the other hand, manual staining method still offers more flexibility, allowing for optimization of a specific antigen-antibody reaction, and hence better results, particularly in research setting. Both methods have pros and cons, but basic principles and procedures remain the same. Overall procedure of IHC is summarized in Table 1. Basic principles of each step will follow with practical pitfalls and tips.
- Tissue handling and fixation
- Ischemia of the resected specimen before fixation results in degradation of protein, RNA, and DNA as well as activation of tissue enzymes and autolysis [4]. Therefore, variation in ischemic time can be a crucial factor affecting IHC results. Alteration in the results of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, human epidermal growth factor 2, and Ki-67 IHC due to variable ischemic times has been reported [5,6]. Fixation is another important cause of variation in the reproducibility of IHC [7]. Surgical specimens are fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin (NBF). This process prevents autolysis and preserves tissue and cellular morphology. For most tissues, fixation for 24 hours in room temperature is recommended. The appropriate tissue to fixative ratio is 1:1 to 1:20. Duration of fixation, fixative formula, and tissue to fixative ratio can affect the extent and intensity of IHC [8,9]. Fixation is also required in frozen sections in certain situations such as evaluating new antibodies. In those cases, acetone- or NBF-fixed frozen sections can be used.
- Some antigens including Ki-67 and phosphoproteins are more vulnerable to ischemia. Overfixation can cause irreversible damage to some epitopes. To avoid ischemic or cold effect resulting in degeneration of protein or tissue enzymes, rapid fixation is important. When using non-additive fixatives such as acetone, the target antigen will normally be fully available, but with compromised morphology. Soluble antigen may be diffused out during the process of IHC if the frozen section is not fixed.
- Sectioning and storage
- The recommended thickness of tissue section for IHC is mostly 4 μm, but it is optional depending on the purpose. Storage of tissue sections may have influence on the results of IHC [10]; storing tissue sections for more than 2 months results in loss of p53 [11]. The mechanism of this epitope degradation is unclear, but water component in and around the tissue sections may cause the antigenic loss [12]. Slide storage conditions that are protected from oxidization by vacuum storage or paraffin coating are important as well as complete removal of water in the slide.
- Thick tissue sections can produce higher background signals as can frozen sections; frozen sections tend to preserve more adhesive molecules, Fc receptors, peroxidase, etc. Soluble antigen may be diffused out during the process of IHC if the frozen section is not fixed. IHC should be done with freshly cut sections.
- Antigen (or epitope) retrieval
- Antibody binding epitopes can be masked in formaldehyde-based fixation due to cross-linkings of amino groups on adjacent molecules, in addition to the formation of methylene bridges [13].
- For this reason, antigen retrieval, an additional step to unmask the epitope, is sometimes required. Optimized antigen retrieval can restore antigenicity to that of frozen sections; thus, antigen retrieval is crucial for IHC standardization for which issues of variations in fixation and handling of specimens must be overcome [14]. In general, antigen retrieval process is not necessary for frozen sections. However, sometimes acetone- and NBF-fixed frozen sections are required to prevent wash out of target antigen, particularly for soluble antigens. In that case, antigen retrieval may serve for better IHC signals.
- The heat induced epitope retrieval (HIER) is the most widely used method for antigen retrieval. Various methods can be used for application of heat: microwave ovens, heating plate, pressure cookers, autoclaves, and water baths in varying conditions including pH 6–10. Generally, using autoclave and microwave oven, the temperature is set at 120°C at full pressure and 750–800 W, respectively and typically for 10 minutes. Using heating plate, incubate at 100°C for 30 mitutes. The best retrieval condition for each Ag-Ab pair needs to be determined empirically through comparison of staining results by various retrieval methods. In addition, enzymatic retrieval is used for limited antigens such as some cytokeratins and immunoglobulins. In such cases, tissue sections are incubated in either trypsin or proteinase for 10–20 minutes at 37°C. Then, terminate the reaction by adding phosphate buffered saline (PBS). However, this method is much more difficult to control.
- Excessive tissue microwaving can destroy antigenicity and morphology. It may result in HIER lipofuscin artifacts. When using HIER, “microwave burn” pattern in loose connective tissue and fat can be identified. The appropriate antigen retrieval is different from antigen to antigen, and antibody to antibody. It should be determined individually for each antigen and antibody. Also, try enzymatic retrieval or no retrieval in addition to HIER at the initial step.
- Protein blocking
- Protein blocking step is required to reduce unwanted background staining. A main cause for the background signal is the nonspecific binding of Fc portion of primary or secondary antibodies. An ideal agent for the protein blocking is 5%–10% normal serum from the same species of secondary antibody. Other agents include protein buffers such as 0.1%–0.5% bovine serum albumin, gelatin, or nonfat dry milk [15]. Recently commercial mixes of synthetic peptides are also being widely used. Incubation time for the blocking step can vary from 30 minutes to overnight. Incubation temperatures also vary from 4°C to room temperature.
- Sufficient washing after the blocking step is critical to remove excess protein that may prevent detection of the target antigen. Choose blocking buffer that yields the highest signal to noise ratio. Nonfat dry milk contains biotin and is inappropriate for use with an avidin-biotin complex system. When using frozen sections, smears and lightly fixed tissues, background staining due to Fc receptor is more prevalent than formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections. Furthermore, it is important to control Fc receptor rich specimens such as lymphoid sections, tonsil sections, and bone marrow preparations. It can be avoided by using either Fc receptor blocking or F(ab’)2 fragments of primary staining antibody instead of whole IgG molecules.
- Endogenous enzyme blocking
- When using peroxidase antiperoxidase system in detection step, blocking of endogenous peroxidase activity is indispensable. Diluted hydrogen peroxide as 3% is widely used for blocking endogenous peroxidase activity [16]. Upon completion of the IHC stain, eosinophils and erythrocytes are used as an index to see whether the blocking step has been adequate or not. Similarly, endogenous alkaline phosphatase (AP), which is prevalent in frozen tissue, should be blocked with levamisol at a concentration of 10 mM [17]. The endogenous biotin in tissues is another issue. Although the level of endogenous biotin has been shown to be much lower in formalin fixation and paraffin embedding, residual activity can still be detected, especially in biotin-rich tissues such as liver and kidney. Endogenous biotin can be blocked by incubating tissue section in avidin solution beforehand (incubate sections in avidin solution for 15 minutes followed by brief rinse in PBS, and then incubate sections in biotin solution for 15 minutes, all at room temperature).
- Tissues with high blood content (e.g., site of heavy hemorrhage), or with intense granulocytic inflammatory infiltrate, need a strong suppression of endogenous peroxidase activity. Some antigen (such as CD4) can be destroyed by 3% H2O2. In this case, an H2O2 concentration as low as 0.5% is recommended [18].
- Antibody selection and validation
- Before performing IHC, a selection of suitable antibody is critical, for which understanding of the target through thorough literature review is the first step. If there are reports of the target molecules using IHC, then the antibody used in the previous reports should be evaluated first. Antibodies used in researches are generally divided into three types with respect to the validity and reliability: well-known antibody with high quality literature evidence, well-known antibody used in alternative species or unverified tissues, and unknown antibody with inconsistent or no literature evidence [2]. Researchers should perform an adequate level of validation depending on the kind of antibody used [19]. Detailed guidance for validating antibody is well summarized in the review article [2].
- Antibodies are generally divided into two categories. Polyclonal antibodies are obtained from experimental animals through repetitive stimulation of antigen. These antibodies bind to multiple different epitopes in a single antigen. On the other hand, monoclonal antibodies react to a single epitope in an antigen. They are obtained from a single clone of hybridoma, which produces antibodies. Both polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies have advantages and disadvantages, respectively (Table 2). Recently, monoclonal antibodies from rabbit or chicken have been introduced. These antibodies may give a better IHC results for antigens that are difficult to stain.
- When an unknown antibody is validated, it is important to select proper positive and negative control tissues. Interpretation of IHC stain pattern in control tissues should be done carefully. Appropriate location, intensity, and signal/noise ratio are determined in this step. Validation of the antibody by non-IHC methods such as western blotting or flow cytometry is also recommended. Afterward, optimization is necessary to tune antibody dilution, incubation times, and blocking for controlled laboratory conditions. Appropriate validation and optimization of IHC staining method can provide equivalent results between laboratories.
- The biologic characteristics and amount of the antigen in the tissue, titration of the antibody, and differences between control and testing samples should be carefully considered. Use the same tissue that was used for optimization or validation for testing IHC. Perform IHC with negative control Ab to disclose any background staining. Competition assay with the immunizing peptide on the optimizing sample is essential if the validation level of the antibody is low (see competition protocol in the study of Prioleau and Schnitt [11]) [20].
- Detection system
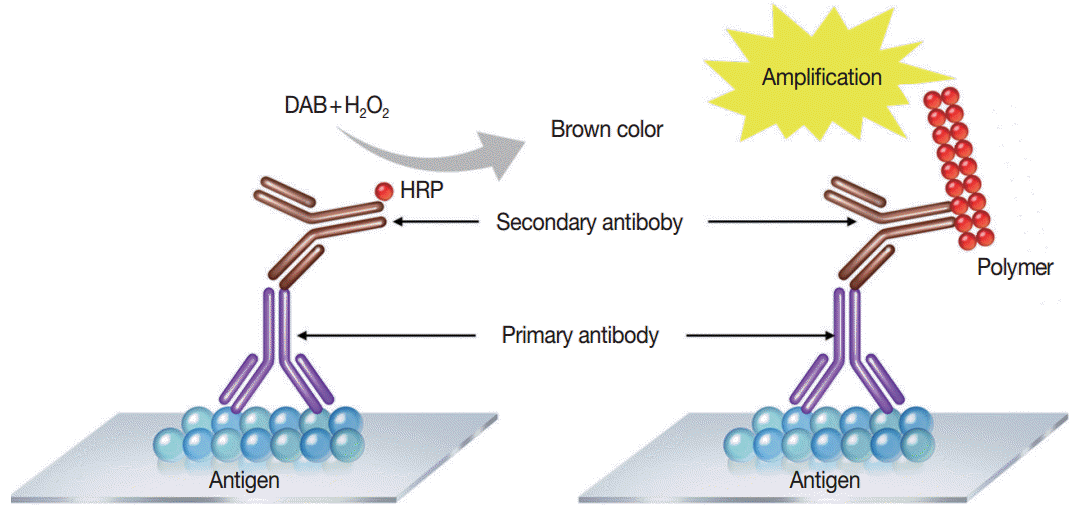
- Immunostaining is the process of detecting specific antigenantibody interaction, and indirect method using secondary antibodies tagged with various labels such as enzymes is commonly used [5]. Commonly used detection systems are as follows: avidinbiotin complex method, labeled streptavidin biotin method, phosphatase anti-phosphatase method, polymer-based detection system (Fig. 1), and tyramine amplification system. In comparison to the standard IHC methods, polymeric and tyramine-based amplification methods have typically increased sensitivity by at least 50-fold or greater. The outcome of an IHC depends on the selection of the optimal methods for signal amplification for the molecule of interest and surrounding tissues [21].
- Another important issue is the use of manual IHC versus automated IHC machines. Automated IHC machine has greatly improved reproducibility and reliability of IHC. However, the automated system does not allow subtle optimization or flexibility in the usage of reagent or retrieval methods. There are advantages and disadvantages.
- When more sensitive methods are used, background signal tends to increase along with the target signal. Use automated IHC machine if a large number of samples are tested, or if the samples are tested over a longer time. AP-based detection system is preferred for tissues rich in endogenous peroxidase, such as bone marrow or lymphoid tissue. Likewise, peroxidase based-detection system may be used for tissues containing many endogenous APs but the enzyme can be easily destroyed by high-temperature antigen retrieval. Biotin-free synthetic polymer system is recommended for tissues with high endogenous biotin such as liver and kidney.
- Several different chromogens are available according to the type of tissue or counterstain. In general, diaminobenzidine (brown) or 3-amino-9-ethyl carbazole-red are routinely used for peroxidase. The choice depends on the type of tissue or counterstain.
- Counter staining
- Counter staining provides contrast to the chromogens for better discrimination of the target signal. In addition, it has a more important role, particularly for pathologists, as it allows researchers to identify the cell type and exact localization of the immunopositives. Hematoxylin is the most commonly used counterstain, although various colors are now being used as techniques of multiplex IHC progress [22]. In the process of multiplex IHC, counterstain should be selected carefully. The most commonly used counterstains are shown in Table 3.
- Troubleshooting
- There are many possible causes for poor staining results, which can be any of the following: weak or absent staining, unwanted background staining, or artifactual staining. Table 4 shows possible situations and solutions that are useful in trouble-shooting [23].
PROCEDURES OF IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY
Pitfalls and tips
Pitfalls and tips
Pitfalls and tips
Pitfalls and tips
Pitfalls and tips
Pitfalls and tips
Pitfalls and tips
- To analyze the IHC data, including diagnostic value of certain molecular expression and prognostic relationship of the biomarkers, results of the IHC should be expressed in numerical values for statistical analysis. In this section, several quantification methods that are widely used are reviewed.
- Assessment of the proportion of immunopositive cells
- In evaluating IHC results, researchers commonly assess the relative percentage of immunopositive cells in relation to the total number of target cells. Each value is usually recorded as a numerical score in every 10% (0, 0%–9%; 1, 10%–19%; 2, 20%–29%; 3, 30%–39%; 4, 40%–49%; 5, 50%–59%; 6, 60%–69%; 7, 70%–79%; 8, 80%–89%; and 9, 90%–100%). This method has a limitation that it does not show the intensity of the IHC staining, resulting in the lack of information regarding the subtle difference in protein expression level. However, it can preclude the interpretational error resulting from inappropriate variation in staining intensity between cases due to differences in tissue status in a large-scale study and among applied batches especially in manual staining.
- Combinative semiquantitative scoring
- Combinative semiquantitative scoring is the most commonly used method in the current prognostic biomarker researches, yielding immunoscores that incorporate both quantitative and qualitative assessments. In addition to the quantitative data from the assessment of relative percentage of immunopositive cells as previously described, intensity of the staining is also evaluated. The intensity is commonly scored from 0 to 3 (0, negative; 1+, weak positive; 2+, moderate positive; and 3+, strong positive). The final immunoscore is calculated by adding or multiplying each score. The Allred score used in breast cancer is one of the best-known combinative scoring systems [24].
- Although researchers can evaluate the IHC results both quantitatively and qualitatively with this method, too many variations can be created according to the combinations, resulting in different interpretations between researchers. Four or five score levels in average are recommended for the best sensitivity and reproducibility of the scoring system [25,26].
- Quantification using spectral image analysis
- As multiplex IHC develops, analysis for multicolor stained specimen is essential. Usual semiquantitative scoring is not appropriate in the analysis of multiplex IHC due to a massive amount of information in a single slide. Thus, the use of spectral image analysis is increasing for the interpretation of multiplex IHC. In spectral unmixing, the optical signal from each chromogen can be isolated and assessed separately and quantitatively [18].
QUANTIFICATION OF THE DATA
- After quantitative analysis of the IHC results, the continuous variables are usually changed into categorical forms, as it is much easier to analyze and make decisions [20].
- The categorization of variables also enables clinicians to stratify patients according to the IHC results of the testing molecules. Cut-off values for immunopositivity are commonly selected by the median and the quartiles of measurements. However, sometimes simply more than 5% or 10% criteria are used. There is no standardized method for setting the cut-off value for the categorization. This lack of standardization sometimes causes inconsistent results between similar studies. Pathologists should be cautious when comparing IHC data between studies. To resolve these problems, there have been many efforts to establish reasonable ways to determine cut-off points. In this section, we introduce two statistical methods that are being frequently used.
- Minimum p-value approaches (maximally selected chi-square statistics)
- By this method, investigators can search cut-off points in a systematic manner. It means that all measured values are analyzed as provisional cut-offs at first. Afterward, the value that has a maximum chi-squared statistic, minimum p-value, or maximum relative risk is selected. However, this method has a demerit of multiple testing. The p-value obtained from this method should be adjusted to offset the effect of multiple testing. In addition, specific statistics software such as SAS (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) or R software is required for this method.
- Application of receiver operating characteristic curves
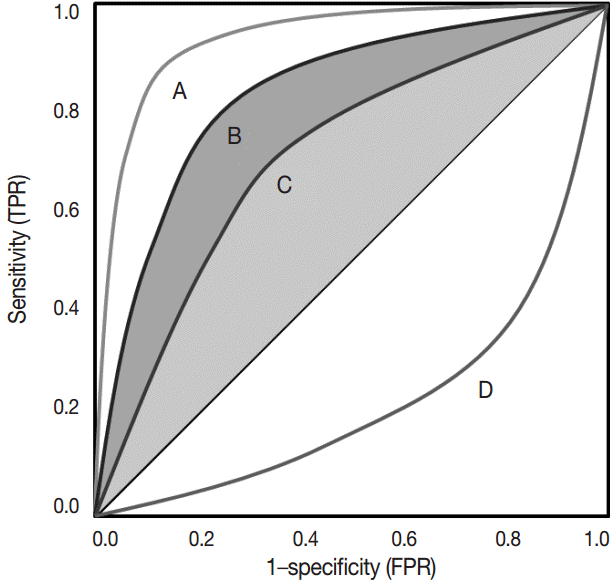
- Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis is another useful method for evaluating the prognostic relevance of biomarkers [24]. ROC curves have been widely used in clinical oncology for evaluation and comparison of the sensitivity and specificity of the diagnostic tests regarding the binary outcomes [27,28]. Recently, it has been increasingly used in the field of pathology research to determine cut-off scores in many cancers [29,30].
- The ROC curve was initially developed to display signal-to-noise ratios. Basically, it is a plot of the ratio between the true positivity (sensitivity) and the false-positivity (1–sensitivity) (Fig. 2). In the ideal test, the ROC curve meets the upper left-hand corner. The diagonal reference line represents whether a test is positive or negative by chance. Performance of the test is quantified as a value of the area under the curve (AUROC). The better performance the test has, the closer to 1 the value of the AUROC is. Researchers can deduce specific cut-offs using various statistical methods. There are some pitfalls. Firstly, ROC curve analysis has to be applied in a test that has a gold standard. If the gold standard is uncertain, the entire interpretation of the results can become dubious.
- Secondly, the cut-offs drawn from the ROC curves do not consider time or censoring of the data. Simply dichotomizing as “alive/censored” or “death” regardless of the follow-up time can be suboptimal in the prognostic research. To overcome this short-coming, additional tests such as Kaplan-Meier survival analysis can be applied.
ANALYSIS OF THE DATA
- IHC has become an indispensible tool for pathologists in both everyday practice and basic research for elucidating pathophysiology of the diseases. In conjunction with this, IHC is also an indispensable tool for validation in biomarker discovery that will eventually lead to a personalized medicine [31]. Even though IHC procedure has recently been automated and standardized, there are many things to be considered to optimize IHC properly and interpret appropriately. Optimization of IHC is particularly important for newly discovered molecules or new antibodies. Specificity and sensitivity of the IHC need to be validated. It is strongly recommended to review a full literature of the target molecule before starting IHC experiment [2]. Interpretation of IHC also needs to be carefully planned. Consideration for stabilizing interobserver consistency and objectifying interpretation of IHC results is crucial. In this review, we attempted to provide basic principles and practical tips for practicing pathologists and residents in pathology training.
CONCLUSION
- 1. Schacht V, Kern JS. Basics of immunohistochemistry. J Invest Dermatol 2015; 135: e30. Article
- 2. O’Hurley G, Sjostedt E, Rahman A, et al. Garbage in, garbage out: a critical evaluation of strategies used for validation of immunohistochemical biomarkers. Mol Oncol 2014; 8: 783-98. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 3. Gustavson MD, Bourke-Martin B, Reilly D, et al. Standardization of HER2 immunohistochemistry in breast cancer by automated quantitative analysis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009; 133: 1413-9. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N. Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2005.
- 5. Pekmezci M, Szpaderska A, Osipo C, Ers¸ahin Ç. The Effect of cold ischemia time and/or formalin fixation on estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 results in breast carcinoma. Patholog Res Int 2012; 2012: 947041.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 6. Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007; 131: 18-43. PubMed
- 7. Cross SS, Start RD, Smith JH. Does delay in fixation affect the number of mitotic figures in processed tissue? J Clin Pathol 1990; 43: 597-9. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Engel KB, Moore HM. Effects of preanalytical variables on the detection of proteins by immunohistochemistry in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2011; 135: 537-43. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 9. Grizzle WE. Special symposium: fixation and tissue processing models. Biotech Histochem 2009; 84: 185-93. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Wester K, Wahlund E, Sundström C, et al. Paraffin section storage and immunohistochemistry: effects of time, temperature, fixation, and retrieval protocol with emphasis on p53 protein and MIB1 antigen. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2000; 8: 61-70. PubMed
- 11. Prioleau J, Schnitt SJ. p53 antigen loss in stored paraffin slides. N Engl J Med 1995; 332: 1521-2. Article
- 12. Xie R, Chung JY, Ylaya K, et al. Factors influencing the degradation of archival formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem 2011; 59: 356-65. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 13. Fox CH, Johnson FB, Whiting J, Roller PP. Formaldehyde fixation. J Histochem Cytochem 1985; 33: 845-53. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Shi SR, Liu C, Taylor CR. Standardization of immunohistochemistry for formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections based on the antigen-retrieval technique: from experiments to hypothesis. J Histochem Cytochem 2007; 55: 105-9. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Vogt RF Jr, Phillips DL, Henderson LO, Whitfield W, Spierto FW. Quantitative differences among various proteins as blocking agents for ELISA microtiter plates. J Immunol Methods 1987; 101: 43-50. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Radulescu RT, Boenisch T. Blocking endogenous peroxidases: a cautionary note for immunohistochemistry. J Cell Mol Med 2007; 11: 1419.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Garba MT, Marie PJ. Alkaline phosphatase inhibition by levamisole prevents 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-stimulated bone mineralization in the mouse. Calcif Tissue Int 1986; 38: 296-302. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. Taylor CR, Levenson RM. Quantification of immunohistochemistry: issues concerning methods, utility and semiquantitative assessment II. Histopathology 2006; 49: 411-24. ArticlePubMed
- 19. Skliris GP, Rowan BG, Al-Dhaheri M, et al. Immunohistochemical validation of multiple phospho-specific epitopes for estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) in tissue microarrays of ERalpha positive human breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2009; 118: 443-53. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 20. Mazumdar M, Glassman JR. Categorizing a prognostic variable: review of methods, code for easy implementation and applications to decision-making about cancer treatments. Stat Med 2000; 19: 113-32. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Hou L, Tang Y, Xu M, Gao Z, Tang D. Tyramine-based enzymatic conjugate repeats for ultrasensitive immunoassay accompanying tyramine signal amplification with enzymatic biocatalytic precipitation. Anal Chem 2014; 86: 8352-8. ArticlePubMed
- 22. Stefanovic´ D, Stefanovic´ M, Nikin Z. Romanowsky-Giemsa as a counterstain for immunohistochemistry: optimizing a traditional reagent. Biotech Histochem 2013; 88: 329-35. ArticlePubMed
- 23. Dabbs DJ. Diagnostic immunohistochemistry: theranostic and genomic applications. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2014.
- 24. Tzankov A, Zlobec I, Went P, Robl H, Hoeller S, Dirnhofer S. Prognostic immunophenotypic biomarker studies in diffuse large B cell lymphoma with special emphasis on rational determination of cut-off scores. Leuk Lymphoma 2010; 51: 199-212. ArticlePubMed
- 25. Shackelford C, Long G, Wolf J, Okerberg C, Herbert R. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of nonneoplastic lesions in toxicology studies. Toxicol Pathol 2002; 30: 93-6. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Thoolen B, Maronpot RR, Harada T, et al. Proliferative and nonproliferative lesions of the rat and mouse hepatobiliary system. Toxicol Pathol 2010; 38(7 suppl):5S-81S. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. Hanley JA. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) methodology: the state of the art. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging 1989; 29: 307-35. PubMed
- 28. Lusted LB. Signal detectability and medical decision-making. Science 1971; 171: 1217-9. ArticlePubMed
- 29. Søreide K. Receiver-operating characteristic curve analysis in diagnostic, prognostic and predictive biomarker research. J Clin Pathol 2009; 62: 1-5. ArticlePubMed
- 30. Zlobec I, Steele R, Terracciano L, Jass JR, Lugli A. Selecting immunohistochemical cut-off scores for novel biomarkers of progression and survival in colorectal cancer. J Clin Pathol 2007; 60: 1112-6. ArticlePubMed
- 31. Yaziji H, Barry T. Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry: what can go wrong? Adv Anat Pathol 2006; 13: 238-46. ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- A best practices framework for spatial biology studies in drug discovery and development: enabling successful cohort studies using digital spatial profiling
David Krull, Premi Haynes, Anil Kesarwani, Julien Tessier, Benjamin J. Chen, Kelly Hunter, Deniliz Rodriguez, Yan Liang, Jim Mansfield, Maxine McClain, Corinne Ramos, Edward Bonnevie, Esperanza Anguiano
Journal of Histotechnology.2025; 48(1): 7. CrossRef - Inhibition of ACSS2 triggers glycolysis inhibition and nuclear translocation to activate SIRT1/ATG5/ATG2B deacetylation axis, promoting autophagy and reducing malignancy and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
Jiang Yang, Haoyu Wang, Bingshu Li, Jingchun Liu, Xiaoyi Zhang, Ying Wang, Jiaxin Peng, Likun Gao, Xinqi Wang, Siyuan Hu, Wenyi Zhang, Li Hong
Metabolism.2025; 162: 156041. CrossRef - AXL/GAS6 signaling governs differentiation of tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer
Suman Purohit, Gunjan Mandal, Subir Biswas, Shauryabrota Dalui, Arnab Gupta, Sougata Roy Chowdhury, Arindam Bhattacharyya
Experimental Cell Research.2025; 444(1): 114324. CrossRef - Gold nanoprism enhanced SERS aptasensor for simultaneous detection of thrombin and VEGF
Pooja Anantha, Piyush Raj, Peng Zheng, Swati Tanwar, Ishan Barman
Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical.2025; 423: 136811. CrossRef - Exploring the Zein/58S Bioactive Glass Nanocomposite for Enhanced Bone Tissue Engineering: A Comprehensive Investigation of Structural, Chemical, Biological, and Osteogenic Properties through in Vitro and in Vivo Studies
Faezeh Esmaeili Ranjbar, Sanam Mohandesnezhad, Mohamad Javad Mirzaei-Parsa, Fatemeh Asadi, Samalireza Divanpour, Mojgan Noroozi Karimabad, Mahboubeh Vatanparast, Mohammad Reza Mirzaei, Gholamhossein Hassanshahi, Lobat Tayebi, Afsaneh Esmaeili Ranjbar
Journal of Polymers and the Environment.2025; 33(1): 462. CrossRef - Brief guide to immunostaining
Gyutae Park, Sieun S. Kim, Jiwon Shim, Seung-Jae V. Lee
Molecules and Cells.2025; 48(1): 100157. CrossRef - Phosphoproteomics guides low dose drug combination of cisplatin and silmitasertib against concurrent chemoradiation resistant cervical cancer
Irene A. George, Janani Sambath, R. E. Dhawale, Manisha Singh, Vinita Trivedi, R. Venkataramanan, Richa Chauhan, Prashant Kumar
Molecular Omics.2025; 21(1): 87. CrossRef - Biarsenical-based fluorescent labeling of metallothioneins as a method for ultrasensitive quantification of poly-Cys targets
Adam Pomorski, Sylwia Wu, Michał Tracz, Alicja Orzeł, Jaroslava Bezdekova, Agata Brambor, Aleksandra Suszyńska, Katarzyna Piekarowicz, Markéta Vaculovičová, Artur Krężel
Analytica Chimica Acta.2025; 1337: 343550. CrossRef - Disrupted methionine cycle triggers muscle atrophy in cancer cachexia through epigenetic regulation of REDD1
Kai Lin, Lulu Wei, Ranran Wang, Li Li, Shiyu Song, Fei Wang, Meiwei He, Wenyuan Pu, Jinglin Wang, Junaid Wazir, Wangsen Cao, Xiaozhong Yang, Eckardt Treuter, Rongrong Fan, Yongxiang Wang, Zhiqiang Huang, Hongwei Wang
Cell Metabolism.2025; 37(2): 460. CrossRef - Sequential MALDI-HiPLEX-IHC and Untargeted Spatial Proteomics Mass Spectrometry Imaging to Detect Proteomic Alterations Associated with Tumour Infiltrating Lymphocytes
Greta Bindi, Nicole Monza, Glenda Santos de Oliveira, Vanna Denti, Farnaz Fatahian, Seyed-Mohammad Jafar Seyed-Golestan, Vincenzo L’Imperio, Fabio Pagni, Andrew Smith
Journal of Proteome Research.2025; 24(2): 871. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Exploration of Polymeric 3D Sponges for Regeneration of Bone
Bhuvaneshwari D. Patil, Kajal P. Chamate, Nikita V. Bhosale, Nutan V. Desai, Prasad V. Kadam, Avinash Sanap, Avinash Kharat, Supriya Kheur, Ravindra V. Badhe
Regenerative Engineering and Translational Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing precision cancer immunotherapy drug development, administration, and response prediction with AI-enabled Raman spectroscopy
Jay Chadokiya, Kai Chang, Saurabh Sharma, Jack Hu, Jennie R. Lill, Jennifer Dionne, Amanda Kirane
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinico‐Pathological Significance of Tumor Infiltrating Immune Cells in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma—Hope or Hype?
Rajkumar K. Seenivasagam, Ashok Singh, Vinay N. Gowda, Dharma R. Poonia, Kinjal S. Majumdar, Thaduri Abhinav, Pallvi Kaul, Achyuth Panuganti, Vikramjit S. Kailey, Rahul Kumar, Nilotpal Chowdhury
Head & Neck.2025; 47(6): 1706. CrossRef - The tumour histopathology “glossary” for AI developers
Soham Mandal, Ann-Marie Baker, Trevor A. Graham, Konstantin Bräutigam, B. F. Francis Ouellette
PLOS Computational Biology.2025; 21(1): e1012708. CrossRef - Micro Immune Response On-chip (MIRO) models the tumour-stroma interface for immunotherapy testing
Alice Perucca, Andrea Gómez Llonín, Oriol Mañé Benach, Clement Hallopeau, Elisa I. Rivas, Jenniffer Linares, Marta Garrido, Anna Sallent-Aragay, Tom Golde, Julien Colombelli, Eleni Dalaka, Judith Linacero, Marina Cazorla, Teresa Galan, Jordi Pastor Viel,
Nature Communications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Deciphering the Interplay of the PD‐L1/MALT1/miR‐200a Axis During Lung Cancer Development
Sherien M. El‐Daly, Sahar S. Abdelrahman, Mona A. El‐Bana, Yasmin Abdel‐Latif, Dalia Medhat, Safaa M. Morsy, Hanaa A. Wafay
Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor restricts development and severity of secondary lymphedema in mice
Yinan Yuan, Sidney M. Levy, Yong Qiang Yeo, Ramin Shayan, Tara Karnezis, Steven A. Stacker, Marc G. Achen
iScience.2025; 28(3): 111948. CrossRef - SpatialKNifeY (SKNY): Extending from spatial domain to surrounding area to identify microenvironment features with single-cell spatial omics data
Shunsuke A. Sakai, Ryosuke Nomura, Satoi Nagasawa, SungGi Chi, Ayako Suzuki, Yutaka Suzuki, Mitsuho Imai, Yoshiaki Nakamura, Takayuki Yoshino, Shumpei Ishikawa, Katsuya Tsuchihara, Shun-Ichiro Kageyama, Riu Yamashita, Wei Li,
PLOS Computational Biology.2025; 21(2): e1012854. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Bone Remodeling Following Compressive Force on Mandibular Condyle
Ioannis Lyros, Ioannis A. Tsolakis, Georgia Kotantoula, Konstantinos Tosios, Vilaras George, Nikolaos Nikitakis, Efstratios Ferdianakis, Theodoros Lykogeorgos, Eleni Fora, Apostolos I. Tsolakis
Biology.2025; 14(3): 228. CrossRef - Age-based changes in structure and functions of the spontaneously hypertensive rats’ heart
I.V. Kandybko, V.G. Babiychuk, L.V. Babiychuk, O.V. Kudokotseva, I.I. Lomakin
Medicine Today and Tomorrow.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of administration routes on the efficacy of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in type 2 diabetic rats
Qiqiang Tao, Youzhi Wu, Huiwen Pang, Pinglei Lv, Wenrui Li, Xuqiang Nie, Felicity Y. Han
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Neuroprotective efficacy of berberine and caffeine against rotenone‐induced neuroinflammatory and oxidative disturbances associated with Parkinson’s disease via inhibiting α-synuclein aggregation and boosting dopamine release
Tasnim S. Waheeb, Mohammad A. Abdulkader, Doaa A. Ghareeb, Mohamed E. Moustafa
Inflammopharmacology.2025; 33(4): 2129. CrossRef - Comparative profiling of surgically resected primary tumors and their lymph node metastases in small-cell lung cancer
K. Csende, B. Ferencz, K. Boettiger, M.D. Pozonec, A. Lantos, A. Ferenczy, O. Pipek, A. Solta, B. Ernhofer, V. Laszlo, E. Megyesfalvi, K. Schelch, V. Pozonec, J. Skarda, V. Skopelidou, Z. Lohinai, C. Lang, L. Horvath, K. Dezso, J. Fillinger, F. Renyi-Vamo
ESMO Open.2025; 10(4): 104514. CrossRef - Integrated workflow for analysis of immune enriched spatial proteomic data with IMmuneCite
Arianna Barbetta, Sarah Bangerth, Jason T. C. Lee, Brittany Rocque, Evanthia T. Roussos Torres, Rohit Kohli, Omid Akbari, Juliet Emamaullee
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Navigating pharmaceuticals: microfluidic devices in analytical and formulation sciences
Ankita Das, Parixit Prajapati
Discover Chemistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunomodulatory Effects of L-Arginine-Modified Silkworm Pupae Protein Enteral Nutrition on Murine Intestinal Morphology and Immunity
Rui Yuan, Tianming Wang, Linling Zhang, Lakshmi Jeevithan, Chunxiao Wang, Xiaohui Li, Wenhui Wu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(7): 3209. CrossRef - Oncogenic gene fusions in cancer: from biology to therapy
Stephen V. Liu, Misako Nagasaka, Judith Atz, Flavio Solca, Leonhard Müllauer
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Direct Expression of CPT1a Enables a High Throughput Platform for the Discovery of CPT1a Modulators
Jason Chen, Tuyen Tran, Anthony Wong, Luofei Wang, Pranavi Annaluru, Vibha Sreekanth, Samika Murthy, Laasya Munjeti, Tanya Park, Utkarsh Bhat, Glynnis Leong, Yumeng Li, Simeng Chen, Natalie Kong, Rushika Raval, Yining Xie, Shreya Somani, Aditi Manohar Bha
Applied Biosciences.2025; 4(2): 25. CrossRef - The microbial landscape of tumors: a deep dive into intratumoral microbiota
Sajjad Asgharzadeh, Maryam Pourhajibagher, Abbas Bahador
Frontiers in Microbiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Neurobehavioral effects of maternal triphenyl phosphite exposure: A comparative experimental study using the valproic acid model
Petek Bilim, Kübra Çelik, Gurur Garip, Ahmet Giray Yardımcı, Buket Şura Yardımcı, Meral Baka
Ege Tıp Dergisi.2025; 64(2): 381. CrossRef - Development of Immunostaining Protocols for 3D Visualization of Pericytes in Human Retinal Flatmounts
Noëlle Bakker, Aïcha A. Croes, Eva Prevaes, Cornelis J. F. van Noorden, Reinier O. Schlingemann, Ingeborg Klaassen
Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry.2025; 73(3-4): 147. CrossRef - Ovarian ROS-dependent IgG accumulation precedes lipofuscin deposition and follicular decline: comparative insights from the bitch and mouse models of ovarian aging
Luís Montenegro, Natália Rigos, Catarina Brandão, Anabela Pinto, Inês Borges, Luís Cardoso, Hugo Carvalho, Henrique Almeida, Ana Martins-Bessa, Elisabete Silva
Frontiers in Aging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Ferrous sulfate and lipopolysaccharide co-exposure induce neuroinflammation, neurobehavioral motor deficits, neurodegenerative and histopathological biomarkers relevant to Parkinson’s disease-like symptoms in Wistar rats
Shivam Kumar Pandey, Anjuman Nanda, Avtar Singh Gautam, Apurva Chittoda, Aman Tiwari, Rakesh Kumar Singh
BioMetals.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A cost- and time-efficient method for high-throughput cryoprocessing and tissue analysis using multiplexed tissue molds
Daniel Reumann, Martin Colombini, Paul Möseneder, Agnieszka Piszczek, Jürgen A. Knoblich
Cell Reports Methods.2025; 5(4): 101023. CrossRef - HER2 alterations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): from biology and testing to advances in treatment modalities
Ahmed Ismail, Aakash Desai, Yanis Boumber
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Toll Like Receptors in the Larynx: Implications for Laryngeal Immunology
Madhu Gowda, Anumitha Venkatraman, Alexandra Mechler‐Hickson, Vlasta Lungova, Susan L. Thibeault
The Laryngoscope.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - What spatial omics is teaching us about field cancerisation in prostate and bladder cancer
Matthew H. V. Byrne, Thineskrishna Anbarasan, Lisa Browning, Dan J. Woodcock
BJU International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - From barriers to solutions: an expert-based algorithm for cholangiocarcinoma and other biliary tract cancers testing in the Era of precision oncology
Albrecht Stenzinger, Nicola Normanno, Angela Lamarca, Lorenza Rimassa, Fréderic Bibeau, Philippe Taniere, Arndt Vogel, Antoine Hollebecque
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Fidelity of Next-Generation Sequencing to Predict Human Epidermal Growth Factor 2 Overexpression Across Solid Tumors
Mya Tran, Christopher A. Fausel, Steven Bray, Guanglong Jiang, Erica Cantor, Santosh Philips, Fei Shen, Bryan P. Schneider
JCO Precision Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Metformin on the Expression of α-7nAch Receptors in Alloxan-induced Diabetic Mouse Model: A Preliminary Study
Elham Rasheed Hameed , Muna Rasheed Hameed, Baidaa Najm Obeed
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2025; 9(1): 18. CrossRef - An Optimized Melanin Depigmentation Method for Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Staining of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues
Chia-Hsing Liu, Shu-Jyuan Chang, Sheau-Fang Yang, Min-Jan Tsai, Kun-Bow Tsai
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 32(4): 679. CrossRef - Toll-like receptors 1, 2, 4, 5, and 6 in gastric cancer
Maarit Eskuri, Niko Kemi, Olli Helminen, Heikki Huhta, Joonas H Kauppila
Virchows Archiv.2024; 485(4): 655. CrossRef - Exploring Natural Killer Cell Testing in Embryo Implantation and Reproductive Failure: An Overview of Techniques and Controversies
Juliana Peron Gothe, Amílcar Castro de Mattos, Carolina Fernanda Silveira, Kelly Cristina Malavazi
Reproductive Sciences.2024; 31(3): 603. CrossRef - Deep Learning–Based H-Score Quantification of Immunohistochemistry-Stained Images
Zhuoyu Wen, Danni Luo, Shidan Wang, Ruichen Rong, Bret M. Evers, Liwei Jia, Yisheng Fang, Elena V. Daoud, Shengjie Yang, Zifan Gu, Emily N. Arner, Cheryl M. Lewis, Luisa M. Solis Soto, Junya Fujimoto, Carmen Behrens, Ignacio I. Wistuba, Donghan M. Yang, R
Modern Pathology.2024; 37(2): 100398. CrossRef - Spatial distribution of trace metals and associated transport proteins during bacterial infection
Raquel Gonzalez de Vega, David Clases, Bliss A. Cunningham, Katherine Ganio, Stephanie L. Neville, Christopher A. McDevitt, Philip A. Doble
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.2024; 416(11): 2783. CrossRef - Advances in cellular and tissue-based imaging techniques for sarcoid granulomas
Junwoo Kim, Girish Dwivedi, Berin A. Boughton, Ankur Sharma, Silvia Lee
American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology.2024; 326(1): C10. CrossRef - Comparison of Immunohistochemistry, Next-generation Sequencing and Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization for Detection of MTAP Loss in Pleural Mesothelioma
Christopher A. Febres-Aldana, Jason C. Chang, Achim A. Jungbluth, Prasad S. Adusumilli, Francis M. Bodd, Denise Frosina, Jerica A. Geronimo, Enmily Hernandez, Helen Irawan, Michael D. Offin, Natasha Rekhtman, William D. Travis, Chad Vanderbilt, Marjorie G
Modern Pathology.2024; 37(3): 100420. CrossRef - The journey towards clinical adoption of MALDI‐MS‐based imaging proteomics: from current challenges to future expectations
Isabella Piga, Fulvio Magni, Andrew Smith
FEBS Letters.2024; 598(6): 621. CrossRef - Interpreting and integrating genomic tests results in clinical cancer care: Overview and practical guidance
Raffaella Casolino, Philip A. Beer, Debyani Chakravarty, Melissa B. Davis, Umberto Malapelle, Luca Mazzarella, Nicola Normanno, Chantal Pauli, Vivek Subbiah, Clare Turnbull, C. Benedikt Westphalen, Andrew V. Biankin
CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.2024; 74(3): 264. CrossRef - p21 as a Predictor and Prognostic Indicator of Clinical Outcome in Rectal Cancer Patients
Li Ching Ooi, Vincent Ho, Jing Zhou Zhu, Stephanie Lim, Liping Chung, Askar Abubakar, Tristan Rutland, Wei Chua, Weng Ng, Mark Lee, Matthew Morgan, Scott MacKenzie, Cheok Soon Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 725. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical characterization of integrin alfa 6 in uterus and cervix of the cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) with MfPV3 infection
Dyah Setyawaty, Silmi Mariya, Silvia A. Prabandari, Ditte Rahbaek Boilessen, Peter Johannes Holst, Huda Shalahudin Darusman
Journal of Medical Primatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Stiffness-dependent MSC homing and differentiation into CAFs – implications for breast cancer invasion
Neha Saxena, Soura Chakraborty, Sarbajeet Dutta, Garvit Bhardwaj, Nupur Karnik, Omshree Shetty, Sameer Jadhav, Hamim Zafar, Shamik Sen
Journal of Cell Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multiplex, Quantitative, High-Resolution Imaging of Protein:Protein Complexes via Hybridization Chain Reaction
Samuel J. Schulte, Boyoung Shin, Ellen V. Rothenberg, Niles A. Pierce
ACS Chemical Biology.2024; 19(2): 280. CrossRef - Evaluating deep learning-based melanoma classification using immunohistochemistry and routine histology: A three center study
Christoph Wies, Lucas Schneider, Sarah Haggenmüller, Tabea-Clara Bucher, Sarah Hobelsberger, Markus V. Heppt, Gerardo Ferrara, Eva I. Krieghoff-Henning, Titus J. Brinker, Vincenzo L’Imperio
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(1): e0297146. CrossRef - Domestic Cat Hepadnavirus Antigens in Lymphoma Tissues. Comment on Beatty et al. Domestic Cat Hepadnavirus and Lymphoma. Viruses 2023, 15, 2294
Chutchai Piewbang, Sabrina Wahyu Wardhani, Jedsada Siripoonsub, Sirintra Sirivisoot, Anudep Rungsipipat, Somporn Techangamsuwan
Viruses.2024; 16(1): 148. CrossRef - In the Rat Hippocampus, Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus Is Associated with Reactive Glia and Concomitant Increased Expression of CD31, PDGFRβ, and Collagen IV in Endothelial Cells and Pericytes of the Blood–Brain Barrier
Grigorios Kyriatzis, Anne Bernard, Angélique Bôle, Michel Khrestchatisky, Lotfi Ferhat
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(3): 1693. CrossRef - Guidelines on antibody use in physiology research
Heddwen L. Brooks, Lisandra E. de Castro Brás, Keith R. Brunt, Megan A. Sylvester, Michelle S. Parvatiyar, Padmini Sirish, Shyam S. Bansal, Rasheed Sule, Ashley L. Eadie, Mark A. Knepper, Robert A. Fenton, Merry L. Lindsey, Kristine Y. DeLeon-Pennell, Ald
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.2024; 326(3): F511. CrossRef - Diagnostic analysis of pleural fluid cell blocks using relevant immunohistochemical markers in clinically suspicious cases of malignancy
Jules Kurian Mathew, Gopalan Nair Rajan, Abhilash Kudilipparambil Kunju
Cytojournal.2024; 21: 8. CrossRef - Differences between male and female patients with pilonidal disease
Bill Chiu, Claire Abrajano, Hiroyuki Shimada, Razie Yousefi, Kyla Dalusag, Madeline Adams, Wendy Su, Thomas Hui, Claudia Mueller, Julie Fuchs, James Dunn
Journal of Pediatric Surgery Open.2024; 6: 100132. CrossRef - Pathological and phylogenetic characteristics of fowl AOAV-1 and H5 isolated from naturally infected Meleagris Gallopavo
Shady Shalaby, Walaa Awadin, Rashid Manzoor, Reham Karam, Mahmoud Mohamadin, Sanaa Salem, Ahmed El-Shaieb
BMC Veterinary Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - β-Sitosterol targets ASS1 for Nrf2 ubiquitin-dependent degradation, inducing ROS-mediated apoptosis via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in ovarian cancer
Haoyu Wang, Jingchun Liu, Zihui Zhang, Jiaxin Peng, Zhi Wang, Lian Yang, Xinqi Wang, Siyuan Hu, Li Hong
Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2024; 214: 137. CrossRef - HCR spectral imaging: 10-plex, quantitative, high-resolution RNA and protein imaging in highly autofluorescent samples
Samuel J. Schulte, Mark E. Fornace, John K. Hall, Grace J. Shin, Niles A. Pierce
Development.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological characteristics and predictors of outcome of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis: a retrospective study
Osama Nady Mohamed, Sharehan Abdelrahman Ibrahim, Rabeh Khairy Saleh, Ahmed S. Issa, Amr Setouhi, Ayman Ahmed Abd Rabou, Mahmoud Ragab Mohamed, Shaimaa F. Kamel
BMC Nephrology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The immunomodulatory impact of naturally derived neem leaf glycoprotein on the initiation progression model of 4NQO induced murine oral carcinogenesis: a preclinical study
Juhina Das, Saurav Bera, Nilanjan Ganguly, Ipsita Guha, Tithi Ghosh Halder, Avishek Bhuniya, Partha Nandi, Mohona Chakravarti, Sukanya Dhar, Anirban Sarkar, Tapasi Das, Saptak Banerjee, Sandip Ghose, Anamika Bose, Rathindranath Baral
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Differential cytokine expression in gastric tissues highlights helicobacter pylori’s role in gastritis
Xing-Tang Yang, Pei-Qin Niu, Xiao-Feng Li, Ming-Ming Sun, Wei Wei, Yan-Qing Chen, Jia-Yi Zheng
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation Can Alter Autonomic Function and Induce an Antiepileptic Effect in Pentylenetetrazol- Induced Seizures in Rats
Eunmi Choi, Taekyung Kim, Sung Jun Hong, Taewoo Kim, Minhee Kang, Young-Min Shon, Eunkyoung Park
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 60112. CrossRef - Coupling imaging mass cytometry with Alcian blue histochemical staining for a single-slide approach
Patrice Hemon, Danivanh Ben-Guigui, Margaux Geier, Marine Castillon, Corentin Paranthoen, Jacques-Olivier Pers, Marion Le Rochais, Arnaud Uguen
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Restoring Impaired Neurogenesis and Alleviating Oxidative Stress by
Cyanidin against Bisphenol A-induced Neurotoxicity: In Vivo and In Vitro
Evidence
Swathi Suresh, Chitra Vellapandian
Current Drug Discovery Technologies.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Pipeline for Evaluation of Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence Models to Quantify Programmed Death Ligand 1 Immunohistochemistry
Beatrice S. Knudsen, Alok Jadhav, Lindsey J. Perry, Jeppe Thagaard, Georgios Deftereos, Jian Ying, Ben J. Brintz, Wei Zhang
Laboratory Investigation.2024; 104(6): 102070. CrossRef - Review of immunohistochemistry techniques: Applications, current status, and future perspectives
Dinku Yigzaw Mebratie, Gashaw Getaneh Dagnaw
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2024; 41(3): 154. CrossRef - Gastric cancer molecular classification based on immunohistochemistry and in‐situ hybridisation and mortality
Maarit Eskuri, Eva‐Maria Birkman, Joonas H Kauppila
Histopathology.2024; 85(2): 327. CrossRef - Endotypes of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Primary and Recurring Nasal Polyps in the Latvian Population
Rudolfs Janis Viksne, Gunta Sumeraga, Mara Pilmane
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(10): 5159. CrossRef - Krüppel-like factor 12 decreases progestin sensitivity in endometrial cancer by inhibiting the progesterone receptor signaling pathway
Haimeng Shi, Jian Li, Tong Yan, Ling Zhou, Yu Zhu, Feifei Guo, Sihui Yang, Xiangyi Kong, Huaijun Zhou
Translational Oncology.2024; 47: 102041. CrossRef - Revealing intact neuronal circuitry in centimeter-sized formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded brain
Ya-Hui Lin, Li-Wen Wang, Yen-Hui Chen, Yi-Chieh Chan, Shang-Hsiu Hu, Sheng-Yan Wu, Chi-Shiun Chiang, Guan-Jie Huang, Shang-Da Yang, Shi-Wei Chu, Kuo-Chuan Wang, Chin-Hsien Lin, Pei-Hsin Huang, Hwai-Jong Cheng, Bi-Chang Chen, Li-An Chu
eLife.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapeutic potential of probiotics to counter Campylobacter infections: An In vitro and In vivo evaluation in mice
Nahla M. Mansour, Abd El-Nasser A. Madboli, Hayam M. Mansour, Alaa M. Saleh, May M.A. Bahr, Mohamed K. Zakaria, Ian Connerton
Food Bioscience.2024; 60: 104383. CrossRef - Revealing intact neuronal circuitry in centimeter-sized formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded brain
Ya-Hui Lin, Li-Wen Wang, Yen-Hui Chen, Yi-Chieh Chan, Shang-Hsiu Hu, Sheng-Yan Wu, Chi-Shiun Chiang, Guan-Jie Huang, Shang-Da Yang, Shi-Wei Chu, Kuo-Chuan Wang, Chin-Hsien Lin, Pei-Hsin Huang, Hwai-Jong Cheng, Bi-Chang Chen, Li-An Chu
eLife.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimization of Formic Acid-Formalin-Based Decalcification Protocol for Rat Calvarial Bone Histology
S. Amitha Banu, Khan Sharun, Merlin Mamachan, Athira Subash, Vadapalli Deekshita, Kirtika Sharma, Karikalan Mathesh, Obli Rajendran Vinodh kumar, Swapan Kumar Maiti, Abhijit M. Pawde, Laith Abualigah, Kuldeep Dhama, Amarpal
Journal of Experimental Biology and Agricultural Sciences.2024; 12(2): 218. CrossRef - Inhibition of NF-kB and COX-2 by andrographolide regulates the progression of cervical cancer by promoting PTEN expression and suppressing PI3K/AKT signalling pathway
Akbar Pasha, Kiran Kumar, S K Heena, I. Arnold Emerson, Smita C. Pawar
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing AI Research for Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Datasets
Alessio Fiorin, Carlos López Pablo, Marylène Lejeune, Ameer Hamza Siraj, Vincenzo Della Mea
Journal of Imaging Informatics in Medicine.2024; 37(6): 2996. CrossRef - Integrated pan-cancer analysis reveals the immunological and prognostic potential of RBFOX2 in human tumors
Fengxian Huang, Long Jin, Xinyue Zhang, Min Wang, Congya Zhou
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hematopoietic Function Restoration by Transplanting Bone Marrow Niches In Vivo Engineered Using Carbonate Apatite Honeycomb Bioreactors
Koichiro Hayashi, Ryo Kishida, Akira Tsuchiya, Kunio Ishikawa
Small Structures.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Consensus Guidelines on Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2)-Low Testing in Breast Cancer in Malaysia
Pathmanathan Rajadurai, Sarala Ravindran, Bang Rom Lee, Suria Hayati Md Pauzi, Seow Fan Chiew, Kean Hooi Teoh, Navarasi S. Raja Gopal, Mastura Md Yusof, Cheng Har Yip
Cancers.2024; 16(13): 2325. CrossRef - Examining the quaternary ammonium chitosan Schiff base-ZnO nanocomposite's potential as protective therapy for rats' cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity
Ebtesam S. Kotb, Heba W. Alhamdi, Mohammad Y. Alfaifi, Omeed Darweesh, Ali A. Shati, Serag Eldin I. Elbehairi, Waleed M. Serag, Yasser A. Hassan, Reda F.M. Elshaarawy
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2024; 276: 133616. CrossRef - Potentially actionable targets in synovial sarcoma: A tissue microarray study
Lore De Cock, Flavia Paternostro, Ulla Vanleeuw, Karo Wyns, Annouschka Laenen, Che-Jui Lee, Raf Sciot, Agnieszka Wozniak, Patrick Schöffski
Translational Oncology.2024; 48: 102057. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical findings of lens capsules obtained from patients with dead bag syndrome
Takayoshi Sumioka, Liliana Werner, Shingo Yasuda, Yuka Okada, Nick Mamalis, Nobuyuki Ishikawa, Shizuya Saika
Journal of Cataract & Refractive Surgery.2024; 50(8): 862. CrossRef - Quality Assurance in Immunocytochemistry: A Review and Practical Considerations
Maria D. Lozano, Ramon Robledano, Allan Argueta
Acta Cytologica.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Spatial multiplexing and omics
Julienne L. Carstens, Santhoshi N. Krishnan, Arvind Rao, Anna G. Sorace, Erin H. Seeley, Sammy Ferri-Borgogno, Jared K. Burks
Nature Reviews Methods Primers.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Applications of Multimodal Artificial Intelligence in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma B Cells
Pouria Isavand, Sara Sadat Aghamiri, Rada Amin
Biomedicines.2024; 12(8): 1753. CrossRef - Functional and structural neurodegenerative activities of Ankaferd BloodStopper in a mouse sciatic nerve model
Ramazan Üstün, Elif Oğuz, Ayşe Şeker, Filiz Taspinar
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Antigen Retrieval Methods for Immunohistochemical Analysis of Cartilage Matrix Glycoproteins Using Cartilage Intermediate Layer Protein 2 (CILP-2) as an Example
Taavi Torga, Siim Suutre, Kalle Kisand, Marina Aunapuu, Andres Arend
Methods and Protocols.2024; 7(5): 67. CrossRef - Single-cell analysis of breast cancer metastasis reveals epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity signatures associated with poor outcomes
Juliane Winkler, Weilun Tan, Catherine M.M. Diadhiou, Christopher S. McGinnis, Aamna Abbasi, Saad Hasnain, Sophia Durney, Elena Atamaniuc, Daphne Superville, Leena Awni, Joyce V. Lee, Johanna H. Hinrichs, Patrick S. Wagner, Namrata Singh, Marco Y. Hein, M
Journal of Clinical Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Analysis of the Expression of the Glycodelin Cytokine in Endometrial Tissue and the Endometrial Polyp, before and after Hysteroscopy, in Infertile Female Patients
Aleksandar Devic, Ana Devic, Marija Sorak, Goran Zajic, Slobodanka Mitrovic
Experimental and Applied Biomedical Research (EABR).2024; 25(2): 165. CrossRef - The presence of cancer-associated fibroblast in breast cavity side margins is in correlation with the expression of oncoproteins by adjacent epithelial cells: a new era in cancerous potential
Zohreh Sadat Miripour, Mina Aminifar, Parisa Hoseinpour, Fereshteh Abbasvandi, Koosha Karimi, Alireza Ghahremani, Mohammad Parniani, Mohammadreza Ghaderinia, Faride Makiyan, Parisa Aghaee, Mohammad Esmaeil Akbari, Mohammad Abdolahad
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic markers in oesophageal and gastric cancer review. Are they ready for clinical practice?
V. Kunene, M. Ding, M. Yap, E.A. Griffiths, P. Taniere, D. Fackrell, S. Butler, G. Contino
ESMO Gastrointestinal Oncology.2024; 6: 100091. CrossRef - Early Alterations of Cytoskeletal Proteins Induced by Radiation Therapy in the Parenchymal Cells of Rat Major Salivary Glands: A Comparative Immunohistochemical Analysis
Sherif S Hassan, Mashael S Alqahtani
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Modified Citrus Pectin’s Effects on Dementia in the Scopolamine-Induced Alzheimer’s Model in Adult Male Wistar Rats
Jale Akgöl, Özden Kutlay, Arzu Keskin Aktan, Fatma Fırat
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2024; 46(12): 13922. CrossRef - Enhanced Expression of N-Cadherin, but Not of E-Cadherin, in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Comparison to Basal Cell Carcinoma
Joanna Pogorzelska-Dyrbuś, Danuta Nowicka-Suszko, Aleksandra Piotrowska, Zdzisław Woźniak, Piotr Dzięgiel, Jacek C. Szepietowski
Cancers.2024; 16(24): 4247. CrossRef - Molecular docking and in vivo/in vitro studies of a novel thiadiazole Schiff base as a hepatoprotective drug against angiogenesis induced by breast cancer
Norah F. Alqahtani, Mohammad Y. Alfaifi, Ali Shati A, Serag Eldin I. Elbehairi, Abdulrahman M. Saleh, Ebtesam S. Kotb, Waleed M. Serag, Reda F. M. Elshaarawy, Heba W. Alhamdi, Yasser A. Hassan
RSC Advances.2024; 14(52): 39027. CrossRef - DCE-MRI Radiomics Analysis in Differentiating Luminal A and Luminal B Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes
Oğuz Lafcı, Pınar Celepli, Pelin Seher Öztekin, Pınar Nercis Koşar
Academic Radiology.2023; 30(1): 22. CrossRef - Lessons Learned, Challenges Taken, and Actions Made for “Precision” Immunohistochemistry. Analysis and Perspectives From the NordiQC Proficiency Testing Program
Søren Nielsen, Michael Bzorek, Mogens Vyberg, Rasmus Røge
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2023; 31(7): 452. CrossRef - Targeting intra‐tumoral heterogeneity of human brain tumors with in vivo imaging: A roadmap for imaging genomics from multiparametric MR signals
Jason G. Parker, Mahsa Servati, Emily E. Diller, Sha Cao, Chang Ho, Robert Lober, Aaron Cohen‐Gadol
Medical Physics.2023; 50(4): 2590. CrossRef - Cortactin expression in a Norwegian cohort of human papilloma virus negative oral squamous cell carcinomas of the mobile tongue
B. Sengüven Toközlü, D. Sapkota, E. M. Vallenari, O. Schreurs, T. M. Søland
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Melatonin effective to reduce the microscopic symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome-related infertility: An experimental study
Gökçe Nur Arık, Gülnur Take Kaplanoğlu, Atiye Seda Yar Sağlam, Zübeyir Elmazoğlu, Aylin Sepici Dinçel, Cemile Merve Seymen
Tissue and Cell.2023; 81: 102015. CrossRef - Exploring the Role of Oxidative Stress in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy: Mechanisms and Implications
Suyash Agrawal, Swarupa Chakole, Nidhi Shetty, Roshan Prasad, Tejaswee Lohakare, Mayur Wanjari
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Imatinib suppresses activation of hepatic stellate cells by targeting STAT3/IL‐6 pathway through miR‐124
Helia Alavifard, Sogol Mazhari, Anna Meyfour, Samaneh Tokhanbigli, Saeid Ghavami, Mohammad Reza Zali, Hamid Asadzadeh Aghdaei, Behzad Hatami, Kaveh Baghaei
Cell Biology International.2023; 47(5): 969. CrossRef - Tissue libraries enable rapid determination of conditions that preserve antibody labeling in cleared mouse and human tissue
Theodore J Zwang, Rachel E Bennett, Maria Lysandrou, Benjamin Woost, Anqi Zhang, Charles M Lieber, Douglas S Richardson, Bradley T Hyman
eLife.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vivo and 3D Imaging Technique(s) for Spatiotemporal Mapping of Pathological Events in Experimental Model(s) of Spinal Cord Injury
Divya Goyal, Hemant Kumar
ACS Chemical Neuroscience.2023; 14(5): 809. CrossRef - Beyond conventional microscopy: Observing kidney tissues by means of fourier ptychography
Marika Valentino, Vittorio Bianco, Lisa Miccio, Pasquale Memmolo, Valentina Brancato, Paolo Libretti, Marcello Gambacorta, Marco Salvatore, Pietro Ferraro
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Endothelial colony forming cell administration promotes neurovascular unit development in growth restricted and appropriately grown fetal lambs
Alexander Bell, Ashalyn P. Watt, Ingrid Dudink, Yen Pham, Amy E. Sutherland, Beth J. Allison, Courtney A. McDonald, Margie Castillo-Melendez, Graham Jenkin, Atul Malhotra, Suzanne L. Miller, Tamara Yawno
Stem Cell Research & Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical probe mediated visualization of protein S-palmitoylation in patient tissue samples
Nancy Schek, Jia-Ying Lee, George M. Burslem, Eric Witze
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - APE1 promotes non-homologous end joining by initiating DNA double-strand break formation and decreasing ubiquitination of artemis following oxidative genotoxic stress
Qin Zhang, Lujie Yang, Han Gao, Xunjie Kuang, He Xiao, Chen Yang, Yi Cheng, Lei Zhang, Xin Guo, Yong Zhong, Mengxia Li
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Swietenine Alleviates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Diabetic Mice via Lipogenesis Inhibition and Antioxidant Mechanisms
Kit-Kay Mak, Shiming Zhang, Jestin Chellian, Zulkefeli Mohd, Ola Epemolu, Albena T. Dinkova-Kostova, Madhu Katyayani Balijepalli, Mallikarjuna Rao Pichika
Antioxidants.2023; 12(3): 595. CrossRef - Influence of Various Light Regimes on Morphofunctional Condition of Transplantable Melanoma B16
David A. Areshidze, Maria A. Kozlova, Maxim V. Mnikhovich, Tatyana V. Bezuglova, Valery P. Chernikov, Zarina V. Gioeva, Aleksey V. Borisov
Biomedicines.2023; 11(4): 1135. CrossRef - How valuable can proteogenomics be in clinical breast cancer research?
Anh M. Tran-Huynh, Matthew V. Holt, Meenakshi Anurag
Expert Review of Proteomics.2023; 20(1-3): 1. CrossRef - Zebrafish Patient-Derived Xenograft Model as a Preclinical Platform for Uveal Melanoma Drug Discovery
Jie Yin, Gangyin Zhao, Helen Kalirai, Sarah E. Coupland, Aart G. Jochemsen, Gabriel Forn-Cuní, Annemijn P. A. Wierenga, Martine J. Jager, B. Ewa Snaar-Jagalska, Arwin Groenewoud
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(4): 598. CrossRef - Prostate malignant tumor and benign prostatic hyperplasia microenvironments in black African men: Limited infiltration of CD8+ T lymphocytes, NK‐cells, and high frequency of CD73+ stromal cells
Pélagie Mougola Bissiengou, Jérôme Gaston Montcho Comlan, Gabrielle Atsame Ebang, Maguette Sylla Niang, Joel Fleury Djoba Siawaya
Cancer Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Porcine circovirus type 3: immunohistochemical detection in lesions of naturally affected piglets
Franciéli Adriane Molossi, Bruno Albuquerque de Almeida, Bianca Santana de Cecco, Caroline Pissetti, Lauren Ventura, Luciano Brandalise, Gustavo Simão, Fabio Vanucci, Tatiane Terumi Negrao Watababe, Itabajara da Silva Vaz Jr., David Driemeier
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Validation of Stimulated Raman Histology for Rapid Intraoperative Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Tumors
Misha Movahed-Ezazi, Mustafa Nasir-Moin, Camila Fang, Isabella Pizzillo, Kristyn Galbraith, Steven Drexler, Olga A. Krasnozhen-Ratush, Seema Shroff, David Zagzag, Christopher William, Daniel Orringer, Matija Snuderl
Modern Pathology.2023; 36(9): 100219. CrossRef - Oral targeted delivery of Imatinib by pH responsive copolymer modulates liver fibrosis in the mice model
Samaneh Siapoush, Hanieh Mousazadeh, Ramazan Rezaei, Behzad Hatami, Sogol Mazhari, Naimeh Hashemi, Mohammad Reza Zali, Kaveh Baghaei
International Journal of Pharmaceutics.2023; 641: 123068. CrossRef - How to use AI in pathology
Peter Schüffler, Katja Steiger, Wilko Weichert
Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer.2023; 62(9): 564. CrossRef - The Utility of Mitochondrial Detection Methods Applied as an Additional Tool for the Differentiation of Renal Cell Tumors
Gorana Nikolic, Maja Zivotic, Sanja Cirovic, Sanja Despotovic, Dusko Dundjerovic, Sanja Radojevic Skodric
Diagnostics.2023; 13(14): 2319. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and Defense Proteins in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
Rudolfs Janis Viksne, Gunta Sumeraga, Mara Pilmane
Medicina.2023; 59(7): 1259. CrossRef - European Society of Toxicologic Pathology (Pathology 2.0 Molecular Pathology Special Interest Group): Review of In Situ Hybridization Techniques for Drug Research and Development
Josep M. Monné Rodríguez, Anna-Lena Frisk, Robert Kreutzer, Thomas Lemarchand, Stephane Lezmi, Chandrassegar Saravanan, Birgit Stierstorfer, Céline Thuilliez, Enrico Vezzali, Grazyna Wieczorek, Seong-Wook Yun, Dirk Schaudien
Toxicologic Pathology.2023; 51(3): 92. CrossRef - Immunohistochemistry in pathology: A review
Mangesh G. Kohale, Anupama V. Dhobale, Nandkishor J. Bankar, Obaid Noman, Kajal Hatgaonkar, Vaishnavi Mishra
Journal of Cellular Biotechnology.2023; 9(2): 131. CrossRef - Potential involvement of IL-32 in cell-to-cell communication between macrophages and hepatoblastoma
Ahmad Adawy, Lianbo Li, Hiroki Hirao, Tomoaki Irie, Daiki Yoshii, Hiromu Yano, Yukio Fujiwara, Shigeyuki Esumi, Masaki Honda, Shinya Suzu, Yoshihiro Komohara, Taizo Hibi
Pediatric Surgery International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidental DCIS within a fibroadenoma
Arnold Chen, Shaveen Kanakaratne, Philip Britten-Jones, Janne Bingham
BMJ Case Reports.2023; 16(9): e254609. CrossRef - The Potential Effect of Simvastatin on Regulatory T cells in Experimentally Induced Autoimmune Thyroiditis in Female Rats
Yaqeen Talib Mohammed, Nadia Hameed Mohammed, Inam Sameh Arif
Al Mustansiriyah Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.2023; 23(4): 443. CrossRef - Prediction of Five-Year Survival Rate for Rectal Cancer Using Markov Models of Convolutional Features of RhoB Expression on Tissue Microarray
Tuan D. Pham
IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics.2023; 20(5): 3195. CrossRef - Comprehensive Analysis of DNA Methyltransferases Expression in Primary and Relapsed Ovarian Carcinoma
Efthymia Papakonstantinou, Ioanna Pappa, Georgios Androutsopoulos, Georgios Adonakis, Ioannis Maroulis, Vasiliki Tzelepi
Cancers.2023; 15(20): 4950. CrossRef - Potential chemopreventive effects of Broccoli extract supplementation against 7, 12 dimethyl Benz(a)anthracene (DMBA) -induced toxicity in female rats
Aya M. Allam, Huda O. AbuBakr, Aya M. Yassin, Ahmed S. Abdel-Razek, Marwa S. Khattab, Eman M. Gouda, Said Z. Mousa
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Punicalagin attenuates myocardial oxidative damage, inflammation, and apoptosis in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats: Biochemical, immunohistochemical, and in silico molecular docking studies
Muthana M. Jghef, Khadija Boukholda, Yassine Chtourou, Bernd L. Fiebich, Mohammed Kebieche, Rachid Soulimani, Fatiha Chigr, Hamadi Fetoui
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2023; 385: 110745. CrossRef - PET and Optical Imaging of Caveolin-1 in Gastric Tumors
Sandeep Surendra Panikar, Shayla Shmuel, Jason S. Lewis, Patrícia M. R. Pereira
ACS Omega.2023; 8(39): 35884. CrossRef - Testing modalities for ALK-driven lung cancer: A narrative review
Shrinidhi Nathany, Mansi Sharma, Ullas Batra
Cancer Research, Statistics, and Treatment.2023; 6(3): 432. CrossRef - Modulation of inflammatory, oxidative, and apoptotic stresses mediates the renoprotective effect of daidzein against glycerol-induced acute kidney injury in rats
Rami B. Kassab, Ahmed A. Elhenawy, AbdulrahmanTheyab, Yousef M. Hawsawi, Osama M. Al-Amer, Atif Abdulwahab A. Oyouni, Ola A. Habotta, Hussam A. Althagafi, Fahad Alharthi, Maha S. Lokman, Khalaf F. Alsharif, Ashraf Albrakati, Ali O. Al-Ghamdy, Ehab Kotb E
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2023; 30(56): 119016. CrossRef - Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) Expression Predicts Need for Early Treatment in Prostate Cancer Patients Managed with Active Surveillance
Elham Ahmadi, Simon Wang, Mohammad Gouran-Savadkoohi, Georgia Douvi, Naghmeh Isfahanian, Nicole Tsakiridis, Brent E. Faught, Jean-Claude Cutz, Monalisa Sur, Satish Chawla, Gregory R. Pond, Gregory R. Steinberg, Ian Brown, Theodoros Tsakiridis
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(22): 16022. CrossRef - Neutralization of p40 Homodimer and p40 Monomer Leads to Tumor Regression in Patient-Derived Xenograft Mice with Pancreatic Cancer
Monica Sheinin, Susanta Mondal, Kalipada Pahan
Cancers.2023; 15(24): 5796. CrossRef - Degree of organ damage and inflammatory markers in sepsis mice models inducted by various doses of lipopolysaccharides
Arifin -, Bambang Purwanto, Dono Indarto, Brian Wasita, Tatar Sumanjar, Eti Poncorini, Soetrisno -
F1000Research.2023; 12: 5. CrossRef -
Detection of
NTRK
Gene Fusions in Solid Tumors: Recommendations from a Latin American Group of Oncologists and Pathologists
Mauricio Cuello, Hernán García-Rivello, Fuad Huamán-Garaicoa, Paulina Irigoyen-Piñeiros, César O Lara-Torres, Manglio M Rizzo, Miguel Ticona-Castro, Rogelio Trejo, Pablo Zoroquiain
Future Oncology.2023; 19(40): 2669. CrossRef - Role of the oral pathologists in various lab investigations - A Brief Review
Sandhya Tamgadge, Neha Modak
Journal of Indian Dental Association.2023; : 27. CrossRef - Expression of fibroblast activation protein alpha in odontogenic keratocyst and ameloblastoma: A cross-sectional immunohistochemical study
Sandhya Tamgadge, Treville Pereira
Journal of Orofacial Sciences.2023; 15(1): 21. CrossRef - Anti‑CXCR4 chemokine receptor, motixafortide, as an adjunct treatment with anti‑TB drugs decreases the bacterial burden by improving drug distribution
Kusuma Davuluri, Amit Singh, Ajay Singh, Vimal Kumar, Shoor Singh, Devendra Chauhan
World Academy of Sciences Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Inverse correlation of CD3 & vascular endothelial growth factor in incisional oral squamous cell carcinoma biopsies predicts nodal metastasis & poor survival of patients
Wafa Khan, Dominic Augustine, Roopa S. Rao
Indian Journal of Medical Research.2023; 157(5): 438. CrossRef - Endoplasmic reticulum-unfolded protein response signalling is altered in severe eosinophilic and neutrophilic asthma
Prabuddha S Pathinayake, David W Waters, Kristy S Nichol, Alexandra C Brown, Andrew T Reid, Alan Chen-Yu Hsu, Jay C Horvat, Lisa G Wood, Katherine J Baines, Jodie L Simpson, Peter G Gibson, Philip M Hansbro, Peter A B Wark
Thorax.2022; 77(5): 443. CrossRef - Tissue cryopreservation using the 3M™ Novec™ 7000 freezing coolant offers a comparable and safe alternative to customary coolants
Victor Nunez, Ashley Cook, Charles Havnar, Sean Flanagan, Nianfeng Ge, Angela Martzall, Robin E. Taylor, Millicent Lu, Oleg Mayba, Oded Foreman
Journal of Histotechnology.2022; 45(2): 85. CrossRef - Immunomagnetic microscopy of tumor tissues using quantum sensors in diamond
Sanyou Chen, Wanhe Li, Xiaohu Zheng, Pei Yu, Pengfei Wang, Ziting Sun, Yao Xu, Defeng Jiao, Xiangyu Ye, Mingcheng Cai, Mengze Shen, Mengqi Wang, Qi Zhang, Fei Kong, Ya Wang, Jie He, Haiming Wei, Fazhan Shi, Jiangfeng Du
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Novel Role of Galectin-3 and Thyroglobulin in Prognosis and Differentiation of Different Stages of Thyroid Cancer and Elucidation of the Potential Contribution of Bcl-2, IL-8 and TNF-α
Tarek M. Okda, Gamal M. K. Atwa, Ahmed Fathy Eldehn, Naief Dahran, Khalaf F Alsharif, Ehab Kotb Elmahallawy
Biomedicines.2022; 10(2): 352. CrossRef - Prognostic value of Dickkopf-1 and ß-catenin expression according to the antitumor immunity of CD8-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in biliary tract cancer
Seo Ree Kim, Hye Sung Won, Ji Hyun Yang, Der Sheng Sun, Kwangil Yim, Mineui Hong, Soon Auck Hong, Jung-Sook Yoon, Sang Hoon Chun, Kee-Hwan Kim, Yoon Ho Ko
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Proficiency Testing to Improve Interobserver Agreement for Mismatch Repair Deficiency Immunohistochemistry: An Invitation to Join CBQA Readout
Raul S. Gonzalez, Catherine J. Streutker, Emina E. Torlakovic
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2022; 30(2): 79. CrossRef - Significance of Single-cell Level Dual Expression of BCL2 and MYC Determined With Multiplex Immunohistochemistry in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Jin Roh, Dok Hyun Yoon, Yoon Kyoung Lee, Hyo-Kyung Pak, Sang-Yeob Kim, Jae Ho Han, Joon Seong Park, Seong Hyun Jeong, Yoon Seok Choi, Hyungwoo Cho, Cheolwon Suh, Jooryung Huh, Dae Ho Lee, Chan-Sik Park
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2022; 46(3): 289. CrossRef - Introducing immunohistochemistry to the molecular biology laboratory
Audrey Chen, Eric Tarapore, Allisen G. To, Davis M. Catolico, Kelly C. Nguyen, Melissa J. Coleman, Rory D. Spence
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education.2022; 50(2): 229. CrossRef - Ki67 and LSD1 Expression in Testicular Germ Cell Tumors Is Not Associated with Patient Outcome: Investigation Using a Digital Pathology Algorithm
Beatriz Chaves Lourenço, Catarina Guimarães-Teixeira, Bianca C. T. Flores, Vera Miranda-Gonçalves, Rita Guimarães, Mariana Cantante, Paula Lopes, Isaac Braga, Joaquina Maurício, Carmen Jerónimo, Rui Henrique, João Lobo
Life.2022; 12(2): 264. CrossRef - Povidone iodine suppresses LPS-induced inflammation by inhibiting TLR4/MyD88 formation in airway epithelial cells
Seung Hoon Lee, Mi-Ra Choi, Jaein Chung, Seung-Hyeon Choi, Soo Kyoung Park, Yong Min Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Moving towards improved surveillance and earlier diagnosis of aquatic pathogens: From traditional methods to emerging technologies
Scott MacAulay, Amy R. Ellison, Peter Kille, Joanne Cable
Reviews in Aquaculture.2022; 14(4): 1813. CrossRef - Automated variable power cold microwave tissue processing: A novel universal tissue processing protocol without using formaldehyde and xylene
Naser Haghbin, Behrouz Oveisi, Amir Parsa Banitaba
Acta Histochemica.2022; 124(4): 151880. CrossRef - Silymarin constrains diacetyl-prompted oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in rats: involvements of Dyn/GDNF and MAPK signaling pathway
Manar Mohammed El Tabaa, Hamdi M. Aboalazm, Mohamed Shaalan, Naglaa Fathy Khedr
Inflammopharmacology.2022; 30(3): 961. CrossRef - A Toolkit for Profiling the Immune Landscape of Pediatric Central Nervous System Malignancies
Jacob S. Rozowsky, Joyce I. Meesters-Ensing, Julie A. S. Lammers, Muriël L. Belle, Stefan Nierkens, Mariëtte E. G. Kranendonk, Lennart A. Kester, Friso G. Calkoen, Jasper van der Lugt
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The histological and microbiological characteristics of bacterial microcolonies in paediatric tonsillar hyperplasia
Ruyan Chen, Sita Tarini Clark, Sharon Waldvogel-Thurlow, Fiona Jane Radcliff, Michael Leigh Hoggard, James Johnston, Richard George Douglas, Kristi Biswas
International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology.2022; 157: 111128. CrossRef - Hepatoprotective activity of Picrorhiza kurroa and Berberis lycium is mediated by inhibition of COX-2 and TGF-β expression in lantadenes-induced sub-chronic toxicity in guinea pigs
Punam Soren, Rinku Sharma, Gorakh Mal, Bikram Singh, Pawan Kumar, Rajendra Damu Patil, Birbal Singh
Phytomedicine Plus.2022; 2(3): 100288. CrossRef - A panoptic review of techniques for finfish disease diagnosis: The status quo and future perspectives
Tina Kollannoor Johny, Thangaraj Raja Swaminathan, Neeraj Sood, Pravata Kumar Pradhan, Kuldeep Kumar Lal
Journal of Microbiological Methods.2022; 196: 106477. CrossRef - Enhanced effect of autologous EVs delivering paclitaxel in pancreatic cancer
Hasan Al Faruque, Eun-Sook Choi, Jung-Hee Kim, Eunjoo Kim
Journal of Controlled Release.2022; 347: 330. CrossRef - Standardization of Manual Method of Immunohistochemical Staining for Breast Cancer Biomarkers at Tertiary Cancer Care Center: An Audit
Manjit K Rana, Amrit Pal S Rana, Aklank Jain, Akhilesh Pathak, Utkarshni Khera, Uttam Sharma, Akriti Jindal, Karuna Singh
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Trans-channel fluorescence learning improves high-content screening for Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics
Daniel R. Wong, Jay Conrad, Noah R. Johnson, Jacob Ayers, Annelies Laeremans, Joanne C. Lee, Jisoo Lee, Stanley B. Prusiner, Sourav Bandyopadhyay, Atul J. Butte, Nick A. Paras, Michael J. Keiser
Nature Machine Intelligence.2022; 4(6): 583. CrossRef - Histopathological, Immunohistochemical and Biochemical Studies of Murine Hepatosplenic Tissues Affected by Chronic Toxoplasmosis
Samah Hassan Yahia, Samia Elsayed Etewa, Nesreen Saeed Saleh, Samira Metwally Mohammad, Nora Ibrahim Aboulfotouh, Ahmad Mansour Kandil, Mohamed Hassan Sarhan, José F. Silveira
Journal of Parasitology Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Development of a Single Molecule Counting Assay to Differentiate Chromophobe Renal Cancer and Oncocytoma in Clinics
Khaled Bin Satter, Zach Ramsey, Paul M. H. Tran, Diane Hopkins, Gregory Bearden, Katherine P. Richardson, Martha K. Terris, Natasha M. Savage, Sravan K. Kavuri, Sharad Purohit
Cancers.2022; 14(13): 3242. CrossRef - LILRB2-mediated TREM2 signaling inhibition suppresses microglia functions
Peng Zhao, Yuanzhong Xu, Lu-Lin Jiang, Xuejun Fan, Zhiqiang Ku, Leike Li, Xiaoye Liu, Mi Deng, Hisashi Arase, Jay-Jiguang Zhu, Timothy Y. Huang, Yingjun Zhao, Chengcheng Zhang, Huaxi Xu, Qingchun Tong, Ningyan Zhang, Zhiqiang An
Molecular Neurodegeneration.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Multiplex Immunofluorescence and the Digital Image Analysis Workflow for Evaluation of the Tumor Immune Environment in Translational Research
Frank Rojas, Sharia Hernandez, Rossana Lazcano, Caddie Laberiano-Fernandez, Edwin Roger Parra
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Establishing a multiplex imaging panel to study T cell development in the thymus in mouse
Amr H. Allam, Sarah M. Russell
STAR Protocols.2022; 3(3): 101472. CrossRef - Limited Accuracy of Pan-Trk Immunohistochemistry Screening for NTRK Rearrangements in Follicular-Derived Thyroid Carcinoma
Elisabetta Macerola, Agnese Proietti, Anello Marcello Poma, Paola Vignali, Rebecca Sparavelli, Alessandro Ginori, Alessio Basolo, Rossella Elisei, Ferruccio Santini, Fulvio Basolo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(13): 7470. CrossRef - Protective effect of green synthesized Selenium Nanoparticles against Doxorubicin induced multiple adverse effects in Swiss albino mice
Mohammad Afsar Khan, Deepti Singh, Amin Arif, Kushneet Kaur Sodhi, Dileep Kumar Singh, Sk Najrul Islam, Absar Ahmad, Kafil Akhtar, Hifzur R. Siddique
Life Sciences.2022; 305: 120792. CrossRef - Runt-Related Transcription Factor 2 (Runx2) Measurement in Phytoestrogen-Induced Bone: A Comparison of Western Blot and Immunohistochemistry Methods
Burhan Ma’arif, Fariza Amanatul Sholihah, Anisah Mahardiani, Begum Fauziyah, Denis Mery Mirza, Mangestuti Agil
Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal.2022; 15(2): 1039. CrossRef - Next-Generation Pathology Using Multiplexed Immunohistochemistry: Mapping Tissue Architecture at Single-Cell Level
Francesca Maria Bosisio, Yannick Van Herck, Julie Messiaen, Maddalena Maria Bolognesi, Lukas Marcelis, Matthias Van Haele, Giorgio Cattoretti, Asier Antoranz, Frederik De Smet
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Pathology-Based Methods in Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches to Cancer Immunotherapy
Olga Kuczkiewicz-Siemion, Kamil Sokół, Beata Puton, Aneta Borkowska, Anna Szumera-Ciećkiewicz
Cancers.2022; 14(15): 3833. CrossRef - Epidermal Stem Cell in Wound Healing of Gliricidia sepium Leaves from Indonesia and the Philippines in Rats (Rattus norvegicus)
Aulanni’am Aulanni’am, Ricadonna Raissa, Wibi Riawan, Dyah Kinasih Wuragil, Fajar Shodiq Permata, Ma Asuncion Guiang Beltran
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(A): 1143. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical analysis of intestinal biopsies in individuals with celiac disease
Adel Alhabbal, Imad Abou Khamis
JGH Open.2022; 6(10): 692. CrossRef - Morphofunctional State and Circadian Rhythms of the Liver of Female Rats under the Influence of Chronic Alcohol Intoxication and Constant Lighting
David A. Areshidze, Maria A. Kozlova
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(18): 10744. CrossRef - Cardioprotective Effect of Taxifolin against Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Injury through Decreasing Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Cell Death, and Activating Nrf2/HO-1 in Mice
Heba M. Obeidat, Osama Y. Althunibat, Manal A. Alfwuaires, Saleem H. Aladaileh, Abdulmohsen I. Algefare, Afaf F. Almuqati, Fawaz Alasmari, Hammad Khalifeh Aldal’in, Abdulkareem A. Alanezi, Bader Alsuwayt, Mohammad H. Abukhalil
Biomolecules.2022; 12(11): 1546. CrossRef - RhoA and vigilin are candidates for immunohistochemical markers for epithelioid malignant mesothelioma
Takuya Hiratsuka, Takushi Yamamoto, Akihiko Yoshizawa, Shinya Toyokuni, Tatsuaki Tsuruyama
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of survivin and p27 expression as potential prognostic markers in urothelial cell carcinoma of urinary bladder in Egyptian patients
Noha Said Helal, Zeinab Omran, Mona Moussa
African Journal of Urology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Thymoquinone-rich black cumin oil attenuates ibotenic acid-induced excitotoxicity through glutamate receptors in Wistar rats
Sibi P Ittiyavirah, Kannan Ramalingam, Arathy Sathyan, R.S. Rajasree, Mohamed Saheer Kuruniyan, Syed Altafuddin Quadri, Muhammed Elayadeth-Meethal, Punnoth Poonkuzhi Naseef
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal.2022; 30(12): 1781. CrossRef - High sensitivity label-free detection of HER2 using an Al–GaN/GaN high electron mobility transistor-based biosensor
Shivanshu Mishra, Pharyanshu Kachhawa, Amber Kumar Jain, Rajiv Ranjan Thakur, Nidhi Chaturvedi
Lab on a Chip.2022; 22(21): 4129. CrossRef - The effect of 1.3 bis(p-Hydroxyphenyl)urea compound on IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α and COX-2 protein expression on λ-Carrageenan-induced rats
Denny Satria, Syukur Berkat Waruwu, Yuandani Yuandani, Hari Purnomo, Urip Harahap
Pharmacia.2022; 69(4): 927. CrossRef - The unilateral involution in the thymus of a 96-year-old male leads to the preservation of structural integrity in one thymic lobe, as assessed by the expression of medullar and cortical antigens and the presence of CD3+ cells
Pranuthi Kanneganti, Joseph Lyle, Julia H. Smith, Heather McGuire, Richaela Denlinger, Malgorzata Simm
Heliyon.2022; 8(11): e11734. CrossRef - Virtual tissue staining in pathology using machine learning
Nir Pillar, Aydogan Ozcan
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2022; 22(11): 987. CrossRef - The Unilateral Involution in the Thymus of a 96-Year-Old Male Leads to the Preservation of Structural Integrity in One Thymic Lobe, as Assessed by the Expression of Medullar and Cortical Antigens and the Presence of CD3+ Cells
Pranuthi Kanneganti, Julia H. Smith, Heather McGuire, Richaela Denlinger, Joseph Lyle, Malgorzata Simm
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Upregulation of TIGIT and PD-1 in Colorectal Cancer with Mismatch-repair Deficiency
Xuebing Zhou, Xiaoling Ding, Hai Li, Chun Yang, Zhanbing Ma, Guangxian Xu, Shaoqi Yang, Dong Zhang, Xiaoliang Xie, Lei Xin, Xiaoli Luo
Immunological Investigations.2021; 50(4): 338. CrossRef - The myokine irisin: localization and effects in swine late medium and large antral ovarian follicle
G. Basini, S. Bussolati, M. Iannarelli, L. Ragionieri, S. Grolli, R. Ramoni, A. Dodi, F. Gazza, F. Grasselli
Domestic Animal Endocrinology.2021; 74: 106576. CrossRef - Heterochronous Metastases of Lung Adenocarcinoma to Pancreas and Liver: A Case Report from Pathological Perspectives
Bo Zhang, Qida Hu, Jiajie Yu, Junsen Wang, Hanjin Yang, Jiongbo Lou, Guoying Cai, Haifeng Huang, Mengqiu Xu, Zhaoying Xiao, Yun Zhang
OncoTargets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4269. CrossRef - Human Adipose Derived Stem Cells Enhance Healing in a Rat Model of Esophageal Injury with Stent
Dana McCloskey, Kimberly Linden, Andrew Lin, Ping Zhang, Jennifer Schweinsburg, Atlee Melillo, Huan Wang, Julieta Barroeta, Spencer Brown, Jeffrey Carpenter, Francis Spitz, David Shersher
Journal of Surgical Research.2021; 267: 458. CrossRef - Quantification of the Immune Content in Neuroblastoma: Deep Learning and Topological Data Analysis in Digital Pathology
Nicole Bussola, Bruno Papa, Ombretta Melaiu, Aurora Castellano, Doriana Fruci, Giuseppe Jurman
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(16): 8804. CrossRef - Deep learning for the classification of medical kidney disease: a pilot study for electron microscopy
Sean Hacking, Vanesa Bijol
Ultrastructural Pathology.2021; 45(2): 118. CrossRef - Multiplexed Plasmonic Nano-Labeling for Bioimaging of Cytological Stained Samples
Paule Marcoux-Valiquette, Cécile Darviot, Lu Wang, Andrée-Anne Grosset, Morteza Hasanzadeh Kafshgari, Mirela Birela, Sergiy Patskovsky, Dominique Trudel, Michel Meunier
Cancers.2021; 13(14): 3509. CrossRef - The Expression of NTAL and Its Protein Interactors Is Associated With Clinical Outcomes in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Carolina Hassibe Thomé, Germano Aguiar Ferreira, Diego Antonio Pereira-Martins, Guilherme Augusto dos Santos, Douglas R. Almeida-Silveira, Isabel Weinhäuser, Gustavo Antônio de Souza, Roos Houtsma, Jan Jacob Schuringa, Eduardo M. Rego, Vitor M. Faça
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.2021; 20: 100091. CrossRef - Quercetin attenuates cisplatin-induced ovarian toxicity in rats: Emphasis on anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic activities
Mardi M. Algandaby
Arabian Journal of Chemistry.2021; 14(7): 103191. CrossRef - A biochemical mechanism for time-encoding memory formation within individual synapses of Purkinje cells
Ayush Mandwal, Javier G. Orlandi, Christoph Simon, Jörn Davidsen, Laurens W. J. Bosman
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(5): e0251172. CrossRef - Alleviation of remote lung injury following liver ischemia/reperfusion: Possible protective role of vildagliptin
Iman O. Sherif, Nora H. Al-Shaalan
International Immunopharmacology.2021; 91: 107305. CrossRef - Raman spectroscopy and group and basis-restricted non negative matrix factorisation identifies radiation induced metabolic changes in human cancer cells
Kirsty Milligan, Xinchen Deng, Phillip Shreeves, Ramie Ali-Adeeb, Quinn Matthews, Alexandre Brolo, Julian J. Lum, Jeffrey L. Andrews, Andrew Jirasek
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Liver Toxicity Testing of Chemicals: A Pragmatic Approach
Andrés Tabernilla, Bruna dos Santos Rodrigues, Alanah Pieters, Anne Caufriez, Kaat Leroy, Raf Van Campenhout, Axelle Cooreman, Ana Rita Gomes, Emma Arnesdotter, Eva Gijbels, Mathieu Vinken
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(9): 5038. CrossRef - The steadfast Au@Pt soldier: Peroxide-tolerant nanozyme for signal enhancement in lateral flow immunoassay of peroxidase-containing samples
Vasily G. Panferov, Irina V. Safenkova, Anatoly V. Zherdev, Boris B. Dzantiev
Talanta.2021; 225: 121961. CrossRef - Use of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated disruption of CNS cell type genes to profile transduction of AAV by neonatal intracerebroventricular delivery in mice
Tess Torregrosa, Sydney Lehman, Sam Hana, Galina Marsh, Shanqin Xu, Kathryn Koszka, Nicole Mastrangelo, Alexander McCampbell, Christopher E. Henderson, Shih-Ching Lo
Gene Therapy.2021; 28(7-8): 456. CrossRef - Hepatoprotective effect of arjunolic acid against cisplatin‐induced hepatotoxicity: Targeting oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis
Iman O. Sherif
Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Topical ozonated virgin coconut oil improves wound healing and increases HSP90α, VEGF-A, EGF, bFGF and CD34 in diabetic ulcer mouse model of wound healing
Renni Yuniati, Prasetyowati Subchan, Wibi Riawan, Matthew Brian Khrisna, Maryam Restiwijaya, Niken Safitri Dyan Kusumaningrum, Muhammad Nur
F1000Research.2021; 9: 580. CrossRef - IHC_Tool: An open-source Fiji procedure for quantitative evaluation of cross sections of testicular explants
Ludovic Dumont, Nicolas Levacher, Damien Schapman, Aurélie Rives-Feraille, Laura Moutard, Marion Delessard, Justine Saulnier, Christine Rondanino, Nathalie Rives
Reproductive Biology.2021; 21(2): 100507. CrossRef - Challenges with Methods for Detecting and Studying the Transcription Factor Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) in the Central Nervous System
Marina Mostafizar, Claudia Cortes-Pérez, Wanda Snow, Jelena Djordjevic, Aida Adlimoghaddam, Benedict C. Albensi
Cells.2021; 10(6): 1335. CrossRef - High‐Dimensional Image Analysis using Histocytometry
Luis Munoz‐Erazo, Alfonso J. Schmidt, Kylie M. Price
Current Protocols.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum matrix metalloproteinase-13 as a diagnostic biomarker for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
Hui Wang, Hong Li, Qingtao Yan, Sumei Gao, Jianfang Gao, Zhenhua Wang, Yi Sun
BMC Cancer.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning Approaches to Classify Primary and Metastatic Cancers Using Tissue of Origin-Based DNA Methylation Profiles
Vijayachitra Modhukur, Shakshi Sharma, Mainak Mondal, Ankita Lawarde, Keiu Kask, Rajesh Sharma, Andres Salumets
Cancers.2021; 13(15): 3768. CrossRef - Effects of Automation on Sustainability of Immunohistochemistry Laboratory
Marija Đorđević, Maja Životić, Sanja Radojević Škodrić, Jelena Nešović Ostojić, Jasmina Marković Lipkovski, Jelena Filipović, Sanja Ćirović, Sanjin Kovačević, Duško Dunđerović
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 866. CrossRef - Kallikrein-11, in Association with Coiled-Coil Domain Containing 25, as a Potential Prognostic Marker for Cholangiocarcinoma with Lymph Node Metastasis
Saeranee Siriphak, Ravinnipa Chanakankun, Tanakorn Proungvitaya, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Doungdean Tummanatsakun, Wunchana Seubwai, Molin Wongwattanakul, Siriporn Proungvitaya
Molecules.2021; 26(11): 3105. CrossRef - Pitfalls and Caveats in Applying Chromogenic Immunostaining to Histopathological Diagnosis
Yutaka Tsutsumi
Cells.2021; 10(6): 1501. CrossRef - A robust unsupervised machine-learning method to quantify the morphological heterogeneity of cells and nuclei
Jude M. Phillip, Kyu-Sang Han, Wei-Chiang Chen, Denis Wirtz, Pei-Hsun Wu
Nature Protocols.2021; 16(2): 754. CrossRef - Clinical implications of lung neuroendocrine neoplasm classification
Jasna Metovic, Marco Barella, Sergio Harari, Linda Pattini, Adriana Albini, Angelica Sonzogni, Giulia Veronesi, Mauro Papotti, Giuseppe Pelosi
Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.2021; 21(4): 377. CrossRef - Comparative protective effects of N-acetylcysteine and melatonin against obesity-induced testicular dysfunction in rats
Sama S. Khalil, Joseph Amin Aziz, Khadiga Ahmed Ismail, Nanees F. El-Malkey
Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology.2021; 99(7): 708. CrossRef - Development of novel quality control material based on CRISPR/Cas9 editing and xenografts for MLH1 protein deficiency testing
Rui Li, Runling Zhang, Ping Tan, Meng Wang, Yuqing Chen, Jiawei Zhang, Dongsheng Han, Yanxi Han, Jinming Li, Rui Zhang
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimization of Mouse-on-Mouse Immunohistochemistry by Utilizing Fluorescent-dye Conjugated Secondary Anti-Mouse Antibody
Shiva Moein, Rezvan Adibi, Alireza Amouheidari, Yousof Gheisari
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2021; 29(6): 473. CrossRef - Multiplex Immunofluorescence and Multispectral Imaging: Forming the Basis of a Clinical Test Platform for Immuno-Oncology
Clifford C. Hoyt
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The changing role of the pathologist in the era of targeted therapy in personalized medicine
Giuseppe D’Abbronzo, Renato Franco
Expert Review of Precision Medicine and Drug Development.2021; 6(5): 295. CrossRef - The advanced development of Cx43 and GAP-43 mediated intercellular networking in IDH1 wildtype diffuse and anaplastic gliomas with lower mitotic rate
Aleksandrs Krigers, Patrizia Moser, Helga Fritsch, Matthias Demetz, Konstantin Brawanski, Claudius Thomé, Christian F. Freyschlag
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2021; 147(10): 3003. CrossRef - Tunable Organelle Imaging by Rational Design of Carbon Dots and Utilization of Uptake Pathways
Shuang E, Chuang He, Jian-Hua Wang, Quanxing Mao, Xuwei Chen
ACS Nano.2021; 15(9): 14465. CrossRef - Adaptive NK Cell Therapy Modulated by Anti-PD-1 Antibody in Gastric Cancer Model
Shahrokh Abdolahi, Zeinab Ghazvinian, Samad Muhammadnejad, Mohammad Ahmadvand, Hamid Asadzadeh Aghdaei, Somayeh Ebrahimi-Barough, Jafar Ai, Mohammad Reza Zali, Javad Verdi, Kaveh Baghaei
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Topical ozonated virgin coconut oil improves wound healing and increases HSP90α, VEGF-A, EGF, bFGF, and CD34 in diabetic ulcer mouse model of wound healing
Renni Yuniati, Prasetyowati Subchan, Wibi Riawan, Matthew Brian Khrisna, Maryam Restiwijaya, Niken Safitri Dyan Kusumaningrum, Muhammad Nur
F1000Research.2021; 9: 580. CrossRef - Automated Quantitative Image Evaluation of Antigen Retrieval Methods for 17 Antibodies in Placentation and Implantation Diagnostic and Research
Julia Fuchs, Olivia Nonn, Christine Daxboeck, Silvia Groiss, Gerit Moser, Martin Gauster, Ingrid Lang-Olip, Dagmar Brislinger
Microscopy and Microanalysis.2021; 27(6): 1506. CrossRef - Prognostic Value of Serum Thyroglobulin and Anti-Thyroglobulin Antibody in Thyroid Carcinoma Patients following Thyroidectomy
Hashem O. Zahra, Gamal A. Omran, Ahmed G. Gewely, Ahmed Fathy Eldehn, Walied Abdo, Ehab Kotb Elmahallawy, Tarek M. Okda
Diagnostics.2021; 11(11): 2080. CrossRef - Hybridization chain reaction enables a unified approach to multiplexed, quantitative, high-resolution immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization
Maayan Schwarzkopf, Mike C. Liu, Samuel J. Schulte, Rachel Ives, Naeem Husain, Harry M. T. Choi, Niles A. Pierce
Development.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Analysis of the Expression of the Glycodelin Cytokine in Endometrial Tissue and the Endometrial Polyp, Before and After Hysteroscopy, in Infertile Female Patients
Aleksandar Dević, Ana Dević, Marija Šorak, Goran Zajić, Slobodanka Mitrović
Serbian Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Experiments from unfinished Registered Reports in the Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology
Timothy M Errington, Alexandria Denis, Anne B Allison, Renee Araiza, Pedro Aza-Blanc, Lynette R Bower, Jessica Campos, Heidi Chu, Sarah Denson, Cristine Donham, Kaitlyn Harr, Babette Haven, Elizabeth Iorns, Jennie Kwok, Elysia McDonald, Steven Pelech, Nic
eLife.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Reconciling the distinct roles of angiogenic/anti-angiogenic factors in the placenta and maternal circulation of normal and pathological pregnancies
Anandita Umapathy, Lawrence W. Chamley, Joanna L. James
Angiogenesis.2020; 23(2): 105. CrossRef - A comparison of methodologies for the staining and quantification of intracellular components of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the root cortex of two varieties of winter wheat
Thomas I. Wilkes, Douglas J. Warner, Veronica Edmonds-Brown, Keith G. Davies, Ian Denholm
Access Microbiology .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Parallel Reaction Monitoring-Mass Spectrometry (PRM-MS)-Based Targeted Proteomic Surrogates for Intrinsic Subtypes in Breast Cancer: Comparative Analysis with Immunohistochemical Phenotypes
Joonho Park, Hyeon Jeong Oh, Dohyun Han, Joseph I. Wang, In Ae Park, Han Suk Ryu, Youngsoo Kim
Journal of Proteome Research.2020; 19(7): 2643. CrossRef - Prognostic value of mitotic checkpoint protein BUB3, cyclin B1, and pituitary tumor-transforming 1 expression in prostate cancer
Elin Ersvær, Wanja Kildal, Ljiljana Vlatkovic, Karolina Cyll, Manohar Pradhan, Andreas Kleppe, Tarjei S. Hveem, Hanne A. Askautrud, Marco Novelli, Håkon Wæhre, Knut Liestøl, Håvard E. Danielsen
Modern Pathology.2020; 33(5): 905. CrossRef - Evaluating the Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages Into M1 and M2 Phenotypes in Human Cancer Tissue: Technicalities and Challenges in Routine Clinical Practice
Sharmilla Devi Jayasingam, Marimuthu Citartan, Thean Hock Thang, Anani Aila Mat Zin, Kai Cheen Ang, Ewe Seng Ch'ng
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the challenges for a new classification of adenomyosis
Marwan Habiba, Stephan Gordts, Marc Bazot, Ivo Brosens, Giuseppe Benagiano
Reproductive BioMedicine Online.2020; 40(4): 569. CrossRef - The importance of FDG-PET/CT parameters for the assessment of the immune status in advanced HNSCC
Toshimitsu Ohashi, Kousuke Terasawa, Mitsuhiro Aoki, Takashi Akazawa, Hirofumi Shibata, Bunya Kuze, Takahiko Asano, Hiroki Kato, Tatsuhiko Miyazaki, Masayuki Matsuo, Norimitsu Inoue, Yatsuji Ito
Auris Nasus Larynx.2020; 47(4): 658. CrossRef - Local secretion of stress hormones increases in alopecia areata lesions after treatment with UVA‐1 phototherapy
Adrian Cuellar‐Barboza, Jesus Alberto Cardenas‐de la Garza, Luis Gerardo Cruz‐Gómez, Oralia Barboza‐Quintana, Juan Pablo Flores‐Gutiérrez, Minerva Gómez‐Flores, Oliverio Welsh, Jorge Ocampo‐Candiani, Maira E. Herz‐Ruelas
Experimental Dermatology.2020; 29(3): 259. CrossRef - Asialoglycoprotein receptor expression in placenta of women with Hepatitis B Virus e Antigen (HBeAg) positive and negative
Agus Priyo Wibowo, Rina Masadah, Berti J. Nelwana, Djumadi Achmad, Gunawan Arsyadi, Maisuri T. Chalid, Andi Alfian Zainuddin
Enfermería Clínica.2020; 30: 255. CrossRef - Comparison of Volume Retention and Biocompatibility of Acellular Dermal Matrix/Hyaluronic Acid Filler to Autologous Fat Grafts in a Mouse Model
Ji Hun Kim, Sun Eung Kim, Yu Jin Kim, Yang Woo Kim, Young Woo Cheon
Aesthetic Plastic Surgery.2020; 44(3): 986. CrossRef - An improved animal model for herpesvirus encephalitis in humans
Julia Sehl, Julia E. Hölper, Barbara G. Klupp, Christina Baumbach, Jens P. Teifke, Thomas C. Mettenleiter, Lynn W. Enquist
PLOS Pathogens.2020; 16(3): e1008445. CrossRef - Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Selective Labeling of Subcellular Organelles
Binesh Unnikrishnan, Ren-Siang Wu, Shih-Chun Wei, Chih-Ching Huang, Huan-Tsung Chang
ACS Omega.2020; 5(20): 11248. CrossRef - Effects of coal-fired PM2.5 on the expression levels of atherosclerosis-related proteins and the phosphorylation level of MAPK in ApoE−/− mice
Siqi Wang, Feifei Wang, Lixin Yang, Qin Li, Yao Huang, Zhiyuan Cheng, Hongqian Chu, Yiming Song, Lanqin Shang, Weidong Hao, Xuetao Wei
BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Hyperspectral and multispectral imaging in digital and computational pathology: a systematic review [Invited]
Samuel Ortega, Martin Halicek, Himar Fabelo, Gustavo M. Callico, Baowei Fei
Biomedical Optics Express.2020; 11(6): 3195. CrossRef - Topical ozonated virgin coconut oil improves wound healing and increases HSP90α, VEGF-A, EGF, bFGF and CD34 in diabetic ulcer mouse model of wound healing
Renni Yuniati, Prasetyowati Subchan, Wibi Riawan, Matthew Brian Khrisna, Maryam Restiwijaya, Niken Safitri Dyan Kusumaningrum, Muhammad Nur
F1000Research.2020; 9: 580. CrossRef - Immune characterization of metastatic colorectal cancer patients post reovirus administration
Ruwan Parakrama, Elisha Fogel, Carol Chandy, Titto Augustine, Matt Coffey, Lydia Tesfa, Sanjay Goel, Radhashree Maitra
BMC Cancer.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - 2-Methoxyestradiol ameliorates metabolic syndrome-induced hypertension and catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibited expression and activity in rats
Ahmad S. Azhar, Zaher F. Zaher, Osama M. Ashour, Ashraf B. Abdel-Naim
European Journal of Pharmacology.2020; 882: 173278. CrossRef - In vitro and in vivo anti-proliferative activity and ultrastructure investigations of a copper(II) complex toward human lung cancer cell NCI-H460
Leide Laura Figueiredo Maciel, William Rodrigues de Freitas, Erika Soares Bull, Christiane Fernandes, Adolfo Horn, João Carlos de Aquino Almeida, Milton Masahiko Kanashiro
Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry.2020; 210: 111166. CrossRef - Immunocytochemistry practices in European cytopathology laboratories—Review of European Federation of Cytology Societies (EFCS) online survey results with best practice recommendations
Irena Srebotnik Kirbiš, Rúben Rodrigues Roque, Massimo Bongiovanni, Margareta Strojan Fležar, Béatrix Cochand‐Priollet
Cancer Cytopathology.2020; 128(10): 757. CrossRef - CdSe quantum dots evaluation in primary cellular models or tissues derived from patients
Carlota Tosat-Bitrián, Valle Palomo
Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine.2020; 30: 102299. CrossRef - Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9) expression in multiple renal epithelial tumour subtypes
Nicholas Baniak, Trevor A Flood, Mark Buchanan, Paola Dal Cin, Michelle S Hirsch
Histopathology.2020; 77(4): 659. CrossRef - PCSK2 expression in neuroendocrine tumors points to a midgut, pulmonary, or pheochromocytoma–paraganglioma origin
Satu Maria Remes, Helena Leijon, Tiina Vesterinen, Johanna Louhimo, Ville Pulkkinen, Sini Ezer, Juha Kere, Caj Haglund, Johanna Arola
APMIS.2020; 128(11): 563. CrossRef - An immunochemistry-based screen for chemical inhibitors of DNA-protein interactions and its application to human CGGBP1
Manthan Patel, Divyesh Patel, Subhamoy Datta, Umashankar Singh
BMC Cancer.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation of VEGF and MMP-2 levels in oral lichen planus: An in vivo immunohistochemical study
Hala H. Hazzaa, Marwa A.M. El Shiekh, Nora Abdelgawad, Ossama M. Gouda, Naglaa M. Kamal
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2020; 10(4): 747. CrossRef - Ginkgo biloba Extract Attenuates Methotrexate-Induced Testicular Injury in Rats: Cross-talk Between Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Apoptosis, and miRNA-29a Expression
Iman O. Sherif, Laila A. Al-Mutabagani, Osama M. Sarhan
Integrative Cancer Therapies.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathological features of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A single-center study in Vietnam
Nguyen Cuong Pham, Thanh Xuan Nguyen, Nguyen Tuong Pham, Thanh Chinh Phan, Hai Thanh Phan
Annals of Cancer Research and Therapy.2020; 28(2): 125. CrossRef - Immunofluorescence Staining of Paraffin Sections Step by Step
Sami Zaqout, Lena-Luise Becker, Angela M. Kaindl
Frontiers in Neuroanatomy.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemistry as an important tool for exploring the insights of various aspects of gastro-intestinal tract
Ritesh Kumar Shukla, N Venkat Appa Rao
The Applied Biology & Chemistry Journal.2020; : 72. CrossRef - Development of a CD63 Aptamer for Efficient Cancer Immunochemistry and Immunoaffinity-Based Exosome Isolation
Zhenguo Song, Jun Mao, Roberto Barrero, Peng Wang, Fengqiu Zhang, Tao Wang
Molecules.2020; 25(23): 5585. CrossRef - Influence of chitosan oligosaccharide on the gelling and wound healing properties of injectable hydrogels based on carboxymethyl chitosan/alginate polyelectrolyte complexes
Xiaojie Lv, Yunen Liu, Subin Song, Changci Tong, Xiuyun Shi, Yan Zhao, Jinsong Zhang, Mingxiao Hou
Carbohydrate Polymers.2019; 205: 312. CrossRef - The interrelationship between gasotransmitters and lead-induced renal toxicity in rats
Ahmed O. Abdel-Zaher, Rasha B. Abd-ellatief, Noha A. Aboulhagag, Hanan S.M. Farghaly, Fahmy M.M. AL-Wasei
Toxicology Letters.2019; 310: 39. CrossRef - Inflammation‐dependent overexpression of c‐Myc enhances CRL4DCAF4 E3 ligase activity and promotes ubiquitination of ST7 in colitis‐associated cancer
Hong Liu, Wenzhu Lu, Hongbo He, Jin Wu, Caiguo Zhang, Hanlin Gong, Chunmei Yang
The Journal of Pathology.2019; 248(4): 464. CrossRef - Candesartan in a rat model of testicular toxicity: New insight on its protective mechanism
Iman O Sherif, Osama M Sarhan
Experimental Biology and Medicine.2019; 244(7): 593. CrossRef - A survival guide to HER2 testing in gastric/gastroesophageal junction carcinoma
Duminda Subasinghe, Nathan Acott, Marian Priyanthi Kumarasinghe
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2019; 90(1): 44. CrossRef - Tumor-Associated Protein Profiles in Kaposi Sarcoma and Mimicking Vascular Tumors, and Their Pathological Implications
Kyoung Bun Lee, Kyu Sang Lee, Hye Seung Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(13): 3142. CrossRef - New Advance in Breast Cancer Pathology and Imaging
Nicoletta Urbano, Manuel Scimeca, Rita Bonfiglio, Elena Bonanno, Orazio Schillaci
Future Oncology.2019; 15(23): 2707. CrossRef - Pathology Services in Nigeria: Cross-Sectional Survey Results From Three Cancer Consortia
Peter Ntiamoah, Ngozi R. Monu, Fatimah B. Abdulkareem, Kayode A. Adeniji, John O. Obafunwa, Akinwumi O. Komolafe, Clayton Yates, Ernest Kaninjing, John D. Carpten, Bodour Salhia, Folake T. Odedina, Marcia Edelweiss, T. Peter Kingham, Olusegun I. Alatise
Journal of Global Oncology.2019; (5): 1. CrossRef - Efficient Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Targeting Oligonucleotide as a Potential Molecule for Targeted Cancer Therapy
Tao Wang, Svetlana Philippovich, Jun Mao, Rakesh N. Veedu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(19): 4700. CrossRef - The Role of MMP8 in Cancer: A Systematic Review
Krista Juurikka, Georgina S. Butler, Tuula Salo, Pia Nyberg, Pirjo Åström
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(18): 4506. CrossRef - Enhancing the Value of Histopathological Assessment of Allograft Biopsy Monitoring
Michelle A. Wood-Trageser, Andrew J. Lesniak, Anthony J. Demetris
Transplantation.2019; 103(7): 1306. CrossRef - Anything You Can Do, I Can Do Better: Can Aptamers Replace Antibodies in Clinical Diagnostic Applications?
Michelle Bauer, Mia Strom, David S Hammond, Sarah Shigdar
Molecules.2019; 24(23): 4377. CrossRef - A nuclear shift of GSK3β protein is an independent prognostic factor in prostate cancer
Till Eichenauer, Mohammad Hussein, Claudia Hube-Magg, Martina Kluth, Franziska Büscheck, Doris Höflmayer, Maria Christina Tsourlakis, Stefan Steurer, Till S. Clauditz, Andreas M. Luebke, Eike Burandt, Waldemar Wilczak, Andrea Hinsch, David Dum, Burkhard B
Oncotarget.2019; 10(18): 1729. CrossRef - Update on Immunohistochemistry for the Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
Kentaro Inamura
Cancers.2018; 10(3): 72. CrossRef - The path to VICTORy – a beginner's guide to success using commercial research antibodies
Simon L. Goodman
Journal of Cell Science.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Translational research: Empowering the role of pathologists and cytopathologists
Heba W. Z. Khella, George M. Yousef
Cancer Cytopathology.2018; 126(10): 831. CrossRef - Periostin involved in the activated hepatic stellate cells-induced progression of residual hepatocellular carcinoma after sublethal heat treatment: its role and potential for therapeutic inhibition
Rui Zhang, Xia-Hui Lin, Min Ma, Jie Chen, Jun Chen, Dong-Mei Gao, Jie-Feng Cui, Rong-Xin Chen
Journal of Translational Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of PKC‑ζ protein levels in normal and malignant breast tissue subtypes
Tracess Smalley, S. Islam, Christopher Apostolatos, Andr� Apostolatos, Mildred Acevedo‑Duncan
Oncology Letters.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Aberrant expression of glycogen synthase kinase‑3β in human breast and head and neck cancer
Andrey Ugolkov, Maria Matsangou, Timothy Taxter, Thomas O'Halloran, Vincent Cryns, Francis Giles, Andrew Mazar
Oncology Letters.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The Pathological Diagnosis and Interpretation of Pathological Results: Emphasis on Immunohistochemical Staining
Jae Ho Han
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2017; 92(1): 36. CrossRef - Activated hepatic stellate cells secrete periostin to induce stem cell-like phenotype of residual hepatocellular carcinoma cells after heat treatment
Rui Zhang, Rong-Rong Yao, Jing-Huan Li, Gang Dong, Min Ma, Qiong-Dan Zheng, Dong-Mei Gao, Jie-Feng Cui, Zheng-Gang Ren, Rong-Xin Chen
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - ALK in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Pathobiology, Epidemiology, Detection from Tumor Tissue and Algorithm Diagnosis in a Daily Practice
Paul Hofman
Cancers.2017; 9(8): 107. CrossRef - Metas-Chip precisely identifies presence of micrometastasis in live biopsy samples by label free approach
Mohammad Saeid Nikshoar, Mohammad Ali Khayamian, Saeid Ansaryan, Hassan Sanati, Milad Gharooni, Leila Farahmand, Farshad Rezakhanloo, Keivan Majidzadeh-A, Parisa Hoseinpour, Shahrzad Dadgari, Leila Kiani-M, Mohammad Saqafi, Masoumeh Gity, Mohammad Abdolah
Nature Communications.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure

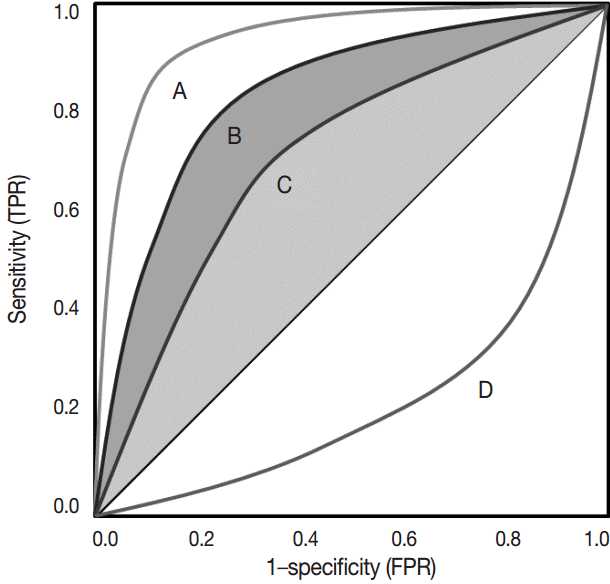
Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
| Step | Protocol |
|---|---|
| Fixation | 10% Neutral buffered formalin for 24 hr in room temperature |
| Frozen section: cold acetone for 1 min | |
| Embedding and sectioning | Paraffin embedding |
| Mostly 4 μm | |
| Frozen sections: between 4 μm and 6 μm in thickness | |
| Deparaffinization and hydration | 60°C hot plate |
| Antigen (or epitope) retrieval | Heat induced epitope retrieval is most widely used |
| Blocking | Normal sera of same species of secondary antibody or premixed |
| Vary from 30 min to overnight, from 4°C to room temperature | |
| Add primary antibody | Antibody dilution by protein blocking solution or premixed Ab diluents |
| Appropriate antibody selection and titration | |
| Incubate | 30–60 min, room temperature |
| Wash (TBS-T) | 3 × 5 min |
| Add secondary antibody | - |
| Incubate | 30–60 min, room temperature |
| Wash | 3 × 5 min, TBS-T |
| Add substrate | 250 μL of 1% DAB, and 250 μL of 0.3% hydrogen peroxide to 5 mL of PBS, 1–3 minutes, room temperature |
| Wash | 3 × 5 min, DW |
| Counterstain | Hematoxylin, 1 min |
| Antibody | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Monoclonal | Great epitope specificity and lower background | Less sensitivity or reactivity to masked epitope in a formalin fixed paraffin embedded sample |
| Better reproducibility | ||
| Polyclonal | Higher sensitivity (recognizing multiple epitopes) | Lesser reproducibility due to batch to batch variability |
| Higher background due to natural antibodies | ||
| Limited production |
| Counterstain | Color | Location | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hematoxylin (4 types: Harris’s, Mayer’s, Carazzi’s, and Gill’s) | Blue | Nucleus | The most popular one |
| Eosin | Red | Cationic group of protein | Eosin is bound by the majority of structures in any tissue |
| Methylene blue | Blue | Nucleus | Good to differentiate between DNA and RNA in tissues |
| Methylene green | Blue/green | Nucleus | |
| Toluidine blue | Deep blue | Nucleus | It will also stain polysaccharides a pink/red color (metachromasia) |
| Problem | Sdution |
|---|---|
| Weak or absent staining | |
| Antigen levels are too low | Prolong incubation time of primary antibody |
| Use a higher sensitivity staining system | |
| Incomplete fixation | Prevent under (> 30 min) or overfixation (> 48 hr) |
| Use of inappropriate fixative | Check manufacturer’s specifications regarding recommended fixative |
| Insufficient dehydration | Operating regular reagent changes (i.e., alcohol) |
| Paraffin too hot | Monitor temperature of paraffin (< 60°C) |
| Embedding and dewaxing at high oven temperature | Oven temperature not to exceed 60°C |
| Heating for antigen retrieval | Optimize antigen retrieval time |
| Reagents not working, reagents in wrong order | Monitor expiration dates, storage parameters, and pH |
| Antibody too dilute, improper antibody dilution | Determine correct concentration |
| Check incubation time and temperature | |
| Partial drying out of tissue during processing | Immerse tissue immediately in fixative |
| Use a huminity or moist chamber during incubation steps | |
| Avoid evaporation with humidity chamber | |
| Chromogen not working, incorrect preparation of chromogen | Add chromogen to labeling sdution |
| Monitor for change in color | |
| Background or artifactual staining | |
| Excessive incubation | Reduce incubation time |
| Necrotic or otherwise damaged tissue | Avoid sampling of necrotic areas |
| Make sure tissue is properly fixed | |
| Antigen diffusion before fixation leading to specific background | Avoid delays in fixation |
| Thick preparation | Cut sections at 4 to 6 mm |
| Inappropriately concentrated antibody | Check titration and concentration |
| Decrease temperature of reaction | |
| Presence of chromogen or undissolved counterstain deposits | Filter the chromogen or counterstain |
| Insure that chromogen is completely dissolved | |
| Incomplete inadequate rinsing of slides | Follow protocol for proper slide rinsing |
| Mildly rinse slide with wash buffer bottle and place in wash bath in 5 min | |
| Endogenous pigments | Check the negative control for the presence of these pigments |
| Use a chromogen of contrasting color |
TBS-T, Tris-buffered saline and Tween 20; DAB, diaminobenzidine; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; DW, dextrose 5% in distilled water.
Toluidine blue stains melanin in green so that brown color of diaminobenzidine can be differentiated.

 E-submission
E-submission




