Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 51(2); 2017 > Article
-
Review
Molecular Testing for Gastrointestinal Cancer - Hye Seung Lee1,2, Woo Ho Kim2, Yoonjin Kwak1,2, Jiwon Koh2, Jeong Mo Bae3, Kyoung-Mee Kim4, Mee Soo Chang2,3, Hye Seung Han5, Joon Mee Kim6, Hwal Woong Kim7, Hee Kyung Chang8, Young Hee Choi9, Ji Y. Park10, Mi Jin Gu11, Min Jin Lhee12, Jung Yeon Kim13, Hee Sung Kim14, Mee-Yon Cho15, , The Gastrointestinal Pathology Study Group of Korean Society of Pathologists
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2017;51(2):103-121.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.01.24
Published online: February 19, 2017
1Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
2Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
3Department of Pathology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
4Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
5Department of Pathology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
6Department of Pathology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
7Department of Pathology, Seegene Medical Foundation, Busan, Korea
8Department of Pathology, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
9Department of Pathology, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hwaseong, Korea
10Department of Pathology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
11Department of Pathology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
12Department of Pathology, Seoul Red Cross Hospital, Seoul, Korea
13Department of Pathology, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea
14Department of Pathology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
15Department of Pathology, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
- Corresponding Author Woo Ho Kim, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 103 Daehak-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul 03080, Korea Tel: +82-2-740-8269 Fax: +82-2-765-5600 E-mail: woohokim@snu.ac.kr
© 2017 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
- With recent advances in molecular diagnostic methods and targeted cancer therapies, several molecular tests have been recommended for gastric cancer (GC) and colorectal cancer (CRC). Microsatellite instability analysis of gastrointestinal cancers is performed to screen for Lynch syndrome, predict favorable prognosis, and screen patients for immunotherapy. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor has been approved in metastatic CRCs with wildtype RAS (KRAS and NRAS exon 2–4). A BRAF mutation is required for predicting poor prognosis. Additionally, amplification of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) and MET is also associated with resistance to EGFR inhibitor in metastatic CRC patients. The BRAF V600E mutation is found in sporadic microsatellite unstable CRCs, and thus is helpful for ruling out Lynch syndrome. In addition, the KRAS mutation is a prognostic biomarker and the PIK3CA mutation is a molecular biomarker predicting response to phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors and response to aspirin therapy in CRC patients. Additionally, HER2 testing should be performed in all recurrent or metastatic GCs. If the results of HER2 immunohistochemistry are equivocal, HER2 silver or fluorescence in situ hybridization testing are essential for confirmative determination of HER2 status. Epstein-Barr virus–positive GCs have distinct characteristics, including heavy lymphoid stroma, hypermethylation phenotype, and high expression of immune modulators. Recent advances in next-generation sequencing technologies enable us to examine various genetic alterations using a single test. Pathologists play a crucial role in ensuring reliable molecular testing and they should also take an integral role between molecular laboratories and clinicians.
- Microsatellite instability
- Microsatellites are short tandem DNA repeats that are randomly dispersed throughout the human genome, showing significant polymorphism between individuals. MSI is defined as a change in the microsatellite region within a tumor in comparison to that of normal tissue, resulting from either deletion or insertion of repeating units. MSI is caused by a defect in the DNA mismatch repair (MMR) mechanism which normally occurs during DNA replication to correct errors [11]. Since the early 1990s, it has been reported that a subset of CRC is microsatellite unstable (MSI-high frequency [MSI-H]), and that MSI represents a novel mechanism for colorectal carcinogenesis [12].
- MSI is the hallmark genetic aberration of Lynch syndrome [11]. Lynch syndrome is currently diagnosed when a pathogenic germline mutation is identified in one of the DNA MMR genes, MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, MSH6, or MLH3, and accounts for 2%–4% of all CRCs. Families who meet the Amsterdam criteria for the diagnosis of Lynch syndrome are referred to as having hereditary nonpolyposis CRC [13]. Screening and diagnosis of Lynch syndrome in clinical practice are required in order to reduce various cancer-related risks in the families. Therefore, screening for Lynch syndrome is necessary in newly diagnosed CRC patients, especially in the young or those with family history. Screening is usually done with MSI analysis and immunohistochemistry (IHC) for the four MMR enzymes MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, and MSH6 [14]. Additionally, the loss of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) expression has been demonstrated in a small subset of Lynch-syndrome–associated CRCs, which is caused by germline EpCAM deletions [15,16]. In Lynch syndrome, the risk of extracolonic lesions is high including gastric, endometrial, renal pelvis/ureter, small bowel, ovarian, brain, hepatobiliary tract, and sebaceous cancers [1,17].
- Sporadic MSI-H is observed in about 15%–20% of sporadic CRCs in Western countries and in about 5%–6% in Eastern countries and is caused by MLH1 promoter hypermethylation and MLH1 expression loss [11,18,19]. In sporadic CRC patients, MSI status is confirmed as a good prognostic marker [9,20,21]. CRCs with MSI-H frequently show high grade morphology, such as mucin production, signet ring cells, medullary features, and undifferentiated histology, but their biological behavior is less aggressive compared to that of microsatellite stable (MSS) or MSI-low frequency (MSI-L) CRCs [1]. MSI-H is observed in about 10% of sporadic GCs and is associated with older age, antral location, and intestinal type histology [22,23]. The independent prognostic value of MSI status in GC remains controversial; however, a recent meta-analysis showed that MSI-H is associated with better overall and disease-specific survival in GC [24]. Recent advances in genome analysis of CRCs and GCs showed that MSI-H is strongly associated with a distinct subtype characterized by elevated mutation rates (“hypermutated”) [25-27]. Cristescu et al. [27] demonstrated that MSI-H GCs have the best overall and disease-free survival among four molecular subtypes. The new American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) cancer staging manual (8th edition) recommended obtaining the results of MSI testing additionally in both GC and CRC patients for clinical care [9].
- It is generally accepted that a defective MMR system is associated with decreased therapeutic response to fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy in CRCs and GCs [28]. In contrast, Le et al. [29] demonstrated that MSI status in CRCs and non-CRCs (including gastric, endometrial, biliary, and small bowel cancers) is an excellent predictive factor for favorable treatment outcome by immune checkpoint blockade with pembrolizumab. Furthermore, high expression of checkpoint molecules, such as PD-1, PD-L1, CTLA-4, LAG-3, and IDO, is characteristic of gastrointestinal cancers with MSI-H phenotype [30-32], which suggests that MSI-H tumors are good candidates for immunotherapy.
- Growing evidence has supported the rationale for universal MSI testing in CRC, which showed a higher sensitivity for identifying Lynch syndrome among newly diagnosed CRC [33]. Considering the significant clinical implications of MSI status from both treatment- and prognostic-related perspective, it is recommend that all patients with newly diagnosed GC or CRC be tested for MSI status. MSI testing can be performed in any advanced tumors for immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment.
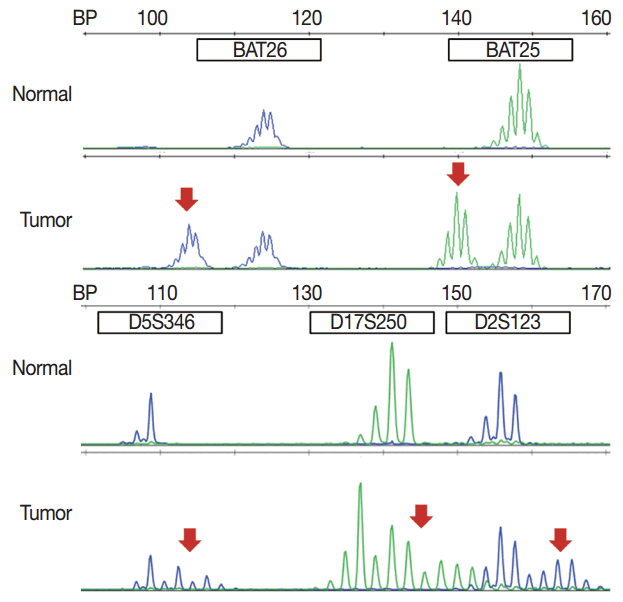
- MSI analysis is performed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of DNA extracted from both tumor and corresponding normal tissue, followed by separation of the amplified product by capillary gel electrophoresis. The results are determined by comparison of the peak patterns with a shift in PCR product size of the tumor compared to that of the normal tissue. Currently, the gold standard of MSI testing is the Bethesda panel [5], which uses PCR for the analysis of the fragment length of five markers: two mononucleotide repeats (BAT25 and BAT26) and three dinucleotide repeats (D5S346, D2S123, and D17S250). Recently developed MSI testing consists of a pentaplex panel of quasimonomorphic mononucleotides markers (NR-27, NR-21, NR-24, BAT-25, and BAT-26), which allows the analysis of MSI in tumors without the need of normal control (reference) DNA [34]. The sensitivity or limit of detection of MSI analysis is approximately 10%, but can vary according to laboratory conditions.
- Confirming the loss of MMR proteins (MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, MSH6) by IHC should also be used for the screening of Lynch syndrome. Since PMS2 and MLH1 form a heterodimer, MLH1 loss is related to PMS2 loss observed by IHC. MSH6 forms a heterodimer with MSH2, thus MSH2 loss occurs with concurrent MSH6 loss. However, loss of PMS2 or MSH6 does not lead to loss of MLH1 or MSH2. When compared to PCR-based method, IHC is known to have sufficient sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values [35]. However, the resting expression level of MMR proteins is very low; thus, a reliable diagnosis requires an adequate amount (quantity) of tissue sample and pathologists’ experiences in daily practice. For the accurate interpretation of loss of MMR proteins in tumor tissue, internal positive controls such as adjacent non-neoplastic glands, lymphocytes, or stromal cells should show strong nuclear positivity. Longer cold ischemia time or under-fixation can cause false negative results.
- Both fresh frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissues are considered suitable for PCR-based methods. Paired PCR results of cancer and matched normal tissues from the same patient are necessary for proper interpretation of the results.
- Approximately 1 cm2 of the tumor and normal tissues is required. Needless to state, the most important requirement of the specimen is a sufficient amount of DNA [36]; one of the most common reasons for false-negative MSI results is low tumor cellularity in the sample, for example, conditions such as mucinous carcinoma. Therefore, to ensure a sufficient proportion of the tumor cells, microdissection of the tumor cell area selected by experienced pathologists is generally recommended and widely implemented in many laboratories. Tumor cells should occupy at least 50%–60% of the examined tissue sections [37].
- In pathologic reports, patient information, such as patient ID, name, gender, and age, order date, ordering physician, and surgical pathologic diagnosis and number should be included. MSI tumors can be divided into three groups: MSI-H, when ≥ 30% of markers exhibit instability; MSI-L, when <30% of markers show instability; and MSS, when none of the markers exhibit instability (Fig. 1). According to the Bethesda panel, MSI-H is defined by having instability of two or more makers, MSI-L is defined by having instability of only one marker, and MSS means none of five markers show instability. The results of MSI must be reported as MSS, MSI-L, or MSI-H. Interpretation of the molecular diagnosis and signature of the pathologist are also required for the final diagnosis.
- MSI analysis should be validated in each pathology laboratory as laboratory-developed tests. Since the requirements for proper validation of MSI tests are not clearly defined, an external program checklist can be referred to for validation, including that of accuracy, precision, reportable range of the test results, analytic sensitivity and specificity, and positive and negative predictive values. It is recommended to directly compare the results of MSI tests to those of MMR protein IHC or MLH1 promoter hypermethylation testing.
- Each pathology laboratory should establish internal quality assurance (QA) instructions for MSI analysis and review all performed MSI tests in regular QA meetings. In each MSI test, specialized pathologists should confirm the examined tumor and normal area. Positive and negative controls should be used in each run of PCR and fragmentation analysis. Additionally, we recommend that both MSI tests and IHC for MMR proteins are performed and compared for reliable test results. All pathology laboratories should participate in external QA programs.
- Somatic mutation analysis
- The proto-oncogene KRAS encodes a GTPase, which is an early player in the EGFR induced RAS/RAF/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. KRAS mutations have important roles in various aspects of carcinogenesis, and KRAS mutations in exon 2 at codons 12 and 13 have been reported to be detected in approximately 35%–45% of CRCs. Negative correlations between KRAS mutations and MSI or BRAF mutations suggest that these molecular alterations are associated with a distinct subset of CRCs and have prognostic significance [38]. MSI-H status is associated with a favorable prognosis [20,21], whereas many previous studies supported the association of KRAS mutation with a poor prognosis [39,40]. AJCC recommended obtaining the results of KRAS mutational testing in CRC patients for predicting patient prognosis [20], and the poor prognostic effect of KRAS mutation is also described in the new AJCC cancer staging manual (8th edition) [9].
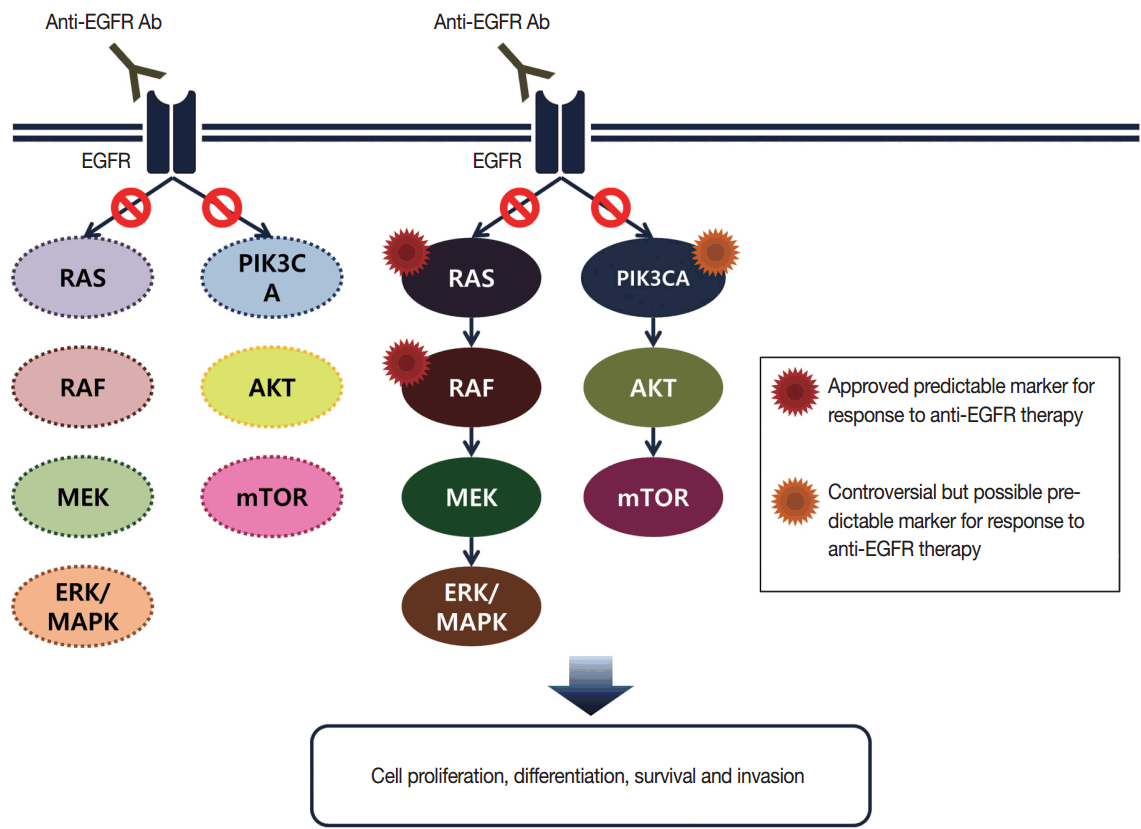
- Targeted therapies directed against EGFR tyrosine kinase have improved treatment efficacy and patients’ survival in various cancers, including CRCs [41]. EGFR blockers cetuximab and panitumumab have proven anti-tumor activity as monotherapies and in combination with chemotherapy and/or radiation in CRC patients [42,43], and EGFR signaling–associated genes have been studied for their relationship with responsiveness to EGFR inhibitors (Fig. 2). KRAS mutations in exon 2 at codons 12 and 13 are associated with resistance to cetuximab and panitumumab, and with poor survival in chemo-refractory metastatic CRC patients [44]. Additionally, oncogenic mutations in KRAS codons 59, 61, 117, and 146 and NRAS codons 12, 13, and 61 have been reported in approximately 3%–5% of CRC samples [45,46]. Recent clinical trials have demonstrated that extended RAS mutation testing, including that for mutations in KRAS and NRAS exons 2 to 4, can be more predictable for lack of responsiveness to EGFR inhibitors than previously proven KRAS exon 2 testing in first-line chemotherapy for metastatic CRC patients [6,47]. Recently, RAS mutation testing is approved as a companion diagnosis for EGFR inhibitor treatment in metastatic CRC patients.
- The oncogenic BRAF mutation has a role in constitutive activation and downstream signaling along the MAPK signaling pathway. BRAF mutations occur in approximately 5%–8% of CRCs and most are the BRAF V600E mutation, however, the BRAF V600E mutation almost never occurs in GCs [48,49]. The BRAF mutation is an early molecular event in the serrated pathway of CRC. Molecular sequencing in serrated pathway CRCs has been reported as BRAF mutation/CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP)/MSI-H or BRAF mutation/CIMP/MSS/p16 loss [50]. Many previous studies have confirmed that the BRAF mutation is associated with poor prognosis in metastatic CRC patients [6,47]. In addition to metastatic CRCs, earlier-stage CRC patients with mutated BRAF have been reported to show significantly worse overall survival than that of patients with wild-type BRAF [51,52]. Especially, this prognostic significance was evident in the MSS CRC group [9,52].
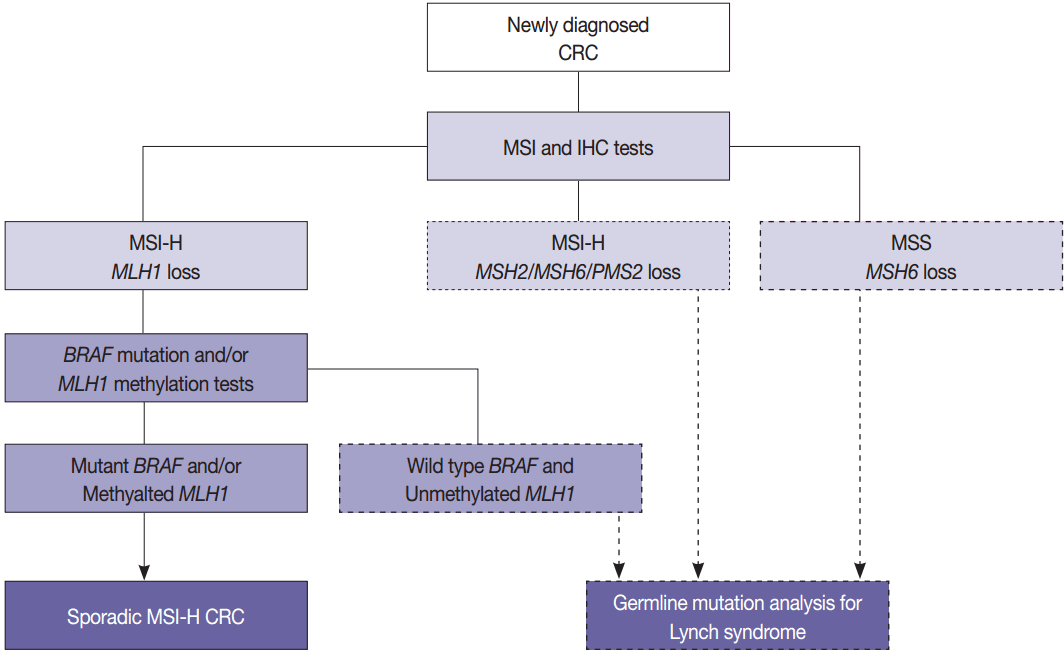
- The BRAF V600E mutation is observed in approximately two thirds of microsatellite unstable CRCs caused by MLH1 hypermethylation and protein loss, but it never occurs in microsatellite unstable CRCs associated with Lynch syndrome [53]. Therefore, newly diagnosed CRC cases should be initially examined by MSI analysis with MMR protein IHC, and then Lynch syndrome can be excluded if both MLH1 loss by IHC and BRAF V600E mutation or MLH1 hypermethylation are observed. Further germline mutational analysis for diagnosing Lynch syndrome is commonly performed in patients with MLH1 loss by IHC and BRAF wild type or unmethylated MLH1 (Fig. 3).
- For targeted therapies directed against EGFR tyrosine kinase in metastatic CRC patients, oncogenic mutations related to the EGFR signaling pathway are also suggested to be clinically relevant. Theoretically, the BRAF V600E mutation is considered a negative predictive marker for response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and several studies have shown that BRAF V600E mutations were significantly predictable for resistance to single-agent EGFR inhibitor [54,55]. The predictive role of the BRAF V600E mutation remains inconclusive owing to its rare prevalence [6,47], but the level of evidence for the BRAF V600E mutation in CRC is I for blocking the effect of anti-EGFR antibody therapy according to the new AJCC cancer staging manual (8th edition) [9].
- In contrast to BRAF mutated melanomas, the results of early clinical trials using BRAF inhibitors were not successful in treating BRAF mutated CRCs [56,57]. However, several clinical trials that combine BRAF and EGFR inhibitors with or without a third agent are currently ongoing or have recently been completed in BRAF mutated CRCs [58].
- In addition to the RAS/RAF/MAPK signaling pathway, activated EGFR can also induce the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/PTEN pathway. PIK3CA mutations in exon 9 and 20 have been studied as effectors of the EGFR downstream signaling pathway, similar to BRAF and RAS, and they might be related to resistance to EGFR inhibitors [59]. However, PIK3CA mutations tend to occur together with KRAS mutations [54,60]. Furthermore, confirmative evidence for a role of PIK3CA mutations in predicting response to cetuximab has not been shown [61]. Therefore, the role of PIK3CA mutations in routine predictive molecular testing for EGFR inhibitor therapy remains controversial.
- The PI3K/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway is frequently dysregulated in human cancers initiated by various molecular alterations including PIK3CA mutations. Janku et al. [62] performed early-phase clinical trials in which PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors were administered to the patients with advanced tumors, and demonstrated that PIK3CA mutation was independently associated with a better response to PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors.
- Many previous studies have reported the prognostic implication of PIK3CA mutations in CRC; some studies have shown a significant correlation between PIK3CA mutations and patient survival, but other studies have not [63]. Although World Health Organization (WHO) classification suggests that PIK3CA mutations are markers for poor prognosis [1], its practical role for predicting a patient’s outcome remains uncertain.
- Recently, experimental evidence suggests that cyclooxygenase 2 inhibition of aspirin down-regulates the PI3K signaling pathway. Liao et al. [64] reported that regular use of aspirin after cancer diagnosis in PIK3CA-mutated CRC patients was associated with a better prognosis [65], which suggests that PIK3CA mutations may serve as molecular biomarkers for predicting response to aspirin therapy.
- Based on confirmative correlation with patient prognosis, KRAS mutation testing is recommended in all patients with newly diagnosed CRC. The results of BRAF mutation testing are required for predicting a patients’ prognosis in both metastatic and earlier stage CRC and for excluding Lynch syndrome in all CRC patients. Especially in metastatic CRC patients, KRAS and NRAS mutational analysis should be performed for predicting the responses to anti-EGFR antibody therapy, and BRAF mutations are essential as poor prognostic biomarkers. Although the prognostic or predictive role of PIK3CA mutation is not clear, molecular testing for PIK3CA mutation may be necessary for predicting response to PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors and aspirin therapy after CRC diagnosis.
- Sanger sequencing is a traditional and well-confirmed method which needs ubiquitous instruments and inexpensive reagents, thus Sanger sequencing has been considered the gold standard method in many pathology laboratories for detecting oncogenic gene mutations [66]. In addition, Sanger sequencing has advantages for genetic mutational analysis such as the ability to identify specific mutations and to detect new mutations, and it has high reliability [66]. However, direct sequencing has some disadvantages including lower sensitivity (about 10%–20%), a multistep time-consuming method, subjective data interpretation, and no standardization [60]. Sequencing is not able to detect small amounts of mutated DNA fragments—especially less than 20% of total DNA—in the sample. Accordingly, the tumor samples should be very carefully prepared for to ensure collection of high tumor content.
- Compared to Sanger sequencing, pyrosequencing is more sensitive, and it can detect approximately 5% of mutant alleles [67]. It has some advantages compared to Sanger sequencing: (1) it is faster and more convenient; (2) the percentage of mutant allele quantity can be obtained; (3) it can be performed in a closed system in a single well; and (4) it can run multiple samples [68]. Therefore, this technology has provided sufficient analytical sensitivity and specificity for identifying KRAS, NRAS, and BRAF mutations in FFPE samples, even those from tissues with low tumor cell contents [69]. Pyrosequencing also has some disadvantages: (1) it requires additional costly instruments as compared to Sanger sequencer, as well as expensive reagents and consumables; (2) its data analysis is complex and challenging; (3) it can only sequence a short length of nucleotide sequence; and (4) it cannot detect new mutations [70]. However, the read length is sufficient for KRAS, NRAS, and BRAF sequencing because hot spots of these mutations are located within short length sequences.
- The detection of KRAS mutations using real-time PCR-based commercial kits has been suggested to be more reliable and sensitive than sequencing methods. The merits of commercial kits using real-time PCR systems are high sensitivity (approximately 1%), fast turn-around time, straightforward data interpretation, a closed-tube with a one-step process, small intra- and inter-lot deviations, and good concordance among the different real-time PCR systems. The disadvantages are that they have a relatively high cost per sample and high DNA input requirements [71]. In addition, they cannot detect all mutations or identify specific mutations.
- The currently used commercial kits for detecting KRAS mutations are as follows: Asuragen, DxS TheraScreen KRAS mutation detection kit, EntroGen, Roche COBAS, TrimGen Mutector II KRAS kit, and ViennaLab [71]. Kim et al. [72] reported that KRAS mutational status was discordant between primary and metastatic sites in 17.5% of samples, using the Sanger sequencing method. In contrast, Miglio et al. [73] demonstrated concordant KRAS mutation status and type of mutation between primary and metastatic tumors and successful amplification in fine needle aspiration biopsy specimens with low tumor cell numbers, using the TheraScreen test. The TheraScreen KRAS RGQ PCR Kit uses Scorpions and ARMS technologies and detects six mutations in codon 12 and one in codon 13 of KRAS. The COBAS KRAS mutation test kit (Roche Molecular Systems, Inc., Branchburg, NJ, USA) is a TaqMelt PCR assay and can detect 19 KRAS mutations in codons 12, 13, and 61. The COBAS test was also reported to have higher sensitivity than Sanger sequencing and can detect minor mutations including G13C, G13R, and Q61H, which are detected in less than 1% of CRCs [60,74].
- Another real-time PCR–based method, the peptide nucleic acid (PNA)–clamp assay, has recently been approved in Korea. The PNA-clamp assay utilizes PNAs that are modified DNA that recognize and bind to their complementary nucleic acid sequences with greater stability and specificity and cannot function as primers for DNA polymerases. PNA-clamp PCR is a low cost and highly sensitive method (0.1% of sensitivity) for detecting mutated genes, and is useful in clinical practice [75]. The PNA-clamp mutation detection kit cannot identify specific mutations.
- For improving detection sensitivity, high-resolution melting analysis, mutant-enriched PCR (enriched PCR–restriction fragment length polymorphism assay), and co-amplification at lower denaturation temperature–PCR methods can be applied in clinical mutation tests [71].
- As mentioned above, mutations in the genes related to the EGFR signaling network may be responsible for resistance to EGFR inhibitors or worse overall survival in CRC patients, but it is difficult and less practical to test all related gene mutations including KRAS exon 2–4, NRAS exon 2–4, BRAF V600E, and PIK3CA in each individual metastatic CRC patient using conventional methods. Therefore, a high-throughput method is more practical or recommended for sequencing multiple EGFR signaling-related genes in a single test to detect various mutations. Recently, several studies have demonstrated the advantages of NGS including high sensitivity and specificity compared to those of PCR-based commercial kits and sequencing methods [70,76]. The above testing methods are summarized in Table 1.
- The sample can be fresh, frozen, or FFPE. Surgical resection, endoscopic or needle biopsies, and cytology specimens are all acceptable sample types for mutation tests. If possible, the resection specimen is recommended for molecular analysis. However, biopsies are more commonly provided in inoperable advanced and metastatic CRC patients, and moreover, only cytology specimens may be available. Therefore, in such cases, the detection method should be successful with low total DNA quantity and highly sensitive for samples with a low tumor to total DNA ratio.
- The tissue specimen should contain cancer cells and a pathologist needs to estimate the content of tumor cells. Tumor cell enrichment by micro- or macro-dissection is required to increase the sensitivity of mutation tests. FFPE blocks are commonly available for mutation tests, but formalin fixation induces DNA denaturation and degradation [77]. Prolonged formalin fixation, decalcification, and prolonged storage of the paraffin blocks negatively affect the integrity of DNA [78], and the specimen quality is important for successful test results. The pathologist has the responsibility of selecting the most appropriate tissue block and tumor area to be tested.
- With patient and clinical information, the absence or presence of a gene mutation should be reported in the pathologic records. If possible, the affected codon and specific change should be indicated. Appropriate nomenclature should be used and ambiguous terms are not recommended in reports. The reports should also include specimen type and test method used.
- The analytical performance of both sequencing and commercial kits should be validated in each laboratory. It is recommended at least 40 samples be tested with many days and runs [79]. Both samples with known and unknown mutational status are recommended for validation. Additional comparative methods may be done with each testing method. The results of the validation should be analyzed by assessing accuracy, precision, analytical sensitivity and specificity, reportable range, and reference range [79].
- Each pathology laboratory should establish internal QA instructions for using each mutation analysis method and review all performed mutation analysis in regular QA meetings. The sequence information of wild- and mutant-types and their clinical significance should be determined. Each PCR test should include positive and negative controls. The laboratory must compare test positivity rate to its reported range, and maintain testing trends including clinical implications of gene mutation, concordance between methods, and positivity rates. All pathology laboratories should participate in external QA programs.
- Gene amplification and rearrangements
- Targeting of oncogenic drivers has been increasingly applied clinically in several advanced human malignancies resulting in improvement of overall survival. At this moment, a few receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors, such as trastuzumab, ramucirumab, and cetuximab, have been approved for targeted therapy. In addition, EGFR family (HER1–4), fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2), and MET are being explored as potential therapeutics and some have been successful in early-stage trials.
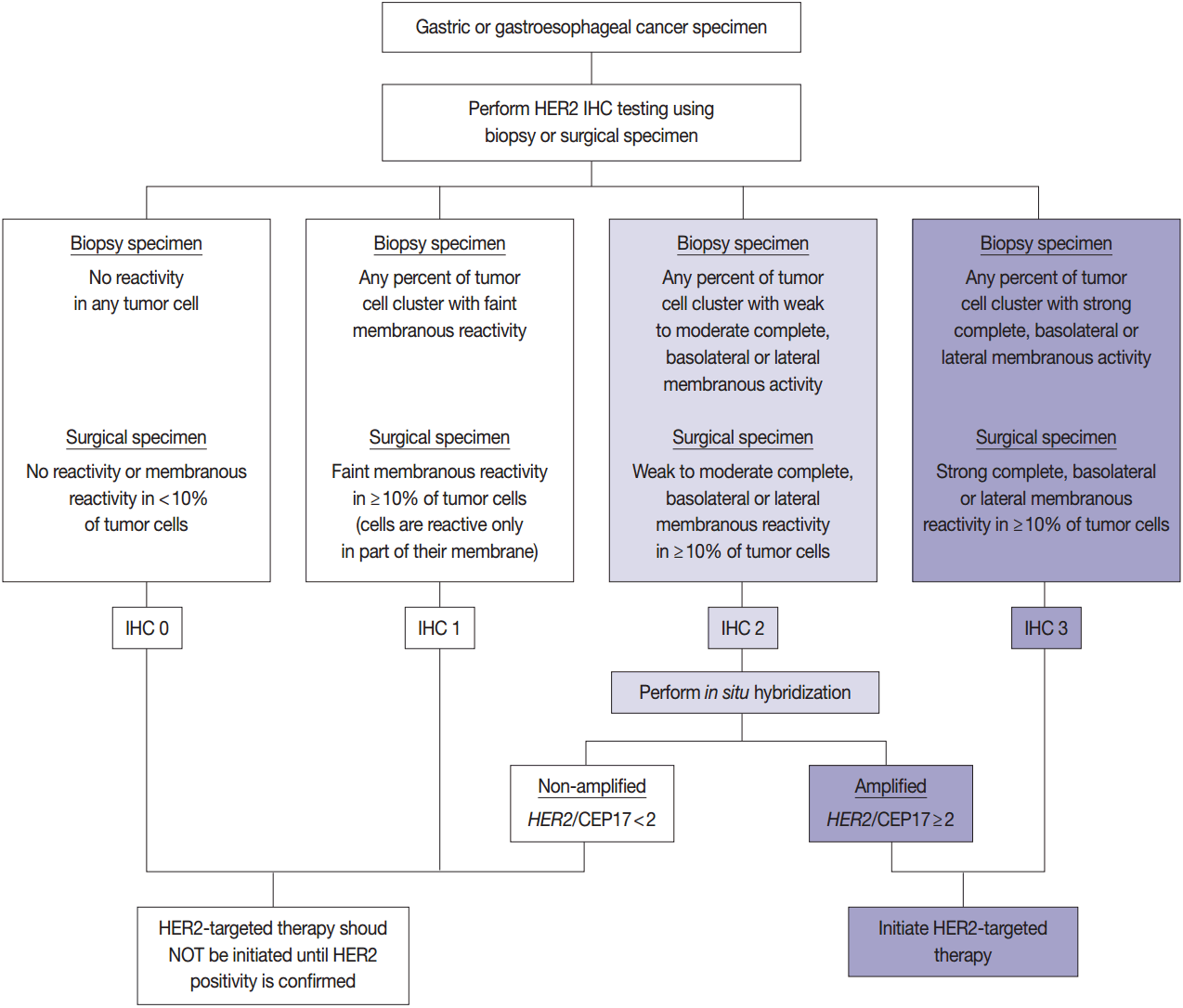
- HER2 has important oncogenic roles including modulation of cell growth, differentiation, and survival. Protein overexpression of HER2 mainly occurs through HER2 gene amplification, resulting in subsequent activation of abnormal cell signaling [80]. After the successful results of the Trastuzumab for Gastric Cancer (ToGA) trial [8], trastuzumab against HER2 has been approved for the treatment of HER2-positive advanced GC. HER2 testing is necessary in daily practice for treatment of advanced GC patients and the recommended HER2 testing algorithm is presented in Fig. 4.
- Following the success of the ToGA trial, HER2 blockade has been of great clinical interest in CRC [81-83]. Somatic HER2 amplification occurs in approximately 2%–7% of metastatic colorectal adenocarcinomas [81-83], and HER2-positivity (IHC3+ or IHC2+/amplification) is observed in about 5% of advanced CRCs [83]. HER2 gene amplification has been reported to be more frequent in rectal cancer than in right or left colon cancer [82]. KRAS mutation and HER2 amplification were suggested to be mutually exclusive [84], but our previous study demonstrated that HER2 amplification might occur in KRAS-mutated CRCs [60]. A few clinical trials with trastuzumab-based combinations have been performed [83,85,86]. Although earlier studies reported controversial results [85], recent trials suggest the possibility of HER2 blockade as a targeted therapy in advanced CRC patients [84]. Together, the HERACLES and MyPathway trials supported preclinical results that targeting HER2 with trastuzumab plus either lapatinib or pertuzumab is more effective than standard combination chemotherapy in HER2-positive CRC patients [83,86].
- For predicting response to EGFR inhibitors such as cetuximab, RAS mutation has been approved as a companion diagnosis. In addition to RAS mutation, gene amplification of the receptor tyrosine kinases HER2 has been shown to bypass EGFR signaling and activate the MEK-ERK cascade, suggesting predictive roles of this gene. This has been supported by a previous study that identified HER2 amplification in samples from metastatic CRC patients who did not benefit from EGFR inhibitor treatment [87].
- Clinical trials using antibodies against FGFR2b are now being conducted in GC patients. Oncogenic activation of FGFR2 via gene amplification occurs in a subset of common cancers, especially diffuse type GC [88,89]. FGFR2 amplification has been detected in about 8% of gastroesophageal cancers [88]. AZD4547 is a selective FGFR1–3 inhibitor with activity in FGFR2 amplified cancer models. In the SHINE trial in advanced GC patients with FGFR2 amplification or polysomy, AZD4547 was well-tolerated, but there was no progression-free survival benefit in the AZD-treated group [90]. However, in a recent translational clinical trial, GCs with high-level clonal FGFR2 amplification have a high response rate to the selective FGFR2 inhibitor AZD4547 [91].
- In addition to HER2 amplification, MET amplification was also found in a small subset of RAS and BRAF wild-type metastatic patients and is suggested to be associated with resistance to cetuximab treatment [92]. MET exon 14 deletion has been postulated to be one potential mechanism for MET protein overexpression [93]. A recent study suggested MET amplification as a novel mechanism of the resistance to EGFR and BRAF combination blockade in BRAF-mutated CRCs; furthermore, the study showed that switching from EGFR to MET inhibition resulted in clinical response of the disease [94].
- KRAS gene amplification is observed in a minor subset of CRC cases (1%–2%) and has been reported to be nearly always mutually exclusive with KRAS mutations [45]. The database by the The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) network has shown that NRAS, BRAF, and CRAF gene amplification can also be observed in a very low prevalence (<1%), but their clinical implication is not clear [26].
- ATP-binding sites in the kinase domains of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and ROS1 share 77% amino acid identity [95]. In vitro evidence suggests that ROS1 may be a more sensitive target than ALK to inhibition by crizotinib [96]. The incidence of ROS1 rearrangement in gastric adenocarcinomas has been reported to be between 0.5% and 1% [95,97].
- Neurotrophic tropomyosin receptor kinase (NTRK) gene rearrangements have oncogenic and transforming potential, and recently have emerged as targets for cancer therapy with developing selective inhibitors [98]. NTRK1, 2, and 3 gene rearrangements occur in several human cancers and they have been reported to have a 0.5% prevalence including TPM3-NTRK1 in CRCs [98]. A novel LMNA-NTRK1 rearrangement was reported in a metastatic CRC patient, who showed response to the pan-TRK inhibitor entrectinib [99].
- HER2 IHC should be routinely performed in all inoperable, locally advanced, recurrent, and metastatic GCs and gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancers at the initial diagnosis and in the diagnosis of recurred or metastatic GCs. If the HER2 IHC results is equivocal of any cause, HER2 genetic testing by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) or silver in situ hybridization (SISH) should be performed. Given that the majority of metastatic GCs are inoperable and need immediate first-line chemotherapy and they are predicted to progress very rapidly, HER2 IHC with or without SISH/FISH should be performed as quickly as possible [100]. Additionally, HER2 testing should be performed at relapse in patients with previously c-erbB2–negative tumors.
- Other gene analyses such as FGFR2, HER2, ROS1, and NTRK are necessary in patients with pretreated metastatic GCs or CRCs for selecting targeted therapy. HER2 and MET amplification status would be helpful for predicting resistance to EGFR inhibitors.
- Dual color FISH is recommended for gene amplification analysis. If possible, dual color SISH is also favored. Although both FISH and SISH, even if single-probe, showed good agreement for HER2 copy number testing in previous studies [101], it is widely accepted that SISH is a more preferred methodology than FISH because SISH is a bright-field methodology and enables pathologists to identify tumor area and HER2-positive area more rapidly, considering marked intratumoral HER2 heterogeneity [100,102]. Moreover, SISH slides can be stored for a longer period of time without bleaching than FISH slides.
- ISH testing should be rejected and repeated if: (1) controls are not as expected, (2) the observer cannot find and count at least 20 invasive tumor cells, (3) >25% of signals are unscorable owing to weak signals, (4) >10% of signals occur over cytoplasm, (5) the nuclear resolution is poor, and (6) auto-fluorescence is strong [103].
- Gene amplification status can also be examined by quantitative real-time PCR and digital PCR for target and reference gene fragments. Previous studies have demonstrated a close correlation between ISH results and quantitative PCR results using tissue or plasma samples, but with weak-to-moderate correlation [104]. This may be due to intratumoral heterogeneity and normal cell contamination. Therefore, ISH in cancer tissue samples is the gold standard method for gene amplification testing. PCR-based methods are not acceptable for confirmatory molecular diagnosis.
- Both surgical resection and biopsy can be used for ISH analysis. However, biopsies are more commonly available because advanced and metastatic gastrointestinal cancers are usually inoperable. Intratumoral heterogeneity of oncogenic gene amplification has been demonstrated by many researchers. Especially, heterogeneous HER2 expression is very common in GC and GEJ cancer, where upwards of 30% of HER2-positive GCs have been reported, and HER2 genetic status is closely correlated with HER2 expression status. Therefore, considering intratumoral HER2 heterogeneity, at least four to six biopsies by endoscopy are needed for sufficient and acceptable tests and to avoid false-negative results. The tissue microarray method is not recommended in routine clinical practice in pathology laboratories owing to HER2 heterogeneity [100,102].
- In order to obtain acceptable ISH results, specimen quality is important which relies on excellent sample fixation and preparation procedures. Regarding the cold ischemia time, it is recommended to transfer the endoscopic biopsy specimens into fixatives within 20 minutes of excision and the surgical excision specimens into fixatives within 1 hour of resection. However, most of the surgical specimens cannot be subject to fixation within less than 1 hour of resection in daily practice; thus, the cold ischemia time should be as short as possible in each pathology laboratory. The Task Force for gastric HER2 testing recommended that laboratories have their own validation results of optimal cold ischemia time for biopsies and surgical specimens for appropriate tissue handling protocols [100]. The fixation should be done using a sufficient amount of 10% neutral buffered formalin and the duration of fixation should be 8–72 hours. Although it may be influenced by primary fixation or storage conditions, sections should not be used if cut >6 weeks earlier [103]. During the preparation, insufficient deparaffinization can result in nuclear bubbles in ISH slides, and over-digestion may result in nuclear holes [102].
- In metastatic GC patients, treatment must be planned with full knowledge of a patient’s HER2 status. When ISH signals are counted, it is recommended for the pathologists to use HER2 IHC slides as screening results and to count signals in the HER2 IHC-positive area in order to overcome heterogeneous HER2 reactivity [104]. At least 20 evaluable and non-overlapping cells from IHC 2+ areas should be counted initially. If ISH results indicate borderline amplification (HER2:CEP17 ratio 1.8–2.2), another 20 cells should be counted to reconfirm the HER2: CEP17 ratio. Only cells with at least one ISH signal for each probe should be counted if dual probes are used. The final diagnosis is defined as “ISH positive” if the HER2:CEP17 ratio is ≥2.0 and “ISH negative” if the HER2:CEP17 ratio is <2.0. The reports of HER2 testing should provide a confirmative HER2 status, and an “equivocal” result, which is defined in the recommendations of HER2 testing in breast cancer, should not be accepted in GC patients [100]. Testing must be reported as ‘indeterminate’ if the interpretation of the HER2 ISH result is precluded owing to technical issues such as poor specimen handling, significant tissue crushing artifact, and edge artifact [105].
- Usually, the diagnostic criteria of gene amplification, including FGFR2 and MET in GC and HER2 and MET in CRC, have been defined as a target gene:reference gene ratio >2 [91], and the positivity criteria have been adopted from the recommendations of the gastric HER2 test. However, the HERACLES trial in metastatic CRC patients defined HER2-positivity criteria as tumors with a HER2 IHC 3+ score in more than 50% of cells or with HER2 IHC 2+ and a HER2:CEP17 >2 in more than 50% of cells by FISH [83]. The final molecular diagnosis should be determined using the validated criteria for each target gene and in each organ.
- In initial performing HER2 testing in GC, 25–50 GC cases should be analyzed in parallel, using IHC and ISH, and the concordance rate of IHC and ISH should be >90% if equivocal IHC 2+ cases are excluded. Since HER2 testing and diagnosis in GC have unique features compared to that of breast cancer, initial set-up and validation must be independent of breast cancer protocols, performed by specifically trained persons in gastric HER2 testing, and documented in GC HER2 testing protocols [100,102]. Other gene amplification tests need to be validated for each gene and organ with full consideration of the differences among genes and organs.
- Each pathology laboratory should establish internal QA instructions for the ISH method and review all performed ISH analysis in regular QA meetings. It is recommended that all SISH slides and several representative images for FISH are stored. If possible, performing parallel analysis such as IHC is also recommended. The laboratory must maintain testing trends including positivity rates and scoring distributions, and record the possible reasons for their variation. All pathology laboratories should participate in external QA programs.
- Epstein-Barr virus
- The EBV is a ubiquitous human herpes virus having a 172-kb DNA genome implicated in the etiology of many human malignancies [106]. The previous studies have demonstrated the presence of EBV in 2%–16% of conventional gastric adenocarcinomas worldwide, but the number of patients with EBV-associated GC is high because of the high incidence of GC, especially in Korea [7]. By TCGA results, EBV-positive GCs have a tendency of CIMP, but do not show a MSI-H phenotype or hMLH1 hypermethylation [25]. EBV-positive GCs were strongly associated with CDKN2A (p16INK4A) promoter hypermethylation and PIK3CA mutation [25]. The PIK3CA mutations were more dispersed in EBV-positive GCs, but localized in the kinase domain (exon 20) in EBV-negative cancers.
- Morphologically, EBV-positive GC has characteristic abundant lymphoid stroma. By WHO classification, gastric carcinoma with lymphoid stroma is an uncommon subtype and is closely associated with the presence of EBV [1]. The high throughput study by the TCGA network revealed that IL-12 mediated immune cell signaling signatures were activated and PD-L1/2 mRNA was overexpressed in EBV-positive GCs [25]. Recent studies supported the relationship between the presence of EBV and aberrant immune checkpoint protein expression by demonstrating high PD-L1 protein expression in EBV-positive GCs [107,108]. Therefore, EBV-positive GCs are suggested to be good candidates for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
- EBV-associated gastric carcinoma has a characteristic heavy lymphoid stroma, but the extent and degree of lymphoid stroma is variable and EBV status cannot be predicted by histologic features only. Furthermore, although EBV and MSI are mutually exclusive in GCs, microsatellite unstable GCs are also associated with lymphocyte-rich histology [109]. Therefore, to determine the EBV status of GC patients, laboratory detection of EBV is necessary in the newly diagnosed GC patients.
- Laboratory detection of EBV may be performed by several published methods [110]: (1) ISH identification of EBV-encoded small RNAs (EBER) directly in tumor cells; (2) EBV clonality assay by Southern blot analysis to distinguish latent form replicative infections; (3) EBV DNA amplification to detect viral DNA in patient tissues; (4) EBV viral load assays to quantitate EBV DNA in blood or body fluids to monitor disease status over time; (5) IHC for LMP1, EBNA1, EBNA2, LMP2A (latent state proteins of EBV), and BZLF1 (lytic state protein; so-called switch protein from lytic to latent state) to detect EBV-producing proteins and distinguish latent from replicative infections; (6) viral culture, which is possible but impractical for clinical use; (7) electron microscopy, which is also impractical; and (8) serology using VCA, EBNA, EA, and heterophile antibodies to monitor disease-association, -regression or -progression over time.
- The presence or absence of EBV is examined by EBER ISH, and it is considered the gold standard for detecting and localizing latent EBV in tissue samples [111]. EBER transcripts are amplified, which represent a reliable target for determining the presence or absence of EBV in tissue sections by ISH. Commercially available EBER probes are labeled with biotin, digoxigenin, or fluorescein (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark; Enzo Diagnostics, Farmingdale, NY, USA; Kreatech Diagnostics, Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Novocastra Laboratories Ltd., Newcastle, UK; Shandon Lipshaw, Pittsburgh, PA, USA; Innogenex, San Ramon, CA; Ventana Medical Systems, Tucson, AZ, USA) [110]. The IHC method has some merits in that it is fast, convenient, and widely used compared with the ISH method. However, LMP1 is undetectable in EBV-associated carcinomas, and BZLF1 is the only characteristic of lytic viral replication [110].
- EBER ISH can be accomplished on paraffin sections from biopsy or surgical excision or on cytology preparations.
- For EBER ISH, specimen quality is also important, which is dependent on good sample fixation and preparation procedures. The recommendations for specimen quality are the same as the other ISH analyses described above. The pathologists should select tumor sections with sufficient tumor cells to be included.
- EBER is usually detected uniformly in all of the tumor cells comprising an EBV-associated malignancy, but only focal EBER expression may be observed in tumors occasionally. EBER ISH signals are interpreted by microscopic examination and only the nuclear EBER positivity in tumor cells is defined as EBV-positive. Microscopic examination has additional advantages including evaluation of cell type and distribution of EBER signals.
- The initial validation of EBER ISH is not different from that of the other ISH methods. It should be noted that nonspecific positivity in the cytoplasm of scattered normal epithelial cell is sometimes observed, and EBER-positive memory B cells are rarely found in some of the GC specimens.
- QA of EBER ISH is also similar to that of the other ISH methods. The internal and external QA programs are mandatory.
MOLECULAR TESTS
Background
Indication
Methodology
Methods
Type of specimen
Specimen requirements
Reporting
Validation of test
Quality assurance
Background
RAS mutations
BRAF mutations
PIK3CA mutations
Indication
Methodology
Method
Sanger sequencing
Pyrosequencing
Real-time PCR–based mutation detection methods
Next-generation sequencing
Type of specimen
Specimen requirements
Reporting
Validation of test
Quality assurance
Background
HER2
FGFR2
MET and others
ROS1 gene rearrangement
NTRK gene rearrangements
Indication
Methodology
Method
Type of specimen
Specimen requirements
Reporting
Validation of test
Quality assurance
Background
Indication
Methodology
Method
Type of specimen
Specimen requirements
Reporting
Validation of test
Quality assurance
- GC and CRC are genetically heterogeneous disorders driven by various genetic alterations [112,113]. Recently, the development of NGS has allowed a sharply increased sequencing capacity and rapid analysis of multiplexed samples [114]. NGS has cast a light on the comprehensive genetic aberration of the disease [115] and enabled the discovery of candidate genes as potential targets in cancer therapy [116]. Through the recent development of molecular genomics, molecular profiling of gastrointestinal carcinoma by large-scale cancer genomics projects has also been performed [25,26]. The TCGA research network completed the genomic sequencing of CRC and classified it based on the molecular feature [25,26].
- In the TCGA report, GCs are divided into two classes: the hypermutated and nonhypermutated tumor. The non-hypermutated tumor includes genomically stable and chromosomally unstable subtypes. EBV-positive and MSI-H subtypes represent the hypermutated tumor and have frequent mutations in PIK3CA and ARID1A. Other studies have discovered that RHOA and CDH1 are possible driver genes in diffuse-type GC [117,118]. The gene mutations that contribute to gastric carcinoma, which have been revealed in previous large-scale studies, are listed in Table 2. CRC was also categorized into the hypermutated and the non-hypermutated tumor. The hypermutated tumors are characterized by elevated levels of MSI and defects in DNA MMR mechanisms. An activating mutation of BRAF is frequently presented in the hypermutated tumor [119,120]. Recurrent mutation of TP53, KRAS, APC, and PIK3CA has been consistently reported in previous studies and it is notable that the significantly frequent KRAS mutation is identified in non-hypermutated tumors (Table 3) [114,119,121].
- In the era of precision medicine, the clinical implication of NGS for multiple biomarker tests has been consistently required. With the aid of TCGA data which highlighted relevant genetic alterations and driver mutations linked to its biological pathway, various panels for multi-gene profile of carcinoma have been suggested. Multi-gene panels should identify a clinically actionable genetic aberration including variants linked to molecular classification, prediction of treatment response, and current/future target of therapy [122]. For instance, the Ion AmpliSeq Colon and Lung Cancer Research Panel includes more than 20 genes, such as RTK genes, RTK signaling genes, and other well-known cancer-related genes. However, these panels have not been fully validated using clinical samples and their inter-laboratory reproducibility has not been shown. Hence, the search for an ideal cancer marker panel and its validation by multi-centered and large-scale studies is still needed.
NEXT-GENERATION SEQUENCING CANCER PANEL
- Remarkable developments in molecular and genomic techniques have increased the importance of molecular classification or grading in gastrointestinal cancers. Molecular testing is necessary for screening hereditary disease, predicting patient prognosis, and predicting the responses to targeted therapy. Standardization and quality control of the pre-analytic, analytic, and postanalytic steps of each molecular test are essential for reliable diagnostic results. In particular, the pathologists are responsible for the selection of appropriate specimen, with sufficient tumor cell quantity and well-preserved nucleic acids, authorizing the test results, and providing reliable molecular and genomic information to the clinician. Because the validation of the test, diagnostic criteria, and interpretation are not the same for each gene or each tumor, pathologists with subspecialty expertise are necessary. Therefore, the pathologists must obtain recent and integrated knowledge, and accumulate their experience in molecular testing.
CONCLUSION
Acknowledgments
| Gene | Classification | Core pathway | Process |
Mutational rate (%) |
Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous study | Hypermutated tumora | Nonhypermutated tumora | |||||
| TP53 | TSG | Cell cycle/apoptosis, DNA damage control | Cell survival | 14–59 | 35 | 50 | 27,116–118,123–127 |
| PIK3CAb | Oncogene | PI3K-AKT | Cell survival | 7–36 | 40 | 12 | 27,116–118,123–127 |
| CDH1c | TSG | APC | Cell fate | 4–36 | - | 11 | 27,116–118,124–126 |
| ARID1Ab | TSG | Chromatin modification | Cell fate | 8–27 | 44 | 14 | 27,116,118,123–126 |
| PTEN | TSG | PI3K-AKT | Cell survival | 0–27 | 13 | - | 27,116,123,125,127 |
| KRAS | Oncogene | RAS/RAF | Cell survival | 0–27 | 19 | 6 | 27,116,118,125,127 |
| RHOAc | Oncogene | RHO/ROCK | Cell survival | 0–23 | - | 6 | 27,116,118 |
| APC | TSG | APC | Cell fate | 3–14 | - | 7 | 27,116,118,123,124 |
| ERBB3 | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 0–10 | 25 | - | 27,116 |
| ERBB2 | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 2–9 | - | 3 | 27,116,118,126,127 |
| CTNNB1 | Oncogene | APC | Cell fate | 2–9 | - | 4 | 27,116,118,124 |
| MET | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 0–9 | - | 116,127 | |
| FBXW7 | TSG | NOTCH | Cell fate | 2–6 | 24 | - | 27,118,127 |
| SMAD4 | TSG | TGF-β | Cell survival | 4–6 | - | 8 | 27,118 |
| EGFR | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 0–6 | - | - | 27,116,127 |
| NRAS | Oncogene | RAS/RAF | Cell survival | 0–5 | - | - | 116,125,127 |
TSG, tumour suppressor gene; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β.
aData of mutation rates are from The Cancer Genome Atlas database; [25]
bMore frequently mutated gene in gastric cancer with microsatellite instability–high frequency feature or Epstein-Barr virus positivity;
cMore frequently mutated gene in gastric cancer with diffuse type of Lauren classification.
| Gene | Classification | Core pathway | Process |
Mutational rate (%) |
Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous study | Hypermutated tumora | Nonhypermutated tumora | |||||
| TP53b | TSG | Cell cycle/apoptosis, DNA damage control | Cell survival | 27–65 | 20 | 60 | 119–121,128,129 |
| KRASb | Oncogene | RAS/RAF | Cell survival | 33–58 | 30 | 43 | 119–121,128–131 |
| APCb,c | TSG | APC | Cell fate | 40–56 | 51 | 81 | 121,129 |
| PIK3CAb | Oncogene | PI3K-AKT | Cell survival | 14–20 | - | 18 | 119,120,128,129,131 |
| BRAFc | Oncogene | RAS/RAF | Cell survival | 5–14 | 46 | - | 119,120,128–131 |
| PTEN | TSG | PI3K-AKT | Cell survival | 2–13 | - | - | 119,128,129 |
| EGFR | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 0–11 | - | - | 128,129,131 |
| SMAD4b | TSG | TGF-β | Cell survival | 2–11 | - | 10 | 119,121,128,129 |
| FBXW7b | TSG | NOTCH | Cell fate | 4–10 | - | 11 | 119,120,128,129 |
| NRAS | Oncogene | RAS | Cell survival | 2–7 | - | 9 | 119,120,128–131 |
| MET | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 2–4 | - | - | 119,120 |
| CTNNB1 | Oncogene | APC | Cell fate | 1–4 | - | 5 | 121,128,129 |
| AKT1 | Oncogene | PI3K | Cell survival | 1–4 | - | - | 119,128,129 |
| ERBB2 | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 1–3 | - | - | 128,129 |
| ALK | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 1–2 | - | - | 120,128,129 |
| MAP2K1 | Oncogene | RAS/RAF | Cell survival | 0–2 | - | - | 119–121,128 |
TSG, tumour suppressor gene; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β.
aData of mutation rates are from The Cancer Genome Atlas database; [26]
bMore frequently mutated gene in nonhypermutated colorectal cancer;
cMore frequently mutated gene in hypermutated colorectal cancer.
- 1. Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Lyon: IARC Press, 2010; 13-177.
- 2. Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C, Ward EM. Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2010; 19: 1893-907. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Oh CM, Won YJ, Jung KW, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2013. Cancer Res Treat 2016; 48: 436-50. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 4. Jung KW, Won YJ, Oh CM, et al. Prediction of cancer incidence and mortality in Korea, 2016. Cancer Res Treat 2016; 48: 451-7. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 5. Boland CR, Thibodeau SN, Hamilton SR, et al. A National Cancer Institute Workshop on Microsatellite Instability for cancer detection and familial predisposition: development of international criteria for the determination of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 5248-57. PubMed
- 6. Douillard JY, Oliner KS, Siena S, et al. Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 1023-34. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Lee HS, Chang MS, Yang HK, Lee BL, Kim WH. Epstein-barr virus-positive gastric carcinoma has a distinct protein expression profile in comparison with epstein-barr virus-negative carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 1698-705. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010; 376: 687-97. PubMed
- 9. Amin MB, Edge S, Greene F, et al. AJCC cancer staging manual. 8th ed. New York: Spinger, 2017; 203-74.
- 10. Jun SY, Kim M, Gu MJ, et al. Clinicopathologic and prognostic associations of KRAS and BRAF mutations in small intestinal adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol 2016; 29: 402-15. ArticlePDF
- 11. Peltomaki P. Role of DNA mismatch repair defects in the pathogenesis of human cancer. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 1174-9. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Ionov Y, Peinado MA, Malkhosyan S, Shibata D, Perucho M. Ubiquitous somatic mutations in simple repeated sequences reveal a new mechanism for colonic carcinogenesis. Nature 1993; 363: 558-61. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Boland CR. Evolution of the nomenclature for the hereditary colorectal cancer syndromes. Fam Cancer 2005; 4: 211-8. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Hampel H. Point: justification for Lynch syndrome screening among all patients with newly diagnosed colorectal cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2010; 8: 597-601. ArticlePubMed
- 15. Kloor M, Voigt AY, Schackert HK, Schirmacher P, von Knebel Doeberitz M, Bläker H. Analysis of EPCAM protein expression in diagnostics of Lynch syndrome. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 223-7. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Huth C, Kloor M, Voigt AY, et al. The molecular basis of EPCAM expression loss in Lynch syndrome-associated tumors. Mod Pathol 2012; 25: 911-6. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Watson P, Vasen HF, Mecklin JP, et al. The risk of extra-colonic, extra-endometrial cancer in the Lynch syndrome. Int J Cancer 2008; 123: 444-9. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 18. Kim JH, Shin SH, Kwon HJ, Cho NY, Kang GH. Prognostic implications of CpG island hypermethylator phenotype in colorectal cancers. Virchows Arch 2009; 455: 485-94. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Thibodeau SN, French AJ, Cunningham JM, et al. Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer: different mutator phenotypes and the principal involvement of hMLH1. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 1713-8. PubMed
- 20. Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A. AJCC cancer staging manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer, 2010; 241-9.
- 21. Sinicrope FA, Rego RL, Halling KC, et al. Prognostic impact of microsatellite instability and DNA ploidy in human colon carcinoma patients. Gastroenterology 2006; 131: 729-37. ArticlePubMed
- 22. Kim JY, Shin NR, Kim A, et al. Microsatellite instability status in gastric cancer: a reappraisal of its clinical significance and relationship with mucin phenotypes. Korean J Pathol 2013; 47: 28-35. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Lee HS, Choi SI, Lee HK, et al. Distinct clinical features and outcomes of gastric cancers with microsatellite instability. Mod Pathol 2002; 15: 632-40. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Choi YY, Bae JM, An JY, et al. Is microsatellite instability a prognostic marker in gastric cancer? A systematic review with meta-analysis. J Surg Oncol 2014; 110: 129-35. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 25. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014; 513: 202-9. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 26. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012; 487: 330-7. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 27. Cristescu R, Lee J, Nebozhyn M, et al. Molecular analysis of gastric cancer identifies subtypes associated with distinct clinical outcomes. Nat Med 2015; 21: 449-56. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 28. Sargent DJ, Marsoni S, Monges G, et al. Defective mismatch repair as a predictive marker for lack of efficacy of fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy in colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 3219-26. PubMedPMC
- 29. Le DT, Uram JN, Wang H, et al. PD-1 blockade in tumors with mismatch-repair deficiency. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 2509-20. PubMedPMC
- 30. Rosenbaum MW, Bledsoe JR, Morales-Oyarvide V, Huynh TG, Mino-Kenudson M. PD-L1 expression in colorectal cancer is associated with microsatellite instability, BRAF mutation, medullary morphology and cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Mod Pathol 2016; 29: 1104-12. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 31. Xiao Y, Freeman GJ. The microsatellite instable subset of colorectal cancer is a particularly good candidate for checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Cancer Discov 2015; 5: 16-8. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 32. Boger C, Behrens HM, Mathiak M, Krüger S, Kalthoff H, Röcken C. PD-L1 is an independent prognostic predictor in gastric cancer of Western patients. Oncotarget 2016; 7: 24269-83. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Moreira L, Balaguer F, Lindor N, et al. Identification of Lynch syndrome among patients with colorectal cancer. JAMA 2012; 308: 1555-65. ArticlePubMed
- 34. Buhard O, Suraweera N, Lectard A, Duval A, Hamelin R. Quasimonomorphic mononucleotide repeats for high-level microsatellite instability analysis. Dis Markers 2004; 20: 251-7. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 35. Lindor NM, Burgart LJ, Leontovich O, et al. Immunohistochemistry versus microsatellite instability testing in phenotyping colorectal tumors. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 1043-8. ArticlePubMed
- 36. de la Chapelle A, Hampel H. Clinical relevance of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 3380-7. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Oh JR, Kim DW, Lee HS, et al. Microsatellite instability testing in Korean patients with colorectal cancer. Fam Cancer 2012; 11: 459-66. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 38. Lin EI, Tseng LH, Gocke CD, et al. Mutational profiling of colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 42334-44. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 39. Richman SD, Seymour MT, Chambers P, et al. KRAS and BRAF mutations in advanced colorectal cancer are associated with poor prognosis but do not preclude benefit from oxaliplatin or irinotecan: results from the MRC FOCUS trial. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 5931-7. ArticlePubMed
- 40. Phipps AI, Buchanan DD, Makar KW, et al. KRAS-mutation status in relation to colorectal cancer survival: the joint impact of correlated tumour markers. Br J Cancer 2013; 108: 1757-64. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 41. Spano JP, Fagard R, Soria JC, Rixe O, Khayat D, Milano G. Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in colorectal cancer: preclinical data and therapeutic perspectives. Ann Oncol 2005; 16: 189-94. ArticlePubMed
- 42. Karapetis CS, Khambata-Ford S, Jonker DJ, et al. K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1757-65. ArticlePubMed
- 43. Van Cutsem E, Kohne CH, Hitre E, et al. Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 1408-17. ArticlePubMed
- 44. Lievre A, Bachet JB, Boige V, et al. KRAS mutations as an independent prognostic factor in patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 374-9. PubMed
- 45. Smith G, Bounds R, Wolf H, Steele RJ, Carey FA, Wolf CR. Activating K-Ras mutations outwith ‘hotspot’ codons in sporadic colorectal tumours: implications for personalised cancer medicine. Br J Cancer 2010; 102: 693-703. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 46. Vaughn CP, Zobell SD, Furtado LV, Baker CL, Samowitz WS. Frequency of KRAS, BRAF, and NRAS mutations in colorectal cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2011; 50: 307-12. PubMed
- 47. Heinemann V, von Weikersthal LF, Decker T, et al. FOLFIRI plus cetuximab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (FIRE-3): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2014; 15: 1065-75. ArticlePubMed
- 48. van Grieken NC, Aoyama T, Chambers PA, et al. KRAS and BRAF mutations are rare and related to DNA mismatch repair deficiency in gastric cancer from the East and the West: results from a large international multicentre study. Br J Cancer 2013; 108: 1495-501. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 49. Lee SH, Lee JW, Soung YH, et al. BRAF and KRAS mutations in stomach cancer. Oncogene 2003; 22: 6942-5. PubMed
- 50. Bettington M, Walker N, Clouston A, Brown I, Leggett B, Whitehall V. The serrated pathway to colorectal carcinoma: current concepts and challenges. Histopathology 2013; 62: 367-86. ArticlePubMed
- 51. Roth AD, Tejpar S, Delorenzi M, et al. Prognostic role of KRAS and BRAF in stage II and III resected colon cancer: results of the translational study on the PETACC-3, EORTC 40993, SAKK 60-00 trial. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 466-74. ArticlePubMed
- 52. Sinicrope FA, Shi Q, Smyrk TC, et al. Molecular markers identify subtypes of stage III colon cancer associated with patient outcomes. Gastroenterology 2015; 148: 88-99. ArticlePubMed
- 53. Palomaki GE, McClain MR, Melillo S, Hampel HL, Thibodeau SN. EGAPP supplementary evidence review: DNA testing strategies aimed at reducing morbidity and mortality from Lynch syndrome. Genet Med 2009; 11: 42-65. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 54. De Roock W, Claes B, Bernasconi D, et al. Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS, and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol 2010; 11: 753-62. PubMed
- 55. Di Nicolantonio F, Martini M, Molinari F, et al. Wild-type BRAF is required for response to panitumumab or cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 5705-12. ArticlePubMed
- 56. Kopetz S, Desai J, Chan E, et al. Phase II pilot study of vemurafenib in patients with metastatic BRAF-mutated colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33: 4032-8. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 57. Corcoran RB, Atreya CE, Falchook GS, et al. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition with dabrafenib and trametinib in BRAF V600-mutant colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33: 4023-31. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 58. Hyman DM, Puzanov I, Subbiah V, et al. Vemurafenib in multiple nonmelanoma cancers with BRAF V600 mutations. N Engl J Med 2015; 373: 726-36. PubMedPMC
- 59. Perrone F, Lampis A, Orsenigo M, et al. PI3KCA/PTEN deregulation contributes to impaired responses to cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Ann Oncol 2009; 20: 84-90. ArticlePubMed
- 60. Nam SK, Yun S, Koh J, et al. BRAF, PIK3CA, and HER2 oncogenic alterations according to KRAS mutation status in advanced colorectal cancers with distant metastasis. PLoS One 2016; 11: e0151865. Article
- 61. Prenen H, De Schutter J, Jacobs B, et al. PIK3CA mutations are not a major determinant of resistance to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 3184-8. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 62. Janku F, Wheler JJ, Naing A, et al. PIK3CA mutation H1047R is associated with response to PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway inhibitors in early-phase clinical trials. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 276-84. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 63. Mei ZB, Duan CY, Li CB, Cui L, Ogino S. Prognostic role of tumor PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Oncol 2016; 27: 1836-48. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 64. Liao X, Lochhead P, Nishihara R, et al. Aspirin use, tumor PIK3CA mutation, and colorectal-cancer survival. N Engl J Med 2012; 367: 1596-606. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 65. Ogino S, Lochhead P, Giovannucci E, Meyerhardt JA, Fuchs CS, Chan AT. Discovery of colorectal cancer PIK3CA mutation as potential predictive biomarker: power and promise of molecular pathological epidemiology. Oncogene 2014; 33: 2949-55. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 66. Franca LT, Carrilho E, Kist TB. A review of DNA sequencing techniques. Q Rev Biophys 2002; 35: 169-200. ArticlePubMed
- 67. Ogino S, Kawasaki T, Brahmandam M, et al. Sensitive sequencing method for KRAS mutation detection by pyrosequencing. J Mol Diagn 2005; 7: 413-21. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 68. Ahmadian A, Ehn M, Hober S. Pyrosequencing: history, biochemistry and future. Clin Chim Acta 2006; 363: 83-94. ArticlePubMed
- 69. Sundstrom M, Edlund K, Lindell M, et al. KRAS analysis in colorectal carcinoma: analytical aspects of pyrosequencing and allele-specific PCR in clinical practice. BMC Cancer 2010; 10: 660.PubMedPMCPDF
- 70. Altimari A, de Biase D, De Maglio G, et al. 454 next generation-sequencing outperforms allele-specific PCR, Sanger sequencing, and pyrosequencing for routine KRAS mutation analysis of formalinfixed, paraffin-embedded samples. Onco Targets Ther 2013; 6: 1057-64. PubMedPMC
- 71. Herreros-Villanueva M, Chen CC, Yuan SS, Liu TC, Er TK. KRAS mutations: analytical considerations. Clin Chim Acta 2014; 431: 211-20. ArticlePubMed
- 72. Kim MJ, Lee HS, Kim JH, et al. Different metastatic pattern according to the KRAS mutational status and site-specific discordance of KRAS status in patients with colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2012; 12: 347.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 73. Miglio U, Mezzapelle R, Paganotti A, et al. Mutation analysis of KRAS in primary colorectal cancer and matched metastases by means of highly sensitivity molecular assay. Pathol Res Pract 2013; 209: 233-6. ArticlePubMed
- 74. Gonzalez de Castro D, Angulo B, Gomez B, et al. A comparison of three methods for detecting KRAS mutations in formalin-fixed colorectal cancer specimens. Br J Cancer 2012; 107: 345-51. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 75. Oh JE, Lim HS, An CH, et al. Detection of low-level KRAS mutations using PNA-mediated asymmetric PCR clamping and melting curve analysis with unlabeled probes. J Mol Diagn 2010; 12: 418-24. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 76. Peeters M, Oliner KS, Parker A, et al. Massively parallel tumor multigene sequencing to evaluate response to panitumumab in a randomized phase III study of metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2013; 19: 1902-12. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 77. Srinivasan M, Sedmak D, Jewell S. Effect of fixatives and tissue processing on the content and integrity of nucleic acids. Am J Pathol 2002; 161: 1961-71. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 78. Nam SK, Im J, Kwak Y, et al. Effects of fixation and storage of human tissue samples on nucleic Acid preservation. Korean J Pathol 2014; 48: 36-42. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 79. Kamel-Reid S, Zhang T, Persons DL, Nikiforova MN, Halling KC. Validation of KRAS testing for anti-EGFR therapeutic decisions for patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012; 136: 26-32. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 80. Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2: 127-37. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 81. Conradi LC, Styczen H, Sprenger T, et al. Frequency of HER-2 positivity in rectal cancer and prognosis. Am J Surg Pathol 2013; 37: 522-31. ArticlePubMed
- 82. Seo AN, Kwak Y, Kim DW, et al. HER2 status in colorectal cancer: its clinical significance and the relationship between HER2 gene amplification and expression. PLoS One 2014; 9: e98528. Article
- 83. Sartore-Bianchi A, Trusolino L, Martino C, et al. Dual-targeted therapy with trastuzumab and lapatinib in treatment-refractory, KRAS codon 12/13 wild-type, HER2-positive metastatic colorectal cancer (HERACLES): a proof-of-concept, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 2016; 17: 738-46. ArticlePubMed
- 84. Schmoll HJ. Targeting HER2: precision oncology for colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol 2016; 17: 685-6. ArticlePubMed
- 85. Ramanathan RK, Hwang JJ, Zamboni WC, et al. Low overexpression of HER-2/neu in advanced colorectal cancer limits the usefulness of trastuzumab (Herceptin) and irinotecan as therapy: a phase II trial. Cancer Invest 2004; 22: 858-65. ArticlePubMed
- 86. Hurwitz H, Hainsworth JD, Swanton C, et al. Targeted therapy for gastrointestinaI (GI) tumors based on molecular profiles: early results from MyPathway, an open-label phase IIa basket study in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 2016; 34 Suppl: 653.Article
- 87. Bertotti A, Migliardi G, Galimi F, et al. A molecularly annotated platform of patient-derived xenografts (“xenopatients”) identifies HER2 as an effective therapeutic target in cetuximab-resistant colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov 2011; 1: 508-23. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 88. Turner N, Grose R. Fibroblast growth factor signalling: from development to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 116-29. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 89. Dieci MV, Arnedos M, Andre F, Soria JC. Fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors as a cancer treatment: from a biologic rationale to medical perspectives. Cancer Discov 2013; 3: 264-79. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 90. Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Mansoor W, et al. A randomized, open-label phase II study of AZD4547 (AZD) versus Paclitaxel (P) in previously treated patients with advanced gastric cancer (AGC) with fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) polysomy or gene amplification (amp): SHINE study. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33 Suppl: 4014.Article
- 91. Pearson A, Smyth E, Babina IS, et al. High-level clonal FGFR amplification and response to FGFR inhibition in a translational clinical trial. Cancer Discov 2016; 6: 838-51. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 92. Bardelli A, Corso S, Bertotti A, et al. Amplification of the MET receptor drives resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov 2013; 3: 658-73. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 93. Lee J, Ou SH, Lee JM, et al. Gastrointestinal malignancies harbor actionable MET exon 14 deletions. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 28211-22. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 94. Pietrantonio F, Oddo D, Gloghini A, et al. MET-driven resistance to dual EGFR and BRAF blockade may be overcome by switching from EGFR to MET inhibition in BRAF-mutated colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov 2016; 6: 963-71. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 95. Davies KD, Doebele RC. Molecular pathways: ROS1 fusion proteins in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2013; 19: 4040-5. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 96. Shaw AT, Ou SH, Bang YJ, et al. Crizotinib in ROS1-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2014; 371: 1963-71. PubMedPMC
- 97. Lee J, Lee SE, Kang SY, et al. Identification of ROS1 rearrangement in gastric adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2013; 119: 1627-35. ArticlePubMed
- 98. Amatu A, Sartore-Bianchi A, Siena S. NTRK gene fusions as novel targets of cancer therapy across multiple tumour types. ESMO Open 2016; 1: e000023. Article
- 99. Sartore-Bianchi A, Ardini E, Bosotti R, et al. Sensitivity to entrectinib associated with a novel LMNA-NTRK1 gene fusion in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2016; 108: djv306.ArticlePubMed
- 100. Kim KM, Bilous M, Chu KM, et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in gastric cancer: recommendations of an Asia-Pacific task force. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2014; 10: 297-307. PubMedPMC
- 101. Fox SB, Kumarasinghe MP, Armes JE, et al. Gastric HER2 Testing Study (GaTHER): an evaluation of gastric/gastroesophageal junction cancer testing accuracy in Australia. Am J Surg Pathol 2012; 36: 577-82. PubMed
- 102. Ruschoff J, Hanna W, Bilous M, et al. HER2 testing in gastric cancer: a practical approach. Mod Pathol 2012; 25: 637-50. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 103. Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 3997-4013. PubMed
- 104. Lee HE, Park KU, Yoo SB, et al. Clinical significance of intratumoral HER2 heterogeneity in gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer 2013; 49: 1448-57. ArticlePubMed
- 105. Koudelakova V, Berkovcova J, Trojanec R, et al. Evaluation of HER2 gene status in breast cancer samples with indeterminate fluorescence in situ hybridization by quantitative real-time PCR. J Mol Diagn 2015; 17: 446-55. ArticlePubMed
- 106. Longnecker RM, Kieff E, Cohen JI. Epstein-Barr virus. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Cohen JI, eds. Fields virology. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Williams and Wilkins, 2013; 1898-959.
- 107. Ma C, Patel K, Singhi AD, et al. Programmed death-ligand 1 expression is common in gastric cancer associated with Epstein-Barr virus or microsatellite instability. Am J Surg Pathol 2016; 40: 1496-506. ArticlePubMed
- 108. Kawazoe A, Kuwata T, Kuboki Y, et al. Clinicopathological features of programmed death ligand 1 expression with tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte, mismatch repair, and Epstein-Barr virus status in a large cohort of gastric cancer patients. Gastric Cancer 2016 Sep 14 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-016-0631-3. ArticlePDF
- 109. Chetty R. Gastrointestinal cancers accompanied by a dense lymphoid component: an overview with special reference to gastric and colonic medullary and lymphoepithelioma-like carcinomas. J Clin Pathol 2012; 65: 1062-5. ArticlePubMed
- 110. Gulley ML. Molecular diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus-related diseases. J Mol Diagn 2001; 3: 1-10. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 111. Ambinder RF, Mann RB. Epstein-Barr-encoded RNA in situ hybridization: diagnostic applications. Hum Pathol 1994; 25: 602-5. ArticlePubMed
- 112. Carethers JM, Jung BH. Genetics and genetic biomarkers in sporadic colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2015; 149: 1177-90. e3. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 113. Chia NY, Tan P. Molecular classification of gastric cancer. Ann Oncol 2016; 27: 763-9. ArticlePubMed
- 114. Chevrier S, Arnould L, Ghiringhelli F, Coudert B, Fumoleau P, Boidot R. Next-generation sequencing analysis of lung and colon carcinomas reveals a variety of genetic alterations. Int J Oncol 2014; 45: 1167-74. ArticlePubMed
- 115. Lin Y, Wu Z, Guo W, Li J. Gene mutations in gastric cancer: a review of recent next-generation sequencing studies. Tumour Biol 2015; 36: 7385-94. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 116. Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2012; 2: 401-4. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 117. Lee YS, Cho YS, Lee GK, et al. Genomic profile analysis of diffusetype gastric cancers. Genome Biol 2014; 15: R55.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 118. Li X, Wu WK, Xing R, et al. Distinct subtypes of gastric cancer defined by molecular characterization include novel mutational signatures with prognostic capability. Cancer Res 2016; 76: 1724-32. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 119. D’Haene N, Le Mercier M, De Nève N, et al. Clinical validation of targeted next generation sequencing for colon and lung cancers. PLoS One 2015; 10: e0138245.
- 120. Mukherjee S, Ma Z, Wheeler S, et al. Chromosomal microarray provides enhanced targetable gene aberration detection when paired with next generation sequencing panel in profiling lung and colorectal tumors. Cancer Genet 2016; 209: 119-29. ArticlePubMed
- 121. Yu J, Wu WK, Li X, et al. Novel recurrently mutated genes and a prognostic mutation signature in colorectal cancer. Gut 2015; 64: 636-45. ArticlePubMed
- 122. Marrone M, Filipski KK, Gillanders EM, Schully SD, Freedman AN. Multi-marker solid tumor panels using next-generation sequencing to direct molecularly targeted therapies. PLoS Curr 2014; 6: ecurrents.eogt.aa5415d435fc886145bd7137a280a971. Article
- 123. Wang K, Kan J, Yuen ST, et al. Exome sequencing identifies frequent mutation of ARID1A in molecular subtypes of gastric cancer. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 1219-23. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 124. Wong SS, Kim KM, Ting JC, et al. Genomic landscape and genetic heterogeneity in gastric adenocarcinoma revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Nat Commun 2014; 5: 5477.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 125. Ali SM, Sanford EM, Klempner SJ, et al. Prospective comprehensive genomic profiling of advanced gastric carcinoma cases reveals frequent clinically relevant genomic alterations and new routes for targeted therapies. Oncologist 2015; 20: 499-507. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 126. Kuboki Y, Yamashita S, Niwa T, et al. Comprehensive analyses using next-generation sequencing and immunohistochemistry enable precise treatment in advanced gastric cancer. Ann Oncol 2016; 27: 127-33. ArticlePubMed
- 127. Bria E, Pilotto S, Simbolo M, et al. Comprehensive molecular portrait using next generation sequencing of resected intestinal-type gastric cancer patients dichotomized according to prognosis. Sci Rep 2016; 6: 22982.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 128. Malapelle U, Pisapia P, Sgariglia R, et al. Less frequently mutated genes in colorectal cancer: evidences from next-generation sequencing of 653 routine cases. J Clin Pathol 2016; 69: 767-71. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 129. Dallol A, Buhmeida A, Al-Ahwal MS, et al. Clinical significance of frequent somatic mutations detected by high-throughput targeted sequencing in archived colorectal cancer samples. J Transl Med 2016; 14: 118.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 130. Sakai K, Tsurutani J, Yamanaka T, et al. Extended RAS and BRAF mutation snalysis using next-generation sequencing. PLoS One 2015; 10: e0121891.
- 131. Magliacane G, Grassini G, Bartocci P, et al. Rapid targeted somatic mutation analysis of solid tumors in routine clinical diagnostics. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 30592-603. ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Spatial and Temporal Tumor Heterogeneity in Gastric Cancer: Discordance of Predictive Biomarkers
Hye Seung Lee
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 192. CrossRef - Korean Practice Guidelines for Gastric Cancer 2024: An Evidence-based, Multidisciplinary Approach (Update of 2022 Guideline)
In-Ho Kim, Seung Joo Kang, Wonyoung Choi, An Na Seo, Bang Wool Eom, Beodeul Kang, Bum Jun Kim, Byung-Hoon Min, Chung Hyun Tae, Chang In Choi, Choong-kun Lee, Ho Jung An, Hwa Kyung Byun, Hyeon-Su Im, Hyung-Don Kim, Jang Ho Cho, Kyoungjune Pak, Jae-Joon Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 5. CrossRef - Elucidating the Role of KRAS, NRAS, and BRAF Mutations and Microsatellite Instability in Colorectal Cancer via Next-Generation Sequencing
Marta Rada Rodríguez, Bárbara Angulo Biedma, Irene Rodríguez Pérez, Javier Azúa Romeo
Cancers.2025; 17(13): 2071. CrossRef - Chitosan and Its Derivative‐Based Nanoparticles in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Molecular Mechanisms of Action and Promising Anticancer Strategies
Zahra Shokati Eshkiki, Fatemeh Mansouri, Amir Reza Karamzadeh, Abolfazl Namazi, Hafez Heydari, Javad Akhtari, Seidamir Pasha Tabaeian, Abolfazl Akbari, Hongda Liu
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Colorectal Cancer: Genetic Underpinning and Molecular Therapeutics for Precision Medicine
Gideon T. Dosunmu, Ardaman Shergill
Genes.2024; 15(5): 538. CrossRef - Effector Function Characteristics of Exhausted CD8+ T-Cell in Microsatellite Stable and Unstable Gastric Cancer
Dong-Seok Han, Yoonjin Kwak, Seungho Lee, Soo Kyung Nam, Seong-Ho Kong, Do Joong Park, Hyuk-Joon Lee, Nak-Jung Kwon, Hye Seung Lee, Han-Kwang Yang
Cancer Research and Treatment.2024; 56(4): 1146. CrossRef - A Standardized Pathology Report for Gastric Cancer: 2nd Edition
Young Soo Park, Myeong-Cherl Kook, Baek-hui Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Dong-Wook Kang, Mi-Jin Gu, Ok Ran Shin, Younghee Choi, Wonae Lee, Hyunki Kim, In Hye Song, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Hee Sung Kim, Guhyun Kang, Do Youn Park, So-Young Jin, Joon Mee Kim, Yoon Jung Choi,
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2023; 23(1): 107. CrossRef - A standardized pathology report for gastric cancer: 2nd edition
Young Soo Park, Myeong-Cherl Kook, Baek-hui Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Dong-Wook Kang, Mi-Jin Gu, Ok Ran Shin, Younghee Choi, Wonae Lee, Hyunki Kim, In Hye Song, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Hee Sung Kim, Guhyun Kang, Do Youn Park, So-Young Jin, Joon Mee Kim, Yoon Jung Choi,
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(1): 1. CrossRef - Korean Practice Guidelines for Gastric Cancer 2022: An Evidence-based, Multidisciplinary Approach
Tae-Han Kim, In-Ho Kim, Seung Joo Kang, Miyoung Choi, Baek-Hui Kim, Bang Wool Eom, Bum Jun Kim, Byung-Hoon Min, Chang In Choi, Cheol Min Shin, Chung Hyun Tae, Chung sik Gong, Dong Jin Kim, Arthur Eung-Hyuck Cho, Eun Jeong Gong, Geum Jong Song, Hyeon-Su Im
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2023; 23(1): 3. CrossRef - Influence of location-dependent sex difference on PD-L1, MMR/MSI, and EGFR in colorectal carcinogenesis
Jina Choi, Nayoung Kim, Ryoung Hee Nam, Jin Won Kim, Chin-Hee Song, Hee Young Na, Gyeong Hoon Kang, Alvaro Galli
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(2): e0282017. CrossRef - Comprehensive Analysis of Epigenetic Associated Genes with Differential
Gene Expression and Prognosis in Gastric Cancer
Songlin An, Xinbao Li, Bing Li, Yan Li
Combinatorial Chemistry & High Throughput Screening.2023; 26(3): 527. CrossRef - Liquid Biopsy in Advanced Colorectal Cancer: Clinical Applications of Different Analytes
Marco Donatello Delcuratolo, Andrea Modrego-Sánchez, Maristella Bungaro, Beatriz Antón-Pascual, Santiago Teran, Valentina Dipace, Silvia Novello, Rocio Garcia-Carbonero, Francesco Passiglia, Cristina Graválos-Castro
Journal of Molecular Pathology.2023; 4(3): 128. CrossRef - Exosomal circ_0001190 Regulates the Progression of Gastric Cancer via miR-586/SOSTDC1 Axis
Chao Liu, Jing Yang, Fengchi Zhu, Zhiying Zhao, Lixue Gao
Biochemical Genetics.2022; 60(6): 1895. CrossRef - Optimization of pre‐analytical and analytical steps for DNA and RNA analysis of fresh cytology samples
Ana Dolinar, Gašper Grubelnik, Irena Srebotnik‐Kirbiš, Margareta Strojan Fležar, Margareta Žlajpah
Cancer Medicine.2022; 11(21): 4021. CrossRef - Retracted: Connexin 43 upregulation by dioscin‐inhibited gastric cancer metastasis by suppressing PI3K/Akt pathway
Food Science & Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Pathology of Gastric Cancer
Moonsik Kim, An Na Seo
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2022; 22(4): 264. CrossRef - Case report: Undifferentiated sarcoma with multiple tumors involved in Lynch syndrome: Unexpected favorable outcome to sintilimab combined with chemotherapy
Jiaying Liu, Xiaona Chang, Guixiang Xiao, Jingmin Zhong, Bo Huang, Jiwei Zhang, Beibei Gao, Gang Peng, Xiu Nie
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The SUMO E3 ligase CBX4 is identified as a poor prognostic marker of gastric cancer through multipronged OMIC analyses
Yi Pan, Qingshang Li, Zhijun Cao, Shuliang Zhao
Genes & Diseases.2021; 8(6): 827. CrossRef - Worldwide variation in lynch syndrome screening: case for universal screening in low colorectal cancer prevalence areas
George Kunnackal John, Vipin Das Villgran, Christine Caufield-Noll, Francis Giardiello
Familial Cancer.2021; 20(2): 145. CrossRef - Tamoxifen Downregulates the Expression of Notch1 and DLL1 Genes in MKN-45 Gastric Cancer Cells
Faranak Khanipouyani, Hassan Akrami
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2021; 52(3): 922. CrossRef - Kallikrein-11, in Association with Coiled-Coil Domain Containing 25, as a Potential Prognostic Marker for Cholangiocarcinoma with Lymph Node Metastasis
Saeranee Siriphak, Ravinnipa Chanakankun, Tanakorn Proungvitaya, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Doungdean Tummanatsakun, Wunchana Seubwai, Molin Wongwattanakul, Siriporn Proungvitaya
Molecules.2021; 26(11): 3105. CrossRef - ISH-based HER2 diagnostics
Josef Rüschoff, Iris Nagelmeier, Bharat Jasani, Oliver Stoss
Der Pathologe.2021; 42(S1): 62. CrossRef - Identification and Analysis of Key Genes Driving Gastric Cancer Through Bioinformatics
Zhao Liu, Shihai Liu, Jing Guo, Libin Sun, Shasha Wang, Yixuan Wang, Wensheng Qiu, Jing Lv
Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers.2021; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Microsatellite Instability in Colorectal Cancer Liquid Biopsy—Current Updates on Its Potential in Non-Invasive Detection, Prognosis and as a Predictive Marker
Francis Yew Fu Tieng, Nadiah Abu, Learn-Han Lee, Nurul-Syakima Ab Mutalib
Diagnostics.2021; 11(3): 544. CrossRef - Metformin attenuates synergic effect of diabetes mellitus and Helicobacter pylori infection on gastric cancer cells proliferation by suppressing PTEN expression
Huibin Lu, Xinwei Han, Jianzhuang Ren, Kewei Ren, Zongming Li, Quanhui Zhang
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine.2021; 25(10): 4534. CrossRef - Recent Advances in the Diagnosis, Staging, Treatment, and Prognosis of Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Literature Review
Zhi-da Chen, Peng-fei Zhang, Hong-qing Xi, Bo Wei, Lin Chen, Yun Tang
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumor immune response and immunotherapy in gastric cancer
Yoonjin Kwak, An Na Seo, Hee Eun Lee, Hye Seung Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(1): 20. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of HER2 copy number between plasma and tissue samples in gastric cancer using droplet digital PCR
Boram Kim, Soo Kyung Nam, Soo Hyun Seo, Kyoung Un Park, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Do Joong Park, Hyung-Ho Kim, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Differential prognostic impact of CD8+ T cells based on human leucocyte antigen I and PD-L1 expression in microsatellite-unstable gastric cancer
Yoonjin Kwak, Jiwon Koh, Yujun Park, Yun Ji Hong, Kyoung Un Park, Hyung-Ho Kim, Do Joong Park, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee
British Journal of Cancer.2020; 122(9): 1399. CrossRef - High-Accuracy Determination of Microsatellite Instability Compatible with Liquid Biopsies
Amanda Bortolini Silveira, François-Clément Bidard, Amélie Kasperek, Samia Melaabi, Marie-Laure Tanguy, Manuel Rodrigues, Guillaume Bataillon, Luc Cabel, Bruno Buecher, Jean-Yves Pierga, Charlotte Proudhon, Marc-Henri Stern
Clinical Chemistry.2020; 66(4): 606. CrossRef - Chitosan: A compound for drug delivery system in gastric cancer-a review
Rana Shafabakhsh, Bahman Yousefi, Zatollah Asemi, Banafsheh Nikfar, Mohammad Ali Mansournia, Jamal Hallajzadeh
Carbohydrate Polymers.2020; 242: 116403. CrossRef - MSI and EBV Positive Gastric Cancer’s Subgroups and Their Link with Novel Immunotherapy
Maria Grazia Rodriquenz, Giandomenico Roviello, Alberto D’Angelo, Daniele Lavacchi, Franco Roviello, Karol Polom
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(5): 1427. CrossRef - Theoretical calculations of molecular descriptors for anticancer activities of 1, 2, 3-triazole-pyrimidine derivatives against gastric cancer cell line (MGC-803): DFT, QSAR and docking approaches
Rhoda Oyeladun Oyewole, Abel Kolawole Oyebamiji, Banjo Semire
Heliyon.2020; 6(5): e03926. CrossRef - Identification of a Clinical Cutoff Value for Multiplex KRASG12/G13 Mutation Detection in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Patients Using Digital Droplet PCR, and Comparison with Sanger Sequencing and PNA Clamping Assay
Kyung Ha Lee, Tae Hee Lee, Min Kyung Choi, In Sun Kwon, Go Eun Bae, Min-Kyung Yeo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(7): 2283. CrossRef - PD-L1 Testing in Gastric Cancer by the Combined Positive Score of the 22C3 PharmDx and SP263 Assay with Clinically Relevant Cut-offs
Yujun Park, Jiwon Koh, Hee Young Na, Yoonjin Kwak, Keun-Wook Lee, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Do Joong Park, Hyung-Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee
Cancer Research and Treatment.2020; 52(3): 661. CrossRef - Clinical and Molecular Assessment of Patients with Lynch Syndrome and Sarcomas Underpinning the Association with MSH2 Germline Pathogenic Variants
Nathália de Angelis de Carvalho, Bianca Naomi Niitsuma, Vanessa Nascimento Kozak, Felipe D’almeida Costa, Mariana Petaccia de Macedo, Bruna Elisa Catin Kupper, Maria Letícia Gobo Silva, Maria Nirvana Formiga, Sahlua Miguel Volc, Samuel Aguiar Junior, Eden
Cancers.2020; 12(7): 1848. CrossRef - Farnesoid X receptor antagonizes Wnt/β-catenin signaling in colorectal tumorigenesis
Junhui Yu, Shan Li, Jing Guo, Zhengshui Xu, Jianbao Zheng, Xuejun Sun
Cell Death & Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - YAP promotes self-renewal of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting expression of L-PTGDS and PTGDR2
Qingli Bie, Xiaozhe Li, Shiqi Liu, Xiao Yang, Zhenwen Qian, Rou Zhao, Xiaobei Zhang, Bin Zhang
International Journal of Clinical Oncology.2020; 25(12): 2055. CrossRef - ISH-basierte HER2-Diagnostik
Josef Rüschoff, Iris Nagelmeier, Bharat Jasani, Oliver Stoss
Der Pathologe.2020; 41(6): 606. CrossRef - Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Trichostatin A Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis by Regulating the PI3K/AKT Signalling Pathway in Gastric Cancer Cells
Xinli An, Zekun Wei, Botian Ran, Hao Tian, Hongyu Gu, Yan Liu, Hongjuan Cui, Shunqin Zhu
Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry.2020; 20(17): 2114. CrossRef - Role of Her-2 in Gastrointestinal Tumours beyond Gastric Cancer: A Tool for Precision Medicine
Csongor G. Lengyel, Baker Habeeb, Shah Z. Khan, Khalid El Bairi, Sara C. Altuna, Sadaqat Hussain, Syed Ayub Mazher, Dario Trapani, Angelica Petrillo
Gastrointestinal Disorders.2020; 3(1): 1. CrossRef - Next-generation Sequencing in the Management of Gastric and Esophageal Cancers
Jill C. Rubinstein, Norman G. Nicolson, Nita Ahuja
Surgical Clinics of North America.2019; 99(3): 511. CrossRef - Molecular profile in Paraguayan colorectal cancer patients, towards to a precision medicine strategy
Tania Fleitas-Kanonnikoff, Carolina Martinez‐Ciarpaglini, Josefina Ayala, Cinthia Gauna, Rita Denis, Ita Yoffe, Silvia Sforza, María Teresa Martínez, Alicia Pomata, Maider Ibarrola‐Villava, Sipan Arevshatyan, Verónica Burriel, Diego Boscá, Oscar Pastor, A
Cancer Medicine.2019; 8(6): 3120. CrossRef - Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive digestive tumors
Anna D. Wagner, Berna C. Özdemir, Josef Rüschoff
Current Opinion in Oncology.2019; 31(4): 354. CrossRef - Assessing molecular subtypes of gastric cancer: microsatellite unstable and Epstein-Barr virus subtypes. Methods for detection and clinical and pathological implications
Carolina Martinez-Ciarpaglini, Tania Fleitas-Kanonnikoff, Valentina Gambardella, Marta Llorca, Cristina Mongort, Regina Mengual, Gema Nieto, Lara Navarro, Marisol Huerta, Susana Rosello, Desamparados Roda, Noelia Tarazona, Samuel Navarro, Gloria Ribas, An
ESMO Open.2019; 4(3): e000470. CrossRef - Current and future molecular diagnostics of gastric cancer
Rachel Sin-Yu Choi, Wing Yin Xenia Lai, Lok Ting Claire Lee, Wing Lam Christa Wong, Xiao Meng Pei, Hin Fung Tsang, Joel Johnson Leung, William Chi Shing Cho, Man Kee Maggie Chu, Elaine Yue Ling Wong, Sze Chuen Cesar Wong
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2019; 19(10): 863. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic significance of human leukocyte antigen class I expression in patients with stage II and III gastric cancer
Yujun Park, Jiwon Koh, Yoonjin Kwak, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Do Joong Park, Hyung-Ho Kim, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2019; 68(11): 1779. CrossRef - Development and Validation of an Easy-to-Implement, Practical Algorithm for the Identification of Molecular Subtypes of Gastric Cancer: Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications
Jiwon Koh, Keun-Wook Lee, Soo Kyung Nam, An Na Seo, Ji-Won Kim, Jin Won Kim, Do Joong Park, Hyung-Ho Kim, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee
The Oncologist.2019; 24(12): e1321. CrossRef - Mechanisms and Therapy for Cancer Metastasis to the Brain
Federica Franchino, Roberta Rudà, Riccardo Soffietti
Frontiers in Oncology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Status of programmed death-ligand 1 expression in sarcomas
Hyung Kyu Park, Mingi Kim, Minjung Sung, Seung Eun Lee, Yu Jin Kim, Yoon-La Choi
Journal of Translational Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Design and synthesis of near-infrared fluorescence-enhancement probes for the cancer-specific enzyme hNQO1
Changyu Zhang, Bei-Bei Zhai, Tao Peng, Zelin Zhong, Lianbin Xu, Qiang-Zhe Zhang, Lu-Yuan Li, Long Yi, Zhen Xi
Dyes and Pigments.2017; 143: 245. CrossRef - Progress in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer
Zheyu Song, Yuanyu Wu, Jiebing Yang, Dingquan Yang, Xuedong Fang
Tumor Biology.2017; 39(7): 101042831771462. CrossRef - Pathologische Einteilung und Diagnostik des Ösophagus- und Magenkarzinoms
S. Förster, A. Tannapfel
Der Gastroenterologe.2017; 12(5): 394. CrossRef - NR4A1-induced increase in the sensitivity of a human gastric cancer line to TNFα-mediated apoptosis is associated with the inhibition of JNK/Parkin-dependent mitophagy
Hongzhu Yan, Feng Xiao, Jue Zou, Chengmin Qiu, Weiwei Sun, Minmin Gu, Li Zhang
International Journal of Oncology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure




Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 4.
| Sanger sequencing | Pyrosequencing | Real-time PCR | PNA-clamp assay | Next generation sequencing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advantage | Gold standard | More rapid and sensitive than Sanger sequencing | Simple and fast | Simple and fast | High-throughput |
| Instrument | Ubiquitous | Not ubiquitous | Depending on kit | Ubiquitous | Costly equipment |
| Sensitivity (%) | 10–20 | 5 | 1 | 0.1 | 1 |
| Method | Labor-intensive, time-consuming | Convenient, closed system | Closed system, one-step process | Closed system, one-step process | Time-consuming |
| Mutant allele quantity (%) | Unmeasurable | Measurable | Unmeasurable | Unmeasurable | Measurable |
| Detect all or new mutation | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| Detect specific mutation | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Data interpretation | Subjective | Less subjective, but complex | Simple and easy | Simple and easy | Complicated (need statistics) |
| Gene | Classification | Core pathway | Process | Mutational rate (%) |
Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous study | Hypermutated tumor |
Nonhypermutated tumor |
|||||
| TP53 | TSG | Cell cycle/apoptosis, DNA damage control | Cell survival | 14–59 | 35 | 50 | 27,116–118,123–127 |
| PIK3CA |
Oncogene | PI3K-AKT | Cell survival | 7–36 | 40 | 12 | 27,116–118,123–127 |
| CDH1 |
TSG | APC | Cell fate | 4–36 | - | 11 | 27,116–118,124–126 |
| ARID1A |
TSG | Chromatin modification | Cell fate | 8–27 | 44 | 14 | 27,116,118,123–126 |
| PTEN | TSG | PI3K-AKT | Cell survival | 0–27 | 13 | - | 27,116,123,125,127 |
| KRAS | Oncogene | RAS/RAF | Cell survival | 0–27 | 19 | 6 | 27,116,118,125,127 |
| RHOA |
Oncogene | RHO/ROCK | Cell survival | 0–23 | - | 6 | 27,116,118 |
| APC | TSG | APC | Cell fate | 3–14 | - | 7 | 27,116,118,123,124 |
| ERBB3 | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 0–10 | 25 | - | 27,116 |
| ERBB2 | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 2–9 | - | 3 | 27,116,118,126,127 |
| CTNNB1 | Oncogene | APC | Cell fate | 2–9 | - | 4 | 27,116,118,124 |
| MET | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 0–9 | - | 116,127 | |
| FBXW7 | TSG | NOTCH | Cell fate | 2–6 | 24 | - | 27,118,127 |
| SMAD4 | TSG | TGF-β | Cell survival | 4–6 | - | 8 | 27,118 |
| EGFR | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 0–6 | - | - | 27,116,127 |
| NRAS | Oncogene | RAS/RAF | Cell survival | 0–5 | - | - | 116,125,127 |
| Gene | Classification | Core pathway | Process | Mutational rate (%) |
Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous study | Hypermutated tumor |
Nonhypermutated tumor |
|||||
| TP53 |
TSG | Cell cycle/apoptosis, DNA damage control | Cell survival | 27–65 | 20 | 60 | 119–121,128,129 |
| KRAS |
Oncogene | RAS/RAF | Cell survival | 33–58 | 30 | 43 | 119–121,128–131 |
| APC |
TSG | APC | Cell fate | 40–56 | 51 | 81 | 121,129 |
| PIK3CA |
Oncogene | PI3K-AKT | Cell survival | 14–20 | - | 18 | 119,120,128,129,131 |
| BRAF |
Oncogene | RAS/RAF | Cell survival | 5–14 | 46 | - | 119,120,128–131 |
| PTEN | TSG | PI3K-AKT | Cell survival | 2–13 | - | - | 119,128,129 |
| EGFR | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 0–11 | - | - | 128,129,131 |
| SMAD4 |
TSG | TGF-β | Cell survival | 2–11 | - | 10 | 119,121,128,129 |
| FBXW7 |
TSG | NOTCH | Cell fate | 4–10 | - | 11 | 119,120,128,129 |
| NRAS | Oncogene | RAS | Cell survival | 2–7 | - | 9 | 119,120,128–131 |
| MET | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 2–4 | - | - | 119,120 |
| CTNNB1 | Oncogene | APC | Cell fate | 1–4 | - | 5 | 121,128,129 |
| AKT1 | Oncogene | PI3K | Cell survival | 1–4 | - | - | 119,128,129 |
| ERBB2 | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 1–3 | - | - | 128,129 |
| ALK | Oncogene | RTK | Cell survival | 1–2 | - | - | 120,128,129 |
| MAP2K1 | Oncogene | RAS/RAF | Cell survival | 0–2 | - | - | 119–121,128 |
PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PNA, peptide nucleic acid.
TSG, tumour suppressor gene; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β. Data of mutation rates are from The Cancer Genome Atlas database; [ More frequently mutated gene in gastric cancer with microsatellite instability–high frequency feature or Epstein-Barr virus positivity; More frequently mutated gene in gastric cancer with diffuse type of Lauren classification.
TSG, tumour suppressor gene; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β. Data of mutation rates are from The Cancer Genome Atlas database; [ More frequently mutated gene in nonhypermutated colorectal cancer; More frequently mutated gene in hypermutated colorectal cancer.

 E-submission
E-submission