Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 54(4); 2020 > Article
-
Review
Clinicopathological characteristics of BRCA-associated breast cancer in Asian patients -
Eun-Kyu Kim1
 , So Yeon Park2
, So Yeon Park2 , Sung-Won Kim,3
, Sung-Won Kim,3
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2020;54(4):265-275.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.04.07
Published online: May 14, 2020
1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
2Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
3Department of Surgery, Daerim St. Mary’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Sung-Won Kim, MD, PhD, Department of Surgery, Daerim St. Mary’s Hospital, 657 Siheung-daero, Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul 07442, Korea Tel: +82-2-829-9515, Fax: +82-2-833-6224, E-mail: brcakorea@gmail.com
© 2020 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

-
Predicting
BRCA
mutation and stratifying targeted therapy response using multimodal learning: a multicenter study
Yi Li, Xiaomin Xiong, Xiaohua Liu, Mengke Xu, Boping Yang, Xiaoju Li, Yu Li, Bo Lin, Bo Xu
Annals of Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics of breast cancer patients tested for germline BRCA1/2 mutations by next‐generation sequencing in Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University
Songporn Oranratnachai, Watchalawalee Yamkaew, Atchara Tunteeratum, Thongchai Sukarayothin, Nareenart Iemwimangsa, Ravat Panvichien
Cancer Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic and predictive biomarkers with therapeutic targets in breast cancer: A 2022 update on current developments, evidence, and recommendations
Clement Chung, Vanessa T.Y. Yeung, Kenneth C.W. Wong
Journal of Oncology Pharmacy Practice.2023; 29(6): 1343. CrossRef - Mutations of TP53 and genes related to homologous recombination repair in breast cancer with germline BRCA1/2 mutations
Jinyong Kim, Kyeonghun Jeong, Hyeji Jun, Kwangsoo Kim, Jeong Mo Bae, Myung Geun Song, Hanbaek Yi, Songyi Park, Go-un Woo, Dae-Won Lee, Tae-Yong Kim, Kyung-Hun Lee, Seock-Ah Im
Human Genomics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - BRCA 1–2 Incidence in Synchronous and Metachronous Breast Cancer: a Tertiary Center Study
Ahmet Dağ, Bilal Arslan, Erkan Güler, Serdar Mermer
Indian Journal of Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Habitat Analysis of Breast Cancer‐Enhanced MRI Reflects BRCA1 Mutation Determined by Immunohistochemistry
Tianming Du, Haidong Zhao, Chen Li
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Factors Associated with BRCA1/2 Gene Mutation in Chinese Populations with Breast Cancer
Guoding Huang, Hongquan Lu, Qizhu Chen, Xinting Huang
International Journal of General Medicine.2022; Volume 15: 6783. CrossRef - Association between fertility treatments and breast cancer risk in women with a family history or BRCA mutations: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiaojing Liu, Jing Yue, Ruqiya Pervaiz, Hanwang Zhang, Lan Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Baseline [18F]FDG PET/CT Semiquantitative Parameters and BRCA Mutational Status and Their Prognostic Role in Patients with Invasive Ductal Breast Carcinoma
Francesco Dondi, Domenico Albano, Pietro Bellini, Luca Camoni, Giorgio Treglia, Francesco Bertagna
Tomography.2022; 8(6): 2662. CrossRef - The clinical and diagnostic characteristics of BRCA-associated breast cancer
M.A. Golotyuk, A.A. Berezhnoy, N.V. Kazantseva, A.V. Dorofeev, S.A. Shevchenko, I.V. Borzunov, N.I. Rozhkova
Onkologiya. Zhurnal imeni P.A.Gertsena.2022; 11(6): 18. CrossRef - The Clinical and Pathological Profile of BRCA1 Gene Methylated Breast Cancer Women: A Meta-Analysis
Ilary Ruscito, Maria Luisa Gasparri, Maria Paola De Marco, Flavia Costanzi, Aris Raad Besharat, Andrea Papadia, Thorsten Kuehn, Oreste Davide Gentilini, Filippo Bellati, Donatella Caserta
Cancers.2021; 13(6): 1391. CrossRef - Changing Patterns in Clinicopathological Characteristics of Breast Cancer and Prevalence of BRCA Mutations: Analysis in a Rural Area of Southern China
Qiuming Wang, Heming Wu, Yongquan Lan, Jinhong Zhang, Jingna Wu, Yunuo Zhang, Liang Li, Donghua Liu, Jinfeng Zhang
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 7371. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure


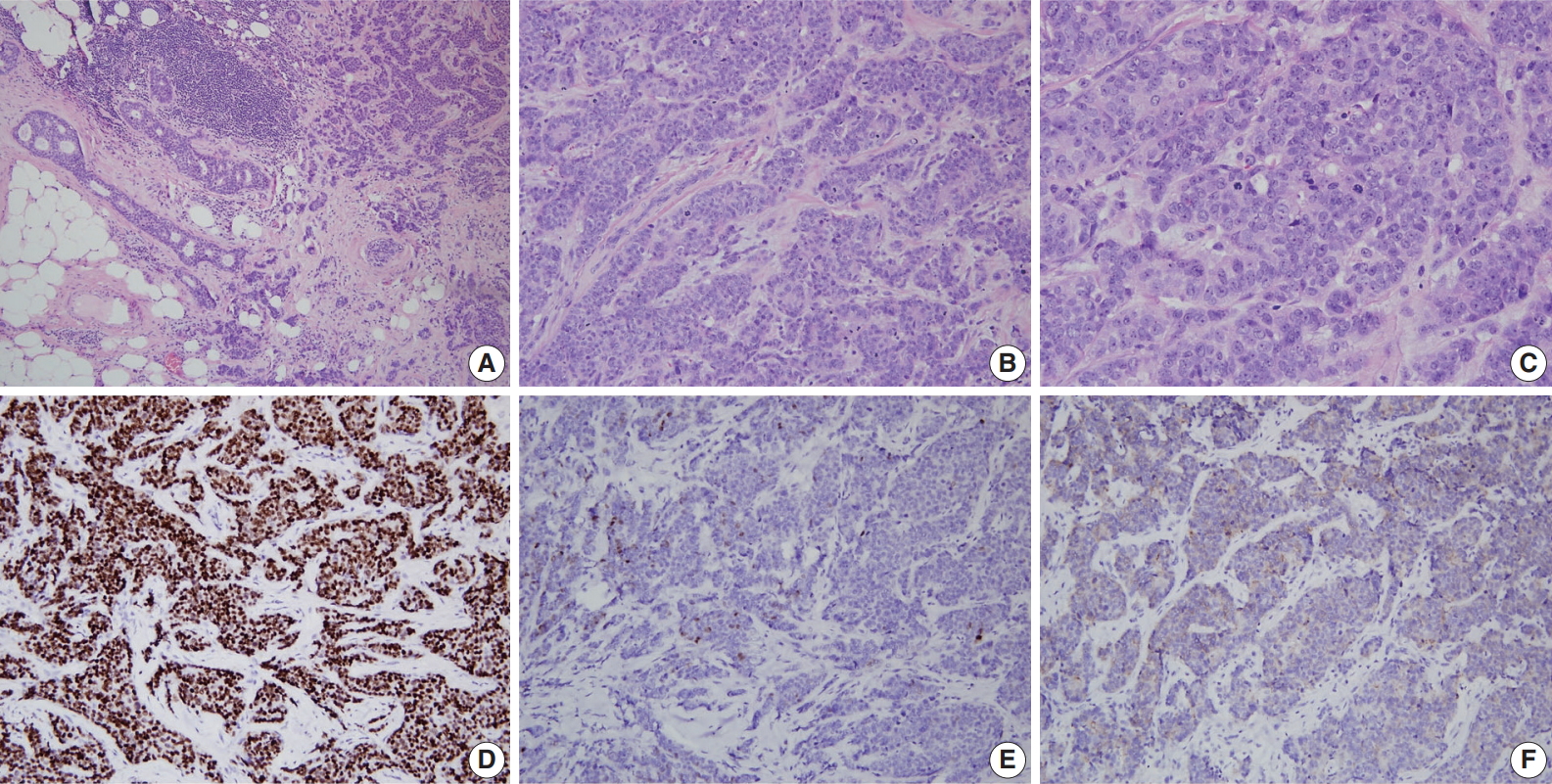
Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
| BRCA1 | BRCA2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Histology | Ductal, no special type (75%); medullary or atypical medullary (10%–20%); rare lobular | Ductal, no special type (75%); medullary or atypical medullary (< 5%); lobular or ductal with lobular features more common than in BRCA1 (~10%) |
| Mitosis | High | Low |
| Prominent lymphocytic infiltration | Often | Rare |
| Histologic grade | High (grade III, 71%–75%) | Intermediate to high (grade II, 43%–45%; grade III, 45%–50%) |
| ER | Negative (73%–90%) | Positive (65%–77%) |
| PR | Negative (79%–81%) | Positive (40%–64%) |
| HER2 | Negative (86%–95%) | Negative (72%–95%) |
| Triple-negative phenotype | Common (57%–75%) | Rare |
| Associated in situ carcinoma | Rare | Common |
| Others | p53 positive (50%–53%); CK5 positive (50%); bcl-2, low; CDKN2A, low; cyclin D1 negative (90%) | p53 positive (40%–52%); CK5 negative (90%); bcl-2, high; CDKN2A, high; cyclin D1 positive (60%) |
ER, estrogen receptor; PR, progesterone receptor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2; CK, cytokeratin; bcl-2, B-cell leukemia/lymphoma-2; CDKN2A, Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A.

 E-submission
E-submission