Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 55(3); 2021 > Article
-
Review
Hepatocellular adenomas: recent updates -
Haeryoung Kim1
 , Young Nyun Park2
, Young Nyun Park2
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2021;55(3):171-180.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.02.27
Published online: April 7, 2021
1Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Pathology, Graduate School of Medical Science, Brain Korea 21 Project, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Young Nyun Park, MD, PhD, Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 50-1 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 03722, Korea, Tel: +82-2-2228-1678, Fax: +82-2-362-0860, E-mail: young0608@yuhs.ac
© 2021 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Prognostic role of selection criteria for liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Review and bibliometric
Pamela Scarlett Espinoza Loyola, Diana Laura Muratalla Bautista, Karen Adela Hernández Bautista, Elizabeth Gil White, José Antonio González Moreno, Daniel Angel Torres del Real, Víctor Manuel Páez Zayas, Carla Escorza-Molina, Fernando Mondragón Rodríguez,
iLIVER.2024; 3(1): 100077. CrossRef - ACG Clinical Guideline: Focal Liver Lesions
Catherine Frenette, Mishal Mendiratta-Lala, Reena Salgia, Robert J. Wong, Bryan G. Sauer, Anjana Pillai
American Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 119(7): 1235. CrossRef - Hepatocellular adenoma update: diagnosis, molecular classification, and clinical course
Sarah Poetter-Lang, Ahmed Ba-Ssalamah, Nina Bastati, Sami A Ba-Ssalamah, Jacqueline C Hodge, Giuseppe Brancatelli, Valérie Paradis, Valérie Vilgrain
British Journal of Radiology.2024; 97(1163): 1740. CrossRef - Fatal rupture of hepatic adenomatosis: Autopsy case and review of the literature
Sarra Ben Abderrahim, Khouloud Chérif, Zeineb Nfikha, Sarra Gharsallaoui, Imen El Aini, Maher Jedidi, Moncef Mokni, Mohamed Ben Dhiab
Journal of Forensic Sciences.2023; 68(4): 1393. CrossRef - Large Hepatocellular Adenoma Presenting with Iron Deficiency Anemia: A Case Report
Young Kwon Koh, Su Hyun Yoon, Sung Han Kang, Hyery Kim, Ho Joon Im, Suhyeon Ha, Jung-Man Namgoong, Kyung-Nam Koh
Clinical Pediatric Hematology-Oncology.2023; 30(1): 25. CrossRef - A Case Report on a Giant Hepatic Inflammatory Adenoma in a Young Female That Presented as Spontaneous Intrahepatic Hematoma
Andreas Kyvetos, Panagiota Voukelatou, Ioannis Vrettos, Spyridon Pantzios , Ioannis Elefsiniotis
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in Histological and Molecular Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Joon Hyuk Choi, Swan N. Thung
Biomedicines.2023; 11(9): 2582. CrossRef - Estrobolome and Hepatocellular Adenomas—Connecting the Dots of the Gut Microbial β-Glucuronidase Pathway as a Metabolic Link
Sandica Bucurica, Mihaela Lupanciuc, Florentina Ionita-Radu, Ion Stefan, Alice Elena Munteanu, Daniela Anghel, Mariana Jinga, Elena Laura Gaman
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(22): 16034. CrossRef - Hepatocellular adenoma: what we know, what we do not know, and why it matters
Paulette Bioulac‐Sage, Annette S H Gouw, Charles Balabaud, Christine Sempoux
Histopathology.2022; 80(6): 878. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure






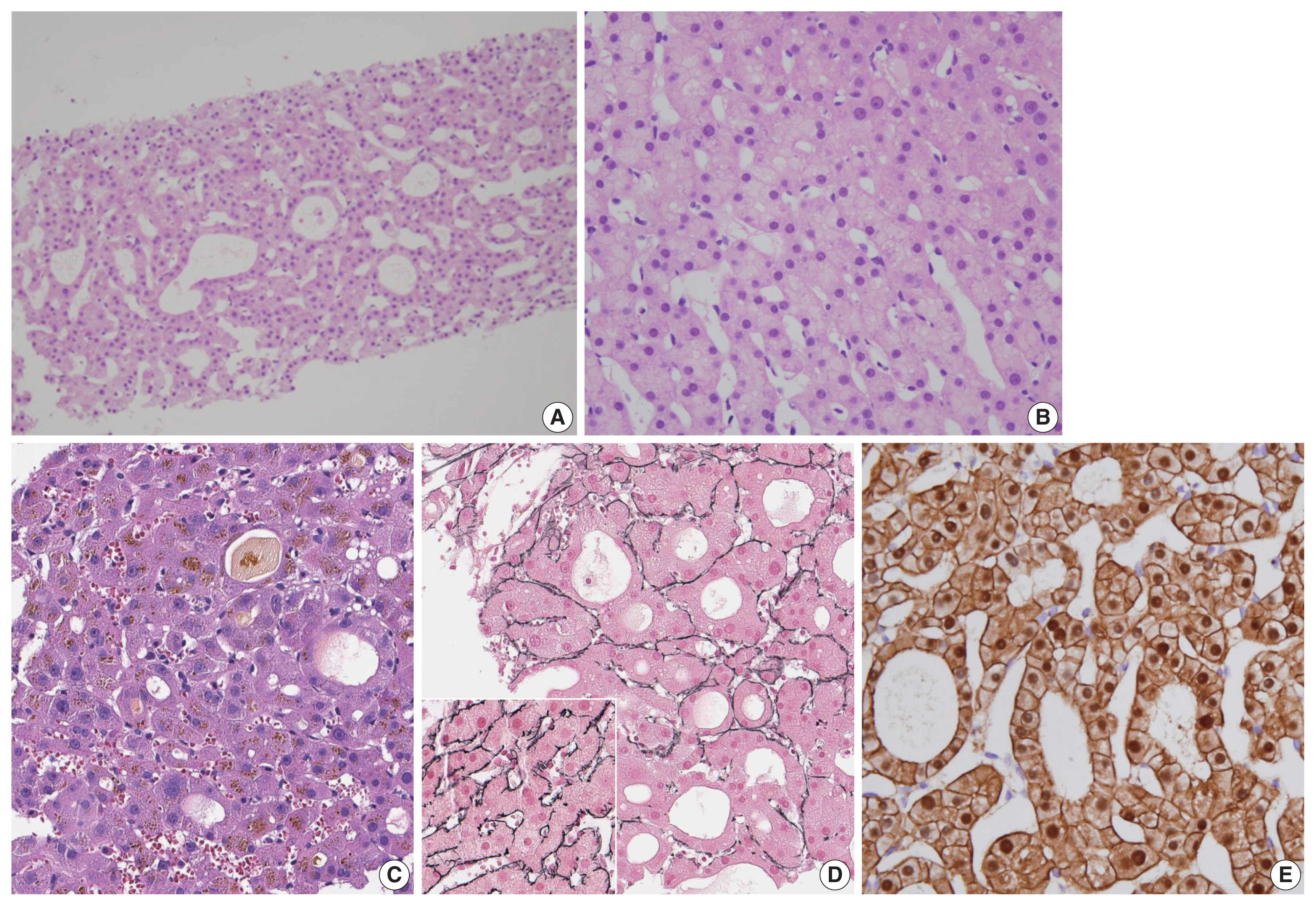
Fig. 1
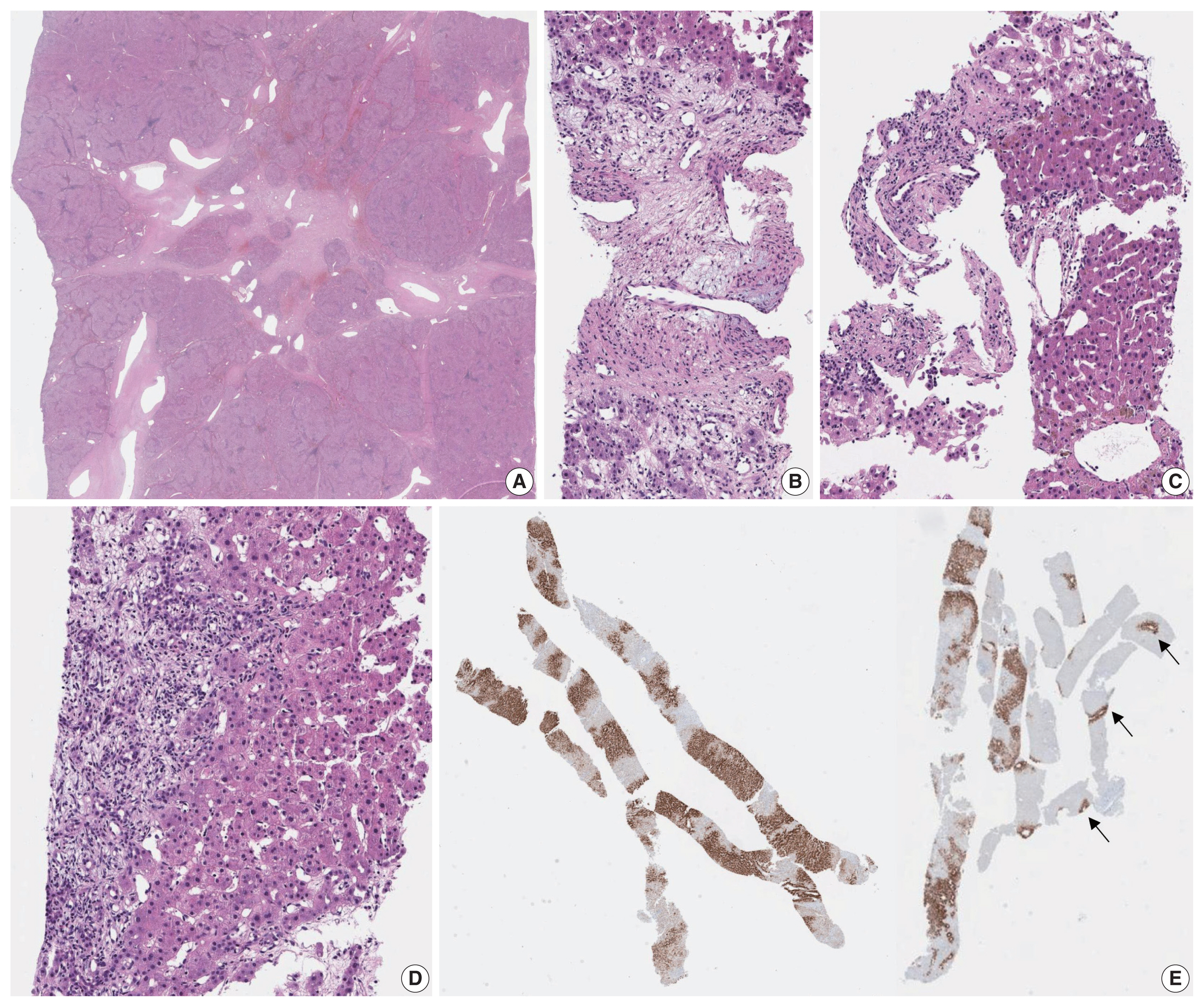
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
| Subtype (frequency, %) | Characteristic features | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||
| Molecular | Clinical | Histopathological | Immunohistochemical | |
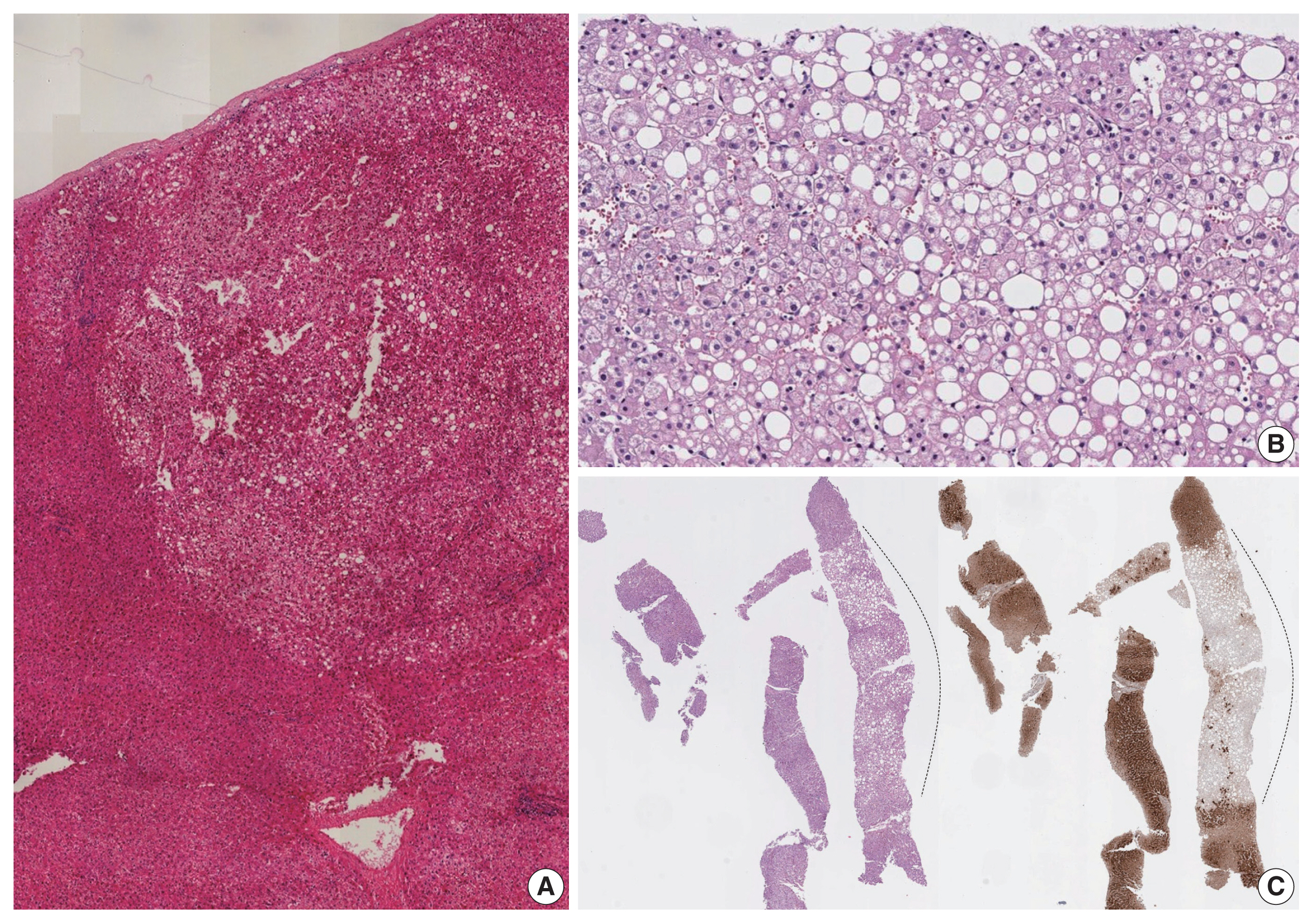
| HNF1A-inactivated HCA (30%–40%) | HNF1A inactivating mutations (germline 10%, somatic 90%) | Female, obesity, MODY3, adenomatosis | Diffuse steatosis | LFABP expression loss |
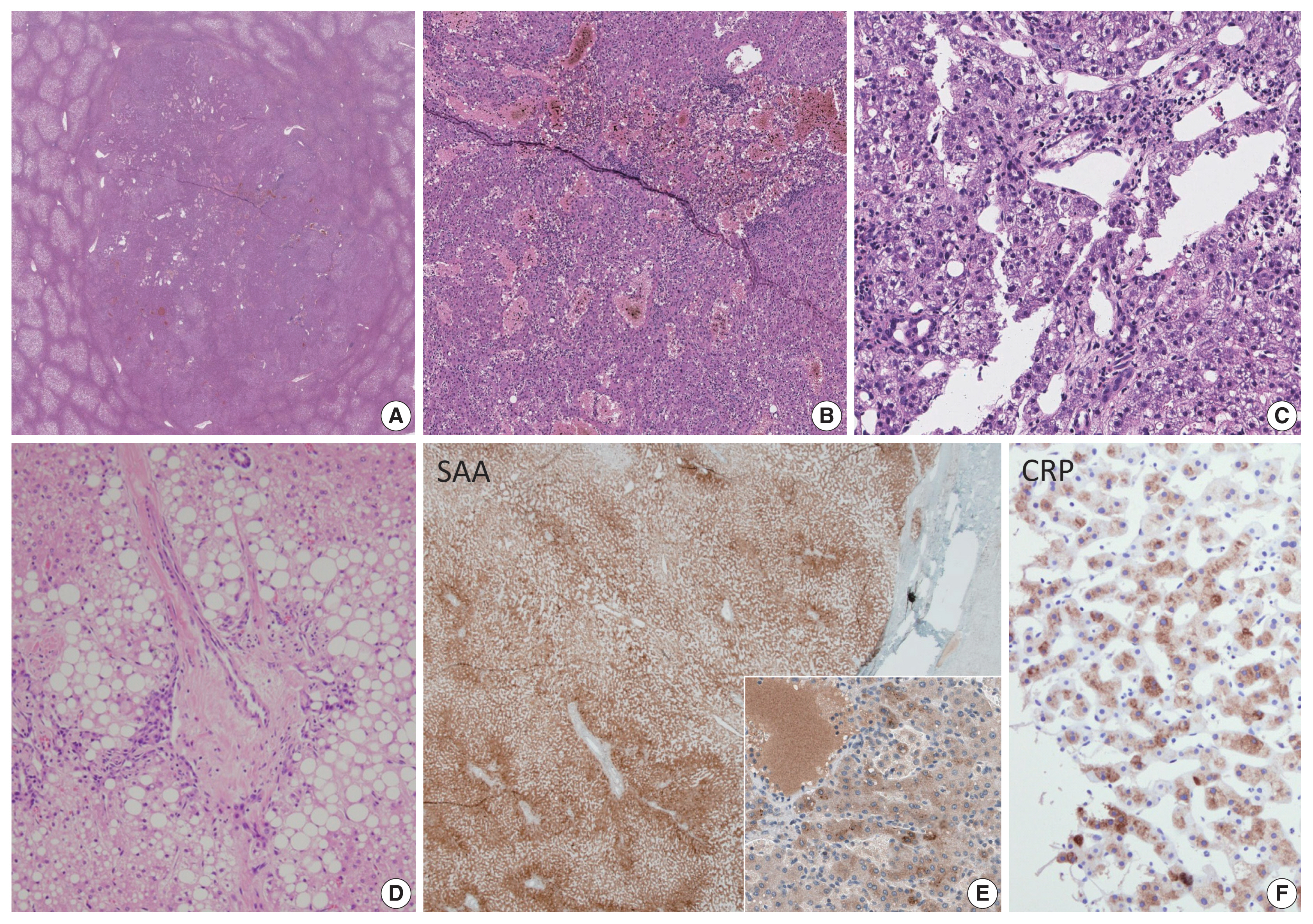
| Inflammatory HCA (40%–50%) | gp130/IL6ST, FRK, STAT3, GNAS, JAK1 mutations | Obesity, metabolic syndrome, alcohol, oral contraceptives | Sinusoidal dilatation Vascular proliferation Inflammatory cell infiltration Ductular reaction Focal steatosis |
SAA, CRP expression |
| β-catenin–activated HCA (10%) | ||||
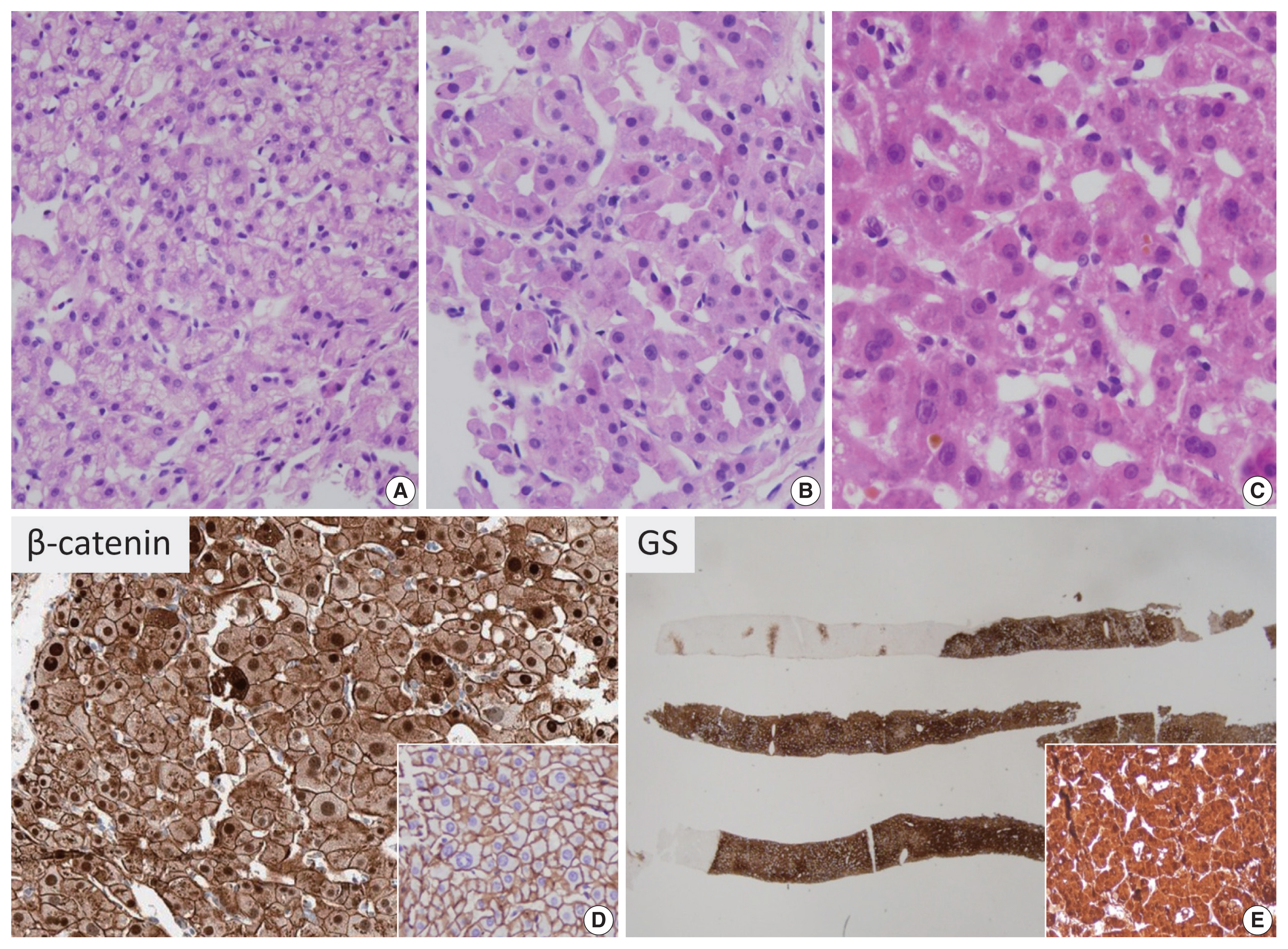
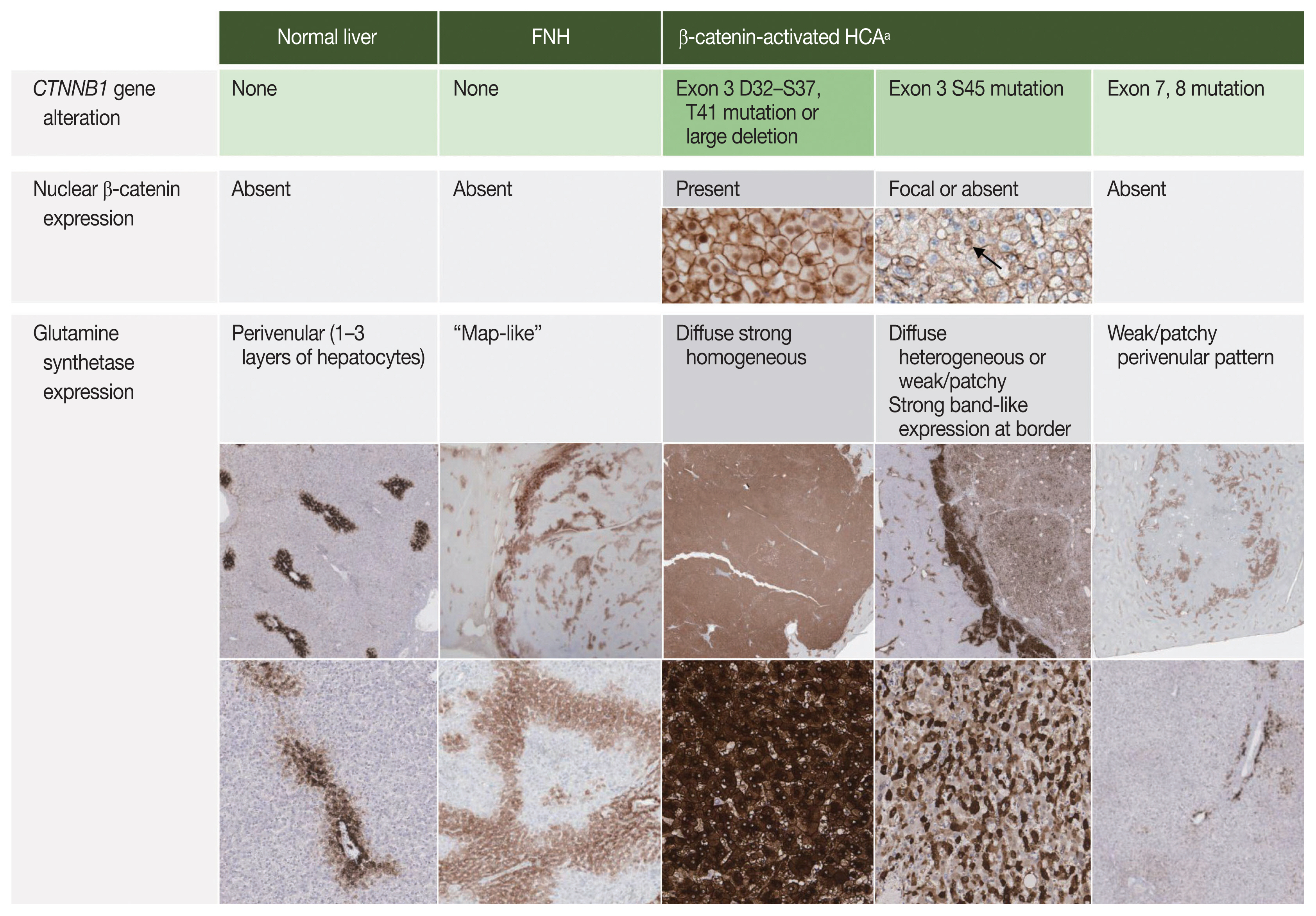
| β-catenin (exon 3)–activated HCA (7%) | CTNNB1 exon 3 activating mutations | Male, young age, anabolic steroids, glycogen storage disease, increased risk of HCC transformation | Cytological and architectural atypia | Nuclear β-catenin expression Diffuse strong GS expression |
| β-catenin (exon 7,8)–activated HCA (3%) | CTNNB1 exon 7 or 8 activating mutations | Low risk of HCC transformation | - | Absent/rare nuclear β-catenin expression GS expression: absent/weak/ patchy |
| β-catenin–activated inflammatory HCA (5%–10%) | gp130/IL6ST, STAT3, FRK, GNAS, JAK1 mutations + CTNNB1 exon 3 or 7/8 mutations | Similar to inflammatory HCA Increased risk of HCC transformation (ex.3) |
Similar to inflammatory HCA Cytoarchitectural atypia (ex.3) |
SAA, CRP expression Nuclear β-catenin, diffuse strong GS expression (ex.3) |
| Sonic hedgehog–activated HCA (4%) | INHBE-GLI1 fusion, resulting in sonic hedgehog pathway activation | Obesity, hemorrhage | Hemorrhage | PTGDS, ASS1 |
| Unclassified HCA (< 7%) | Unknown | - | - | - |
HCA, hepatocellular adenoma; MODY3, maturity-onset diabetes type 3; LFABP, liver fatty acid binding protein; SAA, serum amyloid A; CRP, C-reactive protein; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; GS, glutamine synthetase; PTGDS, prostaglandin D2 synthase; ASS1, argininosuccinate synthase 1.

 E-submission
E-submission