Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 55(6); 2021 > Article
-
Original Article
A multicenter study of interobserver variability in pathologic diagnosis of papillary breast lesions on core needle biopsy with WHO classification -
Hye Ju Kang1
 , Sun Young Kwon2
, Sun Young Kwon2 , Ahrong Kim3
, Ahrong Kim3 , Woo Gyeong Kim4
, Woo Gyeong Kim4 , Eun Kyung Kim5
, Eun Kyung Kim5 , Ae Ree Kim6
, Ae Ree Kim6 , Chungyeul Kim6
, Chungyeul Kim6 , Soo Kee Min7
, Soo Kee Min7 , So Young Park8
, So Young Park8 , Sun Hee Sung9
, Sun Hee Sung9 , Hye Kyoung Yoon10
, Hye Kyoung Yoon10 , Ahwon Lee11
, Ahwon Lee11 , Ji Shin Lee12
, Ji Shin Lee12 , Hyang Im Lee13
, Hyang Im Lee13 , Ho Chang Lee14
, Ho Chang Lee14 , Sung Chul Lim15
, Sung Chul Lim15 , Sun Young Jun16
, Sun Young Jun16 , Min Jung Jung17
, Min Jung Jung17 , Chang Won Jung18
, Chang Won Jung18 , Soo Youn Cho19
, Soo Youn Cho19 , Eun Yoon Cho19
, Eun Yoon Cho19 , Hye Jeong Choi20
, Hye Jeong Choi20 , So Yeon Park21
, So Yeon Park21 , Jee Yeon Kim22
, Jee Yeon Kim22 , In Ae Park23
, In Ae Park23 , Youngmee Kwon1
, Youngmee Kwon1
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2021;55(6):380-387.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.07.29
Published online: October 6, 2021
1Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea
2Department of Pathology, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, Korea
3Department of Pathology, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
4Department of Pathology, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea
5Department of Pathology, Eulji University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
6Department of Pathology, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea
7Department of Pathology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea
8Department of Pathology, MizMedi Hospital, Seoul, Korea
9Department of Pathology, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Seoul, Korea
10Department of Pathology, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea
11Department of Pathology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
12Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea
13Department of Pathology, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea
14Department of Pathology, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea
15Department of Pathology, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea
16Department of Pathology, Incheon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Incheon, Korea
17Department of Pathology, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea
18Department of Pathology, Green Cross Laboratories, Yongin, Korea
19Department of Pathology, Sungkyunkwan University Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
20Department of Pathology, Ulsan University Hospital, Ulsan, Korea
21Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
22Department of Pathology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
23Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Youngmee Kwon, MD, PhD, Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center, 323 Ilsan-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang 10408, Korea Tel: +82-31-920-1742, Fax: +82-31-920-1369, E-mail: ymk@ncc.re.kr
© 2021 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
-
Background
- Papillary breast lesions (PBLs) comprise diverse entities from benign and atypical lesions to malignant tumors. Although PBLs are characterized by a papillary growth pattern, it is challenging to achieve high diagnostic accuracy and reproducibility. Thus, we investigated the diagnostic reproducibility of PBLs in core needle biopsy (CNB) specimens with World Health Organization (WHO) classification.
-
Methods
- Diagnostic reproducibility was assessed using interobserver variability (kappa value, κ) and agreement rate in the pathologic diagnosis of 60 PBL cases on CNB among 20 breast pathologists affiliated with 20 medical institutions in Korea. This analysis was performed using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for cytokeratin 5 (CK5) and p63. The pathologic diagnosis of PBLs was based on WHO classification, which was used to establish simple classifications (4-tier, 3-tier, and 2-tier).
-
Results
- On WHO classification, H&E staining exhibited ‘fair agreement’ (κ = 0.21) with a 47.0% agreement rate. Simple classifications presented improvement in interobserver variability and agreement rate. IHC staining increased the kappa value and agreement rate in all the classifications. Despite IHC staining, the encapsulated/solid papillary carcinoma (EPC/SPC) subgroup (κ = 0.16) exhibited lower agreement compared to the non-EPC/SPC subgroup (κ = 0.35) with WHO classification, which was similar to the results of any other classification systems.
-
Conclusions
- Although the use of IHC staining for CK5 and p63 increased the diagnostic agreement of PBLs in CNB specimens, WHO classification exhibited a higher discordance rate compared to any other classifications. Therefore, this result warrants further intensive consensus studies to improve the diagnostic reproducibility of PBLs with WHO classification.
- Study design and case selection
- We evaluated the interobserver variability and agreement rates in 60 PBL cases on CNB among 20 breast pathologists affiliated with 20 medical institutions in Korea. Sixty PBL cases were recruited from 20 medical institutions that participated in this study. The consensus meeting of the Korean Breast Pathology Study Group (KBPSG) verified and determined the pathologic diagnosis of 60 PBL cases on CNB. Fig. 1 displays the composition of pathologic diagnoses in all 60 PBL cases. Each case constitutes one H&E and two IHC stained slides for both cytokeratin 5 (CK5) and p63. Initially, 60 H&E-stained slides were circulated to 20 breast pathologists for review. Subsequently, IHC stained slides for CK5 and p63 in the same 60 cases were circulated to the same 20 breast pathologists and re-reviewed. Interobserver variability and agreement rates were analyzed for the pathologic diagnosis of PBLs in H&E and IHC stains. Additionally, we conducted a detailed review of the challenging cases of differential diagnoses observed among our 60 PBL cases.
- Diagnostic classification of PBLs
- Pathologic classification of PBLs was conducted based on the 4th edition of the WHO classification of tumors of the breast [9]. In this classification [9], the PBLs were classified into 10 categories comprising intraductal papillomas (IDP), IDPs with atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH), IDPs with ductal carcinomas in situ (DCIS), IDPs with lobular carcinomas in situ (LCIS), papillary carcinomas in situ (PCIS), encapsulated papillary carcinomas (EPC), solid papillary carcinomas (SPC), EPCs with invasion, SPCs with invasion, and invasive papillary carcinomas (IPC). Of the WHO classification, intraductal papillary neoplasms (IDPN) were defined as a category including IDP, IDP with ADH, IDP with DCIS, IDP with LCIS, and PCIS. EPC and SPC were categorized into EPC/SPC.
- In addition, using the WHO classification, we created simple classifications of PBL using 4-tier, 3-tier, and 2-tier systems as follows: 4-tier consisted of benign, atypical, in situ, and invasive; 3-tier consisted of benign, in situ, and invasive; 2-tier consisted of benign and malignant (Table 1). For instance, if EPC was diagnosed, it was categorized into in situ in the 4-tier system and malignant in the 2-tier system.
- Immunohistochemistry
- For each CNB specimen of cases, IHC staining for CK5 and p63 was performed. IHC staining for CK5 was conducted using antibodies against CK5 (XM26, Leica Biosystems, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK) with 1:200 antibody dilution and a detection kit (Ivew DAB kit, Ventana, Tucson, AZ, USA). IHC staining for p63 was performed using antibodies against p63 (BC4A4, Biocare Medical, Pacheco, CA, USA) with 1:100 antibody dilution and a detection kit (Ultraview DAB kit, Ventana). According to the manufacturer’s protocol, all the procedures of IHC staining were processed by a Ventana BenchMark XT system (Ventana).
- Statistical analysis
- Fleiss’s kappa values for interobserver variability were used in analyzing diagnostic reproducibility in H&E and IHC staining among 20 breast pathologists. Interobserver variability was classified into five categories (0.00–0.20, poor; 0.21–0.40, fair; 0.41–0.60, moderate; 0.61–0.80, substantial; and 0.81–1.00, excellent agreement) to identify the level of reproducibility. Additionally, the average of the agreement rates in H&E and IHC staining of 60 cases was calculated in four diagnostic classifications. The agreement rate was determined by the proportion of pathologic diagnosis from 20 pathologists that was consistent with that from the consensus meeting of KBPSG. Statistical analyses were performed using STATA ver. 16.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
- Interobserver variability and agreement rates in H&E and IHC staining in each classification are presented in Table 2. In the WHO classification, H&E staining exhibited ‘fair agreement’ (κ = 0.21). Kappa values increased inversely with the number of categories in the diagnostic classification (4-tier: κ =0.31, 3-tier: κ =0.42, and 2-tier: κ =0.44). IHC staining improved the interobserver variability in all classifications. In IHC staining, overt improvement in reproducibility was observed in 4-tier (‘fair agreement’ to ‘moderate agreement’) and 2-tier (‘moderate agreement’ to ‘substantial agreement’). The agreement rate also exhibited similar findings with kappa values for interobserver variability. The agreement rate was generally higher in IHC staining compared to H&E staining in all classifications. Within the same staining methods, simpler diagnostic classification tended to have a higher agreement rate.
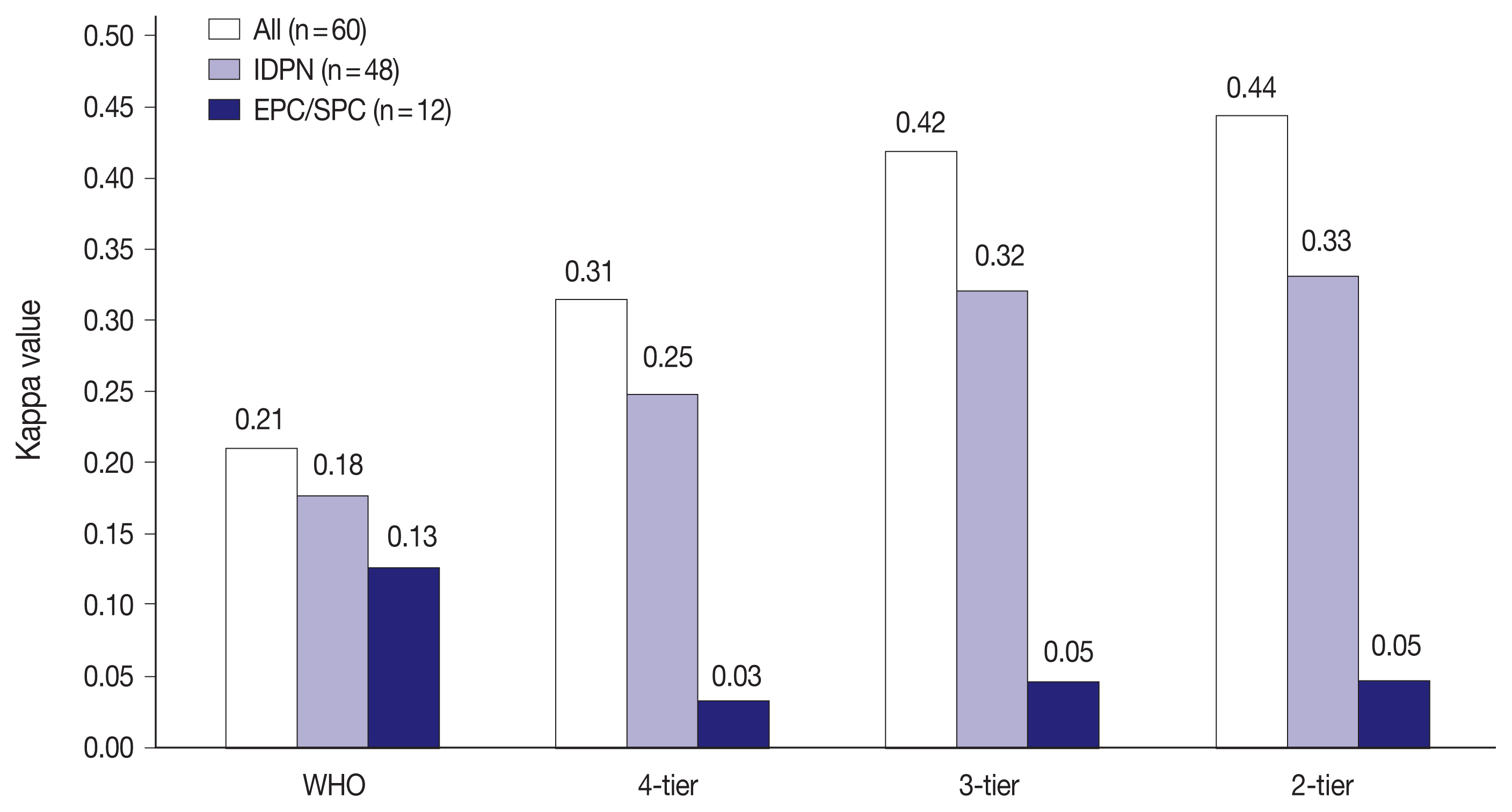
- Fig. 2 shows the interobserver variability in H&E staining for all 60 PBL cases, IDPN, and EPC/SPC in each classification. There were 48 cases of IDPN and 12 cases of EPC/SPC in this study. Kappa values for IDPN and EPC/SPC were lower than that for all 60 PBL cases in all classifications. IDPN had lower reproducibility than all the 60 PBL cases, despite the same reproducibility (‘fair agreement’) in 4-tier. EPC/SPC exhibited the lowest kappa value with ‘poor agreement’ (WHO: κ = 0.13, 4-tier: κ = 0.03, 3-tier: κ = 0.05, and 2-tier: κ = 0.05).
- IHC staining generally improved the interobserver reliability in all 60 PBL cases and IDPN in all classifications (Fig. 3). The reproducibility of IDPN improved to the same level of all 60 PBL cases except that in 2-tier (all 60 PBL cases: ‘substantial agreement’ and IDPN: ‘moderate agreement’). However, the kappa values were lowest in EPC/SPC with ‘poor agreement’ (WHO: κ = 0.16, 4-tier: κ = 0.04, 3-tier: κ = 0.05, and 2-tier: κ = 0.06) similar to that in H&E staining, which demonstrated that IHC staining did not improve the diagnostic agreement of EPC/SPC in contrast with all 60 PBL cases and IDPN.
- In our 60 cases, five cases were particularly challenging for differential diagnosis with a relatively high discordance rate (Table 3). The presence of apocrine metaplasia (Supplementary Fig. S1) and flat epithelial atypia-like features (Supplementary Fig. S2) made it difficult to distinguish benign from malignant intraductal lesions. Regarding the differential diagnosis between in situ and invasive lesions, we found three challenging cases including one large cystic mass with no myoepithelial cells along the papillae (Supplementary Fig. S3), one with a solid multinodular pattern and smooth contours (Supplementary Fig. S4), and one with a predominant solid multinodular and jigsaw pattern (Supplementary Fig. S5).
RESULTS
- For 60 PBL cases obtained from CNB, we assessed the interobserver variability and agreement rates in pathologic diagnoses among 20 breast pathologists. In an analysis with the WHO classification, pathologic diagnosis in H&E staining showed ‘fair agreement’ (κ = 0.21) with an agreement rate of 47.0%. This result is comparable to those of previous studies in line with ours. In H&E staining for 57 cases of PBLs, three pathologists demonstrated a substantial agreement (κ = 0.79) in reproducibility and an 86% agreement rate with seven diagnostic categories [11]. Additionally, an analysis with five diagnostic categories indicated moderate agreement (κ = 0.54) and a 44% agreement rate in 129 PBL cases by H&E staining among four pathologists [12].
- Compared with the previous results, it seems that our kappa values and agreement rates are relatively low. The plausible explanations for this finding may be the number of pathologists and the complexity of the diagnostic categories. Our study was performed to assess interobserver variability within 10 diagnostic categories among 20 pathologists. The number of pathologists and diagnostic categories is greater than those of other studies conducted with three pathologists with seven categories [11] and four pathologists with five categories [12].
- It seems that the greater number of pathologists makes it harder to obtain a consistent diagnosis for any lesion compared to fewer pathologists. Moreover, a more complicated diagnostic category contributes to lower reproducibility as found in our study. We observed improved reproducibility in simple diagnostic categories, showing the highest kappa value (0.44) and agreement rate (80.0%) in 2-tier. Additionally, the characteristics of diagnostic classification may contribute to the change of reproducibility in our study. The WHO classification features determinacy in diagnosis. However, the pathology category classification (B1–B5) published by the UK National Health Service Breast Screening Programme (NHSBSP) allows for probability in differential diagnosis [14]. In practice, the use of these reporting systems exhibited higher reproducibility (κ = 0.54) compared to our study (κ = 0.21) [12]. Therefore, it is assumed that the adoption of this diagnostic classification would lead to the higher reproducibility in our cases.
- Elmore et al. [15] investigated the concordance rate of the pathologic diagnosis of non-PBLs on CNB among 115 pathologists recruited from eight U.S. states with consensus-derived reference diagnoses. Their study showed that the overall concordance rate was 75.3% (95% confidence interval, 73.4% to 77.0%; 5,194 of 6,900 interpretations). The diagnostic concordance rate on CNB is lower in PBLs (63.3% in our study and 44% in the previous study [12]) compared to non-PBLs (75.3%) with similar diagnostic categories despite fewer pathologists, indicating more complicated diagnostic difficulty in PBLs.
- Multicenter studies are thought to be superior to single-center studies in presenting generalized results in breast pathology. However, to my knowledge, there has been no multicenter study examining the reproducibility of PBLs [15]. In contrast, our study was conducted for 20 pathologists from 20 multiple medical institutions, conferring more generalizability on our findings in PBLs. Additionally, it is noted that our results were derived from breast pathologists. One study indicated that breast pathologists are more accurate in diagnosing CNB guided PBLs compared to non-breast pathologists [13]. In that study, interobserver variability was ‘fair agreement’ (κ = 0.38) between the breast pathologists and non-breast pathologists. Therefore, our results suggest the difficulty in diagnosing PBLs even in breast pathologists, warranting improving diagnostic accuracy for PBLs.
- IHC staining increases diagnostic accuracy and improves interobserver variability [16]. CK5 is used in distinguishing between hyperplastic and neoplastic epithelial proliferation in PBLs [17,18]. p63 is a nuclear protein that is specific for myoepithelial cells without manifestation in blood vessels and myofibroblasts [19,20]. IHC staining helps to make an accurate diagnosis on PBLs through the ability of CK5 and p63 in identifying monoclonal epithelial proliferation and the presence of myoepithelial cells [17,21], respectively. Our study also showed that the application of IHC staining generally improved interobserver variability and agreement rates in diagnosing PBLs. Nonetheless, it is noted that the utilization of IHC staining is limited in EPC/SPC with very low kappa values.
- EPC and SPC are distinctive variants of PCIS, each accounting for < 1% of breast carcinomas [22]. Morphological differentiation in H&E staining has a decisive role in diagnosing EPC/SPC because IHC staining is less helpful. Despite differential points including cystic versus solid and single versus multiple in morphology [23], some cases on CNB practically exhibit overlaps like a transition from single to multiple ductal lesions and cystic to solid appearance with a gradual cystic filling of proliferation [24]. Additionally, definitive cut-off criteria have yet to be determined, which may decrease the diagnostic agreement rates among pathologists. Supplementary Table S1 presents the distribution of histologic patterns and pathologic diagnoses of 12 EPC/SPC cases based on 2-tier or 4-tier classifications, revealing that most pathologists diagnosed most EPC/SPC cases as malignant in 2-tier classification. Nonetheless, it is interesting that kappa values remained low in 2-tier classification for EPC and SPC. This was attributed to the technical limitations of the formula used to calculate kappa values. In cases where the observed agreement was asymmetrically lopsided, kappa values can be drastically lowered due to increased chance agreement rates [25]. Therefore, the tipping effect of lopsided pathologic diagnoses by 20 pathologists induced low kappa values even in 2-tier classification.
- We intended to describe five challenging histologic patterns of PBL with diagnostic pitfalls even in IHC staining, specifically apocrine metaplasia, flat epithelial atypia-like features, large cystic masses with no myoepithelial cells along the papillae, and predominant solid multinodular masses with smooth contours or jigsaw patterns. Benign PBLs are often exaggerated by the presence of apocrine metaplasia [10]. Apocrine metaplasia is characterized by abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm with CK5 (−) and a lack of myoepithelial cells with p63 (−) [26,27]. Therefore, the first case with apocrine metaplasia confounded the distinction between benign and malignant intraductal lesions, leading to a diagnostic disagreement even in IHC staining. The WHO classification defined flat epithelial atypia as columnar cell lesions with nuclear atypia [9]. In contrast with non-PBLs, no definite concept of flat epithelial atypia associated with PBLs has been suggested or proposed until now. In the second case with flat epithelial atypia-like features, we observed a high proportion of diagnosis in IDP with ADH (30%) and IDP with DCIS (35%). This heterogeneous diagnosis may be attributable to the difficulty in determining the size (≥ 3 mm in DCIS or < 3 mm in ADH) of histologically identical epithelial proliferation [10]. The third case with a large cystic pattern revealed that PCIS was the most common diagnosis (70%), followed by EPC (20%). EPC is histologically similar to PCIS in some ways, but EPC is characterized by a single cystic or nodular pattern without myoepithelial cells along the papillae and at the periphery, occasionally forming a thick fibrous capsule [10]. The helpful point of distinguishing PCIS from EPC is the presence of myoepithelial cells at the periphery of the PCIS [28]. However, our case presented completely CK5 (−) and sparsely and focally p63 (+) at the periphery, potentially leading to diagnostic disagreement. It is important to differentiate between in situ and invasive lesions for the management and prognostication of PBLs [24]. In the fourth case with a solid multinodular pattern, there were smooth contours and focal suspected microinvasions without immunoreactivity of both CK5 and p63. Although SPC occupied 90% of diagnoses, it was classified as both in situ (60%) and invasive (30%). The fifth case with a solid multinodular and jigsaw pattern was challenging to distinguish between in situ and invasive lesions. Moreover, a solid multinodular pattern suggested SPC, but a fragmented lesion may be misinterpreted as one that fell out of a cystic lesion reminiscent of EPC. Limited materials and fragmented samples in CNB specimens may be the main factors contributing to these disagreements of diagnoses. Interestingly, all 12 cases of EPC/SPC were categorized to the latter three histologic patterns for not only challenging but also helping differential diagnoses as shown in Supplementary Table S1. In papillary carcinomas that were difficult to differentiate between in situ and invasive lesions, such as the above fourth and fifth cases, it is recommended to diagnose them as PCIS or of uncertain invasiveness on CNB to avoid overtreatment, especially in the current era of preoperative (neoadjuvant) chemotherapy.
- Our study has some limitations. First, we could not include very rare cases such as IDP with LCIS, EPC with invasion, and IPC because of their extreme rarity especially on CNB. Therefore, PBL cases included in this study actually belong to seven categories as shown in Fig. 1 in contrast to 10 categories of the WHO classification. Second, our cases did not have information on the final diagnosis from excisional biopsy or surgical resection. Although the consensus meeting of KBPSG proposed the pathologic diagnosis of 60 PBL cases, their diagnoses were not likely to guarantee the correctness of the diagnosis. Third, there was no clinical and radiologic information about the 60 PBL cases in our raw data. The absence of this information may be an obstacle in determining an accurate diagnosis and prognosis. Fourth, we did not use the most recently updated version of the WHO classification published in 2019. Nonetheless, because there was no difference between the 4th and 5th editions in diagnosing and classifying PBLs, the concern for the discrepancy between the two versions is minimal [8,9].
- In conclusion, our study demonstrated that interobserver variability in the pathologic diagnosis of PBLs was unsatisfactory among 20 breast pathologists from 20 multiple medical institutions. Although IHC staining improved interobserver variability and agreement rates in diagnosing PBLs, diagnostic reproducibility was still limited in specific cases including EPC/SPC. Therefore, more intensive consensus studies are necessary to improve the diagnostic agreement and categorization of PBLs with the WHO classification. Further studies should continue to develop effective modalities in distinguishing PBLs especially on CNB.
DISCUSSION
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information
The Data Supplement is available with this article at https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.07.28.
Ethics Statement
This study was approved by the National Cancer Center Institutional Review Board with a waiver of informed consent (NCC2018-0214).
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets generated or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: IAP, ARK, YK. Data curation: SYK, ARK, WGK, EKK, CK, SKM, SYP, SHS, HKY, AL, JSL, HIL, HCL, SCL, SYJ, MJJ, CWJ, SYC, HJC, IAP. Formal analysis: HJK, YK. Funding acquisition: AK, JYK, YK. Investigation: HJK, YK. Methodology: AK, JYK, YK. Project administration: SYP, EYC, YK. Resources: SYK, AK, WGK, EKK, CK, SKM, SHS, HKY, AL, JSL, HIL, HCL, SYJ, MJJ, HJC, EYC, SYP, JYK, IAP, YK. Supervision: IAP, AK, YK. Validation: HJK, YK. Visualization: HJK, YK. Writing—original draft: HJK. Writing—review & editing: HJK, YK. Approval of final manuscripts: all authors.
Conflicts of Interest
S.Y.P., editor-in-chief of the Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine, were not involved in the editorial evaluation or decision to publish this article. All remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Funding Statement
This study was supported by the Korean Society of Pathologists Grant.
Acknowledgments


| Diagnostic classification | H&E staining | IHC staining | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||
| κ | Agreement rate (%) | κ | Agreement rate (%) | |
| WHO | 0.21 | 47.0 | 0.37 | 60.5 |
| 4-tier | 0.31 | 63.3 | 0.51 | 76.4 |
| 3-tier | 0.42 | 76.7 | 0.56 | 84.3 |
| 2-tier | 0.44 | 80.0 | 0.62 | 87.5 |
- 1. Tay TK, Tan PH. Papillary neoplasms of the breast: reviewing the spectrum. Mod Pathol 2021; 34: 1044-61. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Jorns JM. Papillary lesions of the breast: a practical approach to diagnosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2016; 140: 1052-9. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Ni YB, Tse GM. Pathological criteria and practical issues in papillary lesions of the breast: a review. Histopathology 2016; 68: 22-32. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Lewis JT, Hartmann LC, Vierkant RA, et al. An analysis of breast cancer risk in women with single, multiple, and atypical papilloma. Am J Surg Pathol 2006; 30: 665-72. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Louwman MW, Vriezen M, van Beek MW, et al. Uncommon breast tumors in perspective: incidence, treatment and survival in the Netherlands. Int J Cancer 2007; 121: 127-35. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Yamaguchi R, Tanaka M, Tse GM, et al. Management of breast papillary lesions diagnosed in ultrasound-guided vacuum-assisted and core needle biopsies. Histopathology 2015; 66: 565-76. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Moon SM, Jung HK, Ko KH, Kim Y, Lee KS. Management of clinically and mammographically occult benign papillary lesions diagnosed at ultrasound-guided 14-gauge breast core needle biopsy. J Ultrasound Med 2016; 35: 2325-32. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Brogi E, Horii R, Mac Grogan G, et al. Papillary neoplasms. In: Lokuhetty D, White VA, Watanabe R, Cree IA, eds. WHO classification of breast tumors. 5th ed.Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2019; 49-67.
- 9. O’Malley F, Visscher D, MacGrogan G, Tan PH, Ichihara S. Intraductal papillary lesions. In: Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH, van de Vijver MJ, eds. WHO classification of tumours of the breast. 4th ed.Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2012; 99-109.
- 10. Rakha EA, Ellis IO. Diagnostic challenges in papillary lesions of the breast. Pathology 2018; 50: 100-10. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Qiu L, Mais DD, Nicolas M, Nanyes J, Kist K, Nazarullah A. Diagnosis of papillary breast lesions on core needle biopsy: upgrade rates and interobserver variability. Int J Surg Pathol 2019; 27: 736-43. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Douglas-Jones A, Shah V, Morgan J, Dallimore N, Rashid M. Observer variability in the histopathological reporting of core biopsies of papillary breast lesions is reduced by the use of immunohistochemistry for CK5/6, calponin and p63. Histopathology 2005; 47: 202-8. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Jakate K, De Brot M, Goldberg F, Muradali D, O’Malley FP, Mulligan AM. Papillary lesions of the breast: impact of breast pathology subspecialization on core biopsy and excision diagnoses. Am J Surg Pathol 2012; 36: 544-51. PubMed
- 14. Ellis IO, Humphreys S, Michell M, et al. Best Practice No 179. Guidelines for breast needle core biopsy handling and reporting in breast screening assessment. J Clin Pathol 2004; 57: 897-902. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Elmore JG, Longton GM, Carney PA, et al. Diagnostic concordance among pathologists interpreting breast biopsy specimens. JAMA 2015; 313: 1122-32. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Koo JS, Han K, Kim MJ, Moon HJ, Kim EK, Park BW. Can additional immunohistochemistry staining replace the surgical excision for the diagnosis of papillary breast lesions classified as benign on 14-gage core needle biopsy? Breast Cancer Res Treat 2013; 137: 797-806. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Boecker W, Moll R, Dervan P, et al. Usual ductal hyperplasia of the breast is a committed stem (progenitor) cell lesion distinct from atypical ductal hyperplasia and ductal carcinoma in situ. J Pathol 2002; 198: 458-67. ArticlePubMed
- 18. Otterbach F, Bankfalvi A, Bergner S, Decker T, Krech R, Boecker W. Cytokeratin 5/6 immunohistochemistry assists the differential diagnosis of atypical proliferations of the breast. Histopathology 2000; 37: 232-40. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Lerwill MF. Current practical applications of diagnostic immunohistochemistry in breast pathology. Am J Surg Pathol 2004; 28: 1076-91. ArticlePubMed
- 20. Hoda SA, Rosen PP. Practical considerations in the pathologic diagnosis of needle core biopsies of breast. Am J Clin Pathol 2002; 118: 101-8. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Collins LC, Carlo VP, Hwang H, Barry TS, Gown AM, Schnitt SJ. Intracystic papillary carcinomas of the breast: a reevaluation using a panel of myoepithelial cell markers. Am J Surg Pathol 2006; 30: 1002-7. ArticlePubMed
- 22. Cui X, Wei S. Composite encapsulated papillary carcinoma and solid papillary carcinoma. Pathol Int 2015; 65: 133-7. ArticlePubMed
- 23. Hashmi AA, Faraz M, Rafique S, Adil H, Imran A. Spectrum of papillary breast lesions according to World Health Organization classification of papillary neoplasms of breast. Cureus 2020; 12: e11026.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Agoumi M, Giambattista J, Hayes MM. Practical considerations in breast papillary lesions: a review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2016; 140: 770-90. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 25. Feinstein AR, Cicchetti DV. High agreement but low kappa: I. The problems of two paradoxes. J Clin Epidemiol 1990; 43: 543-9. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Tramm T, Kim JY, Tavassoli FA. Diminished number or complete loss of myoepithelial cells associated with metaplastic and neoplastic apocrine lesions of the breast. Am J Surg Pathol 2011; 35: 202-11. ArticlePubMed
- 27. Cserni G. Benign apocrine papillary lesions of the breast lacking or virtually lacking myoepithelial cells-potential pitfalls in diagnosing malignancy. APMIS 2012; 120: 249-52. ArticlePubMed
- 28. Wei S. Papillary lesions of the breast: an update. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2016; 140: 628-43. ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Beyond the benign: A rare case report of myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma
Arslan Ahmad, Muhammad Ammar, Muhammad Hasnain Saleem Choudary, Muhammad Nouman Sadiq, Rana Uzair Ahmad, Nouman Aziz
Radiology Case Reports.2025; 20(5): 2500. CrossRef - Invasive papillary carcinoma of the breast
Shijing Wang, Qingfu Zhang, Xiaoyun Mao
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recommendations for Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning in Pathology: A Concept Paper From the College of American Pathologists
Matthew G. Hanna, Niels H. Olson, Mark Zarella, Rajesh C. Dash, Markus D. Herrmann, Larissa V. Furtado, Michelle N. Stram, Patricia M. Raciti, Lewis Hassell, Alex Mays, Liron Pantanowitz, Joseph S. Sirintrapun, Savitri Krishnamurthy, Anil Parwani, Giovann
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2024; 148(10): e335. CrossRef - Encapsulated papillary carcinoma of the breast: A single institution experience
Liang Xu, Qixin Mao, Qiuming Liu, Yufeng Gao, Lihua Luo, Chungen Guo, Wei Qu, Ningning Yan, Yali Cao
Oncology Letters.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High-risk and selected benign breast lesions diagnosed on core needle biopsy: Evidence for and against immediate surgical excision
Aparna Harbhajanka, Hannah L. Gilmore, Benjamin C. Calhoun
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(11): 1500. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure



Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
| WHO | 4-tier | 3-tier | 2-tier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intraductal papilloma | Benign | Benign | Benign |
| IDP with ADH | Atypical | ||
| IDP with DCIS | In situ | In situ | Malignant |
| IDP with LCIS | |||
| Papillary carcinoma in situ | |||
| Encapsulated papillary carcinoma | |||
| Solid papillary carcinoma | |||
| EPC with invasion | Invasive | Invasive | |
| SPC with invasion | |||
| Invasive papillary carcinoma |
| Diagnostic classification | H&E staining | IHC staining | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| |||
| κ | Agreement rate (%) | κ | Agreement rate (%) | |
| WHO | 0.21 | 47.0 | 0.37 | 60.5 |
| 4-tier | 0.31 | 63.3 | 0.51 | 76.4 |
| 3-tier | 0.42 | 76.7 | 0.56 | 84.3 |
| 2-tier | 0.44 | 80.0 | 0.62 | 87.5 |
| Challenging case | Challenging point (%) | Diagnosis (agreement rate, n/20) |
|---|---|---|
| Apocrine metaplasia | Benign (55) | IDP (30%, 6/20) |
| IDP with ADH (25%, 5/20) | ||
| Malignant (45) | IDP with DCIS (35%, 7/20) | |
| PCIS (10%, 2/20) | ||
| Flat epithelial atypia-like features | Benign (30) | IDP with ADH (30%, 6/20) |
| Malignant (70) | IDP with DCIS (35%, 7/20) | |
| PCIS (20%, 4/20) | ||
| EPC (15%, 3/20) | ||
| Large cystic pattern with fibrous capsule but no or rare myoepithelial cells | In situ (95) | IDP with DCIS (5%, 1/20) |
| PCIS (70%, 14/20) | ||
| EPC (20%, 4/20) | ||
| Invasive (5) | IPC (5%, 1/20) | |
| Solid multinodular pattern with smooth contours but no or rare myoepithelial cells | In situ (65) | EPC (5%, 1/20) |
| SPC in situ (60%, 12/20) | ||
| Invasive (35) | SPC invasive (30%, 6/20) | |
| IPC (5%, 1/20) | ||
| Solid multinodular and jigsaw pattern with ragged contours but no myoepithelial cells | In situ (75) | PCIS (20%, 4/20) |
| EPC (40%, 8/20) | ||
| SPC in situ (15%, 3/20) | ||
| Invasive (25) | SPC invasive (10%, 2/20) | |
| IPC (15%, 3/20) |
PBL, papillary breast lesion; WHO, World Health Organization; IDP, intraductal papilloma; ADH, atypical ductal hyperplasia; DCIS, ductal carcinoma in situ; LCIS, lobular carcinoma in situ; EPC, encapsulated papillary carcinoma; SPC, solid papillary carcinoma.
H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; IHC, immunohistochemistry; PBL, papillary breast lesion; WHO, World Health Organization classification; 4-tier, 4-tier classification; 3-tier, 3-tier classification; 2-tier, 2-tier classification.
IHC staining, immunohistochemical staining for CK5 and p63; IDP, intraductal papilloma; ADH, atypical ductal hyperplasia; DCIS, ductal carcinoma in situ; PCIS, papillary carcinoma in situ; EPC, encapsulated papillary carcinoma; IPC, invasive papillary carcinoma; SPC, solid papillary carcinoma.

 E-submission
E-submission





