Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 57(1); 2023 > Article
-
Review
Inflammatory bowel disease–associated intestinal fibrosis -
Ji Min Park1
 , Jeongseok Kim2
, Jeongseok Kim2 , Yoo Jin Lee2
, Yoo Jin Lee2 , Sung Uk Bae3
, Sung Uk Bae3 , Hye Won Lee1
, Hye Won Lee1
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2023;57(1):60-66.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.11.02
Published online: January 10, 2023
1Department of Pathology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
2Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
3Division of Colorectal Surgery, Department of Surgery, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Hye Won Lee, MD, PhD, Department of Pathology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, 1095 Dalgubeol-daero, Dalseo-gu, Daegu 42601, Korea, Tel: +82-53-258-4260, Fax: +82-53-258-7382, E-mail: hwlee@dsmc.or.kr
© 2023 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
- Fibrosis is characterized by a proliferation of fibroblasts and excessive extracellular matrix following chronic inflammation, and this replacement of organ tissue with fibrotic tissue causes a loss of function. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, and intestinal fibrosis is common in IBD patients, resulting in several complications that require surgery, such as a stricture or penetration. This review describes the pathogenesis and various factors involved in intestinal fibrosis in IBD, including cytokines, growth factors, epithelial-mesenchymal and endothelial-mesenchymal transitions, and gut microbiota. Furthermore, histopathologic findings and scoring systems used for stenosis in IBD are discussed, and differences in the fibrosis patterns of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are compared. Biomarkers and therapeutic agents targeting intestinal fibrosis are briefly mentioned at the end.
- Fibrosis is an irreversible process that occurs as a consequence of chronic inflammation. It results in persistent luminal narrowing and strictures. Anti-inflammatory agents do not prevent or treat fibrosis in IBD, even if they improve the inflammation [13]. Because the fibrotic process is not affected by various IBD treatments, researchers have focused on inflammation-independent mechanisms, such as genetic factors, environmental risks, and the gut microbiota, which are known to affect the prognosis of fibrosis [14]. Moreover, intestinal fibrosis can be observed alongside excessive deposition of ECM and activated mesenchymal cells in the intestinal wall [15]. The main known drivers of this fibrosis mechanism are soluble molecules (cytokines and growth factors), the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), the endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EnMT), and the gut microbiota.
- Genetic factors
- Genetic research on IBD has proposed several genetic pathways for its pathogenesis [16,17]. However, relations between those gene mutations and intestinal fibrosis have not yet been well studied. In one bioinformatics study, researchers hypothesized that similar molecular pathways would be involved in fibrosis in various organs and thus measured gene expressions found in kidney fibrosis and liver cirrhosis in Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). They found that fibrosis in different organs had different gene signatures. C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9 (CXCL9) and CD52 were upregulated in both CD and UC, whereas thrombospondin 2 (THBS2), matrix gla protein (MGP), protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type C (PTPRC), and decorin (DCN) were upregulated only in CD. In UC, CXCL9, CD52, and granzyme A (GZMA) were upregulated, and DCN, which was elevated in CD, was downregulated [18].
- Nucleotide binding oligomerization domain containing 2 (NOD2) has been most studied in association with IBD. Various polymorphisms related to the NOD2 gene have been reported and are known to be related to fibrogenesis in UC and CD [19–23]. The NOD2 gene was also suggested as a predictive marker for the progression of CD fibrosis [24]. Within the innate immune system, Toll-like receptors 4 (TLR) and signal transducers and activators of the transcription 3 (STAT3) might be a mechanism for intestinal fibrosis [19,25,26], and interleukin-23 receptor (IL23R), interleukin-12 subunit beta (IL12B), and Janus kinases 2 (JAK2), which are related to the Th17 pathway, could also be involved [25,27–29]. CX3CR1-mediating chemokines [30] and autophagy genes (autophagy related 16 like 1 [ATG16L1] and immunity-related GTPase family M protein [IRGM]) were reported to have an association with stricture disease [25,31]. However, the exact mechanism remains obscure because fucosyltransferase 2 (FUT2) appears to change the composition of the gut microbiota, which is presumed to be able to induce fibrosis [32]. Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) plays a broad role in initiating inflammation and fibrosis [33,34]. Matrix metallopeptidase 3 (MMP3) encodes a proteinase that degrades most components of the ECM. Membrane-associated guanylate kinase inverted 1 (MAGI1), which is associated with a mechanism that disrupts the tight junction of intestinal epithelial cells, is a gene factor potentially associated with fibrosis (Table 1) [35,36]. Because the number of studies is too small for generalization, more genome-wide association studies and next generation sequencing studies are needed to reveal genetic factors involved with fibrosis in IBD [16].
- Cytokines and growth factors
- Local fibroblasts in fibrotic foci proliferate in response to various growth factors and cytokines. platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), basic-fibroblast growth factor, insulin like growth factor 1, epidermal growth factor, CTGF, tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), IL-1β, and IL-6 can act as major proliferating factors [12,14,37]. The proliferating fibroblasts recruit various inflammatory cells, T cells, eosinophils, and mast cells. Inflammatory mediators, such as PDGF-A, PDGF-B, IGF-1, and fibronectin, are also involved in local fibroblastic proliferation and the migration of fibroblasts to the ECM of an inflamed area. In addition, intestinal stellate cells are differentiated into fibroblasts at inflammatory sites using TGF-β [38]. Furthermore, though the molecular pathway is not well established, the capacity of adult bone marrow to derive fibroblast precursors recently became clear, and several cytokines, such as IL-10 or other growth factors, are considered to be part of that pathway [14,39,40].
- Critical role of adipose tissue
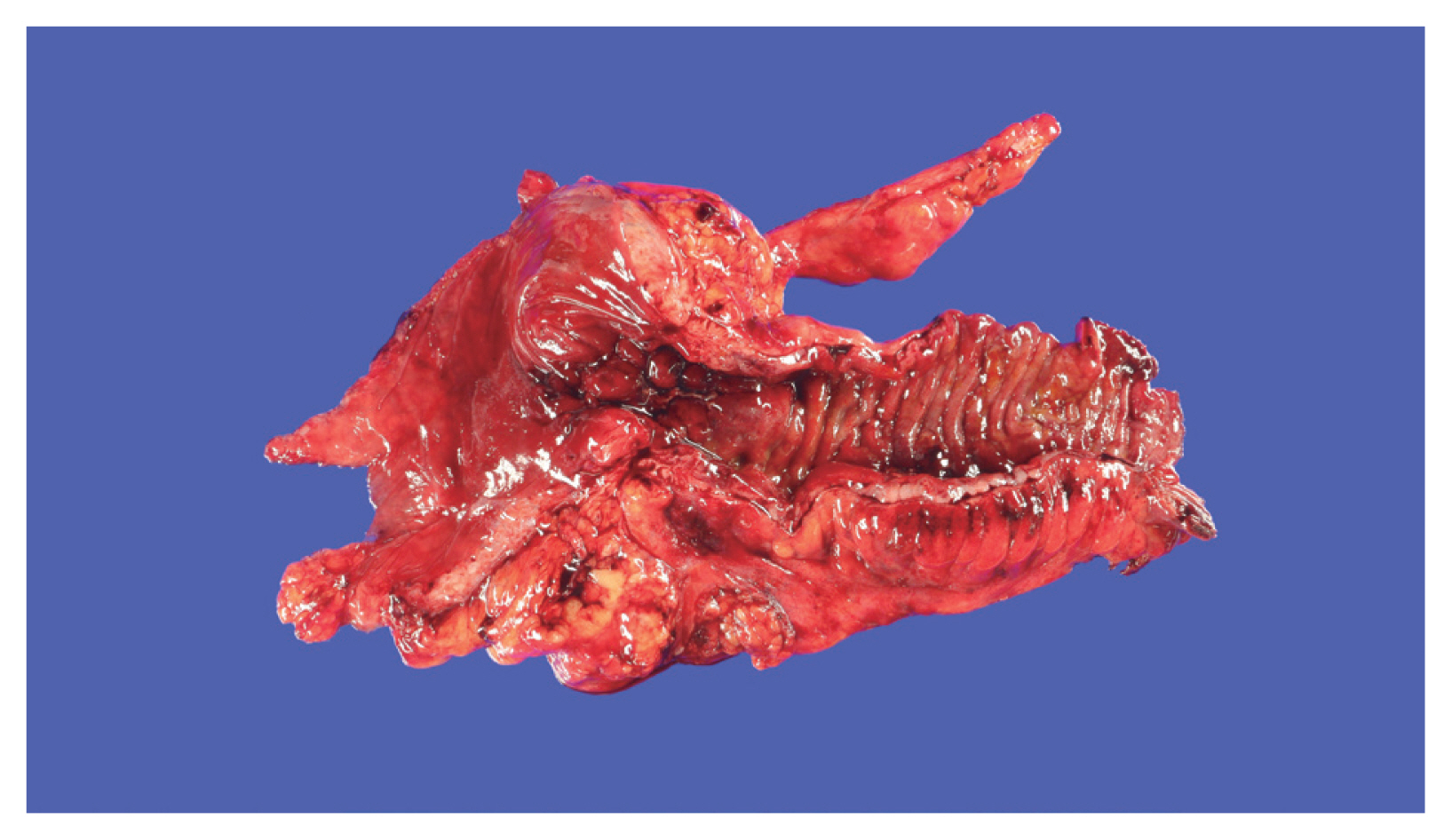
- The role of adipose tissue is essential in inducing hyperplasia of the muscularis propria and subsequent stricture formation in CD [41]. In IBD research, interest is increasing in the role of various bioactive substances secreted by mesenteric fat [42]. Creeping fat is a unique and pathognomonic phenomenon in CD that was first reported by Crohn in 1932 [43]. Creeping fat is defined as > 50% coverage of the exterior intestinal surface with proliferation and ectopic extension of mesenteric adipose tissue (Fig. 1). In the proliferated adipose tissue surrounding the intestine, numerous mediators play crucial roles in inflammation and immunity that lead to the development and progression of IBD [41,44]. Mediators secreted by fat tissue include adipokines (adiponectin, leptin, resistin, C1q/TNF-related protein 3 [CTRP-3], and fatty acids), cytokines (TNF-α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ [PPAR-γ], macrophage colony-stimulating factor, monocyte chemoattracted protein-1, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5), and growth factors (ghrelin and vascular endothelial growth factor). Those secretions attract and activate various immune cells [45,46]. Therefore, cases of cobblestone mucosa and proper muscle hyperplasia are common in specimens surgically resected to treat CD complications and result in a thick intestinal wall and stricture formation (Fig. 1) [47].
- EMT and EnMT
- The EMT is a well-known phenomenon in malignant neoplasms and literally describes a phenomenon in which tumor cells with epithelial features acquire a mesenchymal tendency to break the resistance of the surrounding ECM, facilitate local migration and invasion, and exhibit aggressive behavior [48]. It is also a mechanism of distant metastasis, in which epithelial cells are attacked by immune cells, or an apoptotic program is initiated when epithelial cells float away from their location, especially when they enter the blood flow, which is the starting point of distant metastases [49].
- In IBD, damaged intestinal epithelial cells are activated, and the EMT pathway is initiated. This change can be shown by a loss of epithelial marker expression (such as cytokeratins and E-cadherin) in the enterocytes of inflamed foci and increased expression of mesenchymal markers (especially fibroblast markers, MMP-2, MMP-9, ferroptosis suppressor protein 1, α-smooth muscle actin [α-SMA], and vimentin) [50].
- In addition, IBD can damage vascular endothelial cells [14]. In the presence of an excessive inflammatory response, such as hypoxia and secondary mechanical stress, endothelial cells are activated and converted into cells with fibroblast properties. This is called the EnMT, in which endothelial markers (VE-cadherin, Von Willebrand factor, and CD31) expressed in cells are lost, and the expression of fibroblast markers increases. In the EnMT, TGF-β, insulin-like growth factor 2, and IL-1b or TNF-α, which are pro-inflammatory components, are inducers [48,51,52]. Occasionally, this process is reversible. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 or hepatocyte growth factor can convert fibroblasts back into endothelial cells. However, the conditions under which this reversal pathway works remain unknown [53,54]. Cellular transitions, i.e., the EMT and EnMT, are sources of new fibroblasts and result in excessive ECM deposition. Fibroblasts also exhibit enhanced migratory ability. Therefore, the submucosal layer, which is composed of loose connective tissue, is replaced with various ECM components. As a result, the condition of the intestinal wall impedes its flexible movement [13].
- Gut microbiota
- The gut microbiota is one key factor in the development of fibrosis in IBD [16]. It consists of bacteria, viruses, archaea, protists, and yeast. The composition of the intestinal microbiota affects the host metabolism and immune systems in various ways, and chronic inflammatory status caused by the gut microbiota can ultimately produce the complications of intestinal fibrosis or strictures [55]. The stability of the intestinal microbiota supports the barrier function of intestinal epithelial cells [56]. If the balance between beneficial and harmful bacteria is destroyed, the intestinal microbial barrier and anti-inflammatory regulatory pathway can be damaged, which can eventually cause severe colitis [57,58]. In one study, the intestinal bacterial diversity of mice was reduced using intestinal radiation and an antibiotic cocktail treatment, and that produced decreased levels of TGF, phosphorylated SMAD3, and SMA proteins, which in turn reduced the chronic inflammation that plays a crucial role in intestinal fibrosis [59]. Preliminary studies of fibrosis and the microbiome have been done [24]. Several studies have suggested that fibronectin and collagen deposition in the intestinal wall is a response to bacterial stimulation of the intestine [60,61]. In addition, several studies have reported that strictures are more frequent in patients with CD who have higher levels of antibacterial antibodies [56,58].
PATHOGENESIS
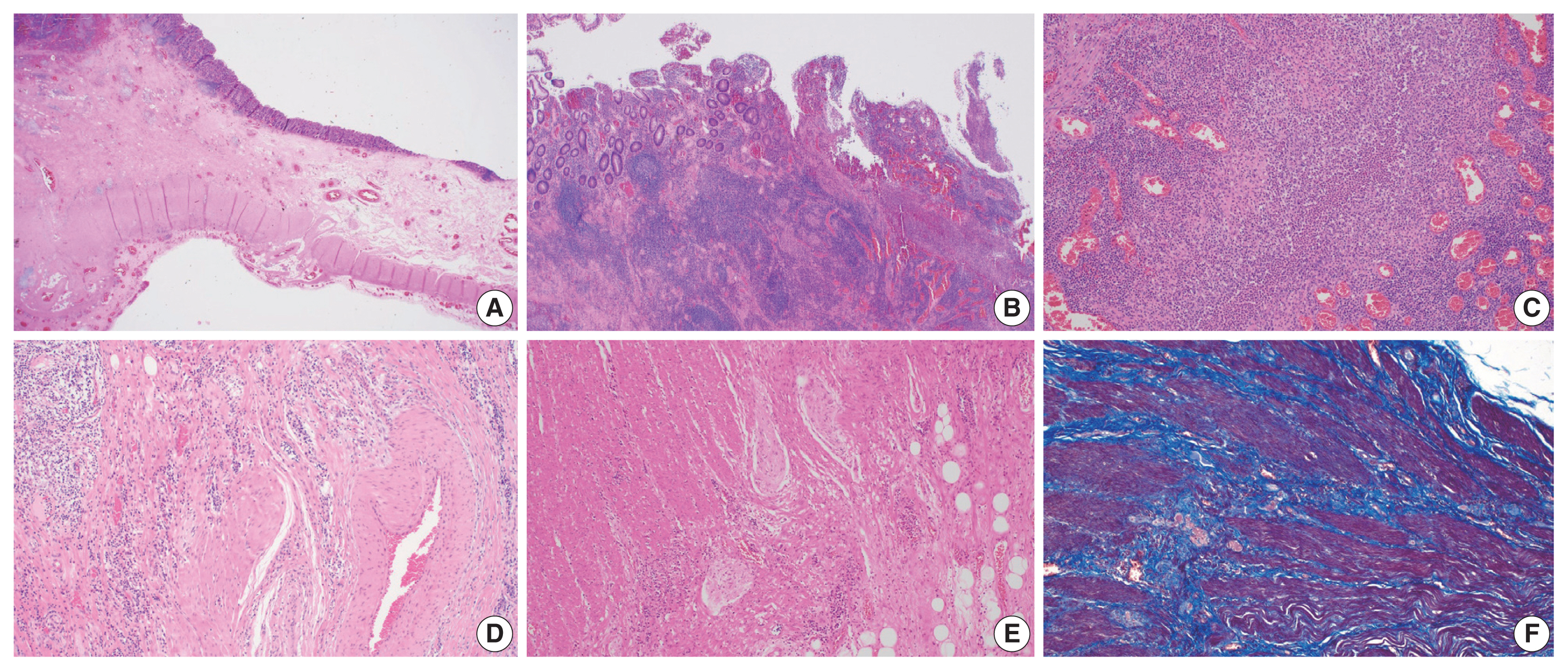
- In IBD-associated fibrosis, the change in the muscular layer, which contributes to the presence of a thickened bowel wall, is notable (Fig. 2A). This results in both hypertrophy and hyperplasia [47]. Although chronic inflammation, represented by basal plasmacytosis, is predominant, IBD can also show a mixed inflammation pattern that is accompanied by active inflammation (Fig. 2B, C). As the disease progresses, increased activation of intestinal myofibroblasts results in the gradual synthesis of ECM and contractile proteins (α-SMA and MYLK) [60]. Young fibroblasts begin to be deposited and gradually progress to fibrosis with increased deposition of ECM (collagen, fibronectin, etc.) [55]. In addition, slowed blood flow is caused by damage to highly branched vessels (Fig. 2D). This condition often becomes refractory to medication. Neuronal cell changes are usually observed in surgical specimens from patients with chronic constipation without a certain organic cause, and similarly in IBD patients, neuronal hypertrophy can be a secondary reactive change [62]; however, it can also act as a mechanism for intestinal stiffening (Fig. 2E). In trichrome stain results, dissection between hyperplastic smooth muscle bundles is observed to be interspersed with fibrosis (Fig. 2F).
- Histopathology scoring systems for stenosis
- In IBD, many scoring systems have been developed to express disease activity, including the Geboes score and Nancy Index of UC and the Crohn’s Disease Activity Index [63,64]. These evaluation methods consider not only the presence of ulcers but also the degree of infiltration of inflammation, submucosal fibrosis, and thickened muscularis propria. Following a recent discussion at the Stenosis Therapy and Antifibrotic Research Consortium, a four-tiered system (none, mild, moderate, and severe) was constructed to include an evaluation of the inflammatory and fibrotic components of each mural layer [55]. In this artificial intelligence era, researchers have endeavored to develop a deep learning model to evaluate intestinal fibrosis in surgical specimens for postoperative recurrence prediction [65,66].
- Differences of intestinal fibrosis in UC and CD
- UC and CD, which belong to the same IBD category but differ in their mechanisms of development and clinical features, also show differences in IBD-related fibrosis [67]. In UC, fibrotic changes are limited to the mucosal and submucosal layers [55]. This can shorten or stiffen the intestine, leading to motility disorders. Because strictures in UC are rare and can be either benign or malignant, a persistent stricture should raise suspicions of cancer [68]. Complications that are mainly due to bowel wall thickening, such as stricture and stenosis, are problematic in CD. Furthermore, diffuse transmural collagen layers down to the muscularis propria and proliferative fibroblastic infiltration are observed. In UC, on the other hand, the progression of intestinal fibrosis does not correlate with disease duration or location; however, inflammatory activity does correlate with medical treatment. In contrast, in CD, the duration and location of the disease and type of treatment are related to the risk of intestinal fibrosis [55,69,70].
- Biomarkers and potential antifibrotic agents
- Gene variants, epigenetic modifiers, antimicrobial antibodies, ECM components, and clinical, endoscopic, or environmental factors can be used to evaluate and predict fibrosis in IBD patients [71]. Fibrosis in CD, which causes several serious sequelae, is reversible, and thus it is important to develop therapeutic agents targeting it [72]. However, no effective therapeutic agents are available to prevent or repair the progression of fibrosis except by suppressing inflammation, though diverse potential antifibrotic therapies have been proposed. Although their mechanism is still unknown, statins (simvastatin) have been reported to effectively inhibit the progression of CD fibrosis [73,74]. In CD, pirfenidone, Rho kinase inhibitors, TGF-β signaling inhibitors, IL-13 inhibitors, and G31P (an antagonist of CXCL8) are also known to be effective [75,76]. GED-0507-34, an agent with a strong affinity for PPAR-γ, has been suggested as an anti-fibrotic agent in UC patients [77].
HISTOPATHOLOGY
- IBD-related intestinal fibrosis is the starting point for serious complications in patients with refractory and poorly controlled chronic IBD. If the uniquely activated profibrotic pathway observed in IBD can be identified, it could be used as a biomarker for targeted therapy. In addition, the gene expression signature of fibrogenesis at diagnosis could predict the risk of surgery. Intestinal fibrosis is an unfavorable result of the harmonic action of intestinal epithelial cells, the microbiota, and various mesenchymal components, such as the adipose tissue, fibroblasts, smooth muscle, neural tissue, and vascular endothelial cells, at the lesion site. It is thus necessary to pay attention to these mechanisms, from analyzing the ECM to developing therapeutic agents that target the main factors affecting pathogenesis, as well as elucidating the mechanisms involved by using various advanced research methods.
CONCLUSION
Ethics Statement
Not applicable.
Availability of Data and Material
All data generated or analyzed during the study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
Code Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: SUB. Figures and data: JMP. Writing—original draft: JMP, JK, YJL. Writing—review & editing: HWL. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Funding Statement
No funding to declare.
| Related genes | Disease entity | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOD2 | CD and UC | Apoptosis and activates NF-κB, induce interleukin 1-beta | [19–23] |
| TLR4 | CD | Initiating innate immune responses | [19] |
| IL23R | CD and UC | Activation of Th17 lymphocytes | [27,28] |
| IL12B | CD | Activation of Th17 lymphocytes | [25] |
| JAK2 | CD | Activation of Th17 lymphocytes | [29] |
| CX3CR1 | CD | Leukocyte chemotaxis and adhesion | [30] |
| STAT3 | CD and UC | Innate immune mechanisms | [25,26] |
| ATG16L1 | CD | Autophagocytosis | [31] |
| IRGM | CD | Autophagocytosis | [25] |
| FUT2 | CD | Affects the composition of the gut microbiota | [32] |
| TGF-β | CD | Initiation of inflammation | [33,34] |
| MMP3 | CD and UC | Mediate degradation of components of the extracellular matrix | [35] |
| MAGI1 | CD | Disruption of epithelial barrier via abrnormality of tight junction of intestinal epithelial cells | [36] |
IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; NOD2, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2; CD, Crohn disease; UC, ulcerative colitis; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; TLR4, Toll-like receptors 4; IL23R, interleukin-23 receptor; IL12B, interleukin-12 subunit beta; JAK2, Janus kinases 2; CX3CR1, C-X3-C motif chemokine receptor 1; STAT3, signal transducers and activators of the transcription 3; ATG16L1, autophagy-related 16-like 1; IRGM, immunity-related GTPase family M protein; FUT2, fucosyltransferase 2; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; MMP-3, matrix metalloproteinase-3; MAGI1, membrane-associated guanylate kinase inverted 1.
- 1. Leask A, Abraham DJ. TGF-beta signaling and the fibrotic response. FASEB J 2004; 18: 816-27. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC. Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020.
- 3. Jun JI, Lau LF. Resolution of organ fibrosis. J Clin Invest 2018; 128: 97-107. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Di Gregorio J, Robuffo I, Spalletta S, et al. The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition as a possible therapeutic target in fibrotic disorders. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020; 8: 607483.PubMedPMC
- 5. Rockey DC, Bell PD, Hill JA. Fibrosis: a common pathway to organ injury and failure. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 1138-49. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Zhang YZ, Li YY. Inflammatory bowel disease: pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20: 91-9. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Zidar N. Histopathology of fibrosis in Crohn’s disease: the importance of understanding its pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 2020; 158: 2313-4. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Hanna MH, Kaiser AM. Update on the management of sigmoid diverticulitis. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27: 760-81. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Speca S, Giusti I, Rieder F, Latella G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of intestinal fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18: 3635-61. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Wynn TA. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J Pathol 2008; 214: 199-210. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Burke JP, Mulsow JJ, O’Keane C, Docherty NG, Watson RW, O’Connell PR. Fibrogenesis in Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2007; 102: 439-48. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Franze E, Monteleone I, Laudisi F, et al. Cadherin-11 is a regulator of intestinal fibrosis. J Crohns Colitis 2020; 14: 406-17. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Rieder F, Fiocchi C, Rogler G. Mechanisms, management, and treatment of fibrosis in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2017; 152: 340-50. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Rieder F, Fiocchi C. Intestinal fibrosis in inflammatory bowel disease: current knowledge and future perspectives. J Crohns Colitis 2008; 2: 279-90. ArticlePubMed
- 15. Derkacz A, Olczyk P, Olczyk K, Komosinska-Vassev K. The role of extracellular matrix components in inflammatory bowel diseases. J Clin Med 2021; 10: 1122.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Graham DB, Xavier RJ. Pathway paradigms revealed from the genetics of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2020; 578: 527-39. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 17. Zhang H, Massey D, Tremelling M, Parkes M. Genetics of inflammatory bowel disease: clues to pathogenesis. Br Med Bull 2008; 87: 17-30. ArticlePubMed
- 18. Jerala M, Hauptman N, Kojc N, Zidar N. Expression of fibrosis-related genes in liver and kidney fibrosis in comparison to inflammatory bowel diseases. Cells 2022; 11: 314.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 19. Gazouli M, Pachoula I, Panayotou I, et al. NOD2/CARD15, ATG16L1 and IL23R gene polymorphisms and childhood-onset of Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16: 1753-8. PubMedPMC
- 20. Andriulli A, Annese V, Latiano A, et al. The frame-shift mutation of the NOD2/CARD15 gene is significantly increased in ulcerative colitis: an *IG-IBD study. Gastroenterology 2004; 126: 625-7. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Wehkamp J, Harder J, Weichenthal M, et al. NOD2 (CARD15) mutations in Crohn’s disease are associated with diminished mucosal alpha-defensin expression. Gut 2004; 53: 1658-64. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Nimmo ER, Prendergast JG, Aldhous MC, et al. Genome-wide methylation profiling in Crohn’s disease identifies altered epigenetic regulation of key host defense mechanisms including the Th17 pathway. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2012; 18: 889-99. ArticlePubMed
- 23. Chuang AY, Chuang JC, Zhai Z, Wu F, Kwon JH. NOD2 expression is regulated by microRNAs in colonic epithelial HCT116 cells. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014; 20: 126-35. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Rieder F, Lawrance IC, Leite A, Sans M. Predictors of fibrostenotic Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2011; 17: 2000-7. ArticlePubMed
- 25. Henckaerts L, Van Steen K, Verstreken I, et al. Genetic risk profiling and prediction of disease course in Crohn’s disease patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009; 7: 972-80. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Nijhuis A, Biancheri P, Lewis A, et al. In Crohn’s disease fibrosis-reduced expression of the miR-29 family enhances collagen expression in intestinal fibroblasts. Clin Sci (Lond) 2014; 127: 341-50. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. Duerr RH, Taylor KD, Brant SR, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory bowel disease gene. Science 2006; 314: 1461-3. PubMedPMC
- 28. Glas J, Seiderer J, Wetzke M, et al. rs1004819 is the main disease-associated IL23R variant in German Crohn’s disease patients: combined analysis of IL23R, CARD15, and OCTN1/2 variants. PLoS One 2007; 2: e819.PubMedPMC
- 29. Cleynen I, Gonzalez JR, Figueroa C, et al. Genetic factors conferring an increased susceptibility to develop Crohn’s disease also influence disease phenotype: results from the IBDchip European Project. Gut 2013; 62: 1556-65. ArticlePubMed
- 30. Brand S, Hofbauer K, Dambacher J, et al. Increased expression of the chemokine fractalkine in Crohn’s disease and association of the fractalkine receptor T280M polymorphism with a fibrostenosing disease Phenotype. Am J Gastroenterol 2006; 101: 99-106. ArticlePubMed
- 31. Fowler EV, Doecke J, Simms LA, et al. ATG16L1 T300A shows strong associations with disease subgroups in a large Australian IBD population: further support for significant disease heterogeneity. Am J Gastroenterol 2008; 103: 2519-26. ArticlePubMed
- 32. Forni D, Cleynen I, Ferrante M, et al. ABO histo-blood group might modulate predisposition to Crohn’s disease and affect disease behavior. J Crohns Colitis 2014; 8: 489-94. ArticlePubMed
- 33. Hume GE, Fowler EV, Lincoln D, et al. Angiotensinogen and transforming growth factor beta1: novel genes in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease. J Med Genet 2006; 43: e51.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Adams AT, Kennedy NA, Hansen R, et al. Two-stage genome-wide methylation profiling in childhood-onset Crohn’s disease implicates epigenetic alterations at the VMP1/MIR21 and HLA loci. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014; 20: 1784-93. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Meijer MJ, Mieremet-Ooms MA, van Hogezand RA, Lamers CB, Hommes DW, Verspaget HW. Role of matrix metalloproteinase, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase and tumor necrosis factor-alpha single nucleotide gene polymorphisms in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13: 2960-6. PubMedPMC
- 36. Alonso A, Domenech E, Julia A, et al. Identification of risk loci for Crohn’s disease phenotypes using a genome-wide association study. Gastroenterology 2015; 148: 794-805. ArticlePubMed
- 37. Rieder F, Brenmoehl J, Leeb S, Scholmerich J, Rogler G. Wound healing and fibrosis in intestinal disease. Gut 2007; 56: 130-9. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Rockey DC. Hepatic fibrosis, stellate cells, and portal hypertension. Clin Liver Dis 2006; 10: 459-79. ArticlePubMed
- 39. Bamba S, Lee CY, Brittan M, et al. Bone marrow transplantation ameliorates pathology in interleukin-10 knockout colitic mice. J Pathol 2006; 209: 265-73. ArticlePubMed
- 40. Brittan M, Wright NA. Gastrointestinal stem cells. J Pathol 2002; 197: 492-509. ArticlePubMed
- 41. Mao R, Kurada S, Gordon IO, et al. The mesenteric fat and intestinal muscle interface: creeping fat influencing stricture formation in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2019; 25: 421-6. ArticlePubMed
- 42. Peyrin-Biroulet L, Gonzalez F, Dubuquoy L, et al. Mesenteric fat as a source of C reactive protein and as a target for bacterial translocation in Crohn’s disease. Gut 2012; 61: 78-85. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 43. Crohn BB, Ginzburg L, Oppenheimer GD. Regional ileitis: a pathologic and clinical entity. JAMA 1932; 99: 1323-9. Article
- 44. Goncalves P, Magro F, Martel F. Metabolic inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease: crosstalk between adipose tissue and bowel. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2015; 21: 453-67. PubMed
- 45. Desreumaux P, Ernst O, Geboes K, et al. Inflammatory alterations in mesenteric adipose tissue in Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 1999; 117: 73-81. ArticlePubMed
- 46. Levine JA, Jensen MD, Eberhardt NL, O’Brien T. Adipocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a mediator of adipose tissue growth. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 1557-64. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 47. Chen W, Lu C, Hirota C, Iacucci M, Ghosh S, Gui X. Smooth muscle hyperplasia/hypertrophy is the most prominent histological change in Crohn’s fibrostenosing bowel strictures: a semiquantitative analysis by using a novel histological grading scheme. J Crohns Colitis 2017; 11: 92-104. ArticlePubMed
- 48. Kalluri R, Neilson EG. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 1776-84. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 49. Zhang D, Wang S, Chen J, et al. Fibulin-4 promotes osteosarcoma invasion and metastasis by inducing epithelial to mesenchymal transition via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Int J Oncol 2017; 50: 1513-30. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 50. Frid MG, Kale VA, Stenmark KR. Mature vascular endothelium can give rise to smooth muscle cells via endothelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation: in vitro analysis. Circ Res 2002; 90: 1189-96. PubMed
- 51. Bates RC, Mercurio AM. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human colonic organoids. Mol Biol Cell 2003; 14: 1790-800. PubMedPMC
- 52. Strutz F, Zeisberg M, Ziyadeh FN, et al. Role of basic fibroblast growth factor-2 in epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Kidney Int 2002; 61: 1714-28. ArticlePubMed
- 53. Yang J, Dai C, Liu Y. A novel mechanism by which hepatocyte growth factor blocks tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005; 16: 68-78. ArticlePubMed
- 54. Kagawa T, Takemura G, Kosai K, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor gene therapy slows down the progression of diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. Nephron Physiol 2006; 102: p92-102. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 55. D’Alessio S, Ungaro F, Noviello D, Lovisa S, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Danese S. Revisiting fibrosis in inflammatory bowel disease: the gut thickens. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022; 19: 169-84. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 56. Chu H, Khosravi A, Kusumawardhani IP, et al. Gene-microbiota interactions contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Science 2016; 352: 1116-20. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 57. Qiu P, Ishimoto T, Fu L, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Liu Y. The gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022; 12: 733992.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 58. Alfredsson J, Wick MJ. Mechanism of fibrosis and stricture formation in Crohn’s disease. Scand J Immunol 2020; 92: e12990.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 59. Zhao Z, Cheng W, Qu W, Shao G, Liu S. Antibiotic alleviates radiation-induced intestinal injury by remodeling microbiota, reducing inflammation, and inhibiting fibrosis. ACS Omega 2020; 5: 2967-77. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 60. Zhao S, Dejanovic D, Yao P, et al. Selective deletion of MyD88 signaling in alpha-SMA positive cells ameliorates experimental intestinal fibrosis via post-transcriptional regulation. Mucosal Immunol 2020; 13: 665-78. PubMedPMC
- 61. Porras AM, Zhou H, Shi Q, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease-associated gut commensals degrade components of the extracellular matrix Preprint at: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.09.503432 . 2022.
- 62. Knowles CH, Farrugia G. Gastrointestinal neuromuscular pathology in chronic constipation. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2011; 25: 43-57. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 63. Mosli MH, Parker CE, Nelson SA, et al. Histologic scoring indices for evaluation of disease activity in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017; 5: CD011256.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 64. Hutchings H, Alrubaiy L. Crohn’s disease activity index. In: Michalos AC, ed. Encyclopedia of quality of life and well-being research. Dordrecht Springer, Netherlands: 2014; 1354-7. Article
- 65. Sofo L, Caprino P, Schena CA, Sacchetti F, Potenza AE, Ciociola A. New perspectives in the prediction of postoperative complications for high-risk ulcerative colitis patients: machine learning preliminary approach. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2020; 24: 12781-7. PubMed
- 66. Udristoiu AL, Stefanescu D, Gruionu G, et al. Deep learning algorithm for the confirmation of mucosal healing in Crohn’s disease, based on confocal laser endomicroscopy images. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 2021; 30: 59-65. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 67. Flynn S, Eisenstein S. Inflammatory bowel disease presentation and diagnosis. Surg Clin North Am 2019; 99: 1051-62. ArticlePubMed
- 68. Gumaste V, Sachar DB, Greenstein AJ. Benign and malignant colorectal strictures in ulcerative colitis. Gut 1992; 33: 938-41. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 69. Mitomi H, Okayasu I, Bronner MP, et al. Comparative histologic assessment of proctocolectomy specimens from Japanese and American patients with ulcerative colitis with or without dysplasia. Int J Surg Pathol 2005; 13: 259-65. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 70. Yamagata M, Mikami T, Tsuruta T, et al. Submucosal fibrosis and basic-fibroblast growth factor-positive neutrophils correlate with colonic stenosis in cases of ulcerative colitis. Digestion 2011; 84: 12-21. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 71. Bettenworth D, Bokemeyer A, Baker M, et al. Assessment of Crohn’s disease-associated small bowel strictures and fibrosis on cross-sectional imaging: a systematic review. Gut 2019; 68: 1115-26. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 72. Agrawal M, Spencer EA, Colombel JF, Ungaro RC. Approach to the management of recently diagnosed inflammatory bowel disease patients: a user’s guide for adult and pediatric gastroenterologists. Gastroenterology 2021; 161: 47-65. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 73. Li C, Yang CW, Park JH, et al. Pravastatin treatment attenuates interstitial inflammation and fibrosis in a rat model of chronic cyclosporine-induced nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2004; 286: F46-57. ArticlePubMed
- 74. Abe Y, Murano M, Murano N, et al. Simvastatin attenuates intestinal fibrosis independent of the anti-inflammatory effect by promoting fibroblast/myofibroblast apoptosis in the regeneration/healing process from TNBS-induced colitis. Dig Dis Sci 2012; 57: 335-44. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 75. Gordon JR, Zhang X, Li F, Nayyar A, Town J, Zhao X. Amelioration of pathology by ELR-CXC chemokine antagonism in a swine model of airway endotoxin exposure. J Agromedicine 2009; 14: 235-41. ArticlePubMed
- 76. Stillie R, Farooq SM, Gordon JR, Stadnyk AW. The functional significance behind expressing two IL-8 receptor types on PMN. J Leukoc Biol 2009; 86: 529-43. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 77. Speca S, Rousseaux C, Dubuquoy C, et al. Novel PPARgamma modulator GED-0507-34 levo ameliorates inflammation-driven intestinal fibrosis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2016; 22: 279-92. PubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Leveraging Organ‐on‐Chip Models to Investigate Host–Microbiota Dynamics and Targeted Therapies for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Tim Kaden, Raquel Alonso‐Román, Johannes Stallhofer, Mark S. Gresnigt, Bernhard Hube, Alexander S. Mosig
Advanced Healthcare Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prominence of Microbiota to Predict Fibrous Stenosis in Crohn’s Disease
Xue Yang, Yan Pan, Cai-Ping Gao, Hang Li, Ying-Hui Zhang, Chun-Li Huang, Lu Cao, Shi-Yu Xiao, Zhou Zhou
Journal of Inflammation Research.2025; Volume 18: 1413. CrossRef - Fibrosierende Erkrankungen im Gastrointestinaltrakt
Elke Roeb
Die Innere Medizin.2025; 66(7): 695. CrossRef - Roles of fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases and IBD-associated fibrosis
Takayoshi Ito, Hisako Kayama
International Immunology.2025; 37(7): 379. CrossRef - Disease Clearance in Ulcerative Colitis: A Narrative Review
Silvio Danese, Laurent Peyrin‐Biroulet, Vipul Jairath, Ferdinando D'Amico, Shashi Adsul, Christian Agboton, Fernando Magro
United European Gastroenterology Journal.2025; 13(6): 902. CrossRef - Gut Microbiota as a Mediator Between Intestinal Fibrosis and Creeping Fat in Crohn's Disease
Caiguang Liu, Rongchang Li, Jing Nie, Jinshen He, Zihao Lin, Xiaomin Wu, Jinyu Tan, Zishan Liu, Longyuan Zhou, Xiaozhi Li, Zhirong Zeng, Minhu Chen, Shixian Hu, Yijun Zhu, Ren Mao
United European Gastroenterology Journal.2025; 13(7): 1092. CrossRef - Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): immunotoxicity at the primary sites of exposure
Emma Arnesdotter, Charlotte B. A. Stoffels, Wiebke Alker, Arno C. Gutleb, Tommaso Serchi
Critical Reviews in Toxicology.2025; 55(4): 484. CrossRef - Disease-Specific Novel Role of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Organ Fibrosis
Harshal Sawant, Alip Borthakur
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(12): 5713. CrossRef - Galectin-3—Insights from Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Thomas Grewal, Hauke Christian Tews, Christa Buechler
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(13): 6101. CrossRef - Revealing Fibrosis Genes as Biomarkers of Ulcerative Colitis: A Bioinformatics Study Based on ScRNA and Bulk RNA Datasets
Yandong Wang, Li Liu, Weihao Wang
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets.2025; 25(9): 710. CrossRef - Fibrosis in Immune-Mediated and Autoimmune Disorders
Magdalena Żurawek, Iwona Ziółkowska-Suchanek, Katarzyna Iżykowska
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(18): 6636. CrossRef - Plasma-activated media inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and ameliorates intestinal fibrosis through the PPARγ/TGF-β1/SMAD3 pathway
Yi You, Yaping Shen, Yan Yang, Xiaoyang Wei, Yuheng Zhou, Foxing Tan, Longcheng Deng, Haolin Du, Sen Wang, Cheng Wang, Yan Huang, Vinay Kumar,
PLOS One.2025; 20(10): e0335225. CrossRef - (R)-Bambuterol attenuates DSS-induced chronic colitis by suppressing inflammation, repairing intestinal barrier, and modulating gut microbiota and serum metabolomic profile
Liangjun Deng, Le Tian, Dan Su, Jiukun Xie, Yuer Qian, Yipeng Li, Shidong Zhang, Shanping Wang, Zhihua Liu
European Journal of Pharmacology.2025; 1008: 178346. CrossRef - Beyond inflammation: what drives the self-perpetuating cycle of fibrosis in IBD?
Yutong Wei, Zhou Zhou, Shiyu Xiao
Annals of Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Neurokinin-1 Receptor Regulation of Fibroblast Phenotype and Function
Scott P. Levick
Receptors.2025; 4(4): 23. CrossRef - Tumor Development in Ulcerative Colitis: Perspectives From Biomechanical Characteristics
Hirotaka Tao
Development, Growth & Differentiation.2025; 67(9): 487. CrossRef - Effects of maternal overnutrition and metabolic challenge in adult life on the histological integrity of the liver and intestinal epithelium in rabbits
Lucía Carolina Cano, Erika Navarrete, Pedro Medina, Juan Pablo Ochoa-Romo, Georgina Díaz, Rodrigo Montúfar-Chaveznava, Rosa María Vigueras-Villaseñor, Ivette Caldelas
Frontiers in Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Full-Thickness Resection of a Non-Lifting Adenoma in an Ulcerative Colitis Patient Using OVESCO: A Case Report
Fei Yang Pan, Rupert Leong, Saurabh Gupta, Talia Fuchs, Viraj Kariyawasam
Case Reports in Gastroenterology.2025; 19(1): 682. CrossRef - Resistance to apoptosis in complicated Crohn's disease: Relevance in ileal fibrosis
M. Seco-Cervera, D. Ortiz-Masiá, D.C. Macias-Ceja, S. Coll, L. Gisbert-Ferrándiz, J. Cosín-Roger, C. Bauset, M. Ortega, B. Heras-Morán, F. Navarro-Vicente, M. Millán, J.V. Esplugues, S. Calatayud, M.D. Barrachina
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2024; 1870(2): 166966. CrossRef - Characterization of patient-derived intestinal organoids for modelling fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Ilaria Laudadio, Claudia Carissimi, Noemi Scafa, Alex Bastianelli, Valerio Fulci, Alessandra Renzini, Giusy Russo, Salvatore Oliva, Roberta Vitali, Francesca Palone, Salvatore Cucchiara, Laura Stronati
Inflammation Research.2024; 73(8): 1359. CrossRef - Food additives impair gut microbiota from healthy individuals and IBD patients in a colonic in vitro fermentation model
Irma Gonza, Elizabeth Goya-Jorge, Caroline Douny, Samiha Boutaleb, Bernard Taminiau, Georges Daube, Marie–Louise Scippo, Edouard Louis, Véronique Delcenserie
Food Research International.2024; 182: 114157. CrossRef - Epigenetic Regulation of EMP/EMT-Dependent Fibrosis
Margherita Sisto, Sabrina Lisi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(5): 2775. CrossRef - Mechanisms and therapeutic research progress in intestinal fibrosis
Yanjiang Liu, Tao Zhang, Kejian Pan, He Wei
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Disease clearance in ulcerative colitis: A new therapeutic target for the future
Syed Adeel Hassan, Neeraj Kapur, Fahad Sheikh, Anam Fahad, Somia Jamal
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(13): 1801. CrossRef - Urinary Hydroxyproline as an Inflammation-Independent Biomarker of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Muriel Huss, Tanja Elger, Johanna Loibl, Arne Kandulski, Benedicta Binder, Petra Stoeckert, Patricia Mester, Martina Müller, Christa Buechler, Hauke Christian Tews
Gastroenterology Insights.2024; 15(2): 486. CrossRef - Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Immune Function, Tissue Fibrosis and Current Therapies
Jesús Cosín-Roger
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(12): 6416. CrossRef - The Diagnosis of Intestinal Fibrosis in Crohn’s Disease—Present and Future
Sara Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, Jolanta Gruszecka, Rafał Filip
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(13): 6935. CrossRef - Role of gut microbiota in Crohn’s disease pathogenesis: Insights from fecal microbiota transplantation in mouse model
Qiang Wu, Lian-Wen Yuan, Li-Chao Yang, Ya-Wei Zhang, Heng-Chang Yao, Liang-Xin Peng, Bao-Jia Yao, Zhi-Xian Jiang
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(31): 3689. CrossRef - Ultrasound of the bowel with a focus on IBD: the new best practice
Christina Merrill, Stephanie R. Wilson
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 50(2): 555. CrossRef - Unveiling the anti-inflammatory potential of 11β,13-dihydrolactucin for application in inflammatory bowel disease management
Melanie S. Matos, María Ángeles Ávila-Gálvez, Antonio González-Sarrías, Nuno-Valério Silva, Carolina Lage Crespo, António Jacinto, Ana Teresa Serra, Ana A. Matias, Cláudia Nunes dos Santos
Food & Function.2024; 15(18): 9254. CrossRef - Gut microbiota and mesenteric adipose tissue interactions in shaping phenotypes and treatment strategies for Crohn’s disease
Anis Hasnaoui, Racem Trigui, Mario Giuffrida
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(46): 4969. CrossRef - Pathways Affected by Falcarinol-Type Polyacetylenes and Implications for Their Anti-Inflammatory Function and Potential in Cancer Chemoprevention
Ruyuf Alfurayhi, Lei Huang, Kirsten Brandt
Foods.2023; 12(6): 1192. CrossRef - Time to eRAASe chronic inflammation: current advances and future perspectives on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system and chronic intestinal inflammation in dogs and humans
Romy M. Heilmann, Georg Csukovich, Iwan A. Burgener, Franziska Dengler
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of the epithelial barrier in intestinal fibrosis associated with inflammatory bowel disease: relevance of the epithelial-to mesenchymal transition
Dulce C. Macias-Ceja, M. Teresa Mendoza-Ballesteros, María Ortega-Albiach, M. Dolores Barrachina, Dolores Ortiz-Masià
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure


Fig. 1
Fig. 2
| Related genes | Disease entity | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOD2 | CD and UC | Apoptosis and activates NF-κB, induce interleukin 1-beta | [ |
| TLR4 | CD | Initiating innate immune responses | [ |
| IL23R | CD and UC | Activation of Th17 lymphocytes | [ |
| IL12B | CD | Activation of Th17 lymphocytes | [ |
| JAK2 | CD | Activation of Th17 lymphocytes | [ |
| CX3CR1 | CD | Leukocyte chemotaxis and adhesion | [ |
| STAT3 | CD and UC | Innate immune mechanisms | [ |
| ATG16L1 | CD | Autophagocytosis | [ |
| IRGM | CD | Autophagocytosis | [ |
| FUT2 | CD | Affects the composition of the gut microbiota | [ |
| TGF-β | CD | Initiation of inflammation | [ |
| MMP3 | CD and UC | Mediate degradation of components of the extracellular matrix | [ |
| MAGI1 | CD | Disruption of epithelial barrier via abrnormality of tight junction of intestinal epithelial cells | [ |
IBD, inflammatory bowel disease;

 E-submission
E-submission




