Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 57(1); 2023 > Article
-
Review
Inflammatory bowel disease–associated intestinal fibrosis -
Ji Min Park1
 , Jeongseok Kim2
, Jeongseok Kim2 , Yoo Jin Lee2
, Yoo Jin Lee2 , Sung Uk Bae3
, Sung Uk Bae3 , Hye Won Lee1
, Hye Won Lee1
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2023;57(1):60-66.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.11.02
Published online: January 10, 2023
1Department of Pathology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
2Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
3Division of Colorectal Surgery, Department of Surgery, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Hye Won Lee, MD, PhD, Department of Pathology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, 1095 Dalgubeol-daero, Dalseo-gu, Daegu 42601, Korea, Tel: +82-53-258-4260, Fax: +82-53-258-7382, E-mail: hwlee@dsmc.or.kr
© 2023 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Leveraging Organ‐on‐Chip Models to Investigate Host–Microbiota Dynamics and Targeted Therapies for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Tim Kaden, Raquel Alonso‐Román, Johannes Stallhofer, Mark S. Gresnigt, Bernhard Hube, Alexander S. Mosig
Advanced Healthcare Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prominence of Microbiota to Predict Fibrous Stenosis in Crohn’s Disease
Xue Yang, Yan Pan, Cai-Ping Gao, Hang Li, Ying-Hui Zhang, Chun-Li Huang, Lu Cao, Shi-Yu Xiao, Zhou Zhou
Journal of Inflammation Research.2025; Volume 18: 1413. CrossRef - Fibrosierende Erkrankungen im Gastrointestinaltrakt
Elke Roeb
Die Innere Medizin.2025; 66(7): 695. CrossRef - Roles of fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases and IBD-associated fibrosis
Takayoshi Ito, Hisako Kayama
International Immunology.2025; 37(7): 379. CrossRef - Disease Clearance in Ulcerative Colitis: A Narrative Review
Silvio Danese, Laurent Peyrin‐Biroulet, Vipul Jairath, Ferdinando D'Amico, Shashi Adsul, Christian Agboton, Fernando Magro
United European Gastroenterology Journal.2025; 13(6): 902. CrossRef - Gut Microbiota as a Mediator Between Intestinal Fibrosis and Creeping Fat in Crohn's Disease
Caiguang Liu, Rongchang Li, Jing Nie, Jinshen He, Zihao Lin, Xiaomin Wu, Jinyu Tan, Zishan Liu, Longyuan Zhou, Xiaozhi Li, Zhirong Zeng, Minhu Chen, Shixian Hu, Yijun Zhu, Ren Mao
United European Gastroenterology Journal.2025; 13(7): 1092. CrossRef - Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): immunotoxicity at the primary sites of exposure
Emma Arnesdotter, Charlotte B. A. Stoffels, Wiebke Alker, Arno C. Gutleb, Tommaso Serchi
Critical Reviews in Toxicology.2025; 55(4): 484. CrossRef - Disease-Specific Novel Role of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Organ Fibrosis
Harshal Sawant, Alip Borthakur
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(12): 5713. CrossRef - Galectin-3—Insights from Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Thomas Grewal, Hauke Christian Tews, Christa Buechler
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(13): 6101. CrossRef - Revealing Fibrosis Genes as Biomarkers of Ulcerative Colitis: A Bioinformatics Study Based on ScRNA and Bulk RNA Datasets
Yandong Wang, Li Liu, Weihao Wang
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets.2025; 25(9): 710. CrossRef - Fibrosis in Immune-Mediated and Autoimmune Disorders
Magdalena Żurawek, Iwona Ziółkowska-Suchanek, Katarzyna Iżykowska
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(18): 6636. CrossRef - Resistance to apoptosis in complicated Crohn's disease: Relevance in ileal fibrosis
M. Seco-Cervera, D. Ortiz-Masiá, D.C. Macias-Ceja, S. Coll, L. Gisbert-Ferrándiz, J. Cosín-Roger, C. Bauset, M. Ortega, B. Heras-Morán, F. Navarro-Vicente, M. Millán, J.V. Esplugues, S. Calatayud, M.D. Barrachina
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2024; 1870(2): 166966. CrossRef - Characterization of patient-derived intestinal organoids for modelling fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Ilaria Laudadio, Claudia Carissimi, Noemi Scafa, Alex Bastianelli, Valerio Fulci, Alessandra Renzini, Giusy Russo, Salvatore Oliva, Roberta Vitali, Francesca Palone, Salvatore Cucchiara, Laura Stronati
Inflammation Research.2024; 73(8): 1359. CrossRef - Food additives impair gut microbiota from healthy individuals and IBD patients in a colonic in vitro fermentation model
Irma Gonza, Elizabeth Goya-Jorge, Caroline Douny, Samiha Boutaleb, Bernard Taminiau, Georges Daube, Marie–Louise Scippo, Edouard Louis, Véronique Delcenserie
Food Research International.2024; 182: 114157. CrossRef - Epigenetic Regulation of EMP/EMT-Dependent Fibrosis
Margherita Sisto, Sabrina Lisi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(5): 2775. CrossRef - Mechanisms and therapeutic research progress in intestinal fibrosis
Yanjiang Liu, Tao Zhang, Kejian Pan, He Wei
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Disease clearance in ulcerative colitis: A new therapeutic target for the future
Syed Adeel Hassan, Neeraj Kapur, Fahad Sheikh, Anam Fahad, Somia Jamal
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(13): 1801. CrossRef - Urinary Hydroxyproline as an Inflammation-Independent Biomarker of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Muriel Huss, Tanja Elger, Johanna Loibl, Arne Kandulski, Benedicta Binder, Petra Stoeckert, Patricia Mester, Martina Müller, Christa Buechler, Hauke Christian Tews
Gastroenterology Insights.2024; 15(2): 486. CrossRef - Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Immune Function, Tissue Fibrosis and Current Therapies
Jesús Cosín-Roger
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(12): 6416. CrossRef - The Diagnosis of Intestinal Fibrosis in Crohn’s Disease—Present and Future
Sara Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, Jolanta Gruszecka, Rafał Filip
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(13): 6935. CrossRef - Role of gut microbiota in Crohn’s disease pathogenesis: Insights from fecal microbiota transplantation in mouse model
Qiang Wu, Lian-Wen Yuan, Li-Chao Yang, Ya-Wei Zhang, Heng-Chang Yao, Liang-Xin Peng, Bao-Jia Yao, Zhi-Xian Jiang
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(31): 3689. CrossRef - Ultrasound of the bowel with a focus on IBD: the new best practice
Christina Merrill, Stephanie R. Wilson
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 50(2): 555. CrossRef - Unveiling the anti-inflammatory potential of 11β,13-dihydrolactucin for application in inflammatory bowel disease management
Melanie S. Matos, María Ángeles Ávila-Gálvez, Antonio González-Sarrías, Nuno-Valério Silva, Carolina Lage Crespo, António Jacinto, Ana Teresa Serra, Ana A. Matias, Cláudia Nunes dos Santos
Food & Function.2024; 15(18): 9254. CrossRef - Gut microbiota and mesenteric adipose tissue interactions in shaping phenotypes and treatment strategies for Crohn’s disease
Anis Hasnaoui, Racem Trigui, Mario Giuffrida
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(46): 4969. CrossRef - Pathways Affected by Falcarinol-Type Polyacetylenes and Implications for Their Anti-Inflammatory Function and Potential in Cancer Chemoprevention
Ruyuf Alfurayhi, Lei Huang, Kirsten Brandt
Foods.2023; 12(6): 1192. CrossRef - Time to eRAASe chronic inflammation: current advances and future perspectives on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system and chronic intestinal inflammation in dogs and humans
Romy M. Heilmann, Georg Csukovich, Iwan A. Burgener, Franziska Dengler
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of the epithelial barrier in intestinal fibrosis associated with inflammatory bowel disease: relevance of the epithelial-to mesenchymal transition
Dulce C. Macias-Ceja, M. Teresa Mendoza-Ballesteros, María Ortega-Albiach, M. Dolores Barrachina, Dolores Ortiz-Masià
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
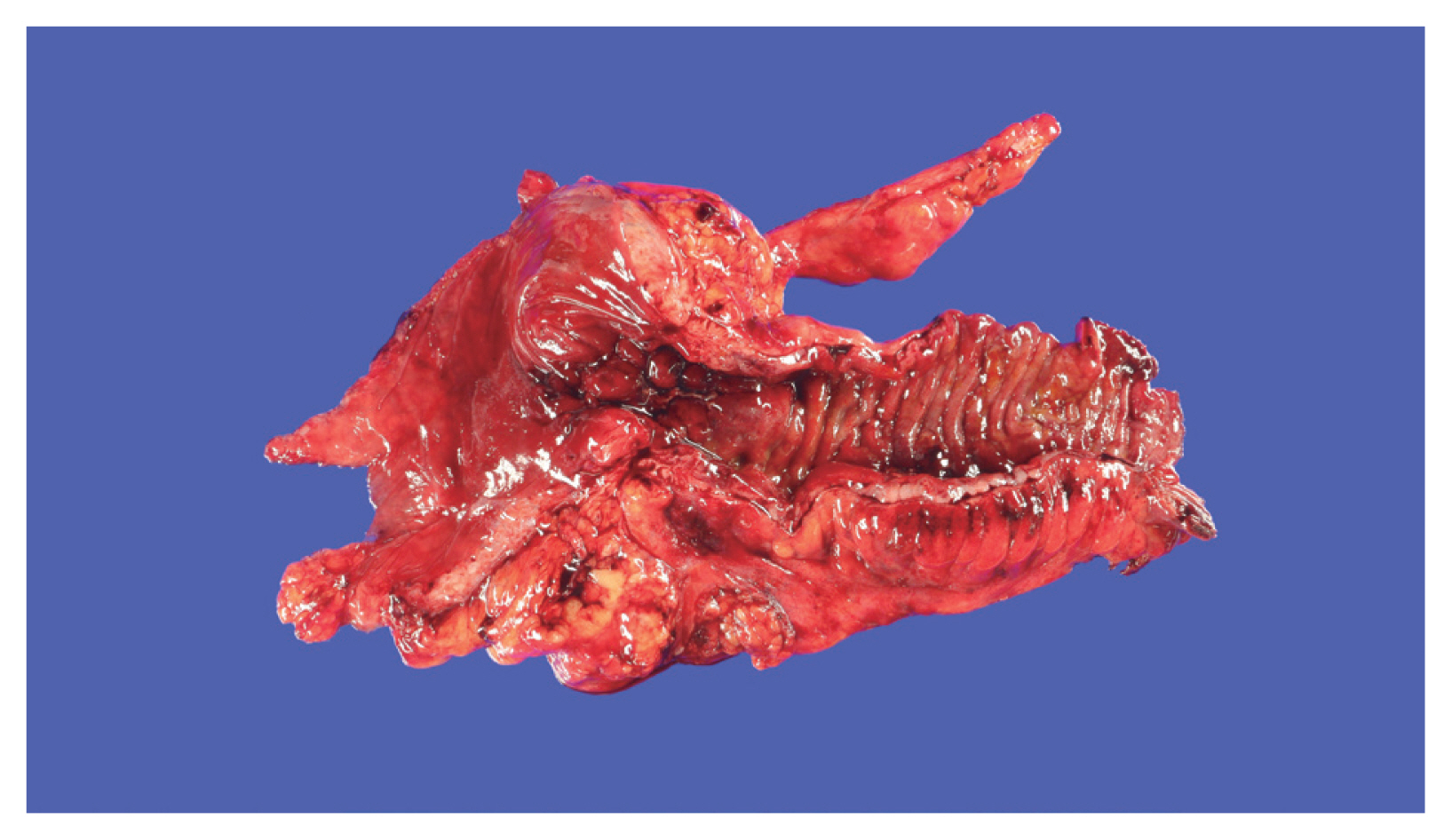
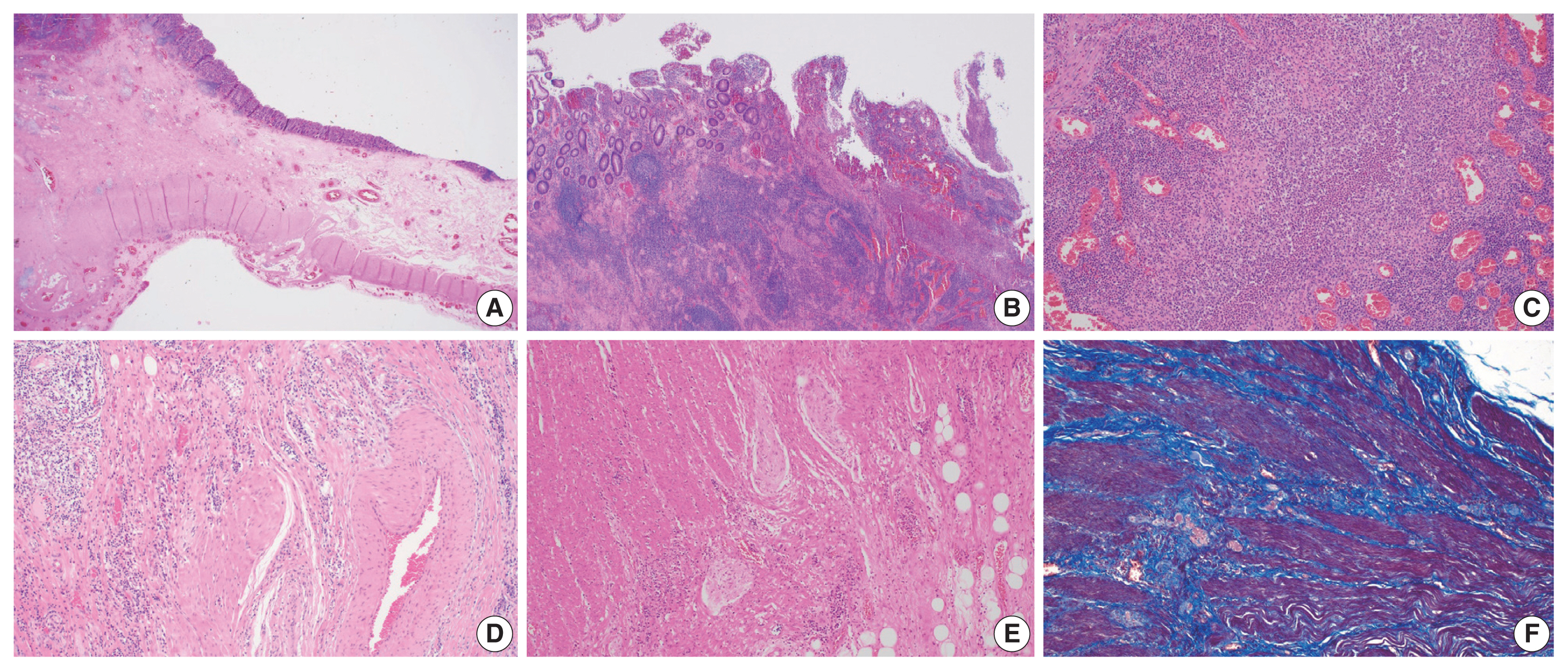
- Figure


Fig. 1
Fig. 2
| Related genes | Disease entity | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOD2 | CD and UC | Apoptosis and activates NF-κB, induce interleukin 1-beta | [ |
| TLR4 | CD | Initiating innate immune responses | [ |
| IL23R | CD and UC | Activation of Th17 lymphocytes | [ |
| IL12B | CD | Activation of Th17 lymphocytes | [ |
| JAK2 | CD | Activation of Th17 lymphocytes | [ |
| CX3CR1 | CD | Leukocyte chemotaxis and adhesion | [ |
| STAT3 | CD and UC | Innate immune mechanisms | [ |
| ATG16L1 | CD | Autophagocytosis | [ |
| IRGM | CD | Autophagocytosis | [ |
| FUT2 | CD | Affects the composition of the gut microbiota | [ |
| TGF-β | CD | Initiation of inflammation | [ |
| MMP3 | CD and UC | Mediate degradation of components of the extracellular matrix | [ |
| MAGI1 | CD | Disruption of epithelial barrier via abrnormality of tight junction of intestinal epithelial cells | [ |
IBD, inflammatory bowel disease;

 E-submission
E-submission