Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 59(1); 2025 > Article
-
Original Article
Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning -
Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen1
 , Minh-Khang Le2
, Minh-Khang Le2 , Sittiruk Roytrakul3
, Sittiruk Roytrakul3 , Shanop Shuangshoti1,4
, Shanop Shuangshoti1,4 , Nakarin Kitkumthorn5
, Nakarin Kitkumthorn5 , Somboon Keelawat1,6
, Somboon Keelawat1,6
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2025;59(1):39-49.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.14
Published online: October 24, 2024
1Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
2Department of Pathology, University of Yamanashi, Chuo City, Japan
3Functional Proteomics Technology Laboratory, National Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, National Science and Technology Development Agency, Pathumthani, Thailand
4Chulalongkorn GenePRO Center, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
5Department of Oral Biology, Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
6Precision Pathology of Neoplasia Research Group, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
-
Corresponding Author: Nakarin Kitkumthorn, DDS, PhD Department of Oral Biology, Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University, No. 6, Yothi Road, Ratchathewit, Bangkok 10400, Thailand Tel: +66-868815947, Fax: +66-22564208, E-mail: nakarinkit@gmail.com
Corresponding Author: Somboon Keelawat, MD Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University and Precision Pathology of Neoplasia Research Group, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, 1873 Rama IV Road, Pathum Wan, Bangkok 10330, Thailand Tel: +66-891151963, Fax: +66-22564208, E-mail: trcskl@gmail.com, Somboon.Ke@chula.ac.th
© The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
-
Background
- Although the criteria for follicular-pattern thyroid tumors are well-established, diagnosing these lesions remains challenging in some cases. In the recent World Health Organization Classification of Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Tumors (5th edition), the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma was reclassified as its own entity. It is crucial to differentiate this variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from low-risk follicular pattern tumors due to their shared morphological characteristics. Proteomics holds significant promise for detecting and quantifying protein biomarkers. We investigated the potential value of a protein biomarker panel defined by machine learning for identifying the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma, initially using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples.
-
Methods
- We developed a supervised machine-learning model and tested its performance using proteomics data from 46 thyroid tissue samples.
-
Results
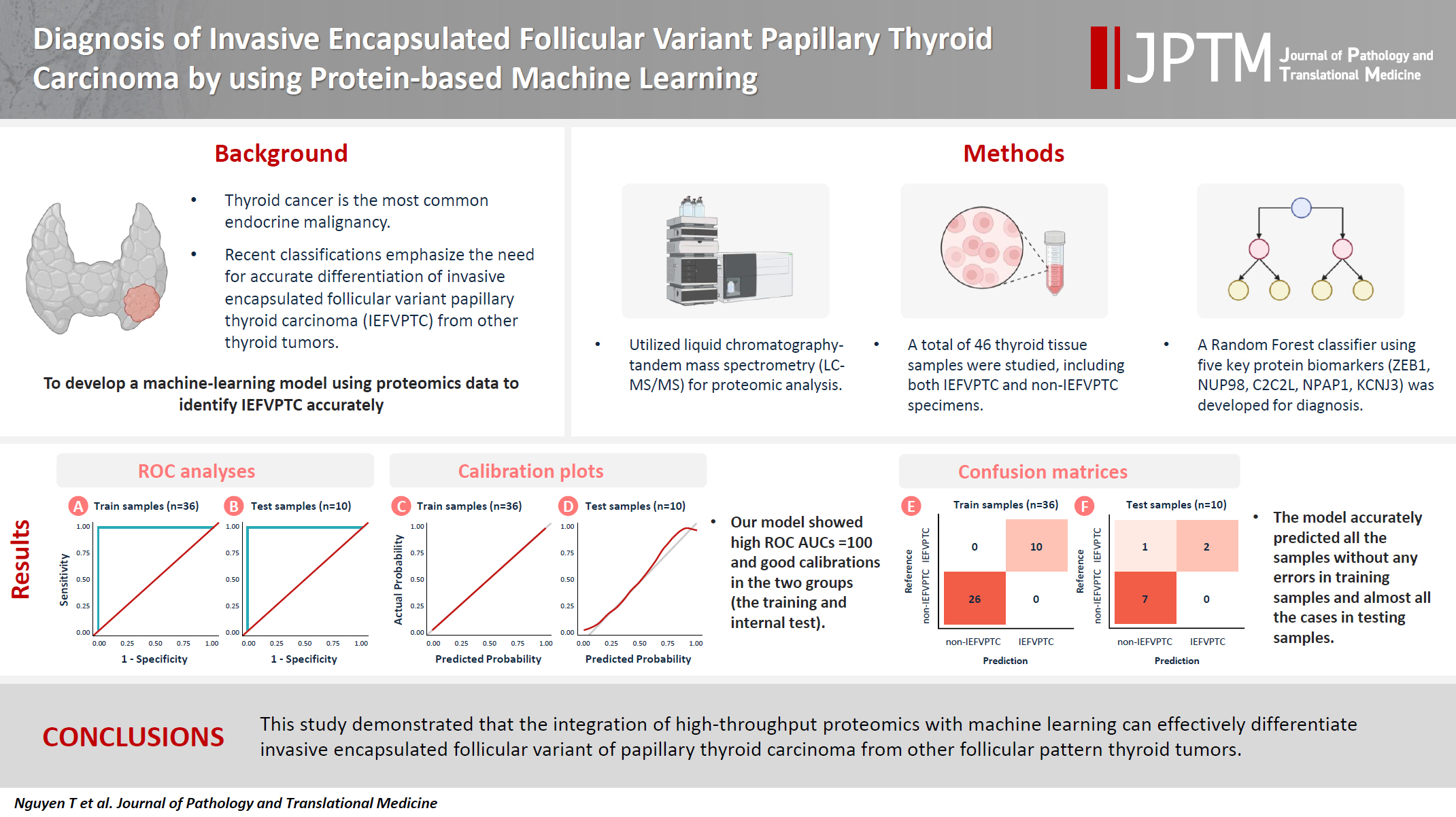
- We applied a random forest classifier utilizing five protein biomarkers (ZEB1, NUP98, C2C2L, NPAP1, and KCNJ3). This classifier achieved areas under the curve (AUCs) of 1.00 and accuracy rates of 1.00 in training samples for distinguishing the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from non-malignant samples. Additionally, we analyzed the performance of single-protein/gene receiver operating characteristic in differentiating the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from others within The Cancer Genome Atlas projects, which yielded an AUC >0.5.
-
Conclusions
- We demonstrated that integration of high-throughput proteomics with machine learning can effectively differentiate the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from other follicular pattern thyroid tumors.
- Thyroid cancer is the most prevalent endocrine malignancy, with detection rates increasing significantly in recent years [1]. This increase is largely attributed to enhanced detection of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), while other types, such as follicular, medullary, and anaplastic thyroid carcinomas, have maintained stable incidence rates [2,3].
- The recent 5th edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Tumors has refined the classification of thyroid tumors by integrating more detailed pathological, molecular, and behavioral characteristics [4]. This has led to the reclassification of invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma (IEFVPTC) as its own entity rather than a subtype of PTC. IEFVPTC has a RAS-like mutational profile similar to those of follicular adenoma (FA), follicular thyroid carcinoma (FTC), and other classifications such as non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) and well-differentiated tumor of uncertain malignant potential (WDT-UMP). Despite their genetic resemblance, IEFVPTC differs from FA/FTC in terms of nuclear features (score 0–1). It shares morphological traits with NIFTP and WDT-UMP, such as the presence of a fibrous capsule and nuclear characteristics similar to PTC (score 2–3) [4-6]. Crucially, IEFVPTC can demonstrate capsular/vascular invasion and metastasis, necessitating aggressive treatment including complete thyroidectomy and adjuvant therapy. In contrast, NIFTP and WDT-UMP are considered low-risk neoplasms, typically managed with lobectomy and close monitoring [6,7].
- Proteins play crucial roles in all biological processes and shape the phenotypes of cells and organisms. They are pivotal as diagnostic biomarkers and targets for therapy. Proteomics presents a viable analytic technique, especially through improvements in mass spectrometry (MS), increasing detection and quantification of a wide range of proteins and facilitating differentiation of various thyroid tumors through their proteomic signatures [8,9]. Although research has been conducted to differentiate FA and FTC [10-12], no study has focused on molecular markers that specifically distinguish IEFVPTC from lower-risk tumors (NIFTP, WDT-UMP). Our goal was to explore the applications and potential of machine learning, combined with protein profiling, in diagnosing and classifying IEFVPTC from follicular thyroid nodules. In this study, we improved the accuracy of techniques for distinguishing malignant follicular thyroid tumors and identified potential immunohistochemistry markers for diagnosing IEFVPTC.
INTRODUCTION
- Study subjects
- Thyroid tumor tissue and nontumor tissue samples were obtained from the Department of Pathology, Chulalongkorn University. The present study was performed using the same cohort and tissue samples (13 IEFVPTC, 11 NIFTP, 12 WDT-UMP, 12 normal thyroid specimens) as in our recent study investigating proteomics profiles [13].
- Protein preparation and shotgun liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry analysis
- Tissue samples were prepared for proteomic analysis as previously described [13]. Two pathologists (T.PX.N. and S.K.) independently evaluated samples and reached consensus based on the 5th edition of the WHO Classification of Tumors of Endocrine Organs [4].
- Protein was extracted from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) specimens using 0.5% sodium dodecyl sulfate, incubated at 50°C for 60 minutes, and then centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 30 minutes. Protein concentration was determined using the bicinchoninic acid method. Five micrograms of each protein sample were reduced with 5 mM dithiothreitol in 10 mM AMBIC at 60ºC for 1 hour, alkylated with 15 mM iodoacetamide in 10 mM AMBIC at room temperature for 45 minutes in the dark, and then digested with sequencing-grade porcine trypsin (1:20 ratio) for 16 hours at 37°C. The proteins were dried in a speed vacuum concentrator and reconstituted in 0.1% formic acid for nano-liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (nanoLC-MS/MS) analysis.
- LC-MS/MS data were collected using an Ultimate3000 Nano/Capillary LC System (Thermo Scientific, Loughborough, UK) connected to a Hybrid quadrupole Q-Tof impact II (Bruker Daltonics, Billerica, MA, USA) with a Nano-captive spray ion source. One microliter of the peptide digest was enriched on a μ-Precolumn 300 μm i.d. × 5 mm C18 Pepmap 100, 5 μm, 100 Å (Thermo Scientific) and separated on a 75 μm I.D. × 15 cm Acclaim PepMap RSLC C18, 2 μm, 100Å, nanoViper (Thermo Scientific) column heated to 60°C. Solvents A and B, containing 0.1% formic acid in water and 0.1% formic acid in 80% acetonitrile, respectively, were used to elute proteins at a 5%–55% gradient of solvent B over 30 minutes at a flow rate of 0.30 μL/min. Electrospray ionization was performed at 1.6 kV. Nitrogen was used as the drying gas at a flow rate of approximately 50 L/hr and to obtain collision-induced dissociation spectra. MS and MS/MS spectra were recorded in positive-ion mode at 2 Hz across the m/z range of 150–2,200, with the collision energy set to 10 eV based on the m/z value. Protein quantification for each sample was conducted using MaxQuant ver. 2.2.0.0, which uses the Andromeda search engine to match MS/MS spectra with the Uniprot Homo sapiens database.
- LC-MS/MS analysis
- An overview of our study design is depicted in Fig. 1. After preprocessing and filtering to include only proteins present in more than 40% of samples within each group, we identified a total of 1,398 proteins from the 46 proteomic data files.
- We aimed to devise a machine-learning model that could differentiate between IEFVPTC and non-IEFVPTC specimens. The non-IEFVPTC samples included NIFTP, WDT-UMP, and normal thyroid tissue.
- The entire set of samples (n = 46) was partitioned into training (n = 36) and internal testing (n = 10) subsets. The training samples underwent peptide/protein screening, model selection, and model development. Conversely, the testing samples were used for model evaluation and sensitivity analysis. The patient characteristics of the corresponding training and internal testing samples are compared in Table 1.
- Protein screening
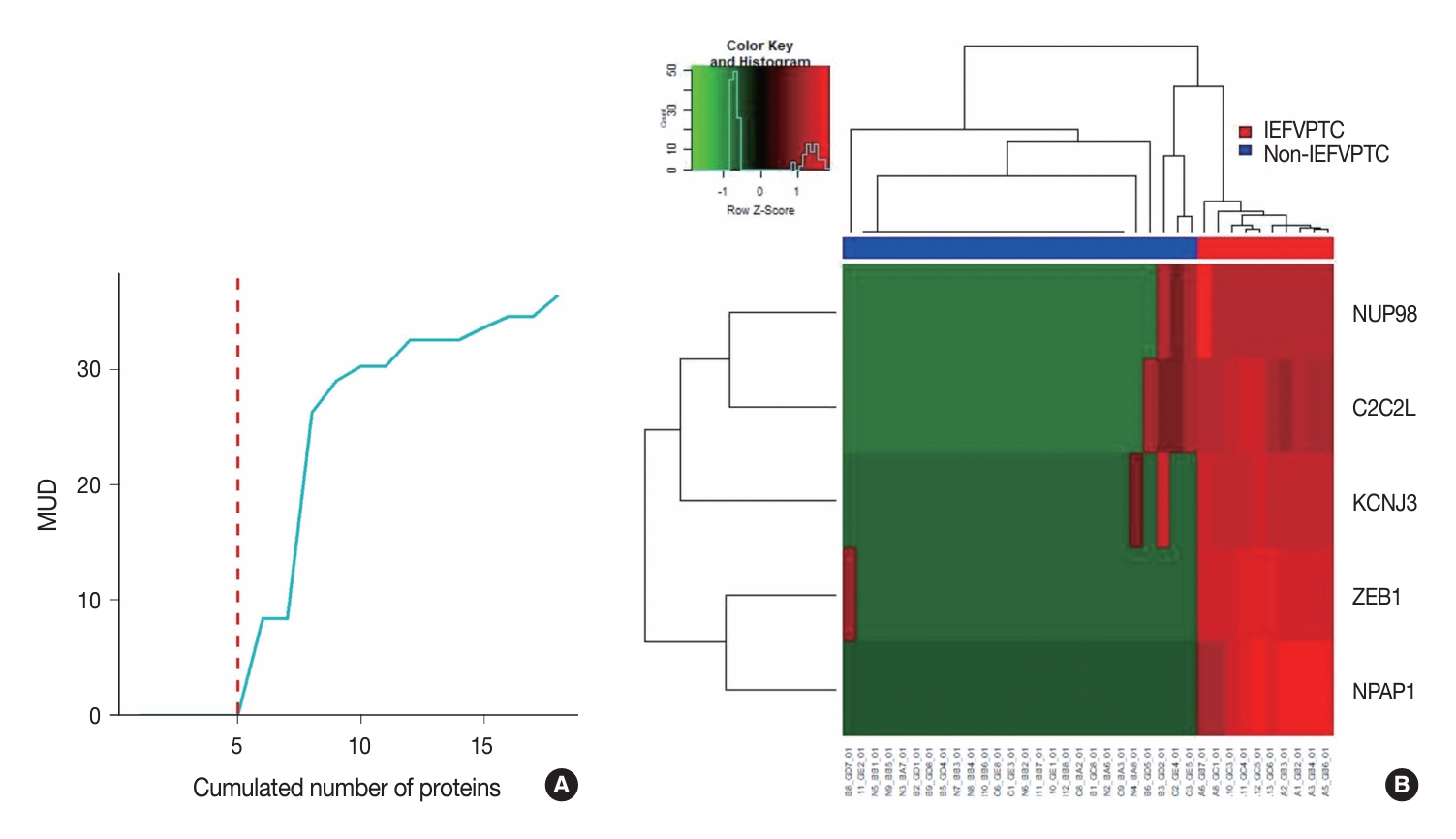
- Our screening process was composed of three steps: diferentially expressed proteins (DEPs) of IEFVPTC (Supplementary Table S1), unsupervised screening, and supervised screening (Fig. 1). First, we selected 181 significant proteins based on the DESeq2 results between IEFVPTC and non-IEFVPTC. The second step of unsupervised protein screening involved computation of the variance to gauge differences in expression across samples. Only proteins with a variance greater than the 90th percentile were selected, effectively excluding those with no expression or constant expression across samples.
- In the supervised screening phase, we restricted our analysis to proteins selected during unsupervised screening. For each protein, we built a logistic regression model and calculated the model univariate deviance (MUD). We then generated a deviance plot to determine the cut-off point for the number of peptides/proteins to be included.
- Model selection and development
- In this process, our aim was to pinpoint the supervised machine-learning model that exhibited the best performance. We carried out a three-fold cross-validation on the training samples. The models under consideration for selection encompassed logistic regression, generalized linear model with elastic net regularization, Naïve Bayes, support vector machine, decision tree, random forest, XGBoost, and multi-layer perceptron (MLP). The model that produced the highest accuracy score was ultimately selected. The 10 internal testing samples that we previously set aside were not involved in this process, and the cross-validation was performed by generating three training groups, each comprising 12 samples. A one-left-out testing approach was implemented to assess the accuracy of these models.
- Prior to training the chosen model, we generated synthetic samples from the training set using the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Techniques (SMOTE) method [14]. The total number of synthetic samples was n = 52, which encompassed 26 samples from each of the non-IEFVPTC and IEFVPTC categories. The selected model was subsequently trained on these SMOTE-created samples.
- Model evaluation and sensitivity analysis
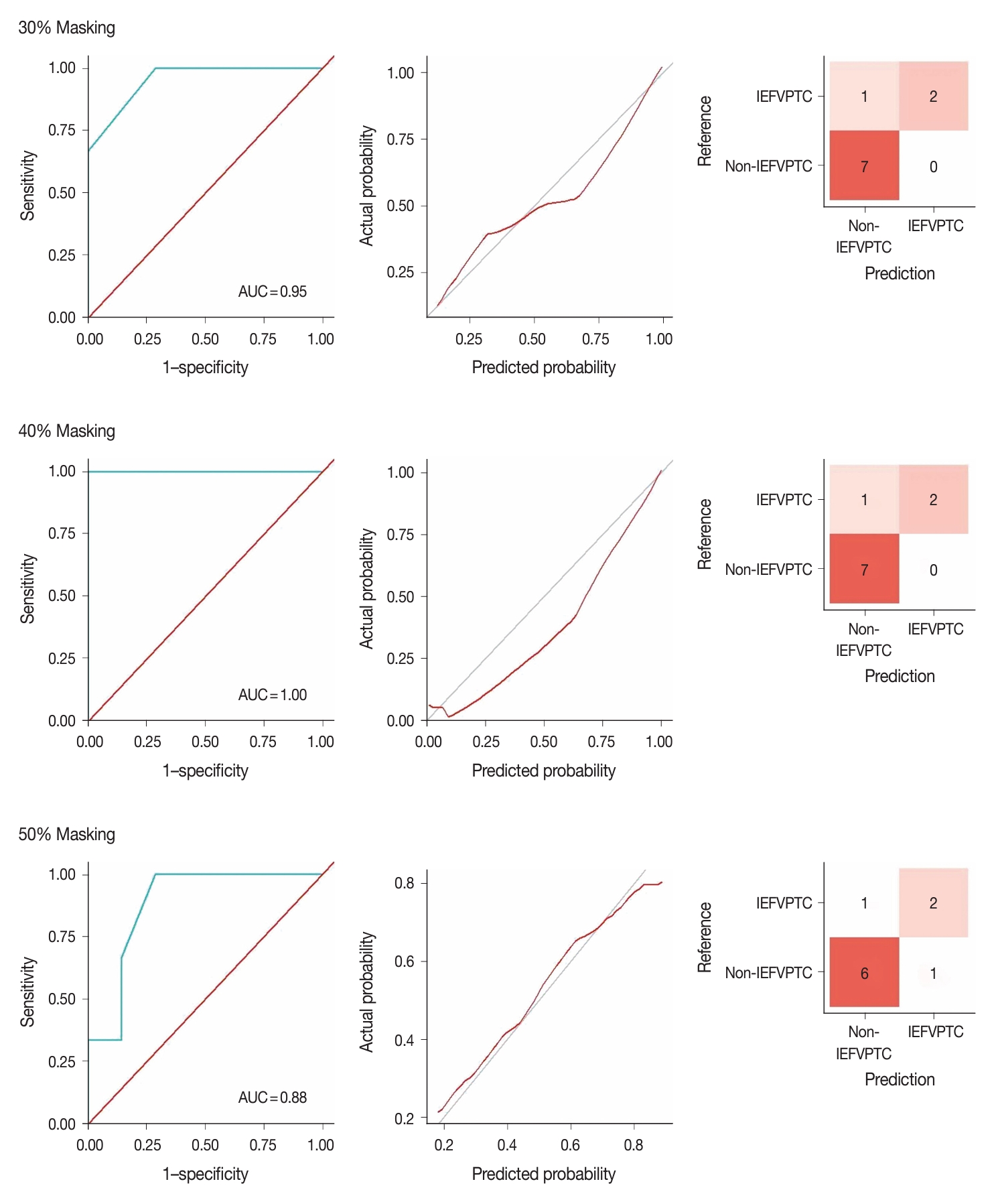
- We conducted three analyses to evaluate the model. We first conducted a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis and model calibration to evaluate model accuracy and stability under the probability score. Subsequently, we constructed a confusion matrix to assess the model’s performance in the classification task. Since the model was constructed using a small dataset, sensitivity analyses were also performed. Typically, sensitivity analyses involve various methods to perturb the features of the test data and examine whether the performance can endure such data anomalies without a significant decrease. In this study, we induced data distortion by applying random masking and creating random missing values. We then employed the Multivariate Imputation by Chained Equations (MICE) algorithm [15] to impute the missing data, resulting in a new and distorted version of the original test samples. The intensity of data distortion escalates when we apply larger random masking as more information is lost. Taking this into account, we generated three masks with 30%, 40%, and 50% missing values.
- External testing of The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset
- We extracted PTC cases from The Cancer Genome Atlas Thyroid Cancer (TCGA-THCA) dataset, which included a total of 507 cases. Our focus was on cases diagnosed as PTC, follicular variant (ICD-0 3 8340/3, n = 107). In light of the recent reclassification of thyroid neoplasms, we aimed to revisit the histopathology of these cases. For this purpose, we selected cases that had available diagnostic whole slide images and gene expression data. These cases were subsequently re-evaluated by a pathologist (T.PX.N. and S.K) and reclassified, with a particular emphasis on IEFVPTC and non-IEFVPTC. The revised diagnoses comprised FTC (n = 5), non-invasive follicular neoplasm (n = 11), non-invasive follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma (FVPTC) (n = 7), and invasive FVPTC (n = 24). Additionally, we identified other diagnoses (n = 60) that were considered irrelevant, including hyperplastic nodules, poorly differentiated thyroid carcinomas, Hürthle cell neoplasms, conventional PTC, adenomatous goiters, and cases with indeterminate morphology. Last, we reassigned cases with relevant diagnoses (n = 47) as non-invasive FVPTC (n = 24) or non-IEFVPTC (n = 23) (Supplementary Table S2) as the external test set.
- Given that the gene expression in the TCGA projects is based on sequencing technology for RNA quantification, it is not an appropriate input for our model, which was trained on LC-MS/MS protein expression data. Instead, we conducted a ROC analysis of protein expression in both the training and internal test sets. Additionally, we performed a ROC analysis of gene expression in the external test set. This approach allowed us to effectively utilize the available data and ensure the compatibility of genes or proteins in our model.
- Statistical analyses
- The descriptive statistics for continuous variables are represented by the median and range, while the number of samples and their respective percentages were used for categorical variables. To compare continuous and categorical variables between cohorts, Wilcoxon’s and chi-square tests were employed, respectively. p-values less than .05 were considered significant in hypothesis testing. All analyses were conducted using ver. 4.3.2 of R software (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
- Patient characteristics
- Table 1 provides a summary of the study cohort characteristics, which are divided into training and internal testing cohorts. The average age of the patients was 43 years, ranging from 24 to 70, with a predominance of women (30 of 46, 65.2%). The most common samples were IEFVPTC (13 of 46, 28.3%), followed by normal tissue (12 of 46, 26.1%), NIFTP (11 of 46, 23.9%), and WDT-UMP samples (10 of 46, 21.7%). There were no significant differences in terms of age (p = .170), sex (p = .987), nuclear score (p = .421), diameter (p = .922), invasion (p = .498), and diagnosis (p = .344).
- Protein screening
- We conducted a three-layer screening process comprising differentially expressed proteins–unsupervised–supervised screening and listed the five resulting proteins with their metrics in Table 2. The optimal proteins were ZEB1, NUP98, C2C2L, NPAP1, and KCNJ3. The rationale for setting the cut-off at five proteins was the significant increase in MUD between the proteins with the 5th and 6th smallest values (Fig. 2A). This heuristic is grounded in the balance between introducing an excessive number of predictive variables that overshadow the number of training samples and the potential reduction in machine learning accuracy. Another key consideration is that incorporating a greater number of predictive variables relative to the size of the training sample may result in overfitting. Finally, the expressions of these selected five proteins across the training samples were visualized as a heatmap (Fig. 2B).
- Model selection
- We summarized the results of cross-validation in Table 3. In this table, three one-left-out accuracy scores of each model were reported as fold 1, fold 2, and fold 3. The means and standard deviations of the accuracy scores of logistic regression, Generalized Linear Model with Elastic Net Regularization, Naïve Bayes, Support Vector Machine, Decision Tree, Random Forest, XGBoost, and MLP were 0.89 (±0.10), 0.92 (±0.09), 0.97 (± 0.05), 0.97 (±0.05), 0.91 (±0.09), 1.00 (±0.00), 0.92 (±0.09), and 0.97 (±0.05), respectively. The random forest classifier model had the highest accuracy score and was selected to construct the final model.
- Model evaluation and sensitivity analysis
- Fig. 3 illustrates the outcomes of the model evaluation using both training and internal testing samples. The ROC analyses (Fig. 3A, B) and model calibration plots (Fig. 3C, D) exhibit the ROC curves and calibration for both the training and internal testing samples. Our model showed high ROC areas under the curve (AUCs) = 1.00 and good calibrations in the two groups. In the confusion matrices (Fig. 3E, F), the model accurately predicted all training samples without any errors and almost all testing samples. In the sensitivity analysis (Fig. 4), distortions of 30%, 40%, and 50% marginally reduced the model performance, with AUCs of 0.95, 1.00, and 0.88 and accuracies of 0.90, 0.90, and 0.80, respectively. Despite these distortions, the calibration plots continued to show that the model was well-calibrated, supporting the robustness of our model.
- Analyses of model proteins in distinguishing IEFVPTC and non-IEFVPTC
- Table 4 presents the outcomes of the single-protein/gene ROC analyses differentiating between IEFVPTC and non-IEFVPTC. All genes had AUCs greater than 0.5 in the external test set, highlighting the significance of combining proteins in discrimination between IEFVPTC and non-IEFVPTC. Overall, these results validate the proteins included in our model.
RESULTS
- Thyroid nodules that display follicular histological characteristics encompass a variety of conditions, ranging from benign to malignant subtypes, such as FA, FTC, NIFTP, WDT-UMP, and IEFVPTC [4,5]. Distinguishing these nodules, especially when they appear as isolated occurrences with follicular morphology, presents a diagnostic challenge for pathologists during histology evaluations, and they cannot be distinguished by cytology. FA can be differentiated from FTC by assessing the grade of nuclear features (0–1) and the presence of capsular or vascular invasion. On the other hand, NIFTP, WDT-UMP, and IEFVPTC share similar nuclear features (2–3) but differ in capsular and vascular invasion characteristics. NIFTP lacks signs of capsular or vascular invasion, in contrast to IEFVPTC, which clearly exhibits such findings. WDT-UMP displays ambiguous patterns regarding capsular or vascular invasion [4].
- According to the revised WHO classification, like FTC, IEFVPTC is recognized as malignant and is categorized into three subtypes: minimally invasive, encapsulated angioinvasive, and widely invasive. Minimally invasive tumors, considered low-risk, might only require local excision for treatment. In contrast, widely invasive or extensive vascular invasion (more than 4 foci) tumors often necessitate complete thyroidectomy and further therapy to prevent recurrence and/or distant metastasis. Such additional treatments are typically determined by individual clinical assessments, which might include factors like large tumor size (over 4 cm), extrathyroidal extension, or metastases [4,7]. On the other hand, NIFTP and WDT-UMP are classified as low-risk neoplasms. These tumors are considered borderline, displaying characteristics that fall between benign and malignant states. While the potential for metastasis exists in these neoplasms, such events are exceedingly rare. For patients with NIFTP and WDT-UMP, a lobectomy followed by vigilant monitoring is vital to prevent tumor progression [4]. Thus, precise diagnosis of IEFVPTC is crucial to avoid unnecessary or potentially detrimental surgical procedures.
- The exploration of machine learning in medical fields is a burgeoning area of interest. Recent research has introduced new methods that enhance the diagnosis of follicular neoplasms. Sun et al. [10] utilized a machine learning model on data-independent acquisition MS, identifying a set of 31 proteins that effectively distinguish between FA and FTC. Their model achieved a high degree of precision, with an AUC of 0.963 and an accuracy rate of 91.7% in their test samples [10]. Additionally, Li et al. [16] developed the Preoperative Risk Assessment Classifier for PTC, which incorporates clinical data, gene mutation details, immune indices, high-throughput proteomics, and machine learning technology to effectively stratify the preoperative risk of PTC, achieving an AUC of 0.925 and an accuracy of 0.844 [16]. This could reduce the incidence of unnecessary surgeries or excessive treatment.
- In this study, we applied machine learning techniques, specifically using the random forest classifier, to analyze shotgun MS data to distinguish between IEFVPTC and non-IEFVPTC cases. Our analysis focused on identifying protein biomarkers within large proteomic datasets pertinent to thyroid cancers. We successfully identified the five proteins C2C2L, KCNJ3, NPAP1, NUP98, and ZEB1 that effectively differentiated malignant from benign conditions, achieving high AUCs and accuracy in training and test cohorts and demonstrating high sensitivity. Detecting the intensities of these five proteins with targeted MS-based proteomics assays combined with our model offers significant potential for clinical applications due to the high accuracy and rapid processing time [17].
- Although there are no existing reports on the roles of these proteins in thyroid cancer, some have been implicated in carcinogenesis. KCNJ3 has been linked with increased disease progression in breast cancer [18]. NUP98 is an oncoprotein that contributes to malignant transformation and is associated with a broad range of hematopoietic malignancies [19]. ZEB1, a transcription factor, facilitates tumor invasion and metastasis by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in carcinoma cells [20]. The roles of the remaining two proteins in cancer have not yet been explored and require further research. Further analysis of individual markers and validation on test data, alongside mRNA expression data from TCGA, revealed that these five proteins could potentially serve as immunohistochemistry markers to distinguish between IEFVPTC and non-IEFVPTC (Supplementary Fig. S1).
- IEFVPTCs are RAS-driven lesions with a similar morphological pattern to FTCs, characterized by a follicular pattern and capsular or vascular invasion, but differing in nuclear features [5]. Like FTC, IEFVPTC also shows correlation between the extent of invasion and patient prognosis [21]. Huang et al. [11] indicated that FTC and FVPTC share proteotypes but are distinct from the benign tumor FA. In this study, we did not collect FTC and FA samples, so we could not perform further analysis to address this question. Instead, we analyzed the expressions of five proteins (ZEB1, NUP98, C2C2L, NPAP1, and KCNJ3) using TCGA data (Supplementary Table S1). The expressions of these five proteins were similarly high in IEFVPTC and FTC (Supplementary Fig. S2).
- Despite the valuable insights provided by our current research, it has certain limitations. First, we employed non-targeted proteomics to analyze peptide profiles in FFPE samples but did not perform validations on fine-needle aspiration (FNA) samples and other FFPE cohorts. Moreover, other follicular-patterned thyroid neoplasms such as FA and FTC were not included in this study and should be explored in future research. Although our sample size was small, this study represents a preliminary effort to identify potential protein markers for IEFVPTC. In the future, we plan to validate these five protein biomarkers (ZEB1, NUP98, C2C2L, NPAP1, and KCNJ3) using immunohistochemistry and to analyze the prognostic roles of these biomarker candidates to determine whether cancer is self-limiting and curable or lethal in a larger sample cohort including both FNA and FFPE samples.
- In summary, our extensive proteomics analysis of thyroid tissue samples led to the identification of five proteins that can be utilized to diagnose IEFVPTC. Our findings contribute to the advancement of molecular diagnosis for follicular-patterned thyroid tumors and have the potential to enhance the diagnostic accuracy of existing molecular tests.
DISCUSSION
Supplementary Information
Ethics Statement
The research was established according to the ethical guidelines of the Helsinki Declaration and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University (COA.No. 1369/2023-IRB 0628/66). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Availability of Data and Material
All data generated or analyzed and its supplementary information files during this study are included in this published article. The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the PRIDE Archive (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/) via the PRIDE partner repository with the data set identifier PXD053567.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: TPXN, SK, NK. Data curation: TPXN, MKL. Formal analysis: TPXN, MKL. Investigation: TPXN, SK. Methodology: TXPN, MKL. Project administration: SK, NK. Resources: TXPN. Supervision: SK, NK. Writing—original draft: TPXN, MKL. Writing—review & editing: TPXN, MKL, SR, SS, NK, SK. Approval of the final manuscript: all authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Funding Statement
This study was supported by Chulalongkorn’s 90-year Schorlaship Ratchadapisek Research and Ratchadapiseksompotch Fund, Graduate Affairs, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, grant number GA67/058. TPXN and SK are recipients. The funder had no role in the design of the study; the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; the writing of the article; or the decision to submit the article for publication.


| Protein | Variance | MUD |
|---|---|---|
| ZEB1 | 76.4 | 5.7 × 10–10 |
| NUP98 | 73.3 | 5.7 × 10–10 |
| C2C2L | 54.6 | 5.7 × 10–10 |
| NPAP1 | 51.7 | 5.7 × 10–10 |
| KCNJ3 | 51.7 | 5.7 × 10–10 |
| Test fold | LRM | LRMNET | NB | SVM | Tree | RF | XGBoost | MLP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold 1 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 1.00 |
| Fold 2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Fold 3 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| Protein/Gene | Train | Internal test | External test |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZEB1 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.67 |
| NUP98 | 0.98 | 0.83 | 0.67 |
| C2C2L | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.57 |
| NPAP1 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 0.60 |
| KCNJ3 | 0.97 | 0.76 | 0.69 |
- 1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021; 71: 209-49. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Miranda-Filho A, Lortet-Tieulent J, Bray F, et al. Thyroid cancer incidence trends by histology in 25 countries: a population-based study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2021; 9: 225-34. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Kitahara CM, Sosa JA. The changing incidence of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2016; 12: 646-53. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 4. WHO classification of tumours of endocrine organs. 5th beta ed. [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2022 [cited 2024 May 20]. Available from: https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int.
- 5. Baloch ZW, Asa SL, Barletta JA, et al. Overview of the 2022 WHO classification of thyroid neoplasms. Endocr Pathol 2022; 33: 27-63. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Na HY, Park SY. Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features: its updated diagnostic criteria, preoperative cytologic diagnoses and impact on the risk of malignancy. J Pathol Transl Med 2022; 56: 319-25. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 7. Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016; 26: 1-133. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Gillet LC, Leitner A, Aebersold R. Mass spectrometry applied to bottom-up proteomics: entering the high-throughput era for hypothesis testing. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif) 2016; 9: 449-72. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Kulyyassov A, Fresnais M, Longuespee R. Targeted liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of proteins: basic principles, applications, and perspectives. Proteomics 2021; 21: e2100153. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 10. Sun Y, Li L, Zhou Y, et al. Stratification of follicular thyroid tumours using data-independent acquisition proteomics and a comprehensive thyroid tissue spectral library. Mol Oncol 2022; 16: 1611-24. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Huang D, Zhang H, Li L, et al. Proteotypic differences of follicularpatterned thyroid neoplasms. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022; 13: 854611.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Suzuki A, Nojima S, Tahara S, et al. Identification of invasive subpopulations using spatial transcriptome analysis in thyroid follicular tumors. J Pathol Transl Med 2024; 58: 22-8. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 13. Nguyen TP, Roytrakul S, Buranapraditkun S, Shuangshoti S, Kitkumthorn N, Keelawat S. Proteomics profile in encapsulated follicular patterned thyroid neoplasms. Sci Rep 2024; 14: 16343.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 14. Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP. SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Intell Res 2002; 16: 321-57. ArticlePDF
- 15. van Buuren S, Groothuis-Oudshoorn K. mice: multivariate imputation by chained equations in R. J Stat Softw 2011; 45: 1-67.
- 16. Li Y, Wu F, Ge W, et al. Risk stratification of papillary thyroid cancers using multidimensional machine learning. Int J Surg 2024; 110: 372-84. ArticlePubMed
- 17. Wenk D, Zuo C, Kislinger T, Sepiashvili L. Recent developments in mass-spectrometry-based targeted proteomics of clinical cancer biomarkers. Clin Proteomics 2024; 21: 6.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 18. Rezania S, Kammerer S, Li C, et al. Overexpression of KCNJ3 gene splice variants affects vital parameters of the malignant breast cancer cell line MCF-7 in an opposing manner. BMC Cancer 2016; 16: 628.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 19. Chandra B, Michmerhuizen NL, Shirnekhi HK, et al. Phase separation mediates NUP98 fusion oncoprotein leukemic transformation. Cancer Discov 2022; 12: 1152-69. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 20. Zhang P, Sun Y, Ma L. ZEB1: at the crossroads of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, metastasis and therapy resistance. Cell Cycle 2015; 14: 481-7. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Xu B, Wang L, Tuttle RM, Ganly I, Ghossein R. Prognostic impact of extent of vascular invasion in low-grade encapsulated follicular cell-derived thyroid carcinomas: a clinicopathologic study of 276 cases. Hum Pathol 2015; 46: 1789-98. ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Misdiagnosed follicular adenoma with 11 year postoperative liver and lung metastases a case report and literature review
Kai-Li Yang, Heng-Tong Han, Shou-Hua Li, Xiao-Xiao Li, Ze Yang, Li-Bin Ma, Yong-Xun Zhao
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure


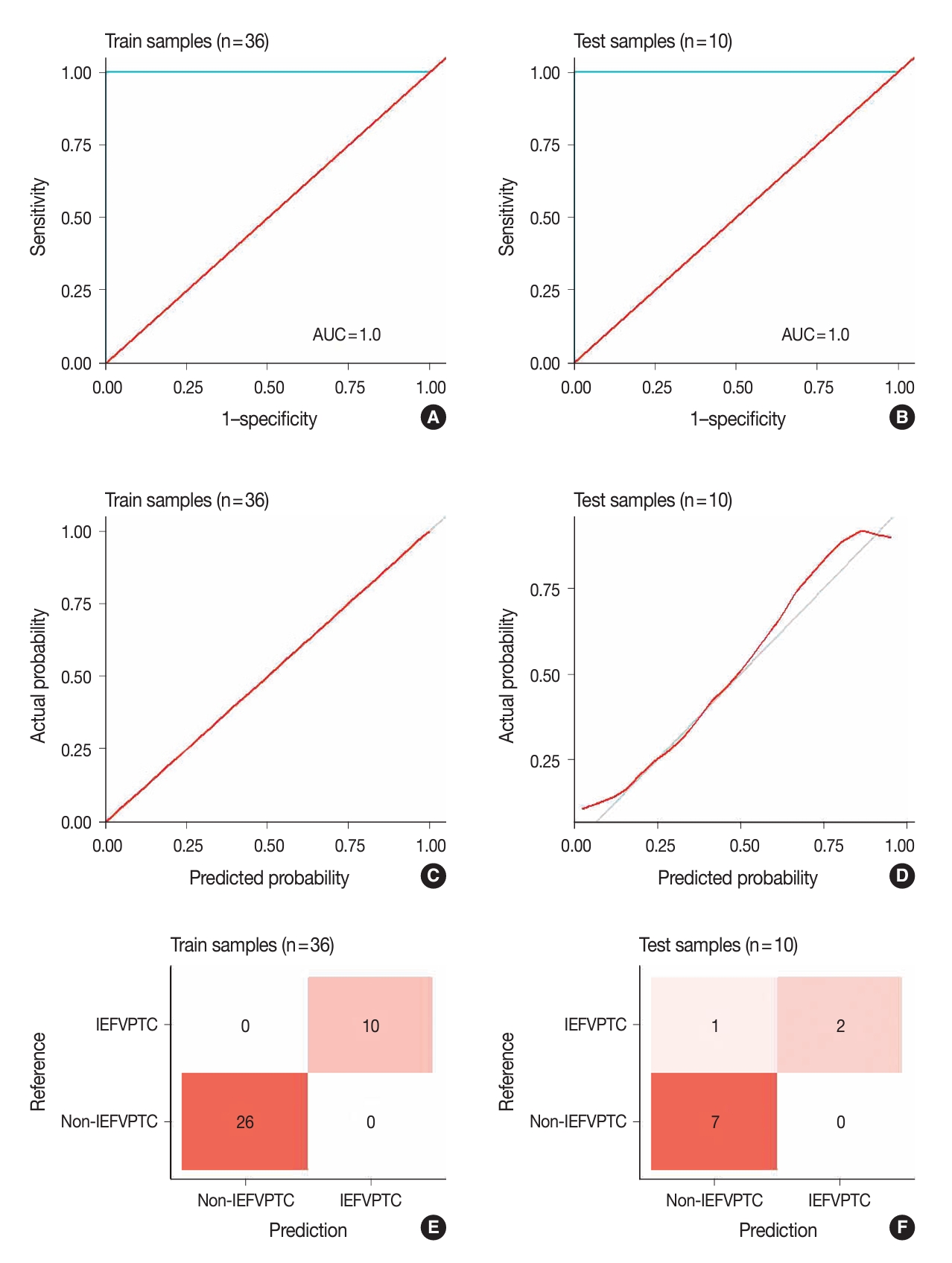


Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 4.
Graphical abstract
| Variable | Train (n = 36) | Test (n = 10) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 42 (24–79) | 52.5 (34–70) | .170 |
| Sex | .987 | ||
| Women | 24 (66.7) | 6 (60.0) | |
| Men | 12 (33.3) | 4 (40.0) | |
| Nuclear score | .421 | ||
| 2 | 6 (16.7) | 2 (20.0) | |
| 3 | 19 (52.8) | 7 (70.0) | |
| No score | 11 (30.6) | 1 (10.0) | |
| Diameter (mm) | 35 (15–84) | 30 (22–70) | .922 |
| Invasion | .498 | ||
| No | 9 (25.0) | 2 (20.0) | |
| Capsular | 6 (16.7) | 2 (20.0) | |
| Vascular | 4 (11.1) | 1 (10.0) | |
| Unclear | 6 (16.7) | 4 (40.0) | |
| Normal tissue | 11 (30.6) | 1 (10.0) | |
| Diagnosis | .344 | ||
| Normal tissue | 11 (30.6) | 1 (10.0) | |
| WDT-UMP | 6 (16.7) | 4 (40.0) | |
| NIFTP | 9 (25.0) | 2 (20.0) | |
| IEFVPTC | 10 (27.8) | 3 (30.0) |
| Protein | Variance | MUD |
|---|---|---|
| ZEB1 | 76.4 | 5.7 × 10–10 |
| NUP98 | 73.3 | 5.7 × 10–10 |
| C2C2L | 54.6 | 5.7 × 10–10 |
| NPAP1 | 51.7 | 5.7 × 10–10 |
| KCNJ3 | 51.7 | 5.7 × 10–10 |
| Test fold | LRM | LRMNET | NB | SVM | Tree | RF | XGBoost | MLP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold 1 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 1.00 |
| Fold 2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Fold 3 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| Protein/Gene | Train | Internal test | External test |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZEB1 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.67 |
| NUP98 | 0.98 | 0.83 | 0.67 |
| C2C2L | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.57 |
| NPAP1 | 1.00 | 0.83 | 0.60 |
| KCNJ3 | 0.97 | 0.76 | 0.69 |
Values are presented as median (range) or number (%). WDT-UMP, well-differentiated tumor of uncertain malignant potential; NIFTP, neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features; IEFVPTC, invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma.
MUD, model univariate deviance.
Accuracy is the metric of comparison. LRM, logistic regression model; LRMNET, LRM with elastic net regularization; NB, Naïve Bayes; SVM, support vector machine; Tree, decision tree; RF, random forest; MLP, multi-layer perceptron.
IEFVPTC, invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma.

 E-submission
E-submission