Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Trouble-makers in cytologic interpretation of the uterine cervix
- Eunah Shin, Jaeeun Yu, Soon Won Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(3):139-146. Published online May 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.04.25
- 3,378 View
- 335 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development and standardization of cytologic screening of the uterine cervix has dramatically decreased the prevalence of squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Advances in the understanding of biology of human papillomavirus have contributed to upgrading the histologic diagnosis of the uterine cervix; however, cytologic screening that should triage those that need further management still poses several difficulties in interpretation. Cytologic features of high grade intraepithelial squamous lesion (HSIL) mimics including atrophy, immature metaplasia, and transitional metaplasia, and glandular lesion masquerades including tubal metaplasia and HSIL with glandular involvement are described with accentuation mainly on the differential points. When the cytologic features lie in a gray zone between the differentials, the most important key to the more accurate interpretation is sticking to the very basics of cytology; screening the background and cellular architecture, and then scrutinizing the nuclear and cytoplasmic details.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pitfalls in Gynecological Cytology: Review of the Common and Less Frequent Entities in Pap Test
Danijela Vrdoljak-Mozetič, Snježana Štemberger-Papić, Damjana Verša Ostojić, Roberta Rubeša, Marko Klarić, Senija Eminović
Acta Cytologica.2024; 68(3): 281. CrossRef - Cytological features of human papillomavirus‐infected immature squamous metaplastic cells from cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2
Mitsuaki Okodo, Kaori Okayama, Koji Teruya, Ruku Shinohara, Shuichi Mizuno, Rei Settsu, Yasuyoshi Ishii, Masahiko Fujii, Hirokazu Kimura, Mizue Oda
Journal of Medical Virology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Pitfalls in Gynecological Cytology: Review of the Common and Less Frequent Entities in Pap Test
- Cytopathologic features of human papillomavirus–independent, gastric-type endocervical adenocarcinoma
- Min-Kyung Yeo, Go Eun Bae, Dong-Hyun Kim, In-Ock Seong, Kwang-Sun Suh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(5):260-269. Published online September 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.07.05
- 2,668 View
- 142 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Gastric-type endocervical adenocarcinoma (GEA) is unrelated to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and is clinically aggressive compared with HPV-associated usual-type endocervical adenocarcinoma (UEA). The cytological diagnosis falls short of a definitive diagnosis of GEA and is often categorized as atypical glandular cells (AGCs). To improve cytologic recognition, cytological findings of HPV-independent GEA were analyzed and the results compared with HPV-associated UEA.
Methods
Cervical Papanicolaou (Pap) smears from eight patients with a histopathologic diagnosis of GEA and 12 control cases of UEA were reviewed. All slides were conventionally prepared and/or liquid-based prepared (ThinPrep) and stained following the Pap method. A mucinous background, architectural, nuclear, and cytoplasmic features were analyzed and compared with UEA.
Results
Preoperative cytologic diagnoses of the eight GEA cases were AGCs, favor neoplastic in three cases, adenocarcinoma in situ in one case, and adenocarcinoma in four cases. Cytologically, monolayered honeycomb-like sheets (p = .002) of atypical endocervical cells with vacuolar granular cytoplasm (p = .001) were extensive in GEA, and three-dimensional clusters (p = .010) were extensive in UEA. Although the differences were not statistically significant, background mucin (p = .058), vesicular nuclei (p = .057), and golden-brown intracytoplasmic mucin (p = .089) were also discriminatory findings for GEA versus UEA.
Conclusions
Although GEA is difficult to diagnose on cytologic screening, GEA can be recognized based on cytologic features of monolayered honeycomb sheets of atypical endocervical cells with abundant vacuolar cytoplasm and some golden-brown intracytoplasmic mucin. UEA cases are characterized by three-dimensional clusters. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors Affecting Clinical Outcomes of Low-risk Early-stage Human Papillomavirus–Associated Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Treated by Surgery Alone: Application of Silva Pattern
Bong Kyung Bae, Hyunsik Bae, Won Kyung Cho, Byoung-Gie Kim, Chel Hun Choi, Tae-Joong Kim, Yoo-Young Lee, Jeong-Won Lee, Hyun-Soo Kim, Won Park
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2024; 43(5): 447. CrossRef - Tall‐columnar glandular cells in SurePath™ liquid‐based cytology Pap sample: Learning from mimics/pitfalls
Nalini Gupta, Vanita Jain, Radhika Srinivasan, Tulika Singh
Cytopathology.2024; 35(4): 510. CrossRef
- Risk Factors Affecting Clinical Outcomes of Low-risk Early-stage Human Papillomavirus–Associated Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Treated by Surgery Alone: Application of Silva Pattern
- Evaluation of human papillomavirus (HPV) prediction using the International Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Criteria and Classification system, compared to p16 immunohistochemistry and HPV RNA in-situ hybridization
- Hezhen Ren, Jennifer Pors, Christine Chow, Monica Ta, Simona Stolnicu, Robert Soslow, David Huntsman, Lynn Hoang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(6):480-488. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.07.18
- 4,883 View
- 162 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The International Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Criteria and Classification (IECC) separated endocervical adenocarcinomas into human papillomavirus (HPV) associated (HPVA) and non–HPV-associated (NHPVA) categories by morphology alone. Our primary objective was to assess the accuracy of HPV prediction by the IECC system compared to p16 immunohistochemistry and HPV RNA in-situ hybridization (RISH). Our secondary goal was to directly compare p16 and HPV RISH concordance.
Methods
Cases were classified by IECC and stained for p16 and HPV RISH on tissue microarray, with discordant p16/HPV RISH cases re-stained on whole tissue sections. Remaining discordant cases (p16/HPV, IECC/p16, IECC/HPV discordances) were re-reviewed by the original pathologists (n = 3) and external expert pathologists (n = 2) blinded to the p16 and HPV RISH results. Final IECC diagnosis was assigned upon independent agreement between all reviewers.
Results
One hundred and eleven endocervical adenocarcinomas were classified originally into 94 HPVA and 17 NHPVA cases. p16 and HPV RISH was concordant in 108/111 cases (97%) independent of the IECC. HPV RISH and p16 was concordant with IECC in 103/111 (93%) and 106/111 (95%), respectively. After expert review, concordance improved to 107/111 (96%) for HPV RISH. After review of the eight discordant cases, one remained as HPVA, four were reclassified to NHPVA from HPVA, two were unclassifiable, and one possibly represented a mixed usual and gastric-type adenocarcinoma.
Conclusions
p16 and HPV RISH have excellent concordance in endocervical adenocarcinomas, and IECC can predict HPV status in most cases. Focal apical mitoses and apoptotic debris on original review led to the misclassification of several NHPVA as HPVA. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Joint detection of multiple HPV-testing technologies and evaluation of clinicopathological characteristics discriminate between HPV-independent and low-copy HPV-associated cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) -an analysis of 3869 cases
Linghui Lu, Tianqi Liu, Shunni Wang, Jing Li, Feiran Zhang, Yan Ning, Yiqin Wang
Gynecologic Oncology.2023; 170: 59. CrossRef - Incidence and Clinicopathologic Characteristics of Human Papillomavirus–independent Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Cervix
Simona Stolnicu, Douglas Allison, Aaron M. Praiss, Basile Tessier-Cloutier, Amir Momeni Boroujeni, Jessica Flynn, Alexia Iasonos, Rene Serrette, Lien Hoang, Andrei Patrichi, Cristina Terinte, Anna Pesci, Claudia Mateoiu, Ricardo R. Lastra, Takako Kiyokawa
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2023; 47(12): 1376. CrossRef - Testing Algorithms for the Diagnosis of Malignant Glandular Tumors of the Uterine Cervix Histotyped per the International Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Criteria and Classification (IECC) System
Máire A. Duggan, Qiuli Duan, Ruth M. Pfeiffer, Mary Anne Brett, Sandra Lee, Mustapha Abubakar, Martin Köbel, Monica Rodriguez, Aylin Sar
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2022; 30(2): 91. CrossRef - Local and Metastatic Relapses in a Young Woman with Papillary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix
Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(3): 599. CrossRef - Clinical correlation of lymphovascular invasion and Silva pattern of invasion in early-stage endocervical adenocarcinoma: proposed binary Silva classification system
Simona Stolnicu, Lien Hoang, Noorah Almadani, Louise De Brot, Glauco Baiocchi, Graziele Bovolim, Maria Jose Brito, Georgia Karpathiou, Antonio Ieni, Esther Guerra, Takako Kiyokawa, Pavel Dundr, Carlos Parra-Herran, Sofia Lérias, Ana Felix, Andres Roma, An
Pathology.2022; 54(5): 548. CrossRef - Reproducibility of Morphologic Parameters of the International Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Criteria and Classification System and Correlation With Clinicopathologic Parameters: A Multi-Institutional Study
Pinar Bulutay, Nihan Haberal, Özlem Özen, Özlem Erdem, Emine H. Zeren, İbrahim Kulac, Çagatay Taskiran, Dogan Vatansever, Ali Ayhan, Nilgün Kapucuoğlu
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2022; 41(5): 447. CrossRef - HPV-Negative Cervical Cancer: A Narrative Review
Francesca Arezzo, Gennaro Cormio, Vera Loizzi, Gerardo Cazzato, Viviana Cataldo, Claudio Lombardi, Giuseppe Ingravallo, Leonardo Resta, Ettore Cicinelli
Diagnostics.2021; 11(6): 952. CrossRef - International Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Criteria and Classification (IECC): An Independent Cohort With Clinical and Molecular Findings
Hezhen Ren, Noorah Almadani, Jennifer Pors, Samuel Leung, Julie Ho, Christine Chow, Monica Ta, Kay J. Park, Simona Stolnicu, Robert Soslow, David Huntsman, Blake C. Gilks, Lynn Hoang
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2021; 40(6): 533. CrossRef
- Joint detection of multiple HPV-testing technologies and evaluation of clinicopathological characteristics discriminate between HPV-independent and low-copy HPV-associated cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) -an analysis of 3869 cases
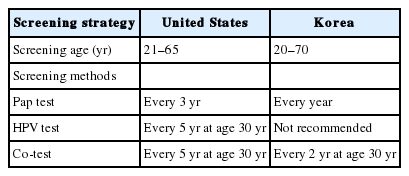
- Clinical management of abnormal Pap tests: differences between US and Korean guidelines
- Seyeon Won, Mi Kyoung Kim, Seok Ju Seong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(3):213-219. Published online April 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.03.11
- 6,054 View
- 153 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cervical cancer has been the most common gynecological cancer in Korea but has become a preventable disease with regular screening and proper vaccination. If regular screening is provided, cervical cancer does not progress to more than carcinoma in situ, due to its comparatively long precancerous duration (years to decades). In 2012, the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology published guidelines to aid clinicians in managing women with abnormal Papanicolaou (Pap) tests, and they soon became the standard in the United States. Not long thereafter, the Korean Society of Gynecologic Oncology and the Korean Society for Cytopathology published practical guidelines to reflect the specific situation in Korea. The detailed screening guidelines and management options in the case of abnormal Pap test results are sometimes the same and sometimes different in the United States and Korean guidelines. In this article, we summarize the differences between the United States and Korean guidelines in order to facilitate physicians’ proper management of abnormal Pap test results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of HR-HPV Infection Concordance Rates in Cervical and Urine Specimens; Proposal of Additional Cervical Screening Process for Women Who Refuse Invasive Cervical Sampling
Dong Hyeok Kim, Hyunwoo Jin, Kyung Eun Lee
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(12): 1949. CrossRef - Analysis of HR-HPV Prevalence among Unvaccinated Busan Women
Dong Hyeok Kim, Kyung Eun Lee
Biomedical Science Letters.2022; 28(4): 229. CrossRef
- Analysis of HR-HPV Infection Concordance Rates in Cervical and Urine Specimens; Proposal of Additional Cervical Screening Process for Women Who Refuse Invasive Cervical Sampling
- Current Status of and Perspectives on Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
- Sung-Chul Lim, Chong Woo Yoo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(4):210-216. Published online May 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.04.11
- 8,323 View
- 263 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Since the introduction of the Papanicolaou (Pap) smear system in 1943, cervicovaginal cytology has been used as a standard screening test for cervical cancer. The dissemination of this test contributed to reductions of the incidence and mortality of cervical cancer worldwide. In Korea, regular health check-ups for industrial workers and their family members were introduced in 1988 and were performed as part of the National Cancer Screening Program in 1999. As a result, the incidence of cervical cancer in Korea has been steadily decreasing. However, about 800 cases of cervical cancer-related deaths are reported each year due to false-negative test results. Hence, new screening methods have been proposed. Liquid-based cytology (LBC) was introduced in 1996 to overcome the limitations of conventional Pap smears. Since then, other LBC methods have been developed and utilized, including the human papilloma virus test—a method with higher sensitivity that requires fewer screenings. In this study, we review current issues and future perspectives related to cervical cancer screening in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A questionnaire study on disparity of cervical cancer prevention programs in Asia‐Oceania
Ka Yu Tse, Kimio Ushijima, Ai Ling Tan, Perapong Intasorn, Jitendra Pariyar, Chih‐Long Chang, Efren J. Domingo, Hiralal Konar, Suresh Kumarasamy, Brahmana Askandar Tjokroprawiro, Sarikapan Wilailak
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2023; 49(4): 1230. CrossRef - Current state of cytopathology residency training: a Korean national survey of pathologists
Uiju Cho, Tae Jung Kim, Wan Seop Kim, Kyo Young Lee, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Hyun Joo Choi
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(2): 95. CrossRef - Meeting the challenges of cervical cancer screening and HPV vaccination in the UK
Roxanne Westwood, Joanna Lavery
Primary Health Care.2022; 32(01): 22. CrossRef - Local and Metastatic Relapses in a Young Woman with Papillary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix
Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(3): 599. CrossRef - Serum Human Epididymis Protein 4 as a Prognostic Marker in Cervical Cancer
Woo Yeon Hwang, Dong Hoon Suh, Kidong Kim, Yong Beom Kim, Jae Hong No
Cancer Control.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - HPV detection and/or cytological diagnostics
Sanja Milenković
Glasnik javnog zdravlja.2022; 96(3): 313. CrossRef - Clinical management of abnormal Pap tests: differences between US and Korean guidelines
Seyeon Won, Mi Kyoung Kim, Seok Ju Seong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(3): 213. CrossRef - Current status of cytopathology practices in Korea: annual report on the Continuous Quality Improvement program of the Korean Society for Cytopathology for 2018
Yosep Chong, Haeyoen Jung, Jung-Soo Pyo, Soon Won Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(4): 318. CrossRef - Cytomorphological Features of Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups in Liquid-Based Cervicovaginal Cytology: A Single Institutional Experience
Youngeun Lee, Cheol Lee, In Ae Park, Hyoung Jin An, Haeryoung Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2019; 53(6): 393. CrossRef
- A questionnaire study on disparity of cervical cancer prevention programs in Asia‐Oceania
- Colloid Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix and Its Immunohistochemical Analysis: A Case Report
- Nermin Koc, Sevcan Arzu Arinkan, Nurver Ozel Ozbay, Selcuk Selcuk
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(1):56-60. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.04.08
- 6,789 View
- 133 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Colloid carcinoma, which is a very rare tumor of the uterine cervix, is composed of an excessive amount of mucus and a relative paucity of tumoral glandular cells within them. Herein, we report a rare case of colloid carcinoma of the cervix with adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS), intestinal and usual types, and endocervical adenocarcinoma (usual type) components. We also discuss the morphological and immunohistochemical characteristics of this tumor. A 51-year-old woman was referred to our outpatient clinic with the symptom of genital bleeding lasting for 5 months. She had a cervix surrounded by an irregular tumor with a diameter of 5 cm. The colloid carcinoma cells were positive for MUC2, MUC5AC, and cytokeratin (CK) 7, focal positive for CDX2, and negative for MUC6 and CK20. Also, the intestinal type AIS showed a similar staining pattern. Colloid carcinoma cells producing mucin showed an intestinal phenotype and AIS. The intestinal type can be considered as a precursor lesion of colloid carcinoma.
- Comparison of Analytical and Clinical Performance of HPV 9G DNA Chip, PANArray HPV Genotyping Chip, and Hybrid-Capture II Assay in Cervicovaginal Swabs
- Ho Young Jung, Hye Seung Han, Hyo Bin Kim, Seo Young Oh, Sun-Joo Lee, Wook Youn Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(2):138-146. Published online January 13, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.10.21
- 7,974 View
- 67 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection can be detected by using several molecular methods, including Hybrid-Capture II (HC2) assay and variable HPV DNA chip tests, although each method has different sensitivities and specificities. Methods: We performed HPV 9G DNA Chip (9G) and PANArray HPV Genotyping Chip (PANArray) tests on 118 cervicovaginal swabs and compared the results with HC2, cytology, histology, and direct sequencing results. Results: The overall and high-risk HPV (HR-HPV) positivity rates were 62.7% and 44.9% using 9G, and 61.0% and 30.5% using PANArray, respectively. The positivity rates for HR-HPV with these two chips were significantly lower than 55.1% when HC2 was used. The sensitivity of overall HPV positivity in detecting histologically confirmed low-grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions or higher was 88.7% for all three tests. The specificity was 58.5% for 9G and 61.5% for PANArray, which was significantly lower than the 72.3% for HC2. With the HR-HPV+ genotype threshold, the sensitivity decreased to 75.5% for 9G and 52.8% for PANArray, which was significantly lower than the 88.7% for HC2. Comparison of the two chips showed concordant results in 55.1% of the samples, compatible results in 16.9%, and discordant results in 28.0%, exhibiting poor agreement in detecting certain HPV genotypes. Compared with direct sequencing, 9G yielded no discordant results, whereas PANArray yielded 31 discordant results (26.7%). Conclusions: Compared with HC2, the HPV genotyping tests showed lower sensitivity in histologic correlation. When the two chips were compared, the 9G was more sensitive and accurate for detecting HR-HPV than the PANArray. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concordance of Anyplex™ II HPV HR assays with reference HPV assays in cervical cancer screening: Systematic review
Habtamu Biazin
Journal of Virological Methods.2022; 301: 114435. CrossRef - The clinical performance of human papillomavirus genotyping using PANArray HPV chip: Comparison to ThinPrep cytology alone and co-testing
Jiyoung Kim, Sun-Young Jun, Lee-So Maeng
Pathology - Research and Practice.2020; 216(9): 153121. CrossRef - Analytic performance of PANArray HPV and HPV 9G DNA chip tests for genotyping of high-risk human papillomavirus in cervical ThinPrep PreservCyt samples
Jiyoung Kim, Sun-Young Jun, Magdalena Grce
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(10): e0224483. CrossRef
- Concordance of Anyplex™ II HPV HR assays with reference HPV assays in cervical cancer screening: Systematic review
- A Ciliated Cyst with Müllerian Differentiation Arising in the Posterior Mediastinum
- So Jung Lee, Chung Su Hwang, Do Youn Park, Gi Young Huh, Chang Hun Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(5):401-404. Published online October 27, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.5.401
- 7,457 View
- 78 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cyst of Hattori: A Rare Cyst in the Posterior Mediastinum
Matthew D. Turner, Elicia Goodale, Barry C. Gibney, Maria Cecilia D. Reyes
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2023; 31(4): 431. CrossRef - A large retroperitoneal Mullerian cyst: case report and review of the literature
Elena Parmentier, Jody Valk, Paul Willemsen, Caroline Mattelaer
Acta Chirurgica Belgica.2021; 121(4): 278. CrossRef - A case of resected Mullerian cyst in posterior mediastinum
Yoshiyuki Susaki, Noriyoshi Sawabata
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2020; 34(2): 137. CrossRef - Serosal Inclusion Cysts and Arteriovenous Fistulas in Paraprostatic Area of a Dog
Daisuke KOJIMA, Kyoko KOJIMA, Kazumi OTA, Yoshihiko KOJIMA
Journal of the Japan Veterinary Medical Association.2020; 73(9): 511. CrossRef - A surgical case of Mullerian cyst in the posterior mediastinum
Yusuke Kita, Yoshimasa Tokunaga, Taku Okamoto
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2019; 33(1): 68. CrossRef - CT and MRI characteristics for differentiating mediastinal Müllerian cysts from bronchogenic cysts
M. Kawaguchi, H. Kato, A. Hara, N. Suzui, H. Tomita, T. Miyazaki, H. Iwata, M. Matsuo
Clinical Radiology.2019; 74(12): 976.e19. CrossRef - A case of Mullerian cyst arising in the posterior mediastinum
Masahiro Adachi, Isao Sano, Shintaro Hashimoto, Ryoichiro Doi, Hideki Taniguchi, Kazuto Shigematsu
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2018; 32(6): 713. CrossRef - Two resected cases of Mullerian cyst in the posterior mediastinum
Shotaro Hashimoto, Masato Hisano, Masato Morimoto
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2018; 32(7): 818. CrossRef - Posterior mediastinal Müllerian cyst: a rare cause of pain in a young woman
Rebecca Weedle, Keith Conway, Igor Saftic, Alan Soo
Asian Cardiovascular and Thoracic Annals.2017; 25(6): 466. CrossRef
- Cyst of Hattori: A Rare Cyst in the Posterior Mediastinum
- Uncommon and Rare Human Papillomavirus Genotypes Relating to Cervical Carcinomas
- Na Rae Kim, Myunghee Kang, Soon Pyo Lee, Hyunchul Kim, Jungsuk An, Dong Hae Chung, Seung Yeon Ha, Hyun Yee Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(1):43-49. Published online February 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.1.43
- 7,352 View
- 49 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Human papillomavirus (HPV) is an oncogenic virus in cervical cancer and most invasive carcinomas (ICs) are caused by HPV16 and 18. However, the roles and contributions of other uncommon and rare genotypes remain uncertain.
Methods HPV genotypes were retrospectively assessed using an HPV DNA chip that can specify up to 32 HPV genotypes. We arbitrarily regarded genotypes accounting for less than 6% of the total as uncommon and rare genotypes.
Results A total of 3,164 HPV-positive cases were enrolled. In groups 2A, 2B, 3, and unclassified HPV genotypes, 2.4% of cases with uncommon HPV genotypes (68, 26, 34, 53, 66, 69, 70, 73, 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 55, 61, 62, 6, and 11) showed high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and ICs. There were no HPV32- and 57-infected cases.
Conclusions We found that the uncommon and rare HPV genotypes may provide incremental etiologic contributions in cervical carcinogenesis, especially HPV68, 70, and 53. Further studies on these uncommon and rare HPV genotypes will be of importance in establishing the significance of genotypes in different regions, especially in planning a strategy for further vaccine development as well as follow-up on the effectiveness of the currently used vaccines.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-risk human papillomavirus diversity among indigenous women of western Botswana with normal cervical cytology and dysplasia
Patricia S. Rantshabeng, Billy M. Tsima, Andrew K. Ndlovu, Keneilwe Motlhatlhedi, Kirthana Sharma, Carol B. Masole, Natasha O. Moraka, Kesego Motsumi, Angela K. T. Maoto-Mokote, Alemayehu B. Eshetu, Leabaneng Tawe, Tendani Gaolathe, Sikhulile Moyo, Lynnet
BMC Infectious Diseases.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus (HPV69/HPV73) Coinfection associated with Simultaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Anus and Presumed Lung Metastasis
Stephanie Shea, Marina Muñoz, Stephen C. Ward, Mary B. Beasley, Melissa R Gitman, Michael D Nowak, Jane Houldsworth, Emilia Mia Sordillo, Juan David Ramirez, Alberto E. Paniz Mondolfi
Viruses.2020; 12(3): 349. CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus Selected Properties and Related Cervical Cancer Prevention Issues
Saule Balmagambetova, Andrea Tinelli, Ospan A. Mynbaev, Arip Koyshybaev, Olzhas Urazayev, Nurgul Kereyeva, Elnara Ismagulova
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2020; 26(18): 2073. CrossRef - Periungual Bowen's disease with a narrow longitudinal melanonychia mimicking periungual warts
Taiyo HITAKA, Michiko HASEGAWA, Akira SHIMIZU, Yuko KURIYAMA, Atsushi TAMURA
Skin Cancer.2019; 33(3): 211. CrossRef - Detection of HPV RNA molecules in stratified mucin-producing intraepithelial lesion (SMILE) with concurrent cervical intraepithelial lesion: a case report
Shiho Fukui, Kazunori Nagasaka, Naoko Iimura, Ranka Kanda, Takayuki Ichinose, Takeru Sugihara, Haruko Hiraike, Shunsuke Nakagawa, Yuko Sasajima, Takuya Ayabe
Virology Journal.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Pitfalls of commercially available HPV tests in HPV68a detection
Hana Jaworek, Katerina Kubanova, Vladimira Koudelakova, Rastislav Slavkovsky, Jiri Drabek, Marian Hajduch, Craig Meyers
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(8): e0220373. CrossRef - Overall accuracy of cervical cytology and clinicopathological significance of LSIL cells in ASC‐H cytology
S. H. Kim, J. M. Lee, H. G. Yun, U. S. Park, S. U. Hwang, J.‐S. Pyo, J. H. Sohn
Cytopathology.2017; 28(1): 16. CrossRef - Human papillomavirus genotyping by Linear Array and Next-Generation Sequencing in cervical samples from Western Mexico
María Guadalupe Flores-Miramontes, Luis Alberto Torres-Reyes, Liliana Alvarado-Ruíz, Salvador Angel Romero-Martínez, Verenice Ramírez-Rodríguez, Luz María Adriana Balderas-Peña, Verónica Vallejo-Ruíz, Patricia Piña-Sánchez, Elva Irene Cortés-Gutiérrez, Lu
Virology Journal.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of human papillomavirus coinfections on the risk of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion and cervical cancer
Adela Carrillo-García, Sergio Ponce-de-León-Rosales, David Cantú-de-León, Verónica Fragoso-Ontiveros, Imelda Martínez-Ramírez, Asunción Orozco-Colín, Alejandro Mohar, Marcela Lizano
Gynecologic Oncology.2014; 134(3): 534. CrossRef - Human papillomavirus 66‐associated subungual squamous cell carcinoma
Jin Hee Kang, Hwa young Ahn, Miri Kim, Shin Taek Oh, Baik Kee Cho, Hyun Jeong Park
The Journal of Dermatology.2014; 41(12): 1119. CrossRef
- High-risk human papillomavirus diversity among indigenous women of western Botswana with normal cervical cytology and dysplasia
- Outcome of "Atypical Squamous Cells" in Cervical Cytology: Follow-up Assessment by Loop Electrical Excision Procedure
- Joon Seon Song, Ilseon Hwang, Gyungyub Gong
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(4):359-364. Published online August 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.4.359
- 7,066 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background We have retrospectively assessed the incidence and outcome of women diagnosed during a hospital-based cytology screening program with "atypical squamous cells (ASC)" and followed-up with loop electrical excision procedure (LEEP).
Methods We analyzed 173,947 cases of cervical smears' follow-up cytology and histology findings. Previous or archival cytology with LEEP results were retrieved for 390 women with ASC of undetermined significance (ASC-US) and 112 with ASC, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (ASC-H).
Results On the follow-up cytology, of the 390 women initially diagnosed with ASC-US, 130 (33.3%) had no follow-up records of smears before LEEP; smears of 18 (4.6%) were negative for cytologic abnormalities, 193 (49.5%) were ASC-US, 24 (6.2%) were ASC-H, 111 (28.5%) were low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL), and 44 (11.4%) were high grade SIL. LEEP findings in these 390 women showed that 183 (46.9%) were negative, 73 (18.7%) were graded as cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) 1, 25 (6.4%) as CIN 2, 102 (26.2%) as CIN 3, and 7 (1.8%) had carcinoma. LEEP was performed in 112 women initially diagnosed with ASC-H; 36 (32.1%) were negative, 4 (3.6%) were graded as CIN 1, 7 (6.3%) as CIN 2, 60 (53.6%) as CIN 3, and 5 (4.5%) with carcinoma.
Conclusions Patients with ASC-H smears were at increased risk of SIL or carcnoma compared with patients with ASC-US. Careful follow-up is required in ASC patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incisal margin condition after LEEP for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia patients and prognosis
Hong Chen, Xiufeang Liu, Lina Xu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2016; 12(2): 1019. CrossRef
- Incisal margin condition after LEEP for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia patients and prognosis
- The Utility of p16INK4a and Ki-67 as a Conjunctive Tool in Uterine Cervical Lesions
- Sangho Lee, Hyunchul Kim, Hyesun Kim, Chulhwan Kim, Insun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(3):253-260. Published online June 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.3.253
- 9,221 View
- 87 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Immunohistochemical staining for p16INK4a and Ki-67 has been used to improve the accuracy in making a diagnosis of the uterine cervix cancer on biopsy. This study was conducted to examine the usefulness of these markers in the pathological diagnosis based on cervical biopsy.
Methods We selected a consecutive series of 111 colposcopically directed cervical punch biopsies. Using these biopsy samples, we performed an immunohistochemical staining for p16INK4a and Ki-67 to establish a diagnosis. The slides were circulated among four pathologists in a sequential order: the hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) slide, H&E slide and p16INK4a-stained slide, and H&E slide, p16INK4a- and Ki-67-stained slides.
Results The overall rates of the concordance in the first, the second, and the third diagnoses were 77.5%, 82.0%, and 82.0%, respectively. The rate of the concordance in the diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasm (CIN) 2/3 was increased from 62.2% to 73.0%. But there was a variability in the rate of the revision of the diagnosis between the pathologists. With the application of criteria for interpreting the expressions of p16INK4a and Ki-67, benign and CIN 1 lesions showed a p16INK4a expression score of 0 or 1. But CIN 2 and CIN 3 lesions showed a p16INK4a expression score of 2 and 3, respectively.
Conclusions The immunostain for p16INK4a and Ki-67 might be useful in reducing an inter-observer variability. But criteria for interpreting both markers should be strictly applied.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Possible role of negative human papillomavirus E6/E7 mRNA as a predictor of regression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2 lesions in hr-HPV positive women
Maria Teresa Bruno, Nazario Cassaro, Salvatore Giovanni Vitale, Arianna Guaita, Sara Boemi
Virology Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of p16, human papillomavirus capsid protein L1 and Ki-67 in cervical intraepithelial lesions: Potential utility in diagnosis and prognosis
Hanan AlSaeid Alshenawy
Pathology - Research and Practice.2014; 210(12): 916. CrossRef - Distribution of Human Papillomavirus 52 and 58 Genotypes, and Their Expression of p16 and p53 in Cervical Neoplasia
Tae Eun Kim, Hwal Woong Kim, Kyung Eun Lee
Korean Journal of Pathology.2014; 48(1): 24. CrossRef - Detection and pathological value of papillomavirus DNA and p16INK4A and p53 protein expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
JINGBO WU, XIAO-JING LI, WEI ZHU, XIU-PING LIU
Oncology Letters.2014; 7(3): 738. CrossRef - p16INK4a Immunohistochemistry in Cervical Biopsy Specimens
Miriam Reuschenbach, Nicolas Wentzensen, Maaike G. Dijkstra, Magnus von Knebel Doeberitz, Marc Arbyn
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2014; 142(6): 767. CrossRef
- Possible role of negative human papillomavirus E6/E7 mRNA as a predictor of regression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2 lesions in hr-HPV positive women
- Composite Tumor of Adenocarcinoma and Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: A Case Report.
- Hye Rim Park, Yong Woo Lee, Young Euy Park
- Korean J Cytopathol. 1990;1(1):111-120.
- 1,708 View
- 37 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the uterine cervix is a distinct subtype of cervical cancer that appears analogous to oat cell carcinoma and carcinoid tumors of the lung. It has been assumed to be derived from the neural crest via argyrophilic cells in the normal endocervix. We have recently encountered a case of small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the uterine cervix coexisting with adenocarcinoma which was argyrophil negative. A 66-year-old multiparous woman was admitted because of vaginal bleeding for 2 months. Cervicovaginal smear revealed several scattered clusters and sheets of monotonous small cells with some peripheral palisading in the background of hemorrhage and necrosis. Radical hysterectomy specimen revealed and ulcerofungating tumor on endocervical canal which was composed of two components. Major component of the tumor was made up of monomorphic population of small oval-shaped tumor cells arranged in sheets and partly in acinar structeres or trabecular fashion. Other component was adenocarcinoma, endocervical well-differentiated type. Argyropilia was present on the Grimelius stain and immunohistochemical studies revealed diffuse positivity to neuron-specific enolase and carcinoembryonic antigen. Electron microscopic examination showed clusters of small round to oval cells, which had a few well-formed desmosomes and several membrane-bound, dense-core neurosectetory granules.
- Liquid-Based Pap Smear Findings of Uterine Cervical Lymphoma: Three Cases Report.
- Jiyoung Kim, Hyesun Kim, Sung Ran Hong, Yi Kyeong Chun, Hy Sook Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(4):437-440.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.4.437
- 2,874 View
- 33 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Malignant lymphoma of the uterine cervix is rarely diagnosed by cytology because it presents as a subepithelial mass. We report three cases of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the uterine cervix with a description of liquid-based pap smear (LBP) findings. All patients were presented with cervical masses, but a suspicion of malignant lymphoma was made in only one case by preoperative LBP. The LBP of two cases showed several atypical lymphoid cells in a clear background. The other case revealed numerous atypical lymphoid cells in a necrotic background. Most tumor cells had an increased N/C ratio, round but focally irregular nuclei, coarse chromatin, and prominent nucleoli. Nuclear blebing, dimpling, and multi-lobulation were also found. Diagnosis of malignant lymphoma by LBP is usually more difficult than by conventional techniques, because of a sparse numbers of cells and the lack of necrotic background. However, well preserved morphological features and a better resolution of nuclear details could be the benefits of LBP.
- Evaluation of Low-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions, Cannot Exclude High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions on Cervical Smear.
- Sung Ran Hong, Bock Man Kim, Hye Sun Kim, Yi Kyeong Chun, Hy Sook Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(5):528-535.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.5.528
- 3,991 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
We examined cervicovaginal smears that contained definite low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) cells and rare atypical cells suggestive of high-grade SIL (HSIL) (ASC-H) or contained borderline dysplastic cells between LSIL and HSIL. Such lesions were classified as LSIL-H. This study aimed to investigate the cytologic and histologic characteristics of LSIL-H category and we evaluated the associated clinical risk.
METHODS
The histologic outcomes of LSIL-H were compared with those of LSIL and ASC-H. Both the cytologic and histologic findings of LSIL-H that were confirmed as cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2 (CIN2) or greater (CIN2+) were investigated.
RESULTS
LSIL-H accounted for 0.09% of the Pap tests. On the follow-up histology, the most frequent outcome was CIN2, and the risk of CIN2+ was higher than that for ASC-H. In the cases of LSIL-H that was histologically confirmed as CIN2+, most of the atypical cells suggestive of HSIL were cytologically similar to those of CIN2, and the corresponding cervical tissues were characterized by small CIN2+ lesions in a large background of flat condyloma/CIN1. The LSIL-H cases not confirmed on initial colposcopically-directed biopsy required further follow-up.
CONCLUSIONS
LSIL-H may be a valid diagnostic category with distinctive features that are different from LSIL or ASC-H. LSIL-H needs further follow-up for the proper management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Clinical Significance of “Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion of Indeterminate Grade” as a Distinct Cytologic Category
Dorothy Wong, Crystal Teschendorf, Grace Y. Lin, Farnaz Hasteh
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2012; 137(5): 753. CrossRef
- The Clinical Significance of “Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion of Indeterminate Grade” as a Distinct Cytologic Category
- The Analysis and Clinical Usefulness of HPV DNA Chip Test in the Uterine Cervix.
- Joo hyeon Jeong, Hyun Yee Cho, Na Rae Kim, Dong Hae Chung, Sanghui Park, Seung Yeon Ha
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(1):77-82.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.1.77
- 3,395 View
- 27 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The genotypes of human papillomavirus (HPV) are important in carcinogenesis in uterine cervical cancer and may be different in geographic distribution.
METHODS
In 2,086 women, we analyzed the prevalence of HPV and HPV genotypes in uterine cervix by HPV-DNA chip test (n = 2,086), cytology (PAP smear, n = 1997) and biopsy (n = 546).
RESULTS
Of the 2,086 cases, 1,019 cases (48.8%) were HPV-positive and 1,067 cases (51.2%) were negative for HPV. Single infection occurred most commonly (72.1% of women). HPV genotypes in the high-risk and low-risk groups, respectively were HPV-16/-58/-18/-52/-53 and HPV-70/-6/-11. The detection rates of HPV-70 in subjects older than 50 years increased significantly (p < 0.05). Infection in high risk subjects was detected in high grade lesions compared with infection in low risk subjects (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
HPV-16/-58/-18/-52/-53/-70/-6/-11 genotypes were common in the patient group similar to findings in East Asia. HPV-70 infection is predominant in those older than 40 years. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current Status of and Perspectives on Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
Sung-Chul Lim, Chong Woo Yoo
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2019; 53(4): 210. CrossRef - Cervical cytology of atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intra-epithelial lesion: significance of age, human papillomavirus DNA detection and previous abnormal cytology on follow-up outcomes
Chang Ohk Sung, Young Lyun Oh, Sang Yong Song
European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology.2011; 159(1): 155. CrossRef - Cytomorphologic Features According to HPV DNA Type in Histologically Proven Cases of the Uterine Cervix
In Ho Choi, So-Young Jin, Dong Wha Lee, Dong Won Kim, Yoon Mi Jeen
The Korean Journal of Pathology.2011; 45(6): 612. CrossRef
- Current Status of and Perspectives on Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea

 E-submission
E-submission




 First
First Prev
Prev



