Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diagnostic distribution and pitfalls of glandular abnormalities in cervical cytology: a 25-year single-center study
- Jung-A Sung, Ilias P. Nikas, Haeryoung Kim, Han Suk Ryu, Cheol Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(6):354-360. Published online November 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.09.05
- 8,503 View
- 154 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Detection of glandular abnormalities in Papanicolaou (Pap) tests is challenging. This study aimed to review our institute’s experience interpreting such abnormalities, assess cytohistologic concordance, and identify cytomorphologic features associated with malignancy in follow-up histology.
Methods
Patients with cytologically-detected glandular lesions identified in our pathology records from 1995 to 2020 were included in this study.
Results
Of the 683,197 Pap tests performed, 985 (0.144%) exhibited glandular abnormalities, 657 of which had tissue follow-up available. One hundred eighty-eight cases were cytologically interpreted as adenocarcinoma and histologically diagnosed as malignant tumors of various origins. There were 213 cases reported as atypical glandular cells (AGC) and nine cases as adenocarcinoma in cytology, yet they were found to be benign in follow-up histology. In addition, 48 cases diagnosed with AGC and six with adenocarcinoma cytology were found to have cervical squamous lesions in follow-up histology, including four squamous cell carcinomas. Among the cytomorphological features examined, nuclear membrane irregularity, three-dimensional clusters, single-cell pattern, and presence of mitoses were associated with malignant histology in follow-up.
Conclusions
This study showed our institute’s experience detecting glandular abnormalities in cervical cytology over a 25-year period, revealing the difficulty of this task. Nonetheless, the present study indicates that several cytological findings such as membrane irregularity, three-dimensional clusters, single-cell pattern, and evidence of proliferation could help distinguishing malignancy from a benign lesion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- “Atypical Glandular Cells” on Cervical Cytology: Correlation Between Glandular Cell Component Volume and Histological Follow‐Up
Havva Gokce Terzioglu, Alessa Aragao, Julieta E. Barroeta
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(2): 71. CrossRef - Expertise in Gynecological Pathology Impacts Diagnosis of Atypical Glandular Cell Category in Cervical Cytology
Havva Gökce Terzioglu, Alessa Aragao, Julieta E. Barroeta
Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease.2025; 29(4): 297. CrossRef - Comparison of Cytological and/or Histopathological Results of Patients with Single and Multiple HPV Positivity
Fatih Mehmet Kaya, Şafak Ersöz, Cihan Comba, Ömer Demir
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Analysis of atypical glandular cells in ThinPrep Pap smear and follow-up histopathology
Tengfei Wang, Yinan Hua, Lina Liu, Bing Leng
Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings.2024; 37(3): 403. CrossRef
- “Atypical Glandular Cells” on Cervical Cytology: Correlation Between Glandular Cell Component Volume and Histological Follow‐Up
- Comparison of papanicolaou smear and human papillomavirus (HPV) test as cervical screening tools: can we rely on HPV test alone as a screening method? An 11-year retrospective experience at a single institution
- Myunghee Kang, Seung Yeon Ha, Hyun Yee Cho, Dong Hae Chung, Na Rae Kim, Jungsuk An, Sangho Lee, Jae Yeon Seok, Juhyeon Jeong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):112-118. Published online January 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.11.29
- 14,348 View
- 267 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The decrease in incidence of cervical dysplasia and carcinoma has not been as dramatic as expected with the development of improved research tools and test methods. The human papillomavirus (HPV) test alone has been suggested for screening in some countries. The National Cancer Screening Project in Korea has applied Papanicolaou smears (Pap smears) as the screening method for cervical dysplasia and carcinoma. We evaluated the value of Pap smear and HPV testing as diagnostic screening tools in a single institution.
Methods
Patients co-tested with HPV test and Pap smear simultaneously or within one month of each other were included in this study. Patients with only punch biopsy results were excluded because of sampling errors. A total of 999 cases were included, and the collected reports encompassed results of smear cytology, HPV subtypes, and histologic examinations.
Results
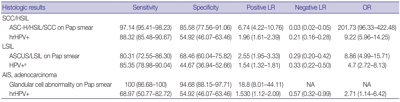
Sensitivity and specificity of detecting high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) were higher for Pap smears than for HPV tests (sensitivity, 97.14%; specificity, 85.58% for Pap smears; sensitivity, 88.32%; specificity, 54.92% for HPV tests). HPV tests and Pap smears did not differ greatly in detection of low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (85.35% for HPV test, 80.31% for Pap smears). When atypical glandular cells were noted on Pap smears, the likelihood for histologic diagnosis of adenocarcinoma following Pap smear was higher than that of high-risk HPV test results (18.8 and 1.53, respectively).
Conclusions
Pap smears were more useful than HPV tests in the diagnosis of HSIL, SCC, and glandular lesions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Nano-Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Kit for Detection and Genotyping of High-Risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Strains Using Dedicated TaqMan Probes
Mohammad Panji, Mohammad Hossein Modarresi, Zahra Azizi, Moloud Absalan, Elahe Motevaseli
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection of cervical precancerous lesions and cancer by small-scale RT-qPCR analysis of oppositely deregulated mRNAs pairs in cytological smears
Anastasia A. Artyukh, Mikhail K. Ivanov, Sergei E. Titov, Victoria V. Dzyubenko, Sergey E. Krasilnikov, Anastasia O. Shumeikina, Nikita A. Afanasev, Anastasia V. Malek, Sergei A. Glushkov, Eduard F. Agletdinov
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - High burden of abnormal cervical smears in South African primary health care: health programmes implications
Olufemi B Omole, Joel M Francis, John M Musonda, Pumla P Sodo, Elizabeth Reji, Nyundu S J Phukuta, Honey L M Mabuza, Joyce S Musonda, Jimmy Akii, John V Ndimande, Olalekan A Ayo-Yusuf
Health Promotion International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis: a study of the microenvironment in cervical cancer (2000-2024)
Yun-Tao Zhang, Yan-Ni Wei, Chen-Chen Liu, Mai-Qing Yang
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Liquid biopsy biomarkers in cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Isaac Kinyua Njangiru, Bizhar Ahmed Tayeb, Hazhmat Ali, Rafl M. Kamil
The Journal of Liquid Biopsy.2025; 10: 100328. CrossRef - Diagnostic Utility of Human Papilloma Virus Testing in Comparison with Pap Cytology and Histopathology in Unvaccinated Women with Cervical High-Grade Dysplasia and Carcinoma in Botswana
Patricia Setsile Rantshabeng, Nametso Dire, Andrew Khulekani Ndlovu, Ishmael Kasvosve
Venereology.2025; 4(4): 15. CrossRef - Challenges in the diagmosis of cervical pathologies
D. Y. Chernov, O. A. Tikhonovskaya, S. V. Logvinov, I. A. Petrov, Y. S. Yuriev, A. A. Zhdankina, A. V. Gerasimov, I. V. Zingalyuk, G. A. Mikheenko
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2024; 22(4): 201. CrossRef - “Barriers and Advantages of Self-Sampling Tests, for HPV Diagnosis: A Qualitative Field Experience Before Implementation in a Rural Community in Ecuador”
Bernardo Vega-Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, Ruth Maldonado - Rengel, Diana López, Dayanara Delgado-López, Gabriela Guerra Astudillo, Veronique Verhoeven
International Journal of Women's Health.2024; Volume 16: 947. CrossRef - Cervical Human Papillomavirus Testing
Carol N. Rizkalla, Eric C. Huang
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2024; 17(3): 431. CrossRef - Segmentation of Overlapping Cells in Cervical Cytology Images: A Survey
E Chen, Hua-Nong Ting, Joon Huang Chuah, Jun Zhao
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 114170. CrossRef - Knowledge and awareness regarding pap test and HPV typing for cervical cancer screening in Edo North, Nigeria
Amina Momodu, Johnsolomon Eghosa Ohenhen, Godfrey Innocent Iyare, Musa Abidemi Muhibi, Godwin Avwioro
Discover Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Colposcopy Value in Young Child-bearing Women: Is New Recommendations Necessary?
Fahimeh Sabet, Avishan Aminizad, Fariba Behnamfar, Tajossadat Allameh, Seyedeh Ghazal Shahrokh, Rostami Koushan, Amirmohammad Taravati, Leila Mousavi Seresht
Advanced Biomedical Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Selection of endogenous control and identification of significant microRNA deregulations in cervical cancer
T. Stverakova, I. Baranova, P. Mikyskova, B. Gajdosova, H. Vosmikova, J. Laco, V. Palicka, H. Parova
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytology Versus Molecular Diagnosis of HPV for Cervical Cancer Screening. Comparison of the Diagnostic Properties of Four Tests in a Rural Community of Cuenca Ecuador
Bernardo Vega Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, Rocío Murillo, Cristina Ochoa Avilés
ESPOCH Congresses: The Ecuadorian Journal of S.T.E.A.M..2023; 3(1): 139. CrossRef - Attitudes towards prevention of cervical cancer and early diagnosis among female academicians
Nurhan Doğan, Gamze Fışkın
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2022; 48(6): 1433. CrossRef - Role of Self-Sampling for Cervical Cancer Screening: Diagnostic Test Properties of Three Tests for the Diagnosis of HPV in Rural Communities of Cuenca, Ecuador
Bernardo Vega Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, José Ortíz Segarra, Ruth Maldonado Rengel, Diana López, María Paz Orellana, Andrea Gómez, María José Vicuña, Jorge Mejía, Ina Benoy, Tesifón Parrón Carreño, Veronique Verhoeven
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4619. CrossRef - Utility of Scoring System for Screening and Early Warning of Cervical Cancer Based on Big Data Analysis
Dan Hou, Binjie Yang, Yangdan Li, Ming Sun
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Urine and Vaginal Self-Sampling versus Clinician-Based Sampling for Cervical Cancer Screening: A Field Comparison of the Acceptability of Three Sampling Tests in a Rural Community of Cuenca, Ecuador
Bernardo Vega Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, José Ortíz S, Ruth Maldonado-Rengel, Diana López, Andrea Gómez, María José Vicuña, Jorge Mejía, Ina Benoy, Tesifón Parrón Carreño, Veronique Verhoeven
Healthcare.2022; 10(9): 1614. CrossRef - Diagnostic distribution and pitfalls of glandular abnormalities in cervical cytology: a 25-year single-center study
Jung-A Sung, Ilias P. Nikas, Haeryoung Kim, Han Suk Ryu, Cheol Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 354. CrossRef - Primary screening of cervical cancer by Pap smear in women of reproductive age group
Ruchi Mishra, Dakshina Bisht, Manisha Gupta
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2022; 11(9): 5327. CrossRef - Comparison of Learning Transfer Using Simulation Problem-Based Learning and Demonstration: An Application of Papanicolaou Smear Nursing Education
Jeongim Lee, Hae Kyoung Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1765. CrossRef - Investigating host-virus interaction mechanism and phylogenetic analysis of viral proteins involved in the pathogenesis
Ahmad Abu Turab Naqvi, Farah Anjum, Alaa Shafie, Sufian Badar, Abdelbaset Mohamed Elasbali, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav, Md. Imtaiyaz Hassan, Timir Tripathi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(12): e0261497. CrossRef - Utility of Human Papillomavirus Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
Mee-seon Kim, Eun Hee Lee, Moon-il Park, Jae Seok Lee, Kisu Kim, Mee Sook Roh, Hyoun Wook Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(5): 1726. CrossRef
- Development of a Nano-Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Kit for Detection and Genotyping of High-Risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Strains Using Dedicated TaqMan Probes
- Morphological Features and Immunohistochemical Expression of p57Kip2 in Early Molar Pregnancies and Their Relations to the Progression to Persistent Trophoblastic Disease
- Marwa Khashaba, Mohammad Arafa, Eman Elsalkh, Reda Hemida, Wagiha Kandil
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):381-387. Published online June 12, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.04.28
- 16,225 View
- 246 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Although the morphological features characteristic of products of conception specimens including molar pregnancies are well described, substantial histopathological similarities are observed between the different entities, especially in cases of early pregnancies. Furthermore, there are no current solid criteria that could predict cases with progression to persistent gestational trophoblastic disease. In this study, we aimed to determine the most specific histopathological and immunohistochemical features required for accurate diagnosis that can reliably predict the clinical behavior.
Methods
Sixty-five cases of products of conception were reviewed clinically and pathologically, and any progression to persistent gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD), if present, was noted. Pathological assessment of the archival material included re-cut sections of 5 μm in thickness, routine staining with hematoxylin and eosin and immunohistochemical staining of p57Kip2.
Results
Certain histopathological criteria were found to be significant in differentiation between complete hydatidiform mole (CHM) and partial hydatidiform mole including villous shape and outline, villous trophoblast hyperplasia, and atypia in extravillous trophoblasts. There were no significant differences in any morphological or immunohistochemical features between cases with or without subsequent development of GTD.
Conclusions
Histopathological diagnosis of molar pregnancy remains problematic especially in early gestation. Their diagnosis should be stated after a constellation of specific histopathological criteria in order not to miss CHM. p57Kip2 immunohistochemistry is of great value in diagnosis of cases that had equivocal morphology by histopathological examination. However, there were no significant features to predict cases that subsequently developed persistent GTD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular Basis of Hydatidiform Moles—A Systematic Review
Shadha Nasser Mohammed Bahutair, Rajani Dube, Manjunatha Goud Bellary Kuruba, Rasha Aziz Attia Salama, Mohamed Anas Mohamed Faruk Patni, Subhranshu Sekhar Kar, Rakhee Kar
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(16): 8739. CrossRef - Diagnosis of hydatidiform moles using p57 immunohistochemistry and chromogenic insitu hybridization: A retrospective study
Mojgan Akbarzadeh-Jahromi, Tara Taheri, Fatemeh Sari Aslani, Akbar Safaei, Fatemeh Pouraminaee, Marjan Zare
International Journal of Reproductive BioMedicine (IJRM).2024; 22(9): 727. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical expression of BCL-2 in hydatidiform moles: a tissue microarray study
Muna Al-Jabri, Suaad Al-Badi, Hunaina Al-Kindi, Mohammad Arafa
Pathologica.2023; 115(3): 148. CrossRef - Persistent gestational trophoblastic disease following ectopic molar pregnancy
I.N. Voloshchuk, I.V. Barinova, S.N. Buyanova, S.A. Petrakova, N.A. Shchukina, M.V. Mgeliashvili
Arkhiv patologii.2021; 83(1): 44. CrossRef - P57 and Ki-67 expression in hydropic abortion and molar pregnancy
Sylvia A. Ashamallah, Mie A. Mohamed, Hany O. Habashy
Egyptian Journal of Pathology.2017; 37(2): 393. CrossRef
- Molecular Basis of Hydatidiform Moles—A Systematic Review
- Prognostic Significance of Heat Shock Protein 70 Expression in Early Gastric Carcinoma
- Youngran Kang, Woon Yong Jung, Hyunjoo Lee, Wonkyung Jung, Eunjung Lee, Bong Kyung Shin, Aeree Kim, Han Kyeom Kim, Baek-hui Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(3):219-226. Published online June 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.3.219
- 9,594 View
- 36 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Overexpression of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) has been observed in many types of cancer including gastric adenocarcinomas, although the exact role of HSP70 in carcinogenesis remains unclear.
Methods The study analyzed a total of 458 radical gastrectomy specimens which were immunohistochemically stained with HSP70, p53, and Ki-67 antibodies.
Results The study determined that the expression of HSP70 was significantly increased in early gastric cancer (EGC) compared to advanced gastric cancer (p<0.001). The HSP70 expression was correlated with well-differentiated tumor type, intestinal type of Lauren classification and the lower pT and pN stage. Negative expression of Ki-67 and p53 expression was associated with poor prognosis. The study did not find any correlation between HSP70 and p53 expression. The study determined that HSP70 expression in the EGC subgroup was associated with a poor prognosis (p=0.009), as well as negative Ki-67 expression (p=0.006), but was not associated with p53. Based on multivariate analysis, HSP70 expression (p=0.024), negative expression of Ki-67, invasion depth and lymph node metastasis were determined to be independent prognostic markers.
Conclusions HSP70 is expressed in the early stages of gastric adenocarcinoma. In EGC, HSP70 is a poor independent prognostic marker and is correlated with a low proliferation index.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Prognostic Importance of Ki-67 in Gastrointestinal Carcinomas: A Meta-analysis and Multi-omics Approach
Mahdieh Razmi, Fatemeh Tajik, Farideh Hashemi, Ayna Yazdanpanah, Fatemeh Hashemi-Niasari, Adeleh Divsalar
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2024; 55(2): 599. CrossRef - Clinicopathological significance of HSP70 expression in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiaolu Wang, Li Xie, Lijing Zhu
BMC Gastroenterology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Beta-sheet-specific interactions with heat shock proteins define a mechanism of delayed tumor cell death in response to HAMLET
Aftab Nadeem, James C.S. Ho, Tuan Hiep Tran, Sanchari Paul, Victoria Granqvist, Nadege Despretz, Catharina Svanborg
Journal of Molecular Biology.2019; 431(14): 2612. CrossRef - Evolving paradigms on the interplay of mitochondrial Hsp70 chaperone system in cell survival and senescence
Shubhi Srivastava, Vinaya Vishwanathan, Abhijit Birje, Devanjan Sinha, Patrick D’Silva
Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2019; 54(6): 517. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic significance and prognostic value of Ki-67 expression in patients with gastric cancer: a meta-analysis
Guanying Luo, Yunzhao Hu, Zhiqiao Zhang, Peng Wang, Zhaowen Luo, Jinxin Lin, Canchang Cheng, You Yang
Oncotarget.2017; 8(30): 50273. CrossRef - Extracellular HSP70-peptide complexes promote the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via TLR2/4/JNK1/2MAPK pathway
Yi Zhe, Yan Li, Dan Liu, Dong-Ming Su, Jin-Gang Liu, Hang-Yu Li
Tumor Biology.2016; 37(10): 13951. CrossRef - The cytomegalovirus protein UL138 induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells by binding to heat shock protein 70
Wenjing Chen, Kezhi Lin, Liang Zhang, Gangqiang Guo, Xiangwei Sun, Jing Chen, Lulu Ye, Sisi Ye, Chenchen Mao, Jianfeng Xu, Lifang Zhang, Lubin Jiang, Xian Shen, Xiangyang Xue
Oncotarget.2016; 7(5): 5630. CrossRef - Targeting the hsp70 gene delays mammary tumor initiation and inhibits tumor cell metastasis
J Gong, D Weng, T Eguchi, A Murshid, M Y Sherman, B Song, S K Calderwood
Oncogene.2015; 34(43): 5460. CrossRef
- The Prognostic Importance of Ki-67 in Gastrointestinal Carcinomas: A Meta-analysis and Multi-omics Approach
- Tumor Budding and Recurrence in Submucosal Invasive Colorectal Cancers of Favorable Histology: Case Reports of Two Early Colorectal Cancers with Advanced Recurrences
- Heae Surng Park, Hee Jin Chang, Ji Won Park, Byung Chang Kim, Dae Kyung Sohn, Chang Won Hong, Ji-Yeon Baek, Sun Young Kim, Hyo Seong Choi, Jae Hwan Oh
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(3):272-277. Published online June 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.3.272
- 10,044 View
- 68 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Complete resection of submucosal invasive colorectal cancer (SICC) showing favorable histology is regarded as curative. We report on two cases of SICC showing recurrence within 5 years despite complete resection. The first patient was a 68-year-old woman with well differentiated rectal adenocarcinoma invading the superficial submucosa, which recurred after 4.7 years. The second patient was a 53-year-old man with pT1N0 moderately differentiated colonic adenocarcinoma. He developed widespread tumor recurrence after 3.9 years. Retrospective pathologic review of the original tumors showed multiple foci of tumor budding at the invasive front. Immunohistochemical staining for D2-40 of deeper levels of the paraffin blocks showed rare foci of small lymphatic invasion. Tumor budding at the invasive front may be an important indicator for SICC aggressiveness or may reflect early lymphatic invasion. More aggressive pathologic examination and follow-up is required for patients with SICC showing tumor budding, even in the absence of unfavorable histologic findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estudio de factores histológicos predictivos de metástasis ganglionar locorregional en adenocarcinoma colorrectal mínimamente invasivo pT1
Isidro Machado, Miriam Valera-Alberni, Fernando Martínez de Juan, José A. López-Guerrero, Alfonso García Fadrique, Julia Cruz, Carmen Martínez Lapiedra, Fernanda Maia de Alcantara, Ricardo Yaya, Jorge Campos, Carlos Fernández-Martos, Rafael Estevan
Gastroenterología y Hepatología.2016; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - Histological factors predicting loco-regional lymph node metastasis in early invasive colorectal adenocarcinoma pT1
Isidro Machado, Miriam Valera-Alberni, Fernando Martínez de Juan, José A. López-Guerrero, Alfonso García Fadrique, Julia Cruz, Carmen Martínez Lapiedra, Fernanda Maia de Alcantara, Ricardo Yaya, Jorge Campos, Carlos Fernández-Martos, Rafael Estevan
Gastroenterología y Hepatología (English Edition).2016; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - Tumor budding in the clinical management of colon and rectal cancer
Viktor H Koelzer, Inti Zlobec, Alessandro Lugli
Colorectal Cancer.2014; 3(4): 387. CrossRef
- Estudio de factores histológicos predictivos de metástasis ganglionar locorregional en adenocarcinoma colorrectal mínimamente invasivo pT1
- Clinicopathologic Features of Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
- Chang Ohk Sung, Suk Jin Choi, Cheol Keun Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(3):138-144.
- 2,470 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an early stage HCC, and it is sometimes difficult to identify the margins of the cancer nodules in the resected specimens.
METHODS
We studied 22 cases of early HCC to investigate the clinicopathologic features of early stage HCC.
RESULTS
Seven of 22 cases were single HCC, and 15 were multicentric HCC. The average tumor size was 1.34 cm (0.4-2.7 cm). Early HCCs didn't destroy the basic architecture of the liver lobules or pseudolobules and the lesions had an indistinct margin. Most tumors were uniformly composed of well-differentiated cancer tissue that was characterized by an increased cell density and an irregular thin-trabecular pattern. The tumor retained a varying number of portal tracts. There was a replacing growth pattern at the tumor-nontumor boundary without tumor capsule. Three of 22 cases had a "nodule-in-nodule" lesion, and the inner nodules consisted of moderately differentiated HCC without portal tracts. All 22 cases showed no vascular invasion. All 7 patients with single early HCC have survived for the past 11-54 months without any local recurrence. But in one patient with single early HCC, multicentric HCC developed 20 months after surgery.
CONCLUSION
The clinicopathologic features of early HCCs are quite different from those of advanced HCCs. The increased recognition of early HCC during routine clinical practice will contribute to improved patient survival.
- A Histopathologic Studies for Endometrium of Early Pregnancy.
- Mi Ja Lee, Kenn Hong Kee, Chae Hong Suh, Ho Jong Jeon
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(4):492-501.
- 1,821 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Endometrium of early pregnancy were compared with nonpregnant endometnum by inimunohistochemical and ultrastructural techniques with respect to glandular and stromal elements of endometrium. The results obtained were as follows: 1. The AS cell in decidua has all the features of actively secreting glandular epithelium and shows the pronounced arrays of glandular endoplasmic reticulum and moderate numbers of ribosomes ultrastructually. Therefore the AS cell indicate considerable protein production, presumably contributing to both cell gowth and the production of secretions. 2. The process of decidualization can be characterized morphologically and immunohistochemically by the accumulation of basement membrane-like materials, such as laminin and type IV collagen which may be related to the hormonal stimulation occuring during pregnancy and trophoblastic attachment. 3. The decidual cells show strong positive for vimentin and some large mature decidual cells show weakly positive for lysozyme and cti- antitrypsin, which might represent more the sequential differentiation of stromal cells into decidual cells than origin of histiocytes. 4. Immunoreactivity with S-100 protein was found in glandular and stromal cells of decidua but negative in endometrium of nonpregnant women. So some humoral factors related to pregnancy stimulate expression of S-100 protein in glandular and stromal cells of decidua.
- Body Stalk Anomaly: Analysis of 10 Autopsy Cases.
- Seung Sook Lee, Je G Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(3):235-242.
- 2,360 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Body stalk anomaly represents an extreme maldevelopment of embryonic body folding and is characterized by absence of the umbilicus and umbilical cord. The failure of complete obliteration of the extraembryonic coelom is responsible for the absence of the umbilical cord formation and the wide-based insertio of the amnioperitoneal membrane onto the placental chorionic plate. We have analyzed 10 autopsy cases of various midline anomalies of the body that could best be classified into body stalk anomaly. All cases were either stillborns or dead immediately after birth. The pregnancy was interrupted due to this anomaly in 6 cases, and their gestational ages varied from 17 weeks to 37 weeks. The affected fetuses were characterized bt absent or vestigial umbilical cord, and ruptured amnion with direct amnioperitoneal connection without the mediation of the umbilical cord. Exomphalos with abdominal wall defect and serve scoliosis were characteristic components of this anomaly, that provided important clues in differentiating other similar anomalies. Other associated anomalies included neural tube defect, intestinal atresia, genitourinary and skeletal defects, pulmonary hypoplasia, single umbilical artery and narrow-spaced chest and abdomen, etc. These findings strongly suggest that anomaly of body stalk represents mechanical teratogenesis due to early amnion repture and subsequent effect, and should be categorized into amniotic band disruption syndrome.
- Pathologic Analysis of Gallbladder Cancer by the Stage and Intestinal Metaplasia with the Diagnostic Significance of CEA and p53.
- Hee Jin Chang, Jung Il Suh
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(7):599-607.
- 2,077 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Twenty cases of gallbladder cancers were examined using 5 mm stepwise tissue sections. We analyzed the clinicopathologic findings of the early (stage 1, II) and advanced carcinoma (stage III, IV, V) and those of carcinoma with or without metaplasia in the tumor. We also performed CEA and p53 immunohistochemical staining and compared their findings with those of normal mucosa and preneoplastic lesions. The results were as follow: 1) All of the early carcinomas (n=5) were incidentally diagnosed after the resection for the gallstone. They were compared to advanced carcinoma (n=15) in the absence of the lymphatic or angioinvasion, recurrence, metastasis and death. 2) Metaplastic and non-metaplastic carcinoma did not reveal any difference of the clinicopathologic findings except age distribution. 3) CEA and p53 were positive in preneoplastic and malignant lesions. The extent of staining was related to the degree of the atypia. From the above results, an early detection of gallbladder cancer is very important for the prognosis of the patients. Since preoperative diagnosis is difficult, thorough pathologic examination of routinely resected gallbladder is necessary for the early diagnosis. CEA and p53 immunohistochemical staining may be helpful in the differential diagnosis of non-neoplastic and neoplastic lesion of the gallbladder.
- Pathological Study on the Early Gastric Cancer.
- Weon Young Choi, Dong Su Suk, Sun Keong Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(3):206-214.
- 2,227 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pathological study was performed on the 135 cases (137 lesion) of early gastric cancer (EGC) diagnosed during the period from 1970 to 1988. The gastrectomy specimens were obtained from Pusan National University Hospital and Pusan Paik Hospital. The statistical analysis was applied on the point of pathological and epidemiological aspects. The results obtained were summarized as follows: 1) The proportion of patients with EGC of all gastric cancer diagnosed in Pusan area during the period of 1970 to 1974 was 1.3%, those during 1975 to 1979 was 1.7%, those during 1980 to 1984 was 7.8%, and those during 1985 to 1988 was 20.0% respectively. 2) The model age group was 6th decade in both sexes. The average age of patients with EGC was 50. 1-year-old in men and 47. 9-year-old in women respectively. The sex ratio (M/F) was 2 : 1 but it was lower for young people than for old people. 3) The proportion of sites involved by the EGC in the stomach was as follows : the antrum 61%, the body 39%, and the cardia and fundus 0.01%. The intestinal type cancer more frequently involved the lower portion than the upper portion of the stomach. 4) Regarding the distribution of the gross types of EGC, the elevated group (Type I, IIa) accounted for 14%, the flat type (Type IIb) accounted for 4%, and the depressed group (Type IIc, III) accounted for 82%. There was no correlation between the gross type and the depth of the lesion. The elevated group was more frequent in intestinal type than in diffuse type. 5) The size distribution of the EGC was as follows : 46% of the lesions were smaller than 2.0 cm in diameter, 47% were between 2.1 to 5.0 cm, and 7% were larger than 5.1 cm. There was no correlation between the size of the lesion and the gross type. 6) The intestinal type of EGC was 77 lesions (56.2%) and the diffuse type 60 lesions (43.8%). The ratio of both types (I/D) was 1.3 : 1, and it was lower for younger people than for old people. 7) Ten of 135 cases (7%) had lymph node metastases. The metastatic rate of EGC confined to submucosa was much higher than that of EGC confined to mucosa only, but the metastatic rate was not related with the size of the lesion.
- Early Gastric Carcinoma with Hepatoid Differentiation: Report of a case with histotopographic analysis.
- Gyeong Hoon Kang, Chong Jai Kim, Yong Il Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(6):594-600.
- 2,096 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 56-year-old man received subtotal gastrectomy for an early gastric carcinoma type IIa+IIc with submucosal invasion. The tumor was made up of mixed papillo-tubular adenocarcinoma and solid carcinomatous portion, the latter comprising approximately four-fifths of the total tumor mass. The solid portion was confined within the submucosa and revealed a mixture of trabecular, compact and pelioid patterns of large polyhedra cells, resembling hepatocellular carcinoma of the liver(Edmondson-Steiner grade 2). Sinusoid-like vascular stroma of classical trabecular hepatocellular carcinoma intervened the tumor cell nests but was not associated with endothelial-cell lining. Immunohistochemical stainings with alpha-fetoprotein and alpha1-antitrypsin gave a strong reactivity in those areas of hepatoid differentiation and in the adjacent minute portion of adenocarcinoma. The findings suggest that a portion of gastric carcinoma may transdifferentiate into cells with hepatoid features along the line of endodermal lineage.
- Histopathologic Findings, and p53 and K-ras Mutational Analysis in Biopsy Specimens Using Fluorescence Bronchoscopy.
- Young Sik Kim, Seol Hee Park, Myung Hee Jung, Eun Chang Choi, I Yong Park, Han Kyeom Kim, Insun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(8):550-558.
- 1,881 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A fluorescence bronchoscope system has been developed for detecting early lung cancer including dysplasia and carcinoma in situ. To determine the histologic findings and genetic alterations of the lung tissues, which were biopsied by the fluorescence bronchoscope, we analyzed 104 specimens from 62 heavy smokers for their histopathology, cell proliferation index, and genetic mutations of p53 and K-ras. We used immunohistochemistry for MIB-1 and p53, and PCR-SSCP and direct DNA sequencing for p53 and K-ras. The histology was variable from reactive conditions to invasive cancers, and consisted of basal cell hyperplasia (26.9%), dysplasia (4.8%), carcinoma in situ (1.9%), squamous cell carcinoma (7.7%), adenocarcinoma (4.8%), and small cell carcinoma (10.6%). The cellular proliferation index of the lesions increased as their aggressiveness increased. p53 and K-ras mutations were detected in 33.7% and 14.4% of all tissues, respectively. In dysplasia, p53 and K-ras mutations were observed in 3 of 5 and in 2 of 5 tissues, respectively. However, these genetic alterations were not found in carcinoma in situ. Interestingly, 28.6% of basal cell hyperplasia showed p53 mutations. In conclusion, these data suggest that the biopsy specimens using fluorescence bronchoscopy show variable histologic findings, ranging from reactive conditions to invasive cancers. In addition, some of the dysplastic lesions are related to p53 and K-ras mutations, although these genetic alterations are also seen in basal cell hyperplasia.
- A Case of Gastric Inverted Hyperplastic Polyp Associated with Gastritis Cystica Profunda and Early Gastric Carcinoma.
- Min Sung Choi, So Young Jin, Dong Won Kim, Dong Wha Lee, Sang Mo Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(1):55-58.
- 2,378 View
- 40 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A gastric inverted hyperplastic polyp is characterized by downward growth of the hyperplastic mucosal components into the submucosa. Lesions are composed of hyperplastic foveolar-type glands, and sometimes coexist with gastritis cystica profunda (GCP). Adenocarcinoma frequen- tly can coexist, but the relationship is not clear. A 71-year-old male was admitted to hospital because of dyspepsia for one month. He underwent a wedge resection of the stomach, after endoscopic biopsies. The gross finding showed a slightly elevated papillary lesion with central depression. Microscopically, the elevated lesion was composed of hyperplastic fundic glands and foveolar cells, and the central depressed lesion showed a nodular inverted proliferation of normal appearing gastric epithelium and glands in the submucosa. An additional proximal gastrectomy specimen exhibited marked GCP and a minute adenocarcinoma at the proximal margin with p53 protein overexpression.

 E-submission
E-submission


 First
First Prev
Prev



