Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Significance of KM55 immunohistochemical staining in the diagnosis and prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Hoe In Jeong, Beom Jin Lim, Minsun Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):69-82. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.17
- 1,704 View
- 111 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
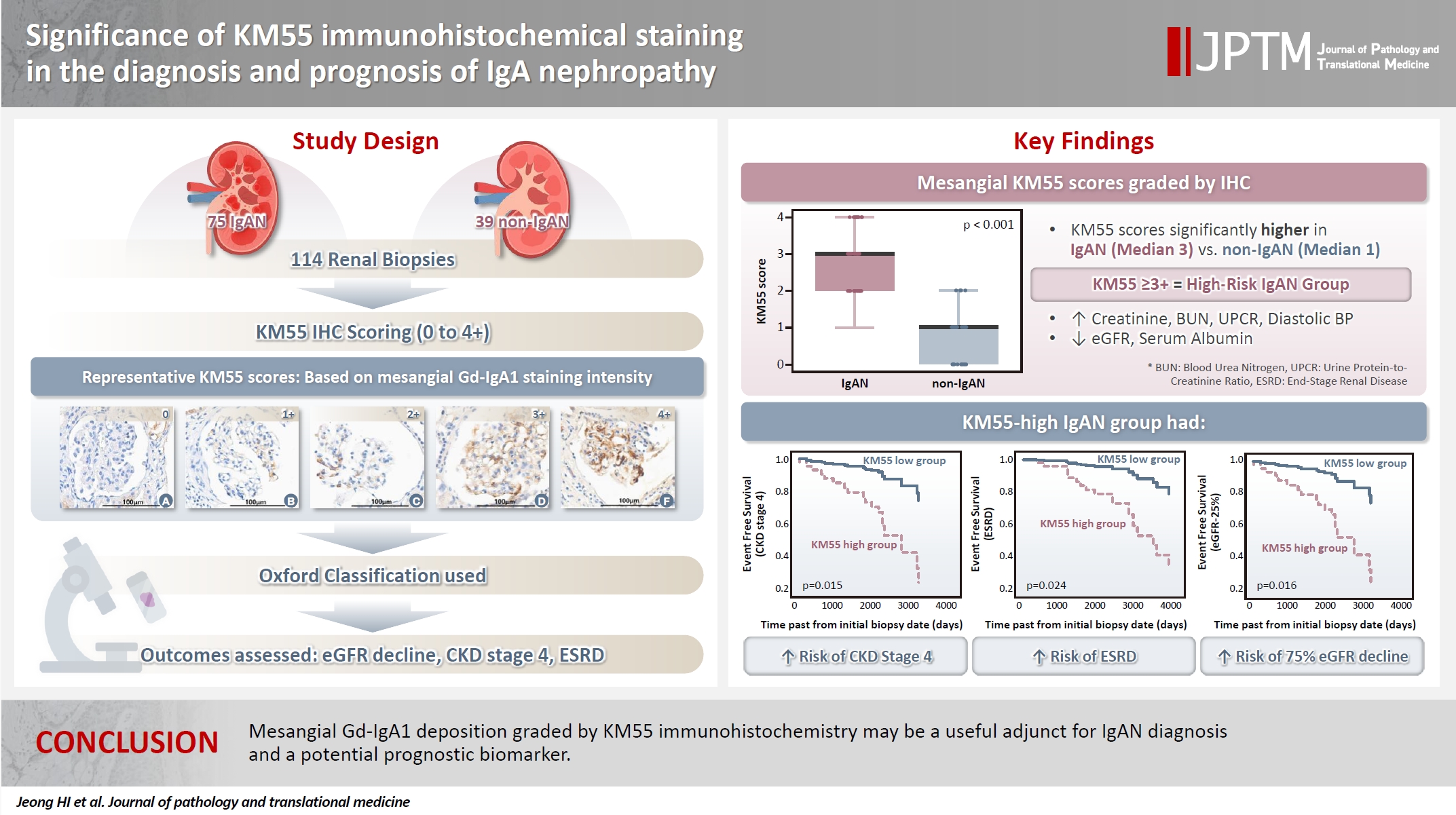
Galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) plays a crucial role in IgA nephropathy (IgAN). The monoclonal antibody KM55 has emerged as a simplified method for detecting Gd-IgA1; however, the clinicopathological significance of immunohistochemistry for Gd-IgA1 remains underexplored. This study evaluated the prognostic and clinicopathological significance of KM55 immunohistochemistry in IgAN. Methods: A total of 114 native kidney biopsies showing at least mild mesangial IgA positivity on immunofluorescence were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were categorized as having IgAN or non-IgAN diseases. The KM55 immunohistochemical staining was graded as 0, 1+, 2+, 3, or 4+. Data on Oxford classification, laboratory parameters, and renal outcomes were collected. Results: The IgAN group showed significantly higher KM55 scores than the non-IgAN group (median: 3 vs. 1; p < .001). IgAN cases were further stratified into KM55-high (≥3+, n = 38) and -low groups (≤2+, n = 37). The KM55-high group had significantly higher diastolic blood pressure, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, urine protein/creatinine ratio, and Oxford mesangial hypercellularity scores, along with lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and serum albumin. Cox analysis revealed significantly poorer outcomes in the KM55-high group for chronic kidney disease stage 4 (p = .015), end-stage renal disease (p = .024), and 75% eGFR decline (p = .016). Conclusions: Mesangial Gd-IgA1 deposition graded by KM55 immunohistochemistry may be a useful adjunct for IgAN diagnosis and a potential prognostic biomarker.
- Concurrent Anti-glomerular Basement Membrane Nephritis and IgA Nephropathy
- Kwang-Sun Suh, Song-Yi Choi, Go Eun Bae, Dae Eun Choi, Min-kyung Yeo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(6):399-402. Published online September 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.08.05
- 8,087 View
- 183 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Anti–glomerular basement membrane (GBM) nephritis is characterized by circulating anti-GBM antibodies and crescentic glomerulonephritis (GN) with deposition of IgG along the GBM. In a limited number of cases, glomerular immune complexes have been identified in anti-GBM nephritis. A 38-year-old female presented azotemia, hematuria, and proteinuria without any pulmonary symptoms. A renal biopsy showed crescentic GN with linear IgG deposition along the GBM and mesangial IgA deposition. The patient was diagnosed as concurrent anti-GBM nephritis and IgA nephropathy. Therapies with pulse methylprednisolone and cyclophosphamide administration were effective. Concurrent cases of both anti-GBM nephritis and IgA nephropathy are rare among cases of anti-GBM diseases with deposition of immune complexes. This rare case of concurrent anti-GBM nephritis and IgA nephropathy with literature review is noteworthy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The importance of the degree of foot process effacement in evaluating the prognosis of IgA nephropathy
Li Gao, Xuan Zhang, Dongrong Yu, Hong Zhu, Qin Zhu
International Urology and Nephrology.2025; 57(10): 3417. CrossRef - Coexistence of anti-glomerular basement membrane disease and IgA nephropathy: an illustrative case and comprehensive literature review
Zewei Chen, Dechao Xu, Fangzheng Cui, Huihui Hou, Zhiguo Mao, Xiang Gao
Renal Failure.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical features and prognosis of patients with anti-GBM disease combined with mesangial IgA deposition
Wei Ning, Ya-fei Zhao, Ya-ru Liu, Yuan-yuan Qi, Zhan-zheng Zhao
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Case of Concurrent Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane Antibody Disease and Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy
Su In Kim, Sung Sun Kim, Chang Seong Kim, Seong Kwon Ma, Soo Wan Kim, Hong Sang Choi
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2024; 99(6): 322. CrossRef - Anti-glomerular basement membrane vasculitis
Claudio Ponticelli, Marta Calatroni, Gabriella Moroni
Autoimmunity Reviews.2023; 22(1): 103212. CrossRef - High-frequency plasma exchange therapy for immunocompromised, type I crescentic glomerulonephritis complicated with IgA nephropathy: A case report and literature review
Huihui Chen, Jingjing Jin, Mei Juan Cheng, Lei He, Wei Zhou, Liping Guo, Zhe Zhe Niu, Xiang Nan Liang, Rong Fang Zhu, Yaling Bai, Jin Sheng Xu
Medicine.2023; 102(3): e32698. CrossRef - Clinical and immunological characteristics of patients with combined anti-glomerular basement membrane disease and IgA nephropathy
Cong-rong Shen, Xiao-yu Jia, Zhao Cui, Xiao-juan Yu, Ming-hui Zhao
Clinical Kidney Journal.2023; 16(9): 1480. CrossRef - Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease with IgA nephropathy: A case report
Chuan Guo, Ming Ye, Shen Li, Ting-Ting Zhu, Xiang-Rong Rao
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(12): 3916. CrossRef - Case Report: Coexistence of Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane Disease, Membranous Nephropathy, and IgA Nephropathy in a Female PatientWith Preserved Renal Function
Wei Qu, Nan Liu, Tianhua Xu, Binyao Tian, Meng Wang, Yanqiu Li, Jianfei Ma, Li Yao
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Great prognosis of concurrent anti-GBM disease and IgA nephropathy in a young woman: A case report
Fu Shaojie, Su Sensen, Huang Jingda, Wang Luyu, Zhang Fei, Yu Jinyu, Xu Zhonggao, Wu Hao
Medicine.2022; 101(37): e30686. CrossRef - Serodiagnosis of Anti-glomerular Basement Membrane Disease Using a Newly Developed Chemiluminescence Immunoassay
Alexander Kühnl, Lea Hartwig, Cornelia Dähnrich, Wolfgang Schlumberger
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - PATHOLOGY AND RENAL OUTCOME OF THREE UNCOMMON FACES OF CRESCENTRIC GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
Keya Basu, Dipankar Sircar, Manimoy Bandopadhyay
INDIAN JOURNAL OF APPLIED RESEARCH.2021; : 7. CrossRef - Pneumocystis pneumonia secondary to intensive immunosuppression treatment for anti-GBM disease complicated with IgA nephropathy
Manyu Zhang, Dingwei Yang, Weixiu Wang, Fuhao Zhao, Xiaoxiao Zhang, Xue Li
Medicine.2021; 100(45): e27728. CrossRef
- The importance of the degree of foot process effacement in evaluating the prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Aberrant Blood Vessel Formation Connecting the Glomerular Capillary Tuft and the Interstitium Is a Characteristic Feature of Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis-like IgA Nephropathy
- Beom Jin Lim, Min Ju Kim, Soon Won Hong, Hyeon Joo Jeong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(3):211-216. Published online April 11, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.02.01
- 10,027 View
- 75 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Segmental glomerulosclerosis without significant mesangial or endocapillary proliferation is rarely seen in IgA nephropathy (IgAN), which simulates idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). We recently recognized aberrant blood vessels running through the adhesion sites of sclerosed tufts and Bowman’s capsule in IgAN cases with mild glomerular histologic change.
Methods
To characterize aberrant blood vessels in relation to segmental sclerosis, we retrospectively reviewed the clinical and histologic features of 51 cases of FSGS-like IgAN and compared them with 51 age and gender-matched idiopathic FSGS cases.
Results
In FSGS-like IgAN, aberrant blood vessel formation was observed in 15.7% of cases, 1.0% of the total glomeruli, and 7.3% of the segmentally sclerosed glomeruli, significantly more frequently than in the idiopathic FSGS cases (p = .009). Aberrant blood vessels occasionally accompanied mild cellular proliferation surrounding penetrating neovessels. Clinically, all FSGS-like IgAN cases had hematuria; however, nephrotic range proteinuria was significantly less frequent than idiopathic FSGS.
Conclusions
Aberrant blood vessels in IgAN are related to glomerular capillary injury and may indicate abnormal repair processes in IgAN. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Twin Glomeruli: a Newly Discovered Marker of Neonephrogenesis in the Ischemia–Reperfusion Injured Adult Mouse Kidney
Hanguk Hwang, Dongju Woo, You Ri Park, Min Jung Kong, Heedong Lee, Kwon Moo Park, Yong Seok Nam, Je-Yong Choi, Sungwook Nam, Eon Jung Nam, Sun-Hee Park, Hongtae Kim, Sang Yeon Lee, Soo Ho Lee, Jeong Ok Lim, Mae Ja Park
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - IgA nephropathy
Maria F. Soares, Ian S.D. Roberts
Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension.2017; 26(3): 165. CrossRef
- Twin Glomeruli: a Newly Discovered Marker of Neonephrogenesis in the Ischemia–Reperfusion Injured Adult Mouse Kidney
- Overview of IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Its Mimickers
- Hyeon Joo Jeong, Su-Jin Shin, Beom Jin Lim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(1):26-36. Published online December 14, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.11.09
- 14,571 View
- 234 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) is the most common form of renal involvement in IgG4-related disease. It is characterized by a dominant infiltrate of IgG4-positive plasma cells in the interstitium and storiform fibrosis. Demonstration of IgG4-positive plasma cells is essential for diagnosis, but the number of IgG4-positive cells and the ratio of IgG4-positive/IgG-positive plasma cells may vary from case to case and depending on the methods of tissue sampling even in the same case. IgG4-positive plasma cells can be seen in TIN associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, or anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis, which further add diagnostic confusion and difficulties. To have a more clear view of IgG4-TIN and to delineate differential points from other TIN with IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltrates, clinical and histological features of IgG4-TIN and its mimickers were reviewed. In the rear part, cases suggesting overlap of IgG4-TIN and its mimickers and glomerulonephritis associated with IgG4-TIN were briefly described.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glycosylation in kidney diseases
Yingying Ling, Fei Cai, Tao Su, Yi Zhong, Ling Li, Bo Meng, Guisen Li, Meng Gong, Hao Yang, Xinfang Xie, Zhenyu Sun, Yang Zhao, Fang Liu, Yong Zhang
Precision Clinical Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - IgG4-related kidney disease: Clinicopathologic features, differential diagnosis, and mimics
Sarwat I. Gilani, Alessia Buglioni, Lynn D. Cornell
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2024; 41(2): 88. CrossRef - Utilizing Immunoglobulin G4 Immunohistochemistry for Risk Stratification in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Associated with Hashimoto Thyroiditis
Faridul Haq, Gyeongsin Park, Sora Jeon, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(3): 468. CrossRef - IgG4-assoziierte Nierenerkrankungen
Christina Thompson, Frank O. Henes, Oliver M. Steinmetz, Simon Melderis
Die Nephrologie.2023; 18(4): 249. CrossRef - Concurrent anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated glomerulonephritis and IgG4-associated tubulointerstitial nephritis with C3 glomerulonephritis
Jianan Feng, Jinyu Yu, Xueyao Wang, Yue Wang, Yang Liu, Zhonggao Xu, Weixia Sun
Medicine.2020; 99(5): e18857. CrossRef - A case of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis as a mimicker of IgG4-related disease
Ryuichiro Kanda, Satoshi Kubo, Kazuhisa Nakano, Akio Kawabe, Aya Nawata, Kentaro Hanami, Shingo Nakayamada, Yoshiya Tanaka
Modern Rheumatology Case Reports.2020; 4(2): 278. CrossRef - Renal tubular acidosis as the initial presentation of Sjögren’s syndrome
Karen Ho, Pouneh Dokouhaki, Mark McIsaac, Bhanu Prasad
BMJ Case Reports.2019; 12(8): e230402. CrossRef - Hypocomplementemic interstitial nephritis with long-term follow-up
Alyssa Penning, Claire Kassakian, Donald C Houghton, Nicole K Andeen
Journal of Clinical Nephrology.2019; 3(1): 042. CrossRef - Immunoglobulin G4-related kidney diseases: An updated review
Maurizio Salvadori, Aris Tsalouchos
World Journal of Nephrology.2018; 7(1): 29. CrossRef - Systemic lupus erythematosus in a patient with an organic lesion of the central nervous system: practicaldifferential diagnosis
E. V. Lebedeva, M. V. Novoseltsev, A. N. Lvov, I. V. Khamaganova
Klinicheskaya dermatologiya i venerologiya.2018; 17(6): 21. CrossRef - Concurrent IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis and IgG4 myeloperoxidase-anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody positive crescentic glomerulonephritis
Tao Su, Li Yang, Zhao Cui, Su-xia Wang, Ming-hui Zhao
Medicine.2017; 96(20): e6707. CrossRef - IgG4-Related Kidney Disease: Report of a Case Presenting as a Renal Mass
Daniele Bianchi, Luca Topazio, Gabriele Gaziev, Valerio Iacovelli, Pierluigi Bove, Alessandro Mauriello, Enrico Finazzi Agrò
Case Reports in Surgery.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef
- Glycosylation in kidney diseases
- Clinicopathologic Features of IgA-Dominant Postinfectious Glomerulonephritis
- Tai Yeon Koo, Gheun-Ho Kim, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(2):105-114. Published online April 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.2.105
- 14,415 View
- 126 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background IgA-dominant acute postinfectious glomerulonephritis (APIGN) is a recently recognized morphologic variant of APIGN, but its clinicopathologic features were not clearly characterized. We will present demographic, clinical and renal biopsy findings from seven patients with IgA-dominant APIGN with a literature review.
Methods All renal biopsy specimens (n=1,119) processed by the Department of Pathology in Hanyang University Hospital from 2005 to 2009 were reviewed. Seven patients with IgA-dominant APIGN were identified, and their clinical data analyzed.
Results All patients had renal failure, hematuria and proteinuria. One was diabetic, and none of the patients had previous renal diseases. Three had clinical infections at the time of presentation: 2 with methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus and one with rickettsial infection. Light microscopically diffuse endocapillary proliferative and exudative glomerulonephritis was found in all cases. Immunofluorescence microscopy showed granular IgA deposits along peripheral capillary walls and in mesangium. Ultrastructurally, subepithelial 'humps' with mesangial deposits were noted. End-stage renal disease developed in two patients, chronic renal failure was stationary in two, and azotemia improved in three.Conclusions Various infections including rickettsiosis preceded IgA-dominant APIGN in both diabetics and nondiabetics. Because the prognosis of IgA-dominant APIGN is poor, early diagnosis based on renal biopsy is required.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Staphylococcus aureus Infection-Related Glomerulonephritis with Dominant IgA Deposition
Mamiko Takayasu, Kouichi Hirayama, Homare Shimohata, Masaki Kobayashi, Akio Koyama
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(13): 7482. CrossRef - A rare case of Immunoglobulin A dominant post-infectious glomerulonephritis (IgA PIGN) in a young patient
A. Saghar, G. Klaus, B. Trutnau, M. Kömhoff, H. J. Gröne, S. Weber
BMC Nephrology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - IgA-Dominant Infection-Associated Glomerulonephritis Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Aurora Pérez, Isidro Torregrosa, Luis D’Marco, Isabel Juan, Liria Terradez, Miguel Ángel Solís, Francesc Moncho, Carmen Carda-Batalla, María J. Forner, Jose Luis Gorriz
Viruses.2021; 13(4): 587. CrossRef - Relationship between blood neutrophil‐lymphocyte ratio and renal tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis in IgA nephropathy patients
Lingxiong Chai, Kedan Cai, Kaiyue Wang, Qun Luo
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Continuing Need for Electron Microscopy in Examination of Medical Renal Biopsies: Examples in Practice
Michifumi Yamashita, Mercury Y. Lin, Jean Hou, Kevin Y.M. Ren, Mark Haas
Glomerular Diseases.2021; 1(3): 145. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic features of infection-related glomerulonephritis with IgA deposits: a French Nationwide study
Elodie Miquelestorena-Standley, Charlotte Jaulerry, Marie-Christine Machet, Nolwenn Rabot, Christelle Barbet, Aurélie Hummel, Alexandre Karras, Cyril Garrouste, Thomas Crepin, Didier Ducloux, Maud Cousin, Catherine Albert, Joseph Rivalan, Emilie Cornec-Le
Diagnostic Pathology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - IgA nephropathy and infections
Cristiana Rollino, Gisella Vischini, Rosanna Coppo
Journal of Nephrology.2016; 29(4): 463. CrossRef - <i>Staphylococcus</i>-associated Glomerulonephritis
Dong Yeol Shin, Sung Han Kim, Ji Wan Lee, Ki Ju Chang, Seung Ha Hwang, Yong Mee Cho, Soon Bae Kim
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2016; 90(2): 148. CrossRef - Use of steroid therapy in immunoglobulin A-dominant poststaphylococcal glomerulonephritis
Mahesh Eswarappa, Vijay Varma, K.C. Gurudev
Hong Kong Journal of Nephrology.2015; 17(2): 46. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic Features of IgA-Dominant Infection-Associated Glomerulonephritis: A Pooled Analysis of 78 Cases
Ru Bu, Qian Li, Zhi-yu Duan, Jie Wu, Pu Chen, Xiang-mei Chen, Guang-yan Cai
American Journal of Nephrology.2015; 41(2): 98. CrossRef - Garland-pattern postinfectious glomerulonephritis with IgA-dominant deposition
Makoto Kanno, Kenichi Tanaka, Hiroshi Kimura, Kimio Watanabe, Yoshimitsu Hayashi, Koichi Asahi, Masaaki Nakayama, Kensuke Joh, Tsuyoshi Watanabe
CEN Case Reports.2014; 3(1): 56. CrossRef
- Staphylococcus aureus Infection-Related Glomerulonephritis with Dominant IgA Deposition
- Podocyte Expression of Osteopontin and FSP-1/S100A4 in Human Crescentic Glomerulonephritis.
- Ghil Suk Yoon, Tae Sook Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(3):237-246.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.3.237
- 3,956 View
- 35 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Osteopontin (OPN) is a cytokine associated with a cell-matrix via integrins. Fibroblast specific protein-1 (FSP-1), known as S100A4, has been implicated in cell migration by non-muscle myosin. We investigated whether the role of OPN and FSP-1/S100A4 expression in their contribution to the podocyte phenotype change to form podocyte bridge and cellular crescent.
METHODS
Glomerular expression of OPN and FSP-1/S100A4 in renal biopsies of 16 patients with crescentic glomerulonephritis (CrGN) and 13 normal renal biopsies were studied by immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS
The expression of OPN and FSP-1/S100A4 was increased in the podocytes of glomeruli, with and without crescents, in patients with CrGN. Neither OPN nor FSP-1/S100A4 was expressed in glomeruli from the normal controls (p<0.01). A significant positive correlation was found between the expression of OPN in glomerular tufts and cellular crescents, and the expression of OPN and FSP-1/S100A4 in glomerular tufts (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The results suggest that OPN plays a role in early podocyte attachment to Bowman's capsule, and FSP-1/S100A4 potentiate podocyte contribution to cellular crescent formation by inducing cellular migration and growth.
- C1q Nephropathy: A Distinct Pathologic Entity.
- Jung Ha Shin, Tae Eun Kim, Kyo Young Lee, Sang In Shim, Yeong Jin Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(4):335-341.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.4.335
- 3,633 View
- 44 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
C1q nephropathy (C1qN) is a controversial diagnostic entity defined by Jennette and Hipp in 1985. The prevalence is very low and a few large scale studies have been reported. Application of the criteria for clinical diagnostics of C1qN may cause confusion with other glomerulonephropathies, such as minimal change disease (MCD) or focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). In order to clarify the confusion with glomerulonephropathies, we did this study to identify the clinicopathological characteristics and the exact disease entity of C1qN.
METHODS
A total of 5,258 kidney biopsies at Kangnam St Mary's Hospital were reviewed. Twenty three cases (0.44%) met the criteria of C1qN. Twenty eight cases showing dominant C1q deposits without electron dense depostis (EDD) grouped as C1q+EDD-, and previously diagnosed typical cases of MCD and FSGS were selected for this study. Four groups were compared to each other with regard to the clinical and pathological aspects of the disease. RESULTS: C1qN patients had an average age of 30.4 years. Eighteen were males and 5 were females. Eighty seven percent had proteinuria and 18% had hematuria. By electron microscopy analysis, 100% had mesangial EDD and 47.8% showed foot process effacement. C1qN had some significant differences compared with C1q+EDD-, MCD and FSGS. CONCLUSIONS: C1qN is clinically and morphologically different from MCD and FSGS. However, additional long term studies are needed to fully define C1qN from other glomerulonephritis with C1q deposits.
- Sequential Studies of Glomerular Crescent Formation in Rabbits with Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane(GBM) Antibody Induced Glomerulonephritis(GN).
- Hye Seon Ahn, Jung Woo Noh, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(3):219-232.
- 2,030 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To investigate the mechanism of crescent formation, sequential pathologic changes from the New Zealand White rabbits with anti-GBM antibody induced GN by administration of guinea pig anti-GBM IgG were studied by light (LM), immunofluorescent (IF) and electron (EM) microscopy. Although no glomerular changes were observed in LM, swelling of the endothelial cells and the epithelial cells were noted in EM by day 2. By day 7, early and cellular crescents were evident. Proteinaceous materials and fibrins were noted in the glomerular capillary lumina (GCL) and Bowman's space (BS) associated with segmental hypercellularity. The GBM damage became progressively severe, followed by focal detachment of the visceral epithelial cells from the GBM. At day 14, fibrin strands, mononuclear cells and collagen fibrils were present between the proliferating extracapillary cells. At day 31, fibrocellular crescents were predominated. Elongated spindle cells, morphologically resembling myofibroblasts, were noted near the Bowman's capsule (BC). A degree of tubular atrophy, interstitial fibrosis, and inflammatory infiltrates increased as it did with fibrous organization of crescent. Intense linear IF staining for IgG and C3 were seen throughout the experiments along the GBM. In conclusion, the progression of crescent from an early "proteinaceous" stage through cellular, fibrocellular and fibrous stages was well documented in this study. Inflammatory cells and coagulation mechanism may activate the initiation of the GBM damage at the early stage. Activated periglomerular mononuclear cells may also cause disruption of BC which facilitates entry of activated periglomerular cells and fibroblasts into BS leading to progressive fibrous crescent formation.
- Acute Renal Failure Associated with Gross Hematuria in a Patient with Focal Glomerulonephritis.
- Hee Jung Kim, Hyeon Joo Jeong, Dae Suk Han
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(3):263-268.
- 2,151 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 58-year-old female with an episode of gross hematuria two months before and fever and chill for the past three days presented oliguric acute renal failure. She has taken NSAID intermittently for 18 years due to rheumatoid arthritis, and herb medicine for one week two months ago when gross hematuria developed. Physical examination revealed mild tenderness on costovertebral angles. Her blood pressure was 170/100 mmHg, the urinalysis showed >300 mg protein with many RBCs and 10-20 WBCs and the serum creatinine was 5.8 mg/dl. A renal biopsy performed on the 4th hospital day showed that it was overwhelmed by severe tubular lesions which reveal intratubular obstruction by massive erythrocyte casts and tubular necrosis. The glomeruli showed focal minimal crescents with many red blood cells entrapped in the crescents and in the capillaries. Immune deposits were not present. A renal failure resolved spontaneously and the patient was discharged three weeks later with creatinine of 2.4 mg/dl. In this patient, acute renal failure was considered to be due to a tubular lesion related to the glomerular bleeding from focal glomerulonephritis revealing minimal crescents.
- The Role of MIB-1 Expression and Apoptosis in Experimental Crescentic Glomerulonephritis.
- Nam Hoon Kim, Wan Seop Kim, Jung Woo Noh, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(4):231-242.
- 2,097 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It has been postulated that programmed cell death via apoptosis may be critical for remodelling of glomeruli after inflammatory injury. To understand the regulatory mechanism of apoptosis in experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis (CGN), we examined the MIB-1 score (proliferation index, PI) and apoptotic index during the progression of experimental CGN to end-stage renal failure. CGN was induced in New Zealand White rabbits by administration of guinea pig anti-GBM IgG after sensitization with guinea pig IgG and their kidneys were analyzed for the development of crescents through sequential renal biopsies. Serum creatinine levels progressively increased in a time course until day 45. The PI in glomeruli, tubular epithelial cells, and interstitium progressively increased during the progression of experimental CGN. The mean numbers of MIB-1 positive intraglomerular nuclei (PI) were significantly correlated with degrees of crescent formation and the numbers of apoptotic cells in the glomeruli, tubules, and interstitium. Significant apoptosis was present from day 1 (15.8 10.16 cells/glomerular cross section) and increased in number with the proliferative lesions as glomerular inflammation continued. Moreover, apoptosis increased during the resolution of the glomerular inflammation, and many apoptotic cells were present in the sclerotic lesions in day 17 (18.6 12.99 cells/glomerular cross section). As glomerular inflammation subsided, cellular crescents progressed to fibrous crescents with a reduction of cellularity by day 45. On day 45, the glomerular PI and the numbers of apoptotic cells were markedly decreased. The correlations found in CGN between the creatinine level and the percentage of crescents, between the percentage of crescent and PI, and between the PI and number of apoptotic cells support the hypothesis that there is a change in the glomerular and tubulo-interstitial apoptosis under pathologic conditions. These findings indicate that apoptosis plays an essential role in the resolution of intra- and extraglomerular inflammation and in the elimination of glomerular cells within the sclerotic regions for progressive CGN. The regulation of the apoptotic phenomenon and increased PI during CGN may be important in the progression of glomerular inflammation and the development of pathologic glomerular sclerosis.
- Image Analysis of Glomerular Changes in Patients with Post-transplant IgA Nephropathy.
- Kye Won Kwon, Hyeon Joo Jeong
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(3):206-211.
- 2,058 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
IgA nephropathy after renal transplantation (post-transplant IgAN) may recapitulate the IgAN of native kidneys, however, little has been reported about the histologic characteristics. The aim of this study is to apply glomerular morphometry using an image analyser to examine the histologic characteristics of post-transplant IgAN.
METHODS
The outer margin of the glomerulus (Bowman's area, BA) and glomerular tuft area (GA) were traced manually. The measured area were automatically calculated by KS300 image analysis system (Kontron, Munchen, Germany). The mesangial area (MA) was calculated with a summing each manually traced mesangial area. The total number of glomerular (GC) and mesangial cells (MC) were counted. Eight cases of renal section obtained by nephrectomy due to renal cell carcinoma (normal control: N-CTRL) and nineteen cases of renal section obtained from post-transplantation patients without IgAN (transplantation control: Tx-CTRL) served as controls.
RESULTS
A total of 35 biopsies were finally selected for measurement. BA and GA of post-transplant IgAN were 1.6 and 1.4 times larger than the N-CTRL, respectively, and were not significantly different from Tx-CTRL. MA was 1.4 times significantly larger than that of the Tx-CTRL. As compared to that of the N-CTRL, it was 1.2 times larger, but this difference was not statistically significant. The GC and MC of post-transplant IgAN and the Tx-CTRL were significantly lower than the N-CTRL. There were no significant correlations between glomerular hypertrophy and duration after renal transplantation, mesangial changes, segmental sclerosis, or degree of renal cortical interstitial fibrosis in post-transplant IgAN.
CONCLUSIONS
Prominent glomerular hypertrophy and mesangial expansion suggest a hyperfiltration injury in post-transplant IgAN and a possible way to glomerulosclerosis.
- Combined IgA Nephropathy and Membranous Glomerulonephritis : A Report of Six Cases.
- Ji Han Jung, Yeong Jin Choi, Yong Soo Kim, Yoon Sik Chang, Byung Kee Bang, Sang In Shim, Chang Suk Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(4):278-283.
- 3,309 View
- 82 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - IgA nephropathy (IgAN) and membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN) are common in adults. However, it is unlikely that these two distinct glomerulonephrites coexist in a renal biopsy. Here, we report clinical and pathological data of six patients with concomitant existence of IgAN and MGN in renal biopsy specimens from 1990 to 2004. Five patients were male and one was female, and their ages ranged from 29 to 71 years. Four patients had microscopic hematuria, five had nephrotic range proteinuria, three had hepatitis B virus infections, three had rheumatoid factors, one had antinuclear antibodies. Two cases were developed after kidney transplant. Immunofluorescence microscopy showed characteristic findings of mesangial IgA deposits and granular IgG deposits on the capillary walls. These were confirmed by electron microscopic findings of immune-type electron-dense deposits in the mesangium and subepithelial capillary basement membranes. The pathogenesis and prognosis of the patients are discussed in this report.
- Immunohistochemical Study on Expression of Extracellular Matrix Components in Glomerular Diseases.
- Sun Hee Sung, In Joon Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(3):288-296.
- 2,016 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Most glomerular lesions are associated with qualitative and quantitative alterations of the extracellular matrix components, having relation to progressive glomerular sclerosis. We aimed to investigate the characteristic alteraltions in distribution of extracellular matrix components, such as fibronectin, laminin, collagen type III and IV in human glomerular diseases by immunohistochemical method. The materials included are 3 nephrectomy as normal control, 51 renal biopsies and I autopsy; 3 normal, 5 minimal change disease, 5 minimal change disease with minimal mesangial lgA deposit, 5 benign recurrent hematuria, 10 focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, 15 lgA nephropathy, 10 membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, 2 diffuse mesangial sclerosis of infancy. Type IV collagen and laminin were present normally in the mesangium, GBM, TBM and interstitial vessels, and were increased at the portion of increased mesangial matrix, of sclerosis and thickened GBM in cases of lgA nephropathy, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, focal segmental glomrulosclerosis and diffuse mesangial sclerosis in the proportion to the glomerular damage. Type III collagen was absent in the normal glomeruli, but was detectable focally and segmentally in cases of membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, IgA nephropathy and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis at the sclerotic portion. Fibronectin was normally detectable mainly in the mesangium, and partly and incompletely in GBM, and was increased at the portion of increased mesangial matrix, sclerosis and thickened GBM in cases of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, IgA nephropathy and diffuse mesangial sclerosis, but was diminshed at the old slcerotic portion or global sclerosis. The expression of these antibodies in cases of minimal change disease, minimal change disease with minimal mesangial IgA deposit, benign recurrent hematuria was not different, quantitatively and qualitatively, from that of normal glomeruli. These findings suggest that progressive glomerular sclerosis was due to the increase of extraceuular matrix components such as type IV collagen, laminin, fibronectin and new appearance of type III collagen, and the expression was in proportion to the degree of sclerosis, but had no relation to the disease entity.
- Expression of Adhesion Molecules in IgA Nephropathy, Diffuse Crescentic Glomerulonephritis, and Minimal Change Disease.
- Kyoung Cheol Moon, So Yeon Park, Hwal Woong Kim, Hyun Soon Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(5):331-340.
- 2,071 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Accumulation of leukocytes within the glomerulus is a key event in the pathogenesis of glomerulonephritis. This process is mediated by pairs of adhesion molecules. We have examined the expression pattern of selectins (E and P), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in 30 renal biopsies with IgA nephropathy, diffuse crescentic glomerulonephritis, and minimal change disease. Normal controls were obtained from four nephrectomy specimens with renal cell carcinoma. ICAM-1 expression was significantly increased in the glomerular endothelial and mesangial cells in cases with IgA nephropathy compared with normal controls. VCAM-1 was expressed in glomerular mesangial cells in all cases with IgA nephropathy and diffuse crescentic glomerulonephritis, but faintly expressed in 3 cases with minimal change disease and not expressed in normal controls. P-selectin was faintly expressed in the glomeruli in cases with IgA nephropathy and diffuse crescentic glomerulonephritis. E-selectin was only expressed in the vascular endothelium in one case with IgA nephropathy and in the other with diffuse crescentic glomerulonephritis. ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 were strongly expressed in the crescents. However, selectin was not expressed in the crescent. These results suggest that adhesion molecules, particularly ICAM-1 and VCAM-1, play an important role in the pathogenesis of glomerular damage and crescent formation in primary glomerular diseases.
- Crescentic Glomerulonephritis in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A case report.
- Ki Ouk Min, Yeong Jin Choi, Byoung Kee Kim, Sun Moo Kim, Sang In Shim
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(1):116-118.
- 2,073 View
- 27 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Crescentic glomerulonephritis in rheumatoid arthritis is described recently with increasing frequency. It can occur directly as a manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis or may be a reaction to drugs such as D-penicillamine and bucillamine. We report a case of crescentic glomerulonephritis in a 46-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis for 20 years who had been treated intermittently with herb medicine or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS). Light microscopic examination showed severe focal segmental and global necrotizing glomerulonephritis with crescent formation in 50% of the glomeruli. Immunofluorescent study revealed scanty amount of mesangial granular deposits of IgA, IgM, C3 and fibrinogen in a diffuse pattern.

 E-submission
E-submission


 First
First Prev
Prev



