Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Low Ki-67 labeling index is a clinically useful predictive factor for recurrence-free survival in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Takashi Masui, Katsunari Yane, Ichiro Ota, Kennichi Kakudo, Tomoko Wakasa, Satoru Koike, Hirotaka Kinugawa, Ryuji Yasumatsu, Tadashi Kitahara
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):115-124. Published online February 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.08
- 5,157 View
- 240 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
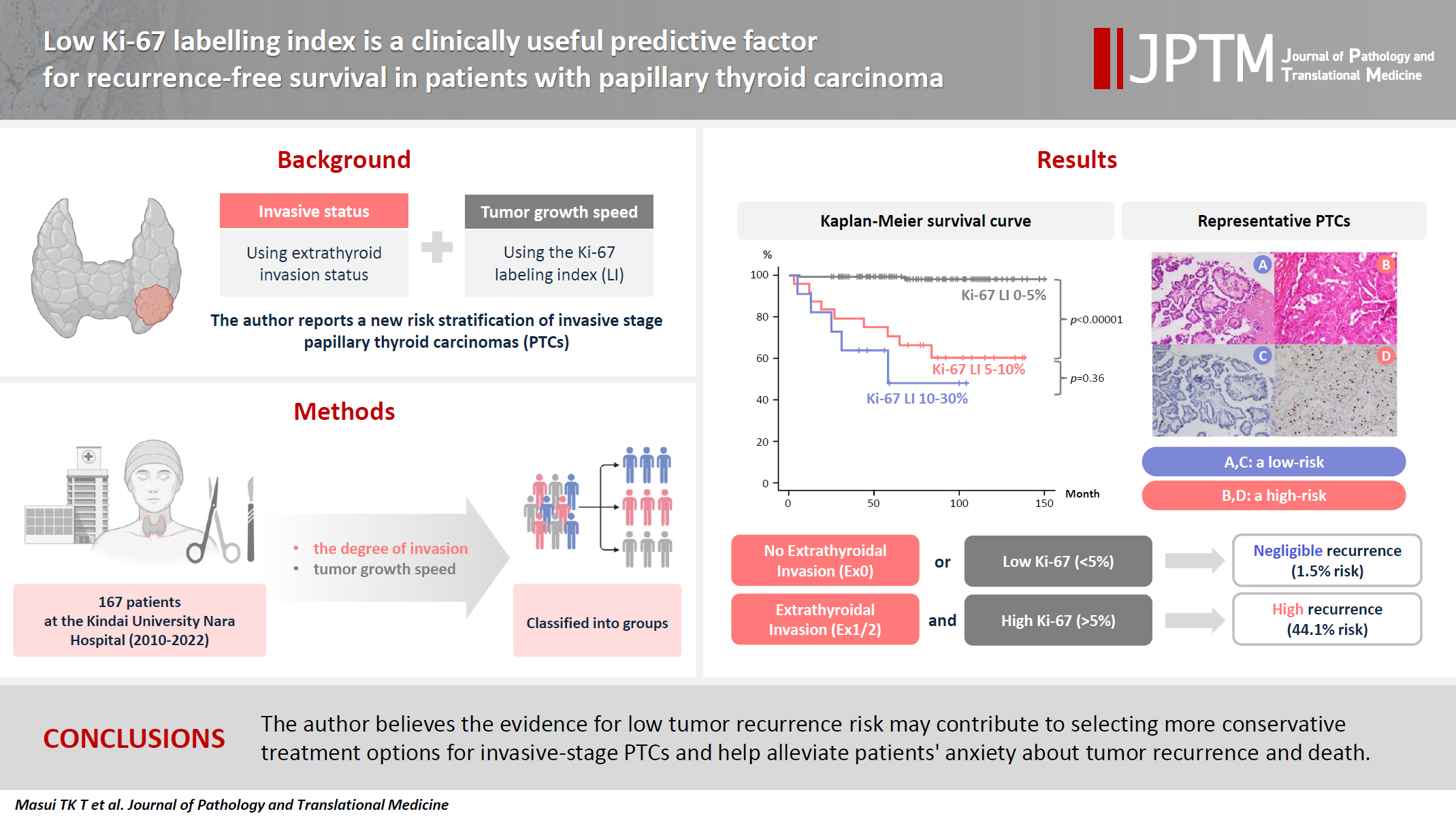
We report a new risk stratification of invasive stage papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs) by combining invasive status, using extrathyroid invasion (Ex) status, and tumor growth speed using the Ki-67 labeling index (LI). Methods: We examined tumor recurrence in 167 patients with PTC who were surgically treated at the Kindai University Nara Hospital between 2010 and 2022. The patients were classified according to the degree of invasion [negative (Ex0) or positive (Ex1, Ex2, and Ex3)] and tumor growth speed expressed with Ki-67 LI, as low (<5%) or high (>5%). This study confirmed previous findings that the disease-free survival (DFS) rate in PTCs significantly differed between patients with a high and low Ki-67 index. Results: When combining Ex status (negative or positive) and Ki-67 proliferation status (low or high), the DFS rate of invasion in the negative, low Ki-67 LI group was only 1.1%, while that of invasion in the positive, high Ki-67 LI was 44.1%. This study reports for the first time that recurrence risks can be stratified accurately when combining carcinoma’s essential two features of extrathyroid invasion status and tumor growth speed. Conclusions: We believe the evidence for low tumor recurrence risk may contribute to use of more conservative treatment options for invasive-stage PTCs and help alleviate patient anxiety about tumor recurrence and death. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress on the Correlation between Three Biomarkers, Ki-67, CAIX and VEGF and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
锦容 马
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2025; 15(09): 326. CrossRef - Immunophenotypic Panel for Comprehensive Characterization of Aggressive Thyroid Carcinomas
Mihail Ceausu, Mihai Alin Publik, Dana Terzea, Carmen Adina Cristea, Dumitru Ioachim, Dana Manda, Sorina Schipor
Cells.2025; 14(19): 1554. CrossRef - High Ki-67 labeling index correlates with aggressive clinicopathological features in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective study
Defi Nurlia Erdian, Maria Francisca Ham, Dina Khoirunnisa, Agnes Stephanie Harahap
Thyroid Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research Progress on the Correlation between Three Biomarkers, Ki-67, CAIX and VEGF and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Review
- Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):265-282. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.11
- 13,756 View
- 593 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the most common thyroid malignancy, characterized by a range of subtypes that differ in their cytologic features, clinical behavior, and prognosis. Accurate cytologic evaluation of PTC using fine-needle aspiration is essential but can be challenging due to the morphologic diversity among subtypes. This review focuses on the distinct cytologic characteristics of various PTC subtypes, including the classic type, follicular variant, tall cell, columnar cell, hobnail, diffuse sclerosing, Warthin-like, solid/trabecular, and oncocytic PTCs. Each subtype demonstrates unique nuclear features, architectural patterns, and background elements essential for diagnosis and differentiation from other thyroid lesions. Recognizing these distinct cytologic patterns is essential for identifying aggressive subtypes like tall cell, hobnail, and columnar cell PTCs, which have a higher risk of recurrence, metastasis, and poorer clinical outcomes. Additionally, rare subtypes such as diffuse sclerosing and Warthin-like PTCs present unique cytologic profiles that must be carefully interpreted to avoid diagnostic errors. The review also highlights the cytologic indicators of lymph node metastasis and high-grade features, such as differentiated high-grade thyroid carcinoma. The integration of molecular testing can further refine subtype diagnosis by identifying specific genetic mutations. A thorough understanding of these subtype-specific cytologic features and molecular profiles is vital for accurate diagnosis, risk stratification, and personalized management of PTC patients. Future improvements in diagnostic techniques and standardization are needed to enhance cytologic evaluation and clinical decision-making in thyroid cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
Adeel M. Ashraf, Faisal Hassan, Adrian A. Dawkins, Julie C. Dueber, Derek B. Allison, Thèrése J. Bocklage
Cytopathology.2026; 37(1): 108. CrossRef - Using a new type of visible light-based emission fluorescence microscope to identify the benign and malignant nature of thyroid tissue during the surgical process: Analysis of diagnostic results
Yu Miao, Liu Xiaowei, Li Muyang, Gao Jian, Chen Lu
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2026; 57: 105324. CrossRef - Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Dina Khoirunnisa, Salinah, Maria Francisca Ham
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 75: 152434. CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shin Je Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyo
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - Structure-based molecular screening and dynamic simulation of phytocompounds targeting VEGFR-2: a novel therapeutic approach for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Shuai Wang, Lingqian Zhang, Wenjun Zhang, Xiong Zeng, Jie Mei, Weidong Xiao, Lijie Yang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shinje Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(3): 307. CrossRef - A Case of Warthin-Like Variant of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Amy Chow, Israa Laklouk
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Propensity score-matched analysis of the ‘2+2’ parathyroid strategy in total thyroidectomy with central neck dissection
Hao Gong, Simei Yao, Tianyuchen Jiang, Yi Yang, Yuhan Jiang, Zhujuan Wu, Anping Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
Original Article
- Expression of Raf-1 Kinase Inhibitory Protein in Extrahepatic Bile Duct Carcinoma.
- Hyun Soo Kim, Gou Young Kim, Sung Jig Lim, Youn Wha Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(3):234-242.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.3.234
- 4,601 View
- 21 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP) recently has been identified as a metastasis suppressor in a variety of human carcinomas. The prognostic significance of RKIP expression in extrahepatic bile duct (EBD) carcinoma has not been studied. The aims of the current study were to evaluate RKIP expression and to determine the prognostic significance of RKIP expression in EBD carcinoma.
METHODS
Immunohistochemical staining for RKIP was performed for 131 cases of EBD carcinoma. The associations of RKIP expression with clinicopathologic parameters and patient outcomes were examined. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify independent predictive parameters for lymphovascular invasion and nodal and distant metastases.
RESULTS
Loss of RKIP expression was observed in 55.0% (72/131) of cases. EBD carcinoma had significantly lower RKIP immunoreactivity than normal EBD (p < 0.001). Loss of RKIP expression was significantly associated with lymphatic invasion (p = 0.030) and nodal metastasis (p = 0.036), but it was not found to be a significant prognostic predictor for overall, disease-free or distant metastasis-free survival. In addition, loss of RKIP expression was an independent predictor for lymphatic invasion (p = 0.027).
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggest that RKIP may play a role in the suppression of lymphatic invasion and nodal metastasis in EBD carcinoma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Down-regulation of osteoprotegerin expression as a novel biomarker for colorectal carcinoma
Hyun-Soo Kim, Gun Yoon, Sung-Im Do, Sung-Joo Kim, Youn-Wha Kim
Oncotarget.2016; 7(12): 15187. CrossRef - Expression of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase at the invasive front of hepatic colorectal metastasis
HYUN-SOO KIM, SUNG-IM DO, BYEONG-JOO NOH, YOUNG IN JEONG, SUN JIN PARK, YOUN WHA KIM
Oncology Letters.2015; 9(3): 1261. CrossRef - Reduced expression of Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein predicts regional lymph node metastasis and shorter survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Hyun-Soo Kim, Kyu Yeoun Won, Gou Young Kim, Soo Cheol Kim, Yong-Koo Park, Youn Wha Kim
Pathology - Research and Practice.2012; 208(5): 292. CrossRef - Expression of Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein in carcinoma of the ampulla of Vater
Hyun-Soo Kim, Sun Ho Lee, Kyu Yeoun Won, Gou Young Kim, Yong-Koo Park, Youn Wha Kim
Virchows Archiv.2012; 460(1): 61. CrossRef - Raf-1 Kinase Inhibitory Protein Expression in Thyroid Carcinomas
Hyun-Soo Kim, Gou Young Kim, Sung-Jig Lim, Youn Wha Kim
Endocrine Pathology.2010; 21(4): 253. CrossRef - Loss of Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Hyun-Soo Kim, Gou Young Kim, Sung-Jig Lim, Youn Wha Kim
Pathology.2010; 42(7): 655. CrossRef
- Down-regulation of osteoprotegerin expression as a novel biomarker for colorectal carcinoma
Case Report
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Metastatic Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma Misinterpreted as Carcinoma: A Case Report.
- Hyun Jung Kim, Sung Jik Lim, Kyeongmee Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2005;16(1):52-56.
- 2,109 View
- 34 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fine-needle aspiration cytology(FNAC) has been used extensively in the diagnosis of metastatic malignancies. However, metastatic soft tissue sarcomas are often overlooked, primarily due to the low frequency with which they occur. Here, we report a rare case of metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma in both cervical lymph nodes, which was detected by FNAC. A 45-year-old woman presented with anosmia, postnasal drip, and sneezing, symptoms which had persisted for 1 month. The patient was found to have a tumorous lesion at the upper portion of the mid-turbinate, with multiple enlarged cervical lymph nodes, and this lesion was examined closely at our facility. FNA cytology smears obtained from both cervical lymph nodes revealed a high degree of cellularity, and displayed cohesive clusters with gland-like spaces, as well as single isolated cells with abundant karyorrhectic debris. The tumor cells exhibited round to oval nuclei containing fine chromatin, occasional small nucleoli, and scanty cytoplasm, or a total lack of cytoplasm. Some of the tumor cells were arranged in multinucleated forms and abundant dense eosinophilic cytoplasms, reminiscent of a rhabdomyoblast. The histological findings of the lymph nodes revealed an outstanding sinusoidal infiltration and a prominent alveolar growth pattern, interspersed with occasional typical rhabdomyoblasts. The immunohistochemical results [desmin(+), myoglobin(+), myogenin (+), pan CK(-), synaptophysin(-), neuron specific enolase(-)] supported a confirmative diagnosis of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is a representative sarcoma, which typically manifests with nodal metastasis and carcinoma-like clustering. The cytopathologist should remain alert upon encountering unusual morphology, so that the possibility of this condition, although somewhat remote, should not be dismissed or overlooked.

 E-submission
E-submission


 First
First Prev
Prev



