Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Study
- Morule-like features in pulmonary adenocarcinoma associated with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: two case reports with targeted next-generation sequencing analysis
- Yoo Jin Lee, Harim Oh, Eojin Kim, Bokyung Ahn, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Youngseok Lee, Yang Seok Chae, Chul Hwan Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):119-122. Published online November 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.09.30
- 6,546 View
- 137 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
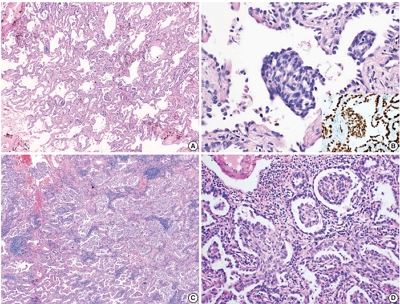
PDF - Morules, or morule-like features, can be identified in benign and malignant lesions in various organs. Morular features are unusual in pulmonary adenocarcinoma cases with only 26 cases reported to date. Here, we describe two cases of pulmonary adenocarcinoma with morule-like features in Korean women. One patient had a non-mucinous-type adenocarcinoma in situ and the other had an acinarpredominant adenocarcinoma with a micropapillary component. Both patients showed multiple intra-alveolar, nodular, whorled proliferative foci composed of atypical spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm. Targeted next-generation sequencing was performed on DNA extracted from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples of the tumors. Results showed unusual epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, which are associated with drug resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, revealing the importance of identifying morule-like features in pulmonary adenocarcinoma and the need for additional study, since there are few reported cases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pulmonary adenocarcinoma in situ with morule - like components: A surgical case report
Mitsuteru Yosida, Mitsuru Tomita, Naoya Kawakita, Teruki Shimizu, Ryou Yamada, Hiromitsu Takizawa, Hisanori Uehara
Respiratory Medicine Case Reports.2024; 48: 102008. CrossRef - Clinicopathological, Radiological, and Molecular Features of Primary Lung Adenocarcinoma with Morule-Like Components
Li-Li Wang, Li Ding, Peng Zhao, Jing-Jing Guan, Xiao-Bin Ji, Xiao-Li Zhou, Shi-Hong Shao, Yu-Wei Zou, Wei-Wei Fu, Dong-Liang Lin, Dong Pan
Disease Markers.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Pulmonary adenocarcinoma in situ with morule - like components: A surgical case report
Brief Case Report
- Adenocarcinoma Arising in an Ectopic Hamartomatous Thymoma with HER2 Overexpression
- Harim Oh, Eojin Kim, Bokyung Ahn, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Youngseok Lee, Yang Seok Chae, Chul Hwan Kim, Yoo Jin Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(6):403-406. Published online August 19, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.06.23
- 5,791 View
- 116 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Branchioma: immunohistochemical and molecular genetic study of 23 cases highlighting frequent loss of retinoblastoma 1 immunoexpression
Martina Bradová, Lester D. R. Thompson, Martin Hyrcza, Tomáš Vaněček, Petr Grossman, Michael Michal, Veronika Hájková, Touraj Taheri, Niels Rupp, David Suster, Sunil Lakhani, Dimitar Hadži Nikolov, Radim Žalud, Alena Skálová, Michal Michal, Abbas Agaimy
Virchows Archiv.2024; 484(1): 103. CrossRef - Adenocarcinoma arising in branchioma with a KRAS and TP53 mutation
Natsuki Taniguchi, Akira Satou, Takanori Ito, Masato Nakaguro, Toyonori Tsuzuki
Pathology International.2023; 73(7): 317. CrossRef - Two Ectopic Hamartomatous Thymomas of Suprasternal Region of the Neck in A Single Patient: A Case Report
Wei WANG, Manmei LONG, Zhichao WANG
Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.2021; 3(1): 51. CrossRef
- Branchioma: immunohistochemical and molecular genetic study of 23 cases highlighting frequent loss of retinoblastoma 1 immunoexpression
Original Article
- Morphometric Analysis of Thyroid Follicular Cells with Atypia of Undetermined Significance
- Youngjin Kang, Yoo Jin Lee, Jiyoon Jung, Youngseok Lee, Nam Hee Won, Yang Seok Chae
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(4):287-293. Published online June 13, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.04.04
- 11,229 View
- 96 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Atypia of undetermined significance (AUS) is a category that encompasses a heterogeneous group of thyroid aspiration cytology. It has been reclassified into two subgroups based on the cytomorphologic features: AUS with cytologic atypia and AUS with architectural atypia. The nuclear characteristics of AUS with cytologic atypia need to be clarified by comparing to those observed in Hashimoto thyroiditis and benign follicular lesions.
Methods
We selected 84 cases of AUS with histologic follow-up, 24 cases of Hashimoto thyroiditis, and 26 cases of benign follicular lesions. We also subcategorized the AUS group according to the follow-up biopsy results into a papillary carcinoma group and a nodular hyperplasia group. The differences in morphometric parameters, including the nuclear areas and perimeters, were compared between these groups.
Results
The AUS group had significantly smaller nuclear areas than the Hashimoto thyroiditis group, but the nuclear perimeters were not statistically different. The AUS group also had significantly smaller nuclear areas than the benign follicular lesion group; however, the AUS group had significantly longer nuclear perimeters. The nuclear areas in the papillary carcinoma group were significantly smaller than those in the nodular hyperplasia group; however, the nuclear perimeters were not statistically different.
Conclusions
We found the AUS group to be a heterogeneous entity, including histologic follow-up diagnoses of papillary carcinoma and nodular hyperplasia. The AUS group showed significantly greater nuclear irregularities than the other two groups. Utilizing these features, nuclear morphometry could lead to improvements in the accuracy of the subjective diagnoses made with thyroid aspiration cytology. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combining structural equation modeling analysis with machine learning for early malignancy detection in Bethesda Category III thyroid nodules
Zeliha Aydın Kasap, Burçin Kurt, Ali Güner, Elif Özsağır, Mustafa Emre Ercin
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine.2025; 167: 103186. CrossRef - Meta-analysis on the utility of morphometry in the cytological differential diagnosis of thyroid neoplasms
Prema Saldanha
MGM Journal of Medical Sciences.2024; 11(1): 49. CrossRef - Gray zone Bethesda category III – Atypia of undetermined significance lesions of the thyroid: Potential diagnostic issues and image morphometry as a useful adjunct to cytomorphology
Tarunpreet Saini, Reetu Kundu, Manish Rohilla, Parikshaa Gupta, Nalini Gupta, Radhika Srinivasan, Uma Nahar Saikia, Pranab Dey
Cytojournal.2024; 21: 38. CrossRef - Morphometric study in thyroid tumors
Iuliana Mohorea, Bogdan Socea, Alexandru Carâp, Dragoș Șerban, Zenaida Ceaușu, Mihail Ceaușu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Usefulness of Immunocytochemistry of CD56 in Determining Malignancy from Indeterminate Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology
Hyunseo Cha, Ju Yeon Pyo, Soon Won Hong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2018; 52(6): 404. CrossRef
- Combining structural equation modeling analysis with machine learning for early malignancy detection in Bethesda Category III thyroid nodules
Letter to the Editor
- Myxoid Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Central Nervous System
- Haeri Han, Sangjeong Ahn, Won Hwangbo, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(6):505-506. Published online December 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.6.505
- 7,237 View
- 47 Download
- 1 Crossref
Original Articles
- Expression of Hepatocyte Growth Factor/c-met by RT-PCR in Meningiomas.
- Na Rae Kim, Yang Seok Chae, Weon Jeong Lim, Seong Jin Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(5):463-468.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.5.463
- 3,923 View
- 33 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is a potent mitogenic cytokine. C-met protein, which is known to be the HGF receptor has transmembrane tyrosine kinase activity and is encoded by the c-met oncogene. The HGF/c-met signaling pathway may play various roles in the carcinogenesis of various organs.
METHODS
We examined HGF and c-met mRNA expression by utilizing reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction on 40 surgically resected intracranial meningiomas (25 benign, 10 atypical, and 5 anaplastic cases).
RESULTS
An HGF overexpression was detected in 28%, 50%, and 80% of the benign, atypical and anaplastic meningiomas, respectively; a high expression of HGF or the coexpression of HGF/c-met was detected in the high grade meningiomas (the atypical and anaplastic cases, p=0.046, p=0.014). An HGF expression was statistically significant in the recurrent meningiomas (p=0.003), and HGF expression was significantly lower than c-met mRNA expression in benign meningiomas (p=0.034).
CONCLUSIONS
There was no correlation between histologic subtypes and HGF/c-met expression. Determination of HGF expression can be used as a molecular predictor for recurrence of meningioimas. These results suggest that HGF and c-met expression in meningiomas may be associated with anaplastic progression.
- Effect of Selective Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitor in TCDD Pre-exposed Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma Cell Line.
- Hae Sung Kim, Kwang Sung Ahn, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Yang Seok Chae, Nam Hee Won, Jong Sang Choi, Chul Hwan Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(1):1-8.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.1.1
- 4,185 View
- 41 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) is related to carcinogenesis and progression of cancer. COX-2 has been detected in thyroid cancer. This suggests that COX-2 inhibitor may be useful to control the growth of thyroid cancer cells as well as the progression of thyroid cancer. Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin (TCDD), acting as an inflammatory cytokine, directly induces the expression of COX-2. We examine whether TCDD controls the effect of COX-2 inhibitor on thyroid cancer cells.
METHODS
The effects of TCDD and celecoxib on thyroid papillary carcinoma cell line (SNU790) were examined using cell proliferation and fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis. Western blot analysis was performed to determine the expressed COX-2 levels and the cell cycle-related proteins. The matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) expression and gelatinolytic activity were examined using real time-polymerase chain reaction and zymography.
RESULTS
TCDD directly induced the growth of SNU790 and the expression of cyclin D1, cyclin A, cyclin E, p21 and COX-2. Celecoxib suppressed the growth of SNU790 and the expression of cyclin D1 and cyclin E. Celecoxib reduced the MMP-2 expression and the gelatinolytic activity, but those effects were decreased in the SNU790 by either pre-treatment with TCDD or co-treatment with TCDD and celecoxib.
CONCLUSIONS
Celocoxib effect is directly reduced depending on the exposure to TCDD. TCDD exposure should be considered in the treatment with Celecoxib. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Histone H3 phosphorylation, immediate-early gene expression, and the nucleosomal response: a historical perspective1This article is part of Special Issue entitled Asilomar Chromatin and has undergone the Journal’s usual peer review process.
Shannon Healy, Protiti Khan, Shihua He, James R. Davie
Biochemistry and Cell Biology.2012; 90(1): 39. CrossRef
- Histone H3 phosphorylation, immediate-early gene expression, and the nucleosomal response: a historical perspective1This article is part of Special Issue entitled Asilomar Chromatin and has undergone the Journal’s usual peer review process.
Case Report
- Hepatoid Thymic Carcinoma: A Case Report.
- Jeong Hyeon Lee, Hyunchul Kim, Yang Seok Chae, Nam Hee Won, Jong Sang Choi, Chul Hwan Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(6):562-565.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.6.562
- 4,292 View
- 31 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report here on a rare case of hepatoid thymic carcinoma in a 34-year-old man. The patient complained of a high fever and headache, and a 6.6cm-sized anterior mediastinal mass was found on chest computed tomography (CT). There was no hepatic mass seen on abdominal CT. The resected mass consisted of epithelioid cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, pleomorphic vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli, and the mass was surrounded by thymic tissue. The tumor cells were immunopositive for cytokeratin 7, alpha-1-antitrypsin, hepatocyte staining, and epithelial membrane antigen, but they were negative for CD5, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and placental alkaline phosphatase, and this all led to a diagnosis of hepatoid thymic carcinoma rather than hepatoid yolk sac tumor. This entity should be included in the differential diagnosis of epithelioid thymic tumors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hepatoid thymic carcinoma in a polycythemia vera patient treated with ropeginterferon Alfa-2b: Clinical, histopathological and molecular correlates
Giuseppe G. Loscocco, Margherita Vannucchi, Raffaella Santi, Andrea Amorosi, Stefania Scarpino, Maria Chiara Siciliano, Paola Guglielmelli, Claudio Tripodo, Arianna Di Napoli, Alessandro M. Vannucchi
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 263: 155648. CrossRef
- Hepatoid thymic carcinoma in a polycythemia vera patient treated with ropeginterferon Alfa-2b: Clinical, histopathological and molecular correlates
Original Articles
- Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations of the Wnt/beta-catenin Signaling Pathway in Cancer of the Ampulla of Vater.
- Gwang Il Kim, Jeong Boon Kim, Sang Bum Park, Young Sik Kim, Han Kyeom Kim, Bom Woo Yeom, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(4):224-231.
- 2,555 View
- 33 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Carcinoma of the ampulla of Vater is rare and its pathogenesis is unclear. The role of epigenetic changes in the APC or CDH1, in the Wnt pathway, has not been reported in ampullary carcinomas.
METHODS
We performed immunohistochemistry on 73 sporadic ampullary carcinomas to identify Wnt-related molecules (APC, beta-catenin, E-cadherin, c-erbB2, cyclin D1) and examined mutations in the CTNNB1, loss of heterozygosity of 5q21, and the methylation status of the CpG island of APC and CDH1.
RESULTS
Thirteen tumors (17.8%) showed abnormal nuclear localization of beta-catenin; this was more prominent in the intestinal type than in the pancreaticobiliary type (p=0.01). The loss of APC correlated with the loss of beta-catenin or c-erb B2 (p<0.01). The prognosis was worse in the group with APC loss than when APC was maintained (p<0.05). There was no mutation identified in CTNNB1. Six (24%) out of 25 informative cases had 5q21 allelic loss. CpG island methylation in APC and CDH1 was detected in 33 (45.2%) and 29 (31.5%) cases, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The absence of mutations in CTNNB1 and the epigenetic alteration of APC and CDH1, might be characteristic changes in the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway during the carcinogenesis of ampullary carcinomas.
- Needle Aspiration Cytology in the Lesions of Central Nervous System: An Experience on the Accuracy of Cytologic Diagnosis.
- Hye Rim Park, Yang Seok Chae, Kap No Lee, Seung Yong Paik, Hung Seob Chung, Ki Chan Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1989;23(3):342-349.
- 2,119 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The cyto-histologic correlation and cytologic accuracy are reported in thirty cases of consecutive aspirated cells and their biopsied tissues of patients with clinical and neuroradiologic evidences of central nervous system tumors and other lesions investigated at the Pathology and Neurosurgery Department, Korea University Hospital, from Apr. 1987 to Apr. 1988. The series comprised of 17 benign and 12 malignant histopathologically verified brain neoplasms and 1 infectious lesion. In 78% of the cases, the cytologic diagnosis was concordant with the histologic diagnosis provided adequate sample was obtained. In 17 benign tumors, the diagnostic rate was 87% ; the diagnostic accuracy for 12 malignant CNS tumors was 63% cytologically. In almost all cases, differentiation of non-neoplastic lesion from neoplastic one and that of benign tumors from malignant ones were possible. Most discordance stemmed from failure to distinguish different types of malignant tumors. In meningioma, neurilemmoma, pituitary adenoma, and medulloblastoma, cytologic diagnostic accuracy was high, but germinoma, malignant ependymoma, and hemangioblastoma were difficult to diagnose by cytology alone.
- Expression of bcl-2 Protein in Colorectal Adenoma and Adenocarcinoma and its Relationship with p53 and Apoptosis.
- Ae Ree Kim, Seong Jin Cho, Nam Hee Won, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(5):417-426.
- 1,929 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Either increased cellular proliferation or decreased death might result in an expansion of their numbers in the oncogenic process. Cellular apoptosis represents an autonomous suicide pathway that helps to restrict the cell number. However bcl-2 and mutant p53 inhibit programmed cell death. To determine whether the bcl-2 gene is activated during colorectal tumorigenesis and whether it has any relationship with p53 and apoptosis, we studied the expression of bcl-2 and p53 in the normal colonic mucosa, in the adenomatous polyps and in the adenocarcinomas using the immunohistochemical method. Also we evaluated the status of apoptosis using the in situ end labeling method. The bcl-2 immunoreactivity was restricted to the basal epithelial cells of all normal colonic mucosa and they were expressed in all adenomas and 86% of adenocarcinomas, especially in the superficial lesion of some tumors. Mutations of p53 were not found in the normal colonic mucosa, but they were present in dysplastic cells of adenomas (52%) and in cancer cells of the adenocarcinomas (47%). Apoptosis was confined to the tips of the normal colonic mucosa. It was more easily detected in the p53-positive adenomas than in the p53-negative adenomas (p=0.010). In the adenocarcinomas, the findings of apoptotic process are not related with p53 mutation (p=0.3) and bcl-2 expression (p=0.187). p53 and bcl-2 are probably one step of several apoptotic processes in the adenocarcinomas.
Case Report
- Metastatic Medullary Carcinoma of Thyroid to Breast; A Case Initially Diagnosed as Primary Invasive Lobular Carcinoma: A Case Report.
- Youngseok Lee, Jungsuk An, Chul Hwan Kim, Bom Woo Yeom, Jong Sang Choi, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(6):412-415.
- 2,290 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Metastasis to the breast from medullary carcinoma of the thyroid is extremely rare. We report a case of metastatic medullary carcinoma of the thyroid which presented as multiple breast masses with ipsilateral axillary lymphadenopathy in a 48-year-old woman. Six years ago, she underwent total thyroidectomy and neck dissection because of palpable neck masses, with a diagnosis of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Histological features of breast masses showed single- file or linear-cord arrangements, with plasmacytoid appearance, and the initial diagnosis was invasive lobular carcinoma. She underwent modified radical mastectomy. The tumor cells were diffusely positive for E-cadherin, calcitonin and thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) and were metastatic medullary carcinoma of thyroid. In the patients with a history of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid, a careful examination is necessary for a breast mass composed of solid and cord-like clusters of small round to ovoid cells with plasmacytoid appearance. Immunohistochemical staining for E-cadherin, calcitonin and TTF-1 could be helpful for differential diagnosis.
Original Article
- The Clinicopathologic Analysis of Kikuchi's Lymphadenitis.
- Jung Woo Choi, Ji Hye Lee, Ju Han Lee, Yang Seok Chae, Insun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(5):289-294.
- 2,141 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Kikuchi's disease has been known as a self-limiting lymphadenitis mostly affecting the cervical lymph nodes of young women.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the clinical data of 77 cases of Kikuchi's lymphadenitis from 1996 to 2003 at Korea University Medical Center.
RESULTS
Histologically, 69 available cases were classified into three types: proliferative (60.8%), necrotizing (33.3%), and xanthomatous type (5.7%). These three types differed in terms of their clinical features, showing tenderness most predominantly in the necrotizing type. In spite of the insufficient numbers of cases, the data on the duration of the disease well correlated with the possible progression of the three histologic types (Kikuch's disease begins as proliferative type, then progress into necrotizing type and finally resolves into xanthomatous type). During the ten-month period of the mean follow-up, the recurrence rate was 7.0%. Three and two patients developed into pulmonary tuberculosis and systemic lupus erythematosus, respectively, but there were no prognostic differences among the three types.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results confirmed that Kikuchi's lymphadenitis is a self-limiting necrotizing lymphadenitis with a low rate of recurrence. Here, we suggest that the classification of histologic types have some meanings because of their differences in certain clinical aspects and possible sequential disease progression.
Case Reports
- Gliosarcoma with Components of Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma and Unclassifiable Spindle Cells: A Case Report.
- Jung Woo Choi, Youngseok Lee, Jung Suk An, Nam Hee Won, Yong Gu Chung, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(1):45-49.
- 2,106 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Gliosarcoma is a distinct disease entity that is characterized by a biphasic tissue pattern with alternating areas displaying glial and mesenchymal differentiation. The tumor in our case was a rare morphologic variant of gliosarcoma with components of anaplastic oligodendroglioma and unclassifiable spindle cells. Spindle cells showed CD34 and S-100 protein immunoreactivity, which was possibly related to peripheral nerve sheath differentiation. This unique feature has not been described previously and so this case expands the spectrum of possible divergent mesenchymal differentiation, and it lends support to pluripotential stem cells being the origin of this tumor.
- Metastatic Germinoma of Spleen from Perichiasmal Area: A Case Report .
- Bong Kyung Shin, Min Kyung Kim, Han Kyeom Kim, Yang Seok Chae, Nam Hee Won, Insun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2001;12(1):61-65.
- 1,915 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 20-year-old young man who had undergone treatment for a suprasellar/perichiasmal tumor 2 years before, was presented with a huge palpable splenic mass. A fine needle aspiration cytology from the splenic mass showed dissociated large pleomorphic tumor cells having irregular nuclear outline, coarse chromatin, and one or two macronucleoli, and scattered small lymphocytes in fine granular background. Above cytologic findings were regarded as the characteristics of germinoma. Differential diagnosis from the large cell lymphoma of spleen was emphasized.
Original Articles
- Immunohistochemical Study for p53 and hsc70 in Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder: Correlation with Histologic Grade, Clinical Stage and DNA Ploidy Pattern.
- Hyuni Cho, Sung Jin Cho, Han Kyeom Kim, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(6):766-775.
- 1,975 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is the most common cancer of the genitourinary tract in Korea and its prognosis is determined by the histologic grade and clinical stage present at initial diagnosis. Recently, an extensive search for a more objective and reproducible method to evaluate the proliferation activity of cancer cells has been done. The p53 gene is located on the short arm of the chromosome 17 and acts as a cancer suppressor gene. Mutant p53 gene induces malignant transformation. Recent studies reveal that the level of mutant p53 protein is elevated in some human tumor and many diverse transformed cell lines. Heat shock proteins(HSPs) are present constitutively in normal cells, where they play an important role in normal cell metabolism. In mammalian cells, they are induced by a variety of physical and chemical stimuli. A protein that belongs to the hsp70 family, called hsc70, is only slightly heat inducible and is found at a higher level in growing cells than in the resting cells. The mutant p53 protein binds with hsc70 and the p53-hsc70 complex has functional significance in the transforming capacity of the mutant p53. We investigated the correlation between the p53 and hsc70 by immunohistochemical methods and with better defined prognostic indicators such as histologic grade, clinical stage, and DNA ploidy pattern in 42 transitional cell carcinomas of the urinary bladder. The results are summarized as follows. p53 expression rate was higher in the DNA aneuploid group than in the DNA diploid group(p=0.061), but there was no significant difference in the histologic grade(p=0.861) or clinical stage(p=0.154). The higher the hsc70 expression rate was, the poorer the tumor differentiation(p=0.000) and the deeper the invasion(p=0.001). The aneuploid group showed a higher hsc70 expression rate than the diploid group(p=0.017). 27 of 42(64.3%) carcinomas showed positivity of both p53 and hsc70. Though statistically insignificant, their correlation showed a relatively low correlation coefficient (P=0.059). In conclusion, we suspect that p53 and hsc70 are closely correlated to each other by comparing the results of this immunohistochemical study, and hsc70 will be a useful prognostic marker in transitional cell carcinomas of the urinary bladder after sufficient follow up studies are performed.
- A Standardized Pathology Report for Gastric Cancer.
- Woo Ho Kim, Cheol Keun Park, Young Bae Kim, Youn Wha Kim, Ho Guen Kim, Han Ik Bae, Kyu Sang Song, Hee Kyung Chang, Hee Jin Chang, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(2):106-113.
- 4,792 View
- 339 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
AND METHODS: The Gastrointestinal Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists developed a standardized pathology reporting format for gastric cancer in collaboration with the Korean Gastric Cancer Association. RESULTS: The diagnostic parameters are divided into two part: the standard part and the optional part. The standard part contains most of the items listed in the Japanese classification, the TNM classification by UICC, the WHO classification, and the Korean Gastric Cancer Association classification. Therefore, the standard part is adequate for routine surgical pathology service. We included detailed descriptions on each item.
CONCLUSIONS
The authors anticipate that this standardization can improve the diagnostic accuracy and decrease the discrepancies that occur in the pathologic diagnosis of gastric cancer. Furthermore, the standard format can encourage large scale multi-institutional collaborative studies.
- Immunohistochemical Staining of Ovarian Tumors.
- Young Seak Kim, Yang Seok Chae, In Sun Kim, Seung Yong Paik
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(1):11-20.
- 2,786 View
- 58 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Forty-four ovairan tumors were immunohistochemically studied for the presence of broad-spectrum keratin, vimentin, desin, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), and alpha 1-antitrypsin (AAT) in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. 1) Among the common epithelial tumors, all the serous carcinomas (4) expressed keratin and AAT, and one additionally CEA. Six mucinous carcinomas exhibited keratin-positivity in two. One endometrioid carcinoma coexpressed keratin and vimentin as well as AAT, but one clear cell carcinoma expressed only keratin. Keratin-and CEA-positivity in epithelial cell nests and vimentin-positivity in stromal cells were observed in two Brenner tumors. Two undifferentiated carcinomas showed keratin-positivity in one and focal CEA positivity in the other. 2) In sex cord-stromal tumors, four out of six granulsa cell tumors, all four thecomas and three fibromas expressed vimentin, and two granulosa cell tumors and two thecomas showed AAT-positivity. The others were negative. 3) Among germ cell tumors, four dysgerminomas showed focal vimentin-positive cells in two and diffuse staining for AAT. Seven endodermal sinus tumors expressed AAT in all. Additionally, AFP were positive in two and CEA in three out of them. One embryonal carcinoma expressed CEA, AAT and AFP. 4) In four metastatic carcinomas, three exhibited keratin-and CEA-positivity, whereas one exhibited keartin-and vimentin-positivity. All showed AAT-positivity. 5) There was no positive case for desmin among ovarian tumors.
Case Reports
- Cytodiagnosis of Primary Small Cell Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder: A Case Report.
- Hye Sun Kim, Aee Ree Kim, Chul Hwan Kim, Yang Seok Chae, Nam Hee Won
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1994;5(2):167-171.
- 1,830 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Samll cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is a rare tumor which occurs in about 0.48% of all bladder tumors. We report cytologic features of small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder in a 66-year-old man who had painless total gross hematuria, which was confirmed by partial cystectomy. In urine cytology, abundant tumor cells appeared in scattered and clustered forms in a bloody background. The tumor cells were small and uniform in size with a high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio. The nuclei of the tumor cells were hyperchromatic, characteristically molded and showed inconspicuous nucleoli. The cytoplasms were scanty and plae blue.
- Pulmonary Cavernous Hemangioma: A case report.
- Seung Yeon Ha, Sang Ae Yoon, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(2):203-205.
- 2,106 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The pulmonary cavernous hemangioma is usually from birth and there may be without symptoms until adulthood. Larger or multiple pulmonary angiomata with considerable pulmonary arteriovenous shunts may cause cyanosis, finger clubbing, dyspnea and frequently accompanyingbruit. Recently, we experienced a case of cavernous hemangioma of the lung. A 34-year-old woman was admitted to our hospital for surgical evaluation of a 4 cm solitary, round nodule in the right upper lobe on the chest X-ray and CT scan. She had no symptoms. Laboratory findings are within normal limits except for elevated glucose levels. At surgery, the mass was well encapsulated and easily excised from the peripheral portion of the posterior segment of the right upper lobe. Grossly, it consisted of a 4 cm in diameter, round, soft, sponge-like, hemorrhagic, slightly lobulated mass with a smooth external surface. Microscopically, the mass was composed of vessels, which were thin walled, dilated and filled with blood. The wall of the abnormal vessels was thin and composed of endothelium and fibrous connective tissue with only a little smooth muscle. Immunohistochemically, the wall of the dilated abnormal vessesls showed negative reaction for cytokeratin(low and high) and epithelial membrane antigen but weakly positive reaction for UEA-1 in focal areas.
Original Articles
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Struma Ovarii Arising in Benign Cystic Teratoma.
- Eun Sook Nam, Young Seek Kim, Yang Seok Chae, Kap No Lee, Seung Yong Paik
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(5):462-466.
- 3,416 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Malignant tumor is found in 1-2% of ovarian benign cystic teratomas. Among these malignant neoplasms, squamous cell carcinoma is by far the most common malignancy, whereas the incidence of struma ovarii is less than 5% in mature teratoma. As far as concerned the struma ovarii, a very small percentage is associated with carcinoid, mucinous or serous cystadenoma, or Brenner tumor. However, any reports of struma ovarii associated with squamous cell carcinoma in the same ovary could not be found in English literature. Recently we have experienced a case of squamous cell carcinoma and struma ovarii arising in an ovarian benign cystic teratoma in 72 year old female patient.
- Plexiform Schwannoma.
- Kyo Beom Lee, Yang Seok Chae, Nam Hee Won, Seung Yong Paik
- Korean J Pathol. 1988;22(1):105-109.
- 1,962 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Three case of plexiform schwannoma displayed multinodular masses and microscopically a multicentric pattern of growth featuring Antoni A cellular component, Verocay bodies and presence of Antoni B areas. Clinically von Recklinghausen's disease was not observed in all cases. The first patient was a 17 year old male who had a protruding nodule of walnut size which was located at the dermis of the left flank for 13 years. The second case, a 25 year old male, had an irregular whitish brown multinodular mass in the choana for 5 years. The last case, a 56 year old woman, had an ovoid yellowish brown mass with multiple nodules in the retroperitoneum.
- A Standardized Pathology Report for Colorectal Cancer.
- Hee Jin Chang, Cheol Keun Park, Woo Ho Kim, Young Bae Kim, Youn Wha Kim, Ho Guen Kim, Han Ik Bae, Kyu Sang Song, Mee Soo Chang, Hee Kyung Chang, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 2006;40(3):193-203.
- 2,883 View
- 154 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
AND METHODS: For standardizing the pathology report and diagnosis of colorectal cancers, the Gastrointestinal Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists has developed a pathology reporting format for colorectal cancer in collaboration with the Korean Society of Coloproctology.
RESULTS
The diagnostic parameters are divided into two parts: the standard part and the optional part. The standard part contains most of the items listed in the Japanese classification, the TNM classification by AJCC, and the WHO classification. We included detailed descriptions on each item.
CONCLUSIONS
The standardized pathology report for colorectal cancers is adequate for its application to routine surgical pathology reports, and it is also helpful to decrease the discrepancies that occur during the pathologic diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Furthermore, this reporting format could encourage nationwide multi-center collaborative studies.
- Malignant Meningioma: Clinical, Radiologic and Pathologic Characteristics.
- Hye Rim Park, Yang Seok Chae, Kap No Lee, Seung Yong Paik
- Korean J Pathol. 1988;22(3):277-284.
- 2,031 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This is a report of the clinico-pathologic findings in six cases of histologically verified malignant meningiomas-three hemangiopericytic and three anaplastic types. They were three males and three females and two of them were reoperated for recurrence. The hemangiopericytic types had similar angiographic and macroscopic features and malignant characteristics such as increased mitoses. The anaplastic types lacked typical arrangement, but had a large number of mitoses, increased cellularity, focal necrosis, pleomorphism, anaplasia, and the adjacent normal parenchymal infiltration. However the metastasis was not yet proven in these cases.
Case Reports
- Cytologic Features of Medullary Carcinoma of the Thyroid Occurring in a Child: A Case Report.
- Jeong Seok Moon, Hye Sun Kim, Seong Jin Cho, Yang Seok Chae, Bom Woo Yeom
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1996;7(2):213-217.
- 1,978 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid gland is a malignant neuroendocrine tumor arising from calcitonin producing-parafollicular cells. The tumor is clinically divided into sporadic and familial form, constituting about 80% and 20%, respectively. Recently, we experienced a case of unilateral and solitary sporadic medullary carcinoma of the left thyroid gland. The patient was a 9 year-old female, who presented with a palpable mass on the anterior lateral neck of 8 months duration without any familial and personal history of neuroendocrine disease. The cytopathologic findings showed spindle cells and plasmacytoid cells in the background of colloid-like materal. The nuclei were eccentrically located, mildly hyperchromatic and pleomorphic, showing speckled chromatin pattern without nuclear inclusion or prominent nucleoli. The cytoplasm was abundant and had a pale granular cyanophilic appearance. No amyloid materal could be identified.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Extranodal Marginal Zone B cell Lymphoma with Abundant Plasma Cells and Eosinophilic Histiocytes in Parotid Gland.
- Youngseok Lee, Jungsuk An, Yang Seok Chae, Bom Woo Yeom, Jong Sang Choi, Chul Hwan Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2007;18(2):165-169.
- 2,046 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The authors present the fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) cytologic findings of a case of extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma (MZBCL), which featured abundant plasma cells and eosinophilic histiocytes arising in both parotid glands. A 49-year-old female presented with palpable masses in both parotid glands. She had been suffering from systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. The lesions were evaluated by FNAC and smears showed a small number of clusters of oncocytic cells with abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm and small nuclei, intermixed with small to medium-sized lymphoid cells containing round to lobulated nuclei, which suggested Warthin's tumor. Some of lymphoid cells had a plasmacytoid appearance, and some scattered large cells contained a large amount of eosinophilic cytoplasm. Bilateral superficial parotidectomy was performed and a histopathologic study indicated MZBCL with abundant plasma cells, intermixed with eosinophilic histiocytes. The presence of oncocytic cells and a mixture of lymphoid and plasma cells indicates Warthin's tumor, but the cytologic features of a relatively monotonous small to medium-sized lymphoid infiltrate suggest the possibility of MZBCL in the clinical setting of an FNAC study performed on a patient suffering from a connective tissue disease.
Original Article
- Expression of p53 and Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Proteins in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma.
- Seong Jin Cho, Hwa Eun Oh, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(7):494-500.
- 2,080 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The p53 gene is believed to play an important role through the mutation and overexpression in the progression of various human malignant tumors. The type IV collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase: MMP-2) initiates the degradation of the extracellular matrix, and consequently may play a role in the tumor invasion and metastasis. To investigate the correlation between clinicopathologic features of the colorectal adenocarcinomas and benign tumors and expression of p53 and MMP-2 proteins, we performed an immunohistochemical study on 40 colorectal adenocarcinomas, 20 adenomas and 20 hyperplastic polyps by using the antibodies to p53 and MMP-2 proteins. The positive expression rate of the p53 protein in adenocarcinomas was 62.5% and significantly higher than in benign tumors. The positive expression rate of the MMP-2 protein was 47.5% in adenocarcinomas, but there was no expression of MMP-2 protein in benign tumors. The difference in p53 and MMP-2 expression rates between malignant and non-malignant tumors was statistically significant. The positive expression rate of p53 protein in the non-metastatic and metastatic adenocarcinomas was 59.1 and 66.7%, respectively. The positive expression rate of MMP-2 protein in the non-metastatic and metastatic adencarcinomas was 45.5 and 50.0%, respectively. The correlation between several clinicopathologic features and expression of p53 and MMP-2 protein was not statistically significant, but the rate of positive MMP-2 immunoreactivity showed a statistically significant difference between Astler-Coller stage B1 C1 group and B2 C2 group of adenocarcinoma (p=0.0431). We concluded that the expression of p53 and MMP-2 protein contributes to the cancer development and MMP-2 may play a certain role in the invasiveness of the colorectal tumor. p53 and MMP-2 protein expression is not correlated with lymph node metastasis.
Case Report
- Sinonasal Undifferentiated Carcinoma: A Case Report .
- Mi Kyung Shin, Yang Seok Chae
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1997;8(1):98-102.
- 2,066 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma(SNUC) is a distinct, relatively rare neoplasm arising in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses composed of undifferentiated epithelial cells and clinically characterized by a fulminant course. We report a case of SNUC in a 56-year old man who have had bilateral neck masses since one month ago before coming to our hospital. The paranasal computed tomography showed soft mass density in the left maxillary sinus and the nasal cavity with bone destruction in the anterior medial and the inferior maxillary sinus wall. This mass was extruded into the left orbital wall. Biopsy of the nasal mass and fine needle aspiration(FNA) of the neck mass were done. FNA revealed medium-sized neoplastic cells forming clusters or individually dispersed. Nuclei were round to oval, slightly to moderately pleomorphic, and hyperchromatic. Chromatin was finely granular, but occasionally was coarsely granular. Nucleoli varied from large to inconspicuous and the cytoplasm was scanty.
Original Articles
- Eosinophilic Granuloma of the Lung.
- Sang Ae Yoon, Won Bo Jo, Yang Seok Chae, Kap No Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(3):270-276.
- 1,897 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Eosinophilic granuloma of the lung, first described by Farrinaci et al. in 1951, is rare. A 35-year-old male smoker presented with recurrent pneumothorax. Open thoracotomy with bleb resection and biopsy was performed. Microscopically there was histological changes consistent with typical eosinophilic granuloma and intertitial fibrosis. The Langerhans cells showed positive reaction for S-100 protein and typical Birbeck granules in their cytoplasm. A brief summary of histopathological aspect of this disease and a review of literature are presented.
- SPARC Expression in Thyroid Follicular Adenomas and Carcinomas.
- Chung Yeul Kim, Seong Jin Cho, Min Kyung Kim, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(12):1016-1021.
- 1,946 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - SPARC, secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine, is a extracellular matrix-associated protein implicated in the modulation of cell adhesion, migration, cell cycle regulation, and angiogenesis. SPARC is expressed in fibrocytes and endothelial cells involved in tissue repair and invasive malignant tumors in the gastrointestinal tract, breast, lung, kidney, adrenal cortex, ovary, and brain. This study was aimed to characterize the different expression of SPARC in the thyroid follicular adenomas and follicular carcinomas. Immunohistochemical staining was performed in paraffin-embedded tissues of 25 follicular adenomas and 15 follicular carcinomas of the thyroid gland. Immunohistochemically, SPARC was not expressed in the 19 follicular adenoma and 2 follicular carcinoma but highly expressed in the 6 follicular adenoma and 13 follicular carcinoma. These findings suggest that SPARC is a potential diagnostic marker of follicular carcinoma and is helpful to distinguish follicular carcinoma from follicular adenoma without vascular or capsular invasion.

 E-submission
E-submission


 First
First Prev
Prev



