Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 49(5); 2015 > Article
-
Original Article
Comparison of Cytologic Characteristics between Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma and Adenoid Basal Carcinoma in the Uterine Cervix - Juhyeon Jeong, Seung Yeon Ha, Hyun Yee Cho, Dong Hae Chung, Jungsuk An
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2015;49(5):396-402.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.07.08
Published online: August 17, 2015
Department of Pathology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea
- Corresponding Author Seung Yeon Ha, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, 21 Namdong-daero 774beon-gil, Namdong-gu, Incheon 21565, Korea Tel: +82-32-460-3073 Fax: +82-32-460-2394 E-mail: syha@gilhospital.com
© 2015 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Adenoid basal carcinoma of the uterine cervix
Anas Mohamed, Tesfalem Korga, Ahlam Ali, Javier Laurini
International Journal of Gynecological Cancer.2025; : 101873. CrossRef - Adenoid Basal Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: A Case Report
Tatsuya Kanuma, Keiko Kigure, Tosio Nishimura, Yuji Ibuki, Shigeru Tsuchida, Harumi Kamiyama, Misa Iijima, Kazuto Nakamura
The KITAKANTO Medical Journal.2016; 66(1): 11. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure


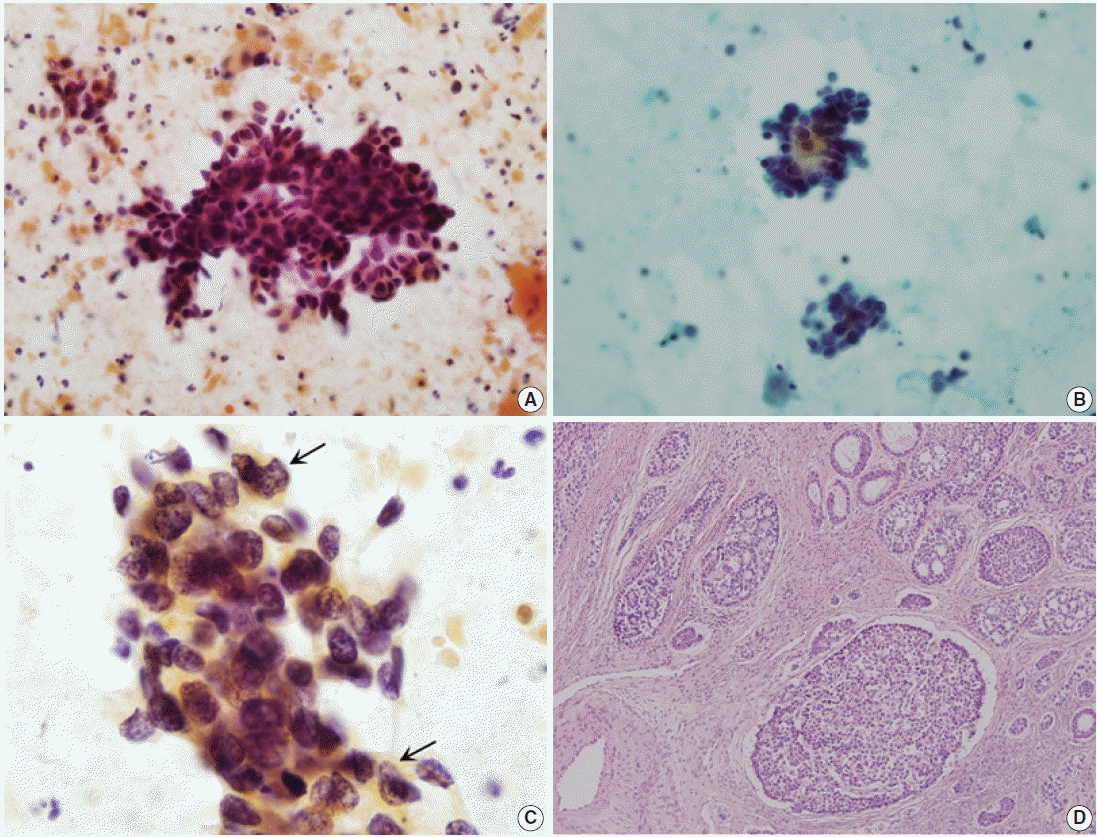
Fig. 1.
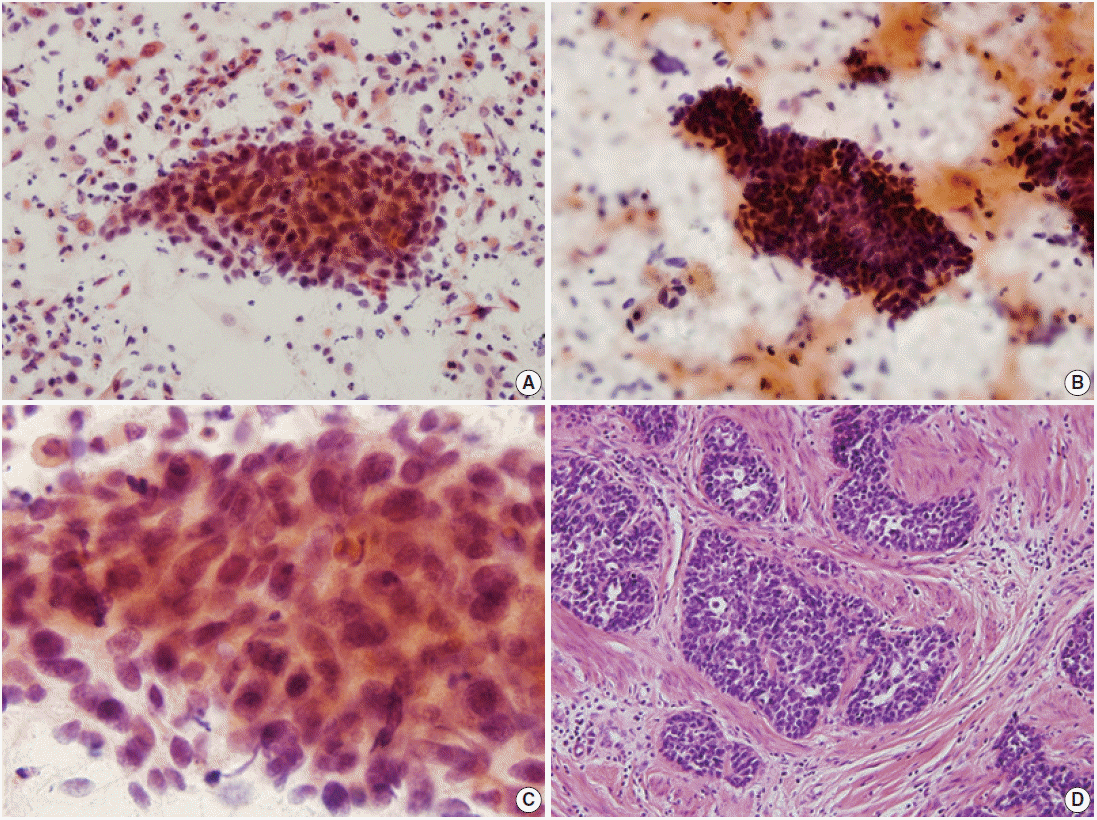
Fig. 2.
| Case No. | Age (yr) | Cytologic diagnosis | Surgical procedure | Histologic diagnosis | Combined lesion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 76 | SCC | Punch biopsy | ACC | - |
| 2 | 45 | AC | Hysterectomy | ACC | - |
| 3 | 68 | MN | Hysterectomy | ACC | SD |
| 4 | 78 | SCC, AC | Punch biopsy | ABC | SCC |
| 5 | 62 | SCC | Hysterectomy | ABC | SCC |
| 6 | 56 | SCC | Hysterectomy | ABC | SCC |
| 7 | 62 | SCC | Hysterectomy | ABC | - |
| 8 | 68 | ASCUS | Hysterectomy | ABC | SCC |
| Cytologic features | Adenoid cystic carcinoma | Adenoid basal carcinoma |
|---|---|---|
| Background | Bloody and necrotic; orangeophilic globules | Necrotic, mostly |
| Architecture | Three-dimensional clusters; occasionally glandular structures; opaque materials in the center of the glands | Three-dimensional clusters of sheets; nuclear overlapping; rarely peripheral palisading |
| N/C ratio | Moderate to high | High |
| Nuclear shape | Round to oval | Round to oval |
| Nuclear size (μm) | 5–7 |
3–4 |
| Nuclear size variation | Mild to moderate |
Mild |
| Mitotic counts (/100–150 cells) | 2–3 | 0–1 |
| Chromatin pattern | Hyperchromatic; coarse granular chromatin pattern | Hyperchromatic; finely granular chromatin pattern |
| Nucleoli | Rarely seen; indistinct, mostly | Rarely seen; small nucleoli, occasionally |
| ACC (n = 117) | ABC (n = 218) | p-value |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Area (µm2) | 18.556 ± 8.655 | 11.017 ± 4.440 | < .001 |
| Circumference (µm) | 23.320 ± 11.412 | 15.920 ± 5.664 | < .001 |
| Major axis (µm) | 5.664 ± 1.537 | 4.612 ± 1.025 | < .001 |
| Minor axis (µm) | 4.127 ± 1.107 | 3.088 ± 0.762 | < .001 |
| Differential diagnosis | Nuclear features | Cytologic features | Structures |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCC, keratinizing | Marked variation in size and shape; irregular nuclear membrane; coarsely granular and irregularly distributed chromatin | Dense orangiophilic | Low cellularity; single cells and less commonly in aggregates |
| SCC, nonkeratinizing | Smaller than HSIL; markedly irregular distributed chromatin | Basophilic | Single or aggregated cells |
| Small cell carcinoma | Small, relatively uniform cells; hyperchromatic with granular or stippled chromatin; frequent mitosis; inconspicuous nucleoli | Scant cyanophilic cytoplasm | Singly and in groups with nuclear molding |
| Endocervical adenocarcinoma | Columnar configuration enlarged, pleomorphic nuclei; irregular nuclear membrane; macronucleoli | Usually finely vacuolated | Abundant abnormal cells; single cells or two-/three-dimensional sheets; discohesive groups |
| Endometrial carcinoma | Variation of nuclear size; loss of nuclear polarity; moderate hyperchromasia; large with clumped chromatin; small to prominent nucleoli | Scant, cyanophilic, often vacuolated; commonly intracytoplasmic neutrophil | Single or small, tight clusters |
| Benign endometrial stromal cells | Small round to oval shape; inconspicuous nucleoli | Scant, basophilic, or occasionally vacuolated | Three-dimensional ball-like clusters; double-contoured cluster (the first half of the menstrual cycle) |
| Atrophy | Intermediate cells with normochromatin; elongated nuclei; mild hyperchromasia | - | Flat, monolayer sheets |
SCC, squamous cell carcinoma; ACC, adenoid cystic carcinoma; AC, adenocarcinoma; MN, other malignant neoplasm; SD, squamous differentiation; ABC, adenoid basal carcinoma; ASCUS, atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance.
Estimate based on major axis in our cases; Estimate based on major axis with standard deviation in our cases.
Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation. ACC, adenoid cystic carcinoma; ABC, adenoid basal carcinoma. Statistical significance was determined by Mann-Whitney U-test.
SCC, squamous cell carcinoma; HSIL, high grade intraepithelial lesion.

 E-submission
E-submission