Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 51(3); 2017 > Article
-
Original Article
An Experimental Infarct Targeting the Internal Capsule: Histopathological and Ultrastructural Changes - Chang-Woo Han, Kyung-Hwa Lee, Myung Giun Noh, Jin-Myung Kim, Hyung-Seok Kim1, Hyung-Sun Kim2, Ra Gyung Kim2, Jongwook Cho2, Hyoung-Ihl Kim2, Min-Cheol Lee
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2017;51(3):292-305.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.02.17
Published online: May 10, 2017
Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Medical School and Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Gwangju, Korea
1Department of Forensic Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School and Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Gwangju, Korea
2Department of Medical System Engineering and School of Mechatronics, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, Gwangju, Korea
- Corresponding Author Min-Cheol Lee, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Medical School and Research Institute of Medical Sciences, 160 Baekseo-ro, Dong-gu, Gwangju 61469, Korea Tel: +82-62-220-4303 Fax: +82-62-220-5697 E-mail: mclee@jnu.ac.kr
© 2017 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Neuroglia and immune cells play different roles in neuroinflammation and neuroimmune response in post-stroke neural injury and repair
Hui Guo, Wen-cao Liu, Yan-yun Sun, Xin-chun Jin, Pan-pan Geng
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2026; 47(2): 273. CrossRef - Animal models of focal ischemic stroke: brain size matters
Blazej Nowak, Piotr Rogujski, Raphael Guzman, Piotr Walczak, Anna Andrzejewska, Miroslaw Janowski
Frontiers in Stroke.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Motor Cortex Plasticity During Functional Recovery Following Brain Damage
Noriyuki Higo
Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics.2022; 34(4): 700. CrossRef - Neurodegeneration, Myelin Loss and Glial Response in the Three-Vessel Global Ischemia Model in Rat
Tatiana Anan’ina, Alena Kisel, Marina Kudabaeva, Galina Chernysheva, Vera Smolyakova, Konstantin Usov, Elena Krutenkova, Mark Plotnikov, Marina Khodanovich
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(17): 6246. CrossRef - Quantitative assessment of demyelination in ischemic stroke in vivo using macromolecular proton fraction mapping
Marina Y Khodanovich, Alena A Kisel, Andrey E Akulov, Dmitriy N Atochin, Marina S Kudabaeva, Valentina Y Glazacheva, Michael V Svetlik, Yana A Medvednikova, Lilia R Mustafina, Vasily L Yarnykh
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism.2018; 38(5): 919. CrossRef - Immunosignals of Oligodendrocyte Markers and Myelin-Associated Proteins Are Critically Affected after Experimental Stroke in Wild-Type and Alzheimer Modeling Mice of Different Ages
Dominik Michalski, Anna L. Keck, Jens Grosche, Henrik Martens, Wolfgang Härtig
Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Administration of Downstream ApoE Attenuates the Adverse Effect of Brain ABCA1 Deficiency on Stroke
Xiaohui Wang, Rongwen Li, Alex Zacharek, Julie Landschoot-Ward, Fengjie Wang, Kuan-Han Hank Wu, Michael Chopp, Jieli Chen, Xu Cui
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(11): 3368. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure




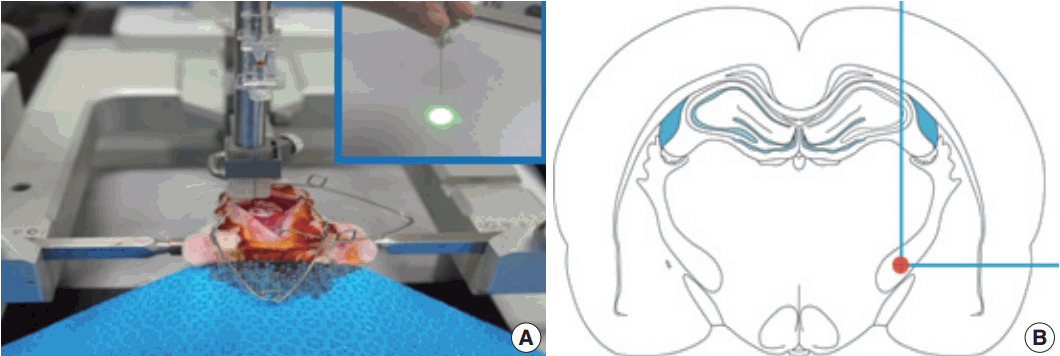
Fig. 1.
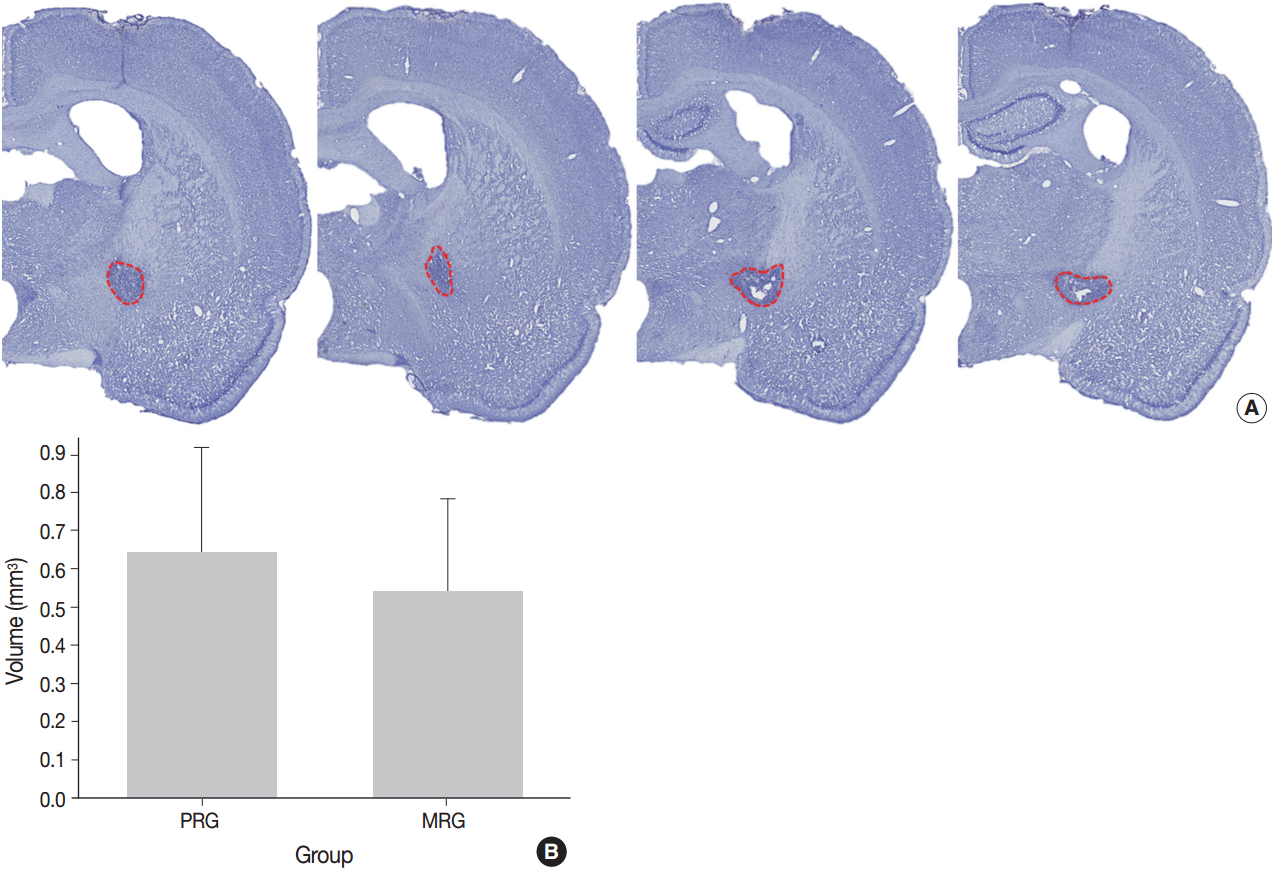
Fig. 2.
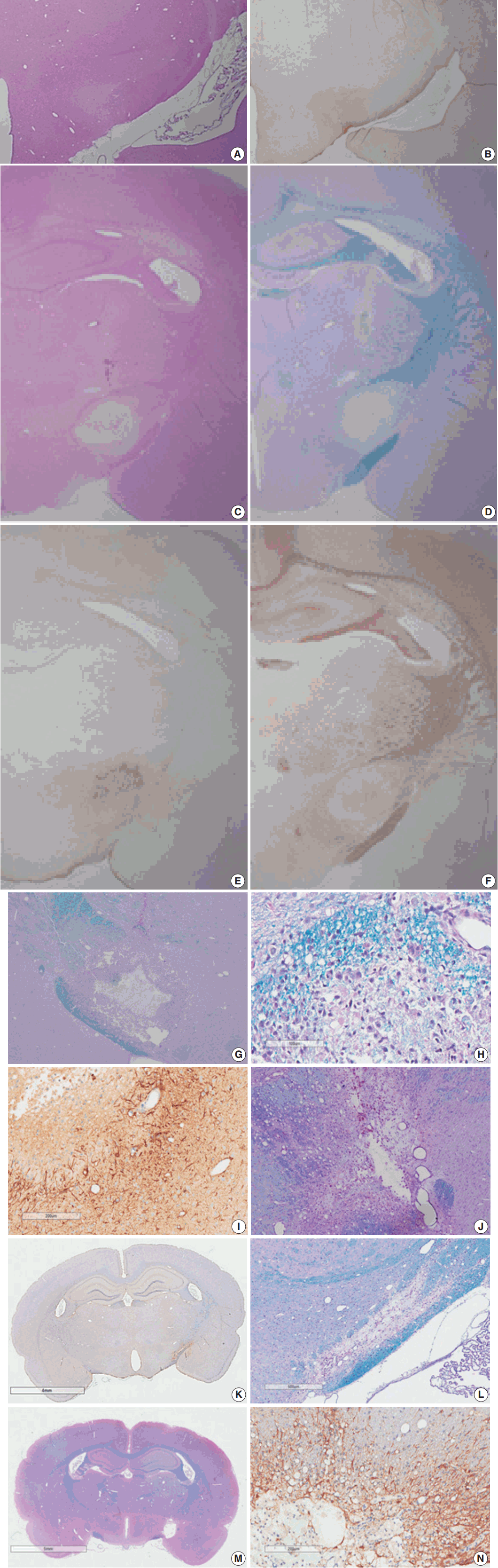
Fig. 3.
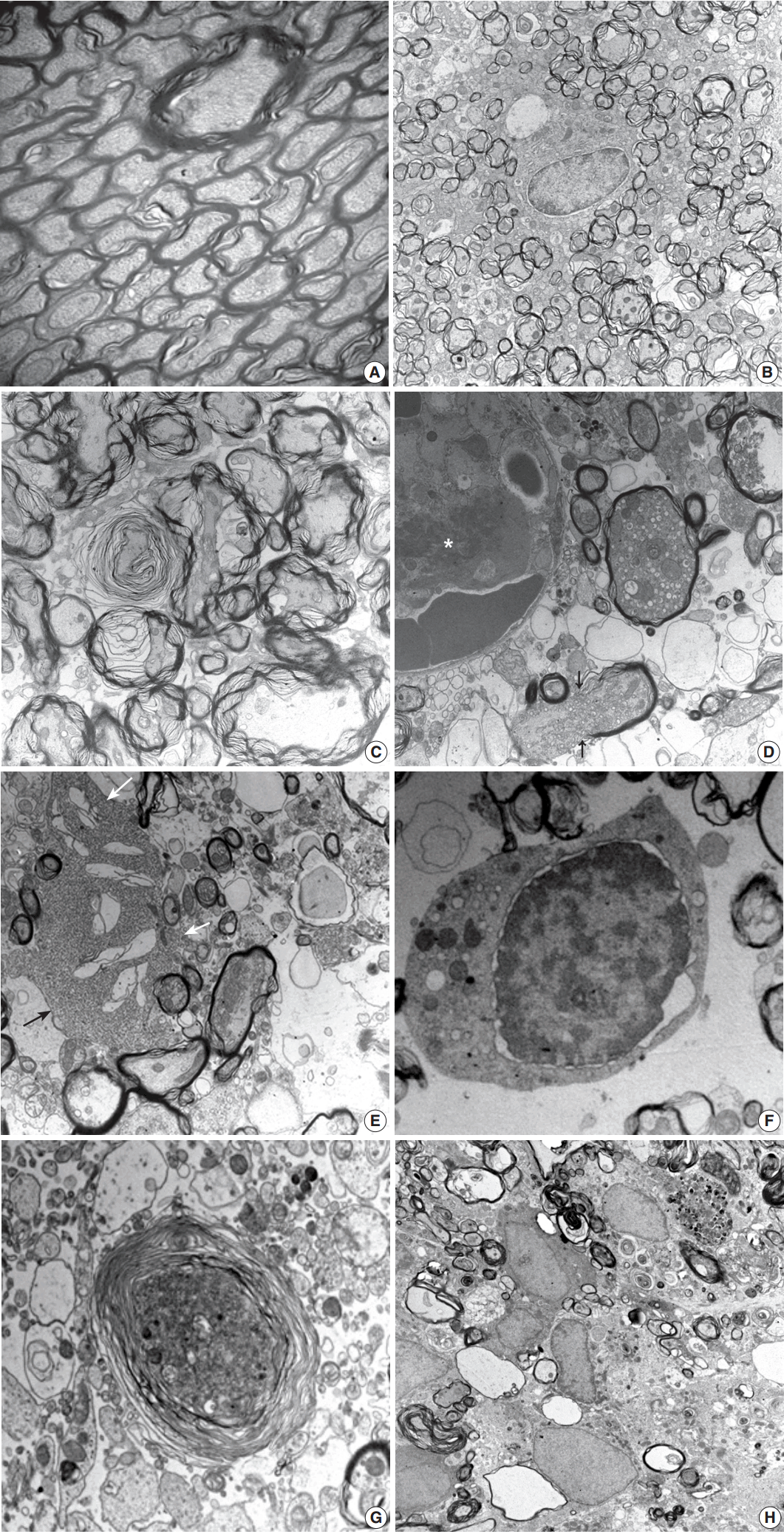
Fig. 4.
| Time of post-ischemia |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 hr | 6 hr | 12 hr | 1 day | 4 days | 7 days | 14 days | 21 days | |
| Light microscopy | ||||||||
| Stroke lesion group | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | a8 |
a8 |
| Sham operation group | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Electron microscopy | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Infarct volume | - | - | - | - | - | - | 14 |
- |
| Time (post-ischemia) | Light microscopy | Electron microscopy |
|---|---|---|
| 3-12 hr | Focal lesion with blurred margin | Nodular swelling and loosening of compact myelin sheath |
| Myelin pallor by H&E and LBPAS stain | Submyelin edema, interstitial | |
| Increased GFAP and decreased NFP immunoreactivity from lesion center | Mild wrinkling of axons, but intact neurofilaments and mitochondria | |
| Reactive astrocytes with hypertrophic processes | ||
| 1 day | Focal lesion on PUC with well-defined margin | Fibrin thrombosis and capillary luminal obstruction |
| Increased GFAP immunopositivity in the lesion and surrounding white matter | Axonal swelling and flooding of organelles, extracellular edema | |
| Rupture of myelin sheath with subsequent demyelination | ||
| Loss of NFP immunopositivity and LBPAS stainability | Reactive astrocytes with hypertrophic processes | |
| No inflammatory cell infiltration | Degeneration and apoptosis of oligodendrocytes | |
| 4 days | Focal infarct with central necrotic cavity surrounded by macrophages engulfing myelin debris | Markedly swollen axons with demyelination forming inflated ball or cystic appearance |
| Loss of myelinated axons of PLIC | Marked extracellular edema with exudation | |
| GFAP immunopositive hypertrophic astrocytes along the border of infarct and its vicinity | Necrosis of cellular elements | |
| Macrophages phagocytized with myelin debris and dense bodies | ||
| 7 days | Focal infarct with necrotic cavity surrounded by macrophages engulfing myelin debris, newly formed capillaries, and reactive astrogliosis | Reduced exudative change |
| Degeneration and loss of myelin sheath, demyelinated axons | ||
| Macrophages phagocytized with myelin debris and dense bodies | ||
| 14 days | Focal infarct with necrotic cavity containing macrophages, hypertrophic astrocytes and newly formed capillaris | Demyelinated axons |
| Astrogliosis | ||
| Macrophages, progressively reduced in number | Macrophages, markedly reduced phagocytic debris | |
| 21 days | Focal infarct with reduced necrotic cavity containing few macrophages and angiogliosis | Demyelinated axons |
| Astrogliosis | ||
| Mecrophages with phagocytic debris still present |
Four rats each for the moderate recovery group (MRG) and poor recovery group (PRG); Seven rats each MRG and PRG for measurement of lesion volume.
H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; LBPAS, luxol fast blue–periodic acid-Schiff; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; NFP, neurofilament protein; PLIC, posterior limb of internal capsule.

 E-submission
E-submission