Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 51(3); 2017 > Article
-
Review
Molecular Testing of Brain Tumor - Sung-Hye Park1,2, Jaekyung Won1, Seong-Ik Kim1, Yujin Lee1, Chul-Kee Park3, Seung-Ki Kim3, Seung-Hong Choi4
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2017;51(3):205-223.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.03.08
Published online: May 12, 2017
1Department of Pathology, Seoul National University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Neurosicence Institute, Seoul National University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
3Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
4Department of Radiology, Seoul National University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding Author Sung-Hye Park, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 103 Daehak-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul 03080, Korea Tel: +82-2-2072-3090 Fax: +82-2-743-5530 E-mail: shparknp@snu.ac.kr
© 2017 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Low-grade Epilepsy-associated Tumors and Other Acquired Causes of Epilepsy
Horst Urbach, Soroush Doostkam
Neuroimaging Clinics of North America.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Navigating rare vascular brain tumors: A retrospective observational study
Sana Ahuja, Dipanker S Mankotia, Naveen Kumar, Vyomika Teckchandani, Sufian Zaheer
Cancer Research, Statistics, and Treatment.2025; 8(2): 92. CrossRef - Author’s reply to Dagar and Mallick
Sana Ahuja, Sufian Zaheer
Cancer Research, Statistics, and Treatment.2025; 8(3): 245. CrossRef - The Clinical Utility of Cell-Free DNA in Brain Tumor Management: A Comprehensive Review
Qama Abuhassan, Hanan Hassan Ahmed, Radhwan Abdul Kareem, Soumya V. Menon, Priya Priyadarshini Nayak, J. Bethanney Janney, Vimal Arora, Aashna Sinha, Saif Aldeen Jaber, Hayder Naji Sameer, Ahmed Yaseen, Zainab H. Athab, Mohaned Adil
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - PTEN regulates expression of its pseudogene in glioblastoma cells in DNA methylation-dependent manner
Tatyana F. Kovalenko, Bhupender Yadav, Ksenia S. Anufrieva, Tatyana D. Larionova, Tatiana E. Aksinina, Yaroslav A. Latyshev, Soniya Bastola, Michail I. Shakhparonov, Amit Kumar Pandey, Marat S. Pavlyukov
Biochimie.2024; 219: 74. CrossRef - CDKN2A/B deletion in IDH-mutant astrocytomas: An evaluation by Fluorescence in-situ hybridization
Manali Ranade, Sridhar Epari, Omshree Shetty, Sandeep Dhanavade, Sheetal Chavan, Ayushi Sahay, Arpita Sahu, Prakash Shetty, Aliasgar Moiyadi, Vikash Singh, Archya Dasgupta, Abhishek Chatterjee, Sadhana Kannan, Tejpal Gupta
Journal of Neuro-Oncology.2024; 167(1): 189. CrossRef - Central neurocytoma exhibits radial glial cell signatures with FGFR3 hypomethylation and overexpression
Yeajina Lee, Tamrin Chowdhury, Sojin Kim, Hyeon Jong Yu, Kyung-Min Kim, Ho Kang, Min-Sung Kim, Jin Wook Kim, Yong-Hwy Kim, So Young Ji, Kihwan Hwang, Jung Ho Han, Jinha Hwang, Seong-Keun Yoo, Kyu Sang Lee, Gheeyoung Choe, Jae-Kyung Won, Sung-Hye Park, Yon
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2024; 56(4): 975. CrossRef - Liquid biopsy in brain tumors: Potential for impactful clinical applications
Tania Eid, Lina Ghandour, Joseph Abi Ghanem, Hazem Assi, Rami Mahfouz
Human Gene.2024; 42: 201333. CrossRef - Diagnostic challenges in complicated case of glioblastoma
Tatiana Aghova, Halka Lhotska, Libuse Lizcova, Karla Svobodova, Lucie Hodanova, Karolina Janeckova, Kim Vucinic, Martin Gregor, Dora Konecna, Filip Kramar, Jiri Soukup, David Netuka, Zuzana Zemanova
Pathology and Oncology Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Drugging Hijacked Kinase Pathways in Pediatric Oncology: Opportunities and Current Scenario
Marina Ferreira Candido, Mariana Medeiros, Luciana Chain Veronez, David Bastos, Karla Laissa Oliveira, Julia Alejandra Pezuk, Elvis Terci Valera, María Sol Brassesco
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(2): 664. CrossRef - BrainBase: a curated knowledgebase for brain diseases
Lin Liu, Yang Zhang, Guangyi Niu, Qianpeng Li, Zhao Li, Tongtong Zhu, Changrui Feng, Xiaonan Liu, Yuansheng Zhang, Tianyi Xu, Ruru Chen, Xufei Teng, Rongqin Zhang, Dong Zou, Lina Ma, Zhang Zhang
Nucleic Acids Research.2022; 50(D1): D1131. CrossRef - A heat shock protein 90 inhibitor reduces oncoprotein expression and induces cell death in heterogeneous glioblastoma cells with EGFR, PDGFRA, CDK4, and NF1 aberrations
Kuan-Ta Ho, Pei-Fan Chen, Jian-Ying Chuang, Po-Wu Gean, Yuan-Shuo Hsueh
Life Sciences.2022; 288: 120176. CrossRef - Bicentric validation of the navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation motor risk stratification model
Tizian Rosenstock, Levin Häni, Ulrike Grittner, Nicolas Schlinkmann, Meltem Ivren, Heike Schneider, Andreas Raabe, Peter Vajkoczy, Kathleen Seidel, Thomas Picht
Journal of Neurosurgery.2022; 136(4): 1194. CrossRef - Foramen magnum meningioma presented as cervical myelopathy in a pregnant COVID-19 patient: A case report
Olivia Josephine Wijaya, Djohan Ardiansyah
Annals of Medicine and Surgery.2022; 77: 103647. CrossRef - The telomere maintenance mechanism spectrum and its dynamics in gliomas
Sojin Kim, Tamrin Chowdhury, Hyeon Jong Yu, Jee Ye Kahng, Chae Eun Lee, Seung Ah. Choi, Kyung-Min Kim, Ho Kang, Joo Ho Lee, Soon-Tae Lee, Jae-Kyung Won, Kyung Hyun Kim, Min-Sung Kim, Ji Yeoun Lee, Jin Wook Kim, Yong-Hwy Kim, Tae Min Kim, Seung Hong Choi,
Genome Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A review of predictive, prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers for brain tumours: towards personalised and targeted cancer therapy
Ernest Osei, Pascale Walters, Olivia Masella, Quinton Tennant, Amber Fishwick, Eugenia Dadzie, Anmol Bhangu, Johnson Darko
Journal of Radiotherapy in Practice.2021; 20(1): 83. CrossRef - Use of a novel navigable tubular retractor system in 1826 minimally invasive parafascicular surgery (MIPS) cases involving deep-seated brain tumors, hemorrhages and malformations
Martina M. Cartwright, Penny Sekerak, Joseph Mark, Julian Bailes
Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery.2021; 23: 100919. CrossRef - Disentangling the therapeutic tactics in GBM: From bench to bedside and beyond
S. Daisy Precilla, Shreyas S. Kuduvalli, Anitha Thirugnanasambandhar Sivasubramanian
Cell Biology International.2021; 45(1): 18. CrossRef - Sequencing of a central nervous system tumor demonstrates cancer transmission in an organ transplant
Marie-Claude Gingras, Aniko Sabo, Maria Cardenas, Abbas Rana, Sadhna Dhingra, Qingchang Meng, Jianhong Hu, Donna M Muzny, Harshavardhan Doddapaneni, Lesette Perez, Viktoriya Korchina, Caitlin Nessner, Xiuping Liu, Hsu Chao, John Goss, Richard A Gibbs
Life Science Alliance.2021; 4(9): e202000941. CrossRef - Radiogenomics of Gliomas
Chaitra Badve, Sangam Kanekar
Radiologic Clinics of North America.2021; 59(3): 441. CrossRef - Chemical analysis of the human brain by imaging mass spectrometry
Akhila Ajith, Yeswanth Sthanikam, Shibdas Banerjee
The Analyst.2021; 146(18): 5451. CrossRef - Correlation between Stage and Histopathological Features and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Glioma Tumors
Andre Lona, Alfansuri Kadri, Irina Kemala Nasution
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(T3): 262. CrossRef - Pediatric Glioma: An Update of Diagnosis, Biology, and Treatment
Yusuke Funakoshi, Nobuhiro Hata, Daisuke Kuga, Ryusuke Hatae, Yuhei Sangatsuda, Yutaka Fujioka, Kosuke Takigawa, Masahiro Mizoguchi
Cancers.2021; 13(4): 758. CrossRef - Discovery of clinically relevant fusions in pediatric cancer
Stephanie LaHaye, James R. Fitch, Kyle J. Voytovich, Adam C. Herman, Benjamin J. Kelly, Grant E. Lammi, Jeremy A. Arbesfeld, Saranga Wijeratne, Samuel J. Franklin, Kathleen M. Schieffer, Natalie Bir, Sean D. McGrath, Anthony R. Miller, Amy Wetzel, Katheri
BMC Genomics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological correlation of glioma patients with respect to immunohistochemistry markers: A prospective study of 115 patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital in North India
Gitanshu Dahuja, Ashok Gupta, Arpita Jindal, Gaurav Jain, Santosh Sharma, Arvind Kumar
Asian Journal of Neurosurgery.2021; 16(04): 732. CrossRef - Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Glioma Progression: Deciphering Cellular Biological Processes to Clinical Applications
Rashmi Rana, Shikha Joon, Kirti Chauhan, Vaishnavi Rathi, Nirmal Kumar Ganguly, Chandni Kumari, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav
Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry.2021; 21(8): 696. CrossRef - A comprehensive overview on the molecular biology of human glioma: what the clinician needs to know
P. D. Delgado-López, P. Saiz-López, R. Gargini, E. Sola-Vendrell, S. Tejada
Clinical and Translational Oncology.2020; 22(11): 1909. CrossRef - Use of Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) in Diagnosis and Tailored Therapies in Solid Tumors
Natalia Magdalena Chrzanowska, Janusz Kowalewski, Marzena Anna Lewandowska
Molecules.2020; 25(8): 1864. CrossRef - From Banding to BAM Files
Adrian M. Dubuc
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2020; 13(2): 343. CrossRef - Mutation profiling of anaplastic ependymoma grade III by Ion Proton next generation DNA sequencing
Ejaz Butt, Sabra Alyami, Tahani Nageeti, Muhammad Saeed, Khalid AlQuthami, Abdellatif Bouazzaoui, Mohammad Athar, Zainularifeen Abduljaleel, Faisal Al-Allaf, Mohiuddin Taher
F1000Research.2020; 8: 613. CrossRef - Assessment of the non-linear optical behavior of cells for discrimination between normal and malignant glial cells
Soraya Emamgholizadeh Minaei, Alireza Ghader, Ali Abbasian Ardakani, Samideh Khoei, Mohammad Hosein Majles Ara
Laser Physics.2020; 30(12): 125601. CrossRef - Mutation profiling of anaplastic ependymoma grade III by Ion Proton next generation DNA sequencing
Muhammad Butt, Sabra Alyami, Tahani Nageeti, Muhammad Saeed, Khalid AlQuthami, Abdellatif Bouazzaoui, Mohammad Athar, Zainularifeen Abduljaleel, Faisal Al-Allaf, Mohiuddin Taher
F1000Research.2019; 8: 613. CrossRef - A Multiplex Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for the Detection of KIAA1549–BRAF Fusion Transcripts in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Pilocytic Astrocytomas
David Bret, Valentin Chappuis, Delphine Poncet, François Ducray, Karen Silva, Fabrice Mion, Alexandre Vasiljevic, Carole Ferraro-Peyret, Carmine Mottolese, Pierre Leblond, Mathieu Gabut, Didier Frappaz, Nathalie Streichenberger, David Meyronet, Pierre-Pau
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy.2019; 23(4): 537. CrossRef - A PTPmu Biomarker is Associated with Increased Survival in Gliomas
Mette L. Johansen, Jason Vincent, Haley Gittleman, Sonya E. L. Craig, Marta Couce, Andrew E. Sloan, Jill S. Barnholtz-Sloan, Susann M. Brady-Kalnay
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(10): 2372. CrossRef -
ATRX Mutations in Pineal Parenchymal Tumors of Intermediate Differentiation
Haydee Martínez, Michelle Nagurney, Zi-Xuan Wang, Charles G Eberhart, Christopher M Heaphy, Mark T Curtis, Fausto J Rodriguez
Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology.2019; 78(8): 703. CrossRef - The role of fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in gliomas: the mutations involved
Vasiliki Georgiou, Vasiliki Gkretsi
Reviews in the Neurosciences.2019; 30(5): 543. CrossRef - The Role of Next Generation Sequencing in Diagnosis of Brain Tumors: A Review Study
Sadegh Shirian, Yahya Daneshbod, Saranaz Jangjoo, Amir Ghaemi, Arash Goodarzi, Maryam Ghavideldarestani, Ahmad Emadi, Arman Ai, Akbar Ahmadi, Jafar Ai
Archives of Neuroscience.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Applied Precision Cancer Medicine in Neuro-Oncology
H. Taghizadeh, L. Müllauer, J. Furtner, J. A. Hainfellner, C. Marosi, M. Preusser, G. W. Prager
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative genomic analysis of driver mutations in matched primary and recurrent meningiomas
Joshua Loewenstern, John Rutland, Corey Gill, Hanane Arib, Margaret Pain, Melissa Umphlett, Yayoi Kinoshita, Russell McBride, Michael Donovan, Robert Sebra, Joshua Bederson, Mary Fowkes, Raj Shrivastava
Oncotarget.2019; 10(37): 3506. CrossRef - Next generation DNA sequencing of atypical choroid plexus papilloma of brain: Identification of novel mutations in a female patient by Ion Proton
Mohiuddin Taher, Amal Hassan, Muhammad Saeed, Raid Jastania, Tahani Nageeti, Hisham Alkhalidi, Ghida Dairi, Zainularifeen Abduljaleel, Mohammad Athar, Abdellatif Bouazzaoui, Wafa El‑Bjeirami, Faisal Al‑Allaf
Oncology Letters.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Pure mechanistic analysis of additive neuroprotective effects between baicalin and jasminoidin in ischemic stroke mice
Peng-qian Wang, Qiong Liu, Wen-juan Xu, Ya-nan Yu, Ying-ying Zhang, Bing Li, Jun Liu, Zhong Wang
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2018; 39(6): 961. CrossRef - The Smad4/PTEN Expression Pattern Predicts Clinical Outcomes in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma
Yumin Chung, Young Chan Wi, Yeseul Kim, Seong Sik Bang, Jung-Ho Yang, Kiseok Jang, Kyueng-Whan Min, Seung Sam Paik
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2018; 52(1): 37. CrossRef - Primary brain tumours in adults
Sarah Lapointe, Arie Perry, Nicholas A Butowski
The Lancet.2018; 392(10145): 432. CrossRef - Epidemiology and Overview of Gliomas
Mary Elizabeth Davis
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2018; 34(5): 420. CrossRef - Toward Precision Medicine: Promising Areas of Research in Glioma
Mary Elizabeth Davis, Dana Bossert, Malbora Manne
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2018; 34(5): 569. CrossRef - Molecular Basis of Pediatric Brain Tumors
Alexia Klonou, Christina Piperi, Antonios N. Gargalionis, Athanasios G. Papavassiliou
NeuroMolecular Medicine.2017; 19(2-3): 256. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure



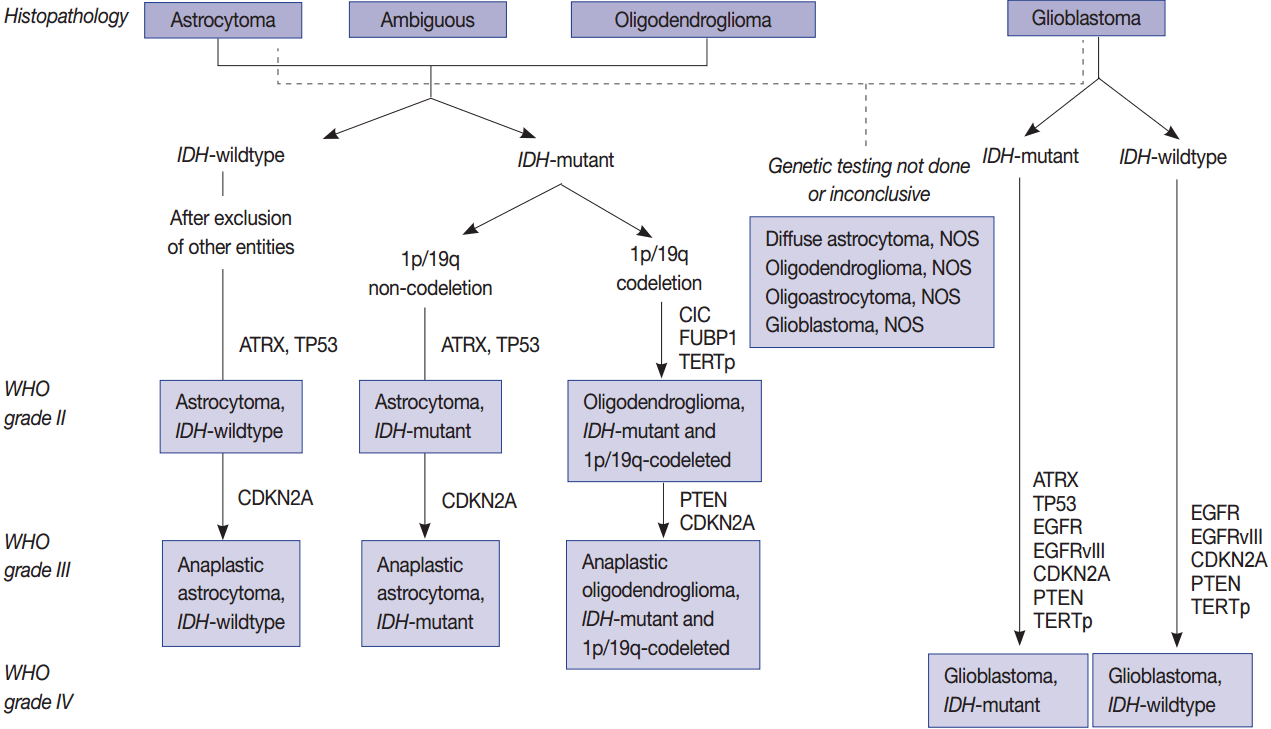
Fig. 1.
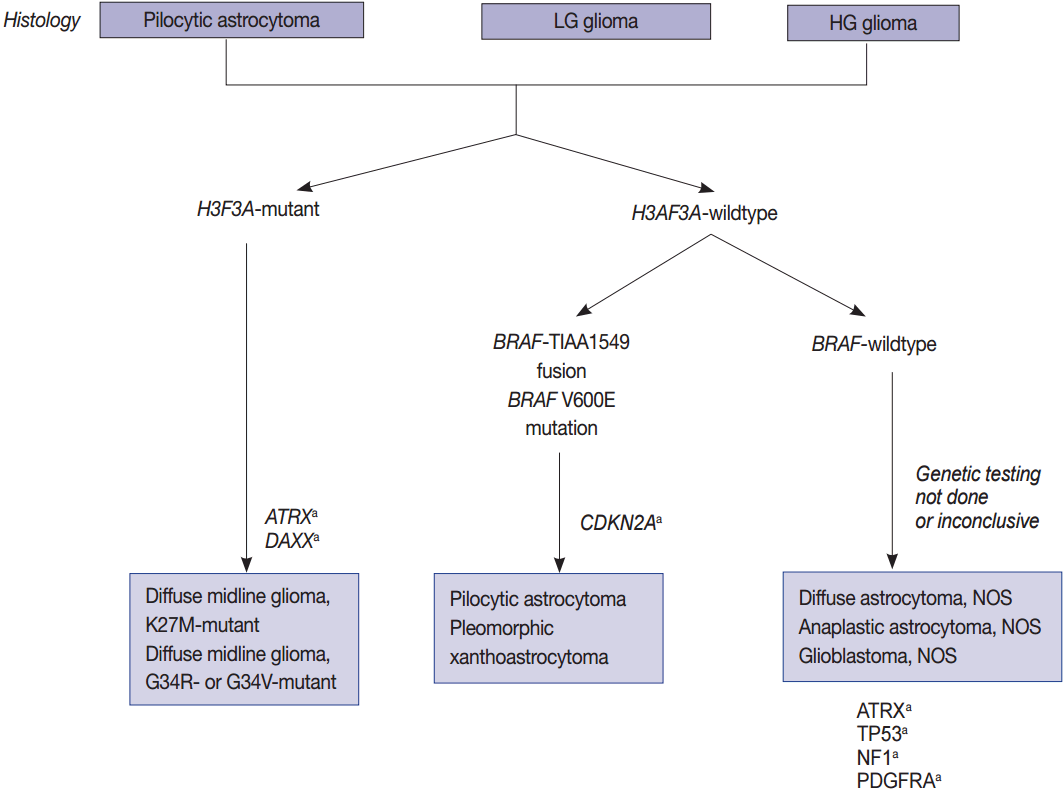
Fig. 2.
Fig. 3.
| WHO grade | Altered genes | Genomic alteration (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Astrocytoma | II, III | IDH mutation | 65 |
| P53 mutation | 96 | ||
| ATRX mutation | 96 | ||
| Glioblastoma | IV | EGFR amplification | 57 |
| PDGFRA amplification | 13 | ||
| EGFRvIII mutation | 20 | ||
| PTEN homozygous deletion | 25–35 | ||
| CDKN2A homozygous deletion | 61 | ||
| BRAF V600E mutation | 1–2 (epithelioid GBM) | ||
| TP53 mutation | 25–35 | ||
| Oligodendroglioma | II, III | IDH mutation | 100 |
| 1p/19q codeletion | 100 | ||
| CIC/FUBP1 mutation | 56/29 | ||
| TERTp mutation | 80–96 | ||
| Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma | I | TSC1 and TSC2 mutation | 100 |
| Pilocytic astrocytoma | I | BRAF-KIAA1549 fusion | 75 (cerebellar tumor) |
| BRAF V600E mutation | 13–15 | ||
| Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma | II, III | BRAF V600E mutation | 66 |
| CDKN2A homozygous deletion | 50 | ||
| Angiocentric glioma | I | MYB-QKI fusion | 100 |
| Ganglioglioma | I, III | BRAF V600E mutation | 25 |
| TSC1 and TSC2 mutation | Unknown | ||
| Craniopharyngioma, papillary type | I | BRAF V600E mutation | 100 |
| Craniopharyngioma, adamantinomatous type | I | CTNNB1 mutation | 100 |
| AT/RT | IV | SMARCB1 deletion/mutation | > 95 |
| IV | SMARCA4 mutation | < 5 | |
| Cribriform tumor | SMACB1 deletion/mutation | 100 | |
| Meningioma, fibrous type | NF2 inactivation mutation (no hot spot) | 45–5550 | |
| TRAF7/KLF4 mutation | 100 (secretory meningioma) | ||
| AKT1 (p.Glu17Lys) mutation | 2.5 | ||
| SMO (p.Trp535Leu) mutation | 5 | ||
| TERTp mutation | 10 | ||
| Langerhans cell histiocytosis | I, III | BRAF V600E mutation | 50–5754 |
| Tumor | Molecular subgroup | Molecular feature | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| LGG | BRAFV600E | 70% of PXA, GG, DA | Good |
| KIAA-BRAF fusion; BRAF duplication | 90% of PA | Good | |
| MYB-QKI rearrangement | High proportion of AG | Good | |
| FGFR1 duplication | PA, DA, DNT | Good | |
| HGG | K27M-mutant | H3.1 and H3.3 K27 mutation, PDGFRA focal amplification, TP53 mutation, ACVR1 mutation | Poor |
| G34R/V-mutant | H3.3 G3 and TP53 mutation | Poor | |
| RTK1 amplified | PDGFRA and EGFR focal amplification, CDKN2A/2B homozygous deletion | Poor | |
| Mesenchymal | NFI mutation, PDGFRA and EGFR focal amplification, CDKN2A/2B homozygous deletion | - | |
| Ependymoma | C11orf95-RELA+ (70% of ST E) | RELA fusion transcripts | Poor |
| RELA fusion - (30% of ST E) | Possibly YAP1 fusion transcripts | Good | |
| Posterior fossa E | Group A: LAMA2 overexpression, | Poor | |
| Group B: NELL2 overexpression | Good | ||
| Spinal cord E (10% of child E) | NF2 mutation, myxopapillary histology | Good | |
| Medulloblastoma | WNT (10%) | Nuclear β-catenin positive, CTNNBI mutations in exon 3, monosomy 6 | Excellent |
| SHH (30%) | Heterogeneous molecular features depending on age of presentation; PTCH1, SMO, and SUFU mutations, GLI2 and MYCN amplification; germline TP53 mutations | Intermediate (except in infants who have a good prognosis) | |
| Group 3 (25%) | By some unknown mechanism; MYC amplification and over expression | Poor | |
| Group 4 (35%) | i(17)q; MYCN amplification | Intermediate | |
| AT/RT | SMARCB1/SHARCA4 mutation | Poor | |
| ETMR | C19MC amplification | Poor |
| Genes and molecules | Biomarker type | PA (%) | PXA (%) | DA/AA (%) | IDH- wildtype GBM (%) | IDH- mutant GBM (%) | DMG, H3 K27M (%) | ODG (%) | Epen (%) | MB (%) | AT/RT (%) | Test method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHO grade | I | II, III | II, III | IV | IV | IV | II/III | II/III | IV | IV | ||
| IDH1 mutation | Diagnostic and prognostic | 0 | - | > 80 | 5-6 | > 95 | 0 | 98 | 0 | 0 | 0 | IHC, sequencing |
| IDH2 mutation | Diagnostic and prognostic | 0 | - | - | 2-5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Sequencing | |
| TP53 mutation | Diagnostic and prognostic | 0 | 6 | 94 | 25-35 | 62-65 | 45-50 | 9-44 | 0 | - | 0 | Sequencing, IHC |
| ATRX mutation | Diagnostic and prognostic | - | 86 | 0 | 90-95 | 50 | - | 0 | - | 0 | IHC, sequencing | |
| Histone K27M mutation | Diagnostic and prognostic | 0 | - | 0 | Pediatric HGG | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | IHC, sequencing |
| Histone G34 mutation | Diagnostic and prognostic | 0 | - | - | Uncertain | - | - | 0 | 0 | - | - | Sequencing |
| Histone K36 mutation | Diagnostic and prognostic | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | - | - | Sequencing |
| 1p/19q codeletion | Diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FISH, CGH |
| CIC mutation | Diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | 49 | 0 | - | - | Sequencing, IHC |
| FUBP1 mutation | Diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | 29 | 0 | - | - | Sequencing, IHC |
| EGFR amp | Prognostic | 0 | - | - | 35-45 | 4 | - | - | 0 | - | - | FISH, CGH, IHC |
| PDGFRA amp | Diagnostic | - | - | 13 | - | 50 | - | - | - | FISH, CGH, IHC | ||
| PTEN HoD | Prognostic | 0 | - | - | 25-35 | 5 | - | - | 0 | - | - | FISH, CGH, IHC |
| CDKN2A HoD | Predictive | 0 | 60 | 11 | 35-50 | - | < 5 | - | 0 | - | - | FISH, CGH, IHC |
| BRAF V600E mutation | Diagnostic and prognostic | 15 | 67 | 0 | 1-2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Sequencing, IHC |
| BRAF-KIAA1549 fusion | Diagnostic and prognostic | 70 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | RT-PCR, FISH (gain) |
| TERT promoter mutation | Diagnostic and prognostic | - | - | - | > 80 | 26 | - | 96 | 0 | 21 | - | Sequencing |
| C11orm-RELA fusion | Diagnostic and prognostic | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | <5 | - | - | RT-PCR, IHC, RNA seq |
| β-Catenin mutation | Diagnostic and prognostic | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0 | 6-9 | - | IHC, sequencing |
| MYC amp | Prognostic | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10–15 | - | FISH, CGH, IHC |
| MYCN amp | Prognostic | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10–15 | - | FISH, CGH |
| SMARCB1 mutation | Diagnostic and prognostic | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | 98 | IHC, sequencing |
| SMARCA4 mutation | Diagnostic and prognostic | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | 1-2 | IHC, sequencing |
| MGMT methylation | Predictive | - | - | 78.5 | 48.5 | 60-80 | - | 85 | 0 | 0 | 0 | MSP-PCR, pyrosequencing, IHC |
| Antibody | Positive loci | Mutated gene status | Positive result | Tumors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATRX | Nucleus | Loss of function mutation | Negative | Diffuse and anaplastic astrocytoma |
| β-Catenin | Nucleus | Gain of function mutation | Focal positive | WNT type medulloblastoma, adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma |
| BRAF VE1 (BRAF V600E) | Cytoplasm | Gain of function mutation | Positive | Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, ganglioglioma, pilocytic astrocytoma, epithelioid glioblastoma, papillary craniopharyngioma |
| BRG1 | Nucleus | Gain of function mutation | Negative | Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor |
| CIC | Nucleus | Loss of function mutation | Negative | Oligodendroglioma (47%) [15] |
| c-MET | Membrane | Overexpression | Positive | Glioblastoma, anaplastic astrocytoma |
| EGFR | Membrane | Overexpression | Positive | Glioblastoma, anaplastic astrocytoma |
| EGFRvIII | Membrane | Overexpression | Positive | Glioblastoma, anaplastic astrocytoma |
| H3 K27M | Nucleus | Gain of function mutation | Positive | Diffuse midline glioma |
| FUBP1 | Nucleus | Loss of function mutation | Negative | Oligodendroglioma (16%) [15] |
| IDH1 (H09) | Nucleus and cytoplasm | Gain of function mutation | Positive | Astrocytoma and oligodendroglioma |
| INI1 | Nucleus | Loss of function mutation | Negative | Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor |
| P16 | Nucleus and cytoplasm | Loss of function mutation | Negative | High grade glioma |
| P53 | Nucleus | Overexpression | Positive | Astrocytic tumors |
| PDGFRA | Membrane | Overexpression | Positive | Glioblastoma, anaplastic astrocytoma |
| PTEN | Cytoplasm | Loss of function mutation | Negative | Glioblastoma |
| RELA (NFKB3) | Cytoplasm | Gain of function mutation | Positive | Cerebral ependymoma |
| STAT6 | Nucleus | Gain of function mutation | Positive | Solitary fibrous tumor/hemangiopericytoma |
| MLH1 | Nucleus | Loss of function mutation | Negative | Gliomas |
| MSH2 | Nucleus | Loss of function mutation | Negative | Gliomas |
| PMS2 | Nucleus | Loss of function mutation | Negative | Gliomas |
| Ki67 | Nucleus | Overexpression | Positive | Brain tumors (for an ancillary test for tumor grading) |
| pHH3 | Nucleus | Overexpression | Positive | Brain tumors (for counting mitoses) |
| GFAP | Nucleus | Expression | Positive | Astrocytic tumors |
| Olig2 | Nucleus | Expression | Positive | Gliomas including astrocytomas and oligodendroglioma |
| Neither neuronal nor ependymal tumors |
| Gene | Full name | Gene location | Forward primer | Reverse primer | Product (bp) | Indication | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IDH1 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 | 2q33.3 | 5´-M13-GTA AAA CGA CGG CCA GTC GGT CTT CAG AGA AGC CA-3´ | 5´-GCG GAT AAC AAT TTC ACA CAG GGC AAA ATC ACA TTA TTG C-3´ | 180–190 | Astrocytic and ODG | Affect citrate metabolism, leading to 2-HG metabolite |
| IDH2 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 | 15q26.1 | 5´-GCT GCA GTG GGA CCA CTA TT-3´ | 5´-TGT GGC GTT GTA CTG CAG AG-3´ | 295–305 | Astrocytic and ODG | Same with IDH1 |
| H3F3A (K27M/K36/G34) | H3 Histone family 3A | 1q42.12 | 5´-CTG GTA AAG CAC CCA GGA AGC-3´ | 5´-CAT GGA TAG CAC ACA GGT TGG T-3´ | 330–340 | DMG | Chromatin structure, gene transcription |
| BRAF V600E | V-RAF murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 | 7q34 | 1st: 5´-GCT TGC TCT GAT AGG AAA ATG AG-3´ | 1st: 5´-GTA ACT CAG CAG CAT CTC AGG-3´ | 245–255 | Gliomas including PXA, GG, PA, epithelioid GBM | MAPK signaling |
| 2nd: 5´-TCA TAA TGC TTG CTC TGA TAG GA-3´ | 2nd: 5´-GGC CAA AAA TTT AAT CAG TGG A-3´ | 230–235 | |||||
| CTNNB1 | Catenin, beta-1 | 3p22.1 | 5´-GAT TTG ATG GAG TTG GAC ATG G-3´ | 5´-TGT TCT TGA GTG AAG GAC TGA G-3´ | 230–235 | Medulloblastoma, WNT subtype, craniopharyngioma, adamantinomatous type | The transmission of the ‘contact inhibition’ signal |
| TERTp | Telomerase reverse transcriptase | 5p15.33 | 5´-M13-GGC CGA TTC GAC CTC TCT-3´ (M13: TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT) | 5´-AGC ACC TCG CGG TAG TGG-3´ (M13: GCG GAT AAC AAT TTC ACA CA) | 300–310 | Gliomas, especially ODG and GBM | Telomerase maintenance |
| MGMT | O6 mentylguanine-DNA methyltransferase | 10q26.3 | 5´-TTT CGA CGT TCG TAG GTT TTC GC-3´ | 5´-GCA CTC TTC CGA AAA CGA AAC G-3´ | 80–90 | Gliomas | Promoter methylation |
| Target probe | Control | Cut off | Indication | Biomarker | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1p deletion | Chr1p36 | 1q25 | 1p < 0.8 and Deleted nuclei > 50% | ODG | Diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive |
| 19q deletion | Chr19q13 | 19p13 | 19q < 0.8 and Deleted nuclei > 50% | ODG, HGG | Diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive |
| BRAF gain | Chr7q34 | CEP7 | Gold signal > 3 | PA | Diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive |
| CDKN2A (9p21.3) homozygous/hemizygous deletion | Chr9p21.3 | CEP9 | HoD ≥ 10% | HGG | Diagnostic and prognostic |
| HeD ≥ 50% | |||||
| EGFR amplification | Chr711.2 | CEP7 | Ratio ≥ 2.0 | HGG | Diagnostic and prognostic |
| PTEN HoD /HeD | Chr10q23.31 | CEP10 | HoD ≥ 10% | HGG | Diagnostic and prognostic |
| HeD ≥ 50% | |||||
| RELA-C11orf95 fusion | Chr11q13.1 | CEP11 | Break apart | S-ependymoma | Diagnostic and prognostic |
| C19MC amplification | Chr19 | CEP19 | Ratio ≥ 2.0 | ODG, GBM | Diagnostic and prognostic |
| SMARCB1 | Chr22q11.23 | CEP22 | NF2 < 0.8 | AT/RT | Diagnostic and prognostic |
WHO, World Health Organization; GBM, glioblastoma; TSC, tuberous sclerosis complex; AT/RT, atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor.
LGG, low grade glioma; PXA, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma; GG, ganglioglioma; DA, diffuse astrocytoma; PA, pilocytic astrocytoma; AG, angiocentric glioma; DNT, dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor; HGG, high grade glioma; ST, supratentorial; PF, posterior fossa; E, ependymoma; WNT, wingless signaling pathway; i, isochromosome; AT/RT, atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor; ETMR, embryonal tumor with multilayer rosettes.
PA, pilocytic astrocytoma; PXA, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma; DA, diffuse astrocytoma; AA, anaplastic astrocytoma; GBM, glioblastoma; DMG, diffuse midline glioma; HGG, high grade glioma; ODG, oligodendroglioma; MB, medulloblastomas; AT/RT, atypical teratoid/ rhabdoid tumor; WHO, World Health Organization; IHC, immunohistochemistry; FISH, fluorescent
ODG, oligodendroglioma; 2-HG, 2-hydroxyglutamate; DMG, diffuse midline glioma; PXA, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma; GG, ganglioglioma; PA, pilocytic astrocytoma; GBM, glioblastoma; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase.
FISH, fluorescent

 E-submission
E-submission